Synthesis of Highly Selective and Stable Co-Cr/SAPO-34 Catalyst for the Catalytic Dehydration of Ethanol to Ethylene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. XRD Anaysis
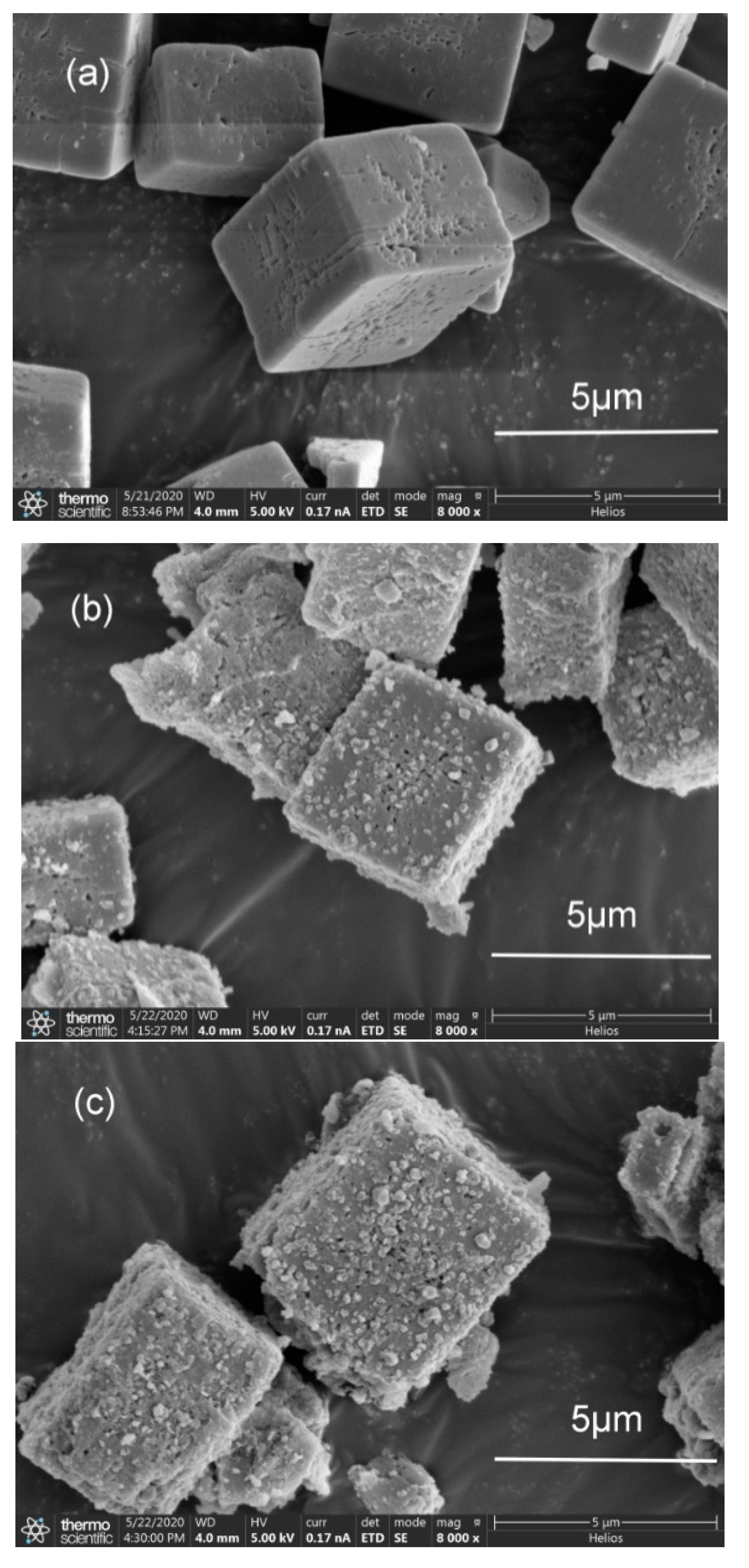
2.2. SEM Analysis
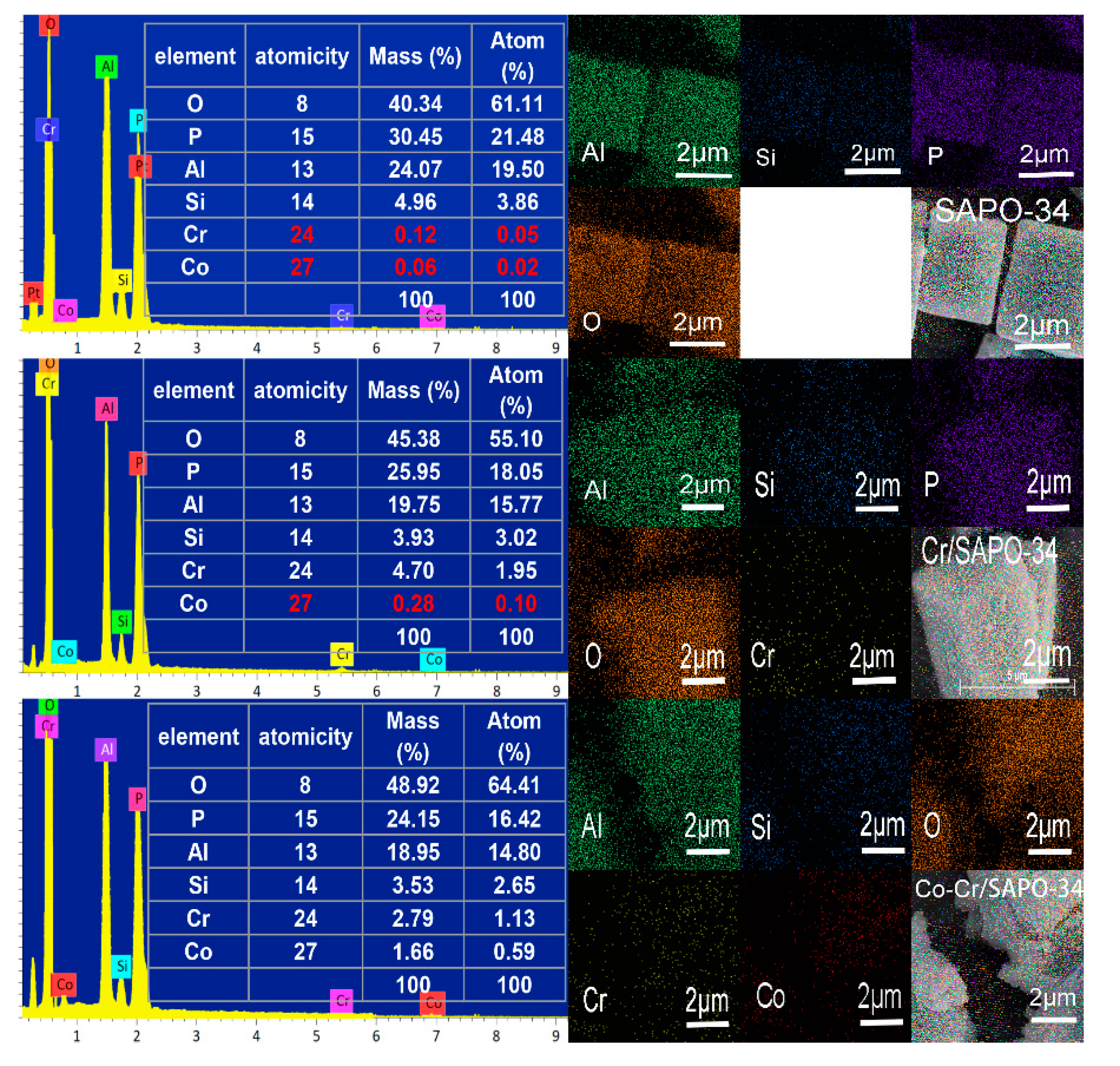
2.3. EDX Analysis
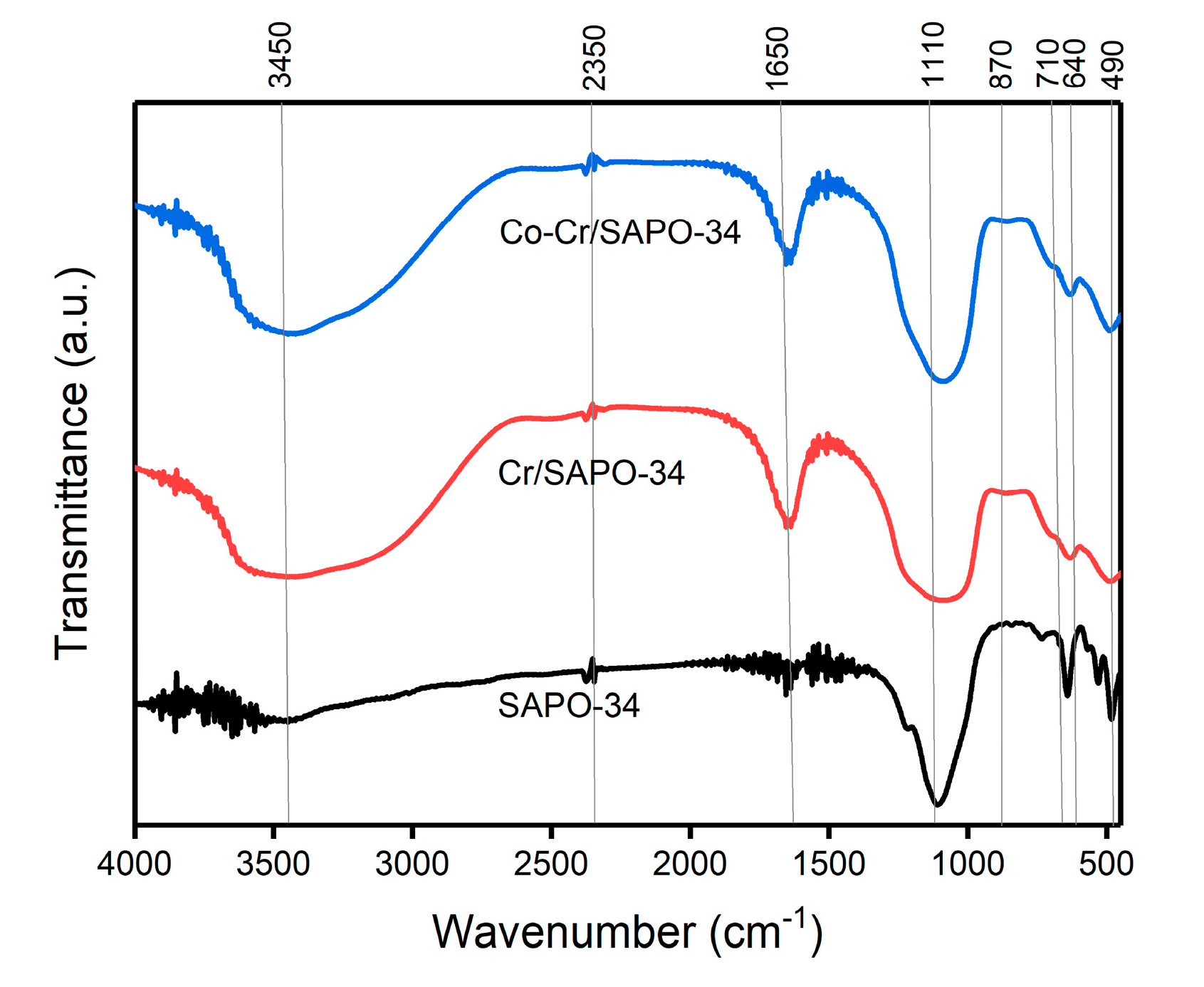
2.4. FT-IR Analysis
2.5. NH3-TPD Analysis
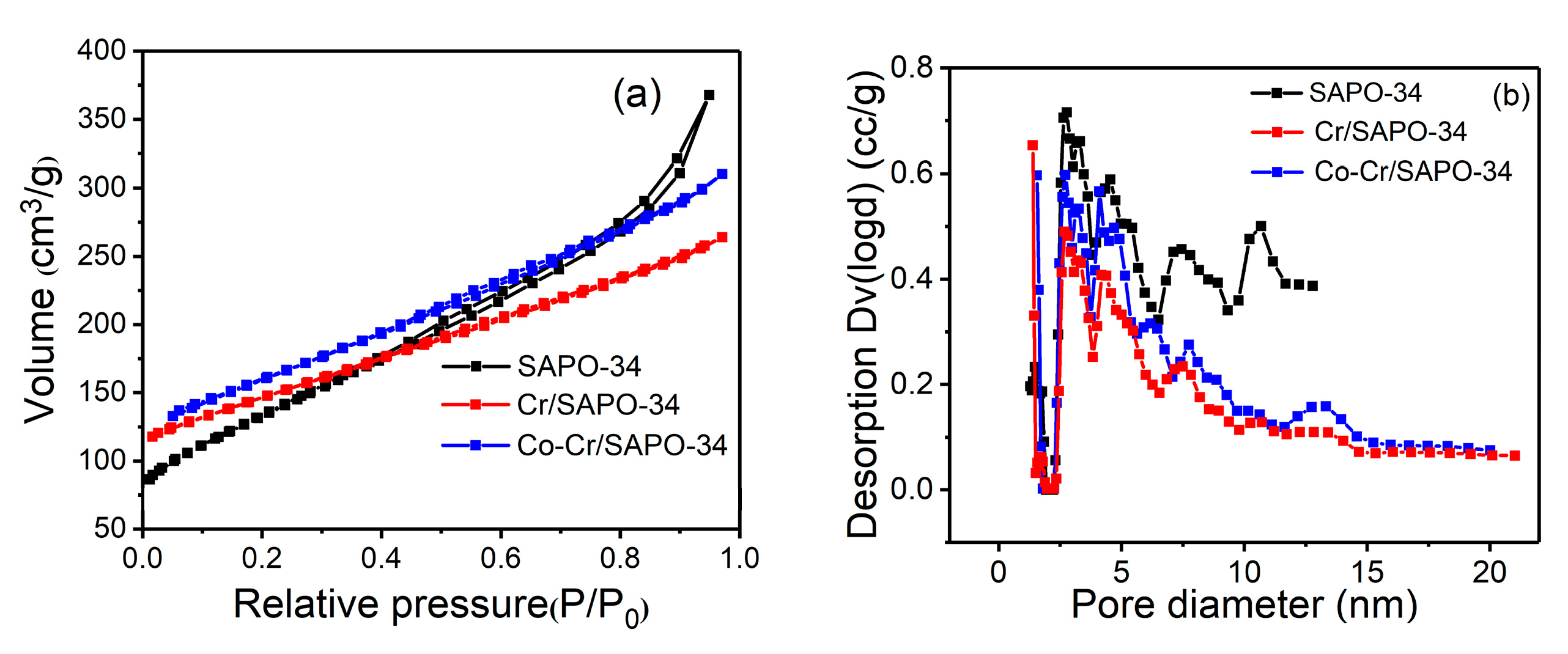
2.6. BET Analysis
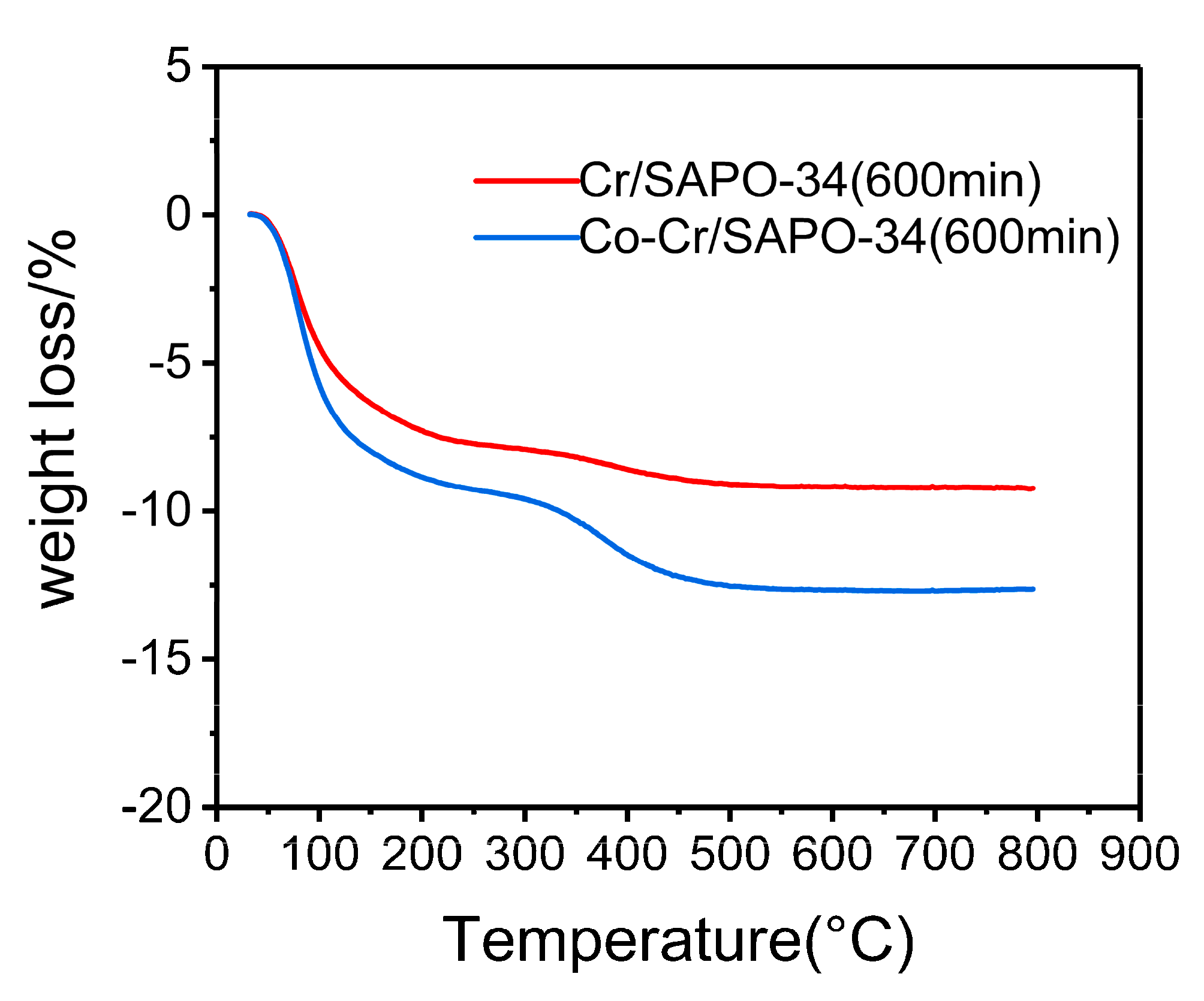
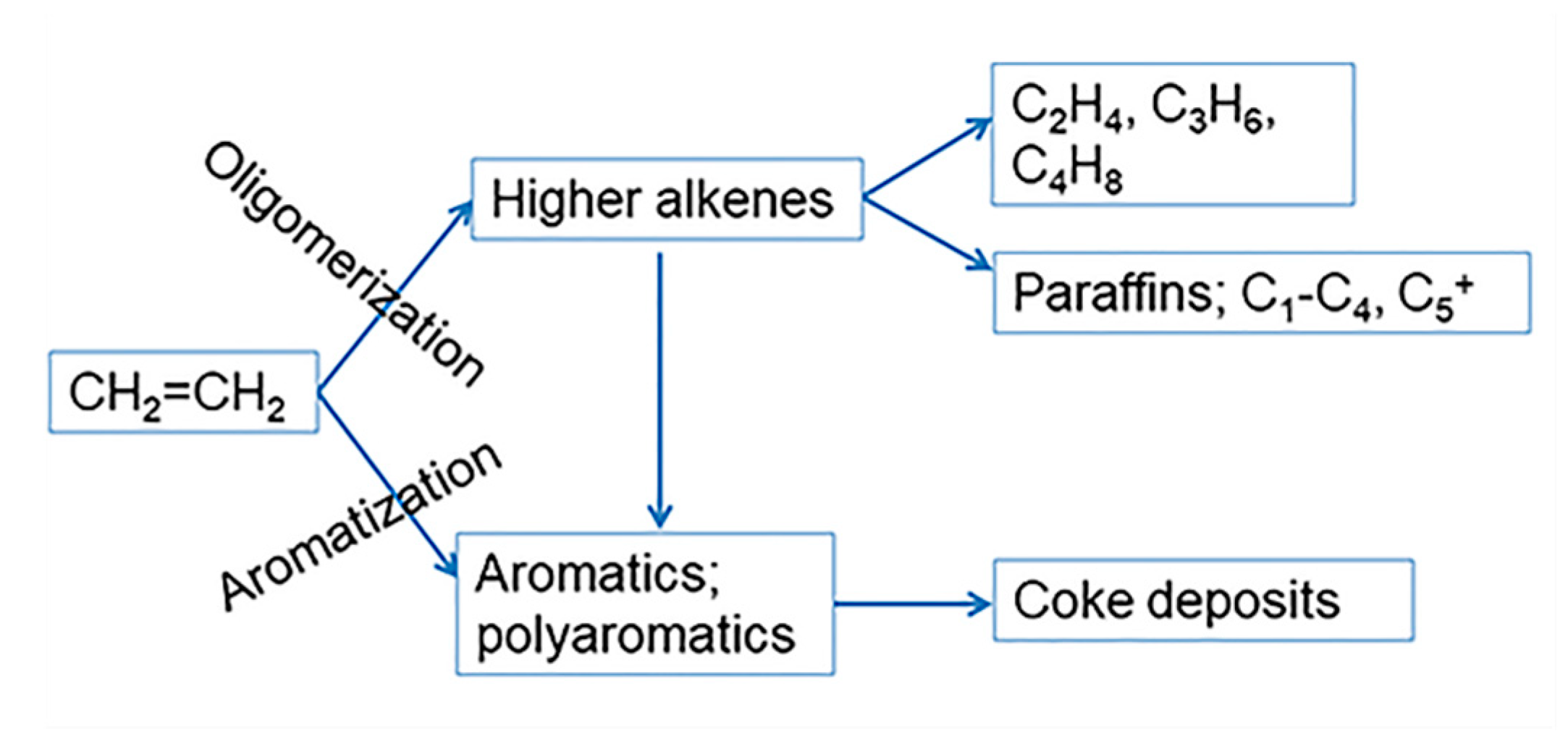
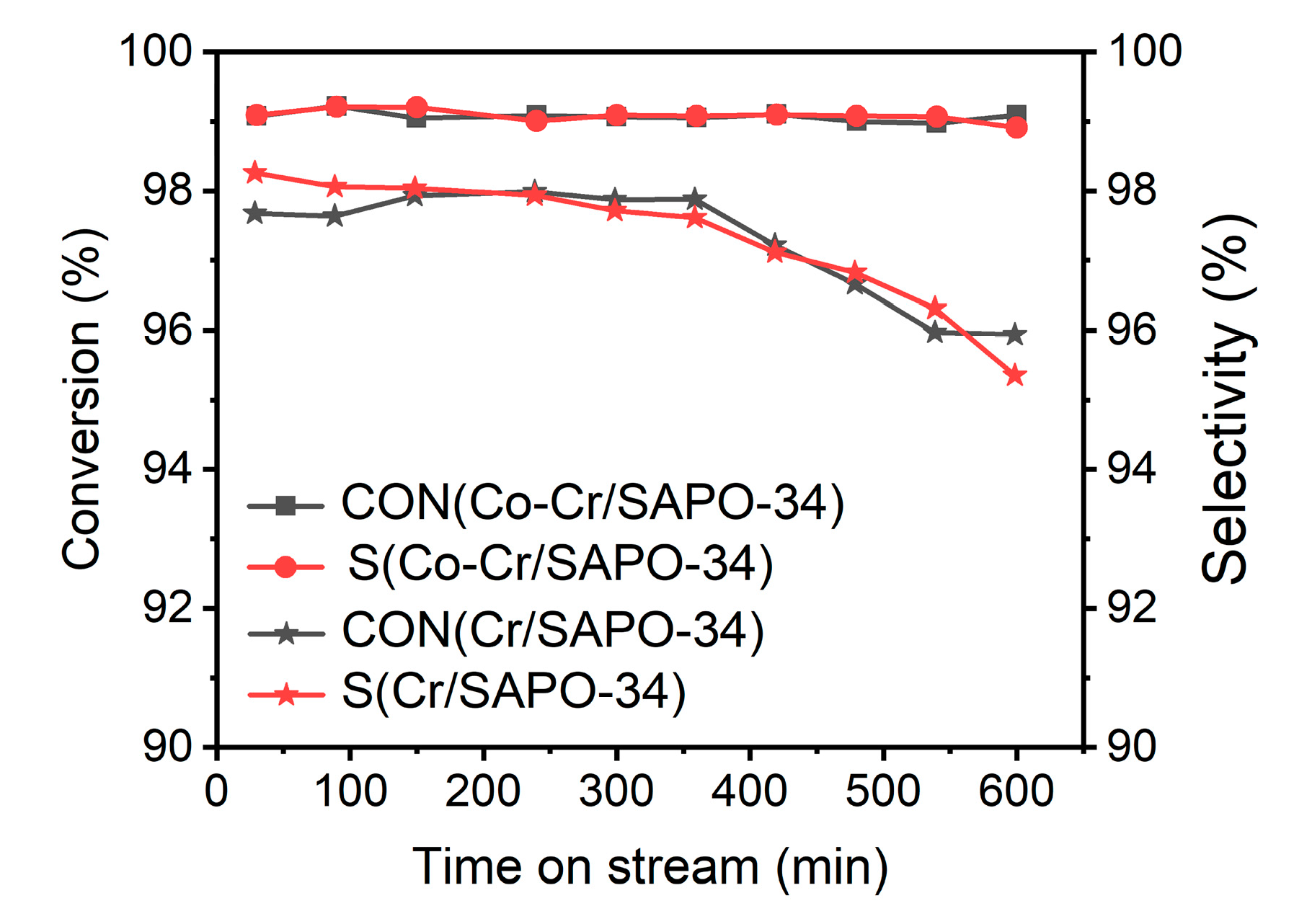
2.7. Coke Formation
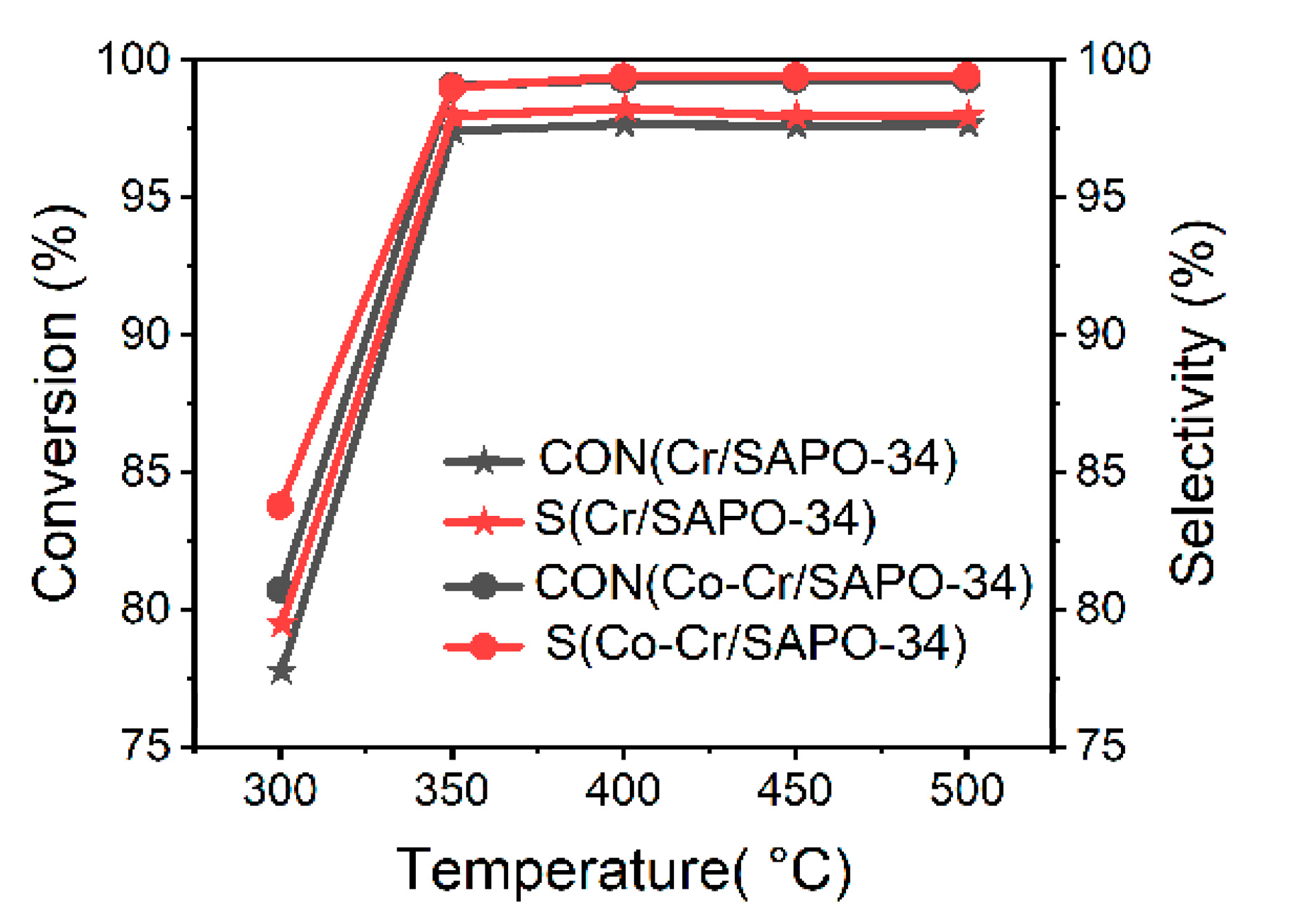
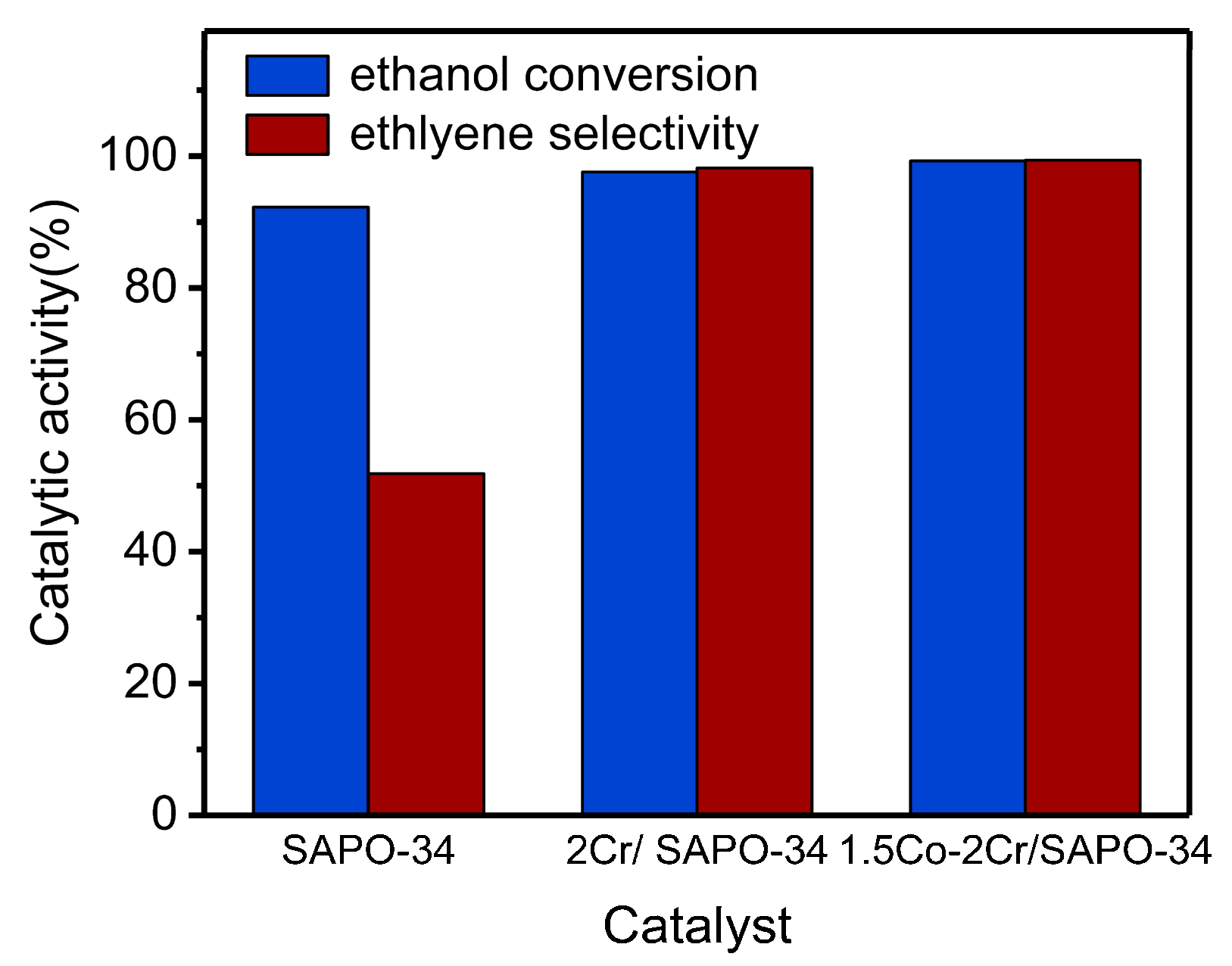
3. Activity Tests of Catalysts
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
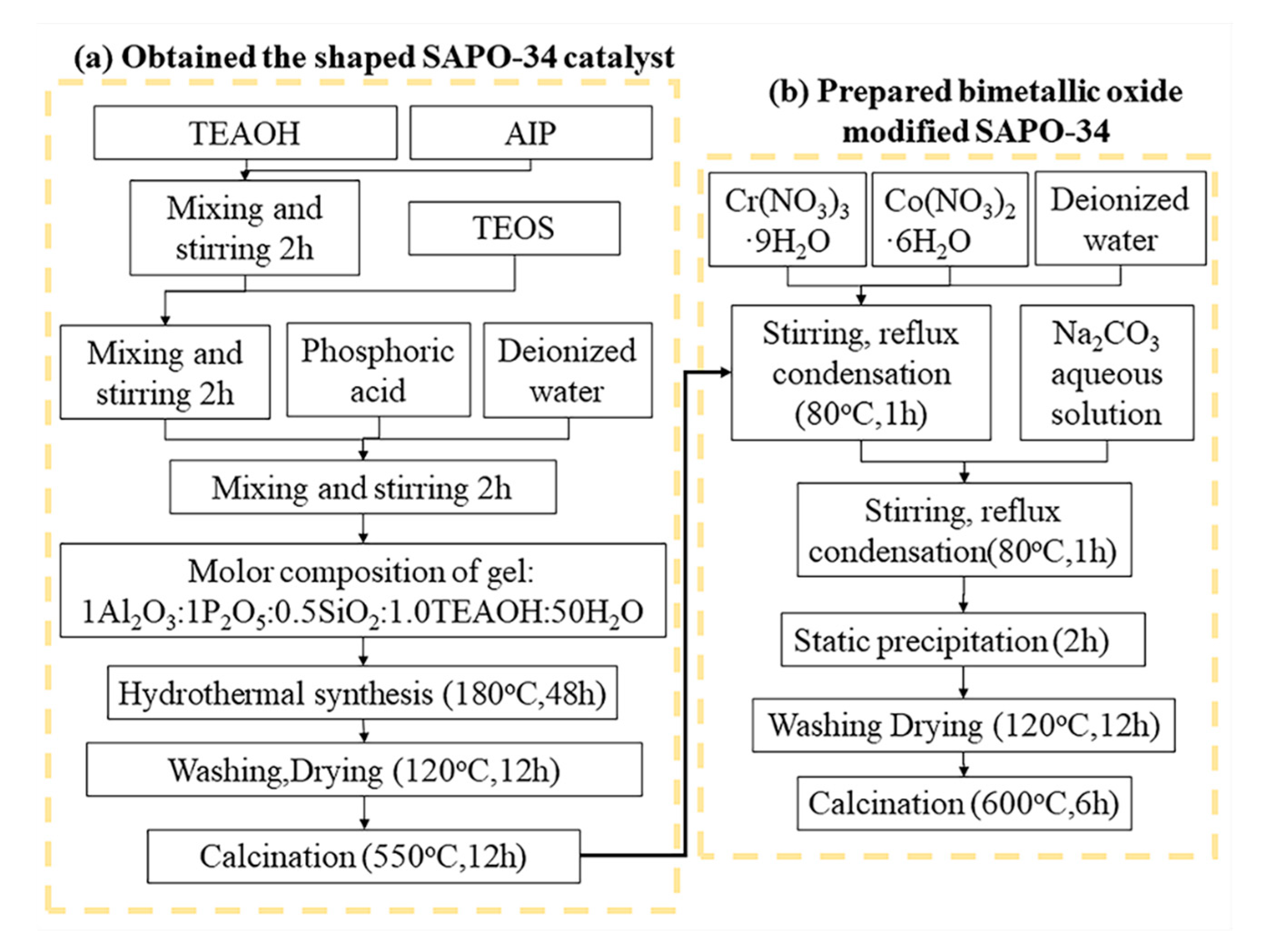
4.2. Catalyst Preparation
4.3. Characterization of Catalysts
4.4. Catalytic Reaction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.Y.; Wu, H.S. Ethylene Formation from Ethanol Dehydration Using ZSM-5 Catalyst. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4287–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedighi, M.; Ghasemi, M.; Sadeqzadeh, M.; Hadi, M. Thorough study of the effect of metal-incorporated SAPO-34 molecular sieves on catalytic performances in MTO process. Powder Technol. 2016, 291, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyvanloo, K.; Sedighi, M.; Towfighi, J. Genetic algorithm model development for prediction of main products in thermal cracking of naphtha: Comparison with kinetic modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Bozzano, A.; Glover, B.; Fuglerud, T.; Kvisle, S. Recent advancements in ethylene and propylene production using the UOP/Hydro MTO process. Catal. Today 2005, 106, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, M.; Keyvanloo, K.; Towfighi, J. Experimental study and optimization of heavy liquid hydrocarbon thermal cracking to light olefins by response surface methodology. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tao, L.; Dai, B.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, X. Dehydration reaction of bio-ethanol to ethylene over modified SAPO catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lu, J.; Wu, L.; Chao, Z. Dehydration of bio-ethanol to ethylene over iron exchanged HZSM-5. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F. Comparison of four catalysts in the catalytic dehydration of ethanol to ethylene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, E.; Haghighi, M.; Pazhohniya, Z.; Aghamohammadi, S. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of nanostructured ZrAPSO-34 powder: Effect of Zr-loading on physicochemical properties and catalytic performance in conversion of methanol to ethylene and propylene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadbakhsh, A.; Farhadi, F.; Khorasheh, F.; Sahebdelfar, S.; Asadi, M.; Feng, Y.Z. Effect of SAPO-34’s composition on its physico-chemical properties and deactivation in MTO process. Appl. Catal. Gen. 2009, 364, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, R.; Haghighi, M.; Asgari, N. Direct synthesis of dimethyl ether on the admixed nanocatalysts of CuO-ZnO-Al2O3 and HNO3-modified clinoptilolite at high pressures: Surface properties and catalytic performance. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, M.; Rooke, J.C.; Chen, L.; Su, B.-L. Synthesis and applications of hierarchically porous catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsbye, U.; Svelle, S.; Bjørgen, M.; Beato, P.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Joensen, F.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. Heterogeneous Catalysis Conversion of Methanol to Hydrocarbons: How Zeolite Cavity and Pore Size Controls Product Selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5810–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Xu, S.; Sun, T.; Guo, X.; Song, C.; Liu, Z. Enhancing