Covalent Organic Frameworks for Simultaneous CO2 Capture and Selective Catalytic Transformation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
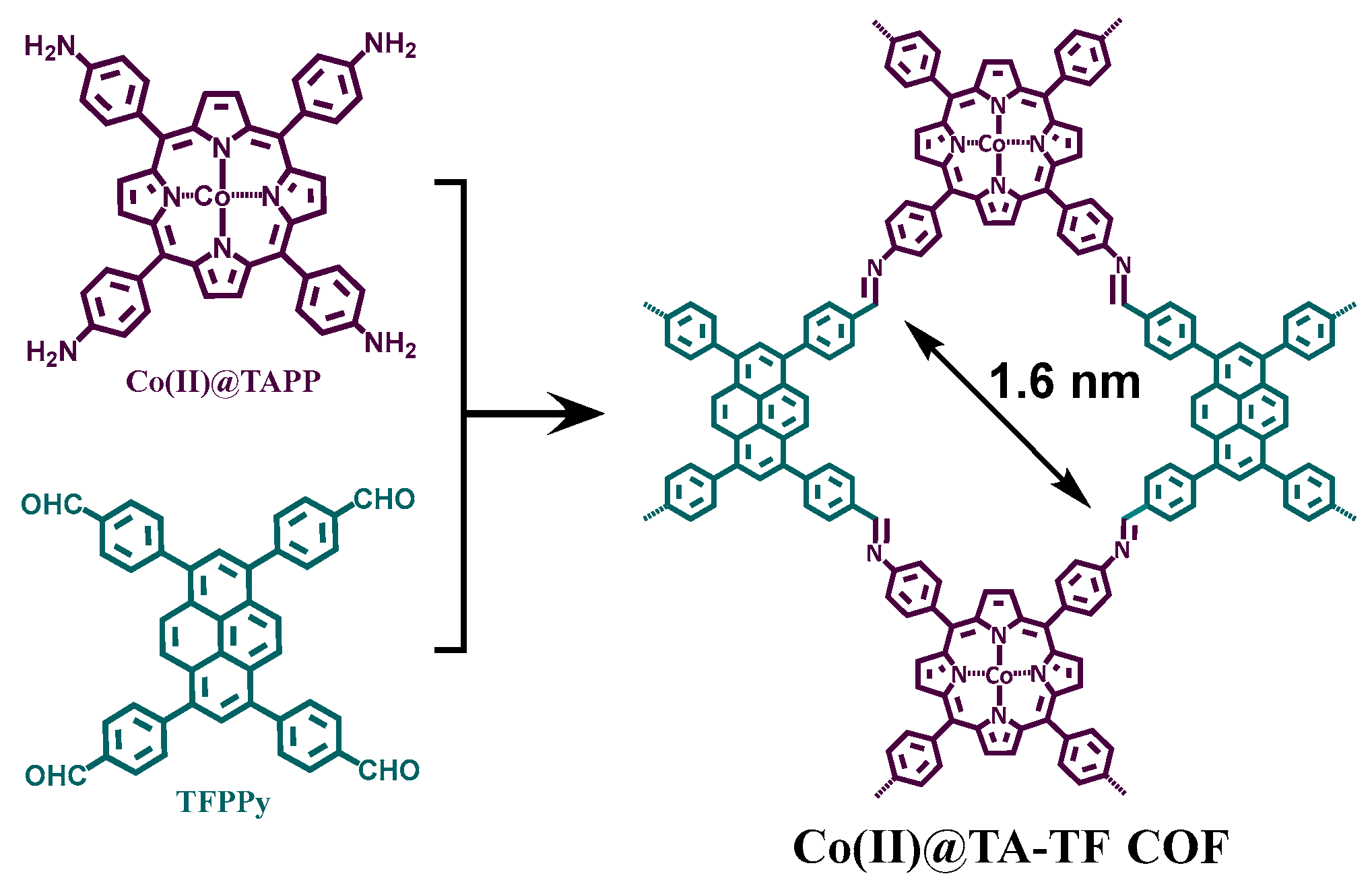
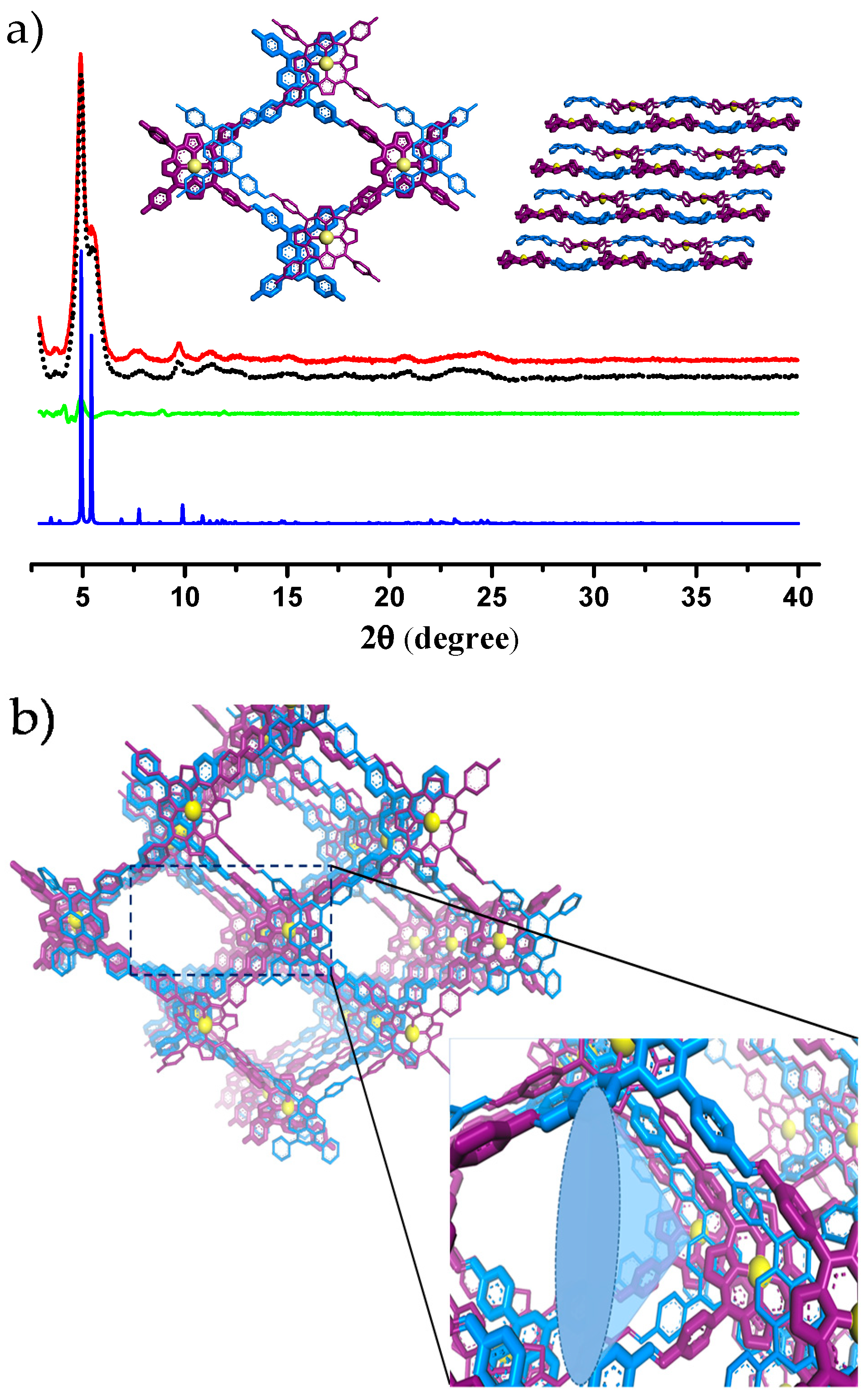
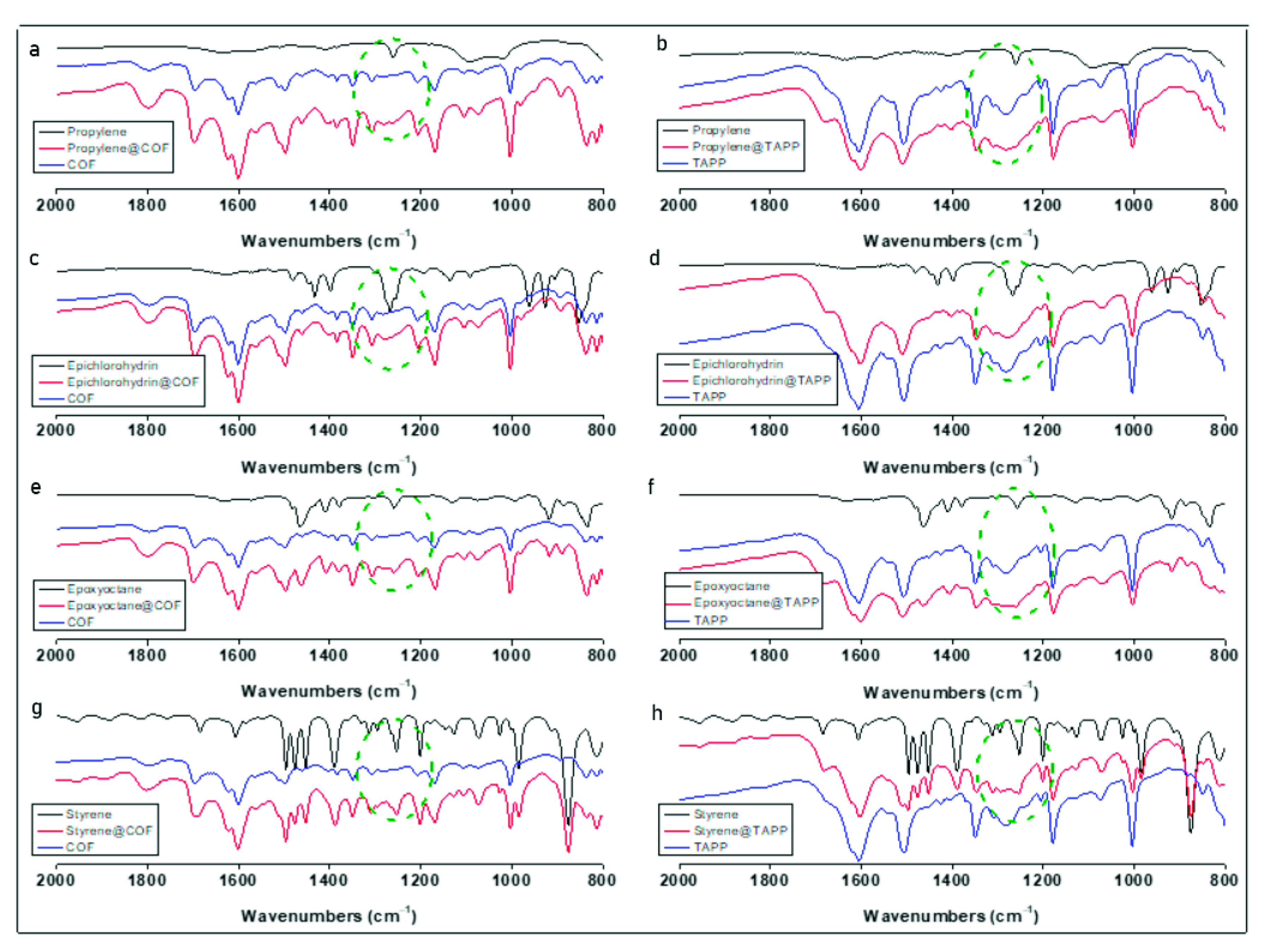
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the COF
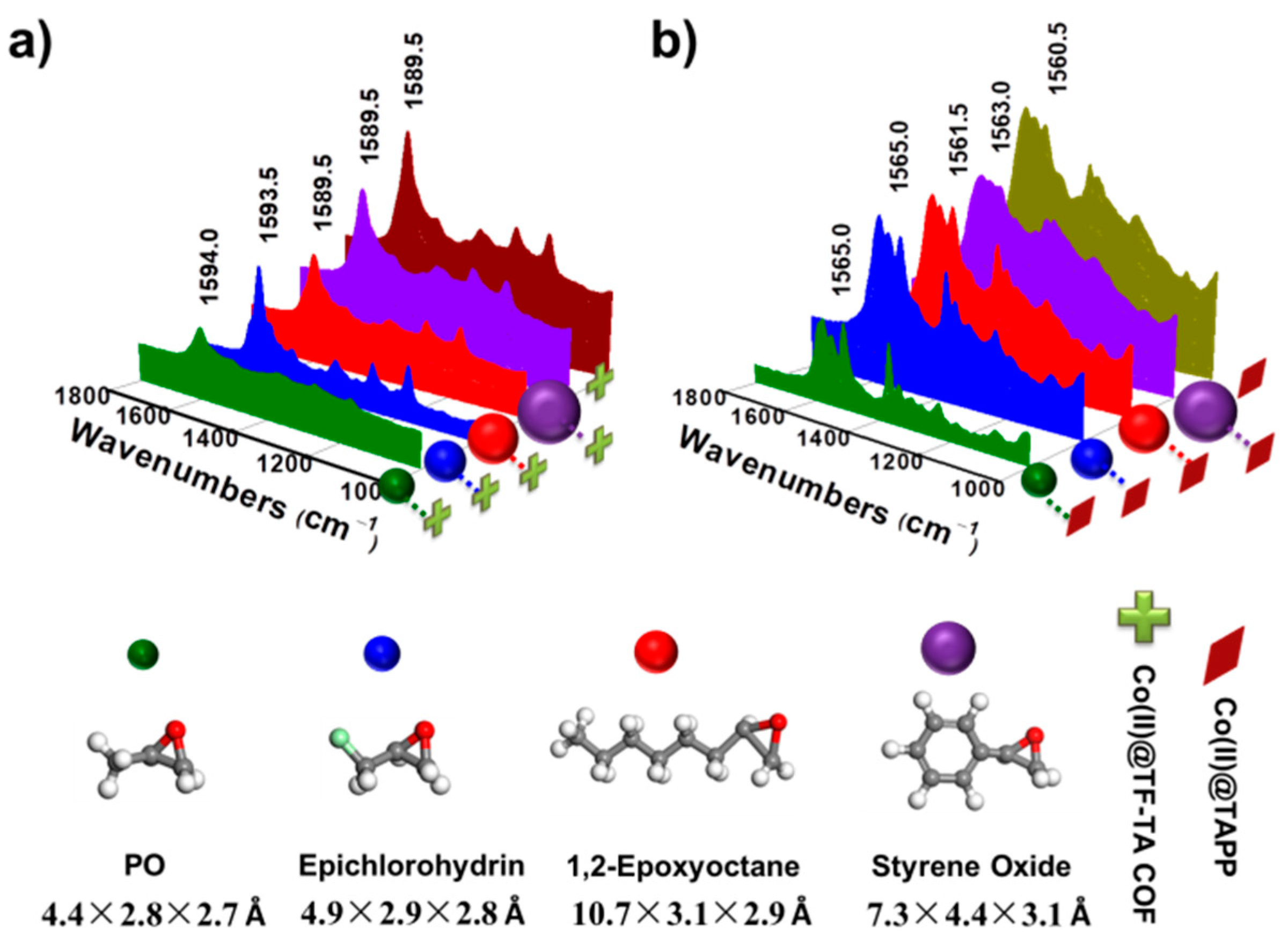
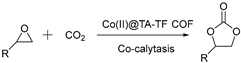
2.2. Catalytic Performance of Co(II)@TA-TF COF
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Synthesis of COF Catalyst
3.2.1. Synthesis of 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)porphyrin (TAPP)
3.2.2. Synthesis of Cobalt(II) 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)porphyrin (Co(II)@TAPP)
3.2.3. Synthesis of 1,3,6,8-Tetrakis(p-formylphenyl)pyrene (TFPPy)
3.2.4. Synthesis of Co(II)@TF-TA COF
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Simulation of PXRD Patterns for Co(II)@TA-TF COF Structures
3.5. General Procedures for CO2 Cycloaddition Reaction with Epoxides
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.H.; Sun, J.L.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Callear, S.K.; David, W.I.F.; Anderson, D.P.; Newby, R.; Blake, A.J.; Parker, J.E.; Tang, C.C.; et al. Selectivity and direct visualisation sulfur dioxide in a decorated porous host. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Z.; Godfrey, H.; Silva, I.D.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Savage, M.; Tuna, F.; McInnes, E.; Teat, S.J.; Gagnon, K.J.; Frogley, M.D.; et al. Modulating supramolecular binding of carbon dioxide in a redox-active porous metal-organic framework. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14212–14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakakura, T.; Choi, J.C.; Yasuda, H. Transformation of carbon dioxide. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2365–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Usov, P.M.; Xu, W.Q.; Celis-Salazar, P.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Kessinger, M.C.; Landaverde-Alvarado, C.; Cai, M.; May, A.M.; Slebodnick, C.; et al. A new class of metal-cyclam-based zirconium Metal–Organic Frameworks for CO2 adsorption and chemical fixation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, C.; Taniguchi, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ema, T. Bifunctional catalysts based on m-phenylene-bridged porphyrin dimer and trimer platforms: Synthesis of cyclic carbonates from carbon dioxide and epoxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darensbourg, D.J. Making plastics from carbon dioxide: Salen metal complexes as catalysts for the production of polycarbonates from epoxides and CO2. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2388–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.M.; Duan, W.L.; Shi, M. Chemical fixation of carbon dioxide Co-catalyzed by a combination of schiff bases or phenols and organic bases. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 14, 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.F.; Zheng, D.M.; Zhang, J.S.; Fan, B.W.; Ma, Y.; Ren, T.G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.L. Protic pyrazolium ionic liquids: An efficient catalyst for conversion of CO2 in the absence of metal and solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2574–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.W.; Zhou, Z.H.; He, L.N. Efficient, selective and sustainable catalysis of carbon dioxide. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3707–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, T.X.; Gu, J.R.; Chen, P.; Chen, T. Highly efficient CO2 fixation into cyclic carbonate by hydroxyl-functionalized protic ionic liquids at atmospheric pressure. Mol. Catal. 2021, 511, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aomchad, V.; Gobbo, S.D.; Yingcharoen, P.; Poater, A.; D’Elia, V. Exploring the potential of group III salen complexes for the conversion of CO2 under ambient conditions. Catal. Today 2021, 375, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xie, S.L.; Gao, X.T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.H.; Yin, G.Q.; Zhou, J. Activation of (salen)CoI complex by phosphorane for carbon dioxide transformation at ambient temperature and pressure. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3908–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ema, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Shimonishi, J.; Maeda, C.; Hasegawa, J. Bifunctional porphyrin catalysts for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and CO2: Structural optimization and mechanistic study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15270–15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, C.; Shimonishi, J.; Miyazaki, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ema, T. Highly active and robust metalloporphyrin catalysts for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from a broad range of epoxides and carbon dioxide. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 6556–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, U.A.; Sher, F.; Hazafa, A.; Rasheed, T.; Al-Shara, N.K.; Lima, E.C.; Shanshool, J. Catalytic Activity of Pt Loaded Zeolites for Hydroisomerization of n-Hexane Using Supercritical CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 22092–22106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, F.; Yaqoob, A.; Saeed, F.; Zhang, S.F.; Jahan, Z.; Klemeš, J.J. Torrefied biomass fuels as a renewable alternative to coal in co-firing for power generation. Energy 2020, 209, 118444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juboori, O.; Sher, F.; Khalid, U.; Niazi, M.; Chen, G.Z. Electrochemical Production of Sustainable Hydrocarbon Fuels from CO2 Co-electrolysis in Eutectic Molten Melts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12877–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Hassan, A.A.; Kausar, F.; Sher, F.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H. Carbon nanotubes assisted analytical detection-Sensing/delivery cues for environmental and biomedical monitoring. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Bashir, O.; Bilal, M.; Ishaq, A.; Dar, M.U.D.; Kumar, R.; Bhat, R.A.; Sher, F. Impact of COVID-related lockdowns on environmental and climate change scenarios. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ran, Z.Z.; Jin, B.S.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhou, C.L.; Sher, F. Simulation of Particle Mixing and Separation in Multi-Component Fluidized Bed Using Eulerian-Eulerian Method: A Review. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Sakthivel, A. Preparation of cyclic carbonate via cycloaddition of CO2 on epoxide using amine-functionalized SAPO-34 as catalyst. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 22, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhin, K.M.; Tharun, J.; Roshan, K.R.; Kim, D.W.; Chung, Y.; Park, D.W. Catalytic performance of zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-95 for the solventless synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and epoxides. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 17, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Moteki, T.; Ogura, M. Carbonate synthesis from carbon dioxide and cyclic ethers over methylated nitrogensubstituted mesoporous silica. Mol. Catal. 2018, 454, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, G.; Han, J.; Zhu, X.; Ge, Q.; Wang, H. Metal-free amino-incorporated organosilica nanotubes for cooperative catalysis in the cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides. Catal. Today 2019, 324, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Jiang, T.; He, J.L.; Han, B.X.; Wu, T.B.; Ding, K.L. CO2 cycloaddition reactions catalyzed by an ionic liquid grafted onto a highly cross-linked polymer matrix. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7255–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, R. Imidazolium- and triazine-based porous organic polymers for heterogeneous catalytic conversion of CO2 into cyclic carbonates. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4855–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Kumar, G.; Ansari, A.; Kureshy, R.I.; Khan, N.H. A nitrogen rich polymer as an organo-catalyst for cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides and its application for the synthesis of polyurethane. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Shi, Z. Bifunctional metal-free porous organic framework heterogeneous catalyst for efficient CO2 conversion under mild and cocatalyst-free conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15050–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Puthiaraj, P.; Ahn, W.S. Hydroxylamine-anchored covalent aromatic polymer for CO2 adsorption and fixation into cyclic carbonates. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9324–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; He, L.N.; Zhou, Y.B. Efficient and recyclable tetraoxo-coordinated zinc catalyst for the cycloaddition of epoxides with carbon dioxide at atmospheric pressure. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, A.A.; Lamb, K.J.; Ozorio, L.P.; Mota, C.J.A.; North, M. Heterogeneous catalysts for cyclic carbonate synthesis from carbon dioxide and epoxides. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 26, 100365–100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, X.H.; Zou, K.; Deng, W.Q. Capture and conversion of CO2 at ambient conditions by a conjugated microporous polymer. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyzavi, M.H.; Klet, R.C.; Tussupbayev, S.; Borycz, J.; Vermeulen, N.A.; Cramer, C.J.; Stoddart, J.F.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. A hafnium-based metal–organic framework as an efficient and multifunctional catalyst for facile CO2 fixation and regioselective and enantioretentive epoxide activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15861–15864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, Y.H.; Yaghi, O.M. Storage of hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide in highly porous covalent organic frameworks for clean energy applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8875–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.T.; Liu, J.D. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) functionalized mixed matrix membrane for effective CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Hopkins, P.E. Heat Transfer Mechanisms and Tunable Thermal Conductivity Anisotropy in Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks with Adsorbed Gases. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 6188–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.P.; Ren, H.; Meng, S.; Yan, Z.J.; Sun, F.X.; Zhu, G.S. A 3D microporous covalent organic framework with exceedingly high C3H8/CH4 and C2 hydrocarbon/CH4 selectivity. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9773–9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Kalidindi, S.B.; Um, Y.; Bureekaew, S.; Schmid, R.; Fischer, R.A.; Hirscher, M. A cryogenically flexible covalent organic framework for efficient hydrogen isotope separation by quantum sieving. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13219–13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.P.; Huang, N.; Xu, H.; Chen, Q.H.; Jiang, D.L. A backbone design principle for covalent organic frameworks: The impact of weakly interacting units on CO2 adsorption. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 4242–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegbauer, L.; Hahn, M.W.; Jentys, A.; Savasci, G.; Ochsenfeld, C.; Lercher, J.A.; Lotsch, B.V. Tunable water and CO2 sorption properties in isostructural azine-based covalent organic frameworks through polarity engineering. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7874–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, L.A.; Crowe, J.W.; Pyles, D.A.; McGrier, P.L. Metalation of a mesoporous three-dimensional covalent organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15134–15137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Wang, P.; Addicoat, M.A.; Heine, T.; Jiang, D.L. Ionic covalent organic frameworks: Design of a charged interface aligned on 1D channel walls and its unusual electrostatic functions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4982–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, K.; Pal, M.