Photo-Fenton Oxidation of Methyl Orange Dye Using South African Ilmenite Sands as a Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
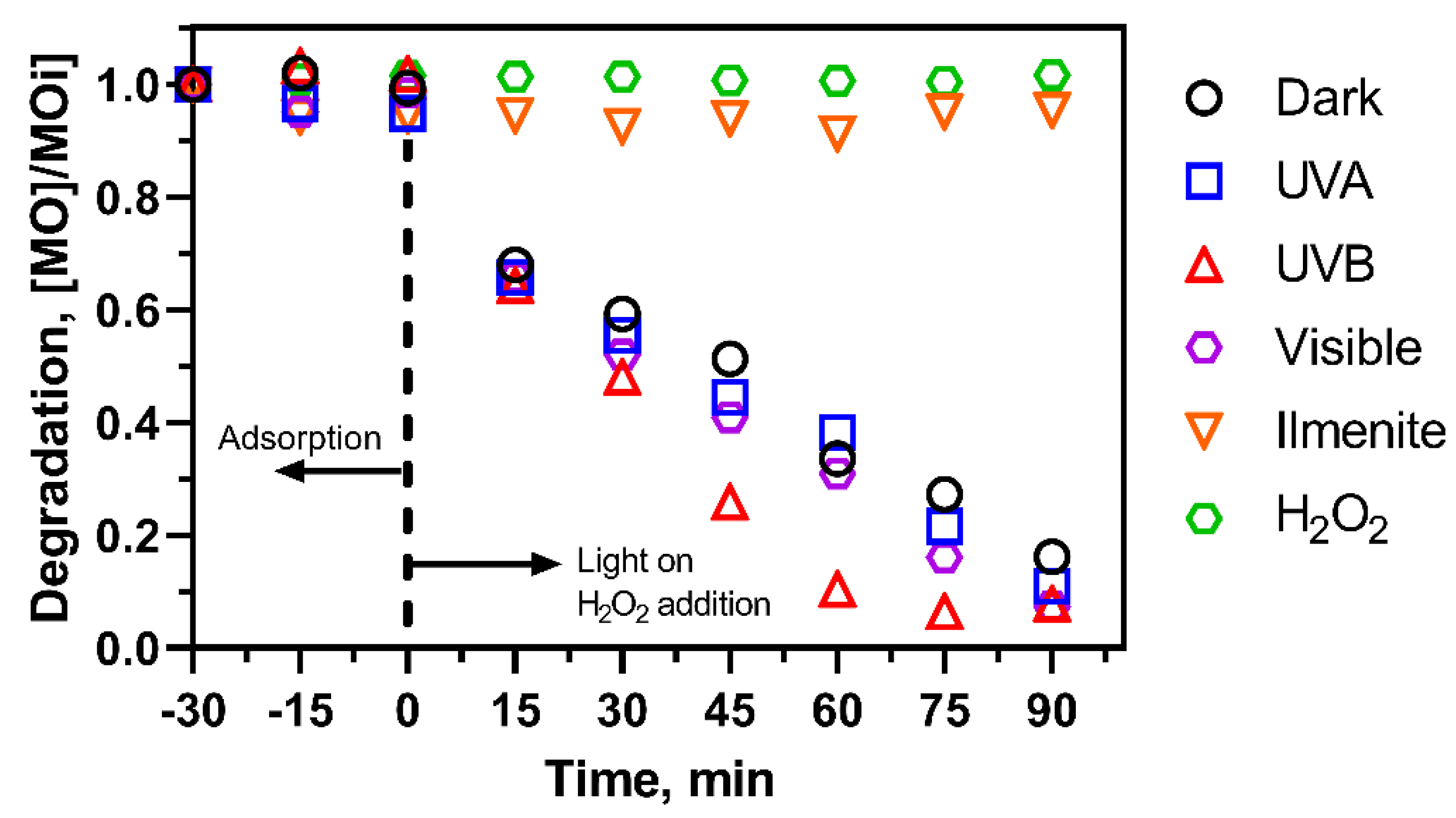
2.2. Control Experiments
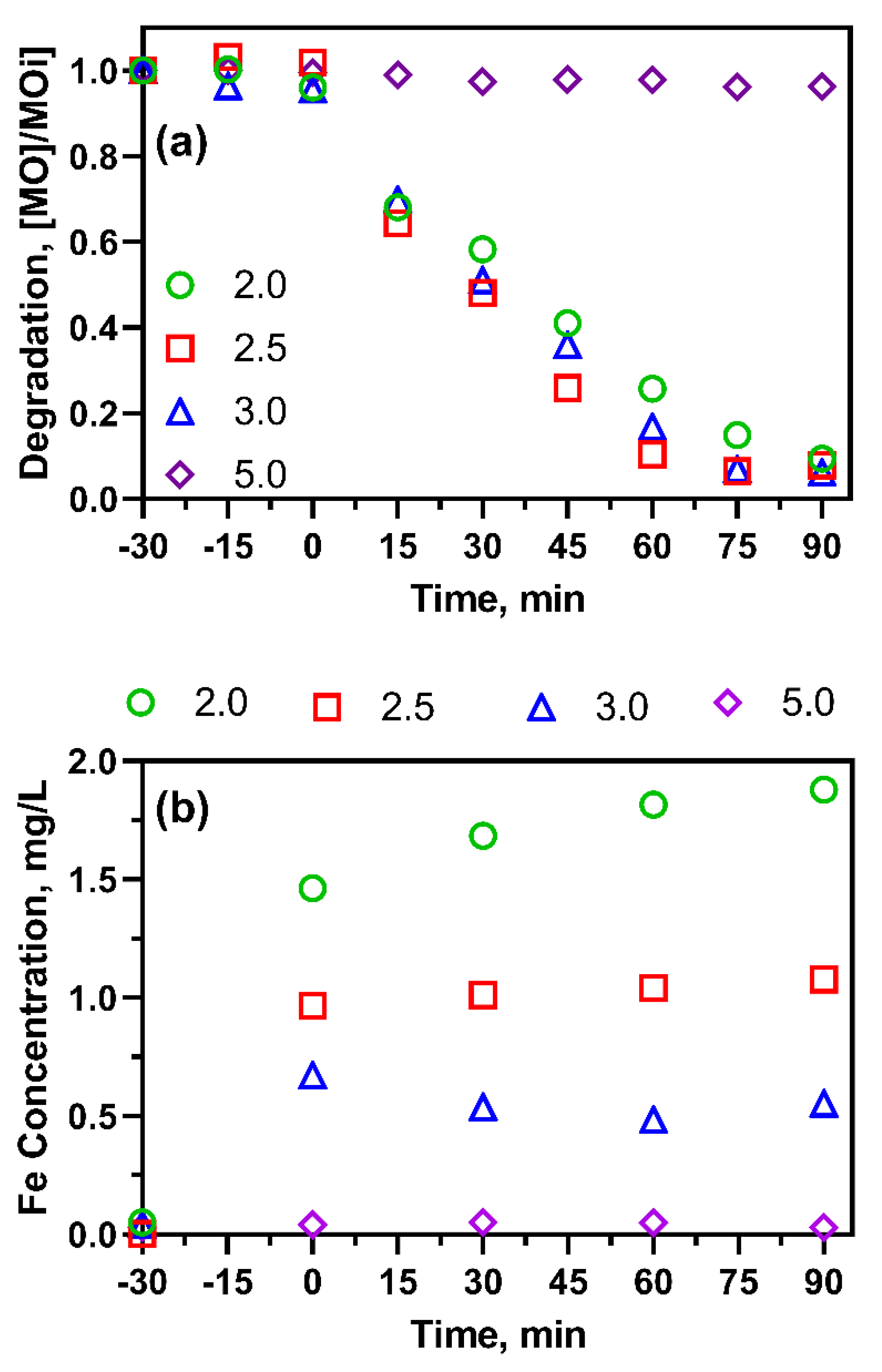
2.3. Effect of pH
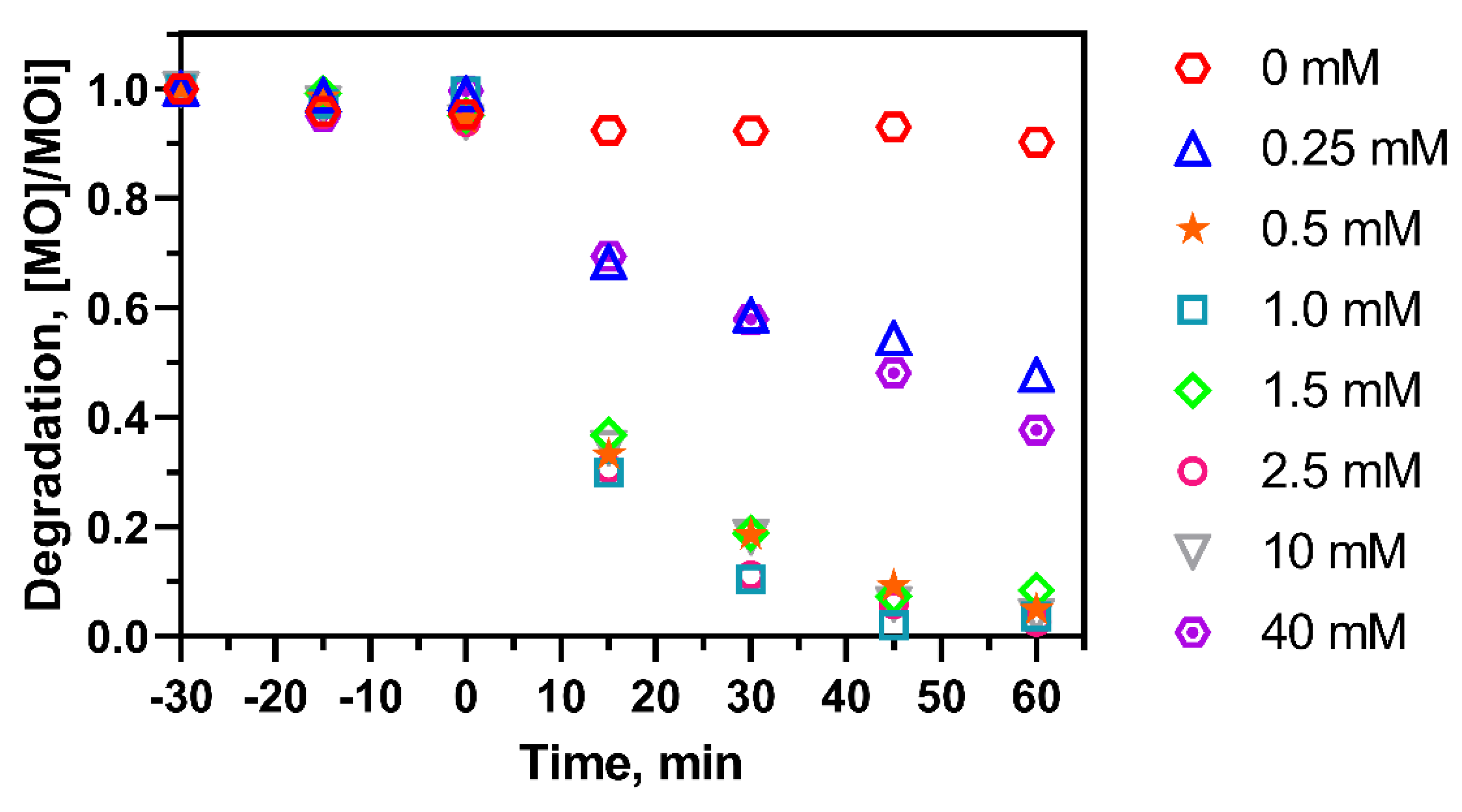
2.4. Effect of Catalyst Loading
2.5. Effect of H2O2 Concentration
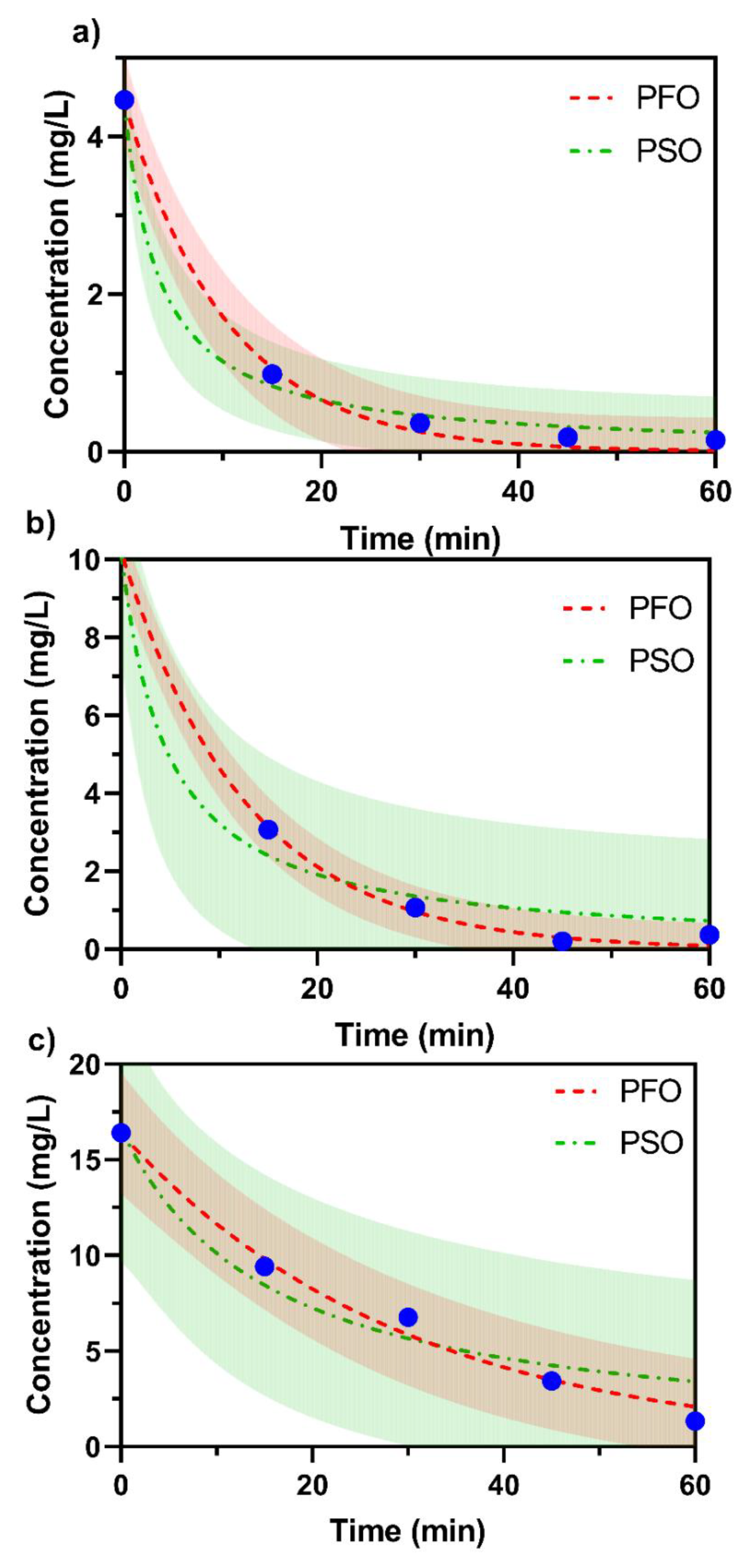
2.6. Effect of Initial MO Concentration
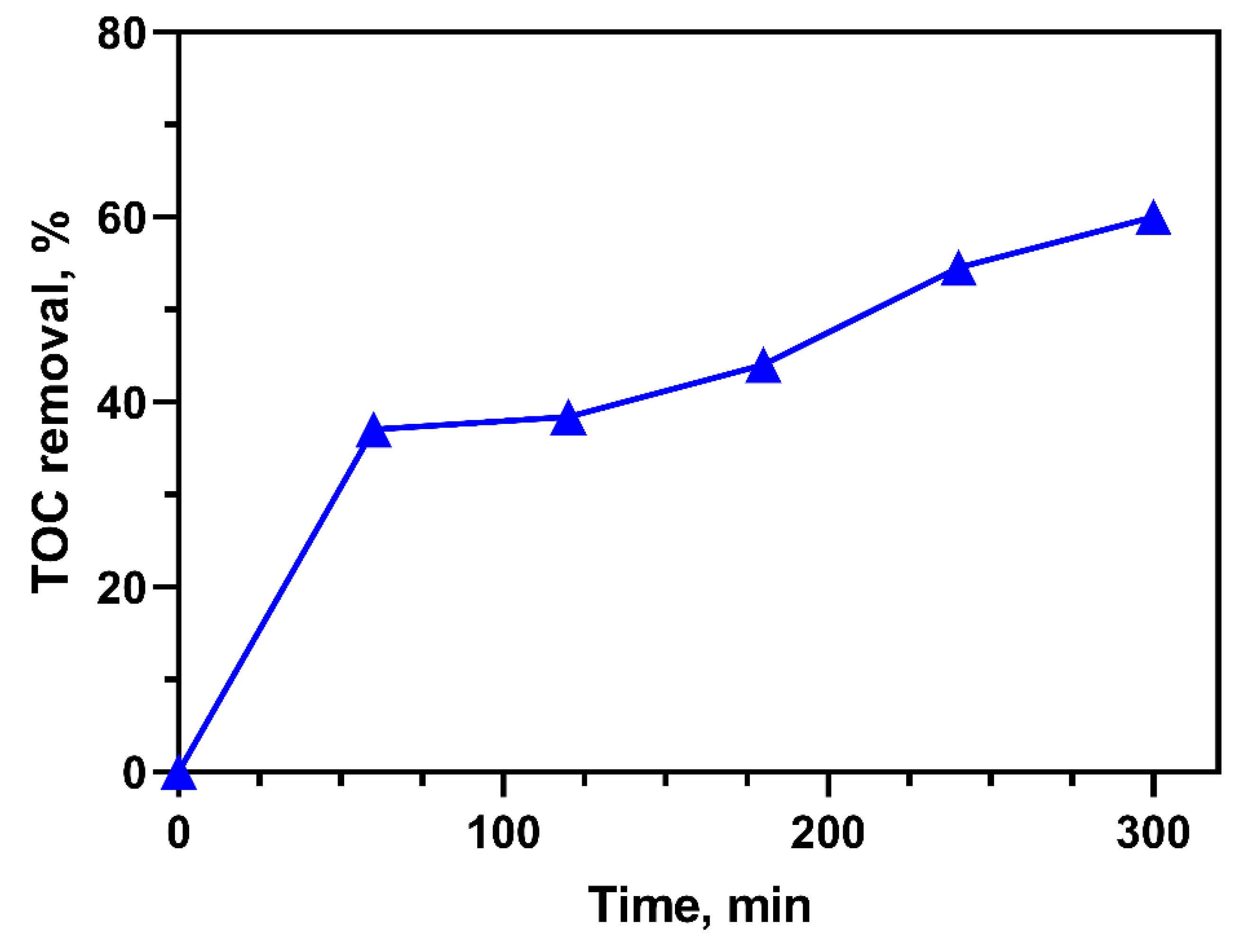
2.7. TOC Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Water Research Commission. Parched prospects: The Emerging Water Crisis in South Africa. Water Wheel 2014, 13, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Pérez, J.A.S. Combination of Advanced Oxidation Processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4141–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.H. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. In Organic Pollutants: An Ecotoxicological Perspective, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, F.I. Hybrid Treatment Systems for Dye Wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 315–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.R.; Zhu, G. Biological Waste Treatment. In Wastewater Treatment and Reuse: Theory and Design Examples; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jelic, A.; Katsou, E.; Malamis, S.; Bolzonella, D.; Fatone, F. Occurrence, Removal, and Fate of PAHs and VOCs in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Literature Review. In Wastewater Treatment: Occurrence and Fate of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs); Forsgren, A.