Probing the Surface Acidity of Supported Aluminum Bromide Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. BET and Pore Size Distribution
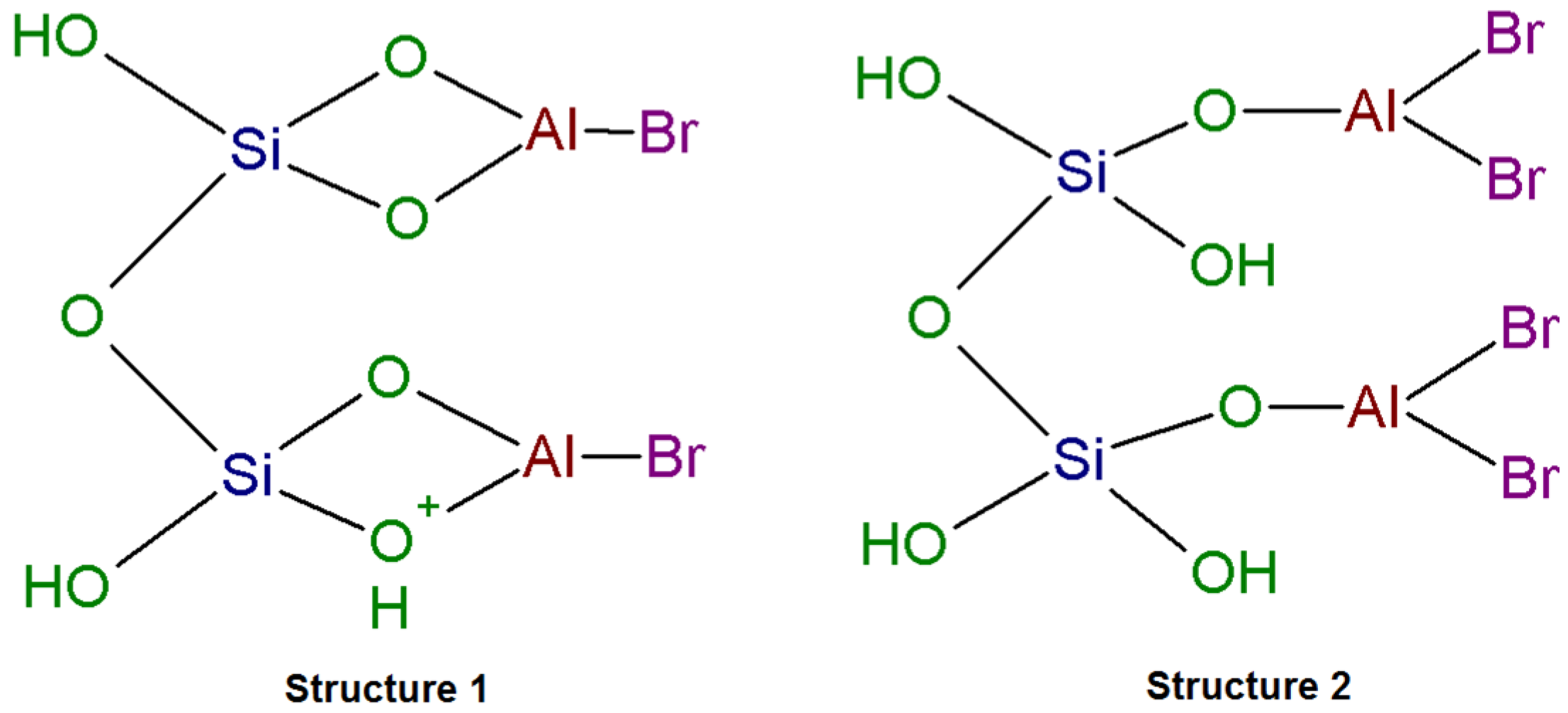
2.2. DRIFTS
2.3. Ammonia-TPD
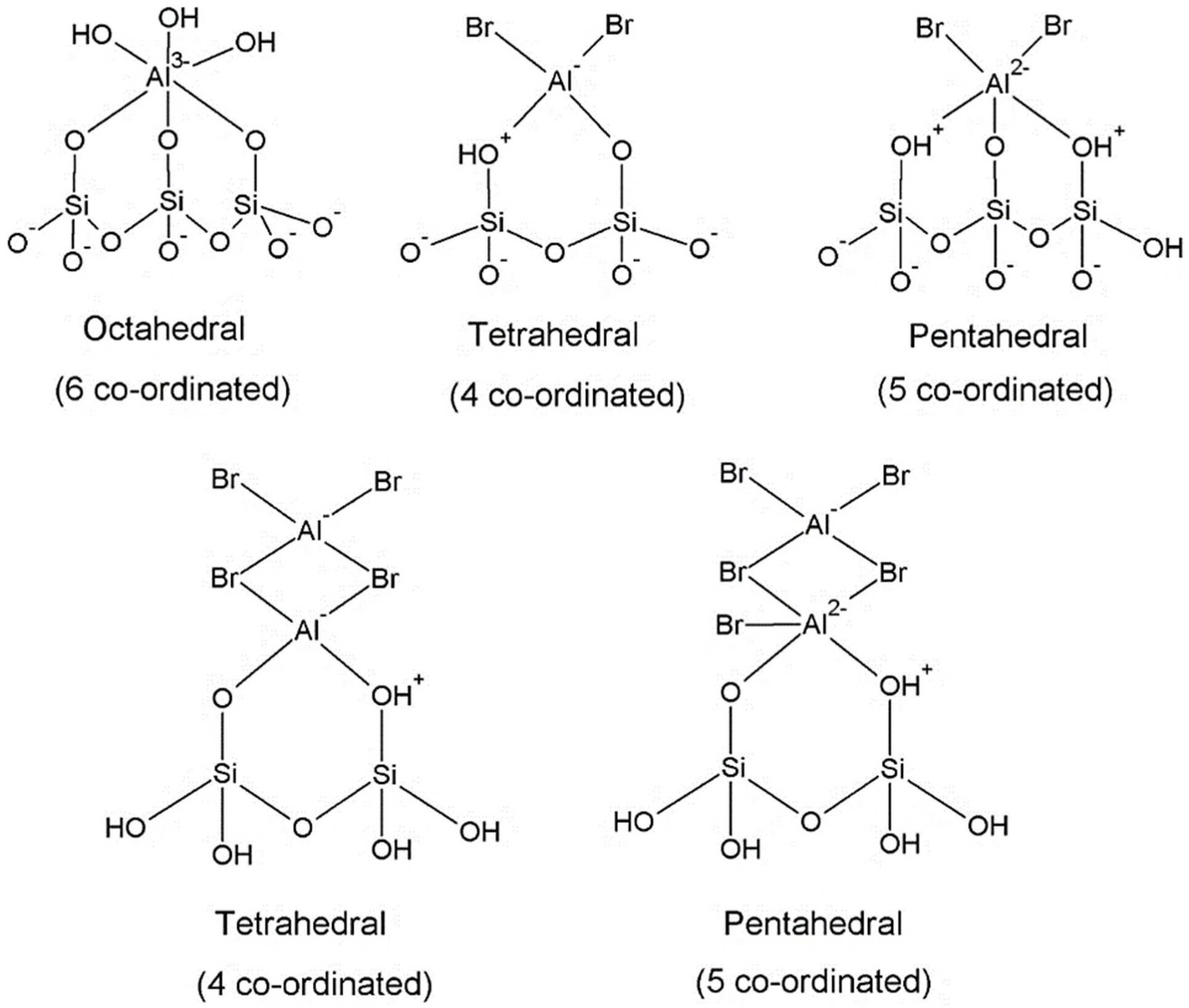
2.4. 27Al MAS NMR
2.5. Double Bond Isomerization of 1-Butene
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. BET and Pore Size Distribution
3.3. Catalyst Preparation
3.4. Elemental Analysis
3.5. DRIFTS
3.6. Ammonia-TPD
3.7. MAS NMR Measurements
3.8. Double Bond Isomerization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arata, K.; Matsuhashi, H. Solid Superacids; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abedin, M.A.; Kanitkar, S.; Bhattar, S.; Spivey, J.J. Methane dehydroaromatization using Mo supported on sulfated zirconia catalyst: Effect of promoters. Catal. Today 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Paul, S. Solid acids: Green alternatives for acid catalysis. Catal. Today 2014, 236, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.A.; Kanitkar, S.; Bhattar, S.; Spivey, J.J. Sulfated hafnia as a support for Mo oxide: A novel catalyst for methane dehydroaromatization. Catal. Today 2020, 343, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitkar, S.; Abedin, M.A.; Bhattar, S.; Spivey, J.J. Methane dehydroaromatization over molybdenum supported on sulfated zirconia catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 575, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.A.; Kanitkar, S.; Bhattar, S.; Spivey, J.J. Mo oxide supported on sulfated hafnia: Novel solid acid catalyst for direct activation of ethane & propane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 602, 117696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.C.; Wu, M.M. Isobutylene Oligomerization Using Supported Acid Catalysts. Google Patents No. 5,326,920, 5 July 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, S.C.; Wu, M.M. Supported Acid Catalysts, Their Preparation and Use in Organic Compound Conversion. Google Patents No. 5,294,578, 15 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Krahl, T.; Kemnitz, E. The very strong solid Lewis acids aluminium chlorofluoride (ACF) and bromofluoride (ABF)—Synthesis, structure, and Lewis acidity. J. Fluor. Chem. 2006, 127, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarset, K.; Shen, Q.; Thomassen, H.; Richardson, A.D.; Hedberg, K. Molecular Structure of the Aluminum Halides, Al2Cl6, AlCl3, Al2Br6, AlBr3, and AlI3, Obtained by Gas-Phase Electron-Diffraction and ab Initio Molecular Orbital Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldman, J.D. Aliphatic Friedel—Crafts Reactions. I. The Alkylation of Butanes by Methyl and Ethyl Bromide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1791–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crafts, J.M.; Friedel, C. Organic