Abstract
Platinum and other metals are very scarce materials widely used in the energy and transportation sector among other sectors. Obtaining Platinum is becoming more difficult due to its scarcity on earth and because of the high amount of energy and water used for its extraction. In this regard, the recycling of platinum is necessary for sustainable technologies and for reaching a circular economy towards this expensive and rare metal. Conventional methods for platinum recycling make use of enormous amounts of energy for its recovery, which makes them not very attractive for industry implementation. Furthermore, these processes generate very toxic liquid streams and gas wastes that must be further treated, which do not meet the green environmental point of view of platinum recycling. Consequently, new advanced technologies are arising aiming to reach very high platinum recovery rates while being environmentally friendly and making a huge reduction of energy use compared with the conventional methods. In this review, conventional platinum recovery methods are summarized showing their limitations. Furthermore, new and promising approaches for platinum recovery are reviewed to shed light on about new and greener ways for a platinum circular economy.
1. Introduction
The upcoming decade is crucial in the fight against climate change [1]. Most world governments agreed, in the last few years, to accelerate the implementation of mitigation politics against the abuse of fossil fuels that are causing global warming. A fast transition to more sustainable technologies, not only in the energy generation, but also all the transportation field, requires a large number of materials like lithium, cobalt, graphite, rare earth elements, and platinum’s group metals (PGM), among others, that are unevenly distributed along the planet and are extremely rare (PGM). In this sense, European Union (EU), for instance, strongly backed up the Hydrogen technologies in their last research program [2], ranging from electrolyzers to fuel cells and batteries. These technologies will allow to store peaks of renewable energy as H2 and its further use as a non-carbon-based fuel. Proton Exchange Membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are devices that use H2 and O2 as fuels and the main and unique output is water. They are portable, scalable, offer a good energy density and what is more important, are a viable alternative to the fossil-fuel powered vehicle, however, and despite decades of research, platinum (Pt) is required as catalyst in both anode and cathode [3,4,5,6,7]. To fulfill the acquired compromises in the reduction of CO2 emissions, the use of PEMFCs as a complement to other technologies seems mandatory, and as a consequence, Pt demand will increase [8,9,10].
Platinum, which is resistant to corrosion, chemically inert, thermally stable, and offers a unique catalytic property in crucial chemical and electrochemical processes, is present in important devices as vehicle catalytic converters (VCCs) or PEMFCs. Furthermore, it’s used in the jewelry and biomedical industry, among other applications [11]. Recent Report on Critical Raw Materials and the Circular Economy of the EU declared Pt as a scarce raw material and established goals of recycling rates for its industrial use allowing a circular economy [12]. Main Pt natural deposits are in South Africa, Canada and Russia and its concentration per cubic meter of the terrain is dramatically low, therefore, its mining has an extremely high environmental impact and cost [10,13,14,15,16]. In contrast, Pt concentration in secondary sources like VCC is much higher. For instance, in VCC the Pt content is up to 2000 g·t−1, while in natural ores, this magnitude does not surpass 10 g·t−1 [17]. In other Pt uses, like jewelry or as fuel cell catalyst, Pt content is even higher than in VCC. Looking into the energy cost and natural resources used, Pt from natural ores requires 18,860–254,860 MJ per Kg of metal and 100,000–1,200,000 m3 of water per ton of metal extracted, while recycled Pt needs 1400–3400 MJ and 3000–6000 m3, respectively [12]. Finally, Pt ores usually contain sulfide minerals, which can drive to extremely dangerous fumes along with tones of CO2 during the smelting and refining process [14]. In contrast, Pt from recycling industry generates significantly lower CO2 and SO2 impact, Saurat et al. stated that Pt from primary ores generates 41.350 and 7267 tons of CO2 and SO2, respectively, per ton of Pt, while in Pt from secondary sources the quantity is lowered to 4407 and 40 tones per ton of Pt. Therefore, Pt recycling is an efficient and more interesting way to obtain Pt, both from an economic and environmental point of view and is mandatory for the technologic conversion that our planet demands [12]. Then, Pt recycling is mandatory for the technologic conversion that our planet demands. Despite this urgent necessity of changing the way of incorporate Pt into the market, in 2019 only 30% of the total Pt demand was covered with recycled Pt [18].
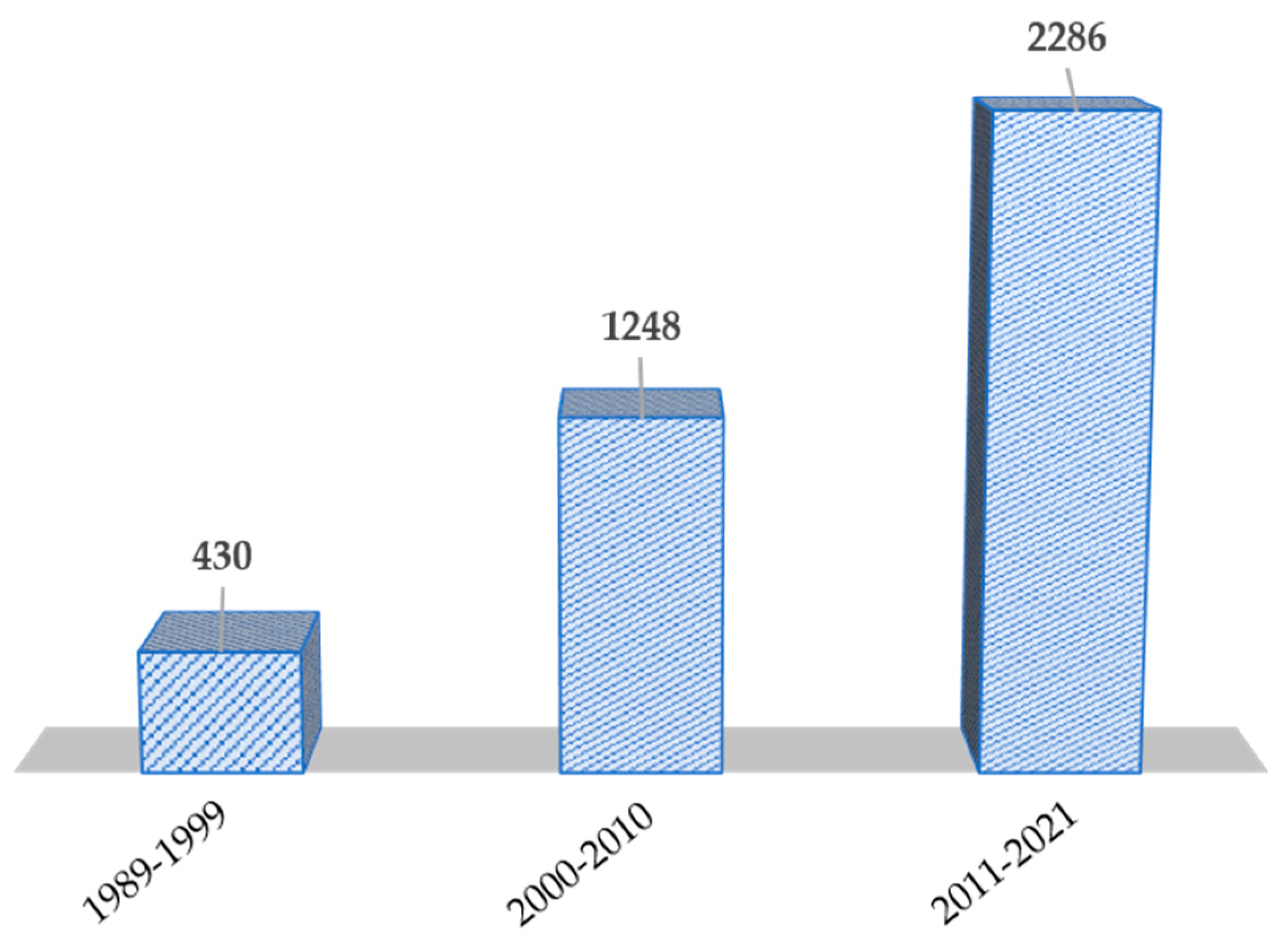
Recycling processes of Pt spent devices are numerous and are increasing in the last few years due to the research in more ambiently friendly ways to perform a Pt circular economy, avoiding excessive use of energy or hazardous liquid/gaseous wastes. Figure 1 depicts that published works on Pt recovery increased more than five times (source scopus) in the last three decades. More in detail, we can distinguish between two different phases, on one hand, in the early 2000′s to 2010 the main concerning was to recover as much Pt as possible without taking special care about the energy consumption or environmental concerns, however, in the last decade and especially in last 4–5 years, the huge increase of publications was due to the shift of Pt recover to sustainable technology. In this regard, 2019 and 2020 scored the maximum number of papers published in the recovery of Pt field with 262 and 285 versus, for instance, the 156 and 164 papers that were published in 2011 and 2012, respectively.
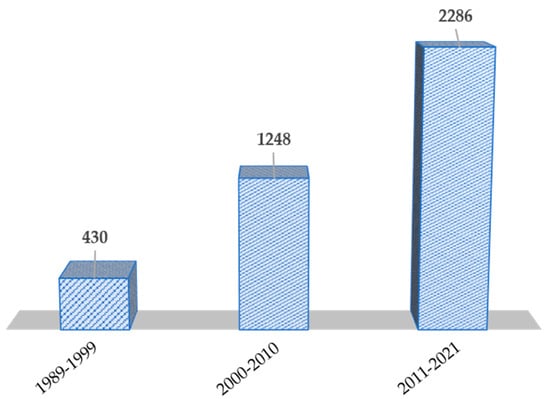
Figure 1.
Number of publications in the field of platinum recovery in last three decades. Data was obtained through Scopus search motor (June 2021).