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ankush Mandal, M.K.; Sharma, M.; Khushboo Pandey, S.; Dubey, K.K. Membrane Technologies for the Treatent of Pharmacceutical Industry Wastewater. In Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies; Bui, X.-T., Chiemchaisri, C., Fujioka, T., Varjani, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ameta, S.C.; Ameta, R. Introduction. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Emerging Green Chemical Technology, 1st ed.; Ameta, S.C., Ameta, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ameta, R.; Chohadia, A.K.; Jain, A.; Punjabi, P.B. Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, G.; He, H. Strategies for enhancing the heterogeneous Fenton catalytic reactivity: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 255, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, A.N.; JHameed, B.H. Heterogeneous catalytic treatment of synthetic dyes in aqueous media using Fenton and photo-assisted Fenton process. Desalination 2011, 269, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Vione, D. Effect of pH on zero valent iron performance in heterogeneous fenton anf fenton-like processes: A review. Molecules 2018, 23, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minella, M.; Bertinetti, S.; Hanna, K.; Minero, C.; Vione, D. Degradation of ibuprofen and phenol with a Fenton-like process triggered by zero-valent iron (ZVI-Fenton). Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, R.S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Adebajo, M.O.; Frost, R.L. A review of iron species for visible-light photocatalytic water purification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7439–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorontsov, A.V. Advancing Fenton and photo-Fenton water treatment through the catalyst design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 372, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Morito, R.; Hatayama, R.; Kawase, Y. Iron redox cycling in hydroxyl radical generation during the photo-Fenton oxidative degradation: Dynamic change of hydroxyl radical concentration. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 106, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Balchi, T. Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treament; Ameta, R., Ameta, S.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda Márquez, J.J.; Levchuk, I.; Sillanpää, M. Application of catalytic wet peroxide oxidation for industrial and urban wastewater treatment: A review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, C.H.; Han, X.; Du, M.; Kai, J.-J.; Tsang, K.F.; Jia, G.; Cheng, K.-C.; Shen, H.-H.; Hsu, H.-Y. Heterogenization of homogeneous photocatalysts utilizing synthetic and natural support materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 4454–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Ilmenite (FeTiO3) as low cost catalyst for advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Domínguez, P.; De Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Naturally occurring iron minerals as inexpensive catalysts for CWPO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.