Abstract
Motor vehicles scrap tires and tube rubbers generate a large amount of waste with different characteristics and compositions, contaminating the environment when not properly disposed. Waste inner tube rubber (isobutylene isoprene) representing a threat to the environment can be used as valuable source of energy. Waste inner tube rubber was pyrolyzed thermally under atmospheric pressure both with and without catalyst. Parameters of temperature, time, and catalyst weight were optimized for catalytic and thermal pyrolysis of isobutylene-isoprene rubber into liquid fuel, using MgO as catalyst. It was found that one-hour heating time at 350 °C using 2 g catalyst (MgO) constitutes a suitable parameter for the maximum conversion of scrap inner tube rubber into oil. The oil obtained was characterized by physical and chemical tests. Among the physical tests, Density, specific gravity, viscosity, kinematic viscosity, analine point and flash point were determined according to IP and ASTM standard valves. The physical tests indicate the presence of aromatic and olefinic hydrocarbons. Among the chemical tests, the phenol test, bromine number, bromine water test, and KMnO4 tests were conducted. The chemical tests are also the support of physical tests conducted. The physical and chemical tests indicate that the oil obtained is a mixture of kerosene, diesel, and light oil and could be used for fuel purposes.
1. Introduction
Human lifestyle is improving rapidly, resulting in the increased demand for high-end freeways and highways, consequently increasing the demand for motor vehicles around the world. The rapid expansion of automobile business has therefore brought up some environmental drawbacks where handlings of waste tires/tubes are one of the fast-growing issues [1]. European Tyre & Rubber Manufacturers’ Association (ETRMA) statistics reported that 1400 million tires are being produced, generating 17 million tons of used tires/tube waste every year [2].
Millions of tires/tubes are either thrown away or buried all over the world which is considered a threat to the ecosystem. As per a concise study, there would be 5000 million tires discarded annually by the year 2030 [3]. These scrap tire/tube rubber due to their non-biodegradable nature repeatedly leads to black pollution, bestowing a threat to the environment by causing land occupation, fire risk, and many more [4].
Scraped inner tube is the type of synthetic rubber, that has the capability of retaining air, is mostly used by the automobile and alike industry. It is a co-polymer of 97–98% isobutylene and 2–3% isoprene prepared at low temperature (100 °C) via Friedel-Craft’s catalyst [5,6].
The combination of various factors like resistance to oxidation, ozone, bacteria and solar radiation makes butyl rubber (BR) a good material for making tire as well as inner tube by automobile industry. Regular butyl rubber is the most preferably used material for inner tubes in a range of lightweight to lifestyle bicycles as well as luxury motorcycles.The development of Butyl rubber can be traced back to the work of Gorianov and Butlerov in early 1870s, and later Otto (1927) in an attempt to yield low molecular weight oily polymers by isobutylene polymerization at room temperature in the presence of sulfuric acid and BF3.
Later on, in 1930, I.G. Farben workers succeeded in producing higher molecular weight polymers by reacting a dilute hydrocarbon solution of isobutylene with BF3 at very low temperatures. In a similar fashion a variety of Lewis acids can be used to initiate such kind of polymerization [5,6].
But these carbon based rubber materials were later on became one of the main environmental issues concerning their proper recycling. Gomes and his coworkers has previously reported various toxicological constituents of rubber granules obtained from used tires [7]. Among several approaches, pyrolysis was considered a plausible approach to deal with such materials for carbon black production as well as alternative fuel resources [8,9].
Czajczynska and co-workers [10] stated that waste tire can be recycled to a useful fuel so as the mentioned risks to human health (many diseases) as well as to environment (wasted tires dumps as habitats for mosquitos and rodents) can be reduced. Although, oil obtained from the recycling of these rubbers may generally contain a variety of compounds and cannot be used directly as fuel but can be used as an alternative to diesel [11].
In this regard several approaches were adopted by different researchers around the globe. Lin and his coworkers [12] reported the thermo-gravimetric conversion (temperature range of 127–677 °C) of scrape Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) in to a useful energy source.
