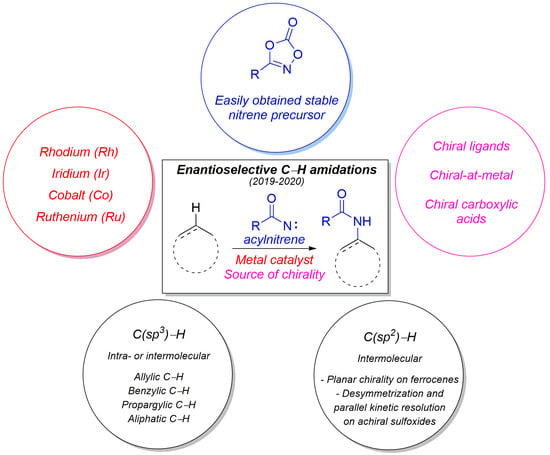
Enantioselective Catalytic C-H Amidations: An Highlight
Abstract
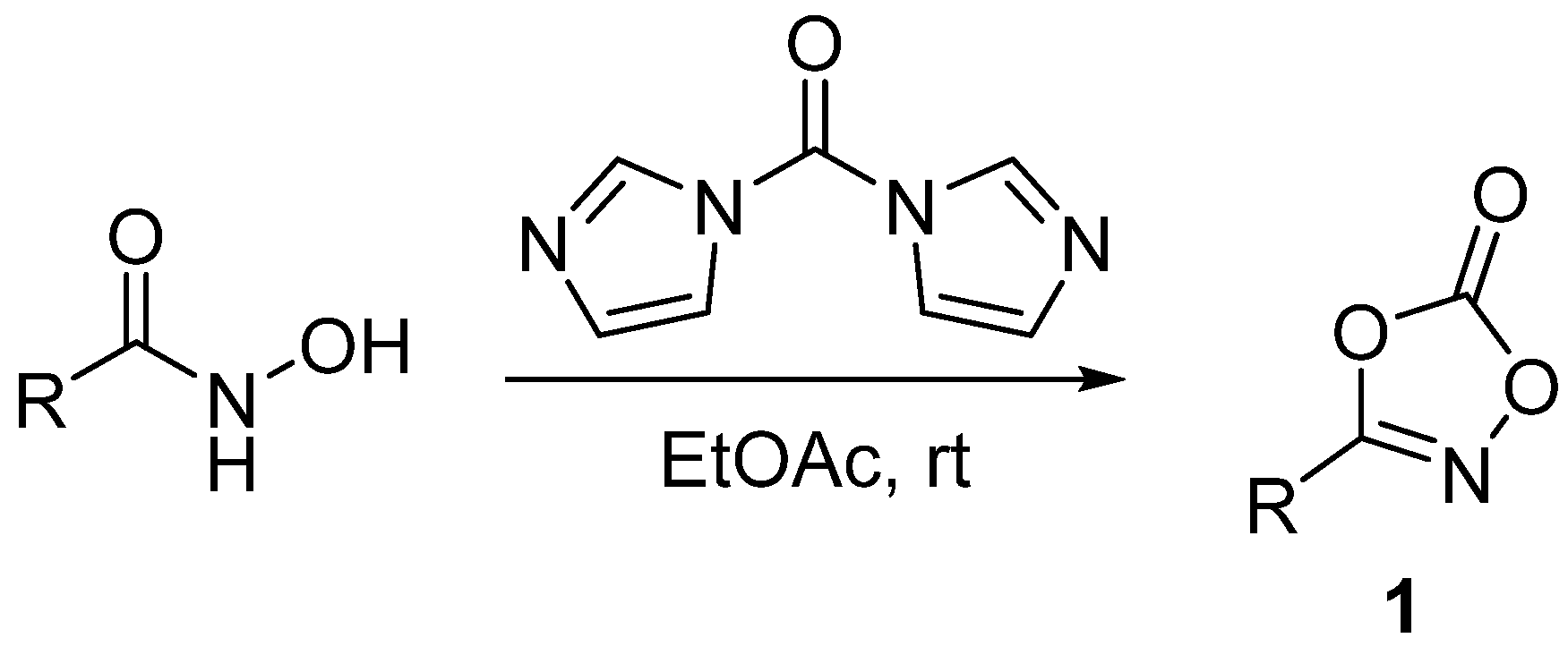
1. Introduction
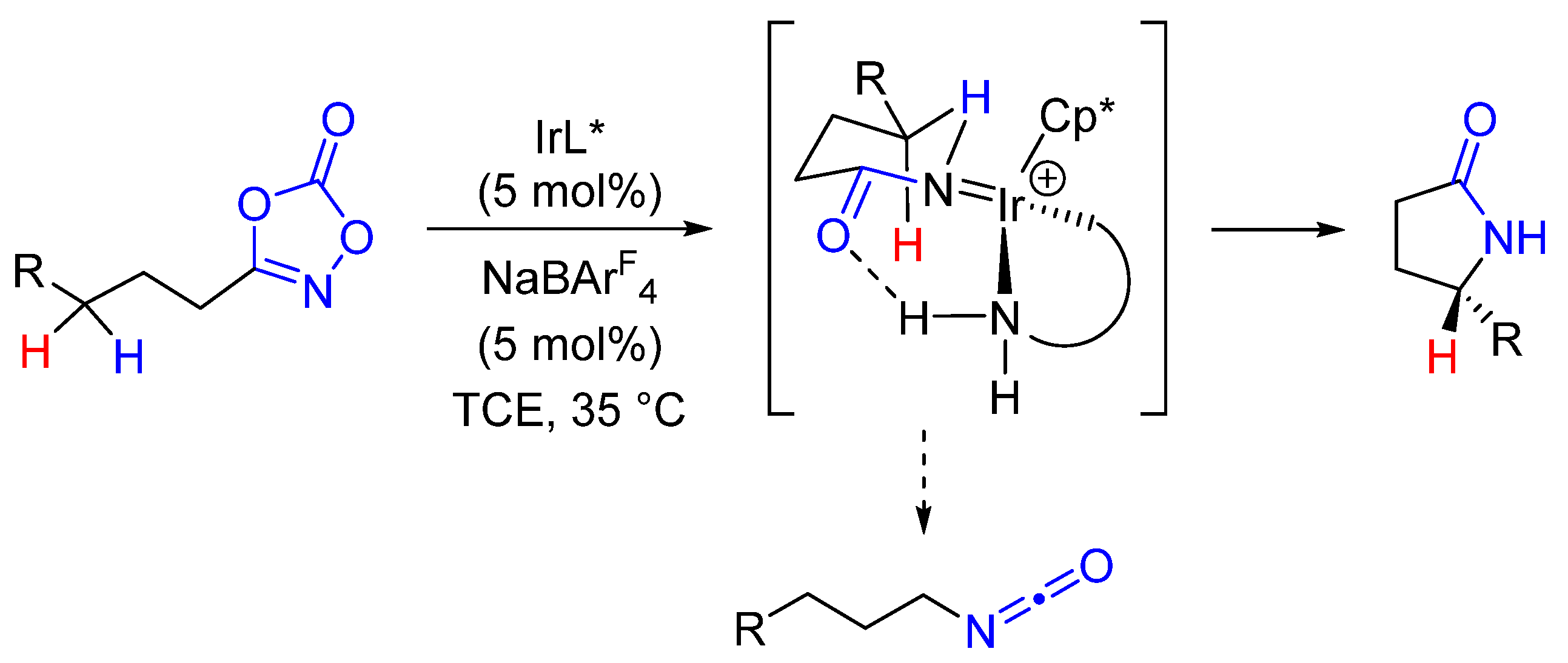
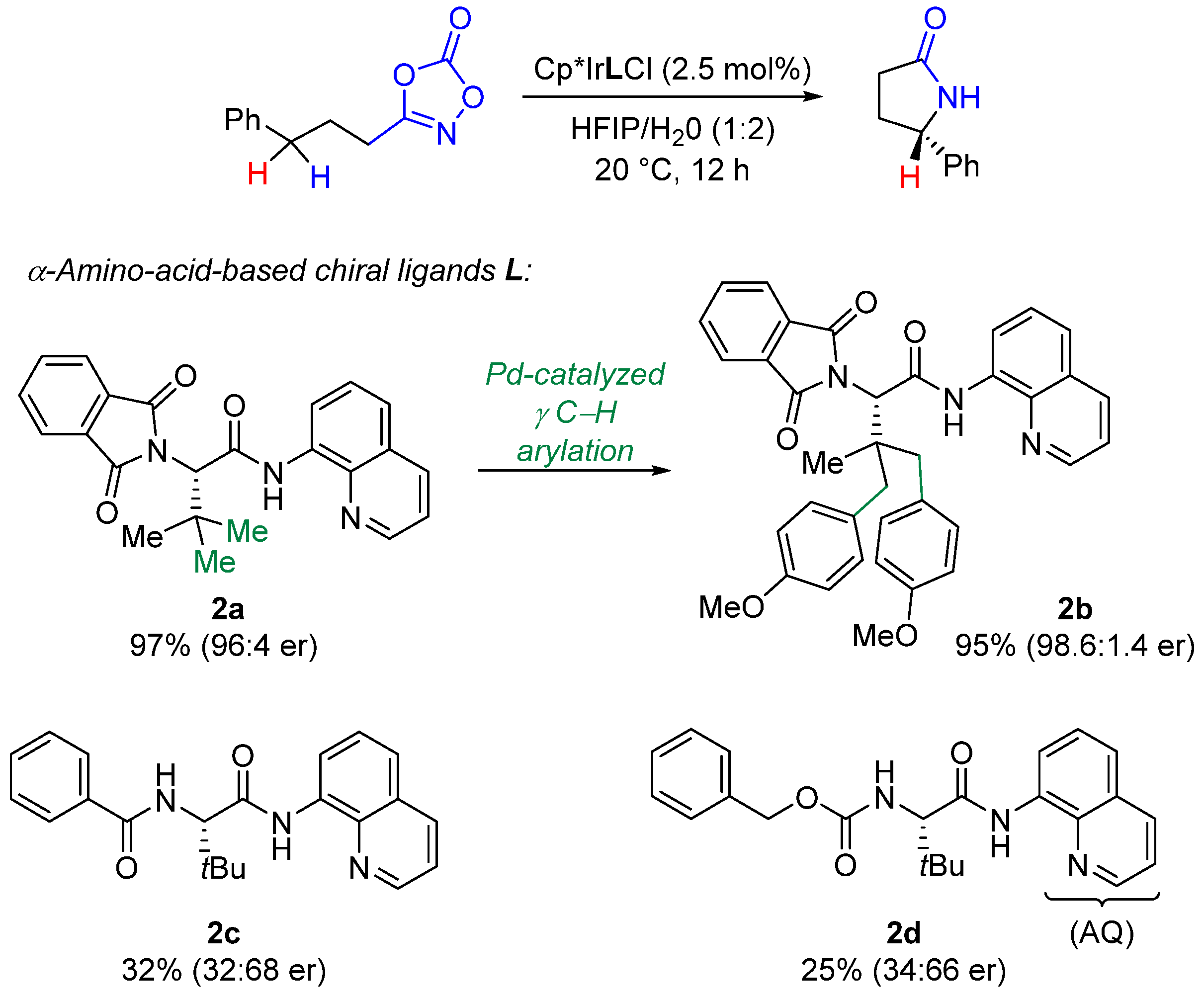
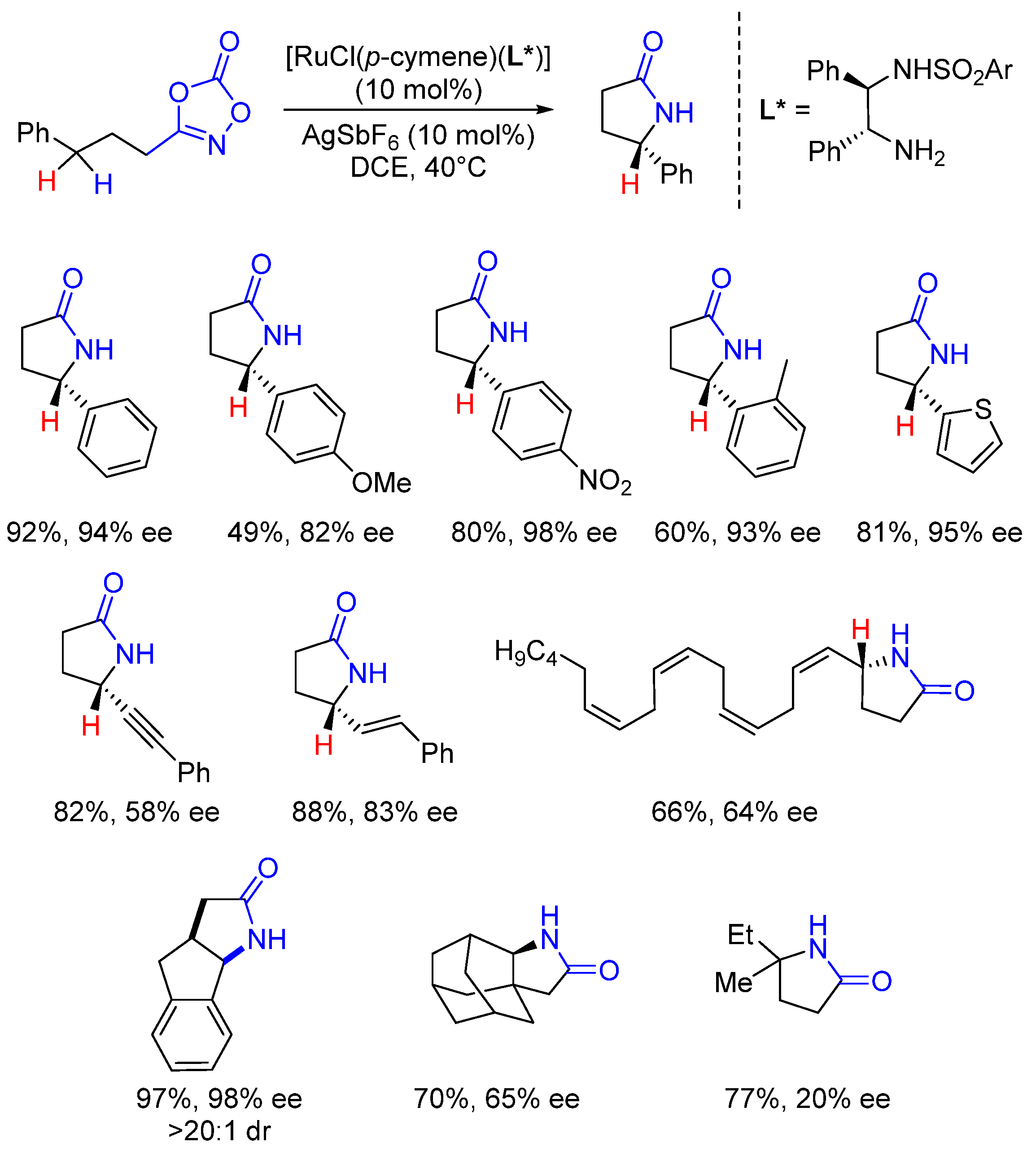
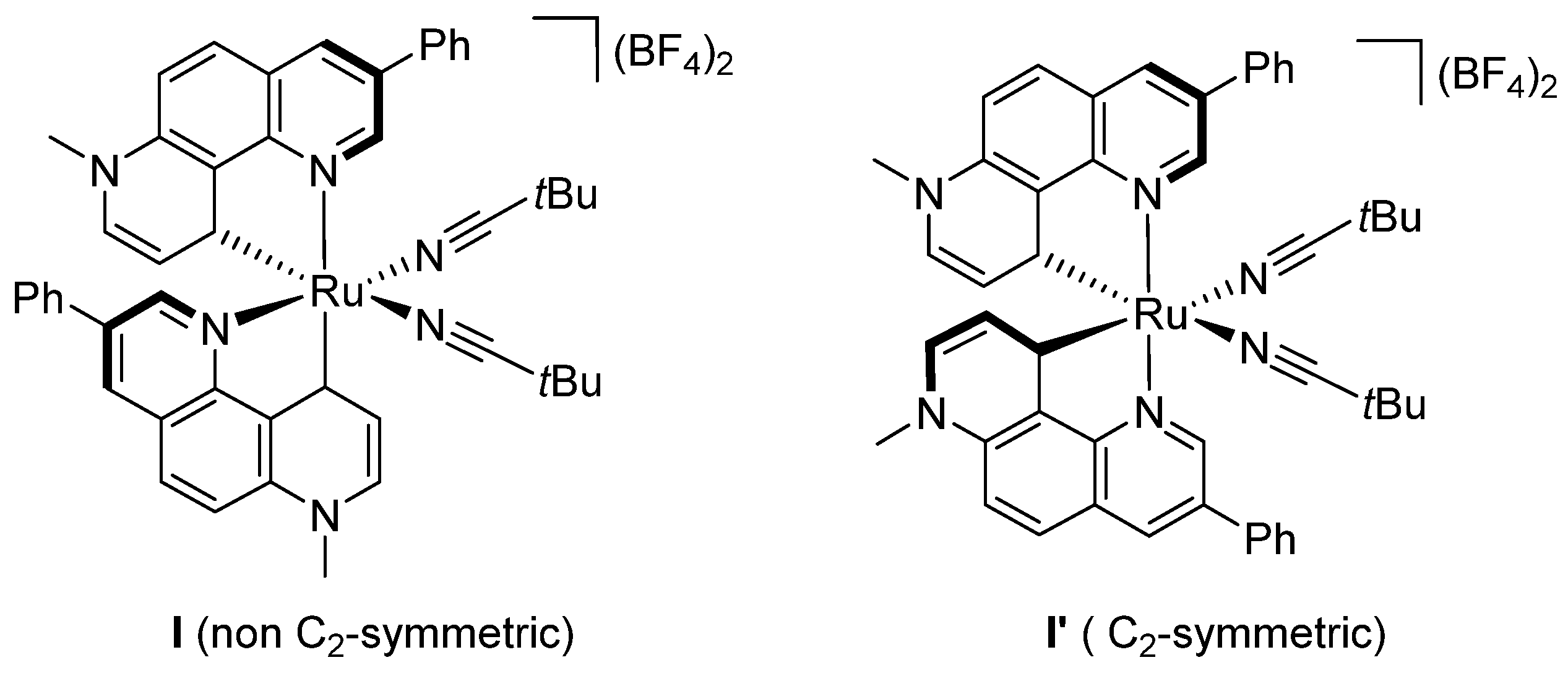
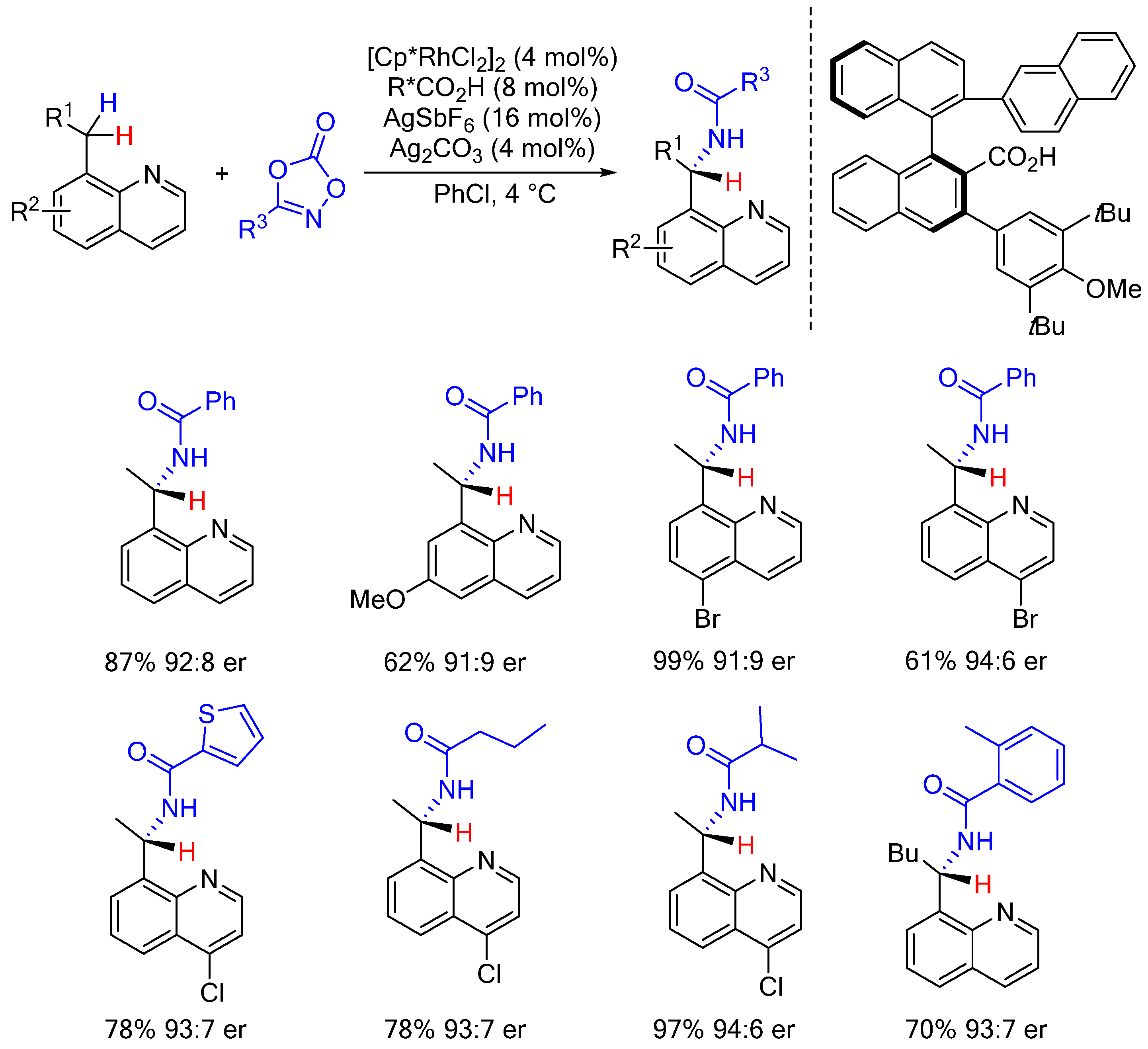
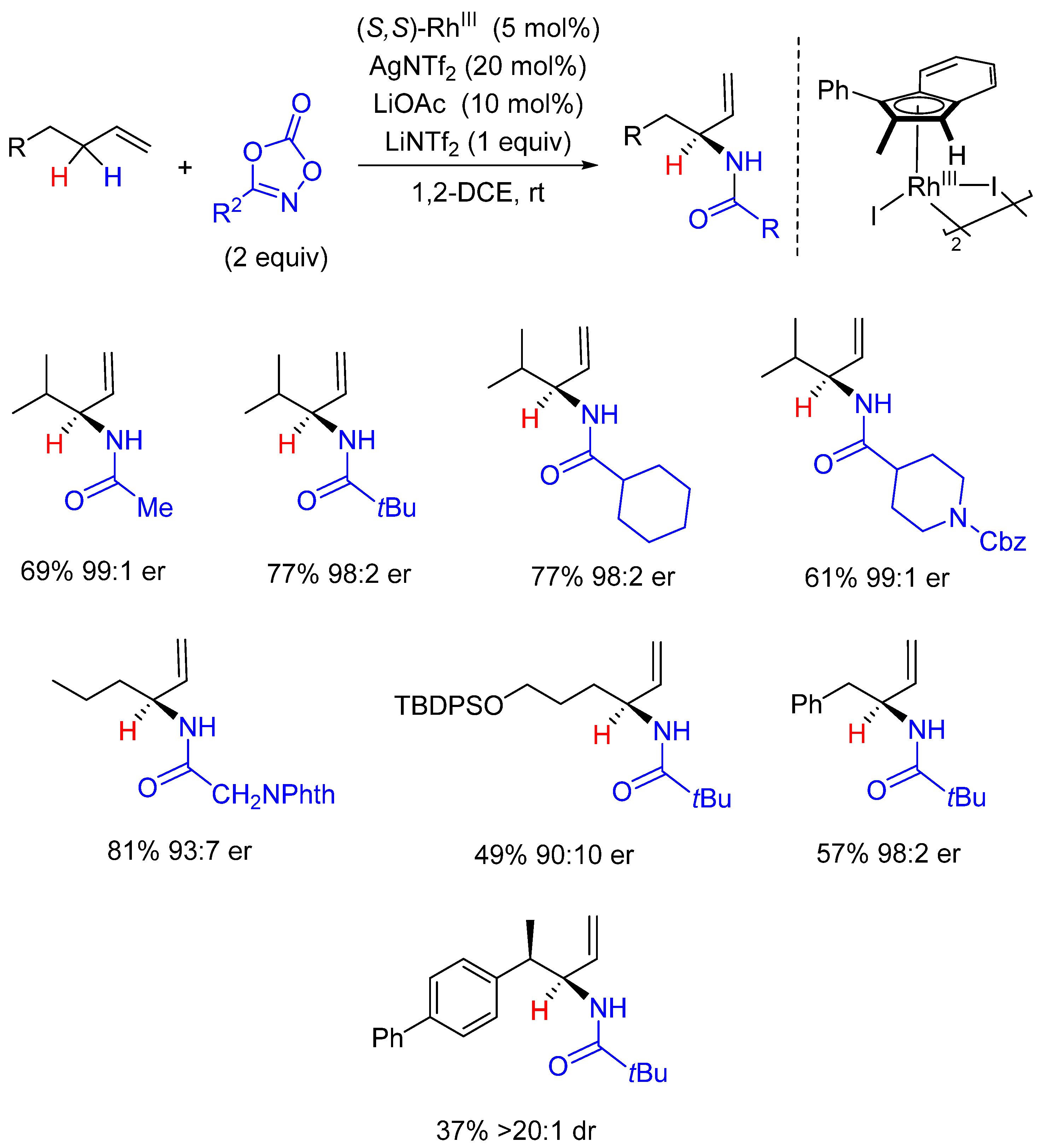
2. Enantioselective C(sp3)-H Amidations
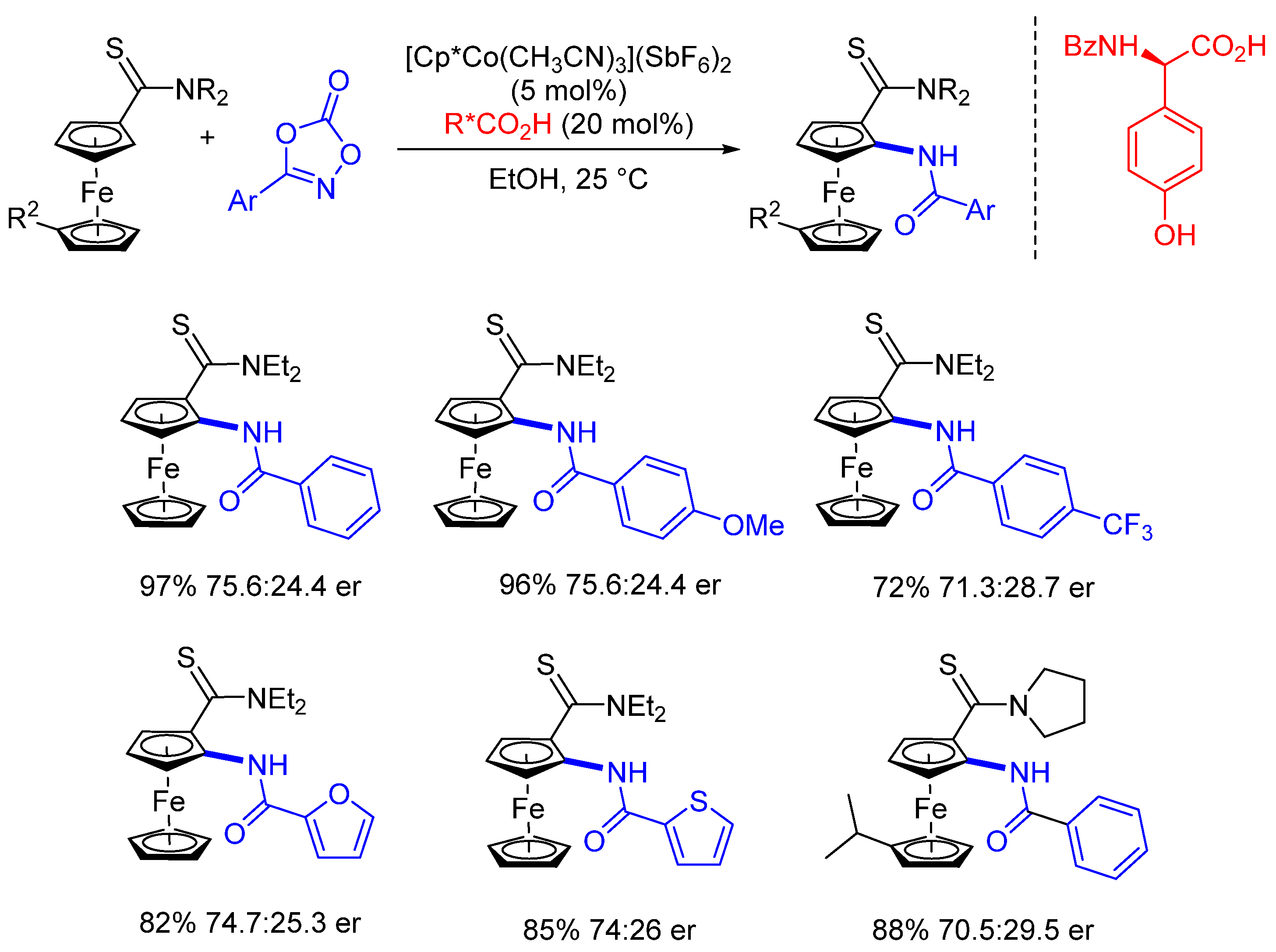
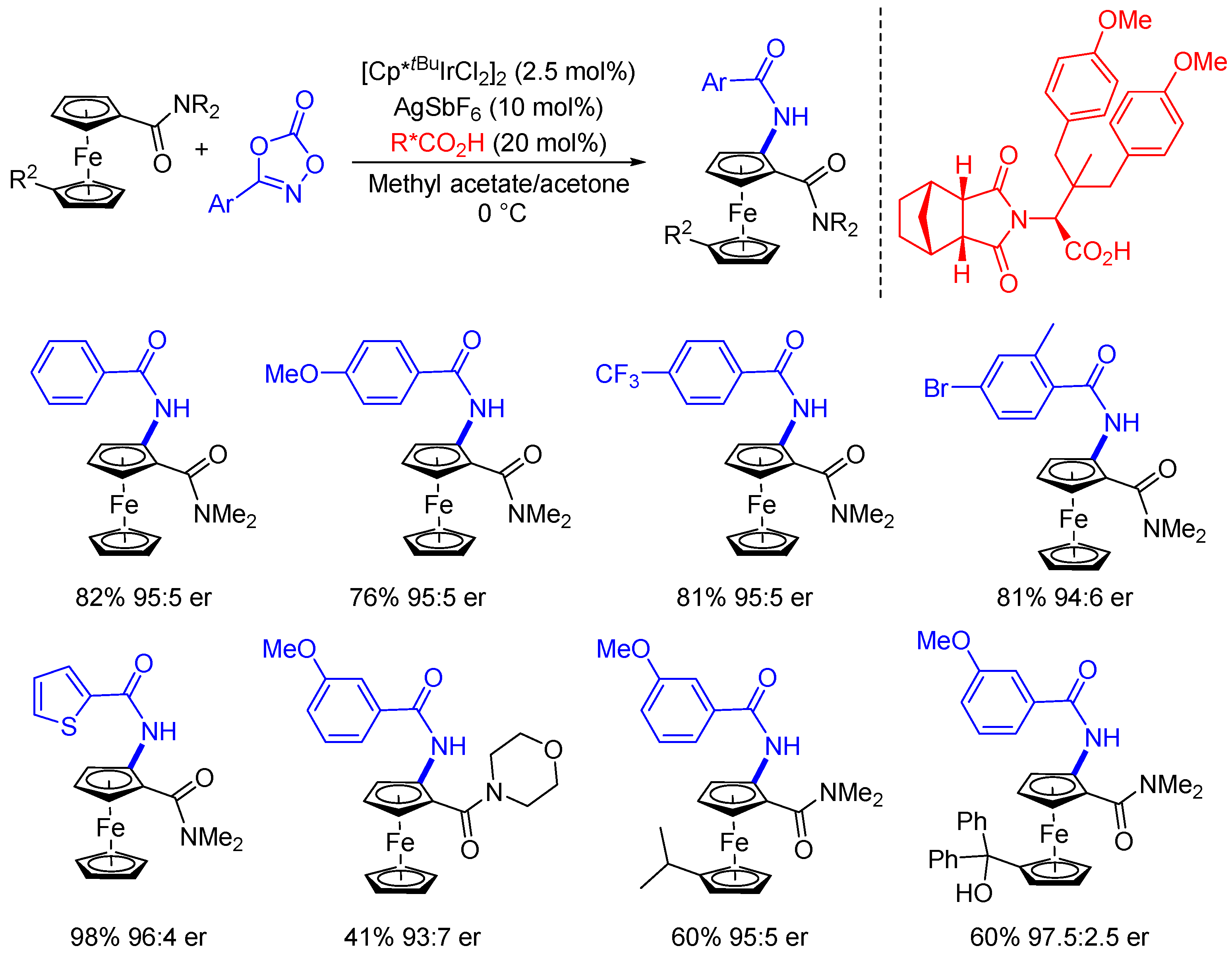
3. Enantioselective C(sp2)-H Amidations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Greenberg, A.; Breneman, C.M.; Liebman, J.F. The Amide Linkage: Structural Significance in Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Materials Science; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, P.; Sharma, A. Synthesis and Biological Importance of Amide Analogues. J. Pharmacol. Med. Chem. 2018, 2, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- de Figueiredo, R.M.; Suppo, J.-S.; Campagne, J.-M. Nonclassical Routes for Amide Bond Formation. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12029–12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Porras, A.; Gamba-Sánchez, D. Recent Developments in Amide Synthesis Using Nonactivated Starting Materials. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11548–11555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Park, K.T.; Kim, J.G.; Chang, S. Mechanistic Studies on the Rh(III)-Mediated Amido Transfer Process Leading to Robust C-H Amination with a New Type of Amidating Reagent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4534–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Jee, S.; Kim, J.G.; Chang, S. Study of Sustainability and Scalability in the Cp*Rh(III)-Catalyzed Direct C-H Amidation with 1,4,2-Dioxazol-5-Ones. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For a recent focus on dioxazolones, see: Van Vliet, K.M.; De Bruin, B. Dioxazolones: Stable Substrates for the Catalytic Transfer of Acyl Nitrenes. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 4751–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For an early example of C-H amidation using stoechiometric [O]: Tsang, W.C.P.; Zheng, N.; Buchwald, S.L. Combined C-H Functionalization/C-N Bond Formation Route to Carbazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14560–14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- For an early example of C-H amidation using stoechiometric [O]: Mei, T.S.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.Q. Pd(II)-Catalyzed Amination of C-H Bonds Using Single-Electron or Two-Electron Oxidants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10806–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Chang, S. Comparative Catalytic Activity of Group 9 [CpMIII] Complexes: Cobalt-Catalyzed C-H Amidation of Arenes with Dioxazolones as Amidating Reagents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14103–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, J.; Chang, S. Highly Robust Iron Catalyst System for Intramolecular C(sp3)−H Amidation Leading to γ-Lactams. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2909–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kwak, J.; Shin, K.; Ryu, J.; Park, Y.; Chang, S. Amination Reaction Using Azides as the Nitrogen Source. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.S.; Laffan, D.; Thomson, C.; Williams, M.T. Analysis of the Reactions Used for the Preparation of Drug Candidate Molecules. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughley, S.D.; Jordan, A.M. The Medicinal Chemist’s Toolbox: An Analysis of Reactions Used in the Pursuit of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3451–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
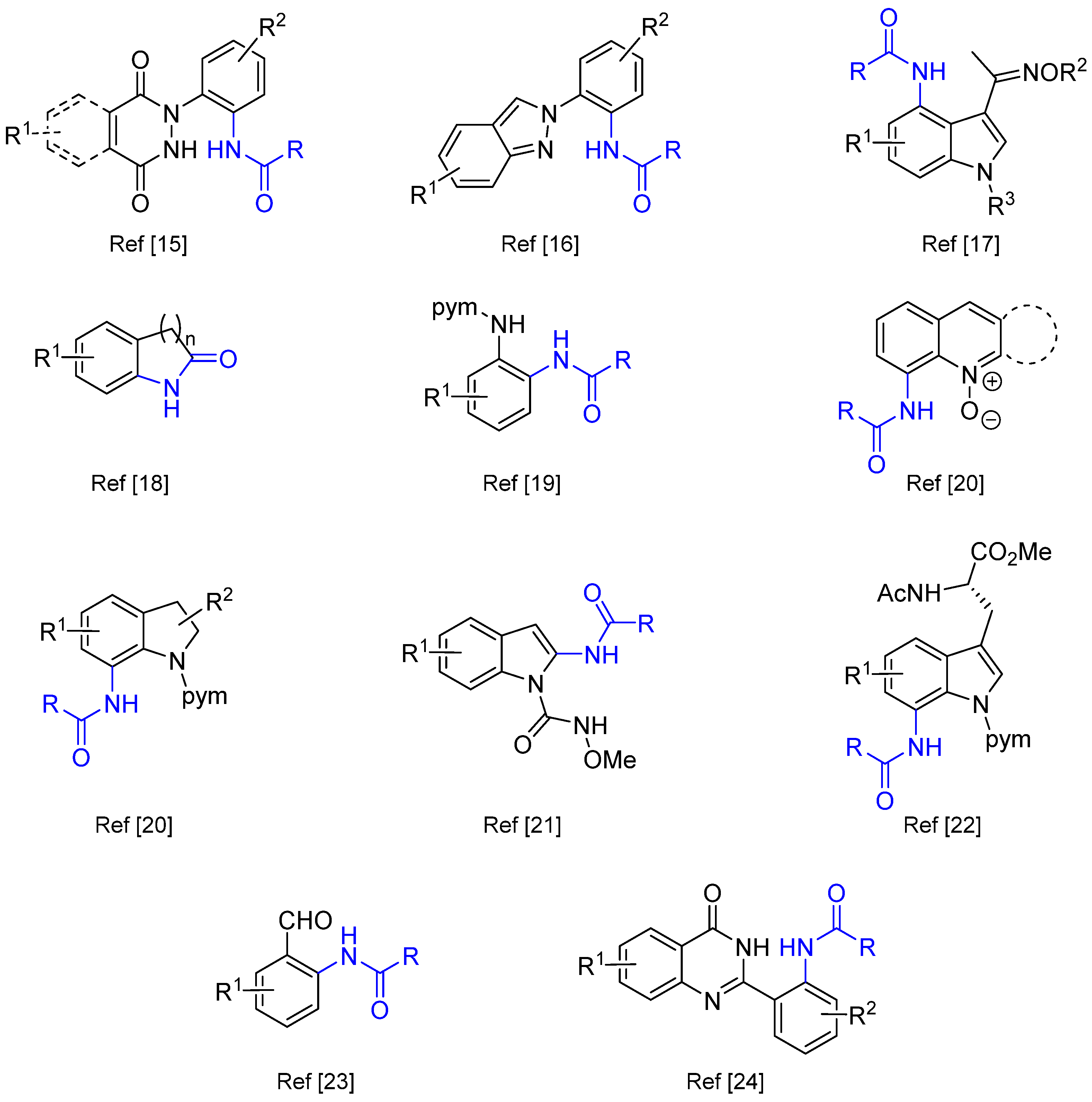