Traditional methods to recycle Pt include pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes. They involve either high-temperature treatments and reactions in the gas phase or dissolving Pt in a suitable solvent/leaching agent, respectively [17,19,20,21,22]. Although both methods have good performance and recovery ratios, they require a pre-existent/large scale industrial facility to be economically feasible, and regrettably produce large amounts of highly toxic wastes (Hydrofluoric acid, NOx, among others) that had to be further treated. Recently, more sustainable and mild Pt recycling methods as selective electrochemical dissolution, bio-leaching, transient dissolution, acid process, or alcohol solvent process are extensively being investigated. These alternative technologies are cleaner, portable, require lower initial economic investment and fit better with the future uses of Pt like PEMFCs and other catalytic processes in the industry that allow, unlike VCCs, a high recovery rate of Pt without degrading completely the support material of the catalytic infrastructure [23,24,25,26].
In this review, we will cover the state of the art of different Pt recovery techniques, both conventional and novel technologies. As we progress along with this text, we will try to highlight which methods are more suitable to achieve better results with the near-future uses of Pt and which ones are necessary to retrieve the Pt that is now in use (for example in VCCs).
2. Recovery Technologies of Pt from Spent Catalysts
2.1. Conventional Technologies
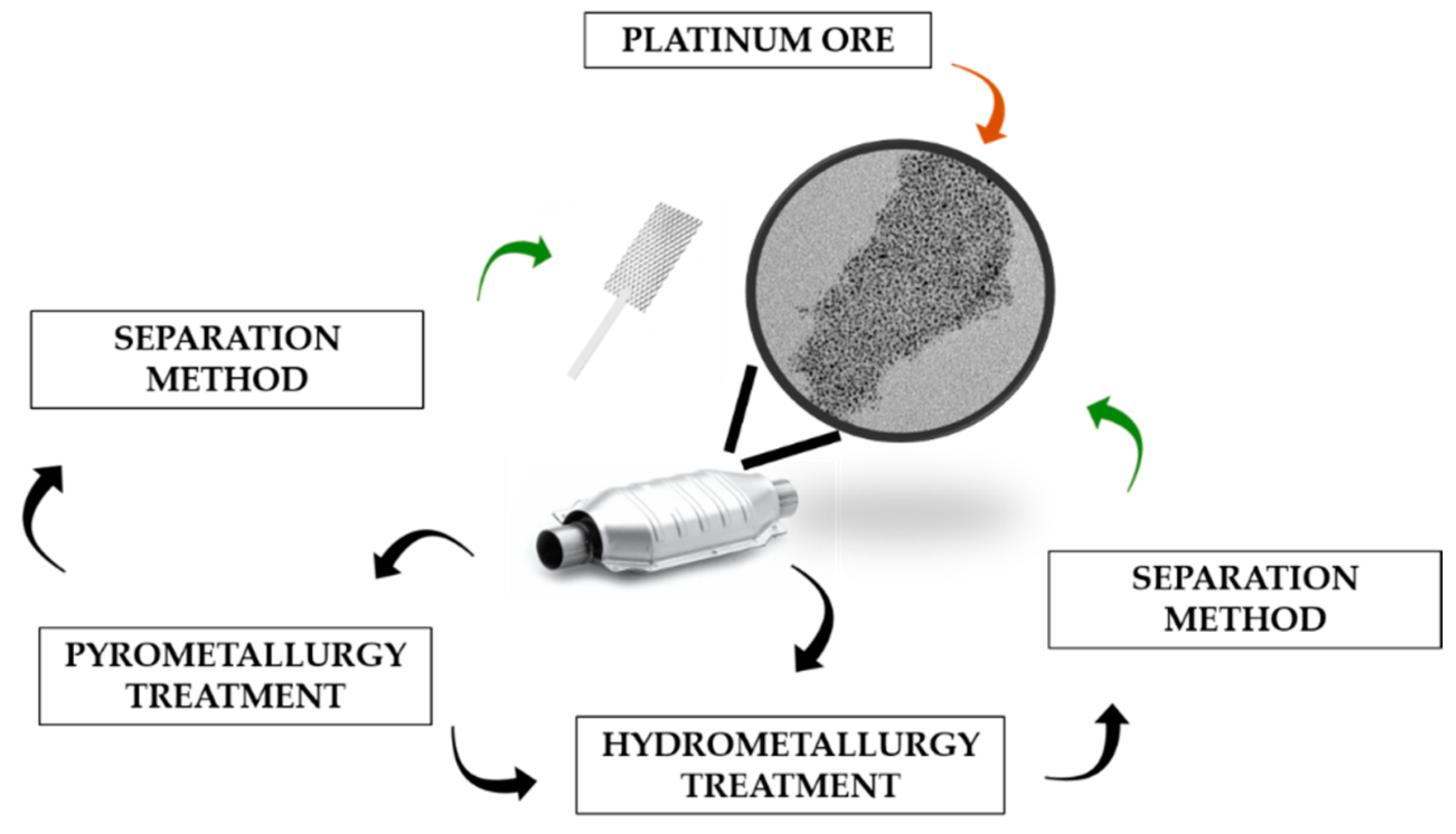
The increasing use of Pt and other PGM since the mid-80′s due to their presence in the VCCs, together with the overwhelming foreseen demand for the next decades, made recycling technologies a feasible option to overcome the expensive Pt production. First pyro/hydrometallurgical Pt recycling technologies used the existing facilities of the same big industries using Pt and other PGM as catalysts or other manufactured materials. On one hand, the pyrometallurgical recycling process consists of a thermal treatment of the used Pt containing materials, usually in a furnace, to achieve volatilization of non-desired compounds (support material, plastics, volatile oxides, among others) and the enrichment in Pt of a metallic phase, while in the other hand, hydrometallurgical recycling process directly leaches metals using highly oxidizing species. Usually, a combination of both techniques is required to perform a complete recycling process. Pyro/hydrometallurgical processes, and specially pyrometallurgical recycling, involve the use and generation of highly hazardous liquid and gaseous wastes. A final separation/precipitation method is usually needed to retrieve Pt from the recycled mix. Figure 2 depicts the Pt production-recycling process using conventional technologies.
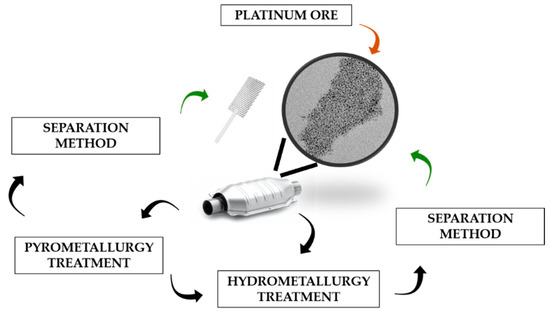
Figure 2.
Different routes of recycling Pt through conventional pyro/hydrometallurgical methods.
2.1.1. Pyrometallurgical Recovery Process
The pyrometallurgy process allows to concentrate valuable of metals from exhausted PGM sources and is a crucial method to recover Pt from spent catalysts [20,27]. In this process, the spent catalyst is physically and chemically transformed through thermal treatment. There are three main pyrometallurgical techniques: chlorination, smelting collection, and sintering processes [28,29]. Unlike hydrometallurgy, the pyrometallurgy process has the advantage of not depending on the initial form of the Pt source and it makes it faster to achieve good results [28]. However, a large amount of energy is consumed in the pyrometallurgy process due to the high temperatures that are required, usually over 1000 °C. In addition, and this is a key point nowadays, it produces massive hazardous gas species that must be further treated or captured [30,31].
Chlorination or carbochlorination shifts Pt and other metal species from spent catalysts or scraps into their corresponding chloride salts at high temperatures. After that, they are separated based on (i) the differences between the metal chlorides, (ii) by repulp washing or (iii) using adsorption on an activated carbon bed [32]. Kim et al. [33] developed this process for the recovery of Pt from spent automotive catalysts where different process parameters were studied such as total gas flow rate, reaction time, temperature, and partial pressures using CO/Cl2 gas mixture to completely extract platinum from the catalysts. A recovery of up to 95.9% of Pt was achieved. Horike et al. [34] created an efficient and environmentally friendly chlorination process for the recovery of Pt using copper (II) chloride (CuCl2) as a chorine source for the chlorination of Pt at 400 °C to 600 °C. Owing to its high chemical stability, pure Pt is insoluble in HCl (aq), therefore, to improve solubility, the scrap containing Pt was then alloyed with Mg, physically mixed with CuCl2 at 500 °C and then dissolved in HCl (aq). Murray et al. [35] presented a method for the recovery of Pt and Pd from spent catalysts in which VCCs were roasted at 600–1200 °C in a chlorine gas fluid field. The separation was subsequently carried out by absorption of Pt and Pd chlorides by an ammonium chloride liquor in water. As a result, the recovery of Pt was up to 90%. Xu et al. [36] pre-treated VCCs by crushing, roasting, and reducing Pt just before the chlorination process, which was further carried out by adding NaCl at 600–700 °C. Then, the product was treated using a hot water stream obtaining the corresponding Pt chloride salt. The Pt recovery yield obtained was 90%. In the chlorination process high purity metals are obtained, however, the main disadvantages are the corrosion of the furnace and associated facilities, and the utilization of hazardous gases as Cl2 which causes health and environmental risks [37]. In general, these environmental concerns and the high energetic cost makes this process undesirable in latest years.
