Magnetite-Based Catalyst in the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation for Different Aqueous Matrices Spiked with Naproxen–Diclofenac Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
2.2. Screening of the Magnetic Catalyst by CWPO
2.3. Optimization of NAP–DCF Removal by CWPO with a Magnetic Catalyst
2.4. Influence of the Operating Parameters: Response Surface Methodology
2.4.1. The Combined Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Dose and pH on the Removal of DCF and NAP
2.4.2. Effect of Temperature on pH and Synergistic Effect of NAP and DCF
2.5. Catalyst Stability
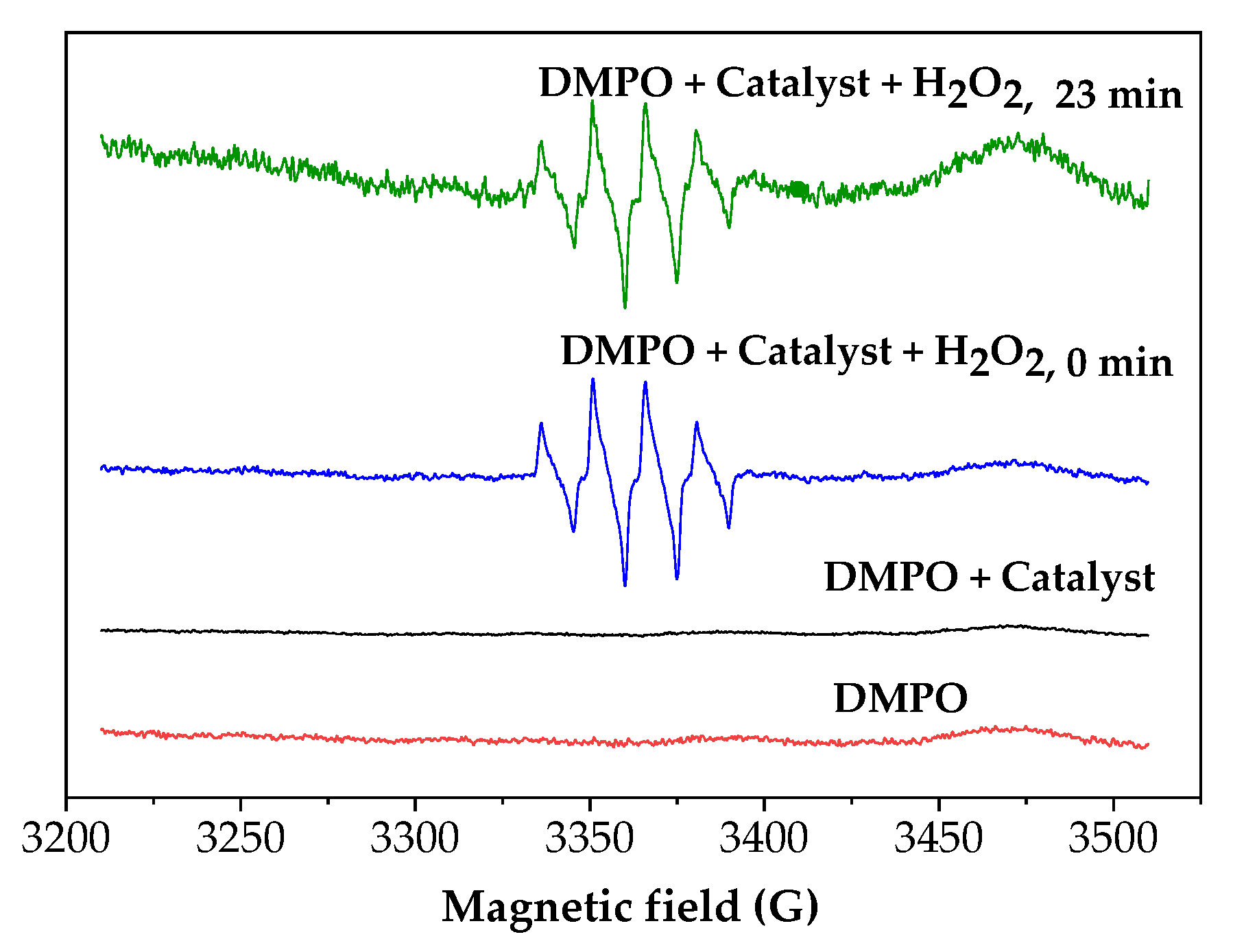
2.6. H2O2 Activation on Fe3O4/MWCNTs
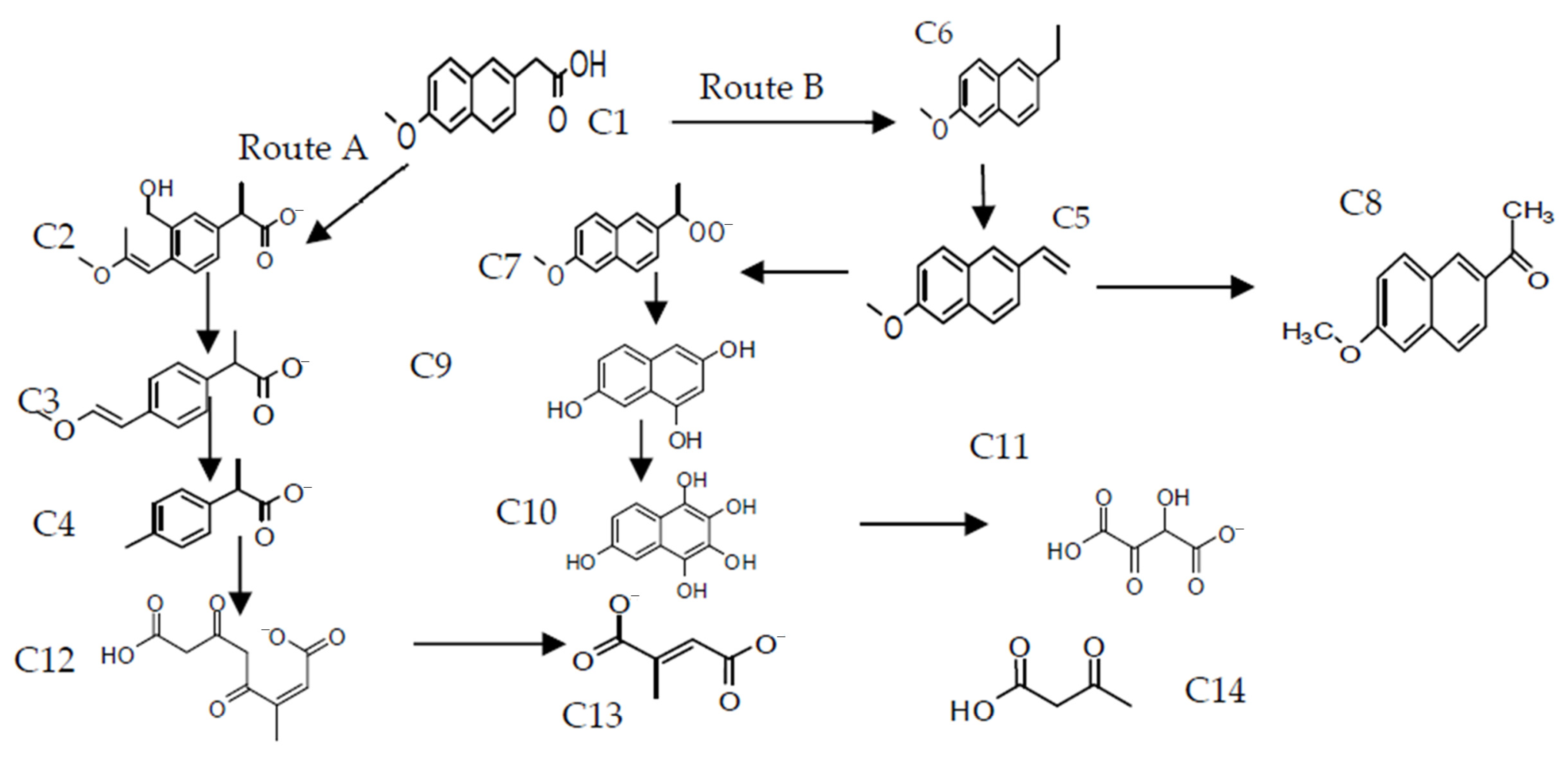
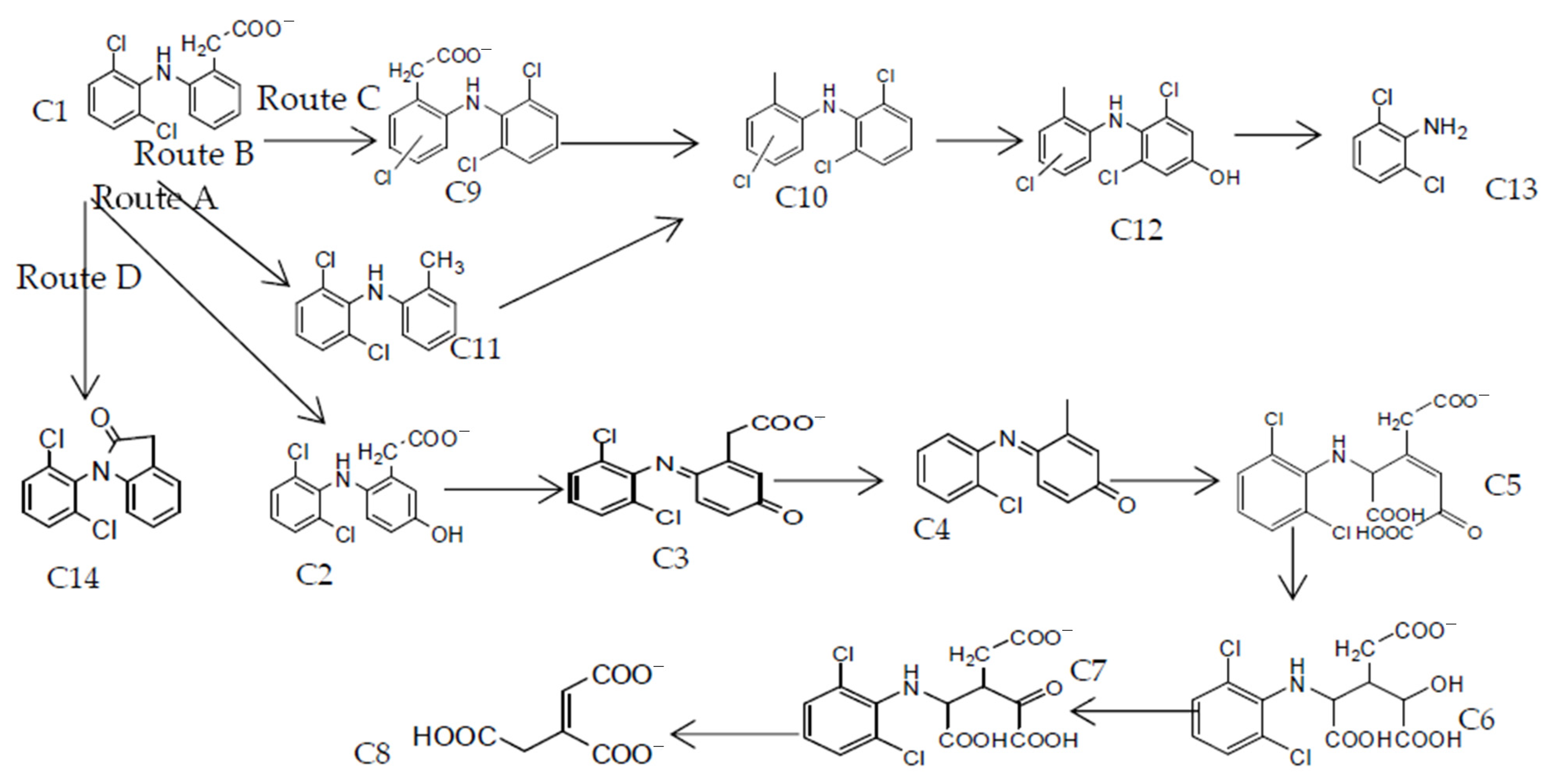
2.7. Proposed Reaction Mechanisms for the Degradation of DCF and NAP by CWPO
2.8. Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation Treatment of Different Real Water Matrices
Effluent Disinfection by CWPO
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of the Catalyst
3.2.1. Functionalization of MWCNTs and Preparation of the Catalyst (Fe3O4/MWCNTs)
3.2.2. Support and Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation Tests
3.4. Statistical Analysis through Response Surface Methodology: Box–Behnken Design
3.5. Analytical Methods
3.6. Microbiological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebele, A.J.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Harrad, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Botero-Coy, A.M.; Moncayo-Lasso, A.; Hernández, F.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Effective elimination of fifteen relevant pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater from Colombia by combination of a biological system with a sonochemical process. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.; Lapworth, D.J.; Civil, W.; Williams, P. Tracking changes in the occurrence and source of pharmaceuticals within the River Thames, UK; from source to sea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier-Larabie, S.; Segura, P.; Gagnon, C. Degradation of the pharmaceuticals diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole and their transformation products under controlled environmental conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashfaq, M.; Noor, N.; Saif-Ur-Rehman, M.; Sun, Q.; Mustafa, G.; Nazar, M.F.; Yu, C.