-C.; Chen, J.-N.; Huang, H.-H. Role of Goethite dissolution in the oxidation of 2-chlorophenol with hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Munoz, M.; De Pedro, Z.M.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Treatment of hospital wastewater through the CWPO-Photoassisted process catalyzed by ilmenite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4337–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Sulfonamides photoassisted oxidation treatments catalyzed by ilmenite. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataquiva-Mateus, A.Y.; Zea, H.R.; Ramirez, J.H. Degradation of Orange II by Fenton reaction using ilmenite as catalyst. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6187–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichapondwa, S.M.; Newman, J.P.; Kubheka, O. Effect of TiO2 phase on the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Phys. Chem. Earth 2020, 118–119, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canas-Martinez, D.M.; Gauthier, G.H.; Pedraza-Avella, J.A. Photo-oxidative and photo-reductive capabilities of ilmenite-rich black sand concentrates using methyl orange as a probe molecule. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, J.E.; Paz, W.S.; García-Muñoz, P.; Zazo, J.A.; Casas, J.A. UV-LED/ilmenite/persulfate for azo dye mineralization: The role ofsulfate in the catalyst deactivation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 219, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.G. Decolorizing Dye Wastewater with Fenton’s Reagent. Water Res. 1992, 26, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelker, B.M.; Morel, F.M.M.; Sulzerger, B. Iron Redox Cycling in Surface Waters: Effect of Humic Substances and Light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rijkenberg, M.J.A.; Gerringe, L.J.A.; Neale, P.J.; Timmermans, K.R.; Buma, A.G.J.; De Baar, H.J.W. UVA viability overrules UVB ozone depletion effects on the photoreduction of iron in the Southern Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rijkenberg, M.J.A.; Fischer, A.C.; Kroon, J.J.; Gerringe, L.J.A.; Timmermans, K.R.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; de Baar, H.J.W. The influence of UV irradiation on the photoreduction of iron in the Southern Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2005, 93, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueder, U.; Jorgensen, B.B.; Kappler, A.; Schmidt, C. Photochemistry of iron in aquatic environments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarian, M.R.; Choi, H.; Fazli, M.; Rasoulifard, M.H. Effect of UV-LED wavelength on direct photolytic and TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of emerging contaminants in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the abatement of organic pollutants from aqueous solution: A review. R. Soc. Chem. 2015, 5, 40552–40577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverskog, B.; Puigdomenech, I. Revised pourbaix diagrams for iron at 25–300 °C. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Melin, V.; Contreras, D.; Moreno, Y.; Mansilla, H. Fenton Reaction Driven by Iron Ligands. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2013, 58, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Antonio Zazo, J.; Casas, J.A. Photocatalytic wet peroxide oxidation process at circumneutral pH using ilmenite as catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.L.; Tichapondwa, S.M. Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Methyl Orange using Naturally-Occurring South African Ilmenite as a Catalyst. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2020, 81, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.; Chen, H.; Peng, T.; Ke, D.; Yi, H. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous suspension of mesoporous titania nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Ferroudj, N.; Combes, A.; Pichon, V.; Abramson, S. Tracking the degradation pathway of three model aqueous pollutants in a heterogeneous Fenton process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Pang, S.; Ouyang, F.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J. A new insight into Fenton and Fenton-like processes for water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Croue, J.-P. Production of Sulfate Radical from Peroxymonosulfate Induced by a Magnetically Separable CuFe2O4 Spinel in Water: Efficiency, Stability, and Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduna, K.; Kumar, N.; Aho, A.; Wärnå, J.; Zrnčević, S.; Murzin, D.Y. Kinetics of Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Phenolics in Olive Oil Mill Wastewaters over Copper Catalysts. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7247–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- García-Muñoz, P.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Barbero, B.; Bahamonde, A.; Casas, J.A. Modified ilmenite as catalyst for CWPO-Photoassisted process under LED light. Chem. Eng. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.A.; Shaban, S.A.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Mahmoud, A.S. Degradation of methyl orange using Fenton catalytic reaction. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganzenko, O.; Trellu, C.; Oturan, N.; Huguenot, D.; Péchaud, Y.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Oturan, M.A. Electro-Fenton treatment of a complex pharmaceutical mixture: Mineralization efficiency and biodegradability enhancement. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.A. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: Kinetic and mechanistic investigations: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Oxidation and coagulation removal of COD from landfil leachate by Fered-Fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
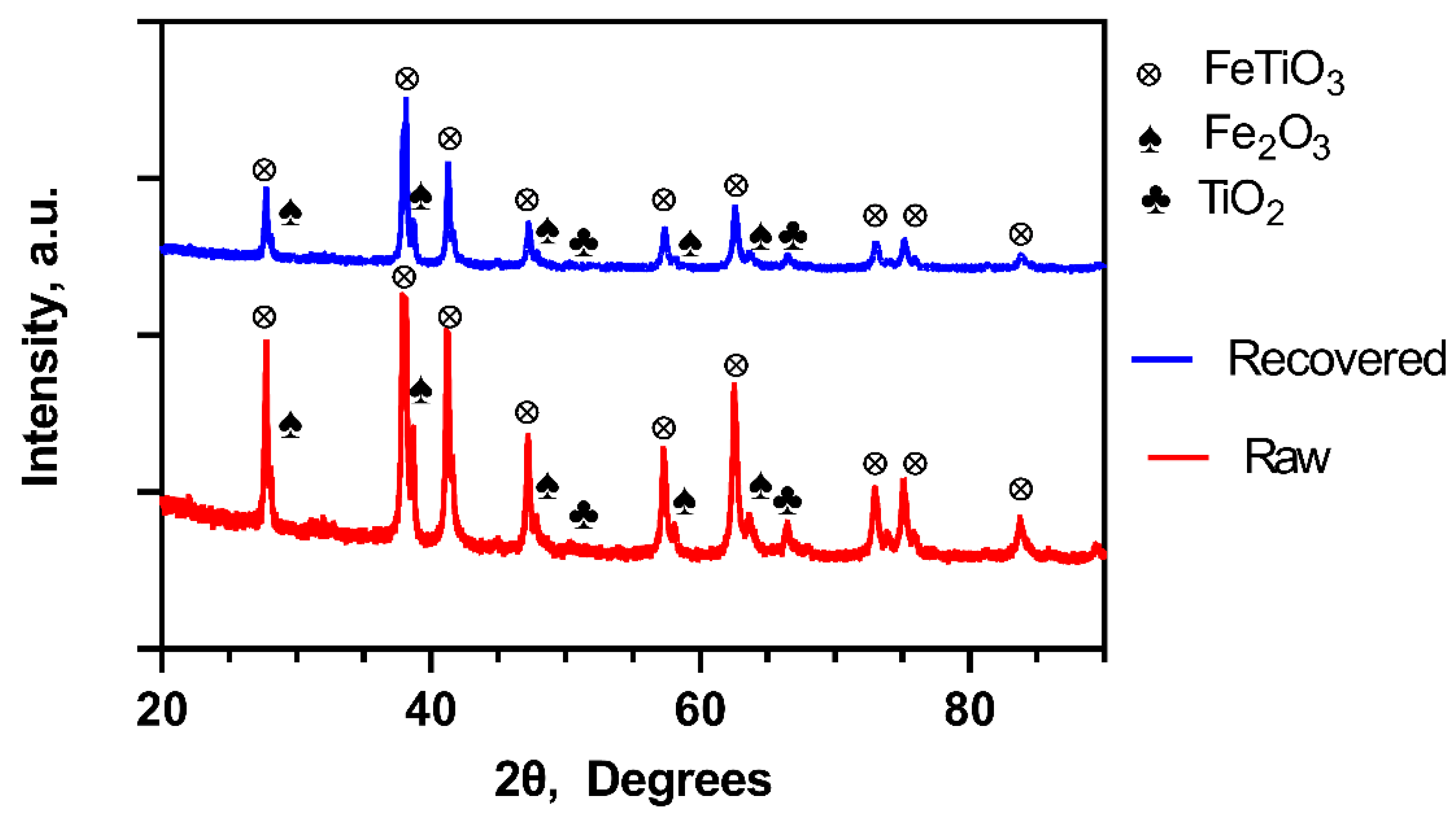
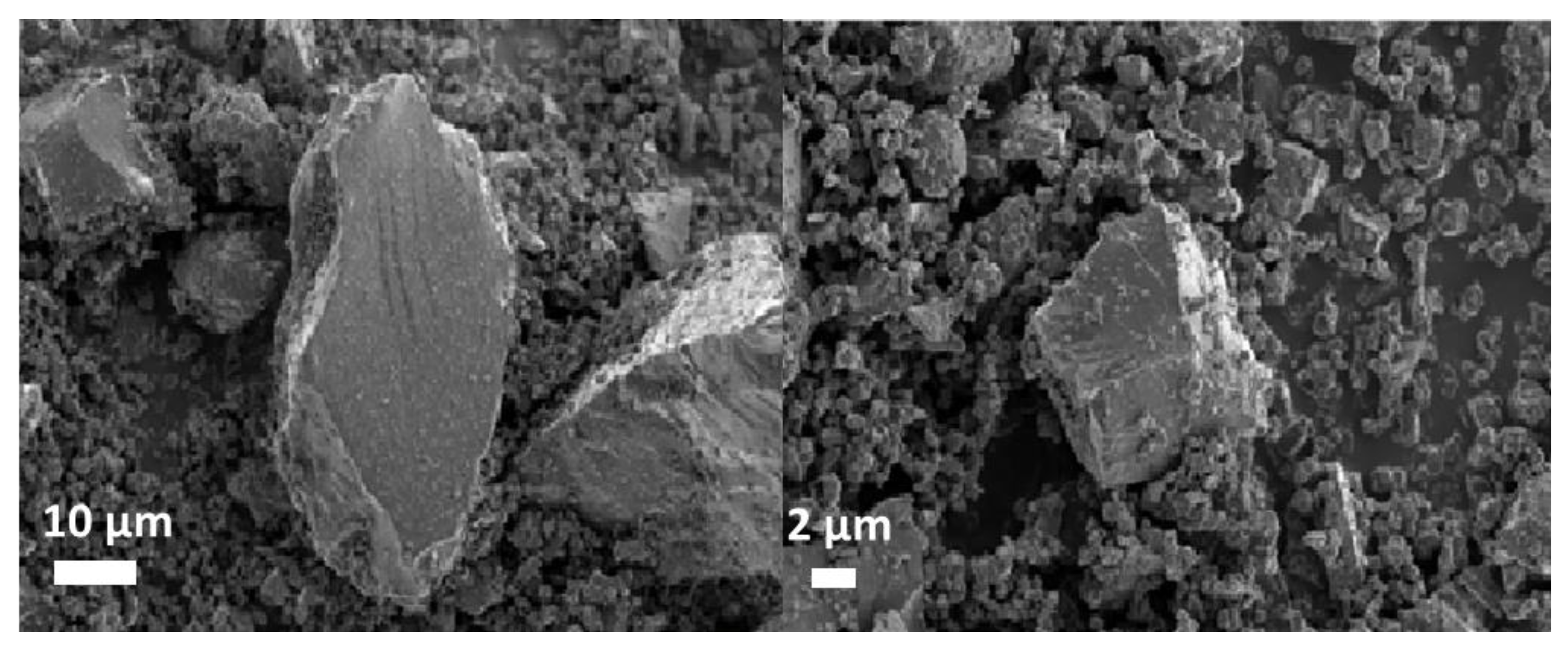


| Study | XRD (%) | XRF (%) | BET (m2/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeTiO3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | Fe | Ti | ||
| Present study (before reaction) | 83.53 | 14.99 | 1.2 | 34.60 | 32.30 | 10.42 |
| Present study (recovered catalyst after reaction) | 82.43 | 16.08 | 1.49 | - | - | - |
| García-Muñoz et al. [21] | 85 | - | 15 | 36 | 37 | 6 |
| Canas-Martinez et al. [28] | 69.50 | 2.81 | 4.18 | NA * | NA * | NA * |
| Silveira et al. [29] | 85 | - | 15 | 36 | 37 | 6 |
