Catalytic Oxidation of HCHO over the Sodium-Treated Sepiolite-Supported Rare Earth (La, Eu, Dy, and Tm) Oxide Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Crystal Structure
2.2. Textural Property and Morphology
2.3. Surface Element Composition and Adsorbed Oxygen Species
2.4. Reducibility
2.5. Surface Acid Property
2.6. Catalytic Performance
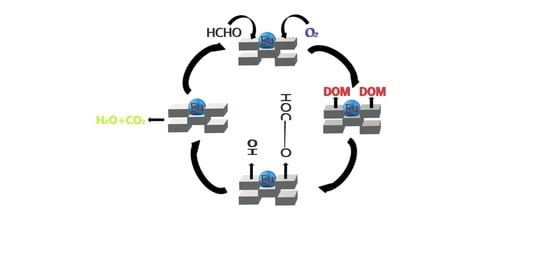
2.7. In Situ DRIFTS and Catalytic Oxidation Mechanism
3. Experimental
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Activity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, M.; Yu, X.; Yang, X.; Ma, X.; Ge, M. Exploration of the active phase of the hydrotalcite-derived cobalt catalyst for HCHO oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, W.; Shao, M.; Wu, Z. Structural effect and reaction mechanism of MnO2 catalysts in the catalytic oxidation of chlorinated aromatics. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Effect of pore size in mesoporous MnO2 prepared by KIT-6 aged at different temperatures on ethanol catalytic oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Xie, S.; Wang, Z.; Dai, H. Catalytic removal of volatile organic compounds using ordered porous transition metal oxide and supported noble metal catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Qu, L.; Fu, M.; Zeng, G.; Fan, C.; Ma, J.; Zhan, F. Catalytic oxidation of NO with O2 over FeMnOx/TiO2: Effect of iron and manganese oxides loading sequences and the catalytic mechanism study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 300, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, X.; Qin, R.; Zeng, Y.; Qu, R.; Zheng, C.; Tu, X. Plasma-catalytic removal of formaldehyde over Cu–Ce catalysts in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 170, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Qu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Q. Formaldehyde catalytic oxidation over hydroxyapatite modified with various organic molecules. Chin. J. Catal. 2014, 35, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Li, J.; Hao, J. Progress in research on catalysts for catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, S.; Uchihori, D.; Utani, K.; Ito, T. Oxidative decomposition of formaldehyde on silver-cerium composite oxide catalyst. Catal. Lett. 1994, 24, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Galván, M.C.; De la Peña O’Shea, V.A.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Arias, P.L. Alumina-supported manganese- and manganese–palladium oxide catalysts for VOCs combustion. Catal. Commun. 2003, 4, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, F.; Yang, H.; Xiong, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Ma, L. Effects of Cu/Fe ratio on structure and performance of attapulgite supported CuFeCo-based catalyst for mixed alcohols synthesis from syngas. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 503, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, G.; Hou, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Understanding of Au-CeO2 interface and its role in catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 260, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, G.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, L. Magnetic Fe3O4/sepiolite composite synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method for efficient removal of Eu(III). Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16943–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Fu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, S.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Excellent performance of Cu-Mn/Ti-sepiolite catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, G. Sepiolite nanofiber-supported platinum nanoparticle catalysts toward the catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde at ambient temperature: Efficient and stable performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, W.; Guo, S. Synthesis of bicrystalline TiO2 supported sepiolite fibers and their photocatalytic activity for degradation of gaseous formaldehyde. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 102, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yan, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, D.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Enhanced catalytic performance of rare earth-doped Cu/H-Sep for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with C3H6. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 431, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwo, G.; Tropp, D.; Serban, C. Adsorption of diquat, paraquat and methyl green on sepiolite: Experimental results and model calculations. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 20, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabah, E.; Çelik, M.S. Interaction of Pyridine Derivatives with Sepiolite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2002, 251, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M.; Tekin, G.; Namli, H. FTIR and zeta potential measurements of sepiolite treated with some organosilanes. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2005, 84, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, B.; Merino, J.; Serratosa, J.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Sepiolite-based materials for the photo-and thermal-stabilization of pesticides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gan, H.; Zhang, G.; Guo, Y. Visible light assisted Fenton-like degradation of rhodamine B and 4-nitrophenol solutions with a stable poly-hydroxyl-iron/sepiolite catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Özcan, A.S. Adsorption of Acid Red 57 from aqueous solutions onto surfactant-modified sepiolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 125, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Yin, X.; He, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Investigation on the delaminated-pillared structure of TiO2-PILC synthesized by TiCl4 hydrolysis method. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2006, 93, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, N.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Hao, Z. Enhanced performances in catalytic oxidation of o-xylene over hierarchical macro-/mesoporous silica-supported palladium catalysts. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belessi, V.; Lambropoulou, D.; Konstantinou, I.; Katsoulidis, A.; Pomonis, P.; Petridis, D.; Albanis, T. Structure and photocatalytic performance of TiO2/clay nanocomposites for the degradation of dimethachlor. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 73, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Gasparotto, A.; Milanov, A.; Tondello, E.; Devi, A.; Fischer, R.A. Nanostructured Dy2O3 films: An XPS Investigation. Surf. Sci. Spectra. 2007, 14, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cario, L.; Palvadeau, P.; Lafond, A. Mixed-valence state of europium in the misfit layer compound (EuS)1.173 NbS2. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wan, Z.; Zhan, Y. Desulfurization of hot coal gas over high-surface-area LaMeOx/MCM-41 sorbents. Fuel 2012, 98, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabongo, G.L.; Mhlongo, G.H.; Mothudi, B.M.; Hillie, K.T.; Mbule, P.S.; Dhlamini, M.S. Structural, photoluminescence and XPS properties of Tm3+ ions in ZnO nanostructures. J. Lumin. 2017, 187, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Diao, G.; Ye, F.; Sun, M.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Promoting Effect of Ce in Ce/OMS-2 Catalyst for Catalytic Combustion of Dimethyl Ether. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setvin, M.; Aschauer, U.; Scheiber, P.; Li, Y.F.; Hou, W.; Schmid, M.; Selloni, A.; Diebold, U. Reaction of O2 with subsurface oxygen vacancies on TiO2 anatase (101). Science 2013, 341, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panov, G.; Dubkov, K.; Starokon, E. Active oxygen in selective oxidation catalysis. Catal. Today 2006, 117, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.A.; Rios, R.V.R.A.; Fabris, J.D.; Sapag, K.; Garg, V.K.; Lago, R.M. Clay–iron oxide magnetic composites for the adsorption of contaminants in water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 22, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandon, M.; Carnö, J.; Järås, S.; Björnbom, E. Total oxidation catalysts based on manganese or copper oxides and platinum or palladium I: Characterisation. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 180, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsoe, N.Y.; Topsoe, H.; Dumesic, J.A. Vanadia/Titania Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction SCR of Nitric-Oxide by Ammonia I. Combined Temperature-Programmed in-Situ FTIR and On-line Mass-Spectroscopy Studies. J. Catal. 1995, 151, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Viswanath, B.; Hegde, M.S.; Madras, G. Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3 over Ti0.9M0.1O2-δ(M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Cu). J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 6002–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, D.A.; Uphade, B.S.; Smirniotis, P.G. TiO2-supported metal oxide catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3I. Evaluation and characterization of first row transition metals. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 421–431. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Zhao, J.; Huo, F.; Wang, D.; Cheng, S.