Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Ferrocene from Flame Spray Pyrolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. General Nanoparticle Characterization
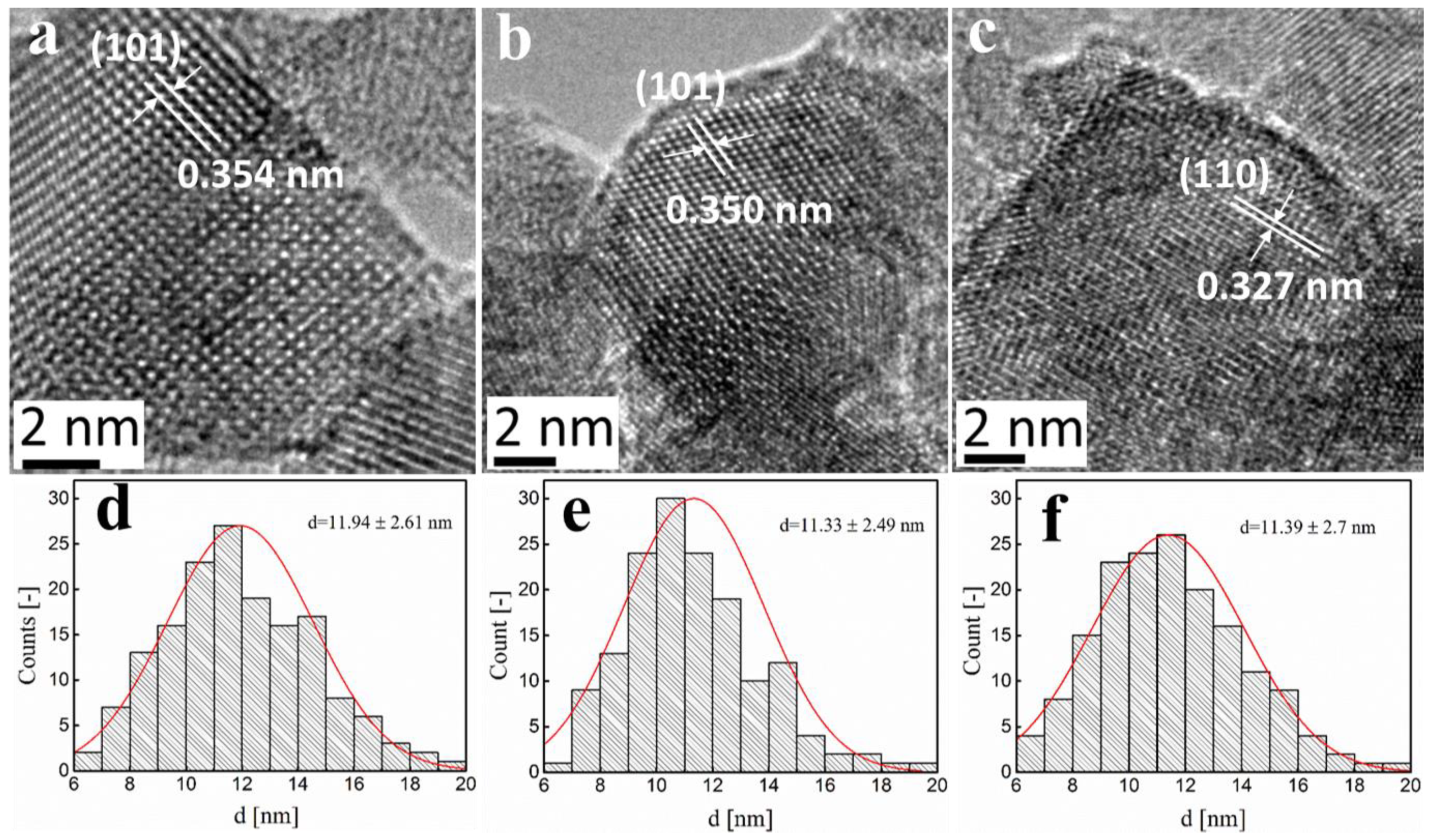
2.2. Fe-TiO2 Morphology
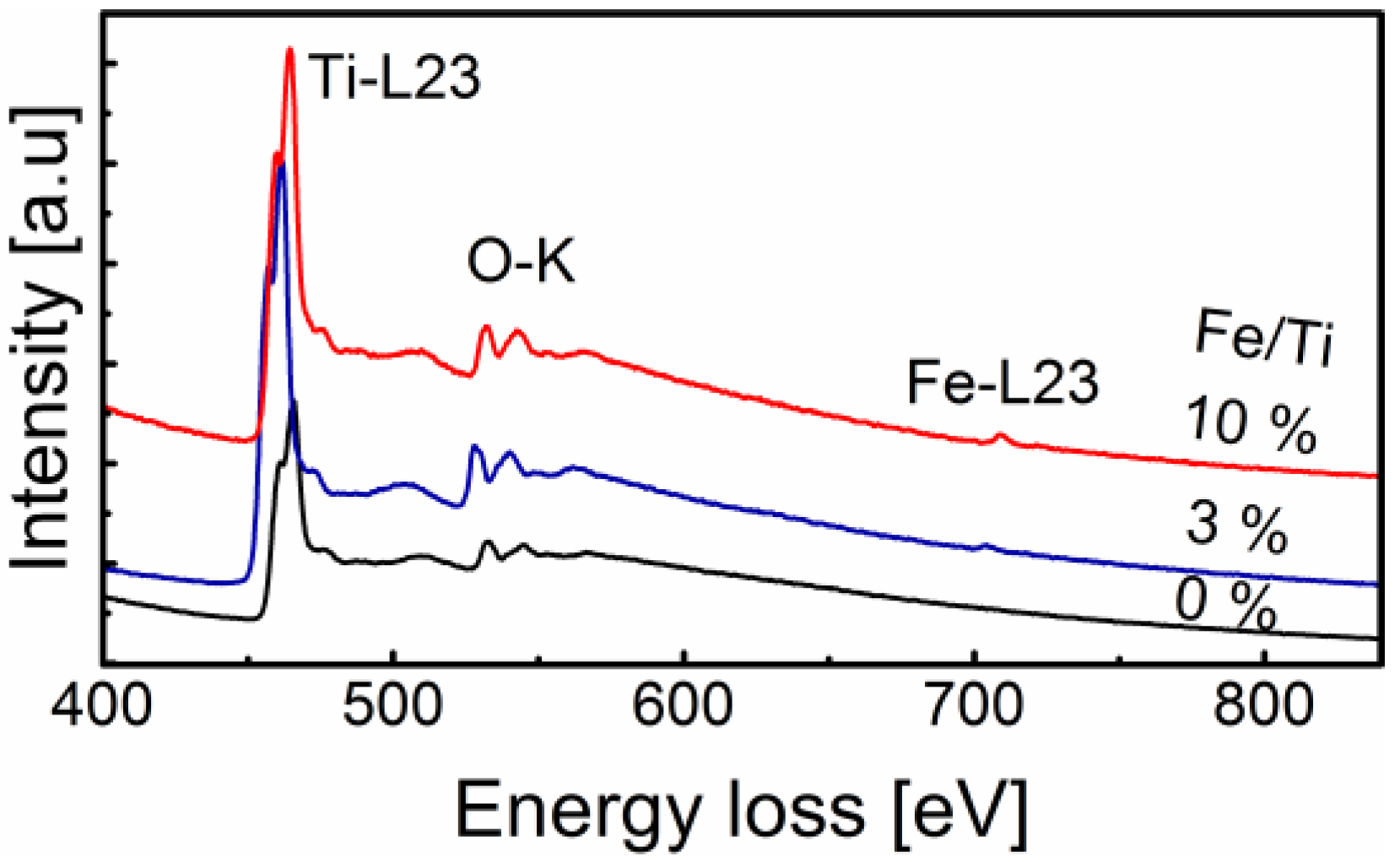
2.3. Surface Chemistry
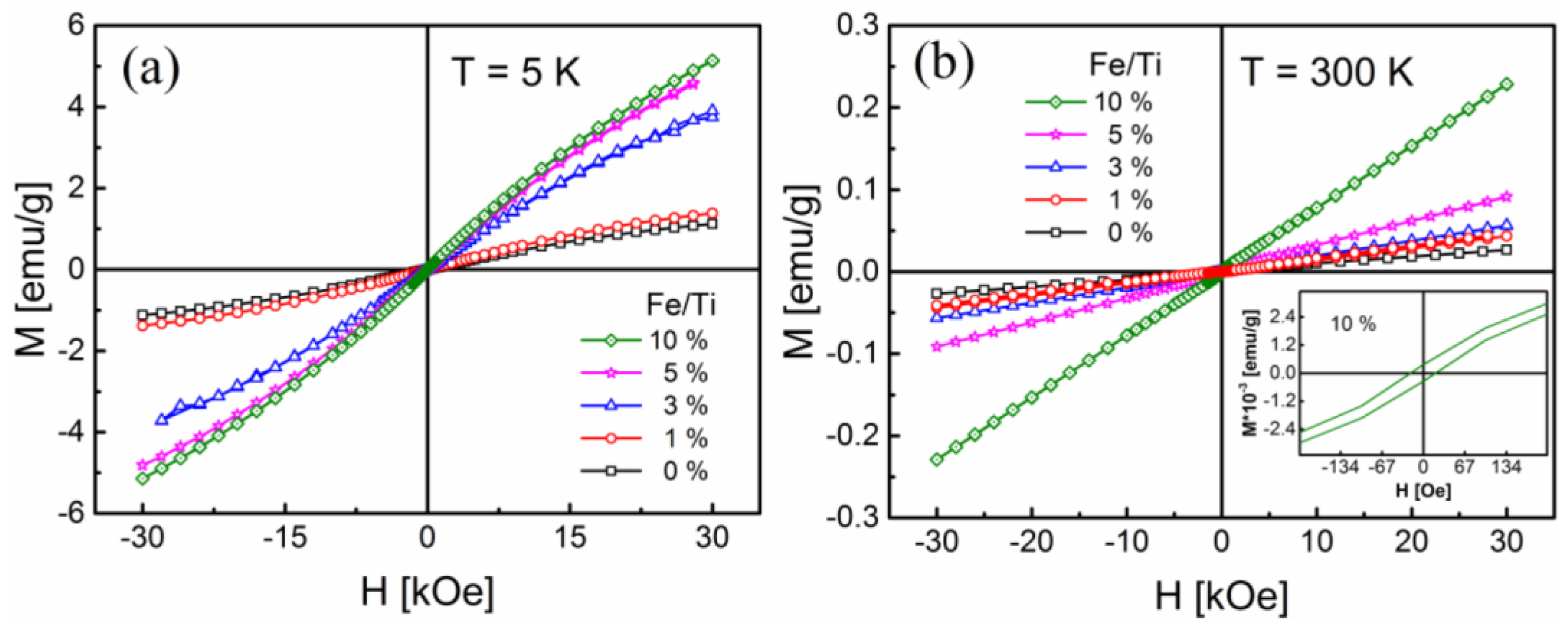
2.4. Magnetic Properties
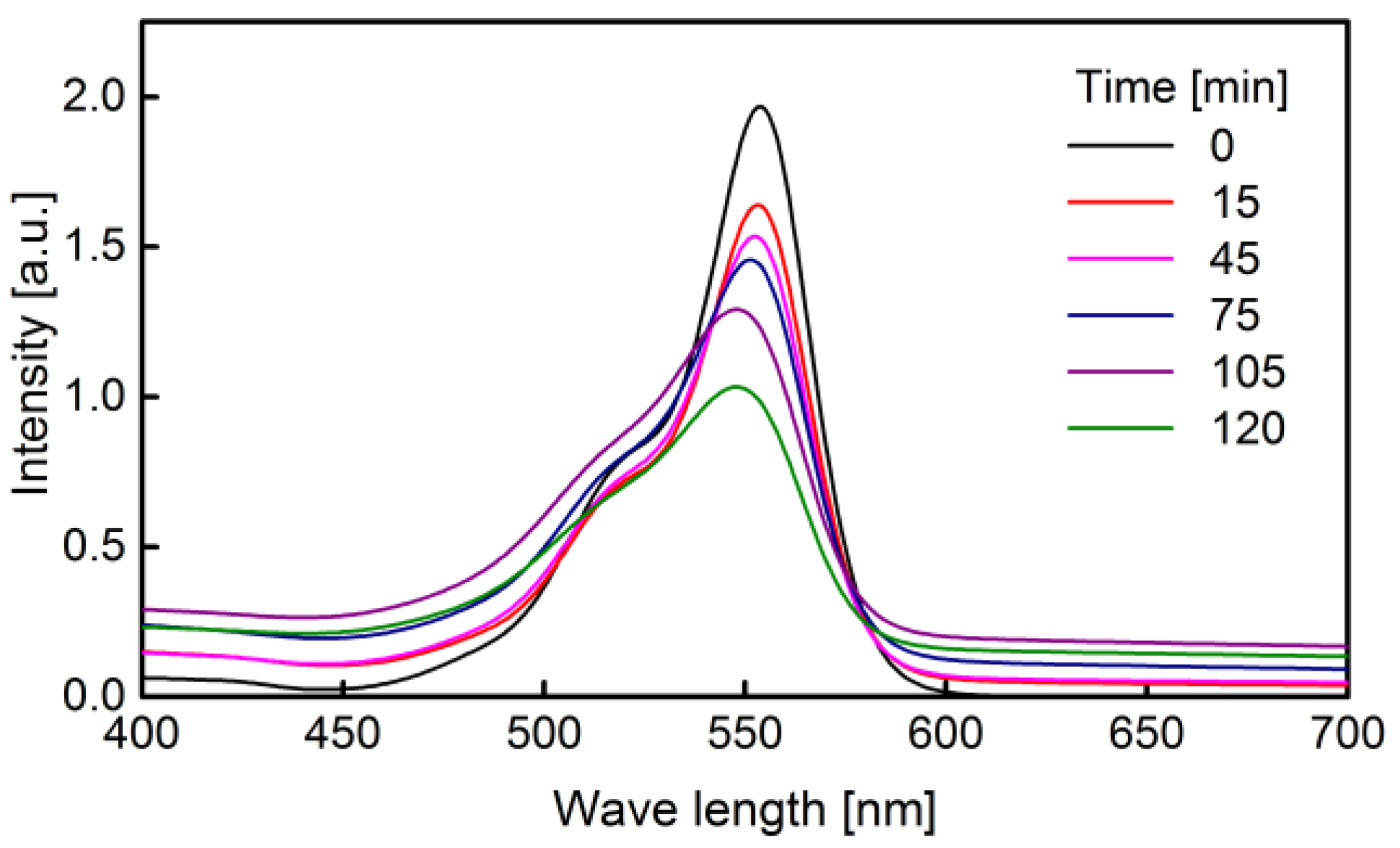
2.5. Optical Properties
3. Photocatalytic Application
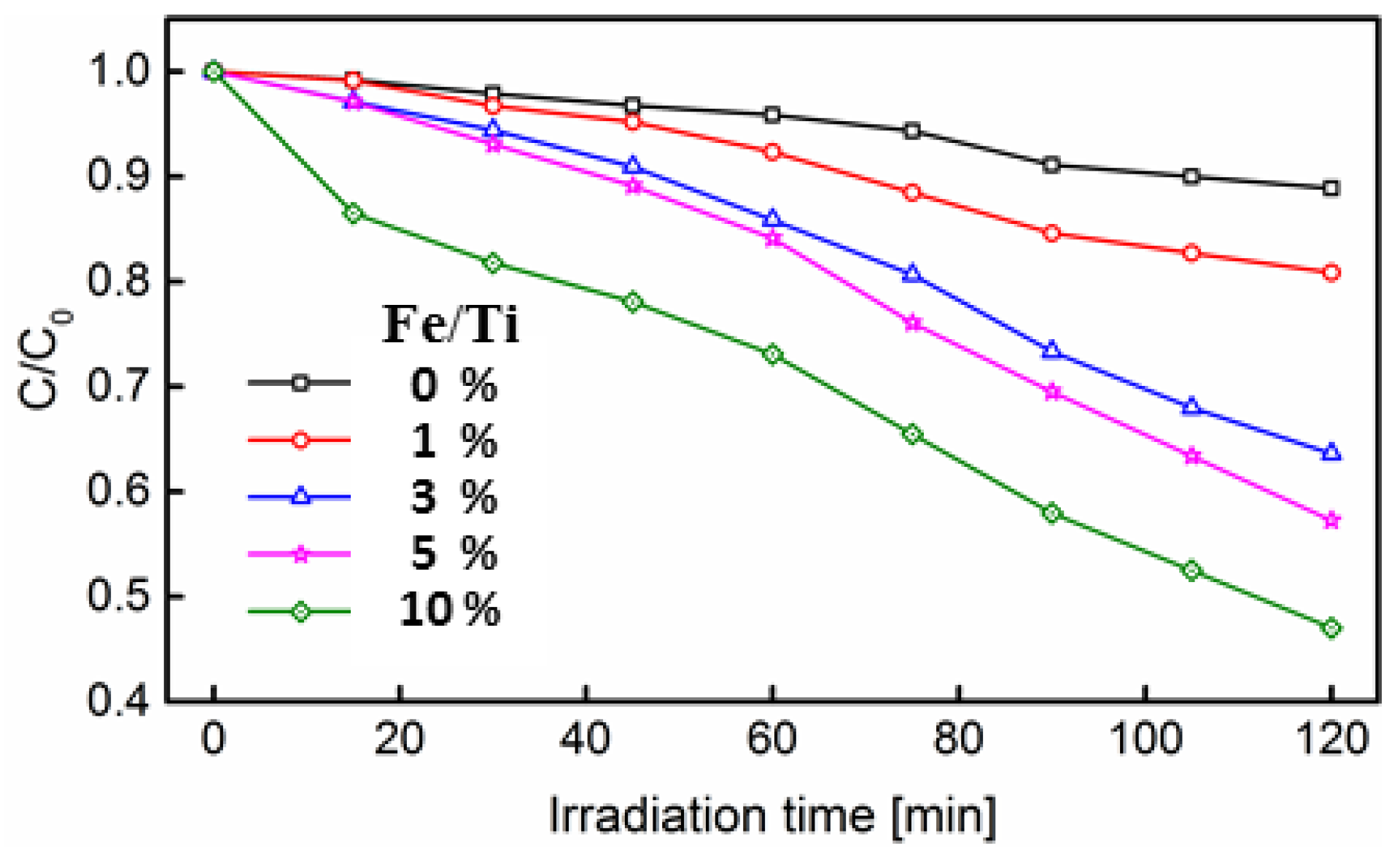
3.1. Photocatalytic Activity Test
3.2. Degradation of Rhodamine B
4. Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schimmoeller, B.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Baiker, A. Flame aerosol synthesis of metal oxide catalysts with unprecedented structural and catalytic properties. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1234–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.; Schimmoeller, B.; Thiebaut, B.; Fernandez, C.; Rao, T.N. Pilot plants for industrial nanoparticle production by flame spray pyrolysis. KONA Powder Part J. 2011, 29, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, W.Y.; Amal, R.; Mädler, L. Flame spray pyrolysis: An enabling technology for nanoparticles design and fabrication. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1324–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, D.H.; Memon, N.K.; Chung, S.H. Investigating the growth mechanism and optical properties of carbon-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2013, 108, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.A.; Memon, N.K.; Mansour, M.S.; Anjum, D.H.; Chung, S.H. Curved wall-jet burner for synthesizing titania and silica nanoparticles. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2015, 35, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, N.K.; Anjum, D.H.; Chung, S.H. Multiple-diffusion flame synthesis of pure anatase and carbon-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, C.L.