- Jeoung, D.; Kim, K.; Han, S.H.; Ghosh, P.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.; An, W.; Kim, H.S.; Mishra, N.K.; Kim, I.S. Phthalazinone-Assisted C–H Amidation Using Dioxazolones Under Rh(III) Catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 7014–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Samanta, S.; Hajra, A. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Ortho-C–H Amidation of 2-Arylindazoles with a Dioxazolone as an Amidating Reagent. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.-B.; Fu, X.-P.; Wu, G.-R.; Zhang, L.-L.; Deng, K.-Z.; Yang, J.-Y.; Xia, C.-C.; Ji, Y.-F. Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed C4-Amidation of Indole-Oximes with Dioxazolones via C–H Activation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 7922–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Li, X.; Duan, S.; Du, Y.; Liu, T.; Fang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Yang, X. Room Temperature Benzofused Lactam Synthesis Enabled by Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed C(sp2)−H Amidation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khake, S.M.; Chatani, N. The Direct Rh(III)-Catalyzed C–H Amidation of Aniline Derivatives Using a Pyrimidine Directing Group: The Selective Solvent Controlled Synthesis of 1,2-Diaminobenzenes and Benzimidazoles. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3655–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.K.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, I.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, U. Co(III)-Catalyzed C–H Amidation of Nitrogen-Containing Heterocycles with Dioxazolones under Mild Conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 9244–9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Lonka, M.R.; Zou, H. Chameleon-like Behavior of the Directing Group in the Rh(III)-Catalyzed Regioselective C–H Amidation of Indole: An Experimental and Computational Study. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10233–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Kuniyil, R.; Kopp, A.; Nascimento Lima, R.; Ackermann, L. Peptide Late-Stage Diversifications by Rhodium-Catalyzed Tryptophan C7 Amidation. Chem 2020, 6, 3428–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ding, J.; Ding, T.-M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sha, F.; Zhang, F.