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu, H.S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; Banerjee, R. Selective molecular separation by interfacially crystallized covalent organic framework thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13083–13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.R.; Gu, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Qiu, S.L.; Yan, Y.S. Cheminform abstract: 3D microporous base-functionalized covalent organic frameworks for size-selective catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2878–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachfule, P.; Kandambeth, S.; Banerjee, R. Highly stable covalent organic framework-au nanoparticles hybrids for enhanced activity for nitrophenol reduction. Chem Commun. 2014, 50, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Jiang, D. Stable, crystalline, porous, covalent organic frameworks as a platform for chiral organocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.S.; Ding, S.Y.; An, W.K.; Wu, H.; Wang, W. Constructing crystalline covalent organic frameworks from chiral building blocks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11489–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, L.M.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Guang, C.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S.; Tan, B.; Cooper, A. Covalent triazine frameworks via a low-temperature polycondensation approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14149–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.H.; Feng, X.L.; Cui, X.H.; Ma, Y.X.; Ding, S.Y.; Wang, W. Salen-based covalent organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6042–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.; Nguyen, N.; Ma, S.Q. Flexibility matters: Cooperative active sites in covalent organic framework and threaded ionic polymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15790–15796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.W.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Multivariate chiral covalent organic frameworks with controlled crystallinity and stability for asymmetric catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8277–8285. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Xia, Q.C.; Huang, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Tan, C.X.; Cui, Y. Chiral covalent organic frameworks with high chemical stability for heterogeneous asymmetric catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8693–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, T.; Hufnagel, A.G.; Kampmann, J.; Kondofersky, L.; Calik, M.; Rotter, J.M.; Evans, A.; Döblinger, M.; Herbert, S.; Peters, K.; et al. Oriented films of conjugated 2D covalent organic frameworks as photocathodes for water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calik, M.; Auras, F.; Salonen, L.M.; Bader, K.; Grill, I.; Handloser, M.; Medina, D.D.; Dogru, M.; Löbermann, F.; Trauner, D.; et