chemistry. J. Chem. Soc. 1877, 32, 725–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; García, H. Lewis Acids: From Conventional Homogeneous to Green Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4307–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasebrook, A.L.; Phillips, N.E.; Lovell, W.G. The Action of Aluminum Halides on n-Pentane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1936, 58, 1944–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummitt, O.; Sensel, E.E.; Smith, W.R.; Burk, R.E.; Lankelma, H.P. The Action of Aluminum Bromide on Paraffin Hydrocarbons. I. n-Hexane and n-Heptane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1945, 67, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbage, J.J.; Garrett, A.B. Phase Rule Studies in Anhydrous Aluminum Bromide. J. Phys. Chem. 1952, 56, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.G. The association equilibrium in the methyl bromide—Aluminum bromide system. estimated bonding strengths of aluminum bromide-addition molecules with methyl bromide, pentene and benzene. J. Phys. Chem. 1960, 64, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.C.; Wallace, W.J. Addition Compounds of Aluminum Halides with Alkyl Halides1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 6279–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, N.; Stark, W.J. Direct Coupling of Bromine-Mediated Methane Activation and Carbon-Deposit Gasification. ChemPhysChem 2007, 8, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Bao, L.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chang, J.; Bao, W.; Chang, L. Preparation of AlCl3/silica gel catalyst for simultaneously removing thiophene and olefins from coking benzene by inclosed grafting method. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 117, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, G.A.; Boegel, J.V.; Gates, B.C. n-butane isomerization catalyzed by supported aluminum chloride. J. Catal. 1982, 78, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maatougui, A.; Azuaje, J.; Sotelo, E.; Caamaño, O.; Coelho, A. Silica-Supported Aluminum Chloride-Assisted Solution Phase Synthesis of Pyridazinone-Based Antiplatelet Agents. ACS Comb. Sci. 2010, 13, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujeni, K.P.; Parvanak, K. Efficient and solvent-free synthesis of bis-indolylmethanes using silica gel supported aluminium chloride as a reusable catalyst. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2011, 22, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámera, R.; Rimada, R.; Romanelli, G.; Autino, J.C.; Vázquez, P. Silica-supported aluminum chloride as catalyst for the tetrahydropyranylation of thymol. Catal. Today 2008, 133–135, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhu, A. Silica-supported aluminum chloride: A recyclable and reusable catalyst for one-pot three-component Mannich-type reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 272, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, V.; Clark, J.H.; Macquarrie, D.J. Cationic polymerization of styrene using mesoporous silica supported aluminum chloride. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 198, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Kob, N.; Drago, R.S.; Nicholas, J.B.; Haw, J.F. A Solid Acid Catalyst at the Threshold of Superacid Strength: NMR, Calorimetry, and Density Functional Theory Studies of Silica-Supported Aluminum Chloride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 12231–12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupp, L.R.; Campanella, V.L.; Rudzinski, D.M.; Beland, F.; Priefer, R. Microwave-assisted silica-supported aluminum chloride-catalyzed Friedel-Crafts alkylation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 5343–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Khanna, A. Synthesis, characterization and kinetics of AlCl3 supported on silica superacid catalysts for the formation of linear alkylbenzenes. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2012, 106, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; He, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Han, D.; Lü, L. A study on structural suitability of immobilized aluminum chloride catalyst for isobutene polymerization. Catal. Today 2001, 69, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Arnold, A.; Buchholz, A.; Wang, W.; Hunger, M. Low-Temperature Modification of Mesoporous MCM-41 Material with Sublimated Aluminum Chloride in Vacuum. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 12140–12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.S.; Lu, M.G.Q.; Song, C. Immobilization of aluminum chloride on MCM-41 as a new catalyst system for liquid-phase isopropylation of naphthalene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 191, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borujeni, K.P.; Massah, A.R. Synthesis and application of polystyrene supported aluminium triflate as a new polymeric Lewis acid catalyst. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Chemo/regioselective Aza-Michael additions of amines to conjugate alkenes catalyzed by polystyrene-supported AlCl3. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamami, B.; Parvanak Borujeny, K. Chemoselective tetrahydropyranylation of alcohols and phenols using polystyrene supported aluminium chloride as a catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, D.; Royer, S.; Trong On, D.; Béland, F.; Kaliaguine, S. Aluminum chloride grafted mesoporous molecular sieves as alkylation catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 79, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, R.S.; Petrosius, S.C.; Chronister, C.W. Characterization and improvements in the synthesis of the novel solid superacid AlCl2(SG)n. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.A.; Kanitkar, S.; Bhattar, S.; Spivey, J.J. Promotional Effect of Cr in Sulfated Zirconia-Based Mo Catalyst for Methane Dehydroaromatization. Energy Technol. 2019, 1900555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Maciel, G.E. Structures of aluminum chloride grafted on silica surface. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1995, 101, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, R.S.; Petrosius, S.C.; Kaufman, P.B. Alkylation, isomerization and cracking activity of a novel solid acid, AlCl2(SG)n. J. Mol. Catal. 1994, 89, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krossing, I. Fluoride Ion Affinity. Available online: https://portal.uni-freiburg.de/molchem/research/lewis-acids/fia (accessed on 20 June 2016).
- Kanitkar, S.; Carter, J.H.; Hutchings, G.J.; Ding, K.; Spivey, J.J. Low Temperature Direct Conversion of Methane using a Solid Superacid. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 5019–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, F.R.J.; Donald, S.; Leverne, C.N. Promoter For Isomerization Reaction. Google Patents No. 2956097, 10 November 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Byron, J.G.; Mcdonald, S.M.F. Aluminum Halide Recycle Isomerization Process. Google Patents No. 3,077,504, 12 February 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Opitz, H.E.; Peake, J.S.; Nebergall, W.H. The Preparation of Monobromosilane and Organic Silyl Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1956, 78, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, R.S.; Getty, E.E. Hydrocarbon Conversion and Polymerization Catalyst and Method of Making and Using Same. Google Patents No. 4,719,190, 12 January 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, E.P. An infrared study of pyridine adsorbed on acidic solids. Characterization of surface acidity. J. Catal. 1963, 2, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaloǧlu Yazıcı, D.; Bilgiç, C. Determining the surface acidic properties of solid catalysts by amine titration using Hammett indicators and FTIR-pyridine adsorption methods. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.-R.; Wei, W.; Wu, D.; Sun, Y.-H. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activities of Mesoporous AlMSU-X with Wormhole-Like Framework Structure. Catal. Lett. 2003, 89, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapurkar, S.E.; Selvam, P. Mesoporous H-AlMCM-48: Highly efficient solid acid catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 254, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J. A Critical Evaluation of the Concepts of Bröunsted Acidity Related to Zeolites. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Grobet, P.J., Mortier, W.J., Vansant, E.F., Schulz-Ekloff, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 37, pp. 333–354. [Google Scholar]