-P. Determination of commonly used pharmaceuticals in hospital waste of pakistan and evaluation of their ecological risk assessment. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2017, 45, 1500392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleuvers, M. Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Nie, E.; Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Cooper, W.J.; Song, W. Degradation of diclofenac by advanced oxidation and reduction processes: Kinetic studies, degradation pathways and toxicity assessments. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, C.; Marchão, L.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Application of advanced oxidation processes for the treatment of recalcitrant agro-industrial wastewater: A review. Water 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaccallo-Aguilar, Y.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Larriba, M.; Águeda, V.; Delgado, J.; Ovejero, G.; Peres, J.; García, J. Naproxen removal by CWPO with Fe3O4/multi-walled carbon nanotubes in a fixed-bed reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaccallo-Aguilar, Y.; de Tuesta, J.D.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Gomes, H.; Larriba, M.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. New insights on the removal of diclofenac and ibuprofen by CWPO using a magnetite-based catalyst in an up-flow fixed-bed reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, K.; Guo, Z.; Yang, T.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xi, M. Heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of tetracyclines using porous magnetic chitosan microspheres as an efficient catalyst compared with two preparation methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, S.A.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Gomes, H.T.; Jorfi, S.; Ahmadi, M. Magnetic titanium/carbon nanotube nanocomposite catalyst for oxidative degradation of Bisphenol A from high saline polycarbonate plant effluent using catalytic wet peroxide oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; Mackay, A. Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulova, N.; Trapido, M.; Dulov, A. Catalytic degradation of picric acid by heterogeneous Fenton-based processes. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomul, F.; Arslan, Y.; Başoğlu, F.T.; Babuçcuoğlu, Y.; Tran, H.N. Efficient removal of anti-inflammatory from solution by Fe-containing activated carbon: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Dhakal, D.; Lee, S.W. Rapid degradation of naproxen by AgBr-α-NiMoO4 composite photocatalyst in visible light: Mechanism and pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzen, M.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Shariatifar, N.; Ahmadloo, M.; Eş, I.; Baghani, A.N.; Yousefinejad, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Azari, A.; Dobaradaran, S.; et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified with iron oxide and silver nanoparticles (MWCNT-Fe3O4/Ag) as a novel adsorbent for determining PAEs in carbonated soft drinks using magnetic SPE-GC/MS method. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Sun, C. The optimization, kinetics and mechanism of m-cresol degradation via catalytic wet peroxide oxidation with sludge-derived carbon catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, D. Efficient removal of atrazine in water with a Fe3O4/MWCNTs nanocomposite as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46059–46066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cai, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L. Effects of water matrices on the degradation of naproxen by reactive radicals in the UV/peracetic acid process. Water Res. 2019, 150, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, M.; Conde, J.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A. Antibiotics abatement in synthetic and real aqueous matrices by H2O2/natural magnetite. Catal. Today 2018, 313, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, P.; Drumm, F.C.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L.; Jahn, S.L. Water treatment plant sludge as iron source to catalyze a heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaccallo, Y.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Marín, M.P.; Gil, M.V.; Larriba, M.; Águeda, V.I.