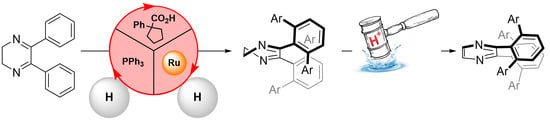
Conformationally Driven Ru(II)-Catalyzed Multiple ortho-C–H Bond Activation in Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives in Water: Where Is the Limit?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. General Method for Catalytic Direct Arylation of Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives
3.3. General Method for Preparation of Arylated Aromatic Pyrazine Products
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Mamari, H.H.; Štefane, B.; Brodnik Žugelj, H. Metal-catalyzed C–H bond functionalization of phenol derivatives. Tetrahedron 2020, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antermite, D.; Bull, J.A. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Directed C(sp3)–H Functionalization of Saturated Heterocycles. Synthesis 2019, 51, 3171–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Yang, K.; Lawrence, B.; Ge, H. Transient Ligand-Enabled Transition Metal-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 2955–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basu, D.; Kumar, S.; Sai Sudhir, V.S.K.; Rakeshwar, B. Transition metal catalyzed C–H activation for the synthesis of medicinally relevant molecules: A Review. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 130, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, D.E.; Larionov, O.V. Recent Advances in the C–H-Functionalization of the Distal Positions in Pyridines and Quinolines. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 8683–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schranck, J.; Tlili, A.; Beller, M. Functionalization of Remote C–H Bonds: Expanding the Frontier. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9426–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, M.E.; Laforteza, B.N.; Yu, J.-Q. Unlocking nature’s C–H bonds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4445–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, A.; Signorile, M.; Boiocchi, M.; Bianchi, B.; Po, R.; Pasini, D. Conjugated Thiophene-Fused Isatin Dyes through Intramolecular Direct Arylation. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11035–11042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, L.G.; Leclerc, M. Direct (Hetero)Arylation: A New Tool for Polymer Chemists. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagui, W.; Doucet, H.; Soulé, J.-F. Application of Palladium-Catalyzed C(sp2)–H Bond Arylation to the Synthesis of Polycyclic (Hetero) Aromatics. Chem 2019, 5, 2006–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancherla, S.; Joergensen, K.B.; Fernández-Ibáñez, M.Á. Recent Developments in Palladium-Catalysed Non-Directed C–H Bond Activation in Arenes. Synthesis 2019, 51, 643–663. [Google Scholar]
- Timsina, Y.N.; Gupton, B.F.; Ellis, K.C. Palladium-Catalyzed C–H Amination of C(sp2) and C(sp3)–H Bonds: Mechanism and Scope for N-Based Molecule Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 5732–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, P.Y.; Wong, S.M.; Kapdi, A.; Kwong, F.Y. Recent developments in palladium-catalysed non-directed coupling of (hetero) arene C–H bonds with C–Z (Z = B, Si, Sn, S, N, C, H) bonds in bi(hetero) aryl synthesis. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 288–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wasa, M.; Chan, K.S.L.; Shao, Q.; Yu, J.-Q. Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations of Alkyl C–H Bonds. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8754–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landge, V.G.; Young, M.C. Teaching an old ligand new tricks. Nature Chem. 2020, 12, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, S.; Chatani, N. Rhodium-Catalyzed C(sp2)– or C(sp3)–H Bond Functionalization Assisted by Removable Directing Groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8304–8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-S.; Qin, L.; Dong, L. Rhodium-catalyzed C–C coupling reactions via double C–H activation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 4554–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Li, X. Substrate Activation Strategies in Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Selective Functionalization of Arenes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S. Recent Advances in C–H Bond Functionalization with Ruthenium-Based Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, C.; Zhu, L.; Qu, L.-B.; Bai, R.; Lan, Y. Mechanistic view of Ru-catalyzed C–H bond activation and functionalization: Computational advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7552–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Jeganmohan, M. Recent advances in the ruthenium(II)-catalyzed chelation-assisted C–H olefination of substituted aromatics, alkenes and heteroaromatics with alkenes via the deprotonation pathway. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8931–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, A.; Papp, A. Ruthenium-Catalyzed C–H Activation and Coupling Reactions in Organic Synthesis. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 20, 381–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Villuendas, P.; Urriolabeitia, E.P. Ru-catalysed C–H functionalisations as a tool for selective organic synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 3413–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-Catalysed sp2 C–H Bond Functionalization by C–C Bond Formation. In Topics in Organometallic Chemistry; Dixneuf, P.H., Bruneau, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 48, pp. 119–193. [Google Scholar]