These results were supported by Miranda and his co-workers [13] while exploring the effect of temperature on the mechanism of tire waste’s pyrolysis. They entrenched the effect of temperature on pyrolysis reactions of tire wastes. In another study R. Edwin Raj and his fellow researchers [14] used fluidized bed combustion system where they reported that slower feed rate at 440 °C may increase the residence time in reactor for maximum oil yield. They investigated physical and chemical properties of product oil (pyrolysis as well as distilled oil) along with the evolved gases during the process to assess the suitability of their product as conventional fuel.
Telnov and his co-workers [15] studied the degradation of butyl rubber via electron beam at 6–10 MeV. The degraded material was re-used to formulate the diaphragm for fabric and roofing purpose.
M. En and his co-workers [16] reported the use of gamma irradiation for degrading iso-butylene-isoprene rubber where the effect of dose rate on degradation was studied. Their findings indicate that samples were better degraded at lower dose rate and under oxidizing atmosphere compared to the degradation at higher dose rate and under nitrogen atmosphere. Perera and fellows [17] investigated the gamma radiation effect on polypropylene blends with sTyrene-butadiene-sTyrene co-polymers where they studied the generation and decay of free radicals using electron spin resonance for the establishment of kinetics involved in the process.
M. Hassan and his fellows [18] described the devulcanization of passenger car tire’s rubber thru mechanical-chemical process where they measured the sol content as well as get content of the devulcanized products. J. Shah and co-worker [19] studied the effect of Calcium carbide catalyst on distribution of pyrolysis product of rubber where they described that temperature increase in the presence of Calcium carbide catalyst increases liquid fraction as well as total evolved gases while decreasing char yield. They reported that their product liquid had high calorific value; GCV (42.8 MJ kg−1) with boiling point of 320 °C. Their results indicated that viscosity, freezing point, specific gravity and diesel index of the liquid product were comparable to diesel fuel.
A review presented by A. Quek and his co-workers reveals [20] that pyrolytic oil products obtained from various types of waste tires as well as their pyrolysis operating conditions may yield useful chemicals such as limonene, aromatic benzene and alike compounds. Similar findings were reported by G. Choi and co-workers [21] who used a fixed bed reactor to pyrolyze waste tire rubber at temperature ranging for 500–800 °C. They reported the presence of aromatic hydrocarbons, limonene along with some heteroatom-containing compounds like 2,4-dimethylquinoline and benzothiazole in their pyrolyzed oil products. G. I. Danmaliki and T. A. Saleh [22] investigated conversion of scrap tires into activated carbon where nitric acid was used to oxidize the functional groups on the surface of the product. The carbonization was optimized at 500 °C along with activation temperature at 900 °C yielding sorbent with a surface area of 473 m2/g.
B.C. Yu and fellows [23] reported a low cost electrochemical means of recycling waste rubber.
R. Vihar and his fellows [24] investigated the use of pyrolysis oil produced from waste tires in a turbocharged heavy-duty engine, where they reported that their product oil can resourcefully be used as a fuel in a turbocharged non-intercooled engine. Their findings suggest the use of pyrolyzed oil for power generation.
S. Luo and Y. Feng [25] utilized the heat of blast-furnace slag as waste energy recycling for production of oil and gas form waste tire pyrolysis where they reported the upgradation of oil quality by increased construction of derived oil and gases such as H2 as well as CO during pyrolysis.
A. H. Ahoor and N. Z. Atashbar [26] used MgCl2 catalyst in a batch reactor for pyrolysis of waste tire under inert atmosphere, where they optimized conditions to 407.3 °C pyrolysis temperature, 12.5 mm particle size, 133.7 mL min−1 flow rate for 1800 s pyrolysis time using 11.5 wt% of catalyst. They reported that the product oil with physical properties such as cetane number, viscosity, and density comparable to the commercial diesel fuel can be used as alternative fuel. Their results indicate that MgCl2 was helpful in reduction of the sulfur content of the final product.
H. Aydin and co-workers [27] reported the use of Ca(OH)2 as catalyst for pyrolysis of waste tire rubber under nitrogen atmosphere, where they described the decrease in sulfur content of the product oil.
E. Yazdani et al. [28] converted waste tire into a distillate mixture of light naphtha (14%), heavy naphtha (4%) and middle distillate (36%) in a rotating kiln reactor at temperature ranging from 400 °C to 1050 °C under inert atmosphere.