- Grünberg, B.; Emmler, T.; Gedat, E.; Shenderovich, I.; Findenegg, G.H.; Limbach, H.-H.; Buntkowsky, G. Hydrogen Bonding of Water Confined in Mesoporous Silica MCM-41 and SBA-15 Studied by 1H Solid-State NMR. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 5689–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Shir, I.; Kababya, S.; Schmidt, A. Molecular Details of Amorphous Silica Surfaces Determine Binding Specificity to Small Amino Acids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 7901–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
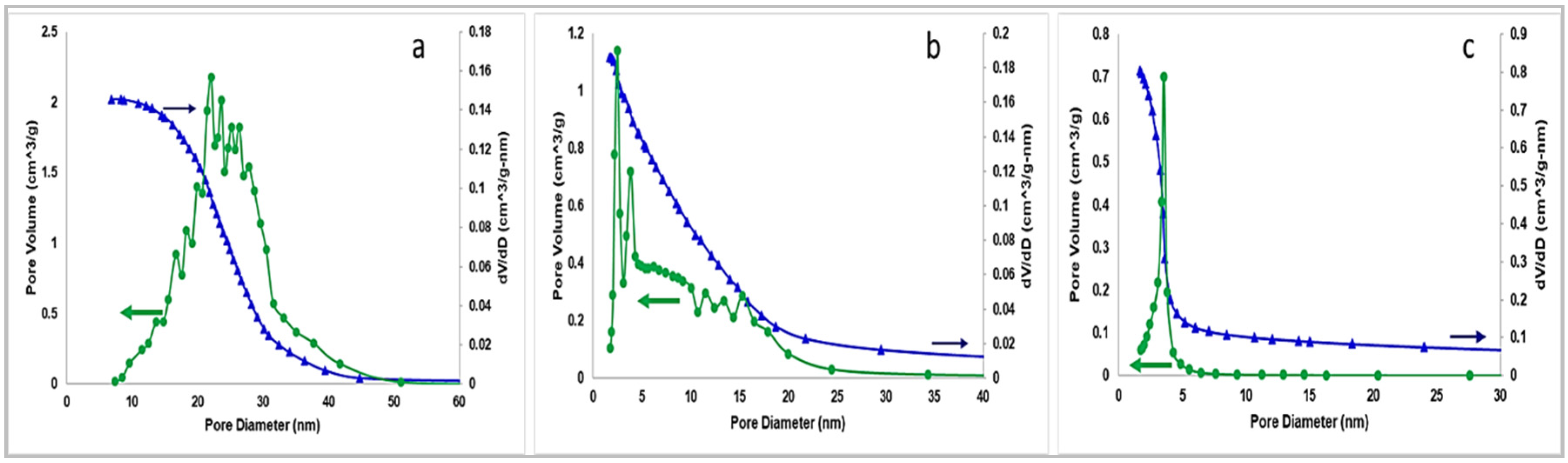






| Catalyst | SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 gel | 300 | 2.00 |
| CMS | 638 | 1.12 |
| SBA-15 | 735 | 0.72 |
| Catalyst | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Si/Al Ratio (from PIXE) | Br/Al Ratio (from XPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABSi | 260 | 18.5 | 0.99 |
| ABCS | 600 | 23.3 | 0.96 |
| ABSB | 717 | 27.1 | 1.01 |
| Catalyst | Peak 1 (°C) | Peak 2 (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| ABSi | 144 | 179 |
| ABCS | 154 | 197 |
| ABSB | 143 | 195 |
| Catalyst | ABSi | ABCS | ABSB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si/Al ratio | 18.5 | 23.3 | 27.1 |
| Ammonia adsorbed (μmol/g) | 606 | 381 | 622 |
| Ammonia adsorbed on corresponding plain support (μmol/g) | 129 (SiO2) | 10.6 (CMS) | 78.9 (SBA-15) |
| Ammonia adsorption coming from Al insertion (μmol/g) | 476 | 371 | 543 |
| Al content (based on 16.64 mmol SiO2/g) | 0.90 mmol | 0.71 mmol | 0.62 mmol |
| NH3/Al | 0.54–0.67 | 0.52–0.53 | 0.87–1.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abedin, M.A.; Kanitkar, S.; Kumar, N.; Wang, Z.; Ding, K.; Hutchings, G.; Spivey, J.J. Probing the Surface Acidity of Supported Aluminum Bromide Catalysts. Catalysts 2020, 10, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080869
Abedin MA, Kanitkar S, Kumar N, Wang Z, Ding K, Hutchings G, Spivey JJ. Probing the Surface Acidity of Supported Aluminum Bromide Catalysts. Catalysts. 2020; 10(8):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080869
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbedin, Md Ashraful, Swarom Kanitkar, Nitin Kumar, Zi Wang, Kunlun Ding, Graham Hutchings, and James J. Spivey. 2020. "Probing the Surface Acidity of Supported Aluminum Bromide Catalysts" Catalysts 10, no. 8: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080869
APA StyleAbedin, M. A., Kanitkar, S., Kumar, N., Wang, Z., Ding, K., Hutchings, G., & Spivey, J. J. (2020). Probing the Surface Acidity of Supported Aluminum Bromide Catalysts. Catalysts, 10(8), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080869