ethylene selectivity in MTO reaction by incorporating metal species in the cavity of SAPO-34 catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Dhupatemiya, P.; Phatanasri, S.; Tomoyuki, I. Synthesis course of the Ni-SAPO-34 catalyst for methanol-to-olefin conversion. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 28, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Ji, S.; Lü, D.; Bai, B.; Sun, Q. Preparation of modified Ce-SAPO-34 catalysts and their catalytic performances of methanol to olefins. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M. Methanol conversion on metal-incorporated SAPO-34s (MeAPSO-34s). J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2000, 160, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotevar, S.; Levec, J. Acidity and catalytic activity of McAPSO-34 (Me = Co, Mn, Cr), SAPO-34, and H-ZSM-5 molecular sieves in methanol dehydration. J. Catal. 1992, 135, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørgen, M.; Svelle, S.; Joensen, F.; Nerlov, J.; Kolboe, S.; Bonino, F.; Palumbo, L.; Bordiga, S.; Olsbye, U. Conversion of methanol to hydrocarbons over zeolite H-ZSM-5: On the origin of the olefinic species. J. Catal. 2007, 249, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Ruiz-Martínez, J.; Mokhtar, M.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Basahel, S.N.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Single-catalyst particle spectroscopy of alcohol-to-olefins conversions: Comparison between SAPO-34 and SSZ-13. Catal. Today 2014, 226, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Sivasanker, S. HZSM-5 catalysed conversion of aqueous ethanol to hydrocarbons. Appl. Catal. Gen. 1997, 148, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadima, A.; Muraza, O. Zeolite catalysts in upgrading of bioethanol to fuels range hydrocarbons: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varzaneh, A.Z.; Towfighi, J.; Kootenaei, A.H.S.; Mohamadalizadeh, A. Effect of cerium and zirconium nanoparticles on the structure and catalytic performance of SAPO-34 in steam cracking of naphtha to light olefins. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2015, 115, 719–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, E.; Haghighi, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanostructured Ce-SAPO-34: High-performance and long-lifetime catalyst with various ceria contents for methanol to light olefins conversion. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 270, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongsomjit, B.; Goodwin, J.G. Co-support compound formation in Co/Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of reduction gas containing CO. Catal. Today 2002, 77, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi-ud-din; Xuanhui, Q.; Ping, L.; Zhang, L.; Ahmad, M. Hydrogen Sorption Improvement of LiAlH4 Catalyzed by Nb2O5 and Cr2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13088–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Gao, C.; Zhong, Z.; Lin, H.; Chen, C. Production of Light Olefins from Catalytic Cracking Bio-oil Model Compounds over La2O3 -Modified ZSM-5 Zeolite. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 5910–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammadi, S.; Haghighi, M.; Charghand, M. Methanol conversion to light olefins over nanostructured CeAPSO-34 catalyst: Thermodynamic analysis of overall reactions and effect of template type on catalytic properties and performance. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 50, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmasi, M.; Fatemi, S.; Taheri Najafabadi, A. Improvement of light olefins selectivity and catalyst lifetime in MTO reaction; using Ni and Mg-modified SAPO-34 synthesized by combination of two templates. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Lu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ni, S. Transformation of syngas to light hydrocarbons over bifunctional CuO-ZnO/SAPO-34 catalysts: The effect of preparation methods. Reac. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2014, 112, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebin, C.; Zhen, Z.; Zhijian, T.; Sheng, H.; Lijun, Y.; Tianshu, L.; Bingchun, W.; Xiangbin, M.; Shanbin, G.; Mingwei, T.; et al. Hydroisomerization performance of platinum supported on ZSM-22/ZSM-23 intergrowth zeolite catalyst. Pet. Sci. 2012, 10, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, T.; Cui, Q.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H. The Catalytic Dehydration of Bio-ethanol to Ethylene on SAPO-34 Catalysts. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundzadeh, H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Sharifi Pajaie, H. Synthesis of highly selective and stable mesoporous Ni–Ce/SAPO-34 nanocatalyst for methanol-to-olefin reaction: Role of polar aprotic N, N-dimethylformamide solvent. Particuology 2018, 40, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F. Parametric Characterization and Influence of Tin on the Performance of Pt−Sn/SAPO-34 Catalyst for Selective Propane Dehydrogenation to Propylene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, J.; Meirer, F.; Yarulina, I.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Ruiz-Martínez, J.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Insights into the Activity and Deactivation of the Methanol-to-Olefins Process over Different Small-Pore Zeolites as Studied with Operando UV–vis Spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4033–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phung, T.K.; Busca, G. Diethyl ether cracking and ethanol dehydration: Acid catalysis and reaction paths. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 272, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañez, M.K.