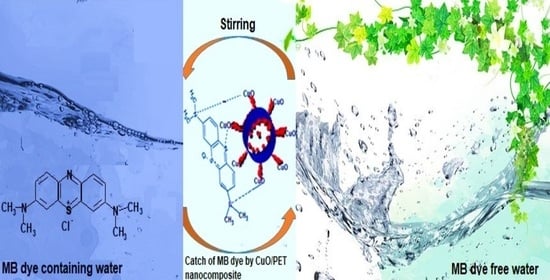
The Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using CuO/PET Nanocomposite in Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.2. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM) Analysis
2.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscope (HR- TEM) Analysis
2.4. Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy Analysis (EDS) and Elements Distribution Mapping (EDM)
2.5. Photodegradation Study of MB Dye
2.6. The Kinetics of MB Degradation by CuO/PET Nanocomposite
2.7. Influence of pH and MB Dye Concentration on Photodegradation
3. Materials and Methods
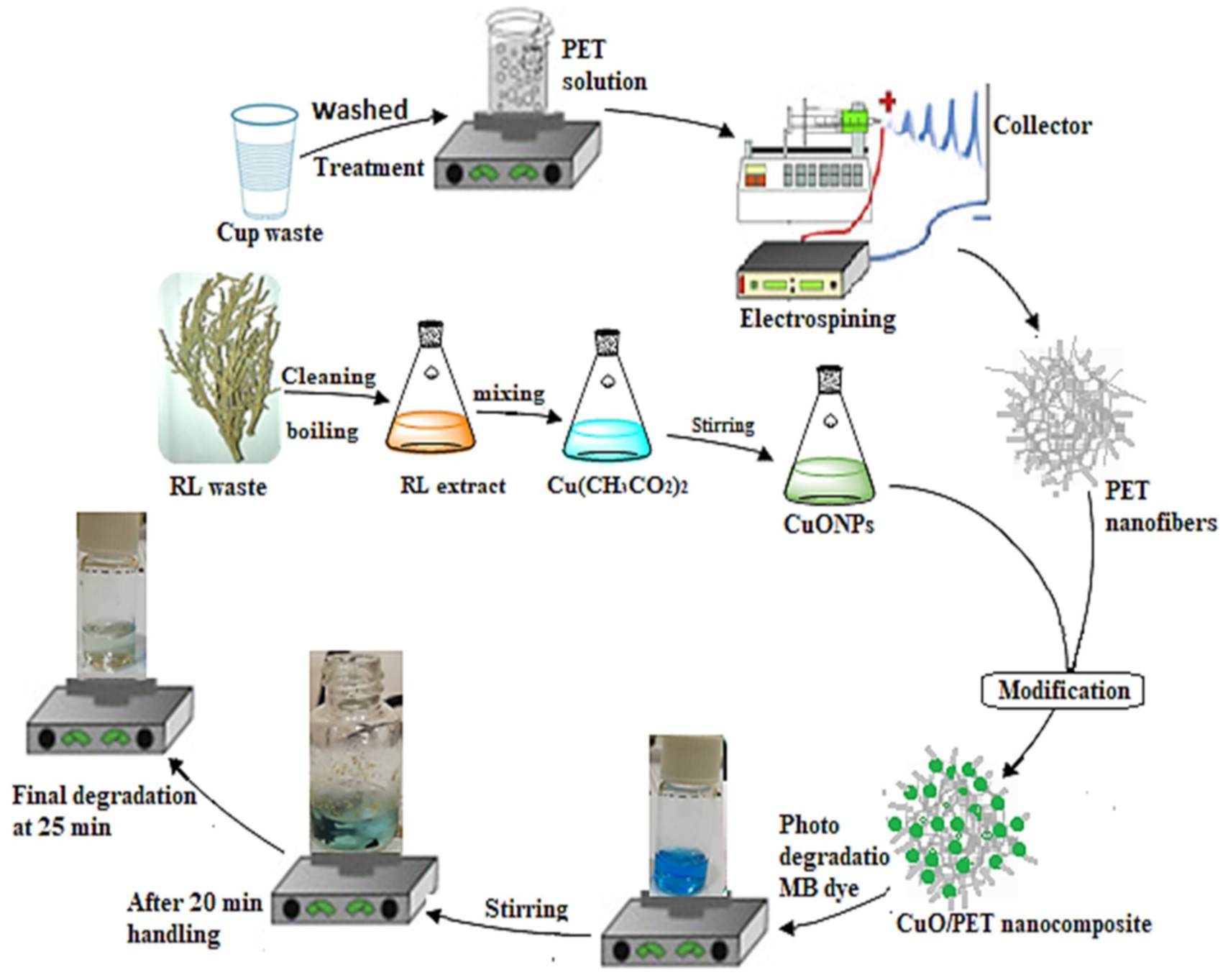
3.1. Preparation of Rhuscoriaria L Stems Extract
3.2. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles CuONPs
3.3. Preparation of PET Nanofiber
- 1 mL/h flow rate,
- 15 cm distance between the needle tip and the collector,
- 5% PET concentration,
- 15 kV for the operating voltage [12].