In the sintering process, Pt is recovered in the presence of plasma by in situ reduction of its oxidized Pt component. Kuo-Chen Chiang et al. [38] developed a thermal plasma process for the recovery of the spent alumina-supported platinum catalysts (Pt/Al2O3) by reduction of platinum oxide (PtO2). Spent catalysts were sintered at >1200 °C for 2–3 h, under plasma conditions that allow decomposing of the organic species and inter/intramolecular water on the surface of the spent catalyst. These reactions produce syngas (CO and H2), which can be used as the reducing agents in the process to obtain metallic platinum. This method has been widely used in the petrochemical industry. Bronshtein et al. [39] showed that Pt can be efficiently recovered from spent VCCs via a sintering process involving chloride salts. The spent catalyst is crushed and mixed with a solution of chloride salts at a catalyst/salt weight ratio of 2.5:6.7, followed by drying and sintering for 2 h in the reactor furnace at 1100 °C. This method does not involve hazardous chemicals, strong acid, or bases and, therefore, there are no additional corrosive gases generated during the process.
The smelting method consists of mixing the Pt waste with a flux, collector, and reducing agents before being smelted in a high-temperature inductive, electric, or plasma furnace at around 1000 °C. Pre-treatment is required prior to smelting. This includes dismantling, incineration of non-metallic components, calcination, and reduction with other metals (lead, iron, copper, among others) named collectors that will help to recover Pt. In the case of supported catalysts, such as alumina, the objective is to melt it in the presence of adequate fluxes to obtain a low viscosity liquid slag. After separating the Pt-enriched metal phase from the slag, the Pt-containing alloy is purified [40]. The metal lead collection is the oldest method used for recovering PGM from spent catalysts. The catalyst is crushed and mixed with PbO, anhydrous borax, sodium carbonate, and potassium bitartrate and then smelted for 2 h at 1100 °C. After that, a separation and purification step are required. Despite being a simple operation process and requiring low smelting temperature, highly toxic PbO gases are emitted during the process [41]. The copper collection process is used for spent catalysts containing cordierite. CuCO3 is used as copper collector, CuO or Cu as flux and SiO2 and CaO as reducing agents. All of them are mixed with the catalyst and smelted at 1400 °C. Pt is then collected at low temperature and high recovery rates are obtained [42,43,44]. Iron can be another economical collector due to its high affinity for PGM. The method is very similar to the copper collection, where Fe powder and CaO are mixed with the VCC and then are together smelted in a plasma arc at 1500 °C–2000 °C. Carrier slag can be separated from Fe alloy owing to their large density differences. Reported recovery rates for Pt are up to 98% [45,46]. More recently, Van Schalkwyk and Eksteen et al. [47,48] reported a new method called a matte collection. Briefly, when spent Pt catalyst is smelted at 1000 °C to 1450 °C, a matte kind of substance appears, which acts as a collector of Pt species. Ni or NiS can be added as an additional collector in presence of Na2CO3 or CaO as flux agents for 30 min at 1050 °C. The obtained Pt recovery rate was up to 90% [49]. From an industrial point of view, copper collection can be effortlessly adapted because of its relatively low cost, high efficiency, and low smelting temperature, furthermore, the collector material can be re-used [28,37].
From the environmental point of view, the pyrometallurgy method generates gas emissions like SO2, which is a severe environmental pollutant. Despite that, pyrometallurgy is the most common industrial solution to recover Pt (often shared facilities) due to its scalability and proven economic viability. For instance, in 2021′s Europe, several PGM refining companies or primary producers such as Johnson Matthey, Heraeus, BASF, Umicore, Anglo America Platinum, and Impala Platinum use their facilities for recycling PGM from VCCs and other secondary Pt sources through pyrometallurgical processes [50,51]. Although pyrometallurgy processes are an effective method to concentrate PGM and reducing the levels of impurities, large amounts of energy are required with the consequent CO2 associated footprint. Therefore, due to new environmental regulations and requirements, other techniques like hydrometallurgy or bio-leaching are closing the gap to industrial use [20].
2.1.2. Hydrometallurgical Recovery Process
Hydrometallurgical Pt recycling involves metal leaching with acid/basic solution in the presence of an oxidant, further separation/concentration, and a final recovery either in the metallic or salt form is required. In contrast to pyrometallurgical methods, significatively lower temperatures are required, can be used from small to larger scale, and produces less problematic and toxic gas wastes. On the other hand, and depending on the material to recycle, a chemical or mechanical pretreatment is often required to (i) reduce refractory Pt oxides formed during its use as a catalyst, (ii) eliminate problematic organic compounds, or (iii) reduce the particle size of the initial sample [52,53]. Several authors demonstrated that an oxidizing agent is key to allow refractory metals like Pt to be dissolved [54,55,56]. Different oxidizing agents have been used, like chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, bromine, nitrogen oxides, among others [54,57,58]. Despite highly acidic media are often used in metal leaching, kinetics, and activation energy to strip Pt from the used catalyst or material are important barriers to overcome an energy viable process. In this sense, it has been demonstrated that complexing agents like Cl− or CN− drops the potential energy barrier enough to perform a feasible leching process [59].
Aqua regia, which is a 3:1 mixture of HCl and HNO3, is one of the most used leaching agents for Pt recycling. In this system, Cl− acts as a complexing agent and the different oxidizing species generated strip Pt from spent catalysts. Massucci et al. [60] summarized the reactions taking place between Pt and the aqua regia environment. Pt in aqua regia media can undergo reaction (1) with the formation of the hexachloroplatinate complex and releasing toxic NO gas. In the same way, this reaction media can evolve into other hazardous gas products like NO2, NOCl, and Cl2 (reactions 2–4).
3Pt + 18HCl + 4HNO3 ←→ 3[PtCl6]2− + 6H+ + 4NO + 8H2O
Pt + 4NO3− + 8H+ → Pt4+ + 4NO2 + 4H2O
HNO3 + 3HCl ←→ NOCl + Cl2 + 2H2O
2NOCl g → 2NO g + Cl2 g
The treatment of catalysts or other Pt sources with aqua regia or other acidic oxidant media generates a metallic-containing solution that needs further treatment to separate Pt from other metallic species. Solvent extraction followed by Pt salt precipitation or direct Pt salt precipitation are the most common techniques used due to their simplicity and low cost.
Tyson et al. proposed a kinetic expression empirically determined for Pt leaching in aqua regia using a defined particle size of material. They also found that the leaching ratio was over 90% [61]. On the other hand, the recycling of a catalyst from the petrochemical industry was investigated by Jafarifar et al. [62]. They investigated two innovative methods, in the first one the sample was refluxed, and in the second one, it was irradiated using a 150 W microwave energy, both with aqua regia as leaching agent. They found 96–98% recovery rates after ionic separation of Pt, precipitated as the ammonium salt. Schreier et al. [63] recycled Pt scraps from the glass industry, along with other scarcest metals like Ir, Rh, or Pd. They investigated how different parameters, like HCl concentration and precipitation temperature of Pt salt affect the global yield of the process. In this sense, it has been demonstrated that to obtain high purity Pt (99.99% Pt powders are obtained) from the leached liqueur, the recovery yield is diminished and vice-versa.
Other authors tried to avoid the environmental problems of using aqua regia by employing other leaching solutions in the presence of chloride as a Pt complexing agent. Kizilaslan et al. proposed using an H2O2 oxidizing agent in combination with HCl at a 1:10 rate obtaining 95% of Pt recovery at mild temperatures (45 °C) [64]. They also studied the influence of temperature and agitation rate, and concluded that while at high temperatures (more than 80 °C) aqua regia was more effective to strip Pt from the sample, at mild temperatures the mixture H2O2:HCl worked better. Shams et al. [65] recovered Pt from a spent dehydrogenation catalyst using cyanide solution and obtained 85% of the recovery. They found that both pH and temperature strongly affect the outcoming recovery rate and stating the optimum sodium cyanide: catalyst weight ratio in 2:1. Other authors like Zanjani et al. [66] tried to use iodide as a complexing agent, however, and despite obtaining promising results, the kinetics of the process is sluggish, and more aggressive conditions than Cl− system is needed. More recently, Robinson et al. [67] used ozone in a concentrated chloride solution and obtained a promising 90% recovery rate for Pt. Furthermore, they calculated the apparent activation energies for the process that found to be 44 kJ/mol for Pt.
In the last years, all the efforts in the hydrometallurgical field were focused on making the process cleaner and environmentally friendly. In this sense, Nguyen et al. claimed an innovative solvometallurgical process using inorganic lixiviants like FeCl3/CH3CN system [68]. An 80% Pt leaching was obtained without using aggressive media or generating corrosive liquid/gas wastes. Hideaki et al. [69] used Zn vapor deposition over Pt samples to enhance its leaching rate, allowing authors to employ diluted aqua regia solutions, and thus, working with a considerably less harmful environment. Suoranta et al. [70] used microwave radiation to assist the leaching process, making it faster and, thus, less expensive than conventional hydrometallurgical leaching. They not only obtained over 90% recovery of Pt, but also leached the supporting alumina phase, which can be further recovered.
2.2. Alternative and Novel Technologies
Traditional pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy produce hazardous gaseous and liquid waste and consume a large amount of energy. Due to the upcoming climate and ambiental problems, new environmentally friendly technologies are required to optimize and minimize energy consumption and environmental impact. Furthermore, these novel technologies that focus on the recovery of Pt also allow recycling of other relevant materials, for instance support materials or reactor membranes.
2.2.1. Selective Electrochemical Dissolution
Platinum is the state-of-art and most frequently used element as an electrocatalyst in emerging technologies like PEMFCs or hydrolyzers, among others [71]. However, some current challenges such as material availability and extraction cost have slowed his commercialization in the last few years. In this sense, platinum electrochemical dissolution appears to be a suitable method to recover platinum from PEMFCs, and thus minimizing the need for expensive primary production. On one hand, a mixture of primary and secondary production using pyrometallurgy is a common practice to recover platinum, especially from spent auto-catalysts. Nevertheless, pyrometallurgy is not suitable for treating large volumes of fuel cell membrane electrode assembly (MEA) recycling, owing to the presence of fluorine compounds. Incineration of the fluoropolymers from carbon support with Teflon® causes the formation of extremely harmful hydrogen fluoride (HF) [72]. On the other hand, the hydrometallurgy process has also been used for MEA recycling, but a high concentration of strong acids and oxidants used, such as HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, and H2O2, can react with fluorinated compounds and end with highly toxic vapors [73].