- De Sarkar, S.; Liu, W.; Kozhushkov, S.I.; Ackermann, L. Weakly Coordinating Directing Groups for Ruthenium(II)- Catalyzed C–H Activation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockiam, P.B.; Bruneau, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed C–H Bond Activation and Functionalization. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5879–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Transition metal-catalyzed C–H bond functionalizations by the use of diverse directing groups. Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 1107–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquet, G.; Chatani, N. Catalytic Functionalization of C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H Bonds by Using Bidentate Directing Groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11726–11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Y. Expanding Structural Diversity; Removable and Manipulable Directing Groups for C–H Activation. Synlett 2013, 24, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, K.M.; Mei, T.-S.; Wasa, M.; Yu, J.-Q. Weak Coordination as a Powerful Means for Developing Broadly Useful C–H Functionalization Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lim, H.N.; Mo, F.; Young, M.C.; Dong, G. Transition metal-catalyzed ketone-directed or mediated C–H functionalization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7764–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambiagio, C.; Schönbauer, D.; Blieck, R.; Dao-Huy, T.; Pototschnig, G.; Schaaf, P.; Wiesinger, T.; Zia, M.F.; Wencel-Delord, J.; Besset, T.; et al. A comprehensive overview of directing groups applied in metal-catalysed C–H functionalisation chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6603–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jie, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, G.; Su, W. Recent advances in directed C–H functionalizations using monodentate nitrogen-based directing groups. Org. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 843–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefane, B.; Brodnik Žugelj, H.; Grošelj, U.; Kuzman, P.; Svete, J.; Požgan, F. Quinazoline-Directed C–H Bond Functionalization Catalyzed by Ruthenium(II) Carboxylate—Construction of Polyconjugated Aryl-Heteroaryl Systems. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzman, P.; Požgan, F.; Meden, A.; Svete, J.; Štefane, B. Synthesis and Reactivity of 2-Arylquinazoline Halidoruthenacycles in Arylation Reactions. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3380–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefane, B.; Fabris, J.; Požgan, F. C–H Bond Functionalization of Arylpyrimidines Catalyzed by an in situ Generated Ruthenium(II) Carboxylate System and the Construction of Tris(heteroaryl)-Substituted Benzenes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 19, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drev, M.; Grošelj, U.; Ledinek, B.; Perdih, F.; Svete, J.; Štefane, B.; Požgan, F. Microwave-Promoted ortho-C−H Bond (Hetero)arylation of Arylpyrimidines in Water Catalyzed by Ruthenium(II)−Carboxylate. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3824–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drev, M.; Grošelj, U.; Ledinek, B.; Perdih, F.; Svete, J.; Štefane, B.; Požgan, F. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Microwave-Promoted Multiple C–H Activation in Synthesis of Hexa(heteroaryl)benzenes in Water. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5268–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.-G.; Zhang, T.; Xie, D.; Xu, Q.-T.; Ling, S.; Zhang, Q. Half-sandwich cycloruthenated complexes from aryloxazolines: Synthesis, structures, and catalytic activities. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 14230–14237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Darcel, C.; Roisnel, T.; Dixneuf, P.H. Cycloruthenation of aryl imines and N-heteroaryl benzenes via C–H bond activation with Ru(II) and acetate partners. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 793, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Roisnel, T.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Cyclometallation of arylimines and nitrogen-containing heterocycles via room-temperature C–H bond activation with arene ruthenium(II) acetate complexes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 10934–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutadla, Y.; Davies, D.L.; Jones, R.C.; Singh, K. The Scope of Ambiphilic Acetate-Assisted Cyclometallation with Half-Sandwich Complexes of Iridium, Rhodium and Ruthenium. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 3438–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, J.-P.; Sortais, J.-B.; Barloy, L.; Pfeffer, M. Cycloruthenated Compounds—Synthesis and Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 817–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.I.; Hartman, T.G.; Rosen, R.T.; Ho, C.T. Formation of pyrazines from the Maillard reaction of glucose and glutamine-amide-15N. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniyar, P.B.; Murumkar, P.R.; Patil, P.S.; Barmade, M.A.; Bothara, K.G. Unequivocal role of pyrazine ring in medicinally important compounds: A review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1607–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Cestau, J.; Bertrand, B.; Blaya, M.; Jones, G.A.; Penfold, T.J.; Bochmann, M. Synthesis and luminescence modulation of pyrazine-based gold(III) pincer complexes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16629–16632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, T.; Enomoto, Y.; Shibamoto, T. A New Method of Pyrazine Synthesis for Flavor Use. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, H.; Matsunaga, K.; Ito, S.; Takata, J.; Karube, Y. The Behavior of Dihydropyrazine with DNA Strand-Breakage Activity in Vivo. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, S.; Hirano, T.; Sugimoto, A.; Kagechika, H.; Takechi, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Latent Enamine Functionality of 5-Methyl-2,3-dihydropyrazines. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, O.; Takechi, S.; Ito, S.; Omori, H.; Katoh, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Effects of Phenyl Derivatives of Dihydropyrazines with Ability to Generate Radical Species on Escherichia coli. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Saibaba, V.; Ravikumar, V.; Rudrawar, S.V.; Daga, P.; Rao, C.S.; Akhila, V.; Hegde, P.; Rao, Y.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2,3-diarylpyrazines and quinoxalines as selective COX-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, Y.-F.; Jin, G.-X. Bis-imine-cyclometalated macrocycles: Synthesis, characterization and observation of solution behaviour. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 4982–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, P.J. Ligand Design in Multimetallic Architectures: Six Lessons Learned. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Weng, L.-H.; Jin, G.-X. Isomers of Cyclometalated Macrocycles Constructed through Olefinic C–H Activation. Organometallics 2014, 33, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-B.; Lin, Y.-J.; Jin, G.-X. Discrete Iridamacrocycle Formation via C–H Activation of an N-Heterocycle. Organometallics 2011, 30, 3905–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-B.; Han, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-J.; Jin, G.-X. Cleavage of C−H Bonds for Building Tetranuclear Half-Sandwich Iridium Macrocycles with Ortho-Metalated Spacers. Organometallics 2010, 29, 2827–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-F.; Li, H.; Wenga, L.-H.; Jin, G.-X. Efficient formation of organoiridium macrocycles via C–H activation directed self-assembly. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3556–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Huang, L.; Yi, F. Iodine-Mediated Efficient Synthesis of 2,3-Dihydro-Pyrazines. J. Chem. Res. 2015, 39, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, L.; Chen, W.; Qian, C. YbCl3-catalyzed one-pot synthesis of dihydropyrazines, piperazines, and pyrazines. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Suneel, K.; Majhi, A. An efficient and convenient protocol for the synthesis of quinoxalines and dihydropyrazines via cyclization–oxidation processes using HClO4·SiO2 as a heterogeneous recyclable catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5371–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.; Baek, Y.; Lee, P.H. Synthesis of Pyrazines from Rhodium-Catalyzed Reaction of 2H-Azirines with N-Sulfonyl 1,2,3-Triazoles. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, D.; Attanasi, O.A.; Filippone, P.; Ignacio, R.; Lillini, S.; Mantellini, F.; Palacios, F.; de los Santos, J.M. Straightforward Access to Pyrazines, Piperazinones, and Quinoxalines by Reactions of 1,2-Diaza-1,3-butadienes with 1,2-Diamines under Solution, Solvent-Free, or Solid-Phase Conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5897–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, A.; Pagire, S.K.; Reiser, O. Visible-Light-Mediated Synthesis of Pyrazines from Vinyl Azides Utilizing a Photocascade Process. Synlett 2017, 28, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gramage-Doria, R.; Achelle, S.; Bruneau, C.; Robin-le Guen, F.; Dorcet, V.; Roisnel, T. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed C–H (Hetero)Arylation of Alkenylic 1,n-Diazines (n = 2, 3, and 4): Scope, Mechanism, and Application in Tandem Hydrogenations. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 1462–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, S.-J.; Xu, D.-Q.; Xia, A.-B.; Wang, Y.-F.; Liu, Y.-K.; Du, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-Y. Pd(OAc)2-catalyzed regioselective aromatic C–H bond fluorination. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6218–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, L.V.; Stowers, K.J.; Sanford, M.S. Insights into Directing Group Ability in Palladium Catalyzed C–H Bond Functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13285–13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naveen; Rajkumar, V.; Babu, S.A.; Gopalakrishnan, B. Pd(II)-Catalyzed Bidentate Directing Group-Aided Chemoselective Acetoxylation of Remote ε-C(sp2)–H Bonds in Heteroaryl–Aryl-Based Biaryl Systems. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 12197–12211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, I.; Derridj, F.; Roisnel, T.; Doucet, H.; Soulé, J.-F. Quinoxaline as an integrated directing group in palladium-catalyzed ortho-C–H bond arylation of the aryl unit of 2-arylquinoxalines. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16036–16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, P.J.; Caygill, G.B. Cyclometallated compounds V. Double cyclopalladation of diphenyl pyrazines and related ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 1990, 395, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Bheeter, C.B.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Sequential Ruthenium(II)-Acetate Catalyzed C–H Bond Diarylation in NMP or Water and Hydrosilylation of Imines. Top. Catal. 2014, 57, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Bheeter, C.B.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Sequential Catalysis for the Production of Sterically Hindered Amines: Ru(II)-Catalyzed C–H Bond Activation and Hydrosilylation of Imines. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Devaraj, K.; Darcel, C.; Dixneuf, P.H. Catalytic C−H bond arylation of aryl imines and oxazolines in water with ruthenium(II)-acetate catalyst. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 5179–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, L.H. The preparation of lysidine, 2,3-dihydro-5,6-diphenylpyrazine and 2,3-diphenylpyrazine. J. Chem. Ed. 1939, 16, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Entry | R (Equiv.) | React. Time (h) | Conv.b (%) | 3/4/5/6/7b(%)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MeCO (2) | 1 | 96 | 31/10/50/2/7 |
| 2d | MeCO (2) | 1 | 77 | 86/4/10/0/0 |
| 3d | MeCO (2) | 1.25 | 93 | 64/4/28/1/3 |
| 4 | MeCO (2) | 0.5 | 86 | 75(53)/3/22(7%)/0/0 |
| 5 | MeCO (4) | 1 | 100 | 0/5/73(58%)/6(3%)/16(10%) |
| 6 | MeCO (4) | 0.5 | 100 | 20/4/65/1/10 |
| 7 | CF3 (4) | 1 | 100 | 0/7(5%)/70(45%)/5/18(13%) |

| Entry | R (Equiv.) | React. Time (h) | 5/6/7/8/9c(%)d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MeCO (6) | 1 | 0/6/78(65%)/2/14(10%) |
| 2 | CF3 (6) | 1 | 22(9%)/14(8%)/60(40%)/4/0 |
| 3 | MeCO (10) | 1 | 0/6/67/5/22 |
| 4 | MeCO (10) | 2 | 0/7/55(40%)/8/30(19%) |
| 5e | MeCO (10) | 4 | 0/2/23(10%)/14(9%)/58(38%) |
| 6e | MeCO (10) | 8 | 0/2/20(10%)/16(10%)/61(40%) |




| Entry | Starting | React. Temperature (°C) | Conv.b (%) | 6a/7a/8a/9a/10ab |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5a | 140 | 100 | 30/30/23/17/0 |
| 2 | 5a | 200 | 100 | 9/0/54/0/37 |
| 3 | 7a | 140 | 57 | 0/0/46/52/2 |
| 4 | 7a | 200 | 100 | 0/0/9/25/66 |

| Entry | React. Time (h) | React. Temperature (°C) | 6a/8ac(%)d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 140 | 80/20 |
| 2 | 1 | 200 | 50(20%)/50(27%) |
| 3 | 4 | 140 | 50/50 |
| 4 | 4 | 200 | 35(11%)/60(19%) |



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hrovat, S.; Drev, M.; Grošelj, U.; Perdih, F.; Svete, J.; Štefane, B.; Požgan, F. Conformationally Driven Ru(II)-Catalyzed Multiple ortho-C–H Bond Activation in Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives in Water: Where Is the Limit? Catalysts 2020, 10, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040421
Hrovat S, Drev M, Grošelj U, Perdih F, Svete J, Štefane B, Požgan F. Conformationally Driven Ru(II)-Catalyzed Multiple ortho-C–H Bond Activation in Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives in Water: Where Is the Limit? Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040421
Chicago/Turabian StyleHrovat, Sara, Miha Drev, Uroš Grošelj, Franc Perdih, Jurij Svete, Bogdan Štefane, and Franc Požgan. 2020. "Conformationally Driven Ru(II)-Catalyzed Multiple ortho-C–H Bond Activation in Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives in Water: Where Is the Limit?" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040421
APA StyleHrovat, S., Drev, M., Grošelj, U., Perdih, F., Svete, J., Štefane, B., & Požgan, F. (2020). Conformationally Driven Ru(II)-Catalyzed Multiple ortho-C–H Bond Activation in Diphenylpyrazine Derivatives in Water: Where Is the Limit? Catalysts, 10(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040421