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Nickel catalysts obtained from hydrotalcites by coprecipitation and urea hydrolysis for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 8225–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rezaei, F.; Ludlow, D.K.; Rownaghi, A.A. Synthesis of SAPO-34@ZSM-5 and SAPO-34@Silicalite-1 Core–Shell Zeolite Composites for Ethanol Dehydration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichana, E.; Wiwatthanodom, W.; Jongsomjit, B.; Li, H. Carbon-Based Catalyst from Pyrolysis of Waste Tire for Catalytic Ethanol Dehydration to Ethylene and Diethyl Ether. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, M.; Murata, K.; Saito, M.; Takahara, I. Ethanol conversion to aromatic hydrocarbons over several zeolite catalysts. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2006, 88, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, C.; Liebert, J.S.; Stratmann, M.M.; Olindo, R.; Lercher, J.A. Comparison of zeolites LaX and LaY as catalysts for isobutane/2-butene alkylation. Appl. Catal. Gen. 2008, 336, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Takahashi, A.; Nakamura, I.; Shimada, H.; Fujitani, T. Study of active sites on the MFI zeolite catalysts for the transformation of ethanol into propylene. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2010, 328, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiong, G.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xin, Q.; Li, C. Coke formation during the methanol conversion to olefins in zeolites studied by UV Raman spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 39, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

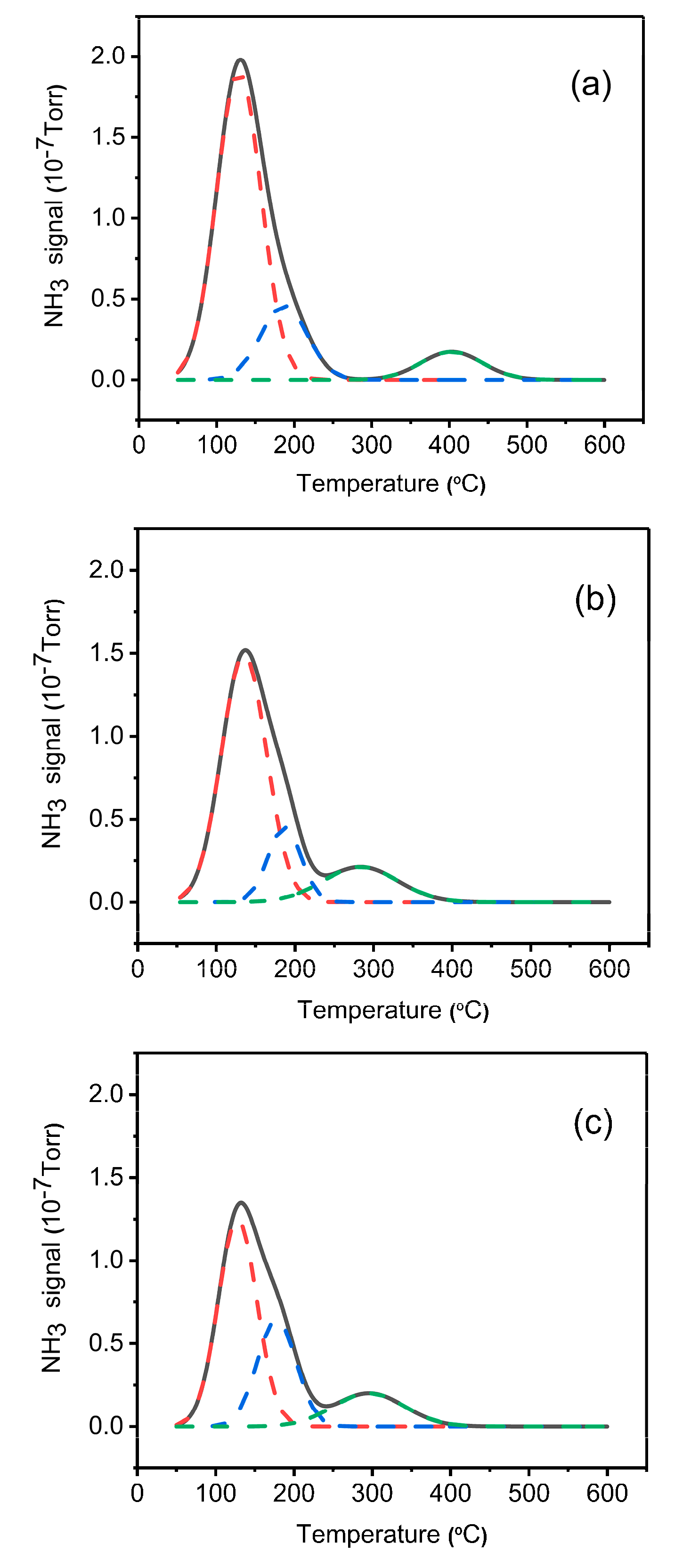




| Samples | Total Acidity/(mmol/g) | Percentage of Acid Sites (% of Total Acid) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Acid | Strong Acid | ||
| SAPO-34 | 0.77 | 73 | 27 |
| Cr/SAPO-34 | 0.65 | 69 | 31 |
