1. Introduction
Layered carbon nitride (CN) compounds are a class of carbon-based materials with high C:N ratios, whose structure was described as consisting of either heptazine or triazine building block units linked together to form conjugated aromatic domains. Among these, polymeric graphitic CN has gained increasing attention across a range of applications, including air purification [
1], water treatment [
2,
3], and photocatalysis [
4,
5], because of its unique electronic structure, high corrosion stability, and large availability of surface chemical functionalities. CN has been identified as a viable system for the water splitting reaction, with and without the presence of metals such as platinum or gold nanoparticles (NPs) [
6]. A thorough review of their applications for water splitting was presented by Mishra et al. [
7]. Other applications include the use of carbon nitride as a support for catalysts, such as nickel NPs for ethanol electro-oxidation [
8], gold NPs for three-component coupling reactions [
9], Ag
2MoO
4 NPs for photocatalytic pollutant degradation [
10], and iron carbide for the oxygen reduction and evolution reactions [
11]. One of the key elements of their effectiveness is the high abundance of N-functional groups, potentially acting as anchoring sites for metal species thereby enabling tuning of physico-chemical properties. A study focusing on the nitrogen species and N-Pd interactions on N-functionalized nanocarbon showed the benefits of the nitrogen atoms in modifying the surface electronic structure of Pd nanoparticles which in turn influence the catalyst performance for several reactions [
12]. Perez-Ramirez exploited this functionality to synthesize single atom palladium on carbon nitride catalysts [
13]. Similar atomic Pd-CN materials were studied by Vile and were utilized for flow hydrogenation of alkynes and nitroarenes, but this could potentially be put to a much wider use as stable, resource-efficient palladium catalysts are highly desirable [
14,
15]. More recently, CN was successfully used to anchor a well-established homogeneous catalyst moiety [Cp*IrCl]
+ for hydrogenation reaction. The coordination at exposed N edge sites led to a primary inner coordination sphere analogous to known homogeneous complexes of the general class [Cp*IrCl(NN-κ2N,N’)]
+ but, due to the restricted steric environment, the selectivity was tuned towards terminal alkynes [
16].
Not only does CN offer N anchoring sites in greater abundance than N-doped graphitic carbon materials, but due to its polymeric nature, it also provides a more flexible structure that can better accommodate metal NPs. Arrigo et al. [
17] demonstrated for the case of direct H
2O
2 synthesis that during reaction conditions the carbon nitride support encapsulates the active Pd NPs phase, maintaining the beneficial electronic modification on the exposed Pd over very long reaction times and preventing the excessive detrimental Pd exposure leading to the unwanted total hydrogenation of O
2 to H
2O.
Protection of the active phase from the harsh reaction condition is one of the challenges to realize in the design of multifunctional materials for catalytic application as this will guarantee a longer lifetime of the catalyst. This is especially true for aqueous phase, early transition metal catalyzed reactions, in which pH dependent dissolution equilibria interfere unfavorably leading to the loss of active sites. In such cases, we propose that, due to the interaction between the nitrogen, the metal, and the flexible polymer structure, CN is an ideal support material to limit the interaction of the active phase with the aqueous environment producing potentially a dynamic, smart, self-healing catalyst. In enzymatic catalysis, such a role is played by the pocket of ligands of the protein component which controls the proton and water transfer to the active sites preventing disruption of the enzymatic activity [
18].
In this study we apply this idea to create a multifunctional system which can function as an oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst. Catalysts for this reaction will commonly comprise of rare and expensive metals, such as palladium or platinum, so a key challenge is to retain this high activity and stability whilst using more inexpensive, earth abundant materials. In addition, catalysts need to show long term stability in basic to neutral media, along with high activity. Our selected system is manganese oxide on graphitic carbon nitride.
Mn oxide-based electrodes were explored for both the ORR and oxygen evolution reaction (OER), as they can potentially be used in reversible fuel cells. Mette et al. [
19] prepared MnOx/CNT catalysts with a range of loadings of MnO, using impregnation and a precipitation method. They demonstrated good activity in OER and stability for a 5 wt.% catalyst prepared by impregnation, under neutral conditions.
Jiao et al. studied manganese oxide nanoparticles on silica for OER, driven by visible light, at room temperature and a pH of 5.8 [
20]. They demonstrated that increasing calcination temperature leads to a decrease in the manganese oxidation state, from 4+ at 500 °C to 2.85+ at 900 °C. The highest OER activity was achieved by a catalyst calcined at 600 °C, which had a high concentration of Mn
2O
3. Studies by Feng et al. showed the effectiveness of graphene oxide supported Mn
3O
4 nanocatalysts for ORR [
21]. Calcination in air was deemed to be important for improving the ORR active site density, whilst incorporation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) lead to an overall improvement of stability and activity, due to the higher conductivity. Various crystalline phases of Mn oxide, along with an amorphous phase, were shown to have strong OER and ORR activity under alkaline conditions, with activity varying significantly with phase [
22,
23].
Huynh et al. studied the OER behavior of manganese oxide films across a pH range covering acidic, neutral, and basic systems [
24]. They noted its comparative stability (versus Co or Ni based films) under strongly acidic conditions. Under alkaline conditions (pH 11.35 to 13.30) they observed Mn in an average oxidation state of 3.68+, showing a mixture of Mn(III) and Mn(IV) species to be present.
