Formation and Functioning of Nickel Bis-(acetylacetonate)-Based Multicomponent Catalytic Systems for Di- and Oligomerization of Ethylene: New Mechanistic Aspects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
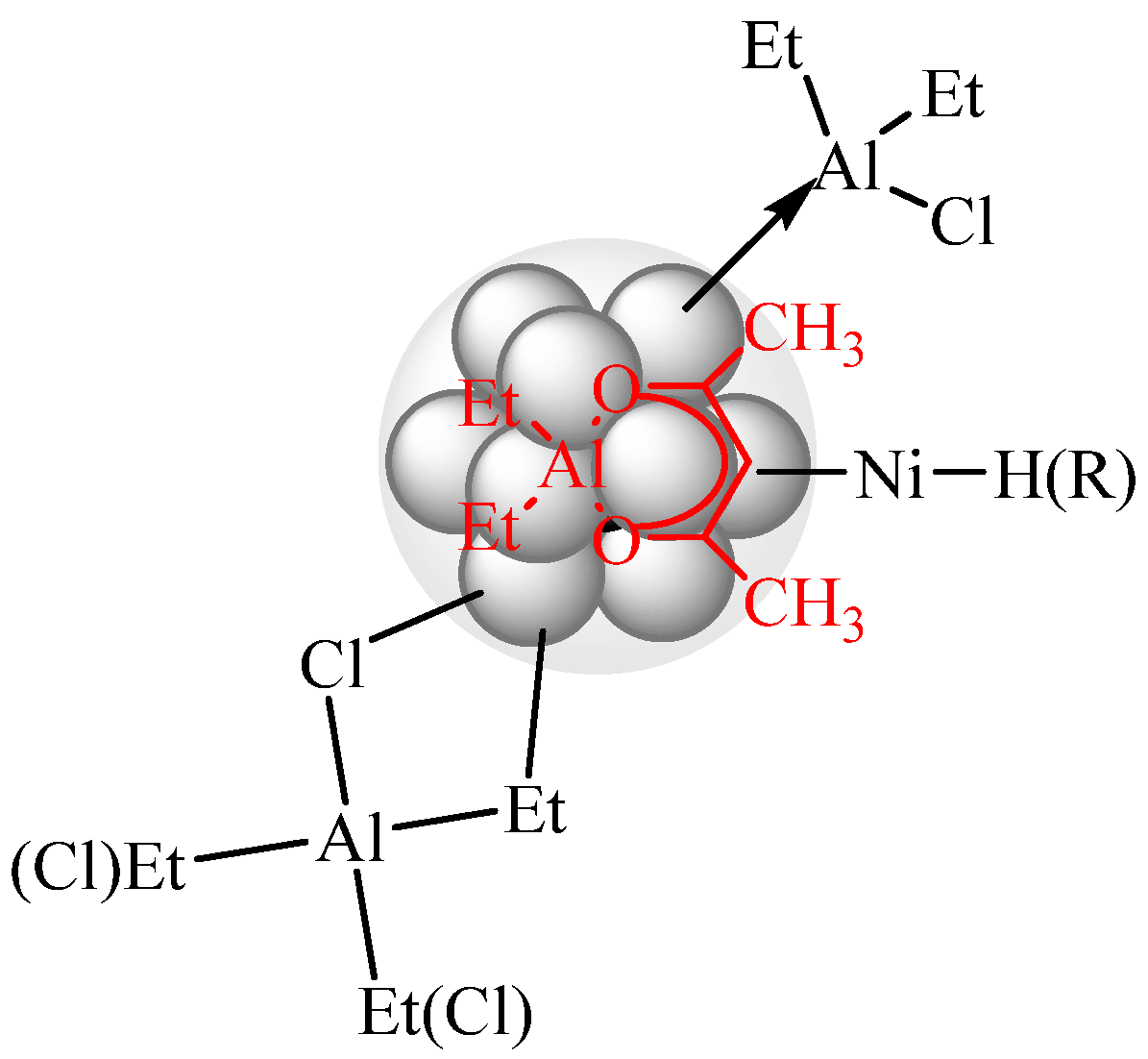
2. Physico-Chemical Aspects of the Formation and Nature of the Activity of Systems Based on Ni(acac)2 and DEAC or EASC
3. The Water Role in the Catalysis of Ethylene Di- and Oligomerization Based on Ni(acac)2 and DEAC or EASC
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belykh, L.B.; Goremyka, T.V.; Rokhin, A.V.; Titova, Y.Y.; Umanets, V.A.; Schmidt, F.K. Reactions of Pd Betta-Diketonate Complexes with Triethylaluminium. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. Khimiya 2005, 31, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, L.B.; Titova, Y.Y.; Umanets, V.A.; Shmidt, F.K. Palladium Hydrogenation Catalysts Modified with Aluminum- and Phosphorus-Containing Compounds and with Alcohols: Effect of Modifiers. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2006, 79, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, L.B.; Titova, Y.Y.; Rokhin, A.V.; Belonogova, L.N.; Shmidt, F.K. Hydrogenation Catalysts Based on Palladium Bisacetylacetonate and Lithium Tetrahydroaluminate: Formation Mechanism and Reasons for Modified Effect of Water. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2008, 81, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, L.B.; Titova, Y.Y.; Rokhin, A.V.; Shmidt, F.K. Generation and Properties of Hydrogenation Catalysts Based on Palladium Bisacetylacetonate and Lithium Alkoxyhydroaluminates. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2008, 81, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, L.B.; Titova, Y.Y.; Rokhin, A.V.; Shmidt, F.K. Formation, Nature of Activity, and Hydrogenation Catalysis by Nickel Bis(Acetylacetonate)–Lithium Tetrahydroaluminate Systems. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2010, 83, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, L.B.; Titova, Y.Y.; Umanets, V.A.; Rokhin, A.V.; Schmidt, F.K. The Role of Lithium Tetrahydroaluminate in the Formation of Nanodimensional Nickel Hydrogenation Catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 401, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.K.; Titova, Y.; Belykh, L.B.; Umanets, V.A.; Khutsishvili, S.S. Formation of the Cobalt Hydrogenation Catalysts at the Action of Lithium Aluminum Hydride and Lithium Tri(Tert-Butoxy)Aluminohydride and Their Properties. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2012, 82, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B.; Rokhin, A.V.; Umanets, V.A.; Schmidt, F.K. Formation and Properties of Nickel Catalysts for Hydrogenation under the Action of Lithium Di- and Tris(Tert-Butoxy)Hydroaluminates. Kinet. Catal. 2012, 53, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, F.K.; Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B. Functions of Organoaluminum and Proton Donor Compounds in the Formation and Functioning of Nanosized Ziegler-Type Nickel-Containing Hydrogenation Catalysts. Kinet. Catal. 2015, 56, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.K.; Titova, Y.Y.; Kolesnikov, S.S.; Belykh, L.B. Nanosized Nickel Ziegler-Type Hydrogenation Catalysts: The Role of Organoaluminum and Proton-Donating Compounds in Their Formation and Optimum Catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 499, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B.; Shmidt, F.K. Ziegler-Type Nickel-Based Hydrogenation Catalysts: The Effect of the Water Content of the Nickel Precursor on the Size and Nature of the Resulting Particles. Kinet. Catal. 