-Y.; Wu, X.-Y.; Li, Q. Cobalt-Catalyzed Ortho-C(sp2)–H Amidation of Benzaldehydes with Dioxazolones Using Transient Directing Groups. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 7342–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeoung, D.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Ghosh, P.; Mishra, N.K.; Hong, S.; Kim, I.S. Site-Selective C–H Amidation of 2-Aryl Quinazolinones Using Nitrene Surrogates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 7134–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
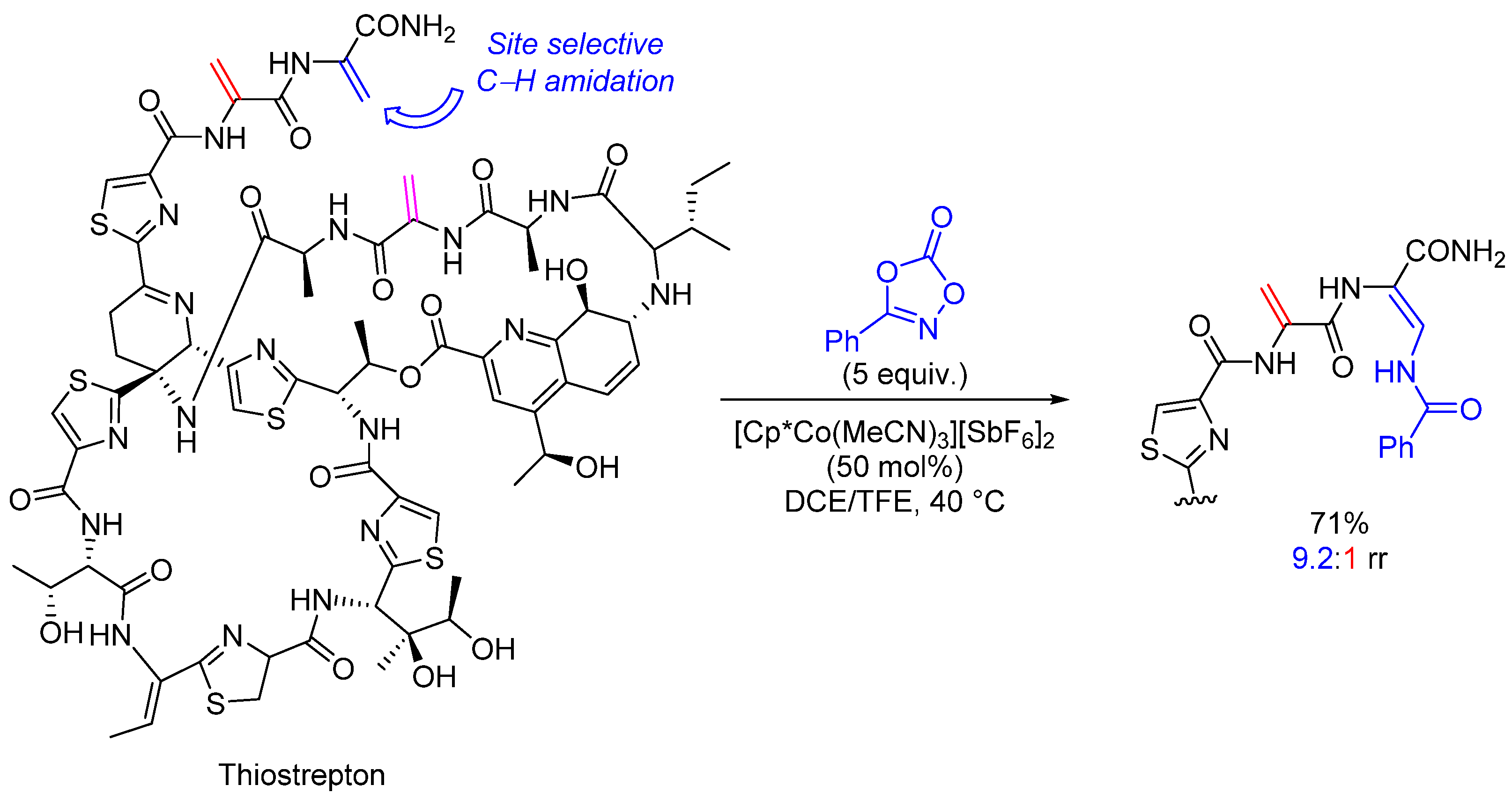
- Scamp, R.J.; deRamon, E.; Paulson, E.K.; Miller, S.J.; Ellman, J.A. Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed C−H Amidation of Dehydroalanine for the Site-Selective Structural Diversification of Thiostrepton. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
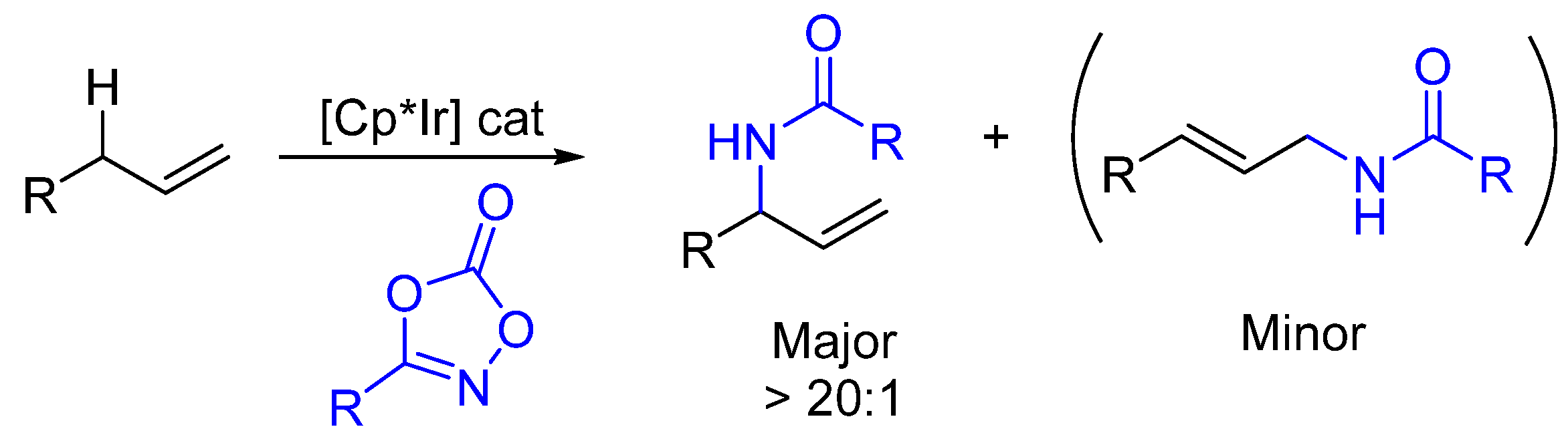
- Lei, H.; Rovis, T. Ir-Catalyzed Intermolecular Branch-Selective Allylic C-H Amidation of Unactivated Terminal Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2268–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knecht, T.; Mondal, S.; Ye, J.; Das, M.; Glorius, F. Intermolecular, Branch-Selective, and Redox-Neutral Cp*Ir III -Catalyzed Allylic C−H Amidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7117–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burman, J.S.; Harris, R.J.; Farr, C.M.B.; Bacsa, J.; Blakey, S.B. Rh(III) and Ir(III)Cp∗ Complexes Provide Complementary Regioselectivity Profiles in Intermolecular Allylic C-H Amidation Reactions. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 5474–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For a recent catalytic metal-free allylic C−H sulfonamidation strategy, see: Teh, W.P.; Obenschain, D.C.; Black, B.M.; Michael, F.E. Catalytic Metal-Free Allylic C−H Amination of Terpenoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16716–16722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak, Ł.; Tan, J.F.