N-doping of water splitting catalysts has been shown to be beneficial on a number of occasions [
23,
24]. The improvements of catalysts with the addition of nitrogen seems to be dependent on the nitrogen–metal interaction, which has been shown to be very significant for a range of metals, including cobalt, tungsten, and manganese. Nitrogen doping of a tungsten carbide catalyst significantly improved the intrinsic activity, whilst also improving its stability [
25]. Similarly, N-doping of a Co/graphene catalyst yielded high activity for OER and ORR, along with high stability in basic environments [
26].
Here we explore the possibility of achieving enhancement and tuning of the catalytic performance of CN in ORR by using Mn. To this goal we explore two different synthetic methods to immobilize Mn oxides: Impregnation [
27] and the oleic acid route [
28], modified from existing procedures. In this way we afford a different particle size, different Mn oxide phase and different metal support interaction. We apply high angle annular scanning dark field transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM), high angle annular scanning bright filed transmission electron microscopy (HAABF-STEM), electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and UV-Vis spectroscopy to elucidate the structure of the synthetized materials with the goal of guiding the synthesis of improved, inexpensive ORR catalysts. We will show that by designing a synthetic protocol aimed to enable metal NPs support interaction, it is possible to tune the catalytic performances of the electrocatalysts.
2. Results
Firstly, we will report the catalytic performance of the catalysts in the ORR in basic solutions. Subsequently we will report the characterization of these materials to ultimately draw a structure function relationship. In total we explore the reactivity and structural characteristic of 4 electrocatalysts: The CN used in this work is a carbon nitride material synthetized using the procedure reported in ref. [
17] and thermally annealed at 500 °C in N
2. Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN is the impregnated Mn on CN synthetized using the procedure reported in in ref. [
17] and thermally annealed at 500 °C in inert atmosphere before the impregnation step; T-MnOx_WI_CN is obtained from Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN but subjected to an additional post-impregnation thermal treatment at 200 °C with the aim to decompose the Mn acetate precursor. MnOx_OAR_CN is the sample obtained by immobilization of preformed NPs on Mn oxide obtained via oleic acid route (OAR) on CN as synthetized without any additional thermal treatment. Additional samples will be prepared as references as indicated in the relevant result sections.
2.1. ORR
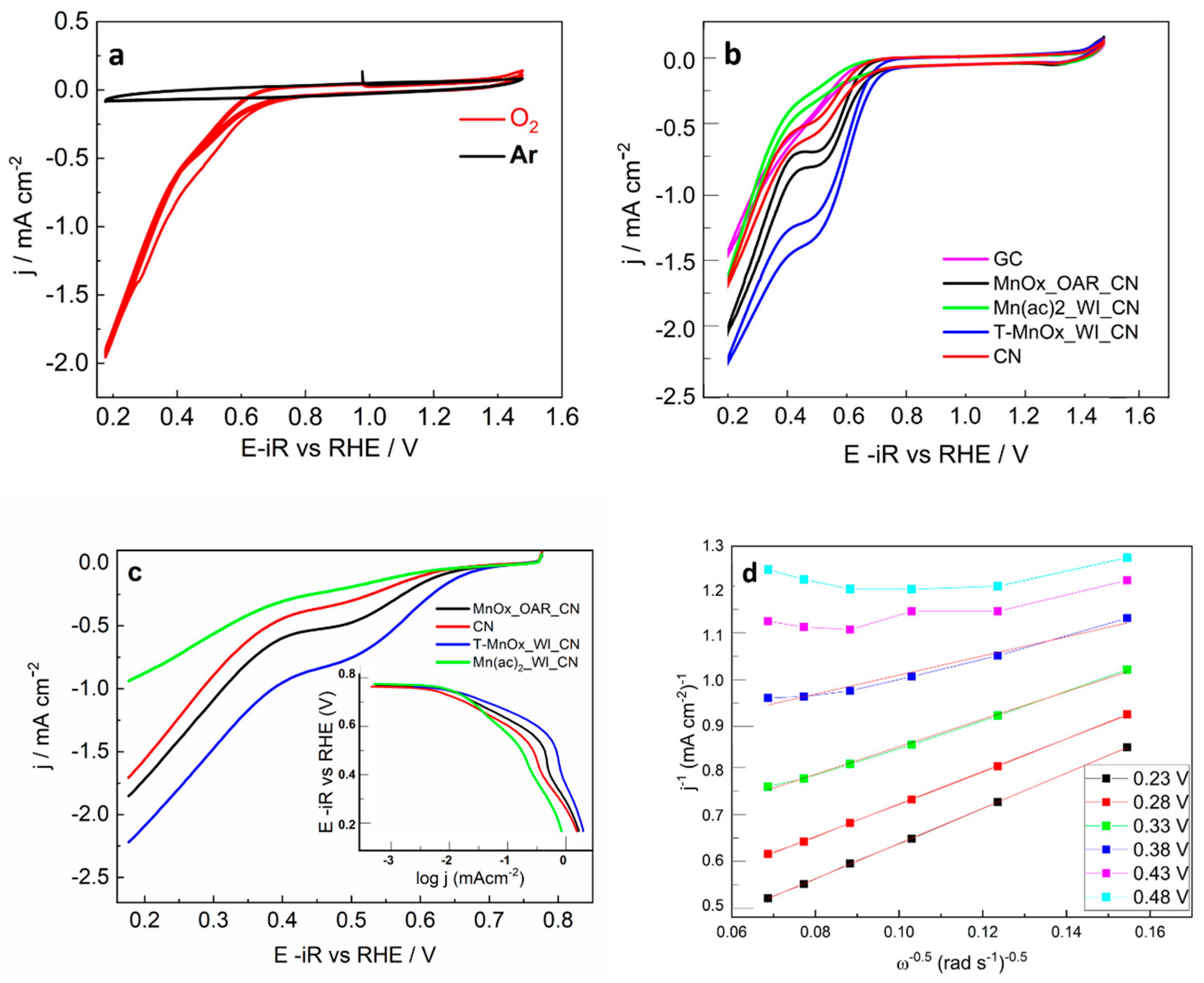
The electrochemical behavior of the carbon nitride and carbon nitride-supported Mn oxide samples mixed with activated carbon was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) in argon saturated solution and O
2 saturated solutions. Under argon saturated solution, the CV profiles for all the samples are dominated by the capacitance behavior of the C support, whereas under O
2, faraday processes due to the oxygen redox chemistry are observed. The comparison of the CV under argon and O
2 is reported for the sample T-MnOx_WI_CN as an example in
Figure 1a. Owing to the higher hydrophobic character of the CN, we observe a reduced capacitance for this sample compared to the Mn-containing samples in which MnOx confers hydrophilic character to the samples.