Literature reveals that scrap tire rubber is pyrolyzed using a variety of catalysts including silica-alumina, mesoporous materials (MCM-type), clays (ZSM-5), zeolites and alike materials. Some synthetic zeolites were also used by different researchers but they are somehow expensive that affect the final cost for industry [29,30]. Shah and co-workers reported the use of MgO catalyst for tire rubber conversion into useful hydrocarbons optimizing temperature and reaction time where they have reported 34% total liquid at 350 °C [31].
In the present study, the use of economic and easily available MgO catalyst for the conversion of waste tube rubber with well optimized conditions of temperature, time, and mass of catalyst is being reported where its influence on the composition and improved yield of derived oil is investigated. The obtained product oils were investigated via various physical and chemical tests in order to ensure its potential use as fuel.
2. Results and Discussion
Condition optimizations for the yield of catalytic cracking of tube rubber were performed in a systematic way, where physical and chemical tests of the oil products were done.
2.1. Temperature Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber
Temperature optimization results of tube rubber are shown in Table 1 and in Figure 1. It can be seen that an increase in temperature from 250 to 350 °C subsequently increases the amount of liquid while decreases char (solid). The total conversion of tube rubber is 99.6% at 350 °C. This indicates the completion of reaction at 350 °C. The maximum conversion of oil took place at 350 °C and was selected as the optimum temperature for further work.

Table 1.
Temperature Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber.

Figure 1.
Temperature Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber.
Other authors also obtained results in the similar range but using high temperature of pyrolysis. They obtained maximum liquid yield (55 wt%) at a pyrolysis temperature of 550 °C while the char yield was as low as 33 wt% and the gas yield was around 11 wt% [32].
Cunliffe and Williams [33] reported 58.2 wt% at 475 °C which was adversely affected by the increase in temperature to 53.1 wt% at 600 °C. Murillo and his fellows [34] reported an increased yield from 42.24 wt% to 60.02% at 425 °C but a decrease to 54.1 wt% at 500 °C. Interestingly, they reported a decrease in char from 50.67 to 26.41 wt% at 450 °C and then remain constant. Que and his co-workers [35] reported 17.7% oil, 49.0% gas and 33.3% char from catalytic conversion waste tires at 430 °C using ZSM-5 zeolite under inert atmosphere. Murugan et al. [36] performed pyrolysis of waste tires from 450 to 650 °C with heating rate of 5 °C min−1 for 2 h and 30 min. They reported 55% liquid fraction and 10% of gas as their products. Kar [37] investigated pyrolysis of used tires reporting 60.0 wt% maximum oil yields at 425 °C, where it decreased to 54.12 wt% at 500 °C with a decrease in char from 50.67 to 26.41 wt% and increase of gas from 2.99 to 20.22 wt%. Literature reveals that increase in temperature consequently decreased the TPO yield, however 400–450 °C in the optimum temperature range for increased tire pyrolysis oil yield [38].
The results confirm that with variations in temperature, changes not only occur in the percent conversion but also in the nature of the products. It was expected that there would be an increase in the temperature polarity of the catalyst due to the increase in vibrational energies of the catalyst. Thus, charge induction also increases, resulting in faster reaction.
2.2. Weight of Catalyst Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber
Table 2 and Figure 2 shows that amount of liquid increases and that of solid decreases with increase of weight of catalyst.

Table 2.
Weight of Catalyst Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber.
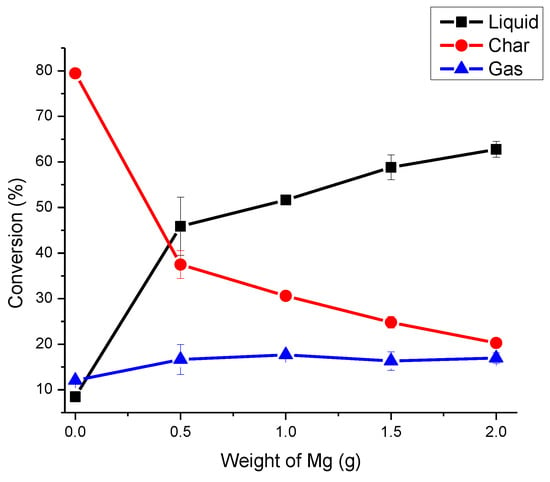
Figure 2.
