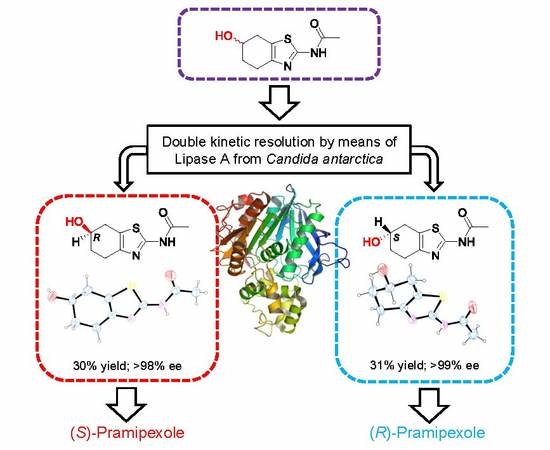
(S)-Pramipexole and Its Enantiomer, Dexpramipexole: A New Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Crystallographic Investigation of Key Enantiomeric Intermediates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discussion and Results
2.1. Lipase-Catalyzed Preparation of Alcohols (R)-4 and (S)-4
2.2. X-ray Crystallography
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Chemistry
3.3.1. rac-2-Acetamido-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazol-6-yl Acetate (rac-9)
3.3.2. General Procedure for Enzyme-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
3.3.3. General Procedure for Enzyme-Catalyzed Transesterification
3.3.4. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Enantioenriched (S)-N-(6-Hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide [(S)-4]
3.3.5. Hydrolysis of Enantioenriched (R)-2-Acetamido-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazol-6-yl Acetate [(R)-9] to Enantioenriched (R)-4
3.3.6. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Enantiopure (S)-N-(6-Hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide [(S)-4]
3.3.7. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Enantiopure (R)-2-Acetamido-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazol-6-yl Acetate [(R)-9]
3.3.8. Hydrolysis of Enantiopure (R)-2-Acetamido-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazol-6-yl Acetate [(R)-9] to Enantiopure (R)-4
3.4. X-ray Crystallography
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonini, A.; Barone, P.; Ceravolo, R.; Fabbrini, G.; Tinazzi, M.; Abbruzzese, G. Role of Pramipexole in the Management of Parkinson’s Disease. Cns. Drugs 2010, 24, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hametner, E.M.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W. Role and clinical utility of pramipexole extended release in the treatment of early Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2012, 7, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloret, S.P.; Rascol, O. Pramipexole extended-release (once-daily formulation) for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozik, M.E.; Mather, J.L.; Kramer, W.G.; Gribkoff, V.K.; Ingersoll, E.W. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of KNS-760704 (dexpramipexole) in healthy adult subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribkoff, V.K.; Bozik, M.E. KNS-760704 [(6R)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-N6-propyl-2, 6-benzothiazole-diamine dihydrochloride monohydrate] for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cns. Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Larriviere, K.S.; Keller, K.E.; Ware, K.A.; Burns, T.M.; Conaway, M.A.; Lacomis, D.; Pattee, G.L.; Phillips, L.H.; Solenski, N.J.; et al. R(+) pramipexole as a mitochondrially focused neuroprotectant: Initial early phase studies in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2008, 9, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudkowicz, M.; Bozik, M.E.; Ingersoll, E.W.; Miller, R.; Mitsumoto, H.; Shefner, J.; Moore, D.H.; Schoenfeld, D.; Mather, J.L.; Archibald, D.; et al. The effects of dexpramipexole (KNS-760704) in individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1652-U1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudkowicz, M.E.; van den Berg, L.H.; Shefner, J.M.; Mitsumoto, H.; Mora, J.S.; Ludolph, A.; Hardiman, O.; Bozik, M.E.; Ingersoll, E.W.; Archibald, D.; et al. Dexpramipexole versus placebo for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (EMPOWER): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworetzky, S.I.; Hebrank, G.T.; Archibald, D.G.; Reynolds, I.J.; Farwell, W.; Bozik, M.E. The targeted eosinophil-lowering effects of dexpramipexole in clinical studies. Blood Cell Mol. Dis. 2017, 63, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panch, S.R.; Bozik, M.E.; Brown, T. Dexpramipexole as an oral steroid-sparing agent in hypereosinophilic syndromes (vol 132, pg 501, 2018). Blood 2018, 132, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospisilik, K. Process for Resolution of 2-amino-6-propylamino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzothiazole. WO2002022591A1, 21 March 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.S.; Mierau, J. Dopamine Autoreceptor Agonists—Resolution and Pharmacological Activity of 2,6-Diaminotetrahydrobenzothiazole and an Aminothiazole Analog of Apomorphine. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, A.; Schulte, M. Process for the Purification of Pramipexole Using Chiral Chromatography. WO2006003471A2, 14 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pathare, D.B.; Jadhav, A.S.; Shingare, M.S. Validated chiral liquid chromatographic method for the enantiomeric separation of pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2006, 41, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Ciceri, S.; Ciuffreda, P.; De Mieri, M.; Romano, D.; Grisenti, P. Baker’s yeast catalyzed preparation of a new enantiomerically pure synthon of (S)-pramipexole and its enantiomer (dexpramipexole). Tetrahedron-Asymmetr. 2014, 25, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, S.; Fassi, P.; Scarpellini, M.; Allegrini, P.; Razzetti, G. Lipase Catalyzed Kinetic Resolution of ethyl 2-(acetylamino)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-6-benzothiazolecarboxyate. EP1808492A1, 18 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Valivety, R.H.; Michels, P.C.; Pantaleone, D.P.; Khmelnitsky, Y.L. Biocatalytic Process for Preparing Enantiomerically Enriched Pramipexole. WO2006012277A2, February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Chiara Sala, M.; Stradi, R.; Ragonesi, L.; Gagliardi, C.; Lanzarotti, P.; Ragg, E.M.; Mori, M.; Meneghetti, F. Full spectroscopic characterization of two crystal pseudopolymorphic forms of the antiandrogen cortexolone 17alpha-propionate for topic application. Steroids 2017, 128, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghetti, F.; Ferraboschi, P.; Grisenti, P.; Reza Elahi, S.; Mori, M.; Ciceri, S. Crystallographic and NMR Investigation of Ergometrine and Methylergometrine, Two Alkaloids from Claviceps purpurea. Molecules 2020, 25, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, G.; Bologna, A.; Allegrini, P.; Razzetti, G.; Lucchini, V. Method for Preparing Intermediates of Pramipexole. WO2005092871A2, 6 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gotor-Fernandez, V.; Brieva, R.; Gotor, V. Lipases: Useful biocatalysts for the preparation of pharmaceuticals. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2006, 40, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.N. Biocatalysis for synthesis of pharmaceuticals. Bioorgan Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1252–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Brady, D. The limits to biocatalysis: Pushing the envelope. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6088–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degueilcastaing, M.; Dejeso, B.; Drouillard, S.; Maillard, B. Enzymatic-Reactions in Organic-Synthesis.2. Ester Interchange of Vinyl Esters. Tetrahedron. Lett. 1987, 28, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lalonde, J.J.; Momongan, M.; Bergbreiter, D.E.; Wong, C.H. Lipase-Catalyzed Irreversible Transesterifications Using Enol Esters as Acylating Reagents - Preparative Enantioselective and Regioselective Syntheses of Alcohols, Glycerol Derivatives, Sugars, and Organometallics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, D.; Peper, S.; Niemeyer, B. Enzyme catalysis in organic solvents: Influence of water content, solvent composition and temperature on Candida rugosa lipase catalyzed transesterification. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 162, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakels, J.L.; Straathof, A.J.; Heijnen, J.J. A simple method to determine the enantiomeric ratio in enantioselective biocatalysis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1993, 15, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.M.; Davies, S.G.; de Sousa, J.A.A. Kinetic resolution strategies. II. Enhanced enantiomeric excesses and yields for the faster reacting enantiomer in lipase mediated kinetic resolutions. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1993, 4, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Girdaukas, G.; Sih, C.J. Quantitative-Analyses of Biochemical Kinetic Resolutions of Enantiomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 7294–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, K.; Kroutil, W. A Computer Program for the Determination of the Enantioselectivity (E-Value) in the Kinetic Resolution of Enantiomers. Available online: http://biocatalysis.uni-graz.at/enantio/DataFiles/Selectivity-Help.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Sih, C.J.; Wu, S.H. Resolution of Enantiomers Via Biocatalysis. Top. Stereochem. 1989, 19, 63–125. [Google Scholar]