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Ho, S.T. Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 photocatalyst by the sol–gel method. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. 2010, 1, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiang, Q.; Zhou, M. Preparation, characterization and visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped titania nanorods and first-principles study for electronic structures. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 90, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Jiang, Z.; Geng, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, D. Carbon and nitrogen co-doped TiO2 with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2741–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Spinu, L.; Zhou, W. Extraordinary Hall effect and ferromagnetism in Fe-doped reduced rutile. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Joji, T.; Inagaki, M.; Iwata, H. Direct formation of iron (III)-doped titanium oxide (anatase) by thermal yydrolysis and its structural property. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ebbinghaus, S.G.; Weidenkaff, A.; Kurz, T.; Krug von Nidda, H.-A.; Klar, P.J.; Güngerich, M.; Reller, A. Controlled iron-doping of macrotextured nanocrystalline titania. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4028–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.-G.; Kamiyama, H.; Katada, M.; Ohashi, N.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Ishigaki, T. Pyrogenic iron (III)-doped TiO2 nanopowders synthesized in RF thermal plasma: Phase formation, defect structure, band gap, and magnetic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10982–10990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Zhu, B.; Huang, W.; Wu, S.; Zhang, S. Synthesis, characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 nanotubes with high photocatalytic activity. Catal. Lett. 2009, 129, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, W.Y.; Amal, R.; Mädler, L.; Pratsinis, S.E. Flame sprayed visible light-active Fe-TiO2 for photomineralisation of oxalic acid. Catal. Today 2007, 120, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, T.; Sung, C.-J.; Yang, Z.; Joshi, A.; Wang, H. Effect of ferrocene addition on sooting limits in laminar premixed ethylene–oxygen–argon flames. Combust. Flame 2004, 139, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Megaridis, C.M. Soot suppression by ferrocene in laminar ethylene/air nonpremixed flames. Combust. Flame 1996, 105, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Wal, R.L.; Hall, L.J. Ferrocene as a precursor reagent for metal-catalyzed carbon nanotubes: Competing effects. Combust. Flame 2002, 130, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, K.; Saito, K. Modeling ferrocene reactions and iron nanoparticle formation: Application to CVD synthesis of carbon nanotubes. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotou, G.P.; Scott, S.J.; Pratsinis, S.E. The role of ferrocene in flame synthesis of silica. Combust. Flame 1995, 101, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Elguézabal, A.; Antúnez, W.; Alonso, G.; Delgado, F.P.; Espinosa, F.; Miki-Yoshida, M. Study of carbon nanotubes synthesis by spray pyrolysis and model of growth. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afre, R.A.; Soga, T.; Jimbo, T.; Kumar, M.; Ando, Y.; Sharon, M. Growth of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes on silicon and quartz substrate by spray pyrolysis of a natural precursor: Turpentine oil. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 414, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Kaihatsu, Y.