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Magnetic Fe3O4/multi-walled carbon nanotubes materials for a highly efficient depletion of diclofenac by catalytic wet peroxideoxidation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22372–22388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.C.; Pedroza, A.M.; Daza, C.E. Magnetic fenton and photo-fenton-like catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes for wastewater treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Shi, W.; He, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y. Fe3O4–MWCNT magnetic nanocomposites as efficient peroxidase mimic catalysts in a Fenton-like reaction for water purification without pH limitation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45809–45815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, I.; Soran, M.-L.; Stegarescu, A.; Opris, O.; Gutoiu, S.; Leostean, C.; Lazar, M.D.; Kacso, I.; Silipas, T.-D.; Porav, A.S. Evaluation of CNT-COOH/MnO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for ibuprofen and paracetamol removal from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Munoz, M.; Gläsel, J.; De Pedro, Z.M.; Domínguez, C.M.; García, J.; Etzold, B.J.; Casas, J.A. Highly efficient removal of pharmaceuticals from water by well-defined carbide-derived carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-J.; Li, X. Preparation and magnetic property of multiwalled carbon nanotubes decorated by Fe3O4 nanoparticles. New Carbon Mater. 2012, 27, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaccallo-Aguilar, Y.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Larriba, M.; Águeda, V.I.; Delgado, J.A.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Optimization parameters, kinetics and mechanism of naproxen removal by catalytic wet peroxide oxidation with a hybrid iron-based magnetic catalyst. Catalysts 2019, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Mora, F.J.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Alvarez-Torrellas, S.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Application of CWPO to the treatment of pharmaceutical emerging pollutants in different water matrices with a ferromagnetic catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, J.; Barzanouni, H.; Mazloomi, S.; Farahani, N.A.A.; Sharafi, K.; Soleimani, P.; Haghighat, G.A. Effective adsorptive removal of reactive dyes by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles: Kinetic, isothermal studies and response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepho, H.P.; Edmondson, R.N. A tutorial on the statistical analysis of factorial experiments with qualitative and quantitative treatment factor levels. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2018, 204, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, C.; Quintanilla, A.; Casas, J.; Rodriguez, J. Kinetics of wet peroxide oxidation of phenol with a gold/activated carbon catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medinas, D.B.; Cerchiaro, G.; Trindade, D.F.; Augusto, O. The carbonate radical and related oxidants derived from bicarbonate buffer. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoeiro, L.E. Transformation of magnetite to hematite and its influence on the dissolution of iron oxide minerals. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2004, 16, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Magnetic activated-ATP@Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an efficient fenton-like heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of ethidium bromide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiao, J.; Cui, C.; Wang, C. Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/gallic acid/graphene oxide magnetic nanocomposites as highly efficient Fenton catalysts. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28979–28986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Application of DLLME to isolation and concentration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environmental water samples. Chromatographia 2010, 72, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.-J.M.; Chen, T.-Y.; Lee, M.; Chang, C.-F.; Liu, Y.-T.; Kuo, Y.-T. Effective anodic oxidation of naproxen by platinum nanoparticles coated FTO glass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulova, N.; Kattel, E.; Trapido, M. Degradation of naproxen by ferrous ion-activated hydrogen peroxide, persulfate and combined hydrogen peroxide/persulfate processes: The effect of citric acid addition. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, I.T.; Chairez Oria, A.S.; Poznyak, A. Ozonation and Biodegradation in Environmental Engineering: Dynamic Neural Network Approach, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Masson Doyma, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Motti, C.A.