3.4. Preparation of CuO/PET Nanocomposite
3.5. Characterization Techniques
3.6. Degradation Experiment
- 1:1 weight ratio of CuO/PET nanocomposite was selected after several optimization experiments then mixed with 5 mL 10 ppm of (MB) dye solution in the 10 mL vial.
- The content was stirred magnetically for 30 min in a dark place to ensure the completion of the adsorption-desorption equilibrium process.
- The component of the reaction was exposed to UV lamp (10 Watt) in which the sample was withdrawn from the vial for a fixed time interval in order to screen the dye degradation using the spectrophotometer.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melinte, V.; Stroea, L.; Chibac-Scutaru, A.L. Polymer Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic Applications. Catalysts 2019, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morsi, R.E.; Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Elkholy, S.G.; Sayed, M.S. Polythiophene modified chitosan/magnetite nanocomposites for heavy metals and selective mercury removal. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.; El-Sayed, R.; Osman, T.A.; Toprak, M.S.; Muhammed, M.; Uheida, A. Composite nanofibers for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes from contaminated water. Environ. Res. 2016, 145, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkeni, L.; Ruano, P.; Delgado, L.L.; Picco, S.; Villegas, L.; Tonelli, F.; Merlo, M.; Rigau, J.; Diaz, D.; Masuelli, M. Modern Electrochemical Methods in Nano, Surface and Corrosion Science; Aliofkhazraei, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Bessegato, G.G.; Guaraldo, T.T.; De Brito, J.F.; Brugnera, M.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Achievements and Trends in Photoelectrocatalysis: From Environmental to Energy Applications. Electrocatalysis 2015, 6, 415–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Bányai, I.; Shi, X. Fabrication and morphology control of electrospun poly(γ-glutamic acid) nanofibers for biomedical applications. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2012, 89, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Yousef, S.; Ali AbdelNaby, M.A.; Osman, T.A.; Hamawandi, B.; Toprak, M.S.; Muhammed, M.; Uheida, A. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and enhanced mechanical properties of PAN/CNTs composite nanofibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chwee, T.L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Huang, Z.-M. Recent development of polymer nanofibers for biomedical and biotechnological applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, C.; Arrechi, A.; Kit, K.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Fabrication, Functionalization, and Application of Electrospun Biopolymer Nanofibers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórski, A.; Bałazy, A.; Gradoń, L. Application of nanofibers to improve the filtration efficiency of the most penetrating aerosol particles in fibrous filters. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 6804–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.W.; De Lannoy, C.-F.; Wiesner, M.R. Cellulose Nanomaterials in Water Treatment Technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5277–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.A.; Abbas, J.A.; Saeed, I.A.; Ahmed, I.H. The application of green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles embedded in polyethylene terephthalate nanofibers in the study of the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.-X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zbořil, R.; Varma, R.S. Cu and Cu-Based Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bondžić, A.M.; Senćanski, M.V.; Vujačić Nikezić, A.V.; Kirillova, M.V.; André, V.; Kirillov, A.M.; Bondžić, B.P. Aminoalcoholate-driven tetracopper(II) cores as dual acetyl and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors: Experimental and theoretical elucidation of mechanism of action. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 205, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhov, G.S.; Bilyachenko, A.N.; Levitsky, M.M.; Shul’Pina, L.S.; Korlyukov, A.A.