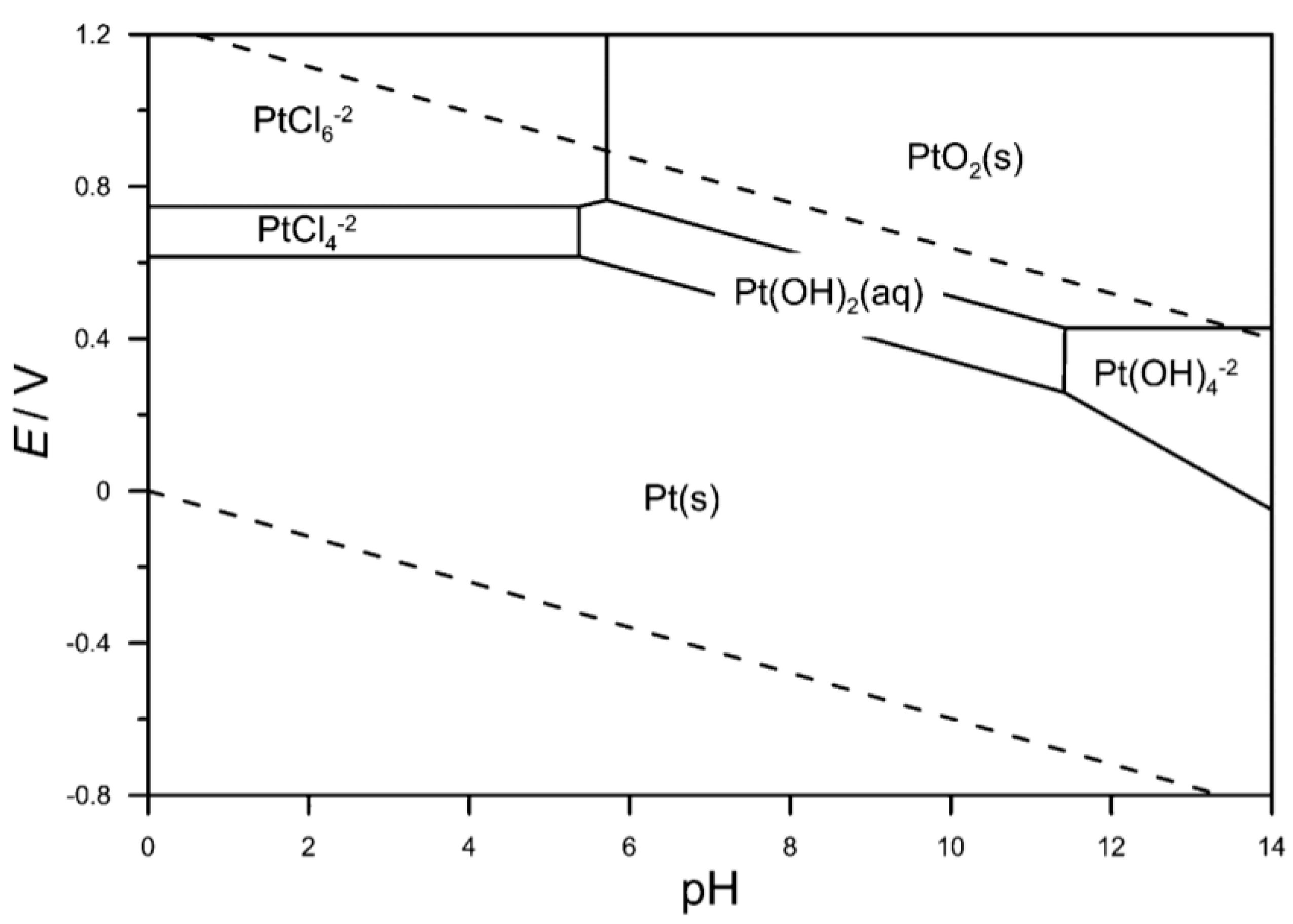
During the last years, Pt electrochemical dissolution has been thoroughly studied by different groups to understand the degradation mechanisms of Pt electrocatalysts [73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82]. Pourbaix diagram (see Figure 3 [83]) suggests that platinum dissolves when exposed to an anodic polarization at potential above 1 V (vs RHE) in strong acidic electrolytes. The platinum dissolution window in the E-pH diagram expands for chloride containing acidic electrolytes because the formation of PtCl4 2− and PtCl6 2− complexes significantly drops the necessary potential to strip the metallic Pt from catalyzers (0.65 V versus RHE).
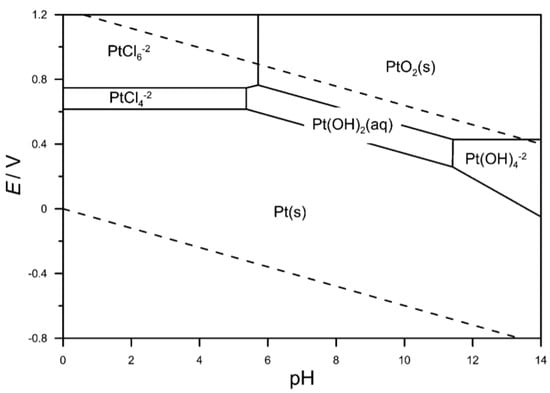
Figure 3.
Pourbaix diagram. E vs pH in an electrolyte containing 0.5 M HCl. The solid lines demarcate the stability regions of varius Pt species, whereas the dashed lines separate the stability regions of water. From Ref. [82].
One of the most significant contributions in this area is potentiodynamic dissolution through both anodic and cathodic sweeps [76,81,82]. Latsuzbaia et al. [84] investigated the influence of chloride ions and oxygen in the dissolution of Pt from a fuel cell electrode by electrochemical potential cycling between 0.5–1.1 V in 0.1 M HCl to recover Pt from Pt nanoparticles. They achieved dissolution rates of 22.5 µg cm−2 per cycle and in a relatively short dissolution timescale of 3–5 h for a 0.35 mg cm−2 Pt loading of on carbon. Kanamura et al. [85] established a recovery method for Pt and Ru from MEAs by square wave potential cycling in dilute acids, leading to a 93.2% of Pt dissolution. They suggested 1.4 V as an optimal upper potential for Pt dissolution. Hodnik et al. [86] demonstrated a complete dissolution of metallic Pt by induced surface potential alteration (transient dissolution). More in detail, they used a cyclic oxidative process, followed by treatment by successive oxidative (ozone) and reductive (carbon monoxide) gases. This treatment triggers a repetitive change in platinum surface oxidation state and ends with Pt dissolution. Raghunandan Sharma et al. [73] developed a highly efficient and environmentally friendly platinum recycling method through potentiodynamic cycling in dilute acidic solutions from fuel cell electrodes. They employed a potential window between 0.4–1.6 V vs. RHE to recover 30 µg Pt/cycle with a scan rate of 100 mV/s in 1 M HCl. Potential cycling instead of pulsed anodic potential seems to be the suitable way to strip Pt from the electrodes, avoiding the formation of refractory Pt oxides.