Figure 1b shows the comparison of the CV measured for all the pure CN samples (not mixed with activated carbon) under O
2 saturated solution including the bare glassy carbon (GC) working electrode. The analysis of the electrocatalytic behavior of the pure samples allows us to identify more clearly the differences in electrocatalytic behavior of the samples.
Figure 1c reports the rotating disk linear voltammetry (LV) of the same samples under O
2 saturated solution. The Tafel curve constructed from these data is reported in the inset of
Figure 1c.
From the Tafel plot in the inset of
Figure 1c it is clear that the ORR is under kinetic control between 0.8 and 0.7 V, dominant kinetic control in the potential region between 0.7 and and 0.5 V (the current depends on the potential applied) and dominant diffusion control (current independent of potential) for potentials below 0.5 V. The ORR onset potential and half-wave potentials obtained from
Figure 1c are summarized in
Table 1 together with the Tafel slopes relative to the samples in the potential range 0.7–0.5V. The current density j in the kinetically controlled region represents the electrochemical reaction rate, where the higher the value of j the higher the catalytic activity towards ORR. We can therefore conclude that the activities vary in this set of samples in the order T-MnOx_WI_CN > MnOx_OAR_CN > CN > Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN. This is also reflected in the value of the Tafel slope in the potential region between 0.7 and 0.5, which is lowest for T-MnOx_WI_CN (100 mV/dec) and highest for the Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN (200 mV/dec). A high value of the Tafel slope indicates a very slow process and conversely a small value of Tafel slope indicates a fast reaction.
Comparable analysis on Pt/C gave a Tafel slope value between 92–104 mV/dec. [
29,
30]. Similarly, carbon nitrides have been shown to have a Tafel slope around 197 mV/dec in nanorod form, or 210 mV/dec in bulk form [
31].
The onset potential and half wave potential for ORR in the kinetically controlled region are very similar for all the samples, with the best performance for the T-MnOx_WI_CN with a value around 0.7 V and 0.58 V, respectively. In general, we noted for these samples a high ohmic resistance due to the poor conductivity of these materials, which causes the high overpotential observed for ORR in these samples. This is a major limiting factor for the application of carbon nitride as discussed in the literature [
32]. In comparison, literature data indicate a value of onset potential at 0.86V, half wave potential of 0.69 V for ORR on NCNTs [
12]. In the diffusion limited region below 0.4 V a well-defined plateau would be expected. A monotone increase of the cathodic current is observed instead, commonly attributed to secondary reactions. This behavior is commonly observed when the availability of sites that can break the O–O bond of O
2 is limited and H
2O
2 is indeed the main reaction product observed [
12]. From the Tafel plot in the inset in
Figure 1c, this region is under dominant diffusion control.
The Koutecky–Levich (KL) plots not corrected for the non-ORR current, were obtained for all the samples from the LV at various electrode rotation rates (ω) (400, 625, 900, 1225, 1600, and 2025 rpm). The KL plots for the ORR show a linear relationship between the current and the rotation rate at a fixed potential only for potentials within the mass-transfer limiting region below 0.4 V.
The number of electrons transferred during the reaction at various potentials in the diffusion limited region are also summarized in
Table 1. The KL plot for the T-MnOx_WI_CN is presented in
Figure 1d as an example.
We can see that at low voltage the number of electrons transferred for the CN is equal to 2e- indicating the prevalent formation of H
2O
2 from oxygen. This is typically observed for C materials [
33]. A similar behavior is shown for the MnOx_OAR_CN; however, note that this latter sample shows superior performance compared to the Mn-free CN indicating the beneficial effect of Mn species. As the potential is increased, the number of electrons transferred increases and approaches the value of 4e- only for the T-MnOx_WI_CN. This indicates that ORR proceeds via a mix of the four-electron and two-electron pathways at these potential values. The addition of Mn into the CN via wet impregnation followed by thermal treatment has a beneficial effect in promoting the 4e- transfer reduction of O
2 to water.
However, at higher voltage, the obtained number of electrons transferred reaches a value above 4e-. We can see that at higher voltage, the data points in the K-L plots in
Figure 1d show significant curvature at high ω numbers which cannot be well described by a linear fit. The slope of the linear fit of these points is lower thus leading to high value of the number of the electrons transferred. This was described in the literature as the result of an increase in the kinetic current with rotation rate at these higher potentials [
34].