Weight of Catalyst Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber.
The release of gases is almost constant with 0.5–2.0 g of catalyst. 2 g of catalyst was selected as optimum weight for cracking of butyl rubber because it produces approximately the same amount of char (carbon black) as present in the formulation of butyl inner tube [5,6].
2.3. Heating Time and Rate Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber

Table 3.
Heating Time and Rate Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber.

Figure 3.
Heating Time and Rate Optimization for Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber.
Maximum formation of oil (liquid) took place at 60 min heating time. The amount of char after 60 min heating remains constant but the amount of gases increases due to further cracking of oil at longer time of cracking. Therefore, 60 min was selected as optimum heating time for further investigations.
By using MgO as catalyst, two types of fractions, i.e., light oil and heavy oil, were obtained and both were physically analyzed (Table 4).

Table 4.
Physical properties of Liquid oil after Cracking of Tube Rubber.
The density of the light oil fraction as well as its distillation data (in the range of 180–340 °C) is similar to the density of diesel fuel.
Distillation test at atmospheric pressure was carried out, for the liquids obtained in catalytic pyrolysis at optimum conditions. The results are presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5. It was observed that 50% volume of such liquid was easily distillable fraction with boiling range between 80 and 200 °C which is the boiling point range specified for commercial petrol. Laresgoiti et al. [39] and Rodriguez et al. [40] obtained about 13% of such liquids from tire pyrolysis at 500 °C.
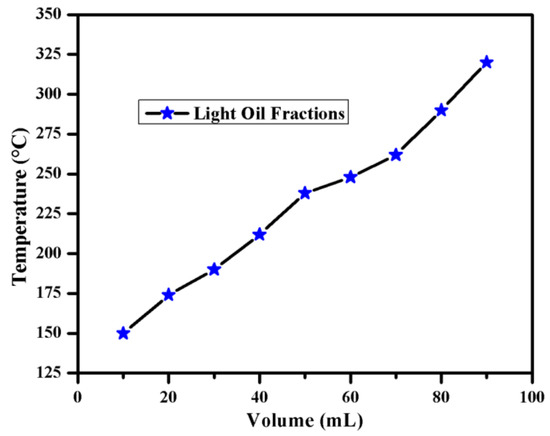
Figure 4.
Distillation of Light Oil Fraction.

Figure 5.
Distillation of Heavy Oil Fraction.
Furthermore, the distillation data for light oil fraction in range of 165–230 °C bear a resemblance to kerosene distillate while distillate in the range of 200–265 °C resembles aromatic kerosene. The viscosity and specific gravity of the product oil are also in the range of aromatic kerosene that further supports the distillation products.
Density of heavy oil fraction is near to density of heavy fuel (0.955 g/mL) oil while its flash point is near to kerosene oil (37–65 °C). The distillation data shows the presence of light oil (80%), light naphtha (10%) and naphthalene oil (10%). 30% of heavy oil fraction (in the range of 158–200 °C) also illustrates the presence of phenol oil, which was further confirmed by phenol determination.
Fuel tests shows that both light and heavy oil fractions are complex mixtures of hydrocarbons.
Oil obtained (mixture of both light and heavy oil) was analyzed chemically. From Bromine Water Test, the solution got faint color immediately which indicates the presence of olefin s in oil. Furthermore, in the potassium permanganate test, the solution lost its color immediately which again confirms the presence of olefins as a major component in oil. From the calibration plot shown in Figure 6, phenol concentration in each sample was determined. The amount of phenols found in heavy oil fraction is 90 µg/100 mL, which was also confirmed by the distillation fraction (158–200 °C) of heavy oil. The distillation temperature range for phenolic oil is (167–194 °C).