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemöller, M. TiO2 photocatalysis of naproxen: Effect of the water matrix, anions and diclofenac on degradation rates. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J.; Freier, U.; Wecks, M.; Hohmann, S. Degradation of diclofenac in water by heterogeneous catalytic oxidation with H2O2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziylan, A.; Dogan, S.; Agopcan, S.; Kidak, R.; Aviyente, V.; Ince, N.H. Sonochemical degradation of diclofenac: Byproduct assessment, reaction mechanisms and environmental considerations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5929–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinar, S.A.; Ziylan-Yavaş, A.; Catak, S.; Ince, N.H.; Aviyente, V. Hydroxyl radical-mediated degradation of diclofenac revisited: A computational approach to assessment of reaction mechanisms and by-products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18458–18469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, F.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Efficient degradation of sulfamethoxazole by catalytic wet peroxide oxidation with sludge-derived carbon as catalysts. Environ. Technol. 2018, 41, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckner, K.F. Comparison of membrane filtration and multiple-tube fermentation by the colilert and enterolert methods for detection of Waterborne Coliform Bacteria, Escherichia coli, and Enterococci used in drinking and bathing water quality monitoring in Southern Sweden. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3079–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, J.J.R.; Levchuk, I.; Sillanpää, M. Application of catalytic wet peroxide oxidation for industrial and urban wastewater treatment: A review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayazi, Z.; Khoshhesab, Z.M.; Norouzi, S. Modeling and optimizing of adsorption removal of Reactive Blue 19 on the magnetite/graphene oxide nanocomposite via response surface methodology. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 25301–25316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
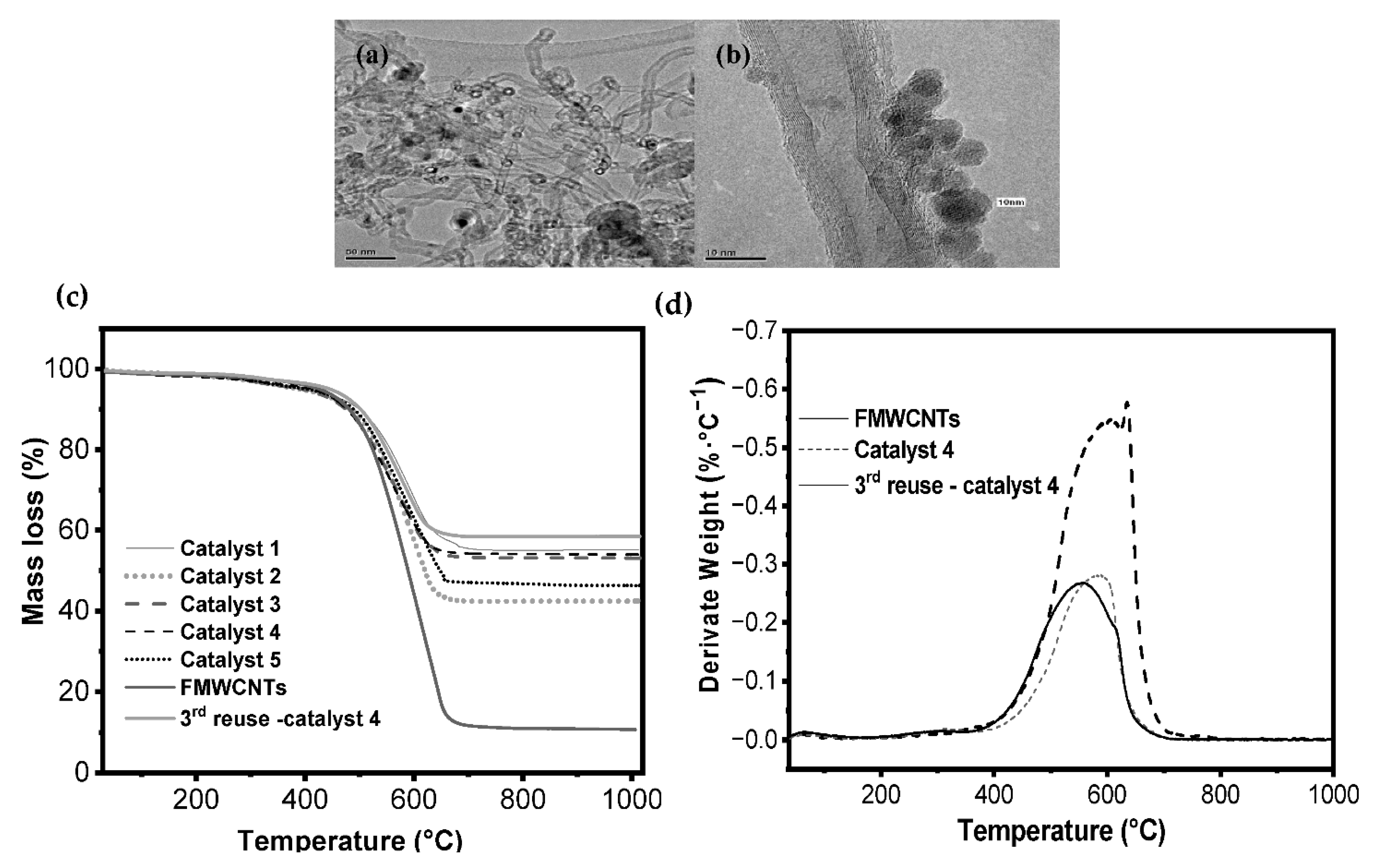

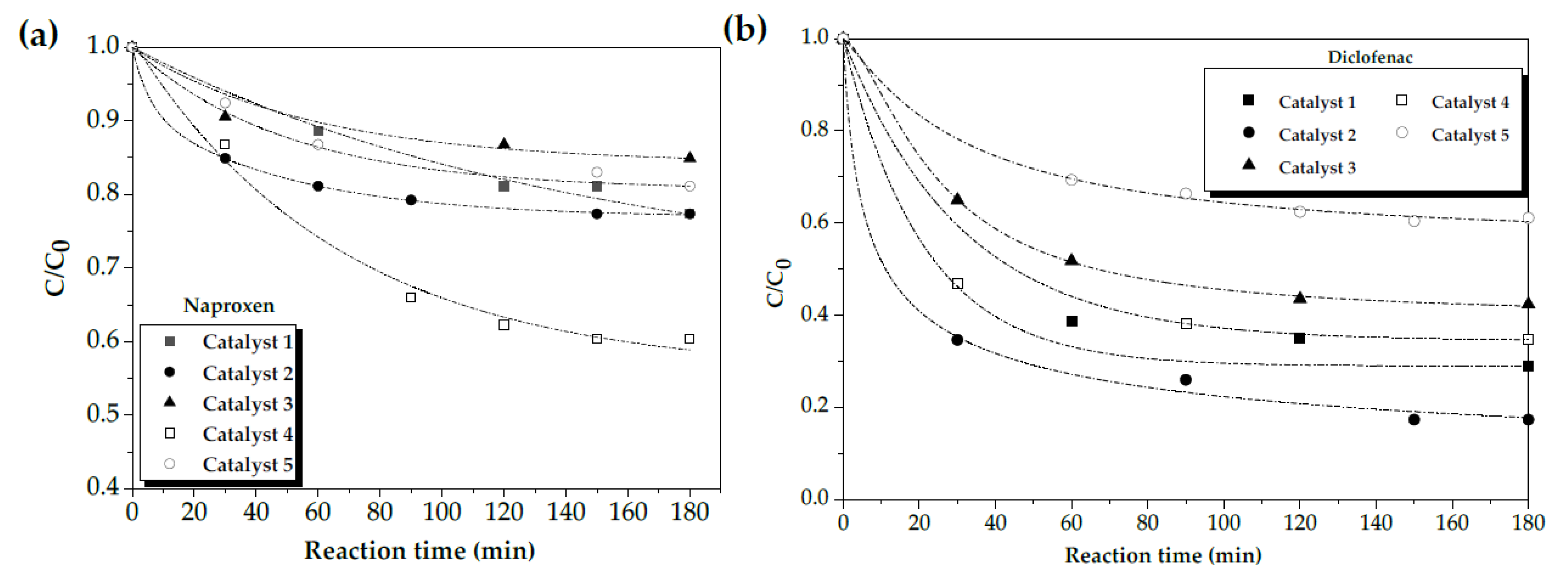