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Rapid synthesis of a BN/CNT composite particle via spray routes using ferrocene/ethanol as a catalyst/carbon source. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafshejani, L.D.; Tangsir, S.; Koponen, H.; Riikonen, J.; Karhunen, T.; Tapper, U.; Lehto, V.-P.; Moazed, H.; Naseri, A.A.; Hooshmand, A. Synthesis and characterization of Al2O3 nanoparticles by flame spray pyrolysis (FSP)-role of Fe ions in the precursor. Powder Technol. 2016, 298, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, S.N.; Haram, S.K. Synthesis and characterization of uncapped γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles prepared by flame pyrolysis of ferrocene in ethanol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2006, 6, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, M.; Pathak, D.K.; Thakur, O.P.; Vankar, V.D.; Kumar, R. Deposition of single phase polycrystalline α-Fe2O3 thin film on silicon and silica substrates by spray pyrolysis. Silicon 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akurati, K.K.; Vital, A.; Klotz, U.E.; Bommer, B.; Graule, T.; Winterer, M. Synthesis of non-aggregated titania nanoparticles in atmospheric pressure diffusion flames. Powder Technol. 2006, 165, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H.; Madler, L.; Strobel, R.; Jossen, R.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Johannessen, T. Independent control of metal cluster and ceramic particle characteristics during one-step synthesis of Pt/TiO2. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.; Conesa, J.; Augugliaro, V.; Palmisano, L.; Schiavello, M.; Sclafani, A. Dinitrogen photoreduction to ammonia over titanium dioxide powders doped with ferric ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ni, C.; Lin, H.; Huang, C.; Shah, S.I. Size dependence of