| Co-Cr/SAPO-34 | 0.67 | 55 | 45 |
| Catalysts | SBET (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Dpore (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAPO-34 | 483 | 0.57 | 2.35 |
| Cr/SAPO-34 | 517 | 0.41 | 1.64 |
| Co-Cr/SAPO-34 | 563 | 0.48 | 1.70 |
| Catalyst | Reaction Temperature (°C) | Ethanol Conversion (%) | Ethylene Selectivity (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZSM-5 | 400 | 99 | 10 | [39] |
| Co/HZSM-5 | 400 | 94.82 | 76.16 | [40] |
| Cr/HZSM-5 | 400 | 93.85 | 23.81 | [40] |
| SAPO-34@ZSM-5 | 400 | 84.5 | 65 | [38] |
| Mn/SAPO-34 | 340 | 99.35 | 98.44 | [6] |
| SAPO-34 | 400 | 92.3 | 51.8 | This work |
| Cr/SAPO-34 | 400 | 97.6 | 98.2 | This work |
| Co-Cr/SAPO-34 | 400 | 99.3 | 99.4 | This work |
| NO. | RT (min) | Name of Compound | Molecular Formula | Structural Formula | Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12.017 | Decane, 2,3,5-trimethyl- | C13H28 | 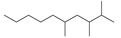 | 72 |
| 2 | 12.778 | Undecane, 4-methyl- | C12H26 |  | 68 |
| 3 | 14.406 | Decane, 2,4,6-trimethyl- | C13H28 | 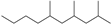 | 47 |
| 4 | 14.65 | Benzaldehyde, 3,5-dimethyl- | C9H10O |  | 95 |
| 5 | 15.064 | Octane, 2,4,6-trimethyl- | C11H24 |  | 53 |
| 6 | 15.271 | Undecane, 2,4-dimethyl- | C13H28 |  | 59 |
| 7 | 15.509 | Hexadecane | C16H34 |  | 72 |
| 8 | 18.252 | Dihydrocoumarin, 4,4,5,7,8-pentamethyl | C13H16O2 | 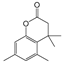 | 64 |
| 9 | 18.575 | 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | C14H22O | 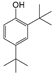 | 96 |
| 10 | 18.794 | Dodecane, 3-methyl- | C13H28 |  | 72 |
| 11 | 20.708 | Heptadecane | C17H36 |  | 97 |
| 12 | 22.75 | Octadecane | C18H38 |  | 93 |
| 13 | 25.713 | Cyclohexadecane | C16H32 | 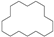 | 93 |
| 14 | 27.913 | Phenol, 2,2′-methylenebis(6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methyl- | C21H28O2 | 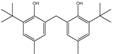 | 91 |