- Farrugia, L. ORTEP-3 for Windows—A version of ORTEP-III with a Graphical User Interface (GUI). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, D.; Pople, J.A. General definition of ring puckering coordinates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker: SAINT Software Reference Manual; Version 6; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of silver and molybdenum microfocus X-ray sources for single-crystal structure determination. J. Appl. crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burla, M.C.; Caliandro, R.; Carrozzini, B.; Cascarano, G.L.; Cuocci, C.; Giacovazzo, C.; Mallamo, M.; Mazzone, A.; Polidori, G. Crystal structure determination and refinement via SIR2014. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Entry | Enzyme | Time (h) | Conversion a (%) | ee (%) a | Config. c of Formed 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetate 9 | Alcohol 4 | |||||
| a | PPL | 168 | 0 | - | - | - |
| b | PFL | 312 | 22 | - | 16 | R |
| c | CAL-A | 30 | 46 | - | 39 | R |
| d | CAL-B | 120 | 54 | 31 b | - | R |
| e | CCL | 120 | 64 | 38 b | - | S |
| f | Alcalase CLEA | 96 | 30 | - | 37 | R |
| Entry | Enzyme | Time (h) | Conversion a (%) | ee a | Config. of Unreacted 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetate 9 | Alcohol 4 | |||||
| a | Alcalase CLEA | 168 | 0 | - | - | - |
| b | Rhizopus oryzae lipase | 168 | 0 | - | - | - |
| c | PPL | 168 | <5 | - | - | S |
| d | Aspergillus niger lipase | 168 | 14 | 20 b | S | |
| e | CAL-B | 7 | 60 | 28 | S | |
| f | CCL | 168 | 20 | 41 b | R | |
| g | PFL | 73 | 20 | 68 b | S | |
| h | CAL-A | 168 | 23 | 68 b | S | |
| Entry | Enzyme | Solvent | Time (h) | Conversion a (%) | ee a (%) | E c | Config. of Unreacted 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetate 9 | Alcohol 4 | |||||||
| a | PFL | Toluene | 72 | 35 | 15 b | 9 | 1 | S |
| b | CAL-A | Toluene | 16 | 62 | 6 b | 10 | 1 | S |
| c | CCL | Toluene | 4 | 45 | 26 b | 20 | 2 | R |
| d | PFL | MIBK | 168 | 33 | 72 b | 26 | 8 | S |
| e | CAL-A | MIBK | 23 | 64 | 61 b | 91 | 12 | S |
| f | CCL | MIBK | 120 | 51 | 53 b | 45 | 5 | R |
| g | PFL | Acetone | 168 | - | - | - | - | - |
| h | CAL-A | Acetone | 168 | 34 | 89 b | 50 | 28 | S |
| i | CCL | Acetone | 168 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Entry | Solvent | Time (h) | Conversion a (%) | ee a (%) | E c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetate 9 | Alcohol 4 | |||||
| a | Acetone + 0.1% H2O | 336 | 32 | 90 b | 37 | 27 |
| b | Acetone/n-hexane 1:1 | 32 | 69 | 47 b | >99 | 14 |
| c | Acetone/n-hexane 2:1 | 95 | 50 | 79 b | 75 | 19 |
| d | Acetone/n-hexane 4:1 | 168 | 45 | 83 b | 68 | 22 |
| (R)-4 | (S)-4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-Bond | H∙∙∙A (Å) | D∙∙∙A (Å) | D-H∙∙∙A (°) | H-Bond | H∙∙∙A (Å) | D∙∙∙A (Å) | D-H∙∙∙A (°) |
| N2-H2∙∙∙Ow1 | 1.98(1) | 2.815(1) | 162.7(1) | O1-H1∙∙∙O2A | 1.94(1) [2.00(1)] | 2.767(1) [2.814(1)] | 162.8(1) [169.6(1)] |
| Ow1-H1A∙∙∙O1 | 2.02(1) | 2.760(1) | 158.4(1) | N2-H2∙∙∙O1A | 2.05(1) [2.07(1)] | 2.853(1) [2.828(1)] | 174.8(1) [165.1(1)] |
| Ow1-H1B∙∙∙O2 | 2.13(1) | 2.826(1) | 171.8(1) | - | - | - | - |
| O1-H1∙∙∙N1 | 2.15(1) | 2.815(1) | 164.0(1) | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciceri, S.; Ferraboschi, P.; Grisenti, P.; Reza Elahi, S.; Castellano, C.; Mori, M.; Meneghetti, F. (S)-Pramipexole and Its Enantiomer, Dexpramipexole: A New Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Crystallographic Investigation of Key Enantiomeric Intermediates. Catalysts 2020, 10, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080941
Ciceri S, Ferraboschi P, Grisenti P, Reza Elahi S, Castellano C, Mori M, Meneghetti F. (S)-Pramipexole and Its Enantiomer, Dexpramipexole: A New Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Crystallographic Investigation of Key Enantiomeric Intermediates. Catalysts. 2020; 10(8):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080941
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiceri, Samuele, Patrizia Ferraboschi, Paride Grisenti, Shahrzad Reza Elahi, Carlo Castellano, Matteo Mori, and Fiorella Meneghetti. 2020. "(S)-Pramipexole and Its Enantiomer, Dexpramipexole: A New Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Crystallographic Investigation of Key Enantiomeric Intermediates" Catalysts 10, no. 8: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080941
APA StyleCiceri, S., Ferraboschi, P., Grisenti, P., Reza Elahi, S., Castellano, C., Mori, M., & Meneghetti, F. (2020). (S)-Pramipexole and Its Enantiomer, Dexpramipexole: A New Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Crystallographic Investigation of Key Enantiomeric Intermediates. Catalysts, 10(8), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080941