New Method of Determining Kinetic Parameters for Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of pH
2.2. Effect of Temperature
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
3.3. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
3.4. Effect of pH and Temperature
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Shudong, H.; Simpson, B.K. Enzymes in food bioprocessing—Novel food enzymes, applications, and related techniques. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, A.; Chakraborty, J.N. Developments in application of enzymes for textile processing. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 145, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamocky, M.; Koller, F. Understanding the structure and function of catalases: Clues from molecular evolution and in vitro mutagenesis. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1999, 72, 19–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, C.L.; Martin, G.K.; Daniel, J.H. Catalase-an “old” enzyme that continues to surprise us. ASM News 2000, 66, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Melik-Adamyan, W.R.; Barynin, V.V.; Vagin, A.A.; Borisov, V.V.; Vainshtein, B.K.; Fita, I.; Murthy, M.R.; Rossmann, M.G. Comparison of beef liver and Penicillium vitale catalases. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 188, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.D.; Andersson, L.A.; Loehr, T.M.; Terner, J.; Goff, H.M. Comparative spectral analysis of mammalian, fungal, and bacterial catalases. Resonance Raman evidence for iron-tyrosinate coordination. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12772–12779. [Google Scholar]
- Chelikani, P.; Fita, I.; Loewena, P.C. Diversity of structures and properties among catalases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fita, I.; Rossmann, M.G. The active center of catalase. J. Mol. Biol. 1985, 185, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebicka, L.; Krych-Madej, J. The role of catalases in the prevention/promotion of oxidative stress. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 197, 110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncar, N.; Fraaije, M.W. Catalases as biocatalysts in technical applications: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3351–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, J.; Mehandia, S.; Singh, G.; Raina, A.; Arya, S.K. Catalase enzyme: Application in bioremediation and food industry. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raducan, A.; Cantemir, A.R.; Puiu, M.; Oancea, D. Kinetics of hydrogen peroxide decomposition by catalase: Hydroxylic solvent effects. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzbauer, B.; Narodoslawsky, M.; Moser, A. Classification system for immobilization techniques. Bioprocess Eng. 1995, 12, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, A.G. Catalase immobilization—A review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Ismail, A.; Dinu, C. IndustriaApplications of Enzymes: Recent Advances, Techniques, and Outlooks. Catalysts 2018, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Lian, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.C. Applications of immobilized biocatalyst in metal–organic frameworks. Catalysts 2018, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronai, I. How the techniques of molecular biology are developed from natural systems. SocArXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooch, B.S.; Kauldhar, B.S.; Puri, M. Isolation and polyphasic characterization of a novel hyper catalase producing thermophilic bacterium for the degradation of hydrogen peroxide. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1759–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadana, A. Enzyme deactivation. Biotechnol. Adv. 1988, 6, 349–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardinois, O.M.; Mestdagh, M.M.; Rouxhet, P.G. Reversible inhibition and irreversible inactivation of catalase in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1295, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadermarzi, M.