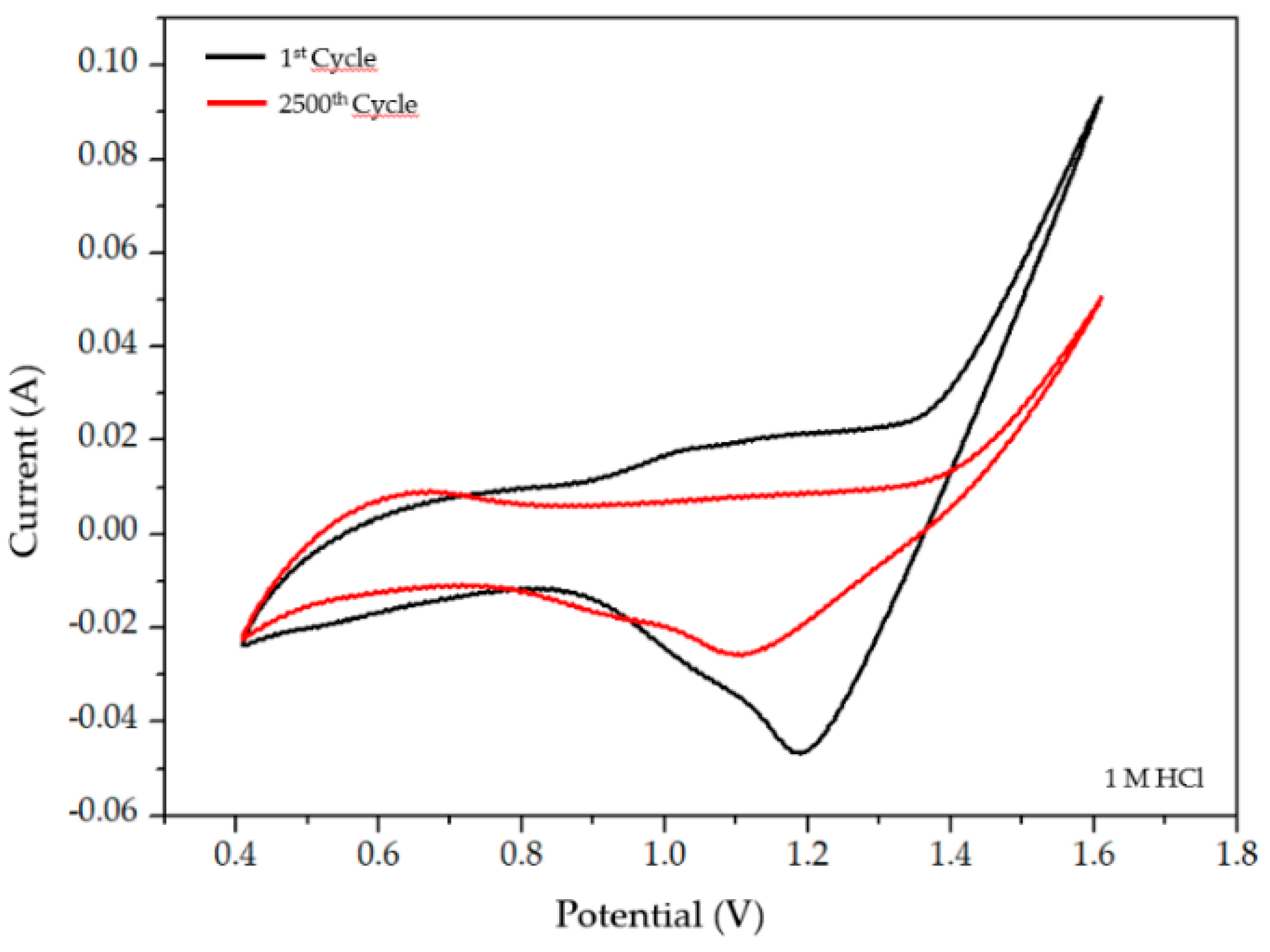
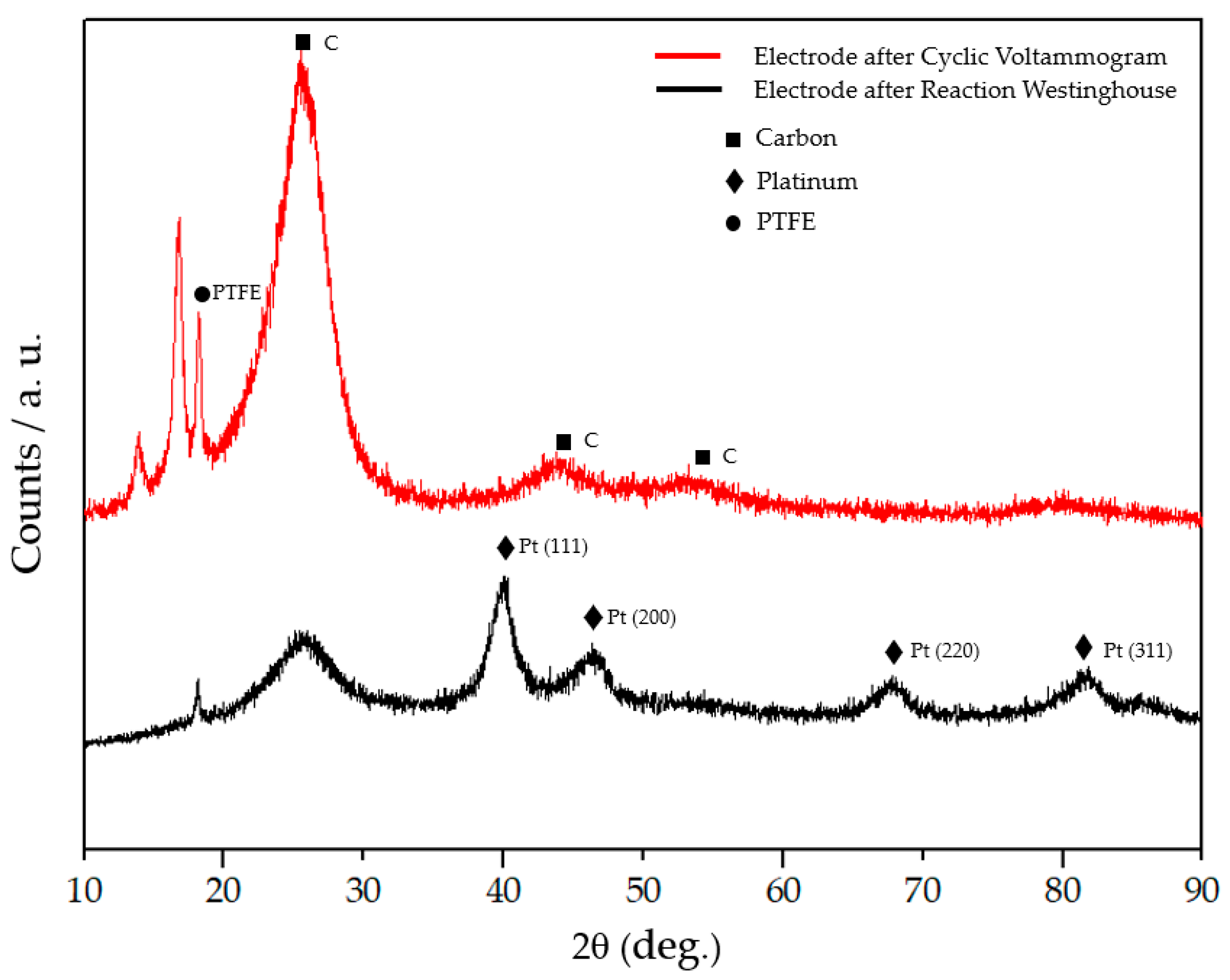
Our group has studied an environmentally friendly method to recover Pt in acidic chloride solutions from MEAs used in the SO2 depolarized electrolysis cell employed in Westinghouse Cycle for hydrogen production using a commercial catalyst with a 40% Pt content on Vulcan carbon (Pt loading of 0.7 mg Pt cm−2) [87,88]. Spent Pt/C electrocatalyst was dissolved by electrochemical treatment under mild conditions to form a Pt-complex in an acidic solution. Electrochemical dissolution of Pt was performed through potential cycling (2500 cycles) between 0.4–1.6 V vs Ag/AgCl at 100 mV/s scan rate in 1 M HCl electrolyte. Figure 4 shows the first cyclic voltammogram of the electrode used in the Westinghouse process (black line), where platinum oxidation and reduction occurs between 1.0–1.6 V. After 2500 cycles, the current decreases, thus showing that platinum has been dissolved (red line). On the other hand, the black line in Figure 5 shows the XRD pattern of the electrode used in the MEA of the electrolyzer for the SO2 depolarized oxidation for hydrogen production of the Westinghouse process (related to the 1st cycle of the voltametric treatment in Figure 4) and the red line shows the same electrode after 2500 cycles of voltametric treatment (related to the red line in Figure 4). More in detail, the Pt electrode used in the electrolyzer of the Westinghouse cycle (black line in Figure 5) presents platinum characteristic peaks of Pt (111), Pt (200), Pt (220), and Pt (311), while Pt signals completely disappeared after 2500 voltametric cycles (red line in Figure 5), and only carbon signals are still present. After the 2500 cycles, the solution was analyzed by UV-vis spectroscopy to quantify the total amount of platinum-complex formed the through electrochemical dissolution process, obtaining that Pt can be recovered from a spent electrode in the Westinghouse cycle in a 60–80% rate.
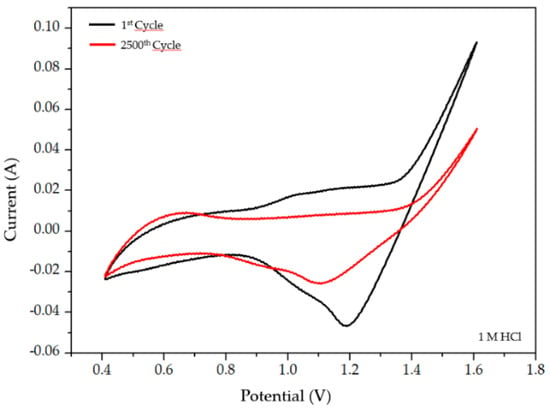
Figure 4.
Voltametric profiles of Pt/C 40/60 electrode former used in a Westinghouse process. Black line corresponds to the 1st and red line to the 2500th cycle in a 1M HCl. Scan rate of 100 mV/s.
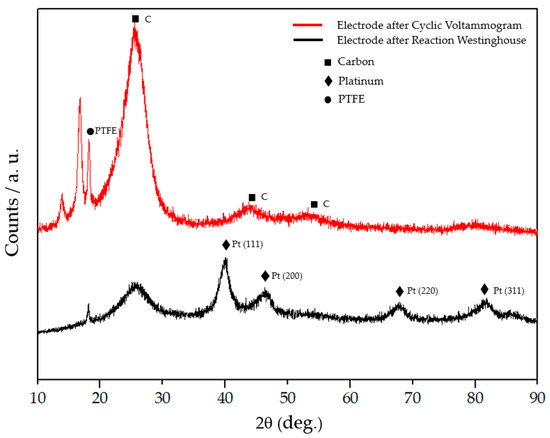
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of Pt/C 40/60 electrode former used in Westinghouse process. Black lines correspond to the electrode before electrochemical dissolution process and red line to the treated electrode (2500 voltametric cycles between 0.4 and 1.6 V).
In summary, electrochemical dissolution allows the recovery of high purity Pt catalyst at mild conditions in terms of pH, temperature, and voltage, offering a suitable techno-environmental performance. The main challenge from the end-of-life electrode in PEMFCs recycling is the complete recycling of all components of the MEAs, Pt catalyst, carbon support, and ionomer used for both membrane and catalyst layer [73,89]. Further efforts are needed to optimize this relatively unexplored recovery process, which gives the opportunity to recover Pt at a small scale and affordable cost for many research groups using Pt materials.