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Nanosized Au supported on three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous β-MnO2: Highly active catalysts for the low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide, benzene, and toluene. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2013, 172, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Chen, P.; Luo, M.; Lu, J. High surface area Au/CeO2 catalysts for low temperature formaldehyde oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 110, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Long, D.; Ling, L.; Qiao, W. Three-dimensional Mn-Cu-Ce ternary mixed oxide networks prepared by polymer-assisted deposition for HCHO catalytic oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 274–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Hao, Z. Catalytic activities and mechanism of formaldehyde oxidation over gold supported on MnO2 microsphere catalysts at room temperature. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Efficient catalytic removal of formaldehyde at room temperature using AlOOH nanoflakes with deposited Pt. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 163, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Crocker, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, A. Catalytic formaldehyde removal by “storage-oxidation” cycling process over supported silver catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Lin, J. Dissociative adsorption of HCOOH, CHOH, and CHO on MCM-41. J. Catal. 2004, 228, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, X.; Crocker, M.; Wang, Y.; Shi, C. FeOx-supported gold catalysts for catalytic removal of formaldehyde at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 154, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Rong, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P. Cerium modified birnessite-type MnO2 for gaseous formaldehyde oxidation at low temperature. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 211, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaSep | 96 | 0.214 | 8.9 |
| La/NaSep | 47 | 0.207 | 17.8 |
| Eu/NaSep | 43 | 0.126 | 10.7 |
| Dy/NaSep | 31 | 0.203 | 26.9 |
| Tm/NaSep | 64 | 0.354 | 24.6 |
| Sample | Temperature (°C) | H2 Consumption (mmol/gcat) | Oads/Olatt Atomic Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Total | ||
| NaSep | – | 633 | – | 0.128 | 0.128 | 2.33 |
| La/NaSep | 458 | 621 | 0.148 | 0.459 | 0.607 | 4.53 |
| Eu/NaSep | 456 | 620 | 0.179 | 0.529 | 0.708 | 7.33 |
| Dy/NaSep | 456 | 619 | 0.169 | 0.476 | 0.645 | 5.66 |
| Tm/NaSep | 474 | 626 | 0.166 | 0.33 | 0.496 | 3.93 |
| Sample | Ammonia Uptake (μmol/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak (150–220 °C) | Medium (220–300 °C) | Strong (300–450 °C) | Total | |
| NaSep | 14 | 9 | 1 | 24 |
| La/NaSep | 17 | 12 | 3 | 32 |
| Eu/NaSep | 25 | 22 | 6 | 53 |
| Dy/NaSep | 19 | 19 | 4 | 42 |
| Tm/NaSep | 15 | 11 | 2 | 28 |
| Catalyst | rcat (mol/(gcat s)) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Eu/NaSep | 3.54 × 10−6 | This study |
| Dy/NaSep | 2.29 × 10−6 | This study |
| La/NaSep | 1.74 × 10−6 | This study |
| Tm/NaSep | 1.47 × 10−6 | This study |
| NaSep | 4.36 × 10−7 | This study |
| 24Mn-19Co-1Ce | 9.20 × 10−8 | [40] |
| 2.5Au/CeO2 | 5.11 × 10−7 | [40] |
| Mn–Cu–Ce mixed oxide | 4.77 × 10−8 | [41] |
| Cu–Mn/TiO2 | 2.55 × 10−8 | [42] |
| Cu–Mn/γ–Al2O3 | 3.06 × 10−8 | [42] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, N.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Cheng, S.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Catalytic Oxidation of HCHO over the Sodium-Treated Sepiolite-Supported Rare Earth (La, Eu, Dy, and Tm) Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts 2020, 10, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030328
Dong N, Ye Q, Chen M, Cheng S, Kang T, Dai H. Catalytic Oxidation of HCHO over the Sodium-Treated Sepiolite-Supported Rare Earth (La, Eu, Dy, and Tm) Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts. 2020; 10(3):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030328
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Ning, Qing Ye, Mengyue Chen, Shuiyuan Cheng, Tianfang Kang, and Hongxing Dai. 2020. "Catalytic Oxidation of HCHO over the Sodium-Treated Sepiolite-Supported Rare Earth (La, Eu, Dy, and Tm) Oxide Catalysts" Catalysts 10, no. 3: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030328
APA StyleDong, N., Ye, Q., Chen, M., Cheng, S., Kang, T., & Dai, H. (2020). Catalytic Oxidation of HCHO over the Sodium-Treated Sepiolite-Supported Rare Earth (La, Eu, Dy, and Tm) Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts, 10(3), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030328