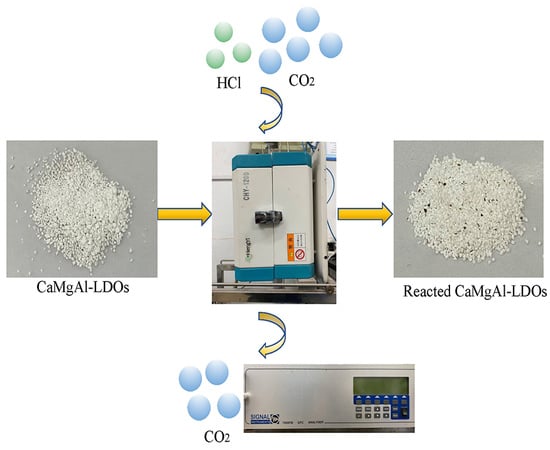
HCl Removal Using Calcined Ca–Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide in the Presence of CO2 at Medium–High Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the As-Synthesized Samples
2.2. Effect of CO2 Concentration on HCl Removal
2.3. Effect of HCl Concentration on Its Removal
2.4. Effect of Particle Size of the LDOs on HCl Removal
2.5. Effect of Gas Velocity on HCl Removal
2.6. Effect of Reaction Temperature on HCl Removal
2.7. Morphology and Components
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Ca–Mg–Al LDOs
3.2. Characterizations
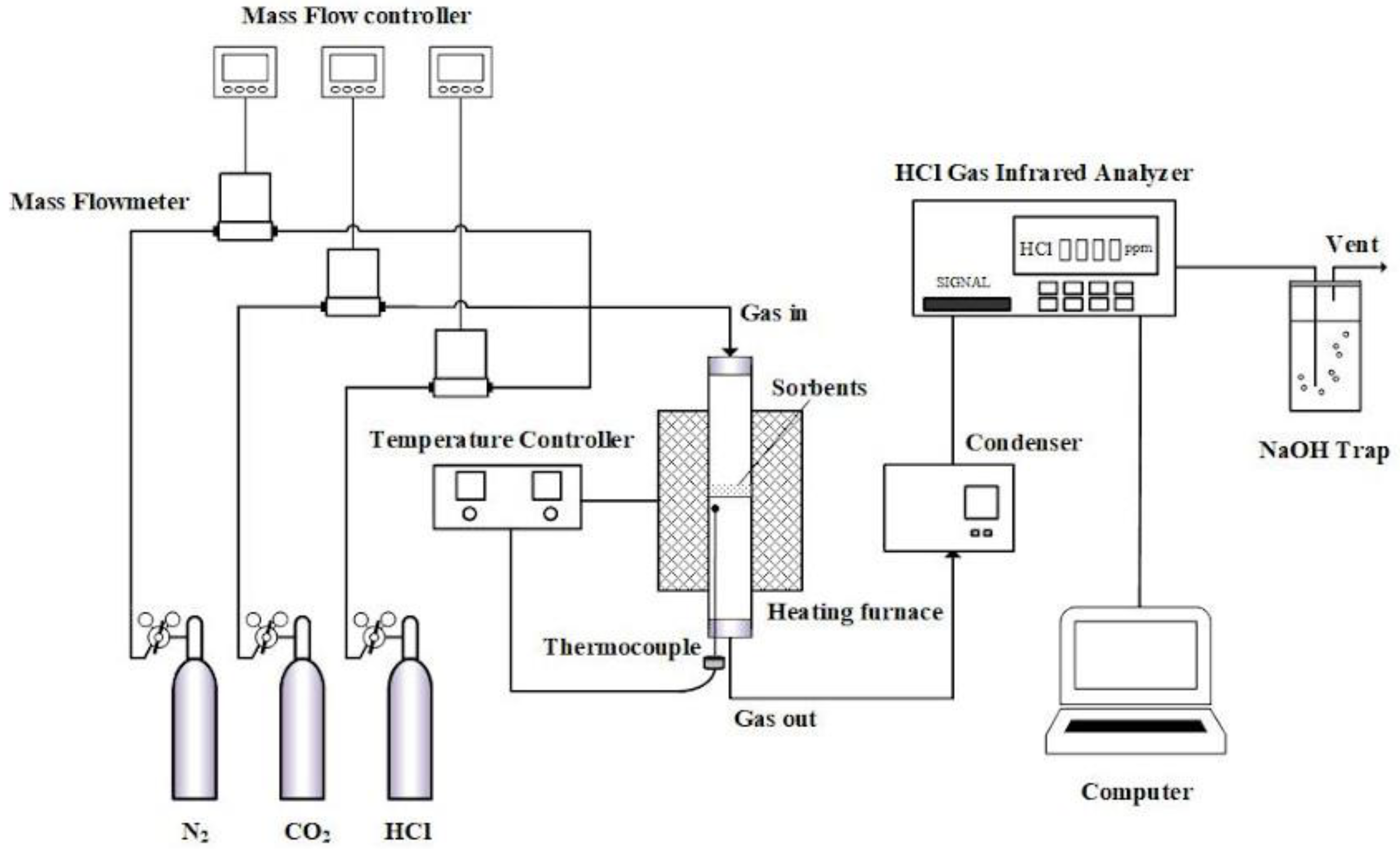
3.3. Experimental Reactor and Procedure
3.4. Data Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Gao, P.; Ni, H. Emission characteristics of parent and halogenated PAHs in simulated municipal solid waste incineration. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Sarnat, S.; Bi, J. Toxicological risk by inhalation exposure of air pollution emitted from China’s municipal solid waste incineration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11490–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beylot, A.; Hochar, A.; Michel, P.; Descat, M.; Ménard, Y.; Villeneuve, J. Municipal solid waste incineration in France: An overview of air pollution control techniques, emissions, and energy efficiency. J. Ind. Ecol. 2018, 22, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Du, C.; Chen, Z.; Buekens, A.; Yan, J. Municipal solid waste incineration in China and the issue of acidification: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Chen, T.; Jin, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, C. Adsorption of HCl on calcined Ca and Zn hydrotalcite-like compounds (HTLs) at medium-high temperature in flue gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Cheng, X.; Su, M.; Ma, X.; Xie, X. Simultaneous CO2/HCl removal using carbide slag in repetitive adsorption/desorption cycles. Fuel 2015, 142, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyang, C.; Han, Y.; Zhong, Z. Study of HCl absorption by CaO at high temperature. Energy Fuel 2009, 23, 3948–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Hui, F.; Yuan, J.; Yu, Q.; Mei, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Lu, J. Ru-Ti oxide based catalysts for HCl oxidation: The favorable oxygen species and influence of Ce additive. Catalysts 2019, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acelas, N.Y.; Flórez, E. Chloride adsorption on Fe- and Al-(hydr)oxide: Estimation of gibbs free energies. Adsorption 2018, 24, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Shi, L. HCl removal using cycled carbide slag from calcium looping cycles. Appl. Energy 2014, 135, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, L.; Gomez-Rico, M.F.; Forsberg, C.; Nordenskjöld, C.; Jansson, S. Reduction of PCDD, PCDF and PCB during co-combustion of biomass with waste products from pulp and paper industry. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Crespo, J.G.; Afonso, C.A.M. Dioxins sources and current remediation technologies—A review. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, C.; Chen, H.; Yen, C. A PID ratio control for removal of in flue gas from refuse municipal incinerators. Control Eng. Pract. 2008, 16, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geysen, D.; Vandecasteele, C.; Jaspers, M.; Brouwers, E.; Wauters, G. Effect of improving flue gas cleaning on characteristics and immobilisation of APC residues from MSW incineration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.S. Advanced experimental analysis of the reaction of Ca(OH)2 with HCl and SO2 during the spray dry scrubbing process. Fuel 2005, 84, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Backman, P.; Backman, R.; Hupa, M. Absorption of HCl by limestone in hot flue gases. Part III: Simultaneous absorption with SO. Fuel 2005, 84, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Backman, P.; Backman, R.; Hupa, M. Absorption of HCl by limestone in hot flue gases. Part II: Importance of calcium hydroxychloride. Fuel 2005, 84, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Backman, P.; Backman, R.; Hupa, M. Absorption of HCl by limestone in hot flue gases. Part I: The effects of temperature, gas atmosphere and absorbent quality. Fuel 2005, 84, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.W.; Kashani-Nejad, S.; Harris, R. Kinetics of MgO chlorination with HCl gas. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2005, 36, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L. Catalytic degradation and dechlorination of PVC-containing mixed plastics via Al–Mg composite oxide catalysts. Fuel 2004, 83, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdone, N.; De Filippis, P. Reaction kinetics of hydrogen chloride with sodium carbonate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 7487–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunokawa, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Shirai, H. Halide compound removal from hot coal-derived gas with reusable sodium-based sorbent. Powder Technol. 2008, 180, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdone, N.; De Filippis, P. Thermodynamic behaviour of sodium and calcium based sorbents in the emission control of waste incinerators. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.; Lim, T.; Dong, Z. Application of layered double hydroxides for removal of oxyanions: A review. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1343–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Dadwhal, M.; Shahrivari, Z.; Ostwal, M.; Liu, P.K.T.; Sahimi, M.; Tsotsis, T.T. Adsorption of arsenic on layered double hydroxides: Effect of the particle size. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 4742–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, I.; Ramírez, E.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E.; Layrac, G.; Tichit, D. Highly basic catalysts obtained by intercalation of La-containing anionic complexes in layered double hydroxides. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 382, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, A.G.; Pigna, M.; Azam, S.M.G.G.; Sommella, A.; Rao, M.A.; Violante, A. Effect of competing ligands on the sorption/desorption of arsenite on/from Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides (Mg–Fe-LDH). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.; Mata, V.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption of carbon dioxide onto hydrotalcite-like compounds (HTlcs) at high temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Neves, V.; Ramos, V.; Silva, R.; Campos, J.; Silva, A.; Malta, L.; Senra, J. Layered double hydroxides as bifunctional catalysts for the aryl borylation under ligand-free conditions. Catalysts 2019, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellattif, M.; Mokhtar, M. MgAl-Layered double hydroxide solid base catalysts for henry reaction: A green protocol. Catalysts 2018, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebout, R.; Tichit, D.; Layrac, G.; Barama, A.; Coq, B.; Cota, I.; Rangel, E.R.; Medina, F. New basic catalysts obtained from layered double hydroxides nanocomposites. Solid State Sci. 2010, 12, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, T.; Jin, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, C. Structural effects of HCl adsorption on Mg–Fe hydrotalcite-like oxides at 350–650 °C in flue gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 14939–14947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhong, W.; Jin, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K. Treatment of hydrochloric acid in flue gas from municipal solid waste incineration with Ca–Mg–Al mixed oxides at medium—High temperatures. Energy Fuel 2014, 28, 4112–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Jing, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Z. Synthesis, sustained release properties of magnetically functionalized organic–inorganic materials: Amoxicillin anions intercalated magnetic layered double hydroxides via calcined precursors at room temperature. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Kang, H.; Ma, S.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X. High adsorption selectivity of ZnAl layered double hydroxides and the calcined materials toward phosphate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Gu, Q.; Jin, B. HCl Removal Using Calcined Ca–Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide in the Presence of CO2 at Medium–High Temperature. Catalysts 2020, 10, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010022
Wu W, Wu Y, Wang T, Wang D, Gu Q, Jin B. HCl Removal Using Calcined Ca–Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide in the Presence of CO2 at Medium–High Temperature. Catalysts. 2020; 10(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wei, Yuanfeng Wu, Tongwei Wang, Decheng Wang, Qinyang Gu, and Baosheng Jin. 2020. "HCl Removal Using Calcined Ca–Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide in the Presence of CO2 at Medium–High Temperature" Catalysts 10, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010022
APA StyleWu, W., Wu, Y., Wang, T., Wang, D., Gu, Q., & Jin, B. (2020). HCl Removal Using Calcined Ca–Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide in the Presence of CO2 at Medium–High Temperature. Catalysts, 10(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010022