al. Extraction of photogenerated electrons and holes from a covalent organic framework integrated heterojunction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17802–17807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.; Bessinger, D.; Reuter, S.; Calik, M.; Ascherl, L.; Hanusch, F.C.; Auras, F.; Bein, T. Oligothiophene-bridged conjugated covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8194–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segura, J.L.; Mancheño, M.J.; Zamora, F. Covalent organic frameworks based on schiff-base chemistry: Synthesis, properties and potential applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5635–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, C.S.; Yaghi, O.M. The atom, the molecule, and the covalent organic framework. Science 2017, 355, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Wang, P.; Jiang, D.L. Covalent organic frameworks: A materials platform for structural and functional designs. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16068–16087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chai, S.Z.; Hu, N.T.; Yang, Z.; Wei, L.M.; Wang, L. The microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of a crystalline two-dimensional covalent organic framework with high CO2 capacity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12178–12181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Chen, X.; Krishna, R.; Jiang, D.L. Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for carbon dioxide capture through channel-wall functionalization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2986–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, N.; Krishna, R.; Jiang, D. Tailor-made pore surface engineering in covalent organic frameworks: Systematic functionalization for performance screening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7079–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, G.; Chen, L. Docking site modulation of isostructural covalent organic frameworks for CO2 fixation. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 4510–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Shao, P.; Feng, X.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Mu, Y.; Liu, X. Covalent organic frameworks: Efficient, metal-free, heterogeneous organocatalysts for chemical fixation of CO2 under mild conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, G.; Cheung, O.; Jia, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, S. Highly porous metalloporphyrin covalent ionic frameworks with well-defined cooperative functional groups as excellent catalysts for CO2 cycloaddition. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 9052–9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Dai, Y.; Ye, B.; Wang, H. Two dimensional covalent organic framework materials for chemical fixation of carbon dioxide: Excellent repeatability and high selectivity. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 10780–10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ju, J.; Yan, Q.; Arumugam, V.; Jing, X.