Similar to the shift of the onset potential for ORR to lower values, the voltage-current profile in the mass transfer limited region deviating from a plateau indicates a hinderance towards the O-O cleavage possibly due to the lack of specific surface chemisorption sites for O
2 or a consequence of the general poor conductivity of these samples. To overcome the electron transfer limitation of the support, we have investigated physical mixtures of the CN-based samples with conductive C materials. The maximum current obtained in the diffusion limited region was not higher, and the electrochemical behavior of the final mechanically mixed composite was dominated by activated C (
Figure 1a for MnOx_WI_CN). This suggests that the Mn phase plays an important role in the activation and reduction of O
2.
The biggest challenge we have faced was the preparation of a stable film of CN on the glassy carbon electrode, which, together with the poor conductivity observed, makes the application of CN in electrocatalysis challenging. Bottom up approaches for the synthesis of CN thin films proved more suitable [
35].
2.2. HAABF-STEM, HAADF-STEM, and EELS Analysis
STEM images in bright field (BF) and dark field (DF) mode are shown in
Figure 2a–d for samples prepared by impregnation method (T-MnOx_WI_CN) and oleic acid route (MnOx_OAR_CN), respectively. EELS mappings at the CK, OK, NK, and Mn L edges for the two samples are also shown in
Figure 3a,b, respectively. For the impregnation route, higher contrast regions reveal the presence of large particles with irregular morphologies (darker region in the HAABF-STEM in
Figure 2a and brighter region in the HAADF-STEM image in
Figure 2b, respectively). These are confirmed as a Mn oxide phase by EELS elemental mapping (
Figure 3a). In contrast, in MnOx_OAR_CN, the higher contrast regions in
Figure 2c,d do not provide a clear picture of the morphology of Mn oxide NPs and their size. From the high-resolution STEM images in
Figure 4 one could also conclude that very small NPs including sub-nanometer NPs are present only in the case of MnO
x_OAR_CN and these appear to have a preferential localization which one could consider to account for the exposed surface of the support. The elemental mapping for this sample in
Figure 3b shows a rather homogeneous distribution of Mn indicating not only the presence of Mn oxide nanoparticles in the nm range but also of a few Mn atom clusters.
Figure 4a shows NPs on the CN support for T-MnOx_WI_CN, where there is no indication for the presence of low nuclearity Mn species on the support. The contrast variation in the image of
Figure 4b is very different than in
Figure 4a. Such a contrast variation indicates that the size of the NPs immobilized on MnOx_OAR_CN is smaller than in the case of T-MnOx_WI_CN, ranging from few nm particles to small cluster and possibly also single atom species. This is expected as the impregnation of the metal precursor is followed by a thermal annealing to decompose the acetate into an oxide phase, which will also favor sintering. Indeed, the use of a surfactant during the synthesis of NPs has the purpose of preventing the poor size control and agglomeration typically observed in wet impregnation [
36,
37]. The quantitative elemental analysis expressed in atom% as determined by EELS is reported in
Table 2. The high concentration and homogeneous distribution of N in these samples is confirmed, with a C:N ratio very close to 1. However, note that it is not possible to obtain information on the CN phase based on the C:N ratios due to fact that the synthetic procedure for the immobilization of the Mn oxide NPs introduces additional C impurities. Moreover, from the elemental analysis, the Mn:O ratio for the MnOx_OAR_CN is 1:6 and therefore one could infer low nuclearity Mn species including single atomic species are also present on this sample.
2.3. XPS Characterization
We analyze the electronic structure of the CN and CN-supported Mn oxide electrocatalysts by means of XPS. The fitted C1s and N1s spectra of the samples are reported in
Figure 5a,b, respectively. In this work, we use the smallest number of components in the fitting that consistently describes spectra lineshapes as well as differences amongst the samples. To describe the nature of the species in the XPS spectra we refer to one of the structural formulas proposed for carbon nitrides with molecular formula C
3N
4, shown in
Figure 5c. Therein the various N and C species are color coded consistent with the colors used for the relative peaks in the fitting of the XPS spectra. The bulk structure of this form of CN, often referred to in the literature as g-C
3N
4, can be described as a network of sp
2/sp
3 N atoms linking tri-s-triazine ring subunits with aromatic π-delocalization. All C1s spectra of the different CN samples show an asymmetric peak (C1 component in blue in the fitted C1s spectrum in
Figure 5a) with maximum at a binding energy (BE) of circa 284.4 eV and a symmetric, more intense peak (C3 component in red) at 288 eV. The first peak is due to C=C bonds in graphitic carbon, whose large FWHM indicates the presence of C atoms in sp
3 bonding or highly defective sp
2 carbon phase and edge terminated C=N or C=O species. The C3 peak is assigned to conjugated N=C-N bonds including quaternary N species, which are typical for CN [
38]. The corresponding N1s XPS spectra show 4 components assigned to pyridine-like C=N species (N1 species at 398.5 eV is the component in red in
Figure 5b), conjugated amine C=N-H species (N2 at 399.9 eV is the component in blue), quaternary N (N3 at 401 eV is the component in green) and NOx species (N4 at 404 eV), respectively. This speciation is consistent with the literature [
32,
38,
39] and indicates that this material is a heptazine-based carbon nitride with a similar abundance of terminal NH
2 groups and sp
2/sp
3 linking N atoms. Regardless of the method of the immobilization of MnOx, the N1s spectra remain largely unchanged, indicating the presence of the same N species with a similar relative distribution. A closer inspection of the fitting procedure reveals the presence of a small component in the case of the impregnated samples, which is shifted by +0.5 eV with respect to the pyridine species (BE = 399 eV insets in
Figure 5b), which indicates the interaction of this species with MnOx particles [
12]. Interestingly, whilst the TEM analysis of the MnOx_OAR_CN indicates possible single atomic species, the N1s XPS analysis does not reveal the introduction of a different N bonding environment upon the immobilization of the Mn NPs via oleic acid route.