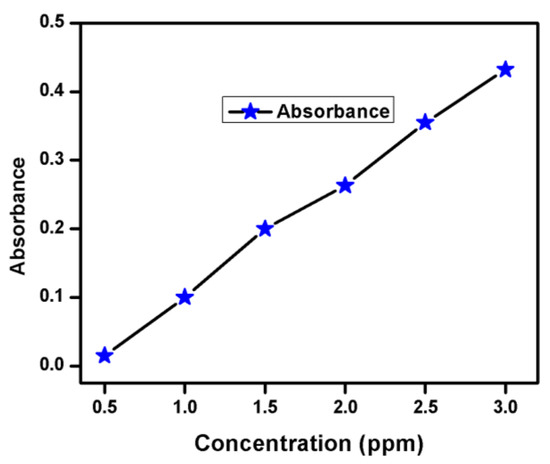
Figure 6.
Determination of phenol using Antipyratic method.
Bromine Number determined for heavy oil fraction (70 g/100 g) indicates the presence of high concentration of olefinic compounds.
3. Material and Methodology
3.1. Material Used
Magnesium oxide (ACS Reagent, 97%, Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), waste tube rubber pieces (Local Market), bromine water solution (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), carbon tetrachloride (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), potassium permanganate (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), A. R. Grade Phenols (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), 4–aminoantipyrene (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Potassium ferricyanide (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Hydrochloric acid (37%, Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Sodium hydroxide (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Ammonia (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Ammonium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Sodium thiosulphate (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Potassium iodide (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Sulphuric acid (98%, Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Mercuric sulphate (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Potassium bromate-Potassium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Sodium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Starch indicator (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany).
3.2. Instruments Used
Spectrophotometer (Spectronic–20D, by Thermo Electron Corporation, Model 333183, Missouri, TX, USA), pH meter (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), Thermocouple (Omega Engineering Company, Deckenpfronn, Germany), digital balance (Mettler Tolledo, Gießen, Germany), ostwald viscometer (Sigma-Aldrich Merck KGaA, Darstadt, Germany), and electric furnace (Nabertherm GmbH, Lilienthal, Germany).
3.3. Pyrolysis Batch Reactor
A Pyrex glass tube of 18 cm length and 3.3 cm width immersed in an automatic programmed electric furnace controlled via a thermocouple was used as batch reactor Batch reactor developed in Rostock University of Germany. (Figure 7).
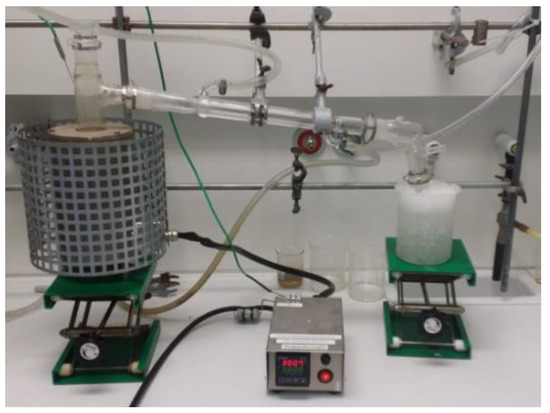

Figure 7.
Batch Reactor Assembly.
3.4. Sample Treatment
Batch reactor having 18 cm length and 3.3 cm width shown in Figure 1, was used to carry out pyrolysis experiments. Magnesium oxide catalyst was premixed with commercial waste tube rubber pieces (5–8 mm cross-section width). Catalyst to tube rubber ratio was 1:5 for experiment. The reactor was heated from 250–350 °C in an automatic programmed electric furnace, where temperature was controlled by a thermocouple. After on hour of heating, glass tube was removed from the reactor and allowed to cool down to room temperature. The pyrolysis products obtained were identified as gas, liquid (oil) and char (solid). The weight of these products was measured accordingly and product composition was calculated via formula:
The efficiency of the reaction was measured by percent conversion using the following formula
3.5. Distillation of Liquid from Catalytic Cracking of Tube Rubber
The distillation of oil obtained from catalytic conversion of tube rubber was carried out in a standard 250 mL round bottom distillation flask attached to a distillation assembly where, 100 mL sample oil was taken in a distillation flask and sample distillates were collected and subjected to further analysis.
3.6. Physical Properties Analysis
Oil obtained (light and heavy oil) from catalytic cracking of tube rubber using magnesium oxide as a catalyst at optimum conditions was analyzed to determine its physical properties, such as density, viscosity, specific gravity, API gravity, kinematic measurement, aniline point, flash point, diesel index, and Kw value via standard methods approved by IP and ASTM.