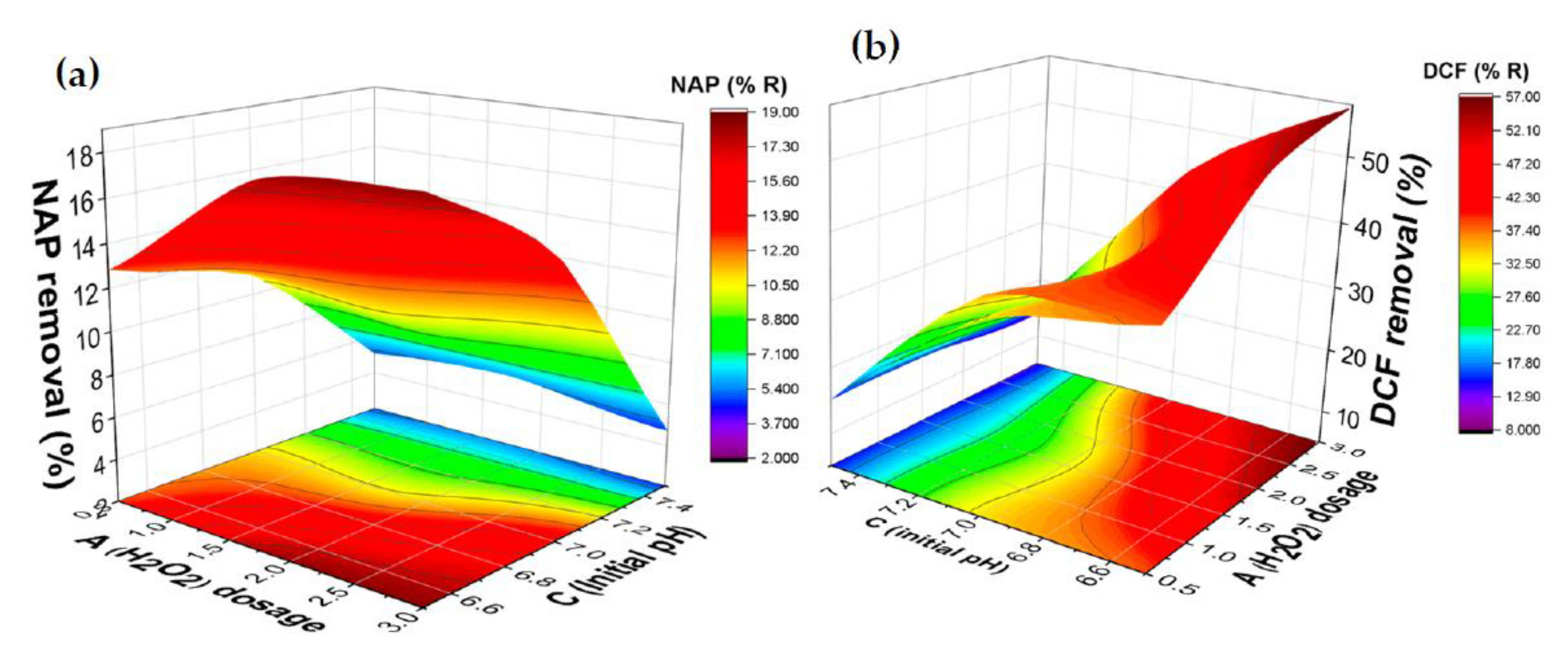

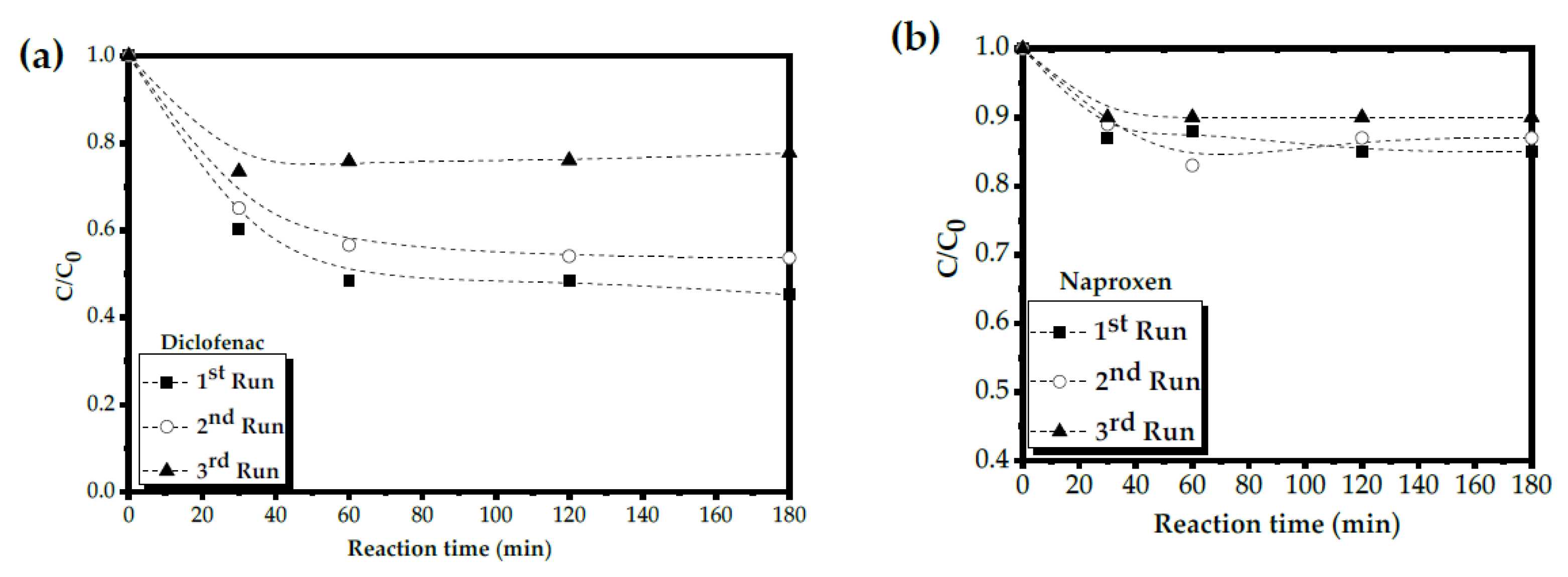

| Material | SBET (m2 g−1) | VMic (cm3 g−1) | VTotal (cm3 g−1) | VMic/VTotal | Average Pore Width (nm) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMWCNTs | 97 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 17.9 |
| Catalyst 4 | 96 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 17.1 |
| Catalyst 5 | 90 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 14.7 |
| FMWCNTs | Catalyst 1 | Catalyst 2 | Catalyst 3 | Catalyst 4 | Catalyst 5 | Third Reuse Catalyst 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % C | 84.47 | 40.72 | 50.0 | 58.0 | 40.72 | 58.0 | 41.65 |
| % Fe | n.d. | 26.22 | 19.5 | 21.0 | 35.0 | 10.6 | 36.1 |
| Actual Values | NAP Removal Efficiency (%) | DCF Removal Efficiency (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° | A (H2O2 dose, mM) | B (T, °C) | C (pH Initial) | Observed | Predicted | Observed | Predicted |
| 1 | 0.50 | 50 | 7.0 | 9.00 | 9.42 | 30.00 | 31.08 |
| 2 | 3.00 | 50 | 7.0 | 11.00 | 11.02 | 34.78 | 35.49 |
| 3 | 0.50 | 70 | 7.0 | 13.00 | 12.98 | 37.50 | 36.79 |
| 4 | 3.00 | 70 | 7.0 | 18.00 | 17.58 | 52.00 | 50.92 |
| 5 | 0.50 | 60 | 6.5 | 12.64 | 12.85 | 37.92 | 38.74 |
| 6 | 3.00 | 60 | 6.5 | 18.47 | 19.08 | 57.00 | 58.19 |
| 7 | 0.50 | 60 | 7.5 | 5.00 | 4.40 | 15.00 | 13.81 |
| 8 | 3.00 | 60 | 7.5 | 4.58 | 4.37 | 13.74 | 12.92 |
| 9 | 1.75 | 50 | 6.5 | 17.00 | 16.37 | 51.00 | 49.09 |
| 10 | 1.75 | 70 | 6.5 | 19.00 | 18.82 | 54.00 | 53.89 |
| 11 | 1.75 | 50 | 7.5 | 2.00 | 2.18 | 8.12 | 8.23 |
| 12 | 1.75 | 70 | 7.5 | 9.22 | 9.85 | 22.66 | 24.56 |
| 13 | 1.75 | 60 | 7.0 | 10.60 | 10.56 | 31.00 | 31.37 |
| 14 | 1.75 | 60 | 7.0 | 10.10 | 10.56 | 31.10 | 31.37 |
| 15 | 1.75 | 60 | 7.0 | 11.00 | 10.56 | 32.00 | 31.37 |
| DF | SS | MS | F | Prob > F (p-Value) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAP | Model | 9 | 373.31 | 41.48 | 85.03 | <0.000 | - |
| Residual | 5 | 2.44 | 0.49 | - | - | - | |
| Lack of fit | 3 | 2.03 | 0.68 | 3.33 | 0.239 | Not significant | |
| Pure error | 2 | 0.41 | 0.20 | - | - | - | |
| Total | 14 | 375.74 | - | - | - | - | |
| DCF | Regression | 9 | 3161.79 | 351.31 | 114.08 | <0.000 | - |
| Residual | 5 | 15.40 | 3.08 | - | - | - | |
| Lack of fit | 3 | 14.79 | 4.93 | 16.25 | 0.059 | Not significant | |