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A. Determination of the kinetic parameters for the “suicide substrate” inactivation of bovine liver catalase by hydrogen peroxide. J. Enzym. Inhib. 1996, 10, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkman, H.N.; Gaetani, G.F. Mammalian catalase: A venerable enzyme with new mysteries. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, C. Structure, protonation state and dynamics of catalase compound II. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadermarzi, M.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. The effects of temperature and pH on the kinetics of reactions between catalase and its suicide substrate hydrogen peroxide. Ital. J. Biochem. 1997, 46, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feuers, R.J.; Pattillo, F.M.; Osborn, C.K.; Adams, K.L.; DeLuca, D.; Smith, W.G. Application of an integrated rate equation to the inactivation of catalase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1993, 15, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, D.C.; Dennis, R.; Smith, W.G. Inactivation of an animal and a fungal catalase by hydrogen peroxide. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 320, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B. Effect of pH upon the reaction kinetics of the enzyme-substrate compounds of catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 194, 471–481. [Google Scholar]
- Góth, L. Heat and pH dependence of catalase. A comparative study. Acta Biol. Hung. 1987, 38, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Cantemir, A.R.; Raducan, A.; Puiu, M.; Oancea, D. Kinetics of thermal inactivation of catalase in the presence of additives. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Miłek, J. Estimation of the kinetic parameters for H2O2 enzymatic decomposition and for catalase deactivation. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, A.M.P.; Oliveira, M.G.; Maugeri, F. Modelling thermal stability and activity of free and immobilized enzymes as a novel tool for enzyme reactor design. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3142–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.J.S.; Ohara, A.; Nishide, T.G.; Albernaz, J.R.M.; Soares, M.H.; Sato, H.H. A new approach for proteases production by Aspergillus niger based on the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the enzymes obtained. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, R.F.; Sizer, I.W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

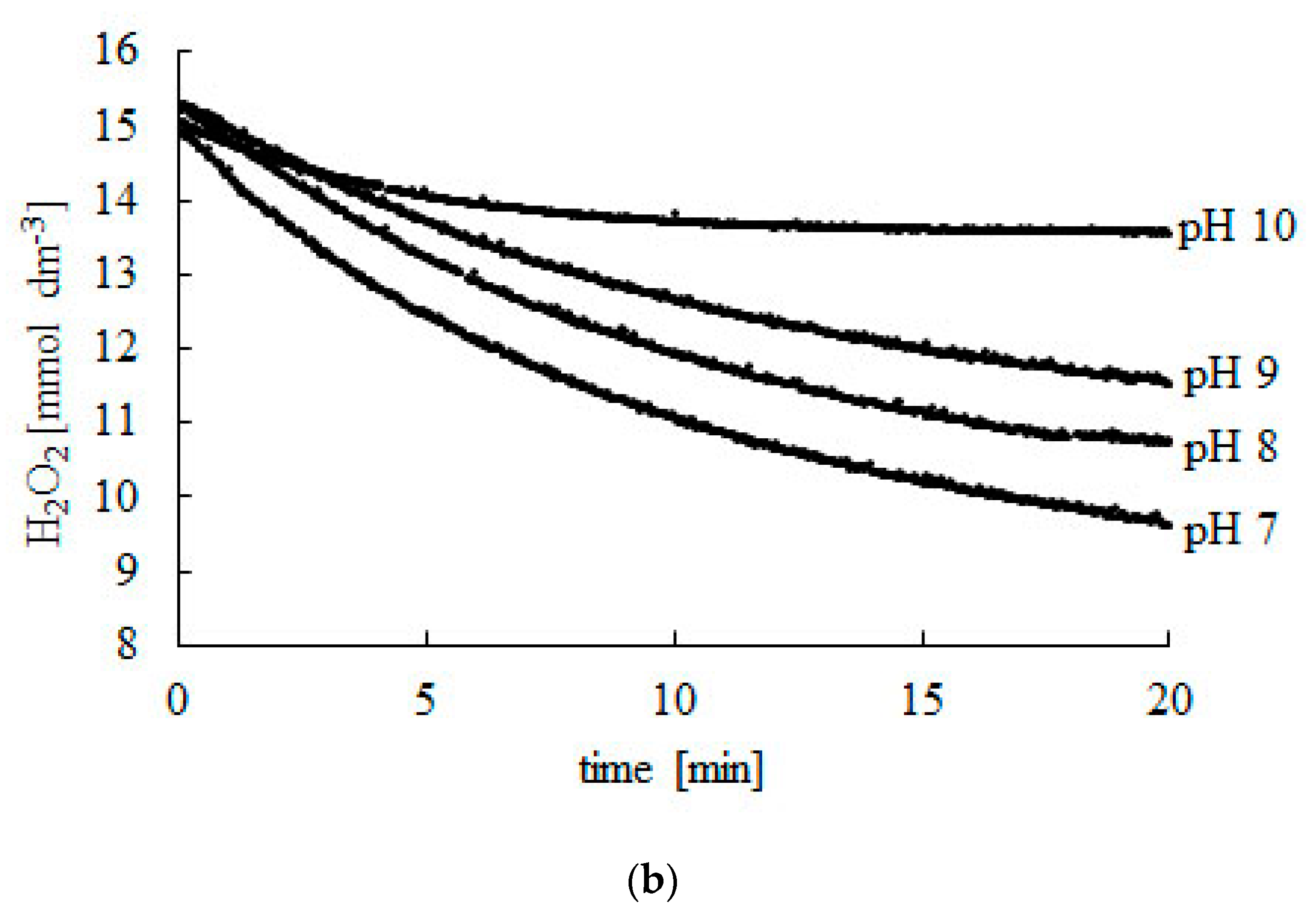





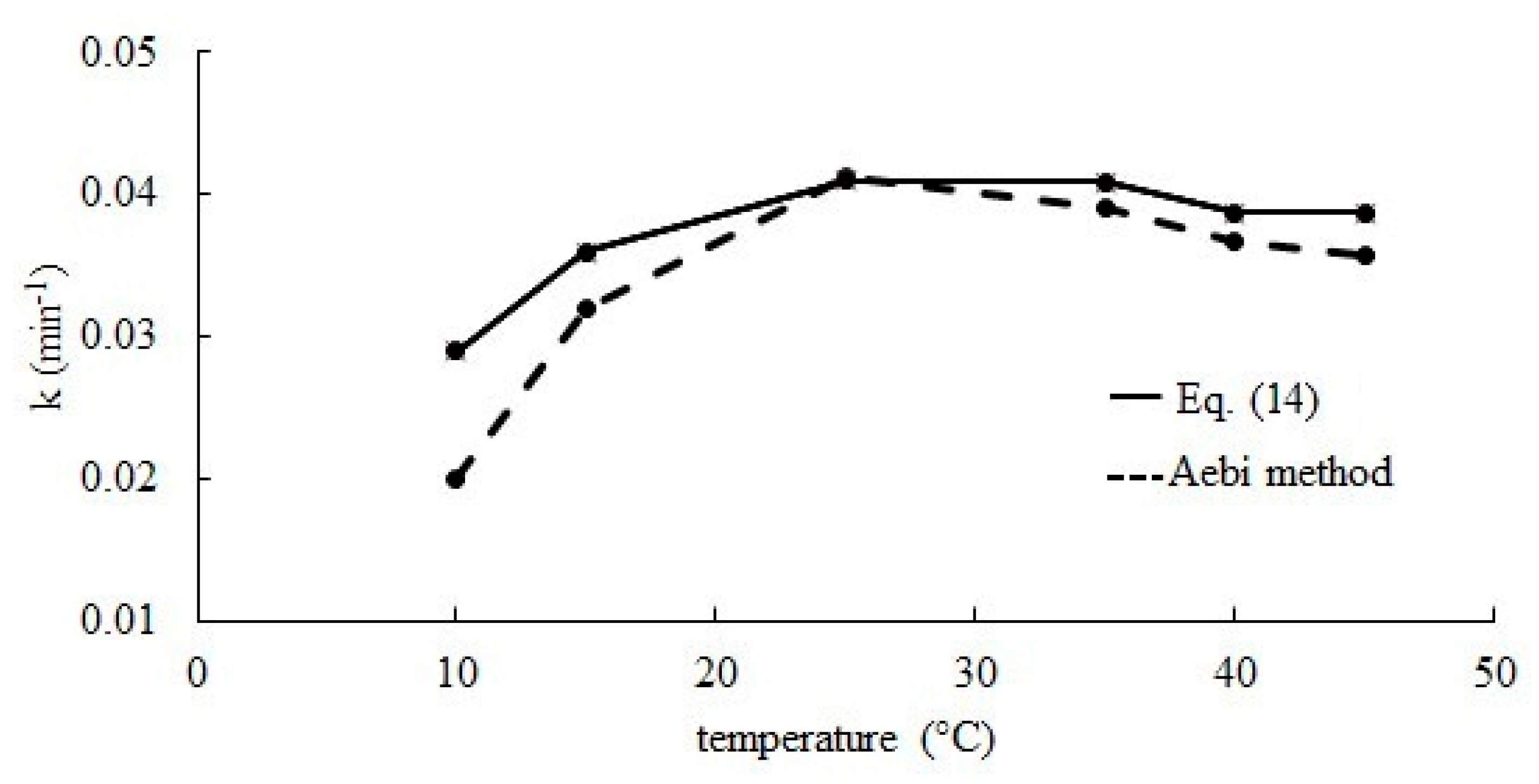
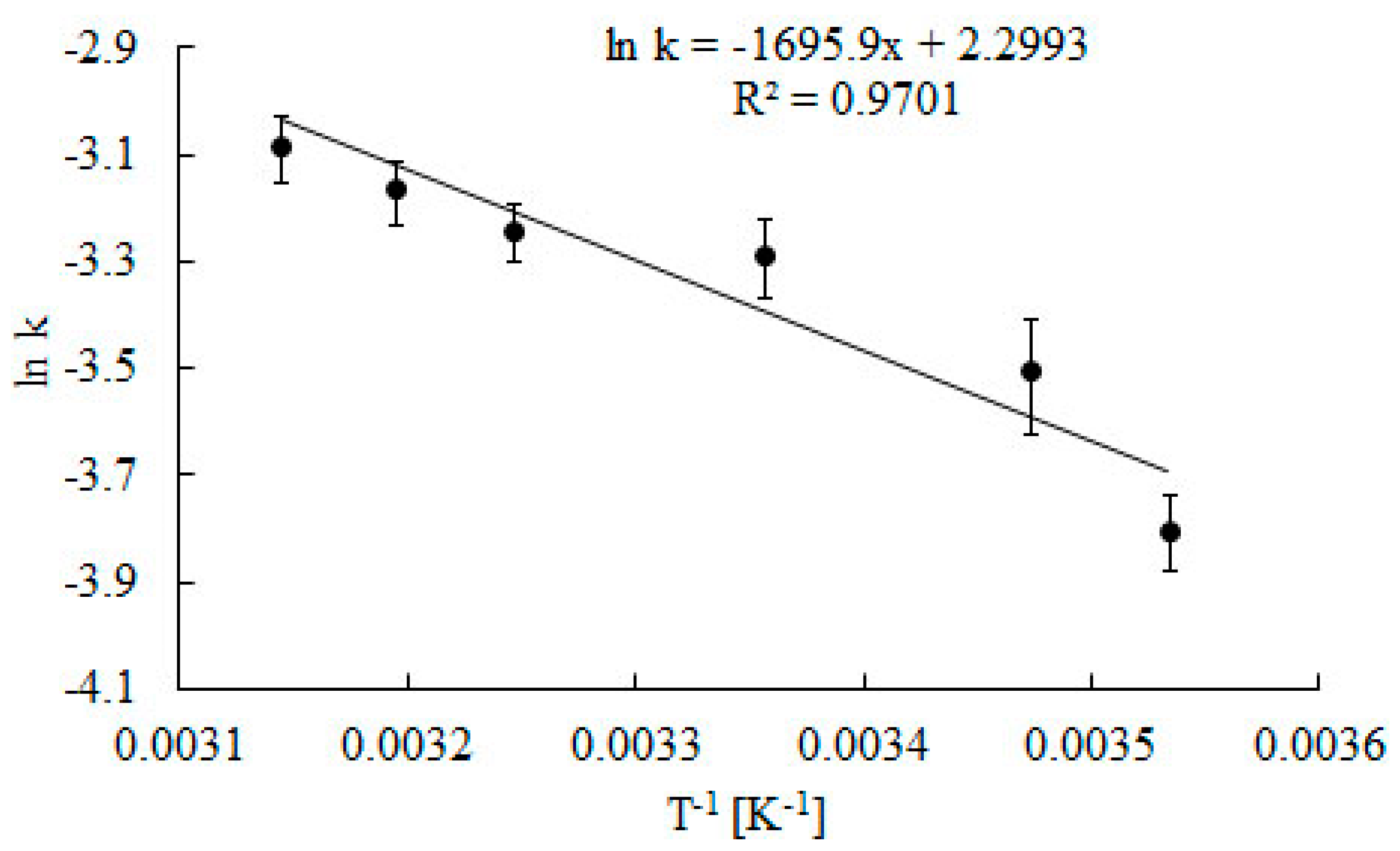
| pH | CS0 (mmol dm−3) | CSF (mmol dm−3) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 15.06 | 11.79 | 40 |
| 4 | 15.02 | 11.61 | 50 |
| 5 | 15.17 | 10.25 | 60 |
| 6 | 15.08 | 9.39 | 70 |
| 7 | 14.98 | 8.70 | 80 |
| 8 | 15.10 | 9.04 | 40 |
| 9 | 14.96 | 10.66 | 40 |
| 10 | 15.05 | 13.48 | 12 |
| Temperature (°C) | kd ± SD (dm3 mol−1 min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.83 ± 0.15 | 0.989 |
| 15 | 2.32 ± 0.21 | 0.994 |
| 25 | 7.85 ± 0.22 | 0.998 |
| 35 | 13.04 ± 0.54 | 0.991 |
| 40 | 16.42 ± 1.90 | 0.990 |
| 45 | 24.81 ± 3.30 | 0.989 |
| 25 | 8.9 | Deluca et al. [26] |
| 25 | 8.34 | Feuers et al. [25] |
| 27 | 6.86 | Ghadermarzi and Moosavi-Movahedi [21] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trawczyńska, I. New Method of Determining Kinetic Parameters for Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase. Catalysts 2020, 10, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030323
Trawczyńska I. New Method of Determining Kinetic Parameters for Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase. Catalysts. 2020; 10(3):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030323
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrawczyńska, Ilona. 2020. "New Method of Determining Kinetic Parameters for Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase" Catalysts 10, no. 3: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030323
APA StyleTrawczyńska, I. (2020). New Method of Determining Kinetic Parameters for Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide by Catalase. Catalysts, 10(3), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030323