3.6.1. Density
In typical standard experiment a specific gravity bottle (25 mL) was taken, washed, cleaned and dried in an oven. The empty specific gravity bottle with lid was then weighed using analytical balance. The bottle was filled with sample having no air bubble and weighed again. The weight of sample was determined and its density was calculated by the following relation:
where, D = Density of sample, M = Mass of the sample, V = Volume of the sample
D = M/V
3.6.2. Specific Gravity
Specific gravity of the product oil was calculated using densities of oil and water via following formula:
3.6.3. API-Gravity
API-Gravity was calculated using following formula:
3.6.4. Viscosity
Following a standard method Ostwald viscometer was washed, cleaned and dried in oven, where in a U-shaped glass tube was used to measure the time of flow of liquid between to fixed marks. The experiment was repeated for water as well. Viscosity was measured using the formula:
where, = Viscosity of sample oil, = Density of sample oil, = Time of flow of sample oil, = Viscosity of water, = Density of water, = Time of flow of water.
3.6.5. Kinematic Viscosity
Kinematic viscosity via standard method can be calculated using following formula:
where, = Viscosity of sample oil, = Density of sample oil
3.6.6. Aniline Point
The aniline point apparatus was washed, cleaned and dried. In outer tube (jacket tube) paraffin was taken and in the inner tube equal volumes (10 mL of each) of sample liquid and aniline was poured. The inner tube also had a thermometer and stirrer fitted in the cork. Then heating was started slowly along with stirring until miscibility was achieved. The temperature was noted at this stage. Then the content of the test tube was allowed to cool. As soon as, the turbidity appeared, again the temperature was noted. Average of the two temperatures was found out as aniline point of the sample liquid.
3.6.7. Flash Point
The cup was filled with sample and the meniscus was adjusted exactly at the filling line. The sample cup was heated with heat and the temperature was initially raised at the rate of 14–17 °C per minute. The test flame was passed across the center of the cup until a flash appeared on the surface of the oil. The temperature was recorded as the flash point.
3.7. Chemical Analysis
Chemical tests to determine the chemical properties of the oil obtained from the catalytic cracking of tube rubber using magnesium oxide as a catalyst at optimum conditions are as follows:
3.7.1. Qualitative Determination by Bromine Water Test
A known amount of 3 mL from liquid sample was mixed with 2 mL of 1% bromine water solution in the presence of carbon tetrachloride. The solution colour got faint immediately that indicated the presence of olefins in oil.
Potassium Permanganate Test:
An amount of 3 mL of liquid was mixed with 5 mL of 0.1% potassium permanganate solution. The solution lost its color immediately which further confirmed the presence of olefins as a major component in oil.
3.7.2. Quantitative Determination by Phenol Test using Antipyrene Method
Sample solution was prepared by mixing known volume of oil sample with 4% NaOH solution (10 mL) and was shaken for 5 min. which later on was extracted and neutralized with dilute hydrochloric acid. A buffer solution of pH = 10 (1 mL) was added to the sample solution (10 mL) followed by the addition of 3% 4–aminoantipyrene solution (2 mL) and 6% potassium ferricyanide solution (8 mL). Final mixture was diluted up to 100 mL with distilled water. The same procedure was applied to standards in the range of 0.05–3 ppm.
Absorbance for all working standards along with samples was measured at 510 nm against blank.
From calibration plot, the concentration of phenol was determined in each sample.
