Radical C–H 18F-Difluoromethylation of Heteroarenes with [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
Synthesis of the Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones 5a–5f
2.2. Radiochemistry
2.2.1. Radiosyntheses of the [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones [18F]5a–[18F]5f
2.2.2. Automated Radiosyntheses of the [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones [18F]5a, [18F]5c, and [18F]5f
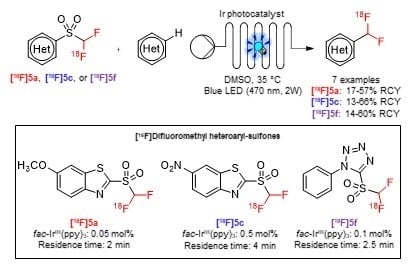
2.2.3. 18F-Difluoromethylation of Heteroarenes with Sulfones [18F]5a, [18F]5c, and [18F]5f
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfides (4a–4f)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones (5a–5f)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Bromofluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfides (6a–6f)
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Difluoromethylated Heteroarenes (8a–8g)
3.2. Radiochemistry
3.2.1. Fully Automated Radiosyntheses of 2-[18F]((Difluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)-6-Methoxybenzo[d]thiazole ([18F]5a), 2-[18F]((Difluoromethyl)sulfonyl)-6-nitrobenzo[d]thiazole ([18F]5c), and 5-[18F]((Difluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)-1-Phenyl-1H-Tetrazole ([18F]5f)
3.2.2. Low-Activity 18F-Labeling Experiments in the Precursors 6a–6f
3.2.3. Isolation and Determination of the Molar Activity of [18F]5a, [18F]5c, and [18F]5f
3.2.4. General Procedure for the C–H 18F-Difluoromethylation of the Heteroarenes 7a–7g with the [18F]difluoromethyl heteroaryl-sulfones [18F]5a, [18F]5c, and [18F]5f
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Bars, D. Fluorine-18 and medical imaging: Radiopharmaceuticals for positron emission tomography. J. Fluorine Chem. 2006, 127, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even-Sapir, E.; Mishani, E.; Flusser, G.; Metser, U. 18F-Fluoride positron emission tomography and positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 37, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, S.; Roeda, D.; Dollé, F.; Kassiou, M. Fluorine-18 chemistry for PET: A concise introduction. Curr. Radiopharm. 2010, 3, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlow, C.; Szames, D.; Dahl, K.; Bernard-Gauthier, V.; Vasdev, N. Fluorine-18: An untapped resource in inorganic chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11835–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Kumar, U. Positron emission tomography: An overview. J. Med. Phys. 2006, 31, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Shon, I.H.; Lin, P. Positron emission tomography: Current status and future challenges. Intern. Med. J. 2010, 40, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquero, J.J.; Kinahan, P. Positron emission tomography: Current challenges and opportunities for technological advances in clinical and preclinical imaging systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 17, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Galaly, T.C.; Gormsen, L.C.; Hutchings, M. PET/CT for staging; Past, present, and future. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 48, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.W.; Long, N.J.; Vilar, R.; Gee, A.D. Synthesis of 11C, 18F, 15O, and 13N radiolabels for positron emission tomography. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8998–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zeng, W. Labeling strategies with F-18 for positron emission tomography imaging. Med. Chem. 2011, 7, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L. 18F-Labeling techniques for positron emission tomography. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, A.F.; Topczewski, J.J.; Ichiishi, N.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J.H. Late-stage [18F]fluorination: New solutions to old problems. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4545–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, O.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. Fluorine-18 radiochemistry, labeling strategies and synthetic routes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preshlock, S.; Tredwell, M.; Gouverneur, V. 18F-Labeling of arenes and heteroarenes for applications in positron emission tomography. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 719–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Born, D.; Pees, A.; Poot, A.J.; Orru, R.V.A.; Windhorst, A.D.; Vugts, D.J. Fluorine-18 labelled building blocks for PET tracer synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4709–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, H.S.; Ma, L.; Vasdev, N.; Liang, S.H. 18F-Labeling of sensitive biomolecules for positron emission tomography. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 15553–15577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coenen, H.H.; Ermert, J. 18F-Labeling innovations and their potential for clinical application. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2018, 6, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüll, J.; Heinrich, M.R. [18F] Fluorine-labeled pharmaceuticals: Direct aromatic fluorination compared to multi-step strategies. Asian, J. Org. Chem. 2019, 8, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Rong, J.; Wang, L.; Vasdev, N.; Zhang, L.; Josephson, L.; Liang, S.H. Chemistry for positron emission tomography: Recent advances in 11C-, 18F-, 13N-, and 15O-labeling reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2580–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meanwell, N.A. Fluorine and fluorinated motifs in the design and application of bioisosteres for drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5822–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.A.; McLoughlin, J.I. Hydrogen bond donor properties of the difluoromethyl group. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrani, Y.; Yeffet, D.; Sod-Moriah, G.; Berliner, A.; Amir, D.; Marciano, D.; Gershonov, E.; Saphier, S. Difluoromethyl bioisostere: Examining the “lipophilic hydrogen bond donor” concept. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessler, C.D.; Rahm, M.; Becker, S.; Goldberg, J.M.; Wang, F.; Lippard, S.J. CF2H, a hydrogen bond donor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9325–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafrani, Y.; Sod-Mariah, G.; Yeffet, D.; Berliner, A.; Amir, D.; Marciano, D.; Elias, S.; Katalan, S.; Ashkenazi, N.; Madmon, M.; et al. CF2H, a functional group-dependent hydrogen-bond donor: Is it a more or less lipophilic bioisostere of OH, SH, and CH3? J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5628–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, J.; Ni, C.; Hu, J. Metal-catalyzed direct difluoromethylation reactions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2017, 6, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerien, D.E.; Barata-Vallejo, S.; Postigo, A. Difluoromethylation reactions of organic compounds. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 14676–14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Xiao, Y.-L.; Zhang, X. Transition-metal (Cu, Pd, Ni)-catalyzed difluoroalkylation via cross-coupling with difluoroalkyl halides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2264–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, A.; Lemaire, C.; Luxen, A. Progress in difluoroalkylation of organic substrates by visible light photoredox catalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 1500–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koike, T.; Akita, M. Recent progress in photochemical radical di- and mono-fluoromethylation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 5413–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, N.; Amir, D.; Greshonov, E.; Zafrani, Y. Recent progress on the synthesis of CF2H-containing derivatives. Synthesis 2019, 51, 4549–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Kraatz, U.; Kugler, M.; Schrage, H.; Uhr, H. Benzazole derivatives with microbiocidal properties. Ger. Offen. DE 19523447 A1 19970102, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta, S.; Stenhagen, I.S.R.; O’Duill, M.; Wolstenhulme, J.; Kirjavainen, A.K.; Forsback, S.J.; Tredwell, M.; Sandford, G.; Moore, P.R.; Huiban, M.; et al. Catalytic decarboxylative fluorination for the synthesis of tri- and difluoromethyl arenes. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2648–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoog, S.; Pfeifer, L.; Khotavivattana, T.; Calderwood, S.; Collier, T.L.; Wheelhouse, K.; Tredwell, M.; Gouverneur, V. Silver-mediated 18F-labeling of aryl-CF3 and aryl-CHF2 with 18F-fluoride. Synlett 2016, 27, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Braun, A.; Wang, L.; Liang, S.H.; Vasdev, N.; Ritter, T. Synthesis of 18F-difluoromethylarenes from aryl (pseudo) halides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10786–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, F.; Stephenson, N.A.; Wang, L.; Rotstein, B.H.; Vasdev, N.; Tang, P.; Liang, S.H. Metal-free 18F-labeling of aryl-CF2H via nucleophilic radiofluorination and oxidative C–H activation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sap, J.B.I.; Wilson, T.C.; Kee, C.W.; Straathof, N.J.W.; amEnde, C.W.; Mukherjee, P.; Zhang, L.; Genicot, C.; Gouverneur, V. Synthesis of 18F-difluoromethylarenes using aryl boronic acids, ethyl bromofluoroacetate and [18F]fluoride. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3237–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trump, L.; Lemos, A.; Lallemand, B.; Pasau, P.; Mercier, J.; Lemaire, C.; Luxen, A.; Genicot, C. Late-stage 18F-difluoromethyl labeling of N-heteroaromatics with high molar activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13149–13154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trump, L.; Lemos, A.; Jacq, J.; Pasau, P.; Lallemand, B.; Mercier, J.; Genicot, C.; Luxen, A.; Lemaire, C. Development of a general automated flow photoredox 18F-difluoromethylation of N-heteroaromatics in an AllinOne synthesizer. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Deng, L.; Tan, P.; Ni, C.; Gu, Y.; Hu, J. Radical fluoroalkylation of isocyanides with fluorinated sulfones by visible-light photoredox catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2743–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Han, X.; Zhu, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Ji, B.; Hao, X.-Q.; Song, M.-P. Visible-light-mediated radical oxydifluoromethylation of olefinic amides for the synthesis of CF2H-containing heterocycles. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13413–13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Wang, X. Visible-light induced di- and trifluoromethylation of N-benzamides with fluorinated sulfones for the synthesis of CF2H/CF3-containing isoquinolinediones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 8748–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Fu, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Ji, B. Visible-light-mediated direct difluoromethylation of alkynoates: Synthesis of 3-difluoromethylated coumarins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 9057–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Fu, W.; Guo, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Ji, B. Visible-light-induced radical di- and trifluoromethylation of β, γ-unsaturated oximes: Synthesis of di- and trifluoromethylated isoxazolines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; You, Q.; Li, R. Synthesis of CF2H-containing oxindoles via hotoredox-catalyzed radical difluoromethylation and cyclization of N-arylacrylamides. J. Fluorine Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.-S.; Li, Y.-Y.; Li, L.; Wang, W.-X.; Feng, T.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, J.-K. Synthesis of difluoromethylated 2-oxindoles and quinoline-2,4-dione via visible light-induced tandem radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 6629–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, Y.; Tomita, R.; Ando, G.; Koike, T.; Akita, M. Oxydifluoromethylation of alkenes by photoredox catalysis: Simple synthesis of CF2H-containing alcohols. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbonnel, E.; Besset, T.; Poisson, T.; Labar, D.; Pannecoucke, X.; Jubault, P. 18F-Fluoroform: A 18F-trifluoromethylating agent for the synthesis of SCF218F-aromatic derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5706–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.J.; Campoli-Richards, D.M. Acyclovir. An updated review of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 1989, 37, 233–309. [Google Scholar]
- Fenton, C.; Keating, G.M.; Lyseng-Williamson, K.A. Moxonidine. A review of its use in essential hypertension. Drugs 2006, 66, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E.; Brogden, R.N. Pentoxifylline (Oxpentifylline). A review of its therapeutic efficacy in the management of peripheral vascular and cerebrovascular disorders. Drugs Aging 1995, 7, 480–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, R.; Kashiwagi, H.; Marouka, K. The direct C–H difluoromethylation of heteroarenes based on the photolysis of hypervalent iodine(III) reagents that contain difluoroacetoxy ligands. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5126–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, C.; Libert, L.; Franci, X.; Genon, J.-L.; Kuci, S.; Giacomelli, F.; Luxen, A. Automated production at the curie level of no-carrier-added 6-[18F]fluoro-l-dopa and 2-[18F]fluoro-l-tyrosine on a FASTlab synthesizer. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Entry | Substrate | NaIO4 (mmol) | RuCl3·xH2O (mmol) | Conversion (%)(b) | RCY (%)(c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [18F]1’ | 0.24 | 0.008 | 100 | 82.9 ± 7.9 (n = 3) |
| 2 | [18F]4a | 0.24 | 0.008 | 35 | 32.1 |
| 3 | [18F]4a | 0.24 | 0.016 | 64 | 59.6 |
| 4 | [18F]4a | 0.72 | 0.016 | 100 | 70.9 ± 6.1 (n = 3) |

| Entry | [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones | RCY (%)(a) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [18F]5a | 10.1 ± 0.8 (n = 3) |
| 2 | [18F]5b | 8.3 ± 0.6 (n = 3) |
| 3 | [18F]5c | 12 ± 0.5 (n = 3) |
| 4 | [18F]5d | 11.2 ± 0.3 (n = 3) |
| 5 | [18F]5e | 7.2 ± 0.2 (n = 3) |
| 6 | [18F]5f | 13.6 ± 0.4 (n = 3) |
| Reagents | [18F]5a | [18F]5c | [18F]5f |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of the radiosynthesis (min) | 73 | 70 | 65 |
| RCY (%)(a) | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.5 | 8.0 ± 0.9 |
| Molar activity (GBq·μmol−1)(b) | 139 ± 17 | 62 ± 12 | 113 ± 17 |

| Entry | Reagents | fac-IrIII(ppy)3 (mol%) | Residence Time (min) | Flow Rate (μL·min−1) | Conversion (%)(b) | RCY (%)(c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [18F]1 | 0.05 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 70 ± 7 (n = 4) |
| 2 | [18F]5a | 0.05 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 57 ± 7 (n = 3) |
| 3 | [18F]5c | 0.05 | 2 | 50 | 17 | 14 ± 1 (n = 3) |
| 4 | [18F]5c | 0.5 | 2 | 50 | 36 | 26 ± 3 (n = 3) |
| 5 | [18F]5c | 0.5 | 4 | 25 | 100 | 51 ± 7 (n = 4) |
| 6 | [18F]5f | 0.05 | 2 | 50 | 73 | 48 ± 8 (n = 3) |
| 7 | [18F]5f | 0.1 | 2 | 50 | 98 | 55 ± 1 (n = 3) |
| 8 | [18F]5f | 0.1 | 2.5 | 40 | 100 | 56 ± 1 (n = 3) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemos, A.L.P.; Trump, L.; Lallemand, B.; Pasau, P.; Mercier, J.; Lemaire, C.; Monbaliu, J.-C.; Genicot, C.; Luxen, A. Radical C–H 18F-Difluoromethylation of Heteroarenes with [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030275
Lemos ALP, Trump L, Lallemand B, Pasau P, Mercier J, Lemaire C, Monbaliu J-C, Genicot C, Luxen A. Radical C–H 18F-Difluoromethylation of Heteroarenes with [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis. Catalysts. 2020; 10(3):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030275
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemos, Agostinho Luís Pereira, Laura Trump, Bénédicte Lallemand, Patrick Pasau, Joël Mercier, Christian Lemaire, Jean-Christophe Monbaliu, Christophe Genicot, and André Luxen. 2020. "Radical C–H 18F-Difluoromethylation of Heteroarenes with [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis" Catalysts 10, no. 3: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030275
APA StyleLemos, A. L. P., Trump, L., Lallemand, B., Pasau, P., Mercier, J., Lemaire, C., Monbaliu, J.-C., Genicot, C., & Luxen, A. (2020). Radical C–H 18F-Difluoromethylation of Heteroarenes with [18F]Difluoromethyl Heteroaryl-Sulfones by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis. Catalysts, 10(3), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030275