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Madron Du Vigné, A.; Smal, V.; Cao, Y.X.; Cramer, N. Catalytic Enantioselective Functionalizations of C-H Bonds by Chiral Iridium Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10516–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanourakis, A.; Docherty, P.J.; Chuentragool, P.; Phipps, R.J. Recent Developments in Enantioselective Transition Metal Catalysis Featuring Attractive Noncovalent Interactions between Ligand and Substrate. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 10672–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Satake, S.; Matsunaga, S. Diverse Approaches for Enantioselective C−H Functionalization Reactions Using Group 9 CpxMIII Catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 7346–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Gu, Z.Y.; Xia, J.B. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Intermolecular C-H Carbonylation toward Amides. Synlett 2021, 32, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Arnold, F.H. Navigating the Unnatural Reaction Space: Directed Evolution of Heme Proteins for Selective Carbene and Nitrene Transfer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Bang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ackermann, L. Manganese(I)-Catalyzed C-H Aminocarbonylation of Heteroarenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14137–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.W.; Han, H.; Li, Y.L.; Wu, X.; Bao, X.; Gu, Z.Y.; Xia, J.B. Intermolecular C−H Amidation of (Hetero)Arenes to Produce Amides through Rhodium-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Nitrene Intermediates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8887–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Dieckmann, M.; Cramer, N. Cooperative Effects between Chiral Cpx–Iridium(III) Catalysts and Chiral Carboxylic Acids in Enantioselective C−H Amidations of Phosphine Oxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15088–15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cramer, N. Enantioselective Synthesis of Chiral-at-Sulfur 