| Munoz et al. [22] | NA * | NA * | NA * | 36.2 | 37.0 | 4 |
| Concentration | First Order | Second Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| κ (min−1) | R2 | κ (L/(mol·min−1) | R2 | |
| 5 mg/L | 0.09538 | 0.996 | 0.06485 | 0.9957 |
| 10 mg/L | 0.07856 | 0.9985 | 0.02120 | 0.9828 |
| 20 mg/L | 0.03429 | 0.9886 | 0.003882 | 0.9476 |
| Irradiation Source | Model | Peak Wavelengths (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| UVA | Philips TL-K 40 W/10 R Actinic BL Reflector | 365 |
| UVB | Exo Terra Reptile UVB 200 18 W, 60 cm | 310–350 |
| Visible | Philips Master Super 80 TL-D 18 W/865 | 440, 560, 640 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butt, A.L.; Mpinga, J.K.; Tichapondwa, S.M. Photo-Fenton Oxidation of Methyl Orange Dye Using South African Ilmenite Sands as a Catalyst. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121452
Butt AL, Mpinga JK, Tichapondwa SM. Photo-Fenton Oxidation of Methyl Orange Dye Using South African Ilmenite Sands as a Catalyst. Catalysts. 2021; 11(12):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121452
Chicago/Turabian StyleButt, Alicia Levana, John Kabangu Mpinga, and Shepherd Masimba Tichapondwa. 2021. "Photo-Fenton Oxidation of Methyl Orange Dye Using South African Ilmenite Sands as a Catalyst" Catalysts 11, no. 12: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121452
APA StyleButt, A. L., Mpinga, J. K., & Tichapondwa, S. M. (2021). Photo-Fenton Oxidation of Methyl Orange Dye Using South African Ilmenite Sands as a Catalyst. Catalysts, 11(12), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121452