2.2.2. Bioleaching
Bioleaching is a biometallurgical process that uses microorganisms, mainly bacteria, to extract metallic ions (Pt, Rh, Pd, among others) from solid samples. Two different approaches, depending on the type of bacteria used, can be held to perform a bioleaching process. On one side, mesophilic bacteria, like Acidithiobacilus ferrooxidans or Acidithibacilus thiooxidans, can leach metallic ions in presence of Fe or sulfur species. These bacteria are autotrophic and chemolithotroph and have been used, not only in precious metal recovery, but also in bio-mining purposes. On the other hand, a second approach using heterotrophic bacteria has been recently developed. It consists in take advantage of the bio-generated cyanide by oxidative decarboxylation of different substrates to leach precious metal ions [90]. Chromobacterium violaceum has been used in this second approach to effectively recover precious metals [91]. This bio-generated cyanide can mobilize precious metallic ions from VCC’s, metallic scraps, or even mining ores, with a significative lower environmental impact due to soft reaction conditions and a lower reactant consumption [92]. Bacteria can be added to the metal-containing sample at the beginning of the process, that is one-step bioleaching [93,94], or rather be cultivated apart and further mixed with the metal source (two-step bioleaching) [95]. Bacteria used in bioleaching require friendly environment to grow and outcome as an efficient leaching agent, but in its process some factors must be considered. In the first place, pH is a key factor because not only affects the bacteria population growing, but also determines the leaching rate, for instance, with cyanide as a leaching agent. In this sense, a compromise must be reached to perform a good bioleaching process [96]. On the other hand, the feedstock chemicals used to grow bacteria control the population and the leaching agent generated. For instance, glycine is a good precursor to generate cyanide with a minimal amount of side products [97]. Finally, dissolved oxygen also plays a double-sided role because is needed for the development of the cyanide producer bacteria and as an oxidant in the leaching process, therefore, precisely controlling the amount of oxygen is mandatory [98].
Bioleaching is still in its first steps and more research is needed to fully understand all the parameters, and thus achieve as good results as more studied pyro and hydrometallurgical processes. One of the first breaking-through studies was performed by Brandl et al. in 2008 [90] where they recovered Pt from spent VCC’s up to 0.2 % after 10 days. This study, far from the numbers of other techniques served as proof of concept to develop a new method to recover Pt in a sustainable way. More recently, Shin et al. [99] developed a biological system for the production and accumulation of cyanide. This system was able to recover 92.1 % of Pt from a spent VCC, closing the gap between bioleaching and other techniques and demonstrating that the accumulation of biogenic cyanide in operating concentrations is possible. This recovery was possible due to the high cyanide concentration reached during the experiment (up to 6594.5 mg/L) and was tested at different temperatures. Karim et al. [100] combined an ultrasound pre-treatment with a two-step bioleaching with Pseudomonas fluorens and Bacilus megaterium to extract Pt and other PGM from a used VCC obtaining a 38% of Pt recovery at pH 9, and thus demonstrating that a noble metal recovery is possible under mild conditions and low-waste generation.
2.2.3. Other Techniques
In the last decade, numerous techniques have been introduced as more environmentally affordable Pt recovery methods [101]. Taninouchi et al. used magnetic separation to concentrate Pt before its further leaching treatment through Ni electro-less or FeCl2 vapor deposition [102,103]. Pt and other PGM were successfully alloyed forming magnetic compounds that were separated from the rest of the catalyst, in this way, the quantity of the sample that has to be further treated diminishes and the energetic and reagent consumption do so. Moving to the pyrometallurgy field, Martinez et al. proposed an alternative chlorination method for VCCs [104]. They used molten salts as a solvent to achieve good recovery rates (up to 40–50%) keeping the temperature lower than the conventional methods, and in this case, despite lowering the energy consumption of the process, the environmental hazardous chlorine derivates still represent a serious problem. In the same scope of lowering the temperature, Ding et al. [105] used a highly efficient iron collector in which Fe-Pt alloys are formed at 1300–1400 °C instead of traditional 2000 °C by adjusting the slag composition and obtaining a Pt recovery of 99.25%. Morcali lowered even more the working temperature to 950 °C, and thus avoiding the use of plasma furnace, by using a flux composed of B2O3, Na2O, and FeS2 and achieving a 99% of Pt recovery [106]. This method represents an advantage from the environmental point of view, not only for the lower energy consumption, but also for using less hazardous chemicals, however, the high cost of some reactants must be considered. Sasaki et al. alloyed Pt in VCCs with Zn as a pretreatment to further be leached in acidic media [69,107]. Pt and Zn form alloys that are easily dissolved in aqua regia and, thus, enhancing recovery rate (near 100%), lowing the time to perform the process, and minimizing the quantity of oxidant needed. They also demonstrated that diluted aqua regia worked as effectively as the undiluted one in the extraction of Pt in a Zn-treated sample.
Although microwaves have been traditionally used in the metallurgical field to perform controlled and more efficient heating [62], some authors recently used microwaves to assist or pretreat the sample before Pt extraction (for example in VCCs). Suoranta et al. [70] performed leaching experiments with HCl and aqua regia at different temperatures (90–210 °C) in a microwave and a traditional oven. They found that, in the microwave oven, both HCl and aqua regia were able to leach and further recover up to 91% Pt of the sample in a shorter time than in a regular oven and thus, becoming a more energy efficient process. A local superheating mechanism is proposed to explain the better performance of microwave-assisted leaching, furthermore, Pt and other PGM particles could be selectively heated due to the properties of the microwaves over regular heating. Spooren et al. used microwaves to roast the VCC in the presence of different oxidants (NaHSO4·H2O or KHSO4 and NaClO3) to convert the Pt in the VCC into a Pt2+ and Pt4+ [108]. Subsequently, a microwave-assisted acidic leaching process with HCl 1M was performed turning into an 85% Pt recovery in only 30 min, that is, a relatively good performing minimizing energetic consumption and the use of aggressive (and hazardous) leaching agents. From the industrial point of view, the VITO company and other partners of the PLATIRUS project upgraded microwave assisted leaching process to the pre-pilot stage and are now ready to prove its viability in a prototype [109]. Other authors like Chen et al., Trinh et al., or Nogueira et al. tried to achieve a greener leaching process by switching to other leaching agents that produce less hazardous fumes and wastes like NaClO3 or CuCl2 [110,111,112]. This is possible due to the use of pre-treatments like oxidations cycles or roasting. In particular, Trinh et al. stepped further and performed a complete recycling of all components of a spent VCC by roasting-assisted leaching.
3. Conclusions and Outlook
Platinum recovery is a crucial process to allow a sustainable shift to greener technologies. Tons of Pt are held in VCC’s that will be gradually substituted by electric or fuel cell/hydrogen vehicles. Due to the high environmental impact and tremendous resource consumption of traditional Pt mining, reinsert most of the Pt of spent VCC’s and other Pt sources in the economy is the only way to move into Pt circular economy, and thus allow the bloom of new and promising technologies that need Pt to work.
In this review, traditional-and most used in industry- recovery technologies are discussed, and it has been stated that they require high energy input and produce large amounts of solid, liquid, and gaseous hazardous waste. In latest years, numerous alternative technologies are proposed to perform a greener Pt recovery, either substituting the existent technologies, like bioleaching or selective electrochemical dissolution, or on the other hand, minimizing energy consumption and/or waste generation of Pyro-Hydrometallurgical approaches. Table 1 groups different Pt recovery processes using traditional and new technologies and focusing on their energy consumption and waste generation. From the authors point of view, a compromise must be held between benefit from the existent Pt recovery plants and improving the processes with environmentally friendly modifications. To achieve this compromise, both public and private resources must point in the same direction and join efforts. Although some green approaches to Pt recovery are shown along with this text, not all are suitable for every type of scrap. In this regard, while selective electrochemical dissolution is a promising technology for recycling Pt from many sources, especially from the catalyzers of the PEMFCs, more aggressive hydrometallurgical methods are best suited to retrieve Pt from VCCs due to its refractory support material.

Table 1.
Comparison of different Pt recovery technologies in terms of Pt recovery rate (%), TRL (Technology Readiness Level from 1–9), energy consumption (being red, yellow and green a high, moderate and low, respectively) and waste generation (being red high volume and toxicity, yellow, moderate volume and toxicity and green, low or negligible waste generation).
In conclusion, despite having promising initial results, some of the environmentally friendly technologies shown in this review are unmatured, so more efforts and funding are necessary to scale them up and substitute the existing commercial technologies. The scale up process needs to be as fast as possible due to the upcoming substitution of combustion vehicles to other technologies. On the other hand, Pt selective electrochemical dissolution will be a key process in the recycling of emerging technology like PEMFCs and may allow keeping Pt as a catalyst in many devices and electrochemical processes.
