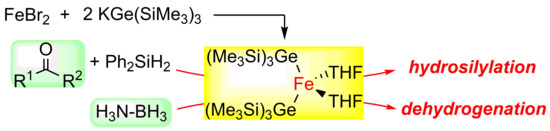
A Four Coordinated Iron(II)-Digermyl Complex as an Effective Precursor for the Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Iron–Digermyl Complex 1
2.2. Catalytic Performance of 1 toward Reduction Reactions
2.3. Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Catalysed by 1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Potassium Tris(trimethylsilyl)germanide
3.2. Synthesis of (THF)2Fe[Ge(SiMe3)3]2 (1)
3.3. General Procedure for the Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds Catalyzed by 1
3.4. General Procedure for the Catalytic Silylation of N2 Catalyzed by 1
3.5. General Procedure for the Dehydrogeantion of Ammonia Borane Catalyzed by 1
3.6. Synthesis of Dinuclear Iron Complex, [Ge(SiMe3)3]Fe(μ-OtBu)2Fe(THF)[Ge(SiMe3)3] (6)
3.7. X-ray Data Collection and Reduction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corey, J.Y. Reactions of Hydrosilanes with Transition Metal Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11291–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, J.Y. Reactions of Hydrosilanes with Transition Metal Complexes and Characterization of the Products. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 863–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, J.Y.; Braddock-Wilking, J. Reactions of Hydrosilanes with Transition-Metal Complexes: Formation of Stable Transition-Metal Silyl Compound. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 175–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, M.; Osakada, K. Sila-and Germametallacycles of Late Transition Metals. Organometallics 2010, 29, 4702–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, T.D. Transition-Metal Silyl Derivatives. In The Chemistry of Organic Silicon Compounds; Patai, S., Rappoport, Z.J., Eds.; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 1415–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Marek, I.; Rappoport, Z. The Chemistry of Organoiron Compounds; Patai, S., Rappoport, Z.J., Eds.; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Plietker, B. (Ed.) Iron Catalysis in Organic Chemistry; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, E.; Yoshikai, N. Low-Valent Iron-Catalyzed C−C Bond Formation−Addition, Substitution, and C−H Bond Activation. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 6061–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, I.; Knölker, H.-J. Iron Catalysis in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3170–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-L.; Li, B.-J.; Shi, Z.-J.; Direct, C.-H. Transformation via Iron Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1293–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolm, C.; Legros, J.; LePaih, J.; Zani, L. Iron-Catalyzed Reactions in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6217–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, S.; Sunada, Y. An isolable iron(ii) bis(supersilyl) complex as an effective catalyst for reduction reactions. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 2891–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Takaya, J.; Iwasawa, N. Use of Formate Salts as a Hydride and a CO2 Source in PGeP-Palladium Complex-CatalyzedHydrocarboxylation of Allenes. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1814–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, J.; Nakamura, S.; Iwasawa, N. Synthesis, Structure, and Catalytic Activity of Palladium Complexes Bearing a Tridentate PXP-Pincer Ligand of Heavier Group 14 Element (X = Ge, Sn). Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, J.; Iwasawa, N. Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of a Mononuclear η2-(Ge–H)palladium(0) Complex Bearing a PGeP-Pincer-Type Germyl Ligand: Reactivity Differences between Silicon and Germanium. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 5012–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrau, J.; Hamida, N.B.; Agrebi, A.; Satge, J. Bis(dimethylgermyl)alkane-iron tetracarbonyls: Synthesis, photolysis, and reactivity. Organometallics 1989, 8, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itazaki, M.; Kamitani, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakazawa, H. Synthesis, Characterization, and Crystal Structure of Germyl(phosphine)iron Complexes, Cp(CO)Fe(PPh3)(GeR3) (R = Et, nBu, Ph), Prepared from Cp(CO)Fe(PPh3)(Me) and HGeR3. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2010, 185, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itazaki, M.; Kamitani, M.; Nakazawa, H. Trans-selective hydrogermylation of alkynes promoted by methyliron and bis(germyl)hydridoiron complexes as a catalyst precursor. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7854–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itazaki, M.; Kamitani, M.; Ueda, K.; Nakazawa, H. Syntheses and Ligand Exchange Reaction of Iron(IV) Complexes with Two Different Group 14 Element Ligands, Cp(CO)FeH(EEt3)(E′Et3) (E, E′ = Si, Ge, Sn). Organometallics 2009, 28, 3601–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G.; Mackay, K.M.; Nicholson, B.K.; Tiel, M.V. Synthesis of iron carbonyl clusters with trigonal-bipyramidal E2Fe3 cores (E = Ge, Si). Crystal structures of (μ3-GeEt)2Fe3(CO)9, [μ3-Ge{Fe(CO)2Cp}]2Fe3(CO)9, and [μ3-Si{Fe(CO)2Cp}]2Fe3(CO)9. Organometallics 1990, 9, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Baumgartner, J.; Marschner, C. Silylgermylpotassium Compounds. Organometallics 2005, 24, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, M.; Kimura, H.; Komuro, T.; Okada, H.; Tobita, H. Synthesis, Structure, and Properties of Three-and Six-Membered Metallacycles Composed of Iron, Germanium, and Sulfur Atoms. Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 990–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobita, H.; Ishiyama, K.; Kawano, Y.; Inomata, S.; Ogino, H. Synthesis of Cationic Germyleneiron Complexes and X-ray Structure of [Cp*(CO)2FeGeMe2·DMAP]BPh4·CH3CN (Cp* = C5Me5, DMAP = 4-(Dimethylamino)pyridine). Organometallics 1998, 17, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Brocks, F.; Weiss, E. Tetraphenylzirkonacyclopentadien-derivate als synthone für tetraphenylthiophenmonoxid und substituierte germanole. J. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 453, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, B.; Dai, X.; Xu, S.; Zhou, X. Novel Rearrangement Reactions. 3. Thermal Rearrangement of the Diruthenium Complex (Me2SiSiMe2)[(η5-C5H4)Ru(CO)]2(μ-CO)2. Organometallics 1998, 17, 5406–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhou, X.; Weng, L. Reactions of Doubly Bridged Bis(cyclopentadienes) with Iron Pentacarbonyl. Organometallics 2003, 22, 5543–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, E.M. Utilizing the Evans method with a superconducting NMR spectrometer in the undergraduate laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 1992, 69, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, C. Paramagnetic Susceptibility by NMR: The “Solvent Correction” Removed for Large Paramagnetic Molecules. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, G.A.; Berry, J.F. Diamagnetic Corrections and Pascal’s Constants. J. Chem. Educ. 2008, 85, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossin, A.; Peruzzini, M. Ammonia–Borane and Amine–Borane Dehydrogenation Mediated by Complex Metal Hydrides. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 8848–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaraman, E.; Nandakumar, A.; Jaiswal, G.; Sahoo, M.K. Iron-catalyzed dehydrogenation reactions and their applications in sustainable energy and catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3177–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, N.T.; Webster, R.L. Iron Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Amine-and Phosphine-Boranes. Isr. J. Chem. 2017, 57, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, R.T.; Gordon, J.C.; Hamilton, C.W.; Henson, N.J.; Lin, P.-H.; Maguire, S.; Murugesu, M.; Scott, B.L.; Smythe, N.C. Iron Complex-Catalyzed Ammonia–Borane Dehydrogenation. A Potential Route toward B–N-Containing Polymer Motifs Using Earth-Abundant Metal Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5598–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glüer, A.; Förster, M.; Celinski, V.R.; Schmedt auf der Günne, J.; Holthausen, M.C.; Schneider, S. Highly Active Iron Catalyst for Ammonia Borane Dehydrocoupling at Room Temperature. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 7214–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.R.; Robertson, A.P.M.; Lee, K.; Manners, I. Photoactivated, Iron-Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Amine–Borane Adducts: Formation of Boron–Nitrogen Oligomers and Polymers. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4099–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, J.R.; Schäfer, A.; Robertson, A.P.M.; Lee, K.; Turner, J.; Whittell, G.R.; Manners, I. Iron-Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling/Dehydrogenation of Amine–Boranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3048–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, J.K.; Bange, C.A.; Farmiloe, S.E.; Waterman, R. Visible Light Photocatalysis Using a Commercially Available Iron Compound. Organometallics 2017, 26, 3891–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Krause, J.A.; Guan, H. Mechanistic Studies of Ammonia Borane Dehydrogenation Catalyzed by Iron Pincer Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11153–11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, A.; Ushiyama, H.; Yamashita, K. Theoretical studies on ammonia borane dehydrogenation catalyzed by iron pincer complexes. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2016, 1090, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgas, N.; Stöger, B.; Veiros, L.F.; Kirchner, K. Access to FeII Bis(σ-B−H) Aminoborane Complexes through Protonation of a Borohydride Complex and Dehydrogenation of Amine-Boranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13874–13879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, N.T.; Mahon, M.F.; Webster, R.L. Phosphine-and Amine-Borane Dehydrocoupling Using a Three-Coordinate Iron(II) β-Diketiminate Precatalyst. Organometallics 2017, 36, 2262–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäcker, A.; Li, Y.; Fritz, M.; Grätz, M.; Ke, Z.; Langer, R. Redox-Active, Boron-Based Ligands in Iron Complexes with Inverted Hydride Reactivity in Dehydrogenation Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7300–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alig, L.; Fritz, M.; Schneider, S. First-Row Transition Metal (De)Hydrogenation Catalysis Based On Functional Pincer Ligands. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2681–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, S.; Luconi, L.; Giambastiani, G.; Rossin, A.; Peruzzini, M.; Golub, I.E.; Filippov, O.A.; Belkova, N.V.; Shubina, E.S. Ammonia Borane Dehydrogenation Catalyzed by (κ4-EP3)Co(H) [EP3 = E(CH2CH2PPh2)3; E = N, P] and H2 Evolution from Their Interaction with NH Acids. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4296–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burla, M.C.; Caliandro, R.; Camalli, M.; Carrozzini, B.; Cascarano, G.L.; De Caro, L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Polidori, G.; Siliqi, D.; Spagna, R. IL MILIONE: a suite of computer programs for crystal structure solution of proteins. J. Appl. Cryst. 2007, 40, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creagh, D.C.; McAuley, W.J. International Tables for Crystallography; Table 6.1.1.4; Wilson, A.J.C., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Ibers, J.A.; Hamilton, W.C. Dispersion corrections and crystal structure refinements. Acta Cryst. 1964, 17, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creagh, D.C.; McAuley, W.J. International Tables for Crystallography; Table 4.2.6.8; Wilson, A.J.C., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Creagh, D.C.; Hubbell, J.H. International Tables for Crystallography; Table 4.2.4.3; Wilson, A.J.C., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- CrystalStructure 4.2.5: Crystal Structure Analysis Package; Rigaku Corporation: Tokyo 196-8666, Japan, 2000–2017.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL Version 2017/1: A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Entry | Ligand | Time (h) | Conv. (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | 24 | ~ 0 |
| 2 | phenanthroline | 24 | 50 |
| 3 c | phenanthroline | 24 | 37 |
| 4 | phenanthroline | 72 | 70 |
| 5 | bathophenanthroline | 24 | 9 |
| 6 | Diamine d | 24 | 24 |
| 7 | iPr2IMMe e | 24 | 32 |
| 8 | TMEDA | 24 | ~ 0 |
| 9 | pyridine | 24 | 5 |

| Entry | Additive | Conv. (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | 5 |
| 2 | tBuOH | 50 |
| 3 c | tBuOH | 72 |
| 4 | tBuNH2 | 76 |
| 5 | diethylamine | 64 |
| 6 | diphenyamine | 61 |
| 7 | 2,4,6-trimethylaniline | 64 |
| 8 | 2,6-diisopropylaniline | 30 |
| 9 | 2-ethylhexanoic acid | 39 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, Y.; Sunada, Y. A Four Coordinated Iron(II)-Digermyl Complex as an Effective Precursor for the Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Catalysts 2020, 10, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010029
Kobayashi Y, Sunada Y. A Four Coordinated Iron(II)-Digermyl Complex as an Effective Precursor for the Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Catalysts. 2020; 10(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Yoshinao, and Yusuke Sunada. 2020. "A Four Coordinated Iron(II)-Digermyl Complex as an Effective Precursor for the Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane" Catalysts 10, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010029
APA StyleKobayashi, Y., & Sunada, Y. (2020). A Four Coordinated Iron(II)-Digermyl Complex as an Effective Precursor for the Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Catalysts, 10(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010029