Ir-Sn-Sb-O Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Physicochemical Characterization and Performance in Water Electrolysis Single Cell with Solid Polymer Electrolyte
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physical and Chemical Properties
2.1.1. Electrical Conductivity
2.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
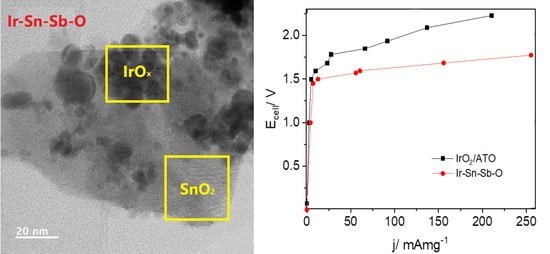
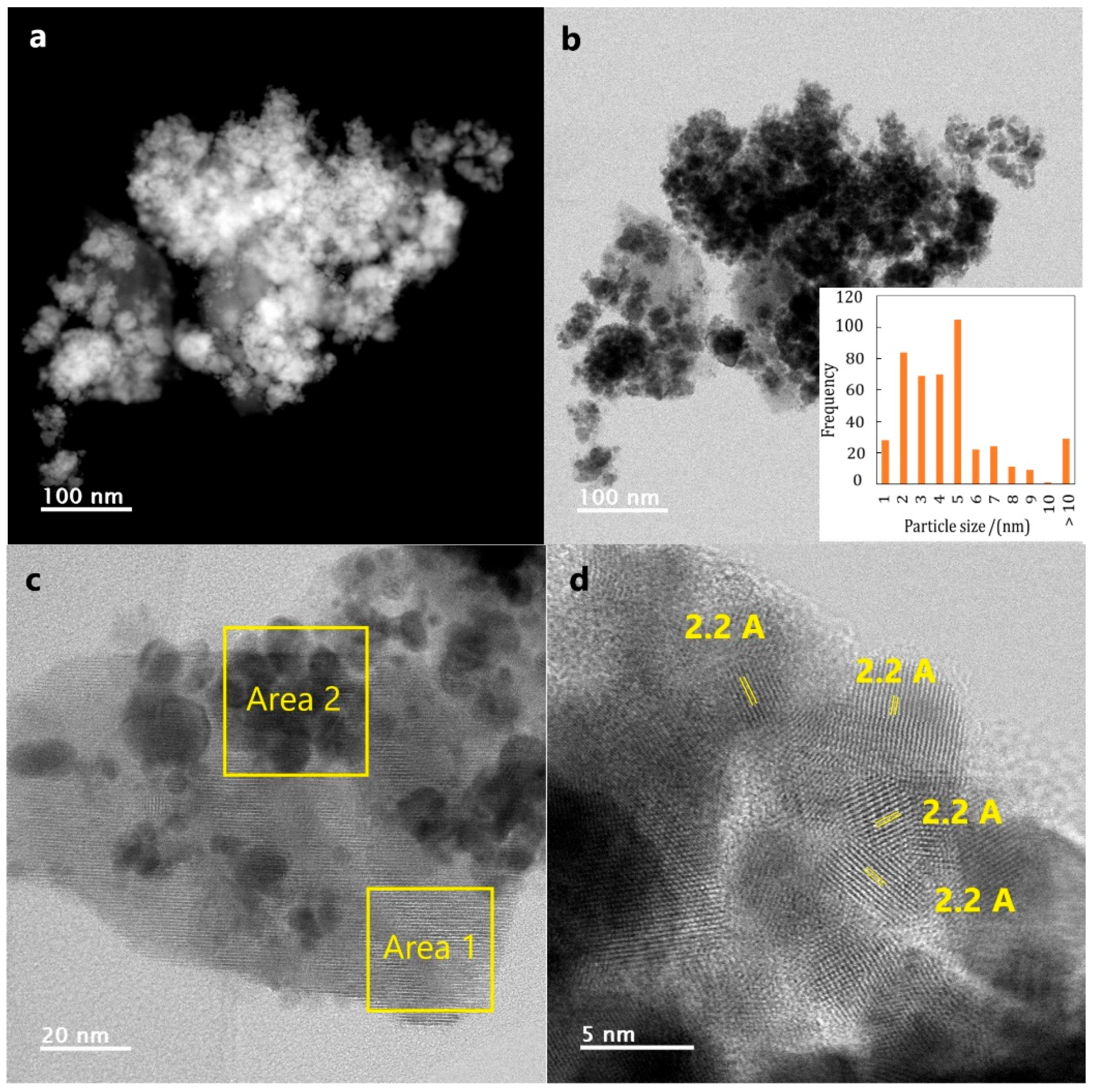
2.1.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.1.4. X-ray Diffraction
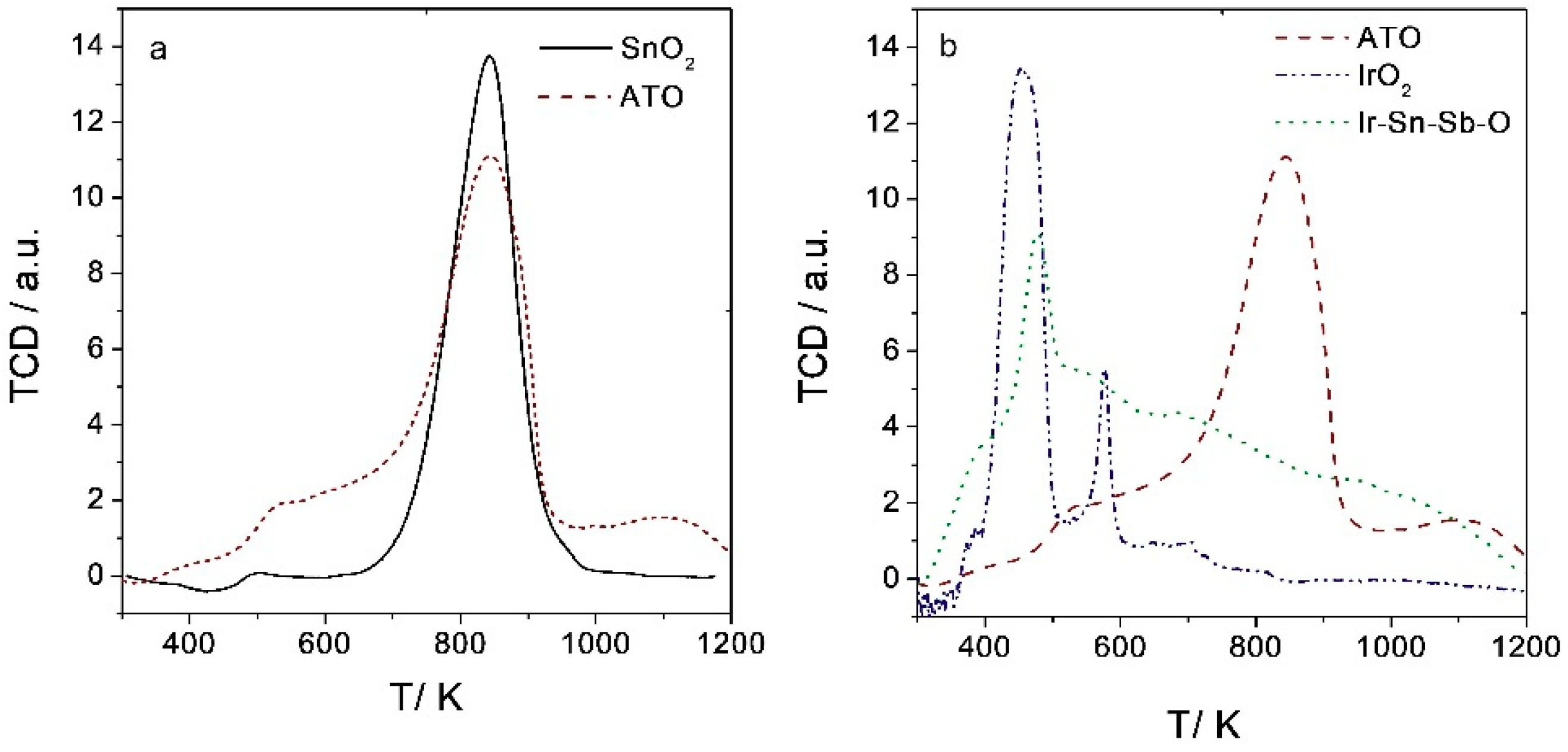
2.1.5. Temperature Programmed Reduction
2.2. Single Cell Electrochemistry
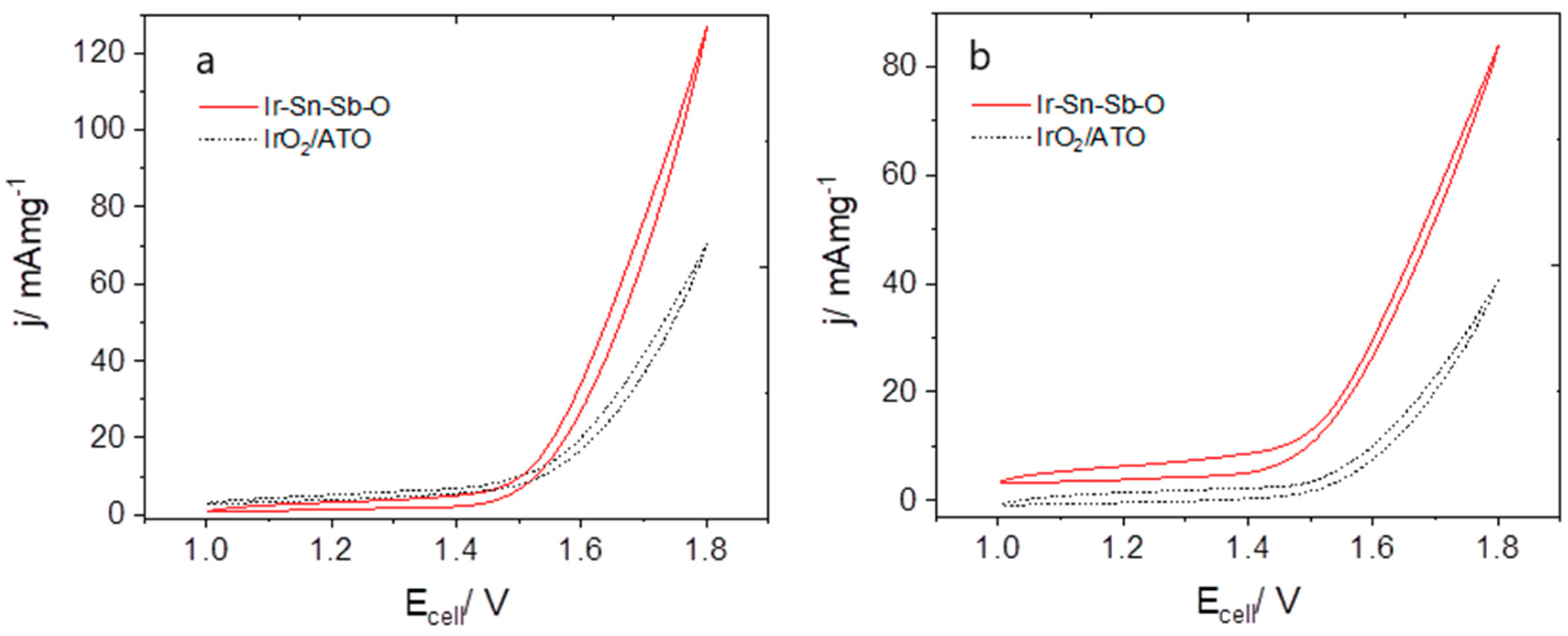
2.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
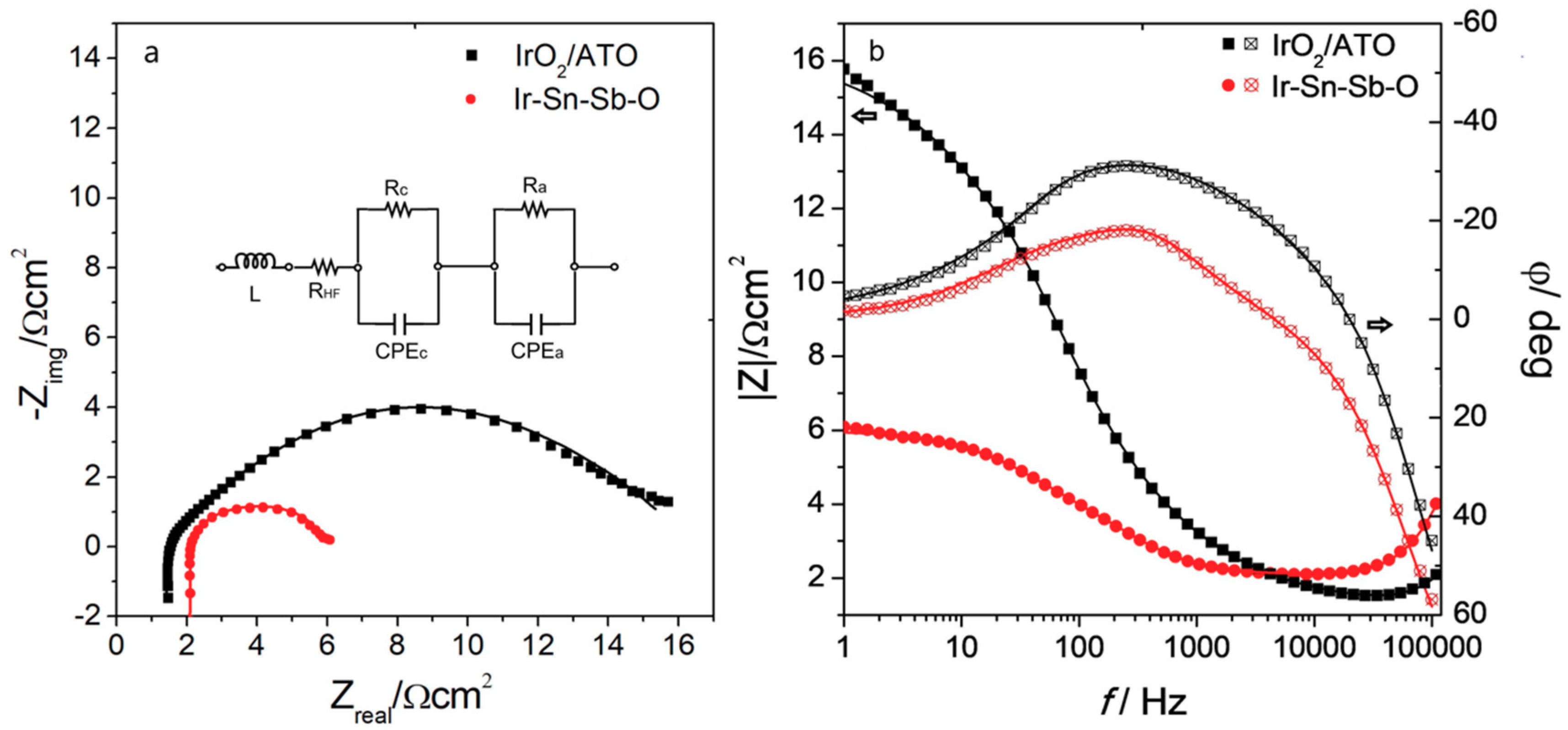
2.2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
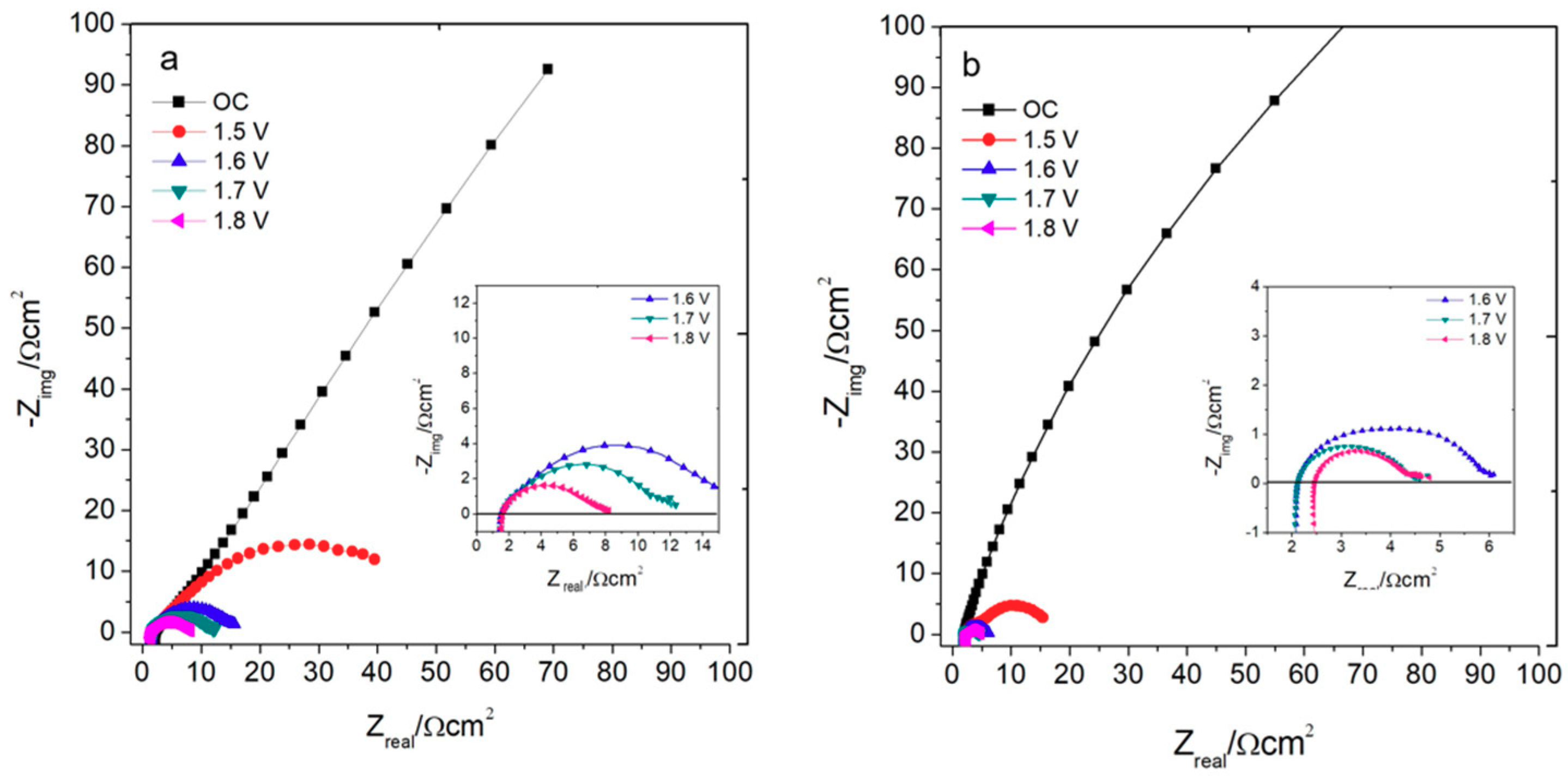
2.2.3. Electrolyser Performance
2.2.4. Chronoamperometry
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mixed Oxide Synthesis
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization
3.3. Membrane Electrode Assembly
3.4. Single Cell Electrochemistry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaubey, R.; Sahu, S.; James, O.; Maity, S. A review on development of industrial processes and emerging techniques for production of hydrogen from renewable and sustainable sources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azwar, M.Y.; Hussain, M.A.; Abdul-Wahab, A.K. Development of biohydrogen production by photobiological, fermentation and electrochemical processes: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, C.; Hochrinner, H. Use of Conventional and Green Hydrogen in the Chemical Industry. In Hydrogen and Fuel Cell; Töpler, J., Lehmann, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 173–186. ISBN 978-3-662-44971-4. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, V.A.; da Silva, L.A.; Boodts, J.F.C.; Trasatti, S. Kinetics and mechanism of oxygen evolution on IrO2-based electrodes containing Ti and Ce acidic solutions. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Sepulveda, M.; Trinh, P.; Malkhandi, S.; Narayanan, S.R.; Jorné, J.; Quesnel, D.J.; Postonr, J.A., Jr.; Manivannan, A. Investigation of Oxygen Evolution Reaction at LaRuO3, La3.5Ru4O13, and La2RuO5. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, L.; Han, B.; Risch, M.; Hong, W.T.; Rao, R.R.; Stoerzinger, K.A.; Shao-Horn, Y. pH dependence of OER activity of oxides: Current and future perspectives. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, P.; Ngameni, R.; Grigoriev, S.A.; Mbemba, N.; Brisset, F.; Ranjbari, A.; Etiévant, C. PEM water electrolyzers: From electrocatalysis to stack development. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 5043–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbli, K.S.; Péra, M.C.; Hissel, D.; Rallières, O.; Turpin, C.; Doumbia, I. Multiphysics simulation of a PEM electrolyser: Energetic Macroscopic Representation approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1382–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandesris, M.; Médeau, V.; Guillet, N.; Chelghoum, S.; Thoby, D.; Fouda-Onana, F. Membrane degradation in PEM water electrolyzer: Numerical modeling and experimental evidence of the influence of temperature and current density. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, B.; Ocon, J.D. Oxygen electrocatalysis in chemical energy conversion and storage technologies. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Mechanism and kinetics of the hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19484–19518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reier, T.; Oezaslan, M.; Strasser, P. Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER) on Ru, Ir, and Pt Catalysts: A Comparative Study of Nanoparticles and Bulk Materials. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamesh, M.-I.; Sun, X. Recent progress on earth abundant electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in alkaline medium to achieve efficient water splitting—A review. J. Power Sources 2018, 400, 31–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Mao, Y. Ultrafine Iridium Oxide Nanorods Synthesized by Molten Salt Method toward Electrocatalytic Oxygen and Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 212, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, M.; Haasch, R.; Mrozek, P.; Wieckowski, A.; De Pauli, C.; Trasatti, S. Characterization of IrO2-SnO2 thin layers by electron and ion spectroscopies. Vacuum 1994, 45, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, S.; Fregonara, G.; Trasatti, S. “Inner” and “outer” active surface of RuO2 electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 1990, 35, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audichon, T.; Mayousse, E.; Morisset, S.; Morais, C.; Comminges, C.; Napporn, T.W.; Kokoh, K.B. Electroactivity of RuO2–IrO2 mixed nanocatalysts toward the oxygen evolution reaction in a water electrolyzer supplied by a solar profile. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16785–16796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherevko, S.; Geiger, S.; Kasian, O.; Kulyk, N.; Grote, J.-P.; Savan, A.; Shrestha, B.R.; Merzlikin, S.; Breitbach, B.; Ludwig, A.; et al. Oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions on Ru, RuO2, Ir, and IrO2 thin film electrodes in acidic and alkaline electrolytes: A comparative study on activity and stability. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Vante, N. Photocatalysis an enhancer of electrocatalytic process. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 9, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Vázquez, V.; Cruz, J.C.; Galván-Valencia, M.; Ledesma-García, J.; Arriaga, L.G.; Guzmán, C.; Durón-Torres, S.M. Electrochemical study of Sb-doped SnO2 supports on the oxygen evolution reaction: Effect of synthesis annealing time. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 10586–10600. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, M.; Guncheva, M.; Zhiryakova, D.; Lazarova, T.; Lalev, G.; Tsoncheva, T. Nanostructured tin dioxide—A promising multipurpose support material for catalytic and biocatalytic applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Chen, M.; Cao, X.; Yin, G.; Shi, P. A novel CNT-SnO2 core–sheath nanocomposite as a stabilizing support for catalysts of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jiang, K.; Wang, H.; Yao, X. The Role of Defect Sites in Nanomaterials for Electrocatalytic Energy Conversion. Chem 2019, 5, 1371–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, A.J.; Salazar-Banda, G.R.; Russell, A.E. Mechanistic insights into electrocatalytic reactions provided by SERS. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 17, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemeyer, A.; Hogan, Z.; Schlichter, M.; Smaka, B.; Streukens, G.; Turner, H.; Volpe, A.; Weinberg, H.; Yaccato, K. High surface area tin oxide. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 317, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Ohkawauchi, H.; Ito, M.; Yahikozawa, K.; Takasu, Y. Preparations of ultrafine IrO2-SnO2 binary oxide particles by a sol-gel process. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 2551–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakia, K.; Datta, M.K.; Velikokhatnyi, O.I.; Jampani, P.H.; Kumta, P.N. Fluorine doped (Ir,Sn,Nb)O2 anode electro-catalyst for oxygen evolution via PEM based water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.G.L.; Sanderson, R.D.; Crouch, A.M. Sol–gel preparation and characterisation of mixed metal tin oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6691–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balko, E.N.; Nguyen, P.H. Iridium-tin mixed oxide anode coatings. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.; Smart, R.S.C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic chemical state quantification of mixed nickel metal, oxide and hydroxide systems. Surf. Interface Anal. 2009, 41, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.P.; Nolan, H.; Duesberg, G.S.; Colavita, P.E.; Lyons, M.E.G. Low-Overpotential High-Activity Mixed Manganese and Ruthenium Oxide Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pauli, C.P.; Trasatti, S. Electrochemical surface characterization of IrO2 + SnO2 mixed oxide electrocatalysts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 396, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintar, A.; Batista, J.; Hočevar, S. Redox Behavior of (CuO)0.15(CeO2)0.85 Mixed Oxide Catalyst Prepared by Sol-Gel Peroxide Method. Acta Chim. Slov. 2005, 52, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, F.K.; Hassan, J.; Wahab, Z.A.; Azis, R.S. Electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of manganese and vanadium mixed oxide prepared by conventional solid state method. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2016, 19, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Tsypkin, M.; Boørresen, B.; Hagen, G.; Tunold, R. Nanocrystalline IrxSn(1-X)O2 electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution in water electrolysis with polymer electrolyte—Effect of heat treatment. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2004, 7, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.; Børresen, B.; Hagen, G.; Tsypkin, M.; Tunold, R. Electrochemical characterisation of IrxSn1−xO2 powders as oxygen evolution electrocatalysts. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 3161–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Børresen, B.; Hagen, G.; Tsypkin, M.; Tunold, R. Hydrogen production by advanced proton exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolysers—Reduced energy consumption by improved electrocatalysis. Energy 2007, 32, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Viramontes, N.J.; Escalante-García, I.L.; Guzmán-Martínez, C.; Galván-Valencia, M.; Durón-Torres, S.M. Electrochemical study of Ir–Sn–Sb–O materials as catalyst-supports for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2015, 45, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-S.; Nong, H.N.; Strasser, P. Preparation of Mesoporous Sb-, F-, and In-Doped SnO2 Bulk Powder with High Surface Area for Use as Catalyst Supports in Electrolytic Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Borresen, B.; Hagen, G.; Tsypkin, M.; Tunold, R. Preparation and characterisation of nanocrystalline IrSnO electrocatalytic powders. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 94, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Vázquez, V.; Galván-Valencia, M.; Ledesma-García, J.; Arriaga, L.G.; Collins-Martínez, V.H.; Guzmán-Martínez, C.; Escalante-Garcia, I.L.; Durón-Torres, S.M. Electrochemical performance of a Sb-doped SnO2 support synthesized by coprecipitation for oxygen reactions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2015, 45, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthiyapura, V.K.; Pasupathi, S.; Su, H.; Liu, X.; Pollet, B.; Scott, K. Investigation of supported IrO2 as electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction in proton exchange membrane water electrolyser. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, V.; Jones, T.E.; Velasco Vélez, J.J.; Massué, C.; Greiner, M.T.; Arrigo, R.; Teschner, D.; Girgsdies, F.; Scherzer, M.; Allan, J.; et al. The electronic structure of iridium oxide electrodes active in water splitting. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 2292–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, V.B.; McNicol, B.D. Evaluation of semiconducting tin oxide as an electrocatalyst support. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1979, 75, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Papadantonakis, K.M.; Lewis, N.S. Principles and implementations of electrolysis systems for water splitting. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessarabov, D.; Millet, P. PEM Water Electrolysis; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; Volume 1, ISBN 9780128111468. [Google Scholar]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4614-8932-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sunde, S.; Lervik, I.A.; Owe, L.-E.; Tsypkin, M. An impedance model for a porous intercalation electrode with mixed conductivity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, B927–B937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Kolb, S.; Sata, N.; Fallisch, A.; Zielke, L.; Thiele, S.; Gago, A.S.; Friedrich, K.A. Comprehensive investigation of novel pore-graded gas diffusion layers for high-performance and cost-effective proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-M.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Cao, C.-N. Oxygen evolution reaction on IrO2-based DSA® type electrodes: Kinetics analysis of Tafel lines and EIS. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, T.; Selamet, O.F. Mathematical modeling and dynamic Simulink simulation of high-pressure PEM electrolyzer system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 13901–13914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Danilovic, N.; Wang, Y.; Willis, W.; Poozhikunnath, A.; Bonville, L.; Capuano, C.; Ayers, K.; Maric, R. Nano-size IrOx catalyst of high activity and stability in PEM water electrolyzer with ultra-low iridium loading. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 239, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttler, A.; Spliethoff, H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power-to-gas and power-to-liquids: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Baglio, V.; Van Dijk, N.; Merlo, L.; Aricò, A.S. Enhanced performance and durability of low catalyst loading PEM water electrolyser based on a short-side chain perfluorosulfonic ionomer. Appl. Energy 2017, 192, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, S.; Bianchi, C.L.; Cappelletti, G.; Ionita, M.; Minguzzi, A.; Rondinini, S.; Vertova, A. Composite ternary SnO2–IrO2–Ta2O5 oxide electrocatalysts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2006, 589, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasatti, S.; Buzzanca, G. Ruthenium dioxide—New interesting electrode material-solid state structure and electrochemical behaviour. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1971, 29, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| P/psi | Ir-Sn-Sb-O | IrO2 | ATO a |
|---|---|---|---|
| σ/S m−1 | |||
| 0 | 11,163 ± 715 | 252 ± 16 | 3.6 ± 0.5 |
| 50 | 87,447 ± 16,179 | 22,191 ± 1681 | 6.4 ± 0.5 |
| 100 | 122,620 ± 6688 | 42,788 ± 2609 | 175 ± 34 |
| 150 | 157,981 ± 15,418 | 87,236 ± 6618 | 308 ± 48 |
| 200 | 270,037 ± 24,019 | 145,357 ± 23,769 | 559 ± 52 |
| Catalyst | Area | Ir | O | Sn | Sb | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element/at.% | ||||||
| ATO | 1 | ----- | 53.28 | 44.55 | 2.17 | ----- |
| 2 | ----- | 66.23 | 31.13 | 2.64 | ----- | |
| 3 | ----- | 69.45 | 30.55 | 0 | ----- | |
| IrO2 | 1 | 22.74 | 71.24 | ----- | ----- | 6.02 |
| 2 | 45.1 | 52.17 | ----- | ----- | 2.73 | |