In contrast, the carbon C1s spectra differ more substantially. The least affected by the MnOx immobilization are the MnOx_OAR_CN and the T-MnOx_WI_CN samples. In the former case, we do not expect significant changes due to the fact that the NPs are preformed and simply adsorbed on the support. The slight enhancement of the lower BE component in the C1s spectra for these samples could be due to some disruption of the carbon nitride at the sp
3 N atoms linking the tri-s-triazine ring subunits as a consequence of the preparation, i.e., the reaction of Mn with the support during the thermal annealing that favors the removal of N species. Moreover, additional carbon impurities, i.e., oleic acid used in the synthesis of the NPs in the case of the MnOx_OAR_CN can also lead to an increase in the C1 peak. We note that the main C1 component in these spectra is much broader than the C=C component in graphite [
40] and we expect that some of the C=N bonding configurations and C=O bonding configuration are included in this C1 component.
In contrast, for the Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN sample we observe a significant increase of the low BE component C1 and a significant reduction of the component C3, the latter being the signature of the sp
3 N atoms linking the tri-s-triazine ring subunits in the CN structure. We also observe the appearance of a new component, C2, at 285.7 eV in the C1s XPS spectrum which is attributed to substitutional C=N or C=O species [
38,
39] in graphitic C. Note that the C2 species differs from the C3 species as it is localized at the edges of a C aromatic domain or a C conjugated species with no electron withdrawing heteroatoms atoms in 3 position with respect to it. The reduction of the C3 peak is in line with a reduced overall intensity in the N1s XPS spectrum of this sample. We therefore conclude that the C1 and C2 components for this sample are predominantly due to contributions of the acetate ligands of the Mn precursor that contains C=O bonds and to a lesser extent due to the C=N bonds of the carbon nitride support. The Mn2p XPS spectra are shown in
Figure 5d. The analysis of the Mn2p XPS is complicated by the overlapping multiplet splitting structures of different possible oxidation states, which makes fitting rather complicated. Nevertheless, we think it is useful to consider the Mn2p XPS here to obtain some insight into the Mn speciation in these samples. Besinger et al. [
41] provided a detailed analysis of the Mn2p XPS for several Mn oxides. Accordingly the Mn2p
3/2 line-shapes for Mn(II), Mn(III), Mn(IV) in MnO, Mn
2O
3, and MnO
2 are rather similar and described by 5–6 peaks in the range between 641–645 eV, which makes the assignment not easily accessible based on chemical shift consideration. The only species that can be identified unambiguously is Mn(II), which is characterized by a low BE component at 640.3 eV unique for this species. From this consideration we can conclude that a Mn(II) species is present not only on the Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN but in all the samples investigated. Of particular interest, the presence of a satellite at 646 eV particularly pronounced for the sample MnOx_OAR_CN, indicate the existence therein of nanostructured MnO phase. The less pronounced satellite feature in the T-MnOx_WI_CN might be an indication of a more abundant Mn(III) species in this sample, or no MnO segregated phase. The EELS Mn L edge spectra for these two samples confirm the presence of a predominantly MnO phase on MnOx_OAR_CN (not shown).
More information about the crystallographic phase of the T-MnOx_WI_CN sample will be provided by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) analysis shown in
Figure 6.
2.4. XRD Characterization
While the MnOx_OAR_CN and Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN showed only diffraction peaks related to the nitride phase (not shown), we were able to characterize the Mn phase in the impregnated sample T-MnOx_WI_CN, consistent with a larger particle size present on this sample. However, the diffraction peaks observed for the Mn oxide phase in the fresh T-MnOx_WI_CN are generally very broad and not very intense, indicating the small size of the crystallites due to the nanoparticulate nature as well as the poor crystallinity of the phase. To confirm their assignment, a temperature programmed XRD experiment was performed for T-MnOx_WI_CN to clearly identify the expected transformation involving the Mn phase. The data recorded in situ at room temperature, 300 °C, and 500 °C in nitrogen atmosphere are presented in
Figure 6. We were able to demonstrate the transition from primarily Mn
3O
4 on the starting materials and up to 300 °C, into a mixture of Mn
2O
3 and Mn(OH)
2.
Prior thermal studies of Mn
3O
4 nanoparticles under nitrogen have consistently shown them to be stable up to 300 °C, with Mn
5O
8 formed at 350 °C and stable to around 550 °C, and eventually Mn
2O
3 at 700 °C [
28]. Other studies showed that nanoparticles starting as Mn
3O
4 were converted to Mn
2O
3 (again, via Mn
5O
8) by 575 °C, which continued to be stable up to 700 °C [
42]. Given the variation in support and preparation, this suggests that the Mn
3O
4 appearing is correctly assigned. The presence of Mn(OH)
2 was not observed elsewhere, indicating there was water presence in our in situ system originating from the sample.