2016, 57, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B.; Shmidt, F.K. Preparation Method Effect on the Properties of Ziegler-Type Hydrogenation Catalysts Based on Bis(Acetylacetonato)Cobalt. Kinet. Catal. 2016, 57, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y. Physico-Chemical Aspects of the Formation and Nature of the Activity of Systems Based on Cobalt, Nickel or Palladium Complexes in Hydrogenation and Oligomerization Reactions. ScD Thesis, Irkutsk State University, Irkutsk, Russia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Sukhov, B.G.; Schmidt, F.K. Nano-Size Bimetallic Ternary Hydrogenation Catalysts Based on Nickel and Copper Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 925, 121485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Schmidt, F.K. Directed Design of Hydrogenation Ziegler Systems. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 4525–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Shmidt, F.K. Role of Water in the Catalysis of Ethylene Di- and Oligomerization and Toluene Alkylation Reactions Based on Nickel Bis(Acetylacetonate) Systems. Kinet. Catal. 2017, 58, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Kon’kova, V.; Sukhov, G.; Schmidt, F.K. Nickel-Containing Nanophases as the Carriers of Catalytic Active Sites in the Ethylene Oligomerization in the Presence of Systems Based on Ni(Acac)2 and Organoaluminum Compounds. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.K. Hydrogenation and Dimerization Catalyzed by Complexes of First Row Transition Metals; Gos. University: Irkutsk, Russia, 1986; p. 231. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, C.T.; Kojima, M. Alkene Oligomerization. Catal. Today 1990, 6, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.D.; Rzhevskaya, N.N.; Shcherbakova, N.V.; Sangalov, Y.A.; Minsker, K.S. On the complexation of organochlorine compounds and water. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1977, 233, 602–605. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, V.D.; Rzhevskaya, N.N.; Shcherbakova, N.V.; Sangalov, Y.A.; Minsker, K.S. Interaction of alkylaluminium chlorides with water. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Khim. 1978, 6, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, T. Structure and Lewis Acid Sites in Alumoxane Compounds. Catal. Today 1995, 23, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dötterl, M.; Alt, H.G. Heavy Metal with a Heavy Impact Olefin Dimerization Reactions in Triphenylbismuth Buffered Chloroaluminate Ionic Liquids.Pdf. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dçtterl, M.; Alt, H.G. Buffered Aluminum Chloride as a Highly Efficient Cocatalyst for Olefin Dimerization and Polymerization. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, F.; Speiser, F.; Braunstein, P.; Braunstein, P.; Saussine, L.; Saussine, L. Dimerization and Oligomerization: Recent Developments with Nickel Complexes Containing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.-X.; Marks, T.J. Cocatalysts for Metal-Catalyzed Olefin Polymerization: Activators, Activation Processes, and Structure-Activity Relationships. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 1391–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Woo, T.K.; Cavallo, L.; Margl, P.M.; Ziegler, T.; January, R.V.; Re, V.; Recei, M.; April, V. The Role of Bulky Substituents in Brookhart-Type Ni(II) Diimine Catalyzed Olefin Polymerization: A Combined Density Functional Theory and Molecular Mechanics Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6177–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaev, D.G.; Froese, R.D.J.; Svensson, M.; Morokuma, K. A Density Functional Study of the Mechanism of the Diimine—Nickel-Catalyzed Ethylene Polymerization Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegbahn, P.E.M. Intrinsic Aptitude of Cationic Methyl- and Ethylpalladium To Associate Ethylene and To Further Undergo Subsequent Migratory Insertion. A Theoretical Study. Organometallics 1996, 15, 5542–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. Homogeneous Catalysis: Understanding the Art; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 423. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, M.M.; Abd El-Maksoud, I.H.; El-maksoud, I.H.A. Spectroscopic and Catalytic Characterization of Ni Nano-Size Catalyst for Edible Oil Hydrogenation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 85, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, A.; Bentrup, U.; Zanthoff, H.; Maschmeyer, D. The Role of Different Ni Sites in Supported Nickel Catalysts for Butene Dimerization under Industry-like Conditions. J. Catal. 2009, 266, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, O.-T.; Wang, H.; Blindheim, U. Niederdruck-Oligomerisation von Mono-Olefinen Mit Löslichen Nickel/Aluminium-Bimetallkatalysatoren, Teil I Entwicklung Neuer Katalysatorsysteme Auf Der Basis von π-Cyclobutadien-Nickel(II)-Verbindungen. Helv. Chim. Acta 1969, 52, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, F.K.; Mironova, L.V.; Kalabin, G.A.; Proidakov, A.G.; Kalabina, A.V. Dimerization of propylene in the presence of catalytic systems based on complexes of nickel with organophosphorus ligands. Neftekhimiya 1976, 16, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, G.; Gillard, R.D.; McCleverty, J.A. (Eds.) Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1987; p. 533. [Google Scholar]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B.; Rokhin, A.V.; Soroka, O.G.; Schmidt, F.K. Catalysis of Dimerization and Oligomerization Reactions of Lower Alkenes by Systems Based on Ni(PPh3)2(C2H4) and Ni(PPh3)nCl (n = 2 or 3). Kinet. Catal. 2014, 55, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedejs, E.; Denmark, S.E. Lewis Base Catalysis in Organic Synthesis; Set-Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; Volume 1–3, p. 1441. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, H. (Ed.) Lewis Acid Reagents. A Practical Approach; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B.; Shmidt, F.K. Comparison of Catalytic Properties of Systems Based on Nickel Complexes with 1,4-Diaza-1,3-Butadiene Ligands in Reactions of Styrene Hydrogenation and Ethylene Polymerization. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2016, 89, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, F.K.; Titova, Y.Y.; Belykh, L.B. The Role of Phosphine and 1,2-Diimine Complexes of Nickel in the Oxidation States 0, +1, and +2 in the Catalyzed Di-, Oligo-, and Polymerization of Ethylene. Kinet. Catal. 2016, 57, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Hamdemir, I.K.; Wang, Q.; Frenkel, A.I.; Li, L.; Yang, J.C.; Menard, L.D.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Ozkar, S.; Yih, K.-H.; et al. Industrial Ziegler-Type Hydrogenation Catalysts Made from Co(Neodecanoate)2 or Ni(2-Ethylhexanoate)2 and AlEt3: Evidence for Nanoclusters and Sub-Nanocluster or Larger Ziegler-Nanocluster Based Catalysis. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6279–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| System Ni(acac)2–DEAC | System Ni(acac)2–EASC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al/Ni | TOF, min−1 | TON, (mol C2H4)/(mol Ni) | TOF, min−1 | TON, (mol C2H4)/(mol Ni) |