thermal stability of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 6663–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lin, J.X.; Wang, L.; Song, K.X. Preparation and characterization of Fe3+-doped TiO2/diatomite composite. Appl. Mech. Mat. 2013, 268–270, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.X.; Dobbins, R.A. Crystallogenesis of particles formed in hydrocarbon combustion. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2000, 159, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaeili, F.; Topcu, S.; Jodhani, G.; Gouma, P.-I. Flame-sprayed pure and Ce-doped TiO2 photocatalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, D.H.; Memon, N.K.; Ismail, M.; Hedhili, M.N.; Sharif, U.; Chung, S.H. Transmission electron microscopy of carbon-coated and iron-doped titania nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 365709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; De Groot, F.; Sawatzky, G.; Voogt, F.; Hibma, T.; Okada, K. In situ XPS analysis of various iron oxide films grown by NO2-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Battiston, G.A.; Berto, D.; Gerbasi, R.; Tondello, E. Chemical vapor deposited Fe2O3 thin films analyzed by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectra 2001, 8, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronniemi, M.; Sainio, J.; Lahtinen, J. Chemical state quantification of iron and chromium oxides using XPS: The effect of the background subtraction method. Surf. Sci. 2005, 578, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapna, K.; Phase, D.; Choudhary, R. Study of valence band structure of Fe doped anatase TiO2 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 043910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Haring, A.J.; Beach, J.A.; Li, M.; Doucette, G.S.; Morris, A.J.; Moore, R.B.; Priya, S. Visible light induced photocatalytic