1,2-Benzothiazines by CpxRhIII-Catalyzed C−H Functionalization of Sulfoximines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15539–15543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Engl, O.D.; Bandar, J.S.; Chant, E.D.; Buchwald, S.L. CuH-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydroamidation of Vinylarenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6672–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Katsuki, T. Asymmetric Nitrene Transfer Reactions: Sulfimidation, Aziridination and C-H Amination Using Azide Compounds as Nitrene Precursors. Chem. Rec. 2014, 14, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qu, J.; Chen, Y. Quinim: A New Ligand Scaffold Enables Nickel-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of α-Alkylated γ-Lactam. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15654–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Zerull, E.E.; Roberts, J.M.; Huang, M.; Guzei, I.A.; Schomaker, J.M. Silver-Catalyzed Enantioselective Propargylic C–H Bond Amination through Rational Ligand Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12930–12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Tian, Y.; Meng, X.; Gu, Q.S.; Liu, X.Y. Enantioselective Copper(I)/Chiral Phosphoric Acid Catalyzed Intramolecular Amination of Allylic and Benzylic C−H Bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, I.S.; Ta, A.N.; Danneman, M.W.; Semakul, N.; Burns, M.; Basch, C.H.; Dippon, V.N.; McNaughton, B.R.; Rovis, T. Asymmetric δ-Lactam Synthesis with a Monomeric Streptavidin Artificial Metalloenzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4815–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enantioselective C-H amidations have been, in part, covered in the following recent review: Woźniak, Ł.; Tan, J.F.