NiO-TiO2 p-n Heterojunction for Solar Hydrogen Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
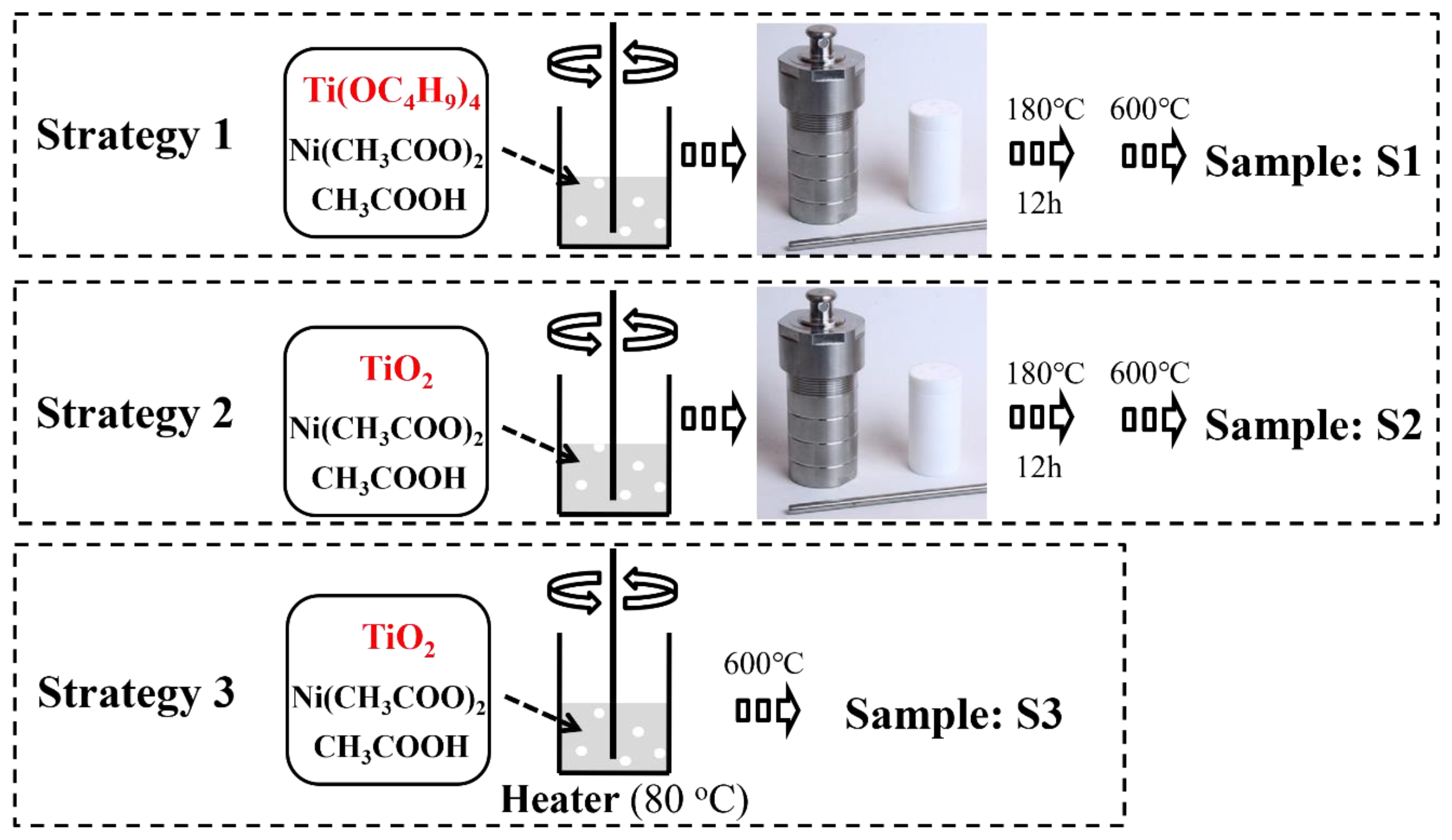
3.2. Synthesis of NiO-TiO2 Photocatalysts
3.2.1. Strategy 1
3.2.2. Strategy 2
3.2.3. Strategy 3
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Photocatalytic H2 Evolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: Mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubacka, A.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.; Colon, G. Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1555–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, A.; Miseki, Y. Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Domen, K. Photocatalytic water splitting: Recent progress and future challenges. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, C.T.; Yen, H.; Kleitz, F.; Do, T.O. Three-dimensional ordered assembly of thin-shell Au/TiO2 hollow nanospheres for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6618–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Li, S.; Liu, B.K.; Wang, D.; Xie, T.F. Highly efficient CdS/WO3 photocatalysts: Z-scheme photocatalytic mechanism for their enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3724–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Qian, F.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, Y. Double-sided CdS and CdSe quantum dot co-sensitized ZnO nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.M.; Wang, W.Z.; Li, D.Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, D. Solar light driven pure water splitting on quantum sized BiVO4 without any cocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3498–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Asakura, K.; Kudo, A. Highly efficient water splitting into H2 and O2 over lanthanum-doped NaTaO3 photocatalysts with high crystallinity and surface nanostructure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3082–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, A.; Viswanath, R.P. Photocatalytic generation of hydrogen over mesoporous CdS nanoparticle: Effect of particle size, noble metal and support. Catal. Today 2007, 129, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.A.; Townsend, T.K.; Osterloh, F.E. Quantum confinement controlled photocatalytic water splitting by suspended CdSe nanocrystals. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ma, Z.; Ren, Z.; Fan, H.; Yang, X. Elementary photocatalytic chemistry on TiO2 surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3701–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, M.Z.; Cao, C.Y.; Huang, J.Y.; Li, S.H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, K.Q.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Lai, Y.K. A review of one-dimensional TiO2 nanostructured materials for environmental and energy applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 6772–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, H.I.; Moon, G.H.; Choi, W. Photoinduced charge transfer processes in solar photocatalysis based on modified TiO2. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moniz, S.J.A.; Shevlin, S.A.; Martin, D.J.; Guo, Z.X.; Tang, J.W. Visible-light driven heterojunction photocatalysts for water splitting—A critical review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 731–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, X.; Li, C.-F.; Yu, W.; Wang, A.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Larter, S.; Li, Y.; Golam Kibria, M.; Hu, J. Carbon quantum dots modified TiO2 composites for hydrogen production and selective glucose photoreforming. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 64, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Wang, A.; Zheng, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Larter, S.; Li, Y.; Su, B.-L.; et al. Plasmon enhanced glucose photoreforming for arabinose and gas fuel co-production over 3DOM TiO2-Au. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 291, 120055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, C.F.; Hu, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Chen, L.H.; Su, B.L. Size effect of bifunctional gold in hierarchical titanium oxide-gold-cadmium sulfide with slow photon effect for unprecedented visible-light hydrogen production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 604, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.H.; Guo, W.B.; Qiu, J.C.; Mou, X.N.; Li, A.X.; Claverie, J.P.; Liu, H. NiO-TiO2 p-n heterostructured nanocables bridged by zero-bandgap rGO for highly efficient photocatalytic water splitting. Nano Energy 2015, 16, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawool, S.A.; Pai, M.R.; Banerjee, A.M.; Arya, A.; Ningthoujam, R.S.; Tewari, R.; Rao, R.; Chalke, B.; Ayyub, P.; Tripathi, A.K.; et al. pn heterojunctions in NiO:TiO2 composites with type-II band alignment assisting sunlight driven photocatalytic H2 generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 221, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Gao, P.; Kong, X.; Jiang, R.; Yang, P.; Chen, Y.; Chi, Q.; Li, B. NiO/Ni/TiO2 nanocables with Schottky/p-n heterojunctions and the improved photocatalytic performance in water splitting under visible light. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Du, C.; Yan, B.; Wang, C.X.; Yang, G.W. Two-dimensional amorphous NiO as a plasmonic photocatalyst for solar H2 evolution. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.T.; Nicolas, Y.; Olivier, C.; Jaegermann, W.; Rockstroh, N.; Junge, H.; Toupance, T. Band alignment investigations of heterostructure NiO/TiO2 nanomaterials used as efficient heterojunction earth-abundant metal oxide photocatalysts for hydrogen production. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 19279–19288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamegawa, T.; Kim, T.H.; Morishima, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Anpo, M. Preferential oxidation of CO impurities in the presence of H2 on NiO-loaded and unloaded TiO2 photocatalysts at 293 K. Catal. Lett. 2009, 129, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhang, S.J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, W. Preparation and activity evaluation of p-n junction photocatalyst NiO/TiO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Chockalingam, K.; Ganapathy, A.; Paramasivan, G.; Govindasamy, M.; Viswanathan, A. NiO/TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic disinfection of bacteria under visible light. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros-Ruiz, S.; Zanella, R.; Collins, S.E.; Hernandez-Gordillo, A.; Gomez, R. Photocatalytic hydrogen production by Au-MxOy (M=Ag, Cu, Ni) catalysts supported on TiO2. Catal. Commun. 2014, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, C.F.; Liu, L.Y.; Palma, B.; Hu, Z.Y.; Renneckar, S.; Larter, S.; Li, Y.; Kibria, M.G.; Hu, J.; et al. n-p Heterojunction of TiO2-NiO core-shell structure for efficient hydrogen generation and lignin photoreforming. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-W.; Yuan, J.-P.; Gao, X.-M.; Liang, E.-Q.; Wang, C.-Y. Structure and optical absorption properties of NiTiO3 nanocrystallites. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, D.; Minguzzi, A.; Recchia, S.; Shahvardanfard, F.; Tomanec, O.; Zboril, R.; Schmuki, P.; Ghigna, P.; Altomare, M. An operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of a NiCu-TiO2 phtoocatalyst for H2 evolution. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8293–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | NiO Content (wt%) | Crystallite Size XRD (nm) | Crystallite Size SEM (nm) | SBET/m2g−1 | Pore Size (nm) | H2 Evolution rate/mmolh−1g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiO | - | 55 | 40–80 | 9.5 | N/A | 2.1 ± 0.2 |
| TiO2 | - | 25 | 20–30 | 31.9 | 5–50 | 6.6 ± 0.7 |
| S1-10% | 1.7 | 20 | 20–40 | 38.0 | 5–50 | 17.7 ± 0.9 |
| S1-20% | 3.3 | 30 | 20–40 | 39.5 | 5–50 | 23.5 ± 1.2 |
| S2-10% | 1.5 | 35 | 25–45 | 36.4 | 5–40 | 16.3 ± 0.8 |
| S2-20% | 3.1 | 35 | 25–45 | 35.6 | 5–40 | 20.4 ± 1.0 |
| S3-10% | 9.8 | 40 | 30–50 | 50.7 | 5–40 | 8.9 ± 0.7 |
| S3-20% | 19.4 | 45 | 30–50 | 52.7 | 5–40 | 8.8 ± 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, D.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, Z. NiO-TiO2 p-n Heterojunction for Solar Hydrogen Generation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121427
Zheng D, Zhao H, Wang S, Hu J, Chen Z. NiO-TiO2 p-n Heterojunction for Solar Hydrogen Generation. Catalysts. 2021; 11(12):1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121427
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Dewen, Heng Zhao, Shanyu Wang, Jinguang Hu, and Zhangxin Chen. 2021. "NiO-TiO2 p-n Heterojunction for Solar Hydrogen Generation" Catalysts 11, no. 12: 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121427
APA StyleZheng, D., Zhao, H., Wang, S., Hu, J., & Chen, Z. (2021). NiO-TiO2 p-n Heterojunction for Solar Hydrogen Generation. Catalysts, 11(12), 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121427









