Effect of the Metal Deposition Order on Structural, Electronic and Catalytic Properties of TiO2-Supported Bimetallic Au-Ag Catalysts in 1-Octanol Selective Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
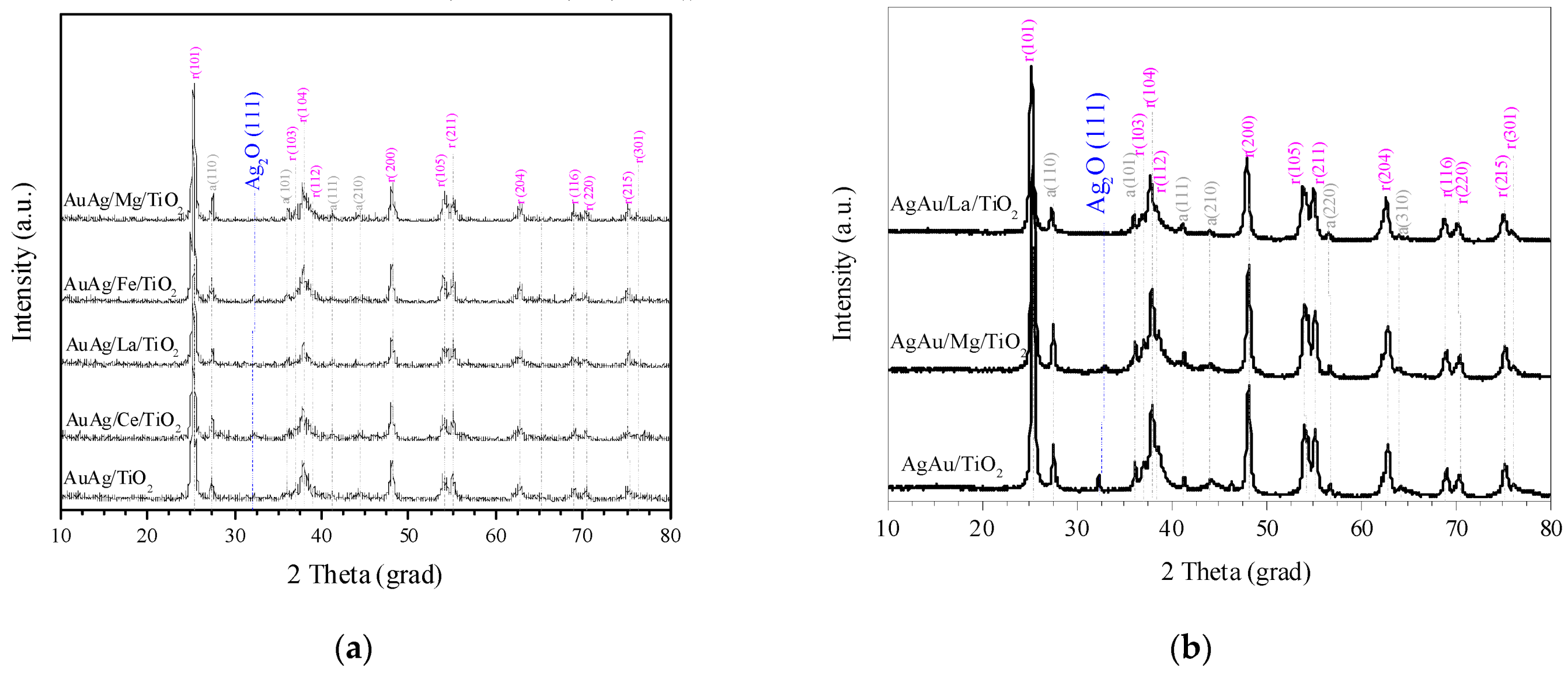
2.1. Characterization Results

2.2. Catalytic Results
2.3. Comparison of Catalytic and Physicochemical Results
2.4. Theoretical Calculations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Characterization of the Samples
3.3. Theoretical Calculations
3.4. Catalytic Tests in 1-Octanol Oxidation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haruta, M. Gold as a Novel Catalyst in the 21st Century: Preparation, Working Mechanism and Applications. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bond, G.C. Gold: A relatively new catalyst. Gold Bull. 2001, 34, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.M.; Fan, K.N.; Dai, W.L. One-pot solvent-free synthesis of sodium benzoate from the oxidation of benzyl alcohol over novel efficient AuAg/TiO2 catalysts. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracey, C.L.; Ellis, P.R.; Hutchings, G.J. Application of copper–gold alloys in catalysis: Current status and future perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, A.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Mou, C.Y.; Zhang, T. Au-Cu Alloy nanoparticles confined in SBA-15 as a highly efficient catalyst for CO oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2008, 27, 3187–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, S.; Song, X.; Ding, B.; Yang, Z. Bimetallic Ag/Au nanoparticles: A low temperature ripening strategy in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2010, 372, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizuka, Y.; Kawamoto, A.; Akita, K.; Date, M.; Tsubota, S.; Okumura, M.; Haruta, M. Effect of Impurity and Pretreatment Conditions on the Catalytic Activity of Au Powder for CO Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2004, 97, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, L.; Cozzoli, P.D. Colloidal heterostructured nanocrystals: Synthesis and growth mechanisms. Nanotoday 2010, 5, 449–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Yu, A. Bimetallic Ag–Au Nanowires: Synthesis, Growth Mechanism, and Catalytic Properties. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7134–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, W.G.; Zielasek, V.; Thiel, K.; Hartwig, A.; Bäumer, M. Effects of particle size, composition, and support on catalytic activity of AuAg nanoparticles prepared in reverse block copolymer micelles as nanoreactors. J. Catal. 2013, 299, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.-Q.; Liu, J.-H.; Lin, S.D.; Lin, T.-S.; Mou, C.-Y. A novel efficient Au-Ag alloy catalyst system: Preparation, activity, and characterization. J. Catal. 2005, 233, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Ke, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Jiang, T.; Gao, J. Investigation of factors influencing the catalytic performance of CO oxidation over Au-Ag/SBA-15 catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 277, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Fe3O4@Carbon Microsphere Supported Ag–Au Bimetallic Nanocrystals with the Enhanced Catalytic Activity and Selectivity for the Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22432–22440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Tan, M.; Ding, W.; Lu, X. P123-stabilized Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles for kinetics of aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol in aqueous solution. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, K.; Dai, W.-L. Surface structural evolution of AuAg/TiO2 catalyst in the transformation of benzyl alcohol to sodium benzoate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucchi, M.; Jouve, A.; Villa, A.; Nagy, G.; Németh, M.; Evangelisti, C.; Zanella, R.; Prati, L. Gold-Silver Catalysts: Ruling Factors for Establishing Synergism. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 4043–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smetana, A.B.; Klabunde, K.J.; Sorensen, C.M.; Ponce, A.A.; Mwale, B. Low-Temperature Metallic Alloying of Copper and Silver Nanoparticles with Gold Nanoparticles through Digestive Ripening. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Sheng Su, D.; Prati, L. New challenges in gold catalysis: Bimetallic systems. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, P.G.N.; Vandezande, P.; Ye, X.P.; Poelman, H.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; De Vos, D.E. Recyclable Au0, Ag0 and Au0–Ag0 nanocolloids for the chemoselective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones to allylic alcohols. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 355, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savara, A.; Chan-Thaw, C.E.; Sutton, J.E.; Wang, D.; Prati, L.; Villa, A. Molecular Origin of the Selectivity Differences between Palladium and Gold–Palladium in Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation: Different Oxygen Adsorption Properties. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Duan, X.; Yuan, Y. Efficient low-temperature selective hydrogenation of esters on bimetallic Au-Ag/SBA-15 catalyst. J. Catal. 2013, 297, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobova, E.; Pestryakov, A.; Shemeryankina, A.; Kotolevich, Y.; Martynyuk, O.; Tiznado Vazquez, H.J.; Bogdanchikova, N. Formation of silver active states in Ag/ZSM-5 catalysts for CO oxidation. Fuel 2014, 138, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobova, E.N.; Pestryakov, A.N.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Cortés Corberán, V. Silver catalysts for liquid-phase oxidation of alcohols in green chemistry: Challenges and outlook. Catal. Today 2019, 333, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobova, E.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Grigoreva, A.; Pakrieva, E.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Peltonen, J.; Kazantsev, S.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Pestryakov, A.; Murzin, D.Y. Catalytic oxidative transformation of betulin to its valuable oxo-derivatives over gold supported catalysts: Effect of support nature. Catal. Today 2021, 367, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, D.M.; Anh, D.T.N.; Singh, P.; Shankar, C.; Maenosono, S. Electronic transfer as a route to increase the chemical stability in gold and silver core–shell nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 185–186, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, H.; Hu, Z.M.; Nakai, H.; Ikeda, K. Activation of O2 on Cu, Ag, and Au surfaces for the epoxidation of ethylene: Dipped adcluster model study. Surf. Sci. 1997, 387, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandell, A.; Bennich, P.; Nilsson, A.; Hernnäs, B.; Björneholm, O.; Mårtensson, N. Chemisorption of CO on Cu(100), Ag(110) and Au(110). Surf. Sci. 1994, 310, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhimi, X.; Zanella, R.; Maturano, V.; Morales, A. Nanocrystalline Ag, and Au-Ag alloys supported on titania for CO oxidation reaction. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.N.; Lee, J.W.; Hong, C.Y.; Mou, C.Y.; Jang, B.W.L. Selective hydrogenation of acetylene in excess ethylene over SiO2 supported Au-Ag bimetallic catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 439–440, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, R.P.; Krafft, J.-M.; Methivier, C.; Casale, S.; Remita, H.; Louis, C.; Thomas, C. On the promoting effect of Au on CO oxidation kinetics of Au-Pt bimetallic nanoparticles supported on SiO2: An electronic effect? J. Catal. 2012, 287, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Liao, S.J.; Song, H.