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Madron Du Vigné, A.; Smal, V.; Cao, Y.X.; Cramer, N. Catalytic Enantioselective Functionalizations of C-H Bonds by Chiral Iridium Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10516–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enantioselective C-H amidations have been, in part, covered in the following recent review: Fanourakis, A.; Docherty, P.J.; Chuentragool, P.; Phipps, R.J. Recent Developments in Enantioselective Transition Metal Catalysis Featuring Attractive Noncovalent Interactions between Ligand and Substrate. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 10672–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enantioselective C-H amidations have been, in part, covered in the following recent review: Yoshino, T.; Satake, S.; Matsunaga, S. Diverse Approaches for Enantioselective C−H Functionalization Reactions Using Group 9 CpxMIII Catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 7346–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enantioselective C-H amidations have been, in part, covered in the following recent review: Hayashi, H.; Uchida, T. Nitrene Transfer Reactions for Asymmetric C–H Amination: Recent Development. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
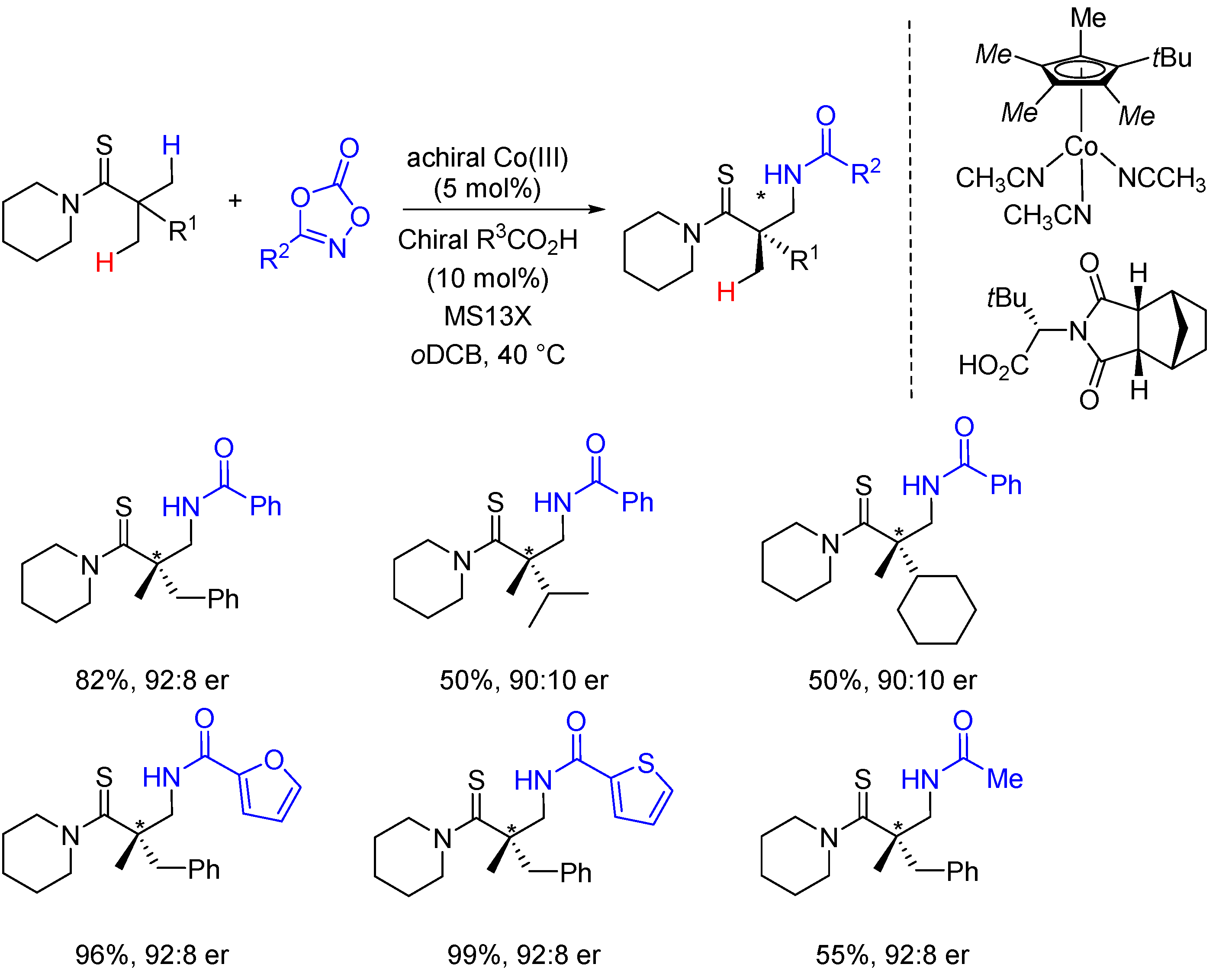
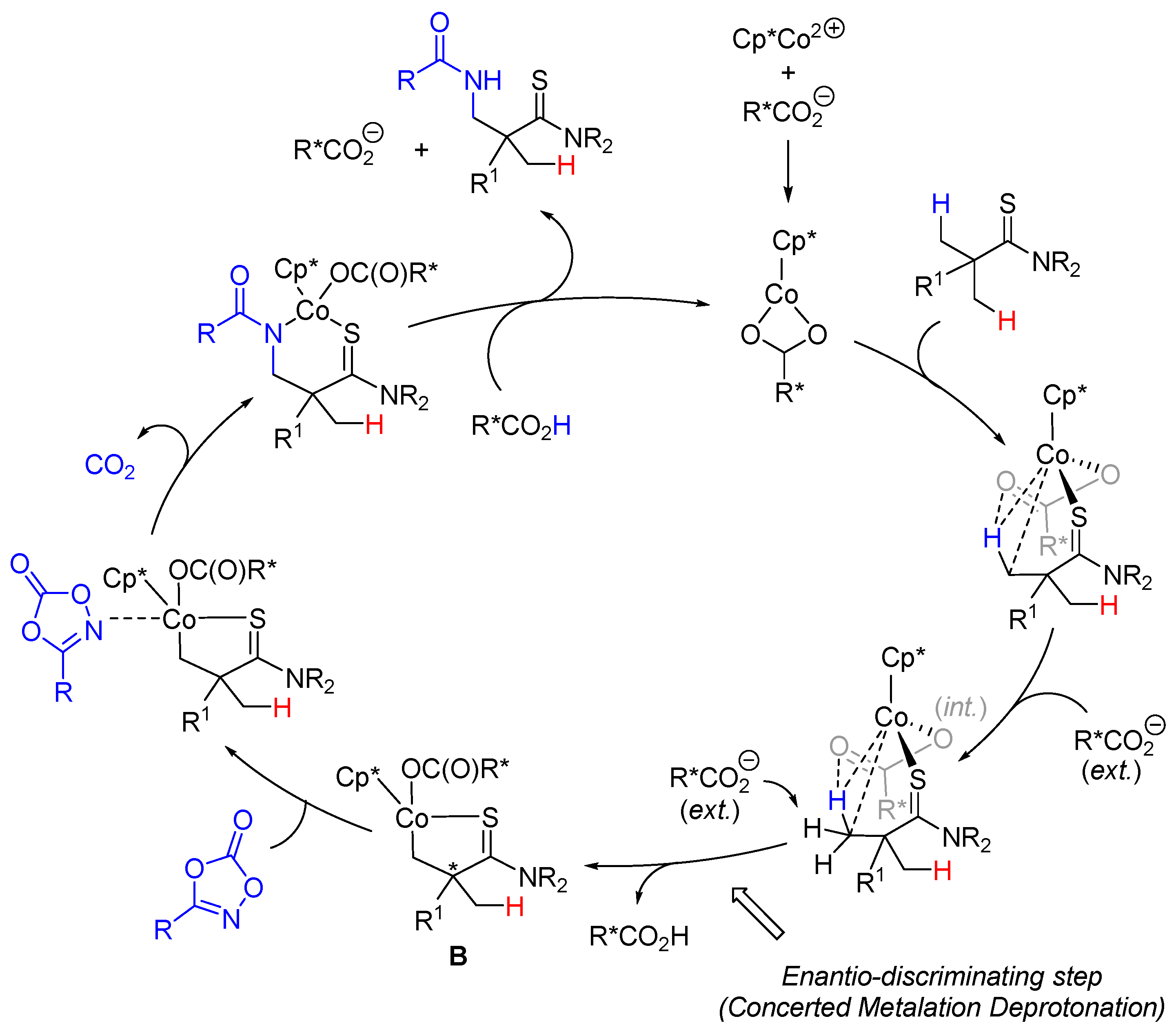
- Fukagawa, S.; Kato, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Kojima, M.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S. Enantioselective C(sp3)–H Amidation of Thioamides Catalyzed by a Cobalt III/Chiral Carboxylic Acid Hybrid System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, D.; Ikeda, K.; Fukagawa, S.; Kojima, M.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S. Chiral 2-Aryl Ferrocene Carboxylic Acids for the Catalytic Asymmetric C(sp3)-H Activation of Thioamides. Organometallics 2019, 38, 3970–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For a racemic version of this reaction, see: Tan, P.W.; Mak, A.M.; Sullivan, M.B.; Dixon, D.J.; Seayad, J. Thioamide-Directed Cobalt(III)-Catalyzed Selective Amidation of C(sp3)-H Bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16550–16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papers have been submitted in 24 October 2018 and in 5 November 2018 respectively.