Author Contributions
J.L. and M.A.R. contributed to the design, Funding acquisition and implementation of the research meanwhile M.A.M., R.G.-F. and S.D.-A. carried out the information search, Data curation and proposed comparative discussions. Frequent group meetings between the authors helped to analyze and organize the findings until obtaining the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha and the FEDER e EU Program, Project ASEPHAM. Grant number “SBPLY/17/180501/000330” and the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness and European Union through the project ID2019–107271RB-I00. Miguel A. Montiel is grateful to the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation for his postdoctoral fellowship, Juan de la Cierva Formación program (FJC2019-039279-I). Therefore, these Institutions are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| VCCs | Vehicle catalytic converter |
| PEMFCs | Proton exchange membrane fuel cells |
| PGM | Platinum group metals |
| MEA | Membrane electrode assembly |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
References
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.; Skea, J.; Shukla, P.R.; Pirani, A.; Moufouma-Okia, W.; Péan, C.; Pidcock, R.; et al. Global Warming of 1.5 °C: An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Commision. Europe’s Moment: Repair and Prepare for the Next Generation; European Commision: Brisel, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, R.; Iqbal, N.; Hanif, S.; Noor, T.; Shi, X.; Zaman, N.; Haider, D.; Rizvi, S.A.M.; Kannan, A.M. Mof-Derived Cupt/Nc Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zignani, S.C.; Baglio, V.; Sebastián, D.; Saccà, A.; Gatto, I.; Aricò, A.S. Towards Highly Performing and Stable PtNi Catalysts in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells for Automotive Application. Materials 2017, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouzgou, A.; Song, S.; Liang, Z.X.; Tsiakaras, P. Non-Precious Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Alkaline Media: Latest Achievements on Novel Carbon Materials. Catalysts 2016, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseeva, E.; Stelmashuk, T.; Danilov, S.; Yang, P.; Levin, O. Bimetallic Cu/Pt Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst for Fuel Cells Cathode Materials. Catalysts 2020, 10, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, C. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Reversal: A Review. Catalysts 2016, 6, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drielsma, J.A.; Russell-Vaccari, A.J.; Drnek, T.; Brady, T.; Weihed, P.; Mistry, M.; Simbor, L.P. Mineral Resources in Life Cycle Impact Assessment—Defining the Path Forward. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, K.D.; Wenzel, H.; Bangs, C.; Petavratzi, E.; Liu, G. Platinum Demand and Potential Bottlenecks in the Global Green Transition: A Dynamic Material Flow Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11541–11551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandell, L.; Lehtilä, A.; Kivinen, M.; Koljonen, T.; Kihlman, S.; Lauri, L.S. Role of Critical Metals in the Future Markets of Clean Energy Technologies. Renew. Energy 2016, 95, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, G. Critical Metals Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Critical Raw Materials; European Commision Report; European Commision: Brisel, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Løvik, A.N.; Hagelüken, C.; Wäger, P. Improving Supply Security of Critical Metals: Current Developments and Research in the EU. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 15, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlakovs, J.; Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; Krievans, M.; Jani, Y.; Horttanainen, M.; Pehme, K.M.; Dace, E.; Setyobudi, R.H.; Pilecka, J.; Denafas, G.; et al. Platinum Group Elements in Geosphere and Anthroposphere: Interplay among the Global Reserves, Urban Ores, Markets and Circular Economy. Minerals 2020, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Jena, M.S.; Mandre, N.R.; Venugopal, R. Platinum Group Elements Mineralogy, Beneficiation, and Extraction Practices–An Overview. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaister, B.J.; Mudd, G.M. The Environmental Costs of Platinum-PGM Mining and Sustainability: Is the Glass Half-Full or Half-Empty? Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelüken, C. Recycling the Platinum Group Metals: A European Perspective. Platin. Met. Rev. 2012, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distribution of Platinum Group Metals Supply Worldwide in 2019, by Source. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/602766/distribution-of-the-supply-of-platinum-group-metals-worldwide-by-source/ (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgical Recovery of Metals from Electronic Waste: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, J.; Kim, B.S.; Kumar, V. Hydrometallurgical Recovery/Recycling of Platinum by the Leaching of Spent Catalysts: A Review. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 133, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X. Progress in Recycling of Precious Metals in Automobile Catalysts. Xiyou Jinshu/Chin. J. Rare Met. 2013, 37, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Tansel, B.; Ying, W. Automotive Wastes. Water Environ. Res. 1995, 67, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Mu, S.; Pan, M. Recycling of Membrane Electrode Assembly of PEMFC by Acid Processing. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 2976–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkareem, M.A.; Elsaid, K.; Wilberforce, T.; Kamil, M.; Sayed, E.T.; Olabi, A. Environmental Aspects of Fuel Cells: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, L.; Chattot, R.; Dubau, L.; Thivel, P.X.; Mandil, G.; Laforest, V.; Bolloli, M.; Vincent, R.; Svecova, L. Closing the Loop: Life Cycle Assessment and Optimization of a PEMFC Platinum-Based Catalyst Recycling Process. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1919–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Keeley, G.P.; Holtz, D.; Grube, T.; Robinius, M.; Müller, M.; Stolten, D. PEM Water Electrolysis: Innovative Approaches towards Catalyst Separation, Recovery and Recycling. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 3450–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, B. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts: A Review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 145, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padamata, S.K.; Yasinskiy, A.S.; Polyakov, P.V.; Pavlov, E.A.; Varyukhin, D.Y. Recovery of Noble Metals from Spent Catalysts: A Review. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2020, 51, 2413–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Tang, H.; Ye, L.; Ma, Y.; Rao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Pyrometallurgical Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts. JOM 2017, 69, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlik, T.; Orac, D.; Petranikova, M.; Miskufova, A.; Kukurugya, F.; Takacova, Z. Leaching of Copper and Tin from Used Printed Circuit Boards after Thermal Treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda, M.W.; Perino, E.; Ruiz, M.D.C. Gold Extraction by Chlorination Using a Pyrometallurgical Process. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Foller, P.C.; Giallombardo, J. Two Step Method for Recovery of Dispersed Noble Metals. EU Patent Application No. 0492691A1, 1 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.H.; Woo, S.I.; Jeon, S.H. Recovery of Platinum-Group Metals from Recycled Automotive Catalytic Converters by Carbochlorination. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horike, C.; Morita, K.; Okabe, T.H. Effective Dissolution of Platinum by Using Chloride Salts in Recovery Process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2012, 43, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, M.J.; Bicek, E.J. Recovery of Metals. U.S. Patent 3,021,209, 13 February 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.Q.; Xu, L. Some Recovery Process for Precious Metals from Spent Automobile Catalyst. China Nat. Res. Recycl. 1998, 10, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Staszak, K. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2018, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, K.C.; Chen, K.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, J.J.; Shen, Y.H.; Yeh, M.Y.; Wong, F.F. Recovery of Spent Alumina-Supported Platinum Catalyst and Reduction of Platinum Oxide via Plasma Sintering Technique. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronshtein, I.; Feldman, Y.; Shilstein, S.; Wachtel, E.; Lubomirsky, I.; Kaplan, V. Efficient Chloride Salt Extraction of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts. J. Sustain. Metall. 2018, 4, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayanuma, Y.; Okabe, T.H.; Maeda, M. Metal Vapor Treatment for Enhancing the Dissolution of Platinum Group Metals from Automotive Catalyst Scrap. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2004, 35, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.; Bennett, C.R.; Harry, J.E.; Patel, M.K.; Cross, M. The Recovery Mechanism of Platinum Group Metals from Catalytic Converters in Spent Automotive Exhaust Systems. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2000, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Ezawa, N. Process of Recovering Platinum Group Metal. U.S. Patent 5,252,305, 12 October 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, J.E. Recovering Platinum-Group Metals from Gabbroic Rocks Metals from Auto Catalysts. JOM 1988, 40, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolliopoulos, G.; Balomenos, E.; Giannopoulou, I.; Yakoumis, I.; Panias, D. Behavior of Platinum Group during Their Pyrometallurgical Recovery from Spent Automotive Catalysts. Open Access Libr. J. 2014, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhoo, Y.; Weng, H.; Liu, W. Study on the Process of Enrichment Platinum Group Metals by Plasma Melting Technology. Precious Met. 2016, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.K.; Redaly, R.G. Precious Metals 1986: Proceedings of the Tenth International Precious Metals Institute Conference; International Precious Metals Institute: Pensacola, FL, USA, 1986; pp. 217–231. [Google Scholar]
- Eksteen, J.J. A Mechanistic Model to Predict Matte Temperatures during the Smelting of UG2-Rich Blends of Platinum Group Metal Concentrates. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schalkwyk, R.F.; Eksteen, J.J.; Akdogan, G. Leaching of Ni-Cu-Fe-S Converter Matte at Varying Iron Endpoints; Mineralogical Changes and Behaviour of Ir, Rh and Ru. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 136, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Fang, W.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, X.T.; Yang, H. Study on Enrichment Method of Platinum, Palladium and Rhodium in Spent Auto-Catalysts. Yejin Fenxi/Metall. Anal. 2016, 36, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Crundwell, F.; Moats, M.; Ramachandran, V.; Robinson, T.; Davenport, W.G. Extractive Metallurgy of Nickel, Cobalt and Platinum Group Metals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffner, F.; Hobbs, C. Process for the Production of a PGM-Enriched Alloy. U.S. Patent 10323302B2, 18 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Aberasturi, D.J.; Pinedo, R.; De Larramendi, I.R.; De Larramendi, J.I.R.; Rojo, T. Recovery by Hydrometallurgical Extraction of the Platinum-Group Metals from Car Catalytic Converters. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornalczyk, A.; Saternus, M. Removal of platinum group metals fron the used autocatalytic converter. Metalurgija 2009, 48, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Angelidis, T.N. Development of a Laboratory Scale Hydrometallurgical Procedure for the Recovery of Pt and Rh from Spent Automotive Catalysts. Top. Catal. 2001, 16–17, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Meng, X. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals and Rhenium from Materials Using Halogen Reagents. U.S. Patent 5,542,957, 6 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.S. Metal Recovery and Rejuvenation of Metal-Loaded Spent Catalysts. Catal. Today 1998, 44, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjanto, S.; Cao, Y.; Shibayama, A.; Naitoh, I.; Nanami, T.; Kasahara, K.; Okumura, Y.; Liu, K.; Fujita, T. Leaching of Pt, Pd and Rh from Automotive Catalyst Residue in Various Chloride Based Solutions. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panda, R.; Jha, M.K.; Pathak, D.D. Commercial Processes for the Extraction of Platinum Group Metals (PGMs). In Rare Metal Technology; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume F5, pp. 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Saguru, C.; Ndlovu, S.; Moropeng, D. A Review of Recent Studies into Hydrometallurgical Methods for Recovering PGMs from Used Catalytic Converters. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 182, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massucci, M.; Clegg, S.L.; Brimblecombe, P. Equilibrium Partial Pressures, Thermodynamic Properties of Aqueous and Solid Phases, and Cl2 Production from Aqueous HCl and HNO3 and Their Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 4209–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, D.R.; Bautista, R.G. Leaching Kinetics of Platinum and Palladium from Spent Automotive Catalysts. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1987, 22, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarifar, D.; Daryanavard, M.R.; Sheibani, S. Ultra Fast Microwave-Assisted Leaching for Recovery of Platinum from Spent Catalyst. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 78, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, G.; Edtmaier, C. Separation of Ir, Pd and Rh from Secondary Pt Scrap by Precipitation and Calcination. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 68, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilaslan, E.; Aktaş, S.; Şeşen, M.K. Towards Environmentally Safe Recovery of Platinum from Scrap Automotive Catalytic Converters. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2009, 33, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Shams, K.; Beiggy, M.R.; Shirazi, A.G. Platinum Recovery from a Spent Industrial Dehydrogenation Catalyst Using Cyanide Leaching Followed by Ion Exchange. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 258, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, A.; Baghalha, M. Factors Affecting Platinum Extraction from Used Reforming Catalysts in Iodine Solutions at Temperatures up to 95 °C. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Lapidus, G.T. Platinum, Palladium and Gold Leaching from Magnetite Ore, with Concentrated Chloride Solutions and Ozone. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 166, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Aktan, E.; Deferm, C.; Fransaer, J.; Binnemans, K. Solvometallurgical Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Maeda, M. Zn-Vapor Pretreatment for Acid Leaching of Platinum Group Metals from Automotive Catalytic Converters. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 147–148, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suoranta, T.; Zugazua, O.; Niemelä, M.; Perämäki, P. Recovery of Palladium, Platinum, Rhodium and Ruthenium from Catalyst Materials Using Microwave-Assisted Leaching and Cloud Point Extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 154, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Riffat, S.; Liu, C.-j. A Comprehensive Review of Pt Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction: Nanostructure, Activity, Mechanism and Carbon Support in PEM Fuel Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 1808–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittstock, R.; Pehlken, A.; Wark, M. Challenges in Automotive Fuel Cells Recycling. Recycling 2016, 1, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.; Nielsen, K.R.; Lund, P.B.; Simonsen, S.B.; Grahl-Madsen, L.; Andersen, S.M. Sustainable Platinum Recycling through Electrochemical Dissolution of Platinum Nanoparticles from Fuel Cell Electrodes. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 4471–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, Y.; Okayasu, T.; Yadav, A.P.; Nishikata, A.; Tsuru, T. Dissolution Mechanism of Platinum in Sulfuric Acid Solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, F779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, S.; Cherevko, S.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Dissolution of Platinum in Presence of Chloride Traces. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 179, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherevko, S.; Kulyk, N.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Durability of Platinum-Based Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts: Dissolution of Bulk and Nanoscale Platinum. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 275–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherevko, S.; Keeley, G.P.; Geiger, S.; Zeradjanin, A.R.; Hodnik, N.; Kulyk, N.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Dissolution of Platinum in the Operational Range of Fuel Cells. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topalov, A.A.; Katsounaros, I.; Auinger, M.; Cherevko, S.; Meier, J.C.; Klemm, S.O.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Dissolution of Platinum: Limits for the Deployment of Electrochemical Energy Conversion? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12613–12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavlišič, A.; Jovanovič, P.; Šelih, V.S.; Šala, M.; Hodnik, N.; Gaberšček, M. Platinum Dissolution and Redeposition from Pt/C Fuel Cell Electrocatalyst at Potential Cycling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F3161–F3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovič, P.; Petek, U.; Hodnik, N.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Gatalo, M.; Šala, M.; Šelih, V.S.; Fellinger, T.P.; Gaberšček, M. Importance of Non-Intrinsic Platinum Dissolution in Pt/C Composite Fuel Cell Catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 21446–21452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myers, D.J.; Wang, X.; Smith, M.C.; More, K.L. Potentiostatic and Potential Cycling Dissolution of Polycrystalline Platinum and Platinum Nano-Particle Fuel Cell Catalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F3178–F3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topalov, A.A.; Cherevko, S.; Zeradjanin, A.R.; Meier, J.C.; Katsounaros, I.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Towards a Comprehensive Understanding of Platinum Dissolution in Acidic Media. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourbaix, M.; Zhang, H.; Pourbaix, A. Presentation of an Atlas of Chemical and Electrochemical Equilibria in the Presence of a Gaseous Phase. Mater. Sci. Forum 1997, 251–254, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latsuzbaia, R.; Negro, E.; Koper, G.J.M. Environmentally Friendly Carbon-Preserving Recovery of Noble Metals from Supported Fuel Cell Catalysts. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamura, S.; Yagyu, M. Electrochemical Dissolution of Platinum and Ruthenium from Membrane Electrode Assemblies of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodnik, N.; Baldizzone, C.; Polymeros, G.; Geiger, S.; Grote, J.P.; Cherevko, S.; Mingers, A.; Zeradjanin, A.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Platinum Recycling Going Green via Induced Surface Potential Alteration Enabling Fast and Efficient Dissolution. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Abad, S.; Millán, M.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Lobato, J. Review of Anodic Catalysts for SO2 Depolarized Electrolysis for “Green Hydrogen” Production. Catalysts 2019, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobato, J.; Díaz-Abad, S.; Peláez, M.C.; Millán, M.; Rodrigo, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Pt on Novel Catalyst Supports for the H2 Production in the Westinghouse Cycle. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 25672–25680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, A.; Iribarren, D.; Dufour, J. End of Life of Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Products: From Technologies to Strategies. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 20965–20977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, H.; Lehmann, S.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Martinelli, D. Biomobilization of Silver, Gold, and Platinum from Solid Waste Materials by HCN-Forming Microorganisms. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 94, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, V.A.; Ting, Y.P. Gold Bioleaching of Electronic Waste by Cyanogenic Bacteria and Its Enhancement with Bio-Oxidation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 71–73, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Lee, J. chun Biometallurgical Recovery of Metals from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment: A Review. Chembioeng. Rev. 2014, 1, 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, A.D.; Deveci, H.; Yazici, E.Y. Bioleaching of Copper from Low Grade Scrap TV Circuit Boards Using Mesophilic Bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 138, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, G.; Ting, Y.P. Pretreatment of E-Waste and Mutation of Alkali-Tolerant Cyanogenic Bacteria Promote Gold Biorecovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işıldar, A.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Rene, E.R.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Lens, P.N.L. Two-Step Bioleaching of Copper and Gold from Discarded Printed Circuit Boards (PCB). Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, T.D.; Lee, J.C.; Pandey, B.D.; Yoo, K.; Jeong, J. Bioleaching of Gold and Copper from Waste Mobile Phone PCBs by Using a Cyanogenic Bacterium. Proc. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askeland, R.A.; Morrison, S.M. Cyanide Production by Pseudomonas Fluorescens and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karim, S.; Ting, Y.P. Recycling Pathways for Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalyst: A Review on Conventional Approaches and Bio-Processes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 170, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, B.S. A Biological Cyanide Production and Accumulation System and the Recovery of Platinum-Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts by Biogenic Cyanide. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Ting, Y.P. Ultrasound-Assisted Nitric Acid Pretreatment for Enhanced Biorecovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalyst. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.B.; Lee, J.-c.; Suh, Y.-j.; Lee, J. A Review on the Recycling Processes of Spent Auto-Catalysts: Towards the Development of Sustainable Metallurgy. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taninouchi, Y.-K.; Okabe, T.H. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts Using Iron Chloride Vapor Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process. Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2018, 49, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taninouchi, Y.K.; Watanabe, T.; Okabe, T.H. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts Using Electroless Nickel Plating and Magnetic Separation. Proc. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, A.M.; Osen, K.S.; Støre, A. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Secondary Sources by Selective Chlorination from Molten Salt Media. Proc. Miner. Met. Mater. Ser. 2020, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Wu, B.; Jian, Z. Highly Efficient Recovery of Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium from Spent Automotive Catalysts via Iron Melting Collection. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcali, M.H. A New Approach to Recover Platinum-Group Metals from Spent Catalytic Converters via Iron Matte. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Maeda, M. Enhanced Dissolution of Pt from Pt-Zn Intermetallic Compounds and Underpotential Dissolution from Zn-Rich Alloys. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 18457–18463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooren, J.; Abo Atia, T. Combined Microwave Assisted Roasting and Leaching to Recover Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, G.; Goosey, E.; Yildiz, D.S.; Loving, E.; Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Yakoumis, I.; Martinez, A.M.; Siriwardana, A.; Unzurrunzaga, A.; et al. Platinum Group Metals Recovery Using Secondary Raw Materials (Platirus): Project Overview with a Focus on Processing Spent Autocatalyst. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2021, 65, 127–147. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Shen, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lv, B.; Wang, F. Effect of O2, H2 and CO Pretreatments on Leaching Rh from Spent Auto-Catalysts with Acidic Sodium Chlorate Solution. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 144–145, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.B.; Lee, J.-c.; Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, S. Total Recycling of All the Components from Spent Auto-Catalyst by NaOH Roasting-Assisted Hydrometallurgical Route. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.A.; Paiva, A.P.; Costa, M.C.; Rosa da Costa, A.M. Leaching Efficiency and Kinetics of the Recovery of Palladium and Rhodium from a Spent Auto-Catalyst in HCl/CuCl2 Media. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 2293–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson Matthey. Pgm Refining. Available online: https://matthey.com/en/products-and-services/precious-metal-products/pgm-refining (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Samotaev, N.; Antonov, A.; Tsarev, G.; Tietz, A. Effective Recycling of Spent Auto Catalytic Converters by Using Electrochlorination Method. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018; Volume 207, p. 03024. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).