| Pure error | 2 | 0.61 | 0.30 | - | - | - | |
| Total | 14 | 3177.16 | - | - | - | - |
| Catalyst 1 | Catalyst 2 | Catalyst 3 | Catalyst 4 | Catalyst 5 | Magnetite | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNT (g) | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0 |
| FeCl2·4H2O (g) | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| FeCl3·6H2O (g) | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| Levels Box–Behnken Design | A (H2O2) (mM) | B (Temperature) (°C) | C (Initial pH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | 0.50 | 50 | 6.5 |
| Medium (0) | 1.75 | 60 | 7.0 |
| High (+1) | 3.00 | 70 | 7.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huaccallo-Aguilar, Y.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Martínez-Nieves, J.; Delgado-Adámez, J.; Gil, M.V.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Magnetite-Based Catalyst in the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation for Different Aqueous Matrices Spiked with Naproxen–Diclofenac Mixture. Catalysts 2021, 11, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040514
Huaccallo-Aguilar Y, Álvarez-Torrellas S, Martínez-Nieves J, Delgado-Adámez J, Gil MV, Ovejero G, García J. Magnetite-Based Catalyst in the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation for Different Aqueous Matrices Spiked with Naproxen–Diclofenac Mixture. Catalysts. 2021; 11(4):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040514
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuaccallo-Aguilar, Ysabel, Silvia Álvarez-Torrellas, Johanny Martínez-Nieves, Jonathan Delgado-Adámez, María Victoria Gil, Gabriel Ovejero, and Juan García. 2021. "Magnetite-Based Catalyst in the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation for Different Aqueous Matrices Spiked with Naproxen–Diclofenac Mixture" Catalysts 11, no. 4: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040514
APA StyleHuaccallo-Aguilar, Y., Álvarez-Torrellas, S., Martínez-Nieves, J., Delgado-Adámez, J., Gil, M. V., Ovejero, G., & García, J. (2021). Magnetite-Based Catalyst in the Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation for Different Aqueous Matrices Spiked with Naproxen–Diclofenac Mixture. Catalysts, 11(4), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040514