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y. Ionization of a covalent organic framework for catalyzing the cycloaddition reaction between epoxides and carbon dioxide. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Yao, B.; Wu, W.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Kan, J.; Dong, Y. Metalloporphyrin and ionic liquid-functionalized covalent organic frameworks for catalytic CO2 cycloaddition via visible-light-induced photothermal conversion. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 12591–12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.R.; Ding, G.R.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, B.H.; Zhang, S.J. Construction of a PPIL@COF core-shell composite with enhanced catalytic activity for CO2 conversion. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, M.; Bag, A.; Ghosh, S.; Mondal, P.; Bordoloi, A.; Islam, S.M. CuxOy@COF: An efficient heterogeneous catalyst system for CO2 cycloadditions under ambient conditions. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitler, E.L.; Koo, B.T.; Novotney, J.L.; Colson, J.W.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Gutierrez, G.D.; Clancy, P.; Dichtel, W.R. A 2D covalent organic framework with 4.7-nm pores and insight into its interlayer stacking. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19416–19421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matesic, L.; Locke, J.M.; Vine, K.L.; Ranson, M.; Bremner, J.B.; Skropeta, D. Synthesis and hydrolytic evaluation of acid-labile imine-linked cytotoxic isatin model systems. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, I.A.; Kratz, F.; Jung, M.; Warnecke, A. Schiff bases derived from p-aminobenzyl alcohol as trigger groups for pH-dependent prodrug activation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 4371–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Chung, W.C.; Wei, Z.; Gu, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Chen, Y.P.; Darensbourg, D.J.; Zhou, H.C. Construction of ultrastable porphyrin Zr metal-organic frameworks through linker elimination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17105–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.Y.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Y.; Williams, K.; Cash, L.; Perez, P.J.; Wojtas, L.; Cai, J.; Chen, Y.S.; Ma, S. Crystal engineering of an nbo topology metal-organic framework for chemical fixation of CO2 under ambient conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2615–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhong, M.M.; Tao, L.; Liu, L.N.; Jayakumar, S.; Li, C.Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.H. The cooperation of porphyrin-based porous polymer and thermal-responsive ionic liquid for efficient CO2 cycloaddition reaction. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Zhang, Z.F.; Hu, S.Q.; Wu, T.B.; Jiang, T.; Han, B.X. MOF-5/n-Bu4NBr: An efficient catalyst system for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and CO2 under mild conditions. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.P.; Ren, W.M.; Luo, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.Z.; Lu, X.B. Enhanced asymmetric induction for the copolymerization of CO2 and cyclohexene oxide with unsymmetric enantiopure salenCo(III) complexes: Synthesis of crystalline CO2-based polycarbonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5682–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Z.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, J.; Lim, S.; Zou, R.Q.; Zhao, Y.L. A triazole-containing metal-organic framework as a highly effective and substrate size-dependent catalyst for CO2 conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.Y.; Manju, M.D.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.W.; Park, D.W. Catalytic performance of quaternary ammonium salts in the reaction of butyl glycidyl ether and carbon dioxide. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 | ||||||
| Entry | Substrate | Pressure | Temperature | Yield b | TON | TOF |
| (MPa) | (K) | (%) | (h−1) | |||
| 1 |  | 0.1 | 313 | 92 | 460 | 9.6 |
| 2 |  | 0.2 | 313 | 94 | 470 | 9.8 |
| 3 |  | 0.5 | 313 | 99 | 495 | 10.3 |
| 4 |  | 0.1 | 298 | 25 | 125 | 2.6 |
| 5 |  | 0.1 | 303 | 60 | 300 | 6.3 |
| 6 |  | 0.1 | 323 | 94 | 470 | 9.8 |
| 7 |  | 0.1 | 343 | 99 | 495 | 10.3 |
| 8 c |  | 0.1 | 313 | 83 | 415 | 8.6 |
| 9 d |  | 0.1 | 313 | 89 | 445 | 9.3 |
| 10 e |  | 0.1 | 313 | 76 | 380 | 7.9 |
| 11 e |  | 0.2 | 313 | 86 | 430 | 8.9 |
| 12 e |  | 0.5 | 313 | 92 | 460 | 9.6 |
| 13 |  | 0.1 | 313 | 99 | 495 | 10.3 |
| 14 |  | 0.1 | 298 | 92 | 460 | 9.6 |
| 15 |  | 0.1 | 313 | 25 | 125 | 2.6 |
| 16 | 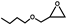 | 0.1 | 313 | 22 | 110 | 2.3 |
| 17 | 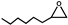 | 0.1 | 313 | 14 | 70 | 1.5 |
| 18 | 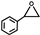 | 0.1 | 313 | 5 | 25 | 0.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zeng, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, B.; Gao, Y. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Simultaneous CO2 Capture and Selective Catalytic Transformation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091133
Li Y, Zhang J, Zuo K, Li Z, Wang Y, Hu H, Zeng C, Xu H, Wang B, Gao Y. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Simultaneous CO2 Capture and Selective Catalytic Transformation. Catalysts. 2021; 11(9):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yaling, Jianqiang Zhang, Kaiming Zuo, Zhongping Li, Yu Wang, Hui Hu, Chaoyuan Zeng, Huanjun Xu, Baoshan Wang, and Yanan Gao. 2021. "Covalent Organic Frameworks for Simultaneous CO2 Capture and Selective Catalytic Transformation" Catalysts 11, no. 9: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091133
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, J., Zuo, K., Li, Z., Wang, Y., Hu, H., Zeng, C., Xu, H., Wang, B., & Gao, Y. (2021). Covalent Organic Frameworks for Simultaneous CO2 Capture and Selective Catalytic Transformation. Catalysts, 11(9), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091133