| 3 | 17.65 | 79.86 | ----- | ----- | 2.49 | |
| Ir-Sn-Sb-O | 1 | 0 | 74.17 | 22.68 | 3.15 | 0 |
| 2 | 26.72 | 57.34 | 6.87 | 7.4 | 1.67 | |
| 3 | 39.15 | 43.18 | 9.93 | 4.78 | 2.96 |
| Catalyst | L/H | RHF/Ω cm2 | Rc/ Ω cm2 | CPEc/F cm−2 | Ra/Ω cm2 | CPEa/F cm−2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IrO2/ATO | 6.26 × 10−7 | 1.38 | 0.38 | 0.0018 | 14.16 | 0.0072 |
| Ir-Sn-Sb-O | 1.03 × 10−6 | 1.91 | 0.13 | 0.0038 | 3.95 | 0.0120 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Viramontes, N.J.; Collins-Martínez, V.H.; Escalante-García, I.L.; Flores-Hernández, J.R.; Galván-Valencia, M.; Durón-Torres, S.M. Ir-Sn-Sb-O Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Physicochemical Characterization and Performance in Water Electrolysis Single Cell with Solid Polymer Electrolyte. Catalysts 2020, 10, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050524
Pérez-Viramontes NJ, Collins-Martínez VH, Escalante-García IL, Flores-Hernández JR, Galván-Valencia M, Durón-Torres SM. Ir-Sn-Sb-O Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Physicochemical Characterization and Performance in Water Electrolysis Single Cell with Solid Polymer Electrolyte. Catalysts. 2020; 10(5):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050524
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Viramontes, Nicté J., Virginia H. Collins-Martínez, Ismailia L. Escalante-García, José R. Flores-Hernández, Marisol Galván-Valencia, and Sergio M. Durón-Torres. 2020. "Ir-Sn-Sb-O Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Physicochemical Characterization and Performance in Water Electrolysis Single Cell with Solid Polymer Electrolyte" Catalysts 10, no. 5: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050524
APA StylePérez-Viramontes, N. J., Collins-Martínez, V. H., Escalante-García, I. L., Flores-Hernández, J. R., Galván-Valencia, M., & Durón-Torres, S. M. (2020). Ir-Sn-Sb-O Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Physicochemical Characterization and Performance in Water Electrolysis Single Cell with Solid Polymer Electrolyte. Catalysts, 10(5), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050524