Consistently to literature data, [
32,
43] two diffraction peaks at ca. 13° (210 plane) and 27° (002 plane) are found for CN, which are attributed to the in-plane packing and inter-planar stacking of conjugated aromatic ring, respectively. This sample shows a much less intense peak due to the in-plane packing and a more intense peak due the inter-planar stacking of conjugated aromatic systems indicating a peculiar morphology for the CN support in this sample, which is characterized by CN particles composed of many narrow ribbon-like platelet crystals stacked together. The diffraction data are consistent with a previous contribution on the characterization of this material by means of near edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (NEXAFS), which has identified a large abundance of terminal sp
2/sp
3 −C=N−H <=> =C−N−H enamine/imine N functionalities with limited in-plane aromatic π delocalization. [
17] Our results are consistent with a g-CN(H) having a poly-heptazine structure likely related to Liebig’s melon structure but containing more laterally extended “graphite-like” units [
32].
It is interesting to note that the diffraction peak shifts to a smaller value upon annealing, indicating an increase of the interlayer distance due to the thermal expansion.
2.5. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
We have further characterized these samples by means of UV-Vis spectroscopy to determine the electronic properties of these materials, which are determined by π–π* transitions of the heterocyclic aromatic building block units causing the typical yellow/brown coloration.
For treated CN, the UV-vis reflectance spectrum in
Figure 7a shows the absorption edge around 488 nm, which is close to values which have previously been reported for carbon nitride [
43]. The variation in light absorption with preparation route and treatment temperature is significant. The MnOx_OAR_CN sample shows the smallest change from the CN. Moreover, these show a lower wavelength than any impregnated catalyst. The addition of Mn acetate on CN via impregnation produces the appearance of absorption features above 500 nm and an apparent shift of the absorption edge to a higher wavelength (see Mn(ac)2_WI_CN, Mn(ac)2_WI_CN* and T-MnOx_WI_CN* in
Figure 7a, where CN* refers to CN used without the 500 °C pretreatment) whereas the post-impregnation thermal treatment at relatively higher temperature causes the disappearance of the absorption at high wavelength (500 °C for T-MnOx_WI_CN
a in
Figure 7, where CN
a refers to a sample with 500 °C post treatment rather than 200 °C). In addition, the absorption of the impregnated samples is significant even at high wavelength (around 50% reflectance at 800 nm). A broad absorption band in the wavelength range 400–700 nm was reported for small Mn oxide NPs [
44] but also for CN thermally treated above 550 °C to increase the graphitic order of the material.
The values of the band gap are summarized in
Table 3 whereas Tauc plot are reported in
Figure 7b. Accordingly, the CN sample presents a band gap of 2.69 eV, which is within the value reported in the literature for g-C
3N
4 [
32]. A similar value of 2.7 eV is found for MnOx_OAR_CN. The addition of Mn via impregnation reduced the band gap to 2.55 eV for the Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN whereas the thermal annealing at very high temperature (here shown for the thermal annealing at 500 °C in inert gas atmosphere for T-MnO
x_WI_CN
a) increases the band gap again. This is possibly correlated to the reduction of the graphitic order, observed in the in situ XRD measurements as an increase of the inter-planar distance between the CN layers and a decrease of the size of the crystalline domains along the (002) plane, which compensate for the beneficial effect of Mn oxide NPs. The reduction of the band gap in the sample containing the Mn synthetized by impregnation is very interesting and provides synthetic direction for fine tuning of the band gap of carbon nitride. To further investigate this, we included here the UV-Vis characterization of CN impregnated with Mn following slightly different routes as indicated in the experimental part. Particularly, Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN* and T-MnOx_WI_CN* were synthetized following the same procedure as for Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN and T-MnOx_WI_CN, however in these last two samples the CN was subjected to a thermal treatment up to 500 °C prior to the impregnation as indicated in the experimental part to remove residual oligomeric species from the CN synthesis. For the former samples Mn acetate was impregnated on the CN as synthetized. Interestingly we notice also a reduced band-gap of 2.63 eV and 2.58 eV for Mn(ac)
2_WI_CN* and T-MnOx_WI_CN*, respectively. This indicates that the thermal annealing at 500 °C preceding the impregnation does not have significant impact on the band gap and confirm that Mn species have a significant influence in the reduction of the band gap. In summary, we can distinguish two groups: CN and CN-supported Mn species in which Mn does not interact with the support (see for example MnO
x_OAR_CN) have a relatively higher band-gap; samples containing Mn species interacting with the support have a relatively smaller band gap. The interaction of Mn with N species as seen by the shift of few pyridine N species in the N1s XPS spectra produces an upshift of the HOMO level thereby reducing the band-gap.
However, the values are very similar to each other and therefore we should not expect significant changes in the semiconducting properties of these materials.
3. Discussion
The electrocatalytic performances of the CN and CN-supported Mn systems show an onset potential for ORR around 0.7 V vs. RHE at a theoretical pH of 13 and a Tafel slope of 100 mV in the best case scenario. The value of the onset potential is rather low which indicates a significant overpotential for the O2 activation and reduction on these systems. We note that the surface pH for these materials might deviate from the bulk pH and therefore the voltages numerical rescaling might be not exact. The Tafel slope is slightly higher than the value reported for Pt at low overpotential (60 mV/dec) and smaller than the value reported for Pt at high overpotentials (120 mV/dec). This is an encouraging result although the mass-transfer limiting current is not very high (circa −1 mA cm−2 below 0.5V in the best case scenario of MnOx_WI_CN).