activity of Fe3+/Ti3+ co-doped TiO2 nanostructures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18033–18037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcells, L.; Frontera, C.; Sandiumenge, F.; Roig, A.; Martínez, B.; Kouam, J.; Monty, C. Absence of ferromagnetism in Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 122501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janisch, R.; Gopal, P.; Spaldin, N.A. Transition metal-doped TiO2 and ZnO-present status of the field. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Stamenov, P.; Gunning, R.; Venkatesan, M.; Paul, K. Ferromagnetism in defect-ridden oxides and related materials. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 053025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, R.; Naik, V.M.; Kharel, P.; Talagala, P.; Naik, R. Room temperature ferromagnetism in spin-coated anatase-and rutile-Ti0.95Fe0.05O2 films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.; Wongsaprom, K.; Alaria, J.; Venkatesan, M. Charge-transfer ferromagnetism in oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 134012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Termin, A.; Hoffmann, M.R. The role of metal ion dopants in quantum-sized TiO2: Correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 13669–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, W.; He, B.; Zhang, J.; Anpo, M. Characterization of Fe–TiO2 photocatalysts synthesized by hydrothermal method and their photocatalytic reactivity for photodegradation of XRG dye diluted in water. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2004, 216, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cao, C.; Erickson, L.; Hohn, K.; Maghirang, R.; Klabunde, K. Photo-catalytic degradation of Rhodamine B on C-, S-, N-, and Fe-doped TiO2 under visible-light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 91, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthi, T.; Madras, G. Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine dyes with nano-TiO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Pan, C.; Yao, W.; Zhu, Y. Visible-light-induced degradation of rhodamine B by nanosized Bi2WO6. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22432–22439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Precursor (control) | Synthesized (ICP) | SSA (BET) | dBET | Anatase | dXRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/Ti | Fe in Fe-TiO2 | ||||
| % | % | [m2/g] | [nm] | % | [nm] |
| 0 | 0.0 | 151 | 9.9 | 91.8 | 16.2 |
| 1 | 0.87 | 118 | 12.6 | 85.8 | 18.8 |
| 3 | 1.56 | 137 | 10.9 | 64.2 | 16.3 |
| 5 | 2.61 | 139 | 10.4 | 42.1 | 12.2 |
| 10 | 5.24 | 140 | 10.2 | 20.9 | 15.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, M.A.; Hedhili, M.N.; Anjum, D.H.; Singaravelu, V.; Chung, S.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Ferrocene from Flame Spray Pyrolysis. Catalysts 2021, 11, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040438
Ismail MA, Hedhili MN, Anjum DH, Singaravelu V, Chung SH. Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Ferrocene from Flame Spray Pyrolysis. Catalysts. 2021; 11(4):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040438
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Mohamed Anwar, Mohamed N. Hedhili, Dalaver H. Anjum, Venkatesh Singaravelu, and Suk Ho Chung. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Ferrocene from Flame Spray Pyrolysis" Catalysts 11, no. 4: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040438
APA StyleIsmail, M. A., Hedhili, M. N., Anjum, D. H., Singaravelu, V., & Chung, S. H. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Ferrocene from Flame Spray Pyrolysis. Catalysts, 11(4), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040438