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Fu, Z.Y.; Su, Y.L. High-performance Pd–Au bimetallic catalyst with mesoporous silica nanoparticles as support and its catalysis of cinnamaldehyde hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2012, 291, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, A.Q.; Chi, Y.S.; Lin, H.P.; Mou, C.Y. Platinum Monolayer on Nonnoble Metal−Noble Metal Core−Shell Nanoparticle Electrocatalysts for O2 Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22701–22704. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, A.Q.; Chi, Y.S.; Lin, H.P.; Mou, C.Y. Synergistic Effect in an Au-Ag Alloy Nanocatalyst: CO Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.-Q.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Chen, Y.-F.; Mou, C.-Y. Au-Ag alloy nanoparticle as catalyst for CO oxidation: Effect of Si/Al ratio of mesoporous support. J. Catal. 2006, 237, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, A.; Aguilar, A.; Louis, C.; Traverse, A.; Zanella, R. Bimetallic Au-Ag/TiO2 catalyst prepared by deposition–precipitation: High activity and stability in CO oxidation. J. Catal. 2011, 281, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittstock, A.; Zielasek, V.; Biener, J.; Friend, C.M.; Baumer, M. Nanoporous gold catalysts for selective gas-phase oxidative coupling of methanol at low temperature. Science 2010, 327, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskaleva, L.V.; Rohe, S.; Wittstock, A.; Zielasek, V.; Kluner, T.; Neyman, K.M.; Baumer, M. Silver residues as a possible key to a remarkable oxidative catalytic activity of nanoporous gold. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4529–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés Corberán, V.; González-Pérez, M.E.; Martínez-González, S.; Gómez-Avilés, A. Green oxidation of fatty alcohols: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 474, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotolevich, Y.; Kolobova, E.; Khramov, E.; Farías, M.H.; Zubavichus, Y.; Tiznado, H.; Martínez-González, S.; Cortés Corberán, V.; Mota-Morales, J.D.; Pestryakov, A.; et al. n-Octanol oxidation on Au/TiO2 catalysts promoted with La and Ce oxides. Molecular Catal. 2017, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kotolevich, Y.; Kolobova, E.; Mamontov, G.; Khramov, E.; Cabrera Ortega, J.E.; Tiznado, H.; Farías, M.H.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Zubavichus, Y.; Cortés Corberán, V.; et al. Au/TiO2 catalysts promoted with Fe and Mg for selective n-octanol oxidation under mild conditions. Catal. Today 2016, 278, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Giorgio, S.; Henry, C.R.; Louis, C. Alternative Methods for the Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7634–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Delannoy, L.; Louis, C. Mechanism of deposition of gold precursors onto TiO2 during the preparation by cation adsorption and deposition–precipitation with NaOH and urea. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 291, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Louis, C. Influence of the conditions of thermal treatments and of storage on the size of the gold particles in Au/TiO2 samples. Catal. Today 2005, 107–108, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotolevich, Y.; Kolobova, E.; Cabrera Ortega, J.E.; Khramov, E.; Pakrieva, E.; Zubavichus, Y.; Cortés Corberán, V.; Zanella, R.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Pestryakov, A. Gold and Silver Catalysts for Liquid Phase n-Octanol Oxidation: Effect of Promoters. Curr. Org. Synth. 2017, 14, 322–331. [Google Scholar]