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; Khrustalev, V.N.; Vologzhanina, A.V.; Shubina, E.S.; Dorovatovskii, P.V.; et al. Coordination Affinity of Cu(II)-Based Silsesquioxanes toward N,N-Ligands and Associated Skeletal Rearrangements: Cage and Ionic Products Exhibiting a High Catalytic Activity in Oxidation Reactions. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 4536–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, T.; Sato, S.; Arai, T.; Akimoto, Y.; Kitazumi, K.; Kosaka, S.; Takahashi, N.; Nishimura, Y.F.; Matsuoka, Y.; Morikawa, T. Low-Overpotential Electrochemical Water Oxidation Catalyzed by CuO Derived from 2 nm-Sized Cu2(NO3)(OH)3 Nanoparticles Generated by Laser Ablation at the Air–Liquid Interface. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 8383–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Puigdomènech, A.O.; De Roo, J.; Van Avermaet, H.; De Buysser, K.; Hens, Z. Scalable Approaches to Copper Nanocrystal Synthesis under Ambient Conditions for Printed Electronics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, S.; Zeebaree, S.; Yaseen, A. Synthesis of copper nanoparticles as oxidising catalysts for multi-component reactions for synthesis of 1,3,4- thiadiazole derivatives at ambient temperature. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 13, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, S.; Zeebaree, S.; Yaseen, A.; Ismail, O.; Zebari, H. Diagnosis of the multiple effect of selenium nanoparticles decorated by Asteriscus graveolens components in inhibiting HepG2 cell proliferation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail Haji Zebari, O.; Yaseen Sharaf Zeebaree, S.; Yaseen Sharaf Zeebaree, A.; Ismail Haji Zebari, H.; Abbas, H.R. Anti-bacterial Activity of Copper Nanoparticles Fabricate via Malva Sylvesteris Leaf Extract. Kurdistan J. Appl. Res. 2019, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestarian, H.; Homayouni-Tabrizi, M.; Soltani, M.; Namvar, F.; Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Shabestarian, H. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Sumac Aqueous Extract and Their Antioxidant Activity. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani, P.; Soltani, M.; Homayouni-Tabrizi, M.; Namvar, F.; Azizi, S.; Mohammad, R.; Moghaddam, A.B. Sumac Silver Novel Biodegradable Nano Composite for Bio-Medical Application: Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2015, 20, 12946–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, P.; Palanisamy, P.N. Low-cost non-conventional activated carbon for the removal of reactive red 4: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Rasayan J. Chem. 2008, 1, 871–883. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical Review; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanpour, M.; Safardoust-Hojaghan, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Degradation of methylene blue and Rhodamine B as water pollutants via green synthesized Co3O4/ZnO nanocomposite. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, C.; Hu, B.; Zhu, J. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue over TiO2 Pretreated with Varying Concentrations of NaOH. Catalysts 2018, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koltsov, I.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Nyga, P.; Smalc-Koziorοwska, J.; Stelmakh, S.; Babyszko, A.; Morawski, A.W.; Lojkowski, W. Novel Photocatalytic Nanocomposite Made of Polymeric Carbon Nitride and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Deng, J.; Pan, K. Fabrication of α-Fe2 O3 @rGO/PAN Nanofiber Composite Membrane for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademola Bode-Aluko, C.A.; Pereao, O.; Kyaw, H.H.; Al-Naamani, L.; Al-Abri, M.Z.; Tay Zar Myint, M.; Rossouw, A.; Fatoba, O.; Petrik, L.; Dobretsov, S. Photocatalytic and antifouling properties of electrospun TiO2 polyacrylonitrile composite nanofibers under visible light. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 264, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, S.K.; Cho, K.; Jeong, B.