| NO. | RT (min) | Name of Compound | Molecular Formula | Structural Formula | Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.361 | Butanoic acid, 2-methylpropyl ester | C8H16O2 | 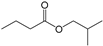 | 72 |
| 2 | 6.726 | Thymol, TMS derivative | C10H14O | 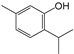 | 50 |
| 3 | 18.362 | 2,6-Dihydroxyacetophenone, 2TMS derivative | C8H8O3 | 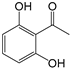 | 50 |
| 4 | 22.348 | Cyclopentadecanone, 2-hydroxy- | C15H28O2 | 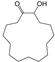 | 97 |
| 5 | 27.895 | Phenol, 2,2′-methylenebis(6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methyl- | C23H32O2 |  | 90 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, P.; Ren, X.; Xiong, D.; Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chen, X. Synthesis of Highly Selective and Stable Co-Cr/SAPO-34 Catalyst for the Catalytic Dehydration of Ethanol to Ethylene. Catalysts 2020, 10, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070785
Niu P, Ren X, Xiong D, Ding S, Li Y, Wei Z, Chen X. Synthesis of Highly Selective and Stable Co-Cr/SAPO-34 Catalyst for the Catalytic Dehydration of Ethanol to Ethylene. Catalysts. 2020; 10(7):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070785
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Peirong, Xiao Ren, Deyuan Xiong, Shilei Ding, Yuanlin Li, Zhaozhou Wei, and Xusong Chen. 2020. "Synthesis of Highly Selective and Stable Co-Cr/SAPO-34 Catalyst for the Catalytic Dehydration of Ethanol to Ethylene" Catalysts 10, no. 7: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070785
APA StyleNiu, P., Ren, X., Xiong, D., Ding, S., Li, Y., Wei, Z., & Chen, X. (2020). Synthesis of Highly Selective and Stable Co-Cr/SAPO-34 Catalyst for the Catalytic Dehydration of Ethanol to Ethylene. Catalysts, 10(7), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070785