Electron microscopy images show that the “OAR” sample has much smaller and better dispersed particles than the “WI” samples. The nanoparticles are prepared before being combined with the support, and there is no post-impregnation high-temperature treatment, so any sintering or agglomeration is not expected. From the elemental mapping and quantitative elemental composition in
Figure 3 and
Table 2, respectively, we conclude that also few atom cluster and single Mn atom species can be present on this sample.
The analysis of the band gap indicated the beneficial effect of the coordination of Mn species to the pyridine N sites regardless of the nature of the Mn phase being in the precursor acetate state, or decomposed to form Mn3O4. In contrast, neither the immobilization of preformed small MnO/Mn3O4 nanoparticles nor single Mn atoms did not significantly modify the band gap. Consistently, N1s XPS analysis does not show differences in these samples compared to the CN with the exception of a different C1s signal for the Mn(ac)2_WI_CN, which is due to the oleic acid ligands. This indicates that these small species are not directly interacting with the CN support probably due to the oleic acid overlayer used as capping agent. However, the addition of Mn leads to an improvement of the performance for the MnOx_OAR_CN corroborating the hypothesis that the promotion effect is not due to a modification of the electronic properties of the support but due to the effect of the Mn phase. Our results indicate that large Mn3O4 particles interacting with the CN support are more active towards the ORR than the small NPs synthetized via the oleic acid route presenting higher percentage of MnO phase.
More interestingly, Mn present as large Mn
3O
4 particles promotes the 4e- transfer reaction of O
2 to H
2O as opposed to the bare CN which catalyzes mainly the formation of H
2O
2, whereas the small MnO NPs and few atoms cluster leads to a predominantly 2e- reaction. A similar selectivity towards 2e- reduction of O
2 was observed for Mn-porphyrin systems [
45]. In contrast, the Mn acetate phase is not very active for the electrocatalytic ORR. From the Pourbaix diagram for Mn, MnO
2 is the thermodynamically stable phase at potentials above 0.4V vs. RHE and pH 13. We can thus postulate that the driving force for the 4e- reduction of oxygen is the tendency of the Mn(III) sites of the Mn
3O
4 phase in the MnOx_WI_CN to be oxidized to Mn(IV) by chemisorbing oxygen. The subsequent proton and electron transfer leads to the desorption of H
2O. Below 0.4 V, Mn(III)-containing oxides are stable, explaining the change in reaction mechanism observed at this potential for the MnOx_WI_CN system from a mixed 4e- and 2e- transfer process to a selective 2e- transfer process. Our experimental observation suggests that Mn(II) species are promoting ORR but with a dominant 2e- transfer process. We therefore conclude that Mn(II) species can act as chemisorption sites for O
2 but are not able to catalyze the dissociation of the O-O bond.
Despite these limitations (general high overpotential and low overall current) which require much effort in design strategies to overcome, the results presented here are encouraging as they show clearly the opportunities for catalytic performance tunability and potential for improvements of these systems whose interest lies on the high chemical stability offered, large availability, and low costs.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. CN Preparation
Carbon nitride synthesis has been described previously [
17]. Carbon nitride was pre-treated by heating to 500 °C for 2 h, in a 50 mL/min flow of nitrogen gas. Samples prepared on treated CN are denoted with CN, whilst those on fresh CN are denoted CN*.
4.2. Nanoparticles Synthesis via Oleic Acid Route
A synthetic method, modified from Park et al. [
27], was used to prepare catalyst MnO
x_OAR_CNx. Manganese (II) acetate dihydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, Dorset, UK) and oleic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, Dorset, UK) were combined in a 1:1 ratio in an excess of dioctyl ether (Sigma-Aldrich, Dorset, UK), and heated to 170 °C for at least 15 min. Once cooled, ethanol was added to precipitate the nanocrystals, which were left to decant for 3 h. The carbon nitride support was added with 2 drops of sulfuric acid (Sigma-Aldrich, Dorset, UK), and the resultant mixture stirred for 15 min. The solid remains were filtered and dried for 24 h, yielding the MnO
x_OAR_CN samples.
4.3. Nanoparticles Synthesis via Impregnation Method
Impregnation, modified from Buller et al., was used to prepare catalysts [
46]. Manganese (II) acetate dihydrate was combined with a 10% ethanol solution and stirred. This mixture was added to the carbon nitride with stirring, before drying at room temperature for 24 h. In the case of T-MnOx_WI_CN, the sample was also heated to 200 °C for 2 h, in a 50 mL/min flow of nitrogen gas.
A complete list of the samples prepared and used in this work is presented in
Table 4.