- Rojluechai, S.; Chavadej, S.; Schwank, J.W.; Meeyoo, V. Catalytic activity of ethylene oxidation over Au, Ag and Au-Ag catalysts: Support effect. Catal. Comm. 2007, 8, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Boothroyd, C.; Zhang, J.X. Size and composition tunable Ag–Au alloy nanoparticles by replacement reactions. Nanotechnol. 2007, 18, 245605–245612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallin, M.P.; Murphy, C. Solution-phase synthesis of sub-10 nm Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles. J. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-F. Synthesis of Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles supported on silica gel via galvanic replacement reaction. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mat. Int. 2013, 23, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuzovskaya, I.V.; Simakov, A.V.; Pestryakov, A.N.; Bogdanchikova, N.E.; Gurin, V.V.; Farías, M.H.; Tiznado, H.J.; Avalos, M. Co-existence of various active gold species in Au-mordenite catalyst for CO oxidation. Catal. Comm. 2007, 8, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolima, W.R.; Pelegrinoa, M.T.; Lima, B.A.; Ferraza, L.S.; Costa, F.N.; Bernardes, J.S.; Rodigues, T.; Brocchi, M.; Seabra, A.B. Green tea extract mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, cytotoxicity evaluation and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Mutreja, V.; Sareen, S. Exceptional antibacterial and cytotoxic potency of monodisperse greener AgNPs prepared under optimized pH and temperature. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspromonte, S.G.; Serra, R.M.; Miró, E.E.; Boix, A.V. AgNaMordenite catalysts for hydrocarbon adsorption and deNOx processes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 407, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysenko, V.S.; Mal’nev, A.F. Optical characteristics of metal blacks. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1969, 10, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Petranovskii, V.; Castillón-Barraza, F.; Concepción-Rosabal, B. Copper-Silver Bimetallic System on Natural Clinoptilolite: Thermal Reduction of Cu2+ and Ag+ Exchanged. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 5580–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurin, V.S.; Bogdanchikova, N.E.; Petranovskii, V.P. Metal clusters and nanoparticles assembled in zeolites: An example of stable materials with controllable particle size. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 19, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.X.; Lv, J.J.; Wang, A.J.; Huang, H.; Feng, J.J. One-step wet-chemical synthesis of gold nanoflower chains as highly active surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 222, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbone, M.; Calcagno, L.; Messina, G.; Baeri, P.; Compagnini, G. Dynamic light scattering and UV–vis spectroscopy of gold nanoparticles solution. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2906–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Blanco, C.; Colina, A.; Heras, A.; Ruiz, V.; López-Palacios, J. Multipulse strategies for the electrosynthesis of gold nanoparticles studied by UV/Vis spectroelectrochemistry. Electrochem. Comm. 2012, 18, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybula, A.; Priebe, J.B.; Pohl, M.-M.; Sobczak, J.W.; Schneider, M.; Zielińska-Jurek, A.; Brückner, A.; Zaleska, A. The effect of calcination temperature on structure and photocatalytic properties of Au/Pd nanoparticles supported on TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 152–153, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestryakov, A.N.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Simakov, A.; Tuzovskaya, I.; Jentoft, F.; Farias, M.; Díaz, A. Catalytically active gold clusters and nanoparticles for CO oxidation. Surf. Sci. 2007, 601, 3792–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Fu, X.; Zhou, J. Dielectric properties of the silver–copper alloy films deposited by magnetron sputtering. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2013, 30, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgul, J.; Łątka, K.; Hnat, I.; Rynkowski, J.; Dzwigaj, S. Identification of iron species in FeSiBEA by DR UV-vis, XPS and Mössbauer spectroscopy: Influence of Fe content. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2013, 168, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotolevich, Y.; Kolobova, E.; Khramov, E.; Cabrera Ortega, J.E.; Farías, M.H.; Zubavichus, Y.; Zanella, R.; Mota-Morales, J.D.; Pestryakov, A.; Bogdanchikova, N.; et al. Identification of subnanometric Ag species, their interaction with supports and role in catalytic CO oxidation. Molecules 2016, 21, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feldheim, D.L.; Foss, C.A. Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; Basel Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 338. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, V.V.; Estrada, M.; Demidova, Y.; Prosvirin, I.; Kriventsov, V.; Cotta, R.F.; Gusevskaya, E.V. Gold nanoparticles supported on magnesium oxide as catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols under alkali-free conditions. J. Catal. 2012, 292, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Li, M.; Liu, J. Synthesis of core–shell Au@Pt nanoparticles supported on Vulcan XC-72 carbon and their electrocatalytic activities for methanol oxidation. Coll. Surf. A 2012, 406, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; del Ángel, G.; Gómez, R.; Galindo-Hernández, F.; Ángeles-Chavez, C. Degradation of the herbicide 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid over Au/TiO2-CeO2 photocatalysts: Effect of the CeO2 content on the photoactivity. Catal. Today 2011, 166, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Hernández, F.; Wang, R.; Gómez, J.A.; Bokhimi, X.; Lartundo, L.; Mantilla, A. Structural modifications in Au/Al2O3–CeO2 mixed oxides as a function of Ce4+ content and its effects in the mineralization of the herbicide diuron. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2012, 243, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rtimi, S.; Baghriche, O.; Sanjines, R.; Pulgarin, C.; Bensimon, M.; Kiwi, J. TiON and TiON-Ag sputtered surfaces leading to bacterial inactivation under indoor actinic light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 256, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mejia, I.M.; Marín, M.; Sanjines, R.; Pulgarín, E.; Mielczarski, C.; Mielczarski, J.; Kiwi, L. Magnetron-sputtered Ag-modified cotton textiles active in the inactivation of airborne bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, C.D.; Riggs, M.; Davis, E.; Müllenberg, G. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer Corporation Physical Electronics Division: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1979; pp. 1–190. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, M.; Wang, J.; Lee, W.-S.; Williams, W.D.; Min Kim, S.; Stach, E.A.; Miller, J.T.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H. Size and Support Effects for the Water-Gas Shift Catalysis over Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Model Al2O3 and TiO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynyuk, O.; Kotolevich, Y.; Vélez, R.; Cabrera Ortega, J.E.; Tiznado, H.; Zepeda Partida, T.; Mota Morales, J.D.; Pestryakov, A.; Bogdanchikova, N. On the high sensitivity of the electronic states of 1 nm gold particles to pretreatments and modifiers. Molecules 2016, 21, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, L.F.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M.; Overbury, S.H. Behavior of Au Species in Au/Fe2O3 Catalysts Characterized by Novel in Situ Heating Techniques and Aberration-Corrected STEM Imaging. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessard, J.D.; Valsamakis, I.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Novel Au/La2O3 and Au/La2O2SO4 catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction prepared via an anion adsorption method. Chem. Comm. 2012, 48, 4857–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M.; Gates, B.C. Atomically Dispersed Supported Metal Catalysts. Ann. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2012, 3, 545–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobova, E.; Kotolevich, Y.; Pakrieva, E.; Mamontov, G.; Farías, M.H.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Cortés Corberán, V.; Pestryakov, A. Causes of activation and deactivation of modified nanogold catalysts during prolonged storage and redox treatments. Molecules 2016, 21, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Su, H.; Lin, Q.; Han, C.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, L.; Qi, C. Au/Cu-Fe-La-Al2O3: A highly active, selective and stable catalysts for preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide. App. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 527, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzing, A.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Carley, A.F.; Landon, P.; Hutchings, G.J. Identification of active gold nanoclusters on iron oxide supports for CO oxidation. Science 2008, 321, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laikov, D.N.; Ustynyuk, Y.A. PRIRODA-04: A Quantum-Chemical Program Suite. New possibilities in the study of molecular systems with the application of parallel computing. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2005, 54, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovnichy, V.; Tikhonravov, A.; Voevodin, V.; Opanasenko, V. Contemporary High Performance Computing: From Petascale Toward Exascale; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 283–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pakrieva, E.; Kolobova, E.; Kotolevich, Y.; Pascual, L.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Kharlanov, A.N.; Pichugina, D.; Nikitina, N.; German, D.; Zepeda Partida, T.A.; et al. Effect of gold electronic state on the catalytic performance of nano gold catalysts in n-octanol oxidation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Catalysts | Aunδ− | Au0 | Au+ | Au3+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤83.6 eV | ~84 eV | ~85–85.5 eV | ~86–87 eV | |
| Au/La/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (76%) | 85.4 (18%) | 86.3 (6%) |
| AuAg/La/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (71%) | 85.0 (23%) | 86.1 (6%) |
| AgAu/La/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (100%) | - | - |
| Au/Mg/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (68%) | 84.9 (23%) | 86.1 (9%) |
| AuAg/Mg/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (73%) | 84.9 (19%) | 86.1 (8%) |
| AgAu/Mg/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (100%) | - | - |
| Au/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (68%) | 84.7 (20%) | 86.0 (12%) |
| AuAg/TiO2 | 84.0 (73%) | 84.8 (19%) | 86.1 (8%) | |
| AgAu/TiO2 | - | 83.1 (95%) | 85.2 (5%) | - |
| Au/Ce/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (81%) | 85.3 (19%) | - |
| AuAg/Ce/TiO2 | - | 84.0 (81%) | 85.7 (19%) | |
| AgAu/Ce/TiO2 | 82.3 (5%) | 84.0 (95%) | - | - |
| Au/Fe/TiO2 | 83.1 (28%) | 84.0 (32%) | 85.0 (29%) | 85.8 (11%) |
| AuAg/Fe/TiO2 | 82.7 (18%) | 84.0 (35%) | 85.2 (33%) | 86.5 (14%) |
| AgAu/Fe/TiO2 | 81.8 (22%) | 84.0 (78%) | - | - |
| Catalyst | Ag+ | Agδ+ | Ag0 | Ag Clusters <2 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 364.0–366.2 | 367.4–367.9 | 368.1–368.4 | >369.0 | |
| Ag/La/TiO2 | - | 367.5 (84%) | 368.7 (16%) | - |
| AuAg/La/TiO2 | - | - | - | 369.1 (80%) 370.3 (15%) 371.8 (5%) |
| AgAu/La/TiO2 | - | - | 368.2 (100%) | - |
| Ag/Mg/TiO2 | - | 367.5 (40%) | 368.3 (47%) | 369.9 (9%) 371.6 (4%) |
| AuAg/Mg/TiO2 | - | - | 368.4 (79%) | 369.6 (17%) 371.0 (4%) |
| AgAu/Mg/TiO2 | - | - | 368.2 (100%) | - |
| Ag/TiO2 | 367.3 (80%) | 368.4 (20%) | - | |
| AuAg/TiO2 | - | 367.9 (81%) | 368.9 (19%) | - |