3.8. Determination of Bromine Number by Mercury Catalyzed Bromate –Bromide Titration
A gram of heavy oil sample was taken in 250 mL volumetric flask. Then, 25 mL of potassium bromate –potassium bromide solution and 20 mL of 10% sulphuric acid were added to the falsk and was shaken for 5 min. To this mixture 10 mL of mercuric sulphate was added and was mixed thoroughly, the mixture was allowed to stand for 7 min. Then 15 mL of 2 N sodium chloride solution was added followed by the addition of 20 mL of 10% potassium iodide solution. The falsk was shake seconds liberating iodine which was titrated against standard 0.1 N sodium thiosulphate solution. About 0.5 mL of starch solution used as indicator to determine the end point. Bromine number was calculated using the formula:
4. Conclusions
Used tube rubber can advantageously be recycled via catalytic pyrolysis method. It has been revealed that conversion of tube rubber in presence of MgO catalyst at lower temperature into valuable liquid is a practicable procedure. Oil obtained from the catalytic conversion of tube rubber at optimized conditions has shown resemblance to conventional fuel, in terms of both physical as well as its chemical properties. Catalytic pyrolysis of tube rubber is a useful recycling process from economic as well as environmental view point. However, more in-depth studies are required to investigate these liquid fractions separately. Furthermore, char obtained during the catalytic process may be a source of activated carbon that can usefully be utilized in various processes such as wastewater treatment. Here, it can be concluded that oils obtained from the catalytic conversion of waste tube rubber might be developed as an alternative to conventional mineral oil.
Author Contributions
Author and all co-others have equally contributed in completion of this work where project design, reaction reactor, assembly set up, methodology and investigation were done by R.M.; software, M.N.U. and S.W.K.; manuscript writing, Y.A.; Statistics and data validation, H.u.R.; manuscript writing and proof reading, A.R.; project administration, M.A.U.M.; funding acquisition and expert opinion, Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by University Laval (Project: CRSSNG).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly acknowledge the guidance and technical support of Hendrik Kosslick, Head of Material Design at Leibniz Institute for catalysis, University of Rostock Germany.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shi, J.; Zou, H.; Ding, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, D. Continuous production of liquid reclaimed rubber from ground tire rubber and its application as reactive polymeric plasticizer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 99, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C.; Ragazzi, M.; Trulli, E.; Istrate, I.A.; Cioca, L.I. Treatment and disposal of Tires: Two EU approaches. A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, B.S.; Gupta, R.C.; Panicker, V.J. Recycling of waste tire rubber as aggregate in concrete: Durability-related performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, S.H.; Brits, M.; Groenewoud, Q.R.; Van Velzen, M.J.M.; Leonards, P.E.G.; De Boer, J. Chlorinated Paraffins in Car Tires Recycled to Rubber Granulates and Playground Tiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H. Exxon Butyl Rubber Compounding and Applications; Exxon Chemical: Yokohama, Japan, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, W.J.; Thomas, R.M. Interpolymer of Isoolefine and Polyolefine. U.S. Patent 2418912A, 15 April 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, J.; Mota, H.; Bordado, J.; Cadete, M.; Sarmento, G.; Ribeiro, A.; Baiao, M.; Fernandes, J.; Pampulim, V.; Custódio, M.; et al. Toxicological assessment of coated versus uncoated rubber granulates obtained from used tires for use in sport facilities. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.G.; Rao, W.Y.; Chen, C.; Tian, B.; Li, X.J.; Li, P.L.; Guo, Q.L. Performance evaluation of bitumen modified with pyrolysis carbon black made from waste Tires. Constr. Build. Mat. 2016, 111, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanoğlua, A.; Yumrutaş, R. Rotary kiln and batch pyrolysis of waste tire to produce gasoline and diesel like fuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 111, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajczyńska, D.; Krzyżyńska, R.; Jouhara, H.; Spencer, N. Use of pyrolytic gas from waste tire as a fuel: A review. Energy 2017, 134, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Ding, K.; Zhang, B.; Deng, A.; Min, M.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Co-pyrolysis of bamboo residual with waste tire over dual catalytic stage of CaO and co-modified HZSM-5. Energy 2017, 133, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Chang, C.Y.; Wu, C.H. Pyrolytic treatment of rubber waste: Pyrolysis kinetics of sTyrene—butadiene rubber. J. Chem. Technol. Biotech. 1996, 66, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Pinto, F.; Gulyurtlu, I.; Cabrita, I. Pyrolysis of rubber Tire wastes: A. kinetic study. Fuel 2013, 103, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.E.; Kennedy, Z.R.; Pillai, B.C. Optimization of process parameters in flash pyrolysis of waste Tires to liquid and gaseous fuel in a fluidized bed reactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 67, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Telnov, A.; Zavyalov, N.; Khokhlov, Y.; Sitnikov, N.; Smetanin, M.; Tarantasov, V.; Shadrin, D.; Shorikov, I.; Liakumovich, A.; Miryasova, F. Radiation degradation of spent butyl rubbers. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2002, 63, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Uzun, C.; Kantoǧlu, Ö.; Erdoǧan, S.; Deniz, V.; Güven, O. Effect of gamma irradiation conditions on the radiation-induced degradation of isobutylene–isoprene rubber. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2003, 208, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.; Albano, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Silva, P.; Ichazo, M. The effect of gamma radiation on the properties of poly-propylene blends with sTirene–butadiene–sTirene copolymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 85, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Badway, N.A.; Elnaggar, M.Y.; Hegazy, E.-S.A. Thermo-mechanical properties of devulcanized rubber/high crystalline polypropylene blends modified by ionizing radiation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Jan, M.R.; Mabood, F. Catalytic conversion of waste Tires into valuable hydrocarbons. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, A.; Balasubramanian, R. Liquefaction of waste tires by pyrolysis for oil and chemicals—A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.G.; Jung, S.H.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, J.S. Total utilization of waste tire rubber through pyrolysis to obtain oils and CO2 activation of pyrolysis char. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 123, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danmaliki, G.I.; Saleh, T.A. Influence of conversion parameters of waste tires to activated carbon on adsorption of dibenzothiophene from model fuels. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.C.; Jung, J.W.; Park, K.; Goodenough, J.B. A new approach for recycling waste rubber products in Li–S batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 10, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljak, T.; Oprešnik, S.R.; Katrašnik, T. Combustion characteristics of tire pyrolysis oil in turbo charged compression ignition engine. Fuel 2015, 150, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Feng, Y. The production of fuel oil and combustible gas by catalytic pyrolysis of waste tire using waste heat of blast-furnace slag. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 136, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahoor, A.H.; Zandi-Atashbar, N. Fuel production based on catalytic pyrolysis of waste tires as an optimized model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkılıç, C.; Aydın, H. Fuel production from waste vehicle tires by catalytic pyrolysis and its application in a diesel engine. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, E.; Hashemabadi, S.H.; Taghizadeh, A. Study of waste tire pyrolysis in a rotary kiln reactor in a wide range of pyrolysis temperature. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Jan, M.R.; Mabood, F.; Shahid, M. Conversion of waste Tires into carbon black and their utilization as ad-sorbent. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2006, 53, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabood, F.; Jan, M.R.; Shah, J.; Jabeen, F.; Alam, S.; Sadiq, M.; Hussain, Z. Catalytic Conversion of Waste Inner tube Rubber (Isobutylene Isoprene) into Valuable Products. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2010, 32, 767–773. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, J.; Rasul Jan, M.; Mabood, F. Catalytic pyrolysis of waste Tire rubber into hydrocarbons via base catalysts. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. (IJCCE) 2008, 27, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, H. Influence of Temperature and Residence Time of Gas on Property of Waste Tire Pyrolysis. J. Biobased Mat. Bioenergy 2020, 14, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Williams, P.T. Composition of oils derived from the batch pyrolysis of Tires. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1998, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, R.; Aylón, E.; Navarro, M.V.; Callén, M.S.; Aranda, A.; Mastral, A.M. The application of thermal processes to valorise waste Tire. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Lan, W.W.; Wu, Y.H.; Yang, J.W.; Wang, D.Z. Pyrolysis of waste tire on ZSM-5 zeolite with enhanced catalytic activities. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, S.; Ramaswamy, M.C.; Nagarajan, G. The use of Tire pyrolysis oil in diesel engines. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, Y. Catalytic pyrolysis of car tire waste using expanded perlite. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiskumar, C.; Karthikeyan, S. Recycling of waste tires and its energy storage application of by-products:A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 22, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laresgoiti, M.F.; Caballero, B.M.; de Marco, I.; Torres, A.; Cabrero, M.A.; Chomón, M.J. Characterization of the liquid products obtained in Tire pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 71, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco Rodriguez, I.; Laresgoiti, M.F.; Cabrero, M.A.; Torres, A.; Chomon, M.J.; Caballero, B. Pyrolysis of scrap Tires. Fuel Process. Technol. 2001, 72, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).