| 12.50 | 80 | 1885 | 147 | 1488 |
| 25.00 | 180 | 3421 | 330 | 3340 |
| 31.25 | 240 | 3744 | 440 | 4480 |
| 37.50 | 250 | 3872 | 458 | 4600 |
| 50.00 | 246 | 3822 | 456 | 4615 |
| 75.00 | 244 | 3797 | 442 | 4538 |
| № Probe | ESR Spectrum of Toluene Solution of Ni(acac)2–50DEAC/50EASC Systems | Ni(acac)2–50DEAC System | Ni(acac)2–50EASC System |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEM Images and Electron Diffraction (in the Inset) | |||
| 1 |  |  |  |
| 2 |  |  |  |
| 3 |  |  | |
| System | Interplanar Distances, Å | Electron Diffraction Profiles, Å | To Agree with |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(acac)2–50DEAC | 2.08 | 2.82 | # 00-003-1051, |
| 2.34 | 2.07 | # 00-004-0850, | |
| 2.60 | 1.74 | # 00-040-1157, | |
| 2.86 | 1.49 | # 00-020-0019, | |
| Ni(acac)2–50EASC | ~2.14 | 2.05 | # 00-003-1051, |
| 2.36 | 1.26 | # 00-004-0850, | |
| 2.57 | 1.21 | # 00-040-1157, | |
| 2.99 | 1.08 | # 00-020-0019 |
| [H2O] × 10−3, mol/L | TOF, min−1 | TON, (mol C2H4)/(mol Ni) | Concentration, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buthen-1 | Buthens-2 | Methyl- pentenes | Linear Heenes | Oligomers | Alkylation Products | |||
| System Ni(acac)2–DEAC | ||||||||
| 1.71 | 50 | 788 | 1.80 | 60.44 | 13.81 | 6.84 | 17.10 | 0.08 |
| 6.76 | 158 | 1383 | 2.09 | 67.01 | 12.02 | 6.23 | 12.64 | 0.08 |
| 11.8 | 206 | 2266 | 2.06 | 61.55 | 19.36 | 9.54 | 7.50 | 0.17 |
| 16.9 | 248 | 3506 | 1.10 | 62.04 | 18.51 | 9.57 | 8.78 | 0.30 |
| 17.9 | 278 | 3359 | 1.57 | 57.99 | 23.61 | 11.96 | 4.87 | 0.30 |
| 30.5 | 416 | 4276 | 1.50 | 47.40 | 28.86 | 15.18 | 7.064 | 0.35 |
| 45.8 | 418 | 3721 | 1.24 | 43.36 | 25.15 | 13.04 | 17.21 | 0.41 |
| 61.0 | 262 | 2138 | 0.95 | 28.80 | 35.64 | 16.98 | 17.64 | 0.47 |
| System Ni(acac)2–EASC | ||||||||
| 1.71 | 402 | 4035 | 0.45 | 57.75 | 21.88 | 10.58 | 9.32 | 0.78 |
| 6.76 | 644 | 7204 | 0.75 | 56.31 | 24.15 | 11.59 | 7.20 | 0.94 |
| 11.8 | 611 | 6661 | 0.81 | 56.48 | 24.21 | 11.45 | 7.05 | 1.28 |
| 16.9 | 451 | 4615 | 0.55 | 56.49 | 24.96 | 11.31 | 6.65 | 1.25 |
| 17.9 | 402 | 3793 | 0.87 | 59.61 | 20.37 | 9.45 | 9.68 | 1.51 |
| 30.5 | 398 | 3721 | 1.45 | 55.50 | 23.57 | 11.96 | 7.52 | 1.73 |
| 45.8 | 386 | 3611 | 1.55 | 53.58 | 24.57 | 12.47 | 7.83 | 2.00 |
| 61.0 | 402 | 4035 | 0.45 | 57.75 | 21.88 | 10.58 | 9.32 | 2.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Titova, Y.Y.; Schmidt, F.K. Formation and Functioning of Nickel Bis-(acetylacetonate)-Based Multicomponent Catalytic Systems for Di- and Oligomerization of Ethylene: New Mechanistic Aspects. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121489
Titova YY, Schmidt FK. Formation and Functioning of Nickel Bis-(acetylacetonate)-Based Multicomponent Catalytic Systems for Di- and Oligomerization of Ethylene: New Mechanistic Aspects. Catalysts. 2021; 11(12):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121489
Chicago/Turabian StyleTitova, Yuliya Yu., and Fedor K. Schmidt. 2021. "Formation and Functioning of Nickel Bis-(acetylacetonate)-Based Multicomponent Catalytic Systems for Di- and Oligomerization of Ethylene: New Mechanistic Aspects" Catalysts 11, no. 12: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121489
APA StyleTitova, Y. Y., & Schmidt, F. K. (2021). Formation and Functioning of Nickel Bis-(acetylacetonate)-Based Multicomponent Catalytic Systems for Di- and Oligomerization of Ethylene: New Mechanistic Aspects. Catalysts, 11(12), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121489