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.; Choi, K.J.; Hong, S.W. Substrate-immobilized electrospun TiO2 nanofibers for photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals: The effects of pH and dissolved organic matter characteristics. Water Res. 2015, 86, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, A.; Mohamed, A.; Aboamera, N.M.; Osman, T.A.; Khattab, A. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes using composite nanofibers under UV irradiation. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasin, S.A.; Abbas, J.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Saeed, I.A. Data of characterization of electrospun waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers. Data Brief 2020, 30, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; Mahar, F.K.; Qureshi, U.A.; Khatri, M.; Khatri, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, I.S. Preparation of colored recycled polyethylene terephthalate nanofibers from waste bottles: Physicochemical studies. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjizadeh, A.; Ajji, A.; Bureau, M.N. Nano/micro electro-spun polyethylene terephthalate fibrous mat preparation and characterization. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, I.N.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T.; Andersson, R.L. Electrospinning of recycled PET to generate tough mesomorphic fibre membranes for smoke filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alzahrani, E. Photodegradation of Eosin Y Using Silver-Doped Magnetic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.-Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.-S. CNT-embedded hollow TiO2 nanofibers with high adsorption and photocatalytic activity under UV irradiation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 622, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubacz, K.; Choina, J.; Dolat, D.; Morawski, A.W. Methylene blue and phenol photocatalytic degradation on nanoparticles of anatase TiO2. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 19, 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, S.A.; Abbas, J.A.; Ali, M.M.; Saeed, I.A.; Ahmed, I.H. Methylene blue photocatalytic degradation by TiO2 nanoparticles supported on PET nanofibres. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 20, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayalu, S.S.; Mangrulkar, P.A.; Kamble, S.P.; Joshi, M.M.; Meshram, J.S.; Labhasetwar, N. Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenolics by N-Doped Mesoporous Titania under Solar Radiation. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Adsorbent | Dye Concentration (mg/L) | Irradiation Light Source | Recorded Time (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT-embedded hollow TiO2 | 10 | UV 800 Watt | 70 | [37] |
| CA–CNT/TiO2–NH2 | 10 | UV 40 Watt | 300 | [31] |
| TiO2 Nanoparticles | 10 | UV 120 Watt | 600 | [38] |
| PET nanofber/CuO nanoparticles | 10 | UV 100 Watt | 60 | [12] |
| PET nanofibers | 10 | UV lamp 10 W | 80 | [39] |
| CuO/PET nanocomposite | 10 | UV lamp 10 W | 30 | this work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasin, S.A.; Sharaf Zeebaree, S.Y.; Sharaf Zeebaree, A.Y.; Haji Zebari, O.I.; Saeed, I.A. The Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using CuO/PET Nanocomposite in Aqueous Solutions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020241
Yasin SA, Sharaf Zeebaree SY, Sharaf Zeebaree AY, Haji Zebari OI, Saeed IA. The Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using CuO/PET Nanocomposite in Aqueous Solutions. Catalysts. 2021; 11(2):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020241
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasin, Suhad Abdulrahman, Samie Yaseen Sharaf Zeebaree, Aymn Yaseen Sharaf Zeebaree, Osama Ismail Haji Zebari, and Ibtisam Abdulmajeed Saeed. 2021. "The Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using CuO/PET Nanocomposite in Aqueous Solutions" Catalysts 11, no. 2: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020241
APA StyleYasin, S. A., Sharaf Zeebaree, S. Y., Sharaf Zeebaree, A. Y., Haji Zebari, O. I., & Saeed, I. A. (2021). The Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using CuO/PET Nanocomposite in Aqueous Solutions. Catalysts, 11(2), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020241