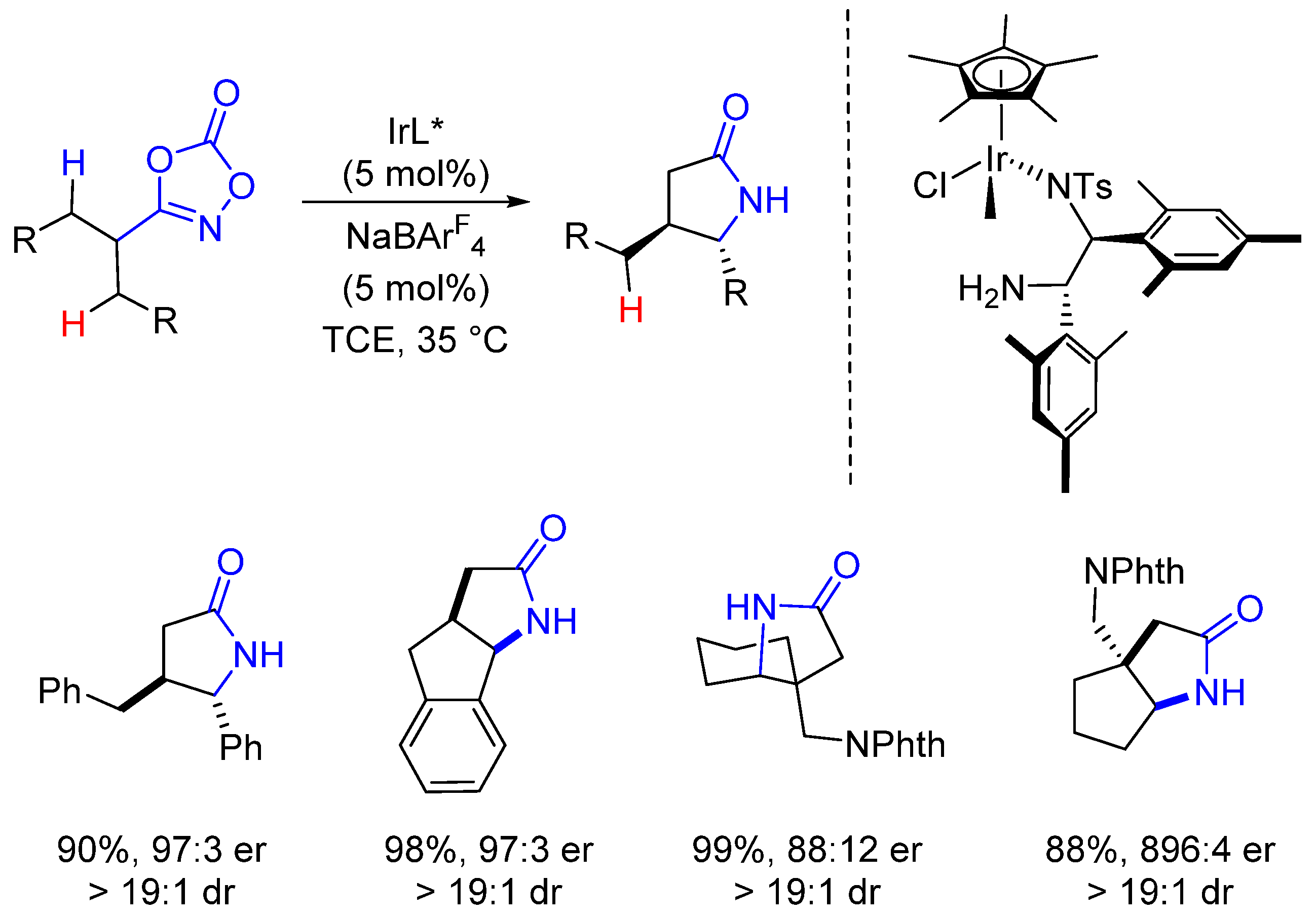
- Park, Y.; Chang, S. Asymmetric Formation of γ-Lactams via C–H Amidation Enabled by Chiral Hydrogen-Bond-Donor Catalysts. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.D.; Ye, L.W. Chiral γ-lactam synthesis via asymmetric C–H amidation. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Park, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Baik, M.H.; Chang, S. Selective Formation of γ-Lactams via C-H Amidation Enabled by Tailored Iridium Catalysts. Science 2018, 359, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Park, Y.; Bai, Z.; Chang, S.; He, G.; Chen, G. Iridium-Catalyzed Enantioselective C(sp3)-H Amidation Controlled by Attractive Noncovalent Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7194–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Chan, C.M.; Yeung, Y.W.; Yu, W.Y. Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Enantioselective γ-Lactams Formation by Intramolecular C-H Amidation of 1,4,2-Dioxazol-5-Ones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3849–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Winterling, E.; Tan, Y.; Hemming, M.; Harms, K.; Houk, K.N.; Meggers, E. Non- C2-Symmetric Chiral-at-Ruthenium Catalyst for Highly Efficient Enantioselective Intramolecular C(sp3)-H Amidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19048–19057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See also: Zhou, Z.; Tan, Y.; Yamahira, T.; Ivlev, S.; Xie, X.; Riedel, R.; Hemming, M.; Kimura, M.; Meggers, E. Enantioselective Ring-Closing C–H Amination of Urea Derivatives. Chem 2020, 6, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukagawa, S.; Kojima, M.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S. Catalytic Enantioselective Methylene C(sp3)-H Amidation of 8-Alkylquinolines Using a Cp*RhIII/Chiral Carboxylic Acid System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18154–18158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, C.M.B.; Kazerouni, A.M.; Park, B.; Poff, C.D.; Won, J.; Sharp, K.R.; Baik, M.H.; Blakey, S.B. Designing a Planar Chiral Rhodium Indenyl Catalyst for Regio- And Enantioselective Allylic C-H Amidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 13996–14004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obtained by chiral HPLC resolution of Rh(I)-COD mixture of enantiomers.
- For a recent review, see: Zu, B.; Guo, Y.; Ke, J.; He, C. Transient- and Native-Directing-Group-Enabled Enantioselective C–H Functionalization. Synthesis 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, P.X.; Yao, Q.J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Huang, D.Y.; Le, M.D.; Song, H.; Liu, L.; Shi, B.F. Cp*Co(III)/MPAA-Catalyzed Enantioselective Amidation of Ferrocenes Directed by Thioamides under Mild Conditions. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, L.S.; Shi, B.F. Achiral CpxIr(III)/Chiral Carboxylic Acid Catalyzed Enantioselective C-H Amidation of Ferrocenes under Mild Conditions. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7117–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Zhu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, N.; Ke, J.; Yu, P.; He, C. Dual-Ligand-Enabled Ir(III)-Catalyzed Enantioselective C-H Amidation for the Synthesis of Chiral Sulfoxides. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7207–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See also: Diesel, J.; Cramer, N. Generation of Heteroatom Stereocenters by Enantioselective C-H Functionalization. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9164–9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Sen, C.; Suresh, E.; Panda, A.B.; Ghosh, S.C. C–H Amidation and Amination of Arenes and Heteroarenes with Amide and Amine Using Cu-MnO as a Reusable Catalyst under Mild Conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 3261–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, B. Rh(III)-Catalyzed Tandem Annulative Redox-Neutral Arylation/Amidation of Aromatic Tethered Alkenes. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 12124–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





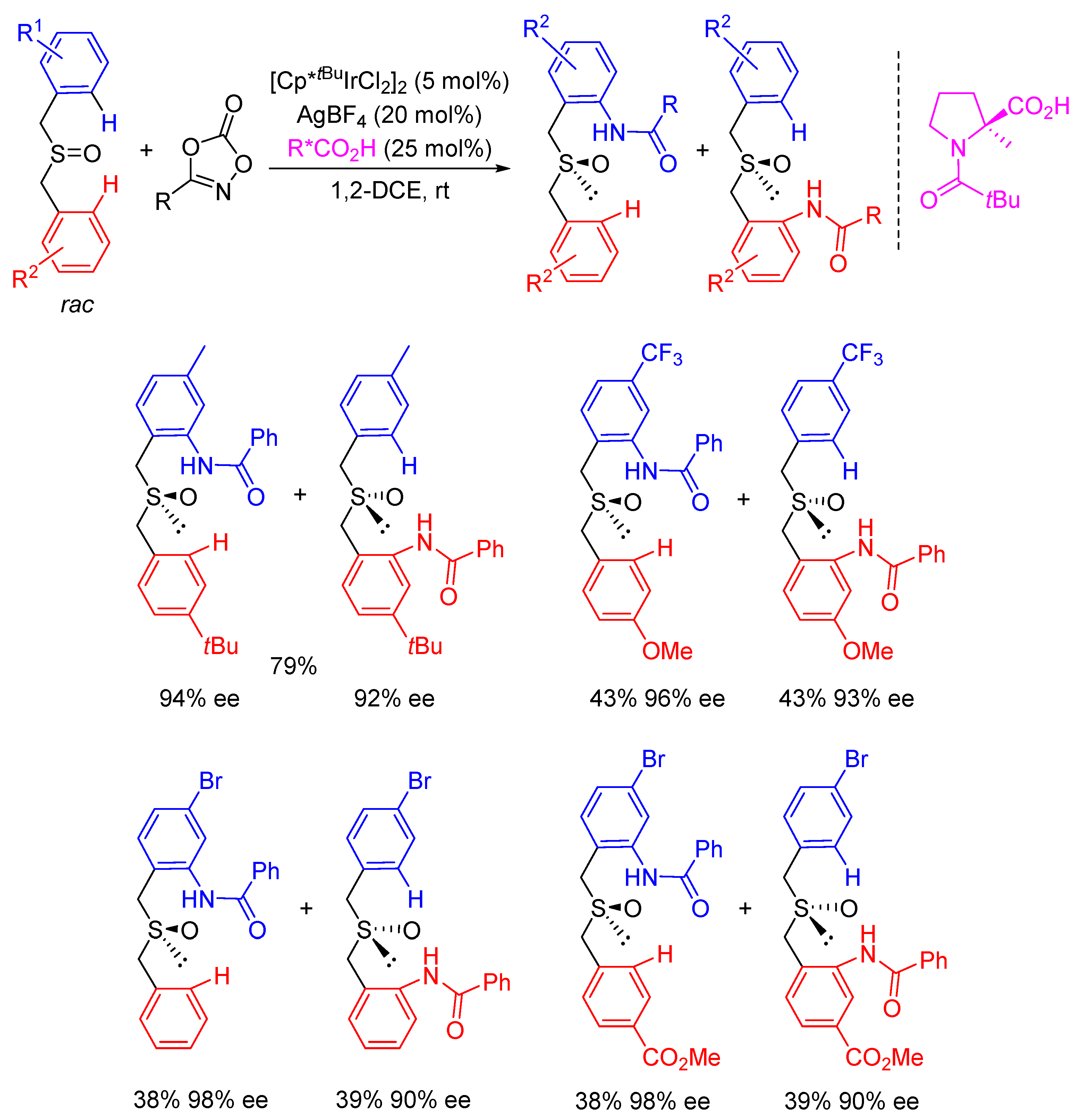
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tosi, E.; de Figueiredo, R.M.; Campagne, J.-M. Enantioselective Catalytic C-H Amidations: An Highlight. Catalysts 2021, 11, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040471
Tosi E, de Figueiredo RM, Campagne J-M. Enantioselective Catalytic C-H Amidations: An Highlight. Catalysts. 2021; 11(4):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040471
Chicago/Turabian StyleTosi, Eleonora, Renata Marcia de Figueiredo, and Jean-Marc Campagne. 2021. "Enantioselective Catalytic C-H Amidations: An Highlight" Catalysts 11, no. 4: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040471
APA StyleTosi, E., de Figueiredo, R. M., & Campagne, J.-M. (2021). Enantioselective Catalytic C-H Amidations: An Highlight. Catalysts, 11(4), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040471