4.4. Characterization
XRD data were collected on a Rigaku SmartLab X-Ray Diffractometer (Rigaku Europe SE, Germany). Diffraction pattern for reference Mn Oxides were taken from the following sources: ICSD Collection Codes:
Al
2O
3: 10425 [
47]; Mn(OH)
2 [
48]: 2359; Mn
2O
3: 9091 [
49]; Mn
3O
4: 68174 [
50]. XPS analyses were performed using PHI VersaProbe II equipment (Physical Electronics, Chanhassen, MN, USA). The survey, C1s, O1s, Mn2p XPS spectra were recorded using an Al Kα (1486.6 eV) X-ray source and an analyzer pass energy of 23.5 eV and 117 eV for the high-resolution core level spectra and for the survey spectrum, respectively. The X-ray beam size was 100 microns at 24.1 W. The freshly prepared catalysts were pre-formed in thin pellets and mounted on the sample holder before being introduced into the vacuum chamber (10
−8 mbar). Then the sample was moved in the main chamber for analysis. Before the analysis, the charge neutralization was performed with simultaneous irradiation of a low-energy electron beam and an ion beam. The XPS peaks were calibrated with respect to the maximum of the most intense, highest BE component in the C1s spectrum which was set to 288. The core levels envelopes were fitted using Casa XPS software after subtraction of a U2 Tougaard background. The fittings of the N1s spectra were performed by considering as many components with a Gaussian–Lorentzian (GL) line-shape as needed to consistently describe structural changes among the samples. The fitting of the spectra was applied consistently to all the spectra by constraining the peak position by ±0.05 eV. Accordingly, the N1s fitting consists of 4 components with full-width at half maximum (FWHM) of 1.2 eV at 398.5 eV (N1), 399 eV (Mn-N), 399.9 eV (N2) and 401 eV (N3) and an additional component with FWHM of 1.7 eV. The C1s was fitted with a component at 284.4 eV with Doniach–Sunjic lineshape and FWHM of 1.4 eV (C1); a GL component at 285.7 eV with FWHM of 1.2 eV (C2) and an additional GL component at 288 eV with FWHM of 1.2 eV (C3).
The UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS) of the samples were recorded using a Shimadzu UV-2600i spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan), equipped with an ISR-2600 Plus integrating sphere, which make possible to obtain the DRS in the wavelength range from 220 to 1400 nm. BaSO4 powder (Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain) was used as reference and the sample was also deposited on a BaSO4 pellet to avoid any interference of the sample holder.
In order to determinate the band gap, the absorption (F(R∞)) spectra were obtained from the measured reflectance (R∞) spectra by applying the Kubelka–Munk function (1):
The band gaps of the samples were calculated using the Tauc method and assuming an indirect transition band gap which can be expressed by Equation (2) where α is the absorption coefficient, h is Planck’s constant, v is the photon frequency, A is a constant, and Eg is the band gap:
TEM analysis was carried out using a JEOL ARM200F cold field FEG probe corrected electron microscope operated at 200 keV (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The samples were ground between two glass slides and dusted onto a holey carbon coated Au TEM grid prior to analysis.
HAADF and BF STEM micrographs were acquired with a beam current of 18 pA and detector collection angles of 37.5 to 128.3 mrad and 0 to 21.9 mrad respectively. STEM EELS SI (spectrum image) maps were acquired using a GATAN Quantum ER dual EELS system using a collection half angle of 52.2 mrad, a probe convergence angle of 23 mrad and a beam current of 41 pAmp. GMS was used for processing of the STEM SI datasets and for extracting the C, N, O and Mn maps.
4.5. Electrode Preparation
Pure CN: 2.5 mg of catalyst powder were dispersed in a mixture of 3.98 mL MilliQ water, 1.00 mL 2-propanol and 20 μL Nafion solution (5 wt.% water and lower aliphatic alcohols, Sigma Aldrich) and homogenized by using a horn sonicator for 30 min. 4 μL of the as-prepared catalyst ink were drop-coated on a 3 mm glassy-carbon (GC) disk (catalyst loading: 28.3 μg cm
−2). The GC-electrode was placed upside down on a motor and spin-dried at 700 rpm for 15 min, following the “Garsany spin coating technique” [
51]. Afterwards, it was dried in air at 60 °C for 10 min.
Mixture of CN and activated carbon: 2.5 mg catalyst powder and 0.5 mg C65 were dispersed in a mixture of 3.98 mL MilliQ water, 1.00 mL 2-propanol and 20 µL Nafion solution (5 wt.% in water and lower aliphatic alcohols, Sigma Aldrich) and homogenized by using a horn sonicator for 30 min. 4 µL of the as prepared catalyst ink were drop-coated on a 3 mm glassy-carbon (GC) disk (catalyst-loading: 28.3 µg cm
−2). The GC-electrode was placed upside down on a motor and spin-dried at 700 rpm for 20 min, following the “Garsany spin coating technique” [
51].
4.6. Electrochemical Measurement
Electrochemical analyses were performed using a Bio-Logic VMP3 multichannel potentiostat/galvanostat with a built-in EIS analyzer. A Metrohm Autolab RRDE-2 Rotator was used for rotating disk electrode (RDE)-measurements. A three electrode configuration was used, with Ag/AgCl (3 M KCl, 0.210 V vs. RHE at 25 °C) and a Pt wire as reference and counter electrode, respectively. The measurements were performed at 25 °C in 0.1 M KOH in a thermostated glass cell (Metrohm). The electrode was bubbled with either Argon or O2 for 25 min. Then, the electrode was placed in the solution to impregnate for 10 min. During the measurements, a flow of oxygen in the headspace was ensured. Prior to the ORR performance tests, ohmic drop was determined by impedance spectroscopy and the following measurements were compensated at 85% of the measured solution resistance. Then, 5 cycles of cyclovoltammetry (CV) at a scan rate of 20 mV s−1 were performed in the potential range of −0.8 to 0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl. Diffusion controlled ORR activity measurements were measured by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) in a 0.6 V potential window at different rotation rates and a scan rate of 5 mV s−1. Between every LSV, 2 cycles of CV were performed in the same potential window to restore the surface of the electrode.