| AgAu/TiO2 | - | 368.1 (95%) | - | 370.6 (5%) |
| Ag/Ce/TiO2 | 366.0 (73%) | 366.5 (19%) | 367.8(8%) | - |
| AuAg/Ce/TiO2 | 366.7 (61%) | 367.6 (39%) | - | - |
| AgAu/Ce/TiO2 | 365.8 (7%) | 367.4 (93%) | - | - |
| Ag/Fe/TiO2 | 366.0 (14%) | - | 368.1 (65%) | 369.3 (21%) |
| AuAg/Fe/TiO2 | 366.8 (32%) | - | 368.3 (21%) | 369.4 (40%) 371.1 (7%) |
| AgAu/Fe/TiO2 | 365.6 (20%) | 367.6 (80%) | - | - |
| Catalyst | Selectivity, mol.% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Octanal | Octyl Octanoate | Octanoic Acid | |||||||
| as-prep. | H2 | O2 | as-prep. | H2 | O2 | as-prep. | H2 | O2 | |
| AuAg/Ce/TiO2 | 86.5 | 0.0 | 75.9 | 7.0 | 0.0 | 24. 8 | 6.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AuAg/Fe/TiO2 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 76.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 23.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AuAg/Mg/TiO2 | 82.1 | 0.0 | 62.1 | - | 0.0 | 31.9 | 7.9 | 0.0 | 6.0 |
| AuAg/La/TiO2 | 52.7 | 83.1 | 34.6 | 47.3 | 14.0 | 61.2 | 0.0 | 2.9 | 4.1 |
| AuAg/TiO2 | 93.5 | 0.0 | 71.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 28.7 | 6.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AgAu/Ce/TiO2 | 92.6 | 95.8 | 95.3 | 7.4 | 4.2 | 4.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AgAu/Fe/TiO2 | 92.2 | 100 | 91.2 | 7.8 | 0 | 8.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AgAu/Mg/TiO2 | 93.9 | 94.2 | 94.3 | 6.1 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AgAu/La/TiO2 | 100 | 91.9 | 86.3 | 0.0 | 8.1 | 13.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AgAu/TiO2 | 93.2 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 6.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Charge | Au10 | Ag10 | AgAu9 | AuAg9 | Au4Ag6 | Ag4Au6 | Au5Ag5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −43 (Au) | - | - | −11 (Au) | −26 (Au) | −26 (Au) | −17 (Au) |
| - | −30 (Ag) | −47 (Ag) | −42 (Ag) | −39 (Ag) | −33 (Ag) | ||
| 1 | −100 (Au) | - | - | −57 (Au) | −73 (Au) | −73 (Au) | −79 (Au) |
| - | −73 (Ag) | −87 (Ag) | - | −86 (Ag) | −94 (Ag) | −85 (Ag) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotolevich, Y.; Pakrieva, E.; Kolobova, E.; Farías, M.H.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Cortés Corberán, V.; Pichugina, D.; Nikitina, N.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Pestryakov, A. Effect of the Metal Deposition Order on Structural, Electronic and Catalytic Properties of TiO2-Supported Bimetallic Au-Ag Catalysts in 1-Octanol Selective Oxidation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070799
Kotolevich Y, Pakrieva E, Kolobova E, Farías MH, Bogdanchikova N, Cortés Corberán V, Pichugina D, Nikitina N, Carabineiro SAC, Pestryakov A. Effect of the Metal Deposition Order on Structural, Electronic and Catalytic Properties of TiO2-Supported Bimetallic Au-Ag Catalysts in 1-Octanol Selective Oxidation. Catalysts. 2021; 11(7):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070799
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotolevich, Yulia, Ekaterina Pakrieva, Ekaterina Kolobova, Mario H. Farías, Nina Bogdanchikova, Vicente Cortés Corberán, Daria Pichugina, Nadezhda Nikitina, Sónia A. C. Carabineiro, and Alexey Pestryakov. 2021. "Effect of the Metal Deposition Order on Structural, Electronic and Catalytic Properties of TiO2-Supported Bimetallic Au-Ag Catalysts in 1-Octanol Selective Oxidation" Catalysts 11, no. 7: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070799
APA StyleKotolevich, Y., Pakrieva, E., Kolobova, E., Farías, M. H., Bogdanchikova, N., Cortés Corberán, V., Pichugina, D., Nikitina, N., Carabineiro, S. A. C., & Pestryakov, A. (2021). Effect of the Metal Deposition Order on Structural, Electronic and Catalytic Properties of TiO2-Supported Bimetallic Au-Ag Catalysts in 1-Octanol Selective Oxidation. Catalysts, 11(7), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070799










