Abstract
Eriochrome Black T (EBT) and chromium (Cr) are considered to be potential pollutants due to their toxicity and severe impact on the environment. In the current study, hydrotalcite-derived Mg-Ca-Al-LDO mixed metal oxide composite was prepared using a conventional co-precipitation method and explored in terms of the removal of Cr and EBT dye from aqueous solution in a batch mode adsorption process. The prepared Mg-Ca-Al-LDH, Mg-Ca-Al-LDO and spent Mg-Ca-Al-LDO adsorbents were characterized to propose the adsorption mechanism. Different adsorption parameters were examined, such as adsorbent dosage, initial concentration, pH, reaction temperature and contact time. The EBT adsorption kinetic results matched strongly with the pseudo-second-order model for both Cr (R2 = 0.991) and EBT (R2 = 0.999). The Langmuir isotherm model exhibited a maximum adsorption capacity of 65.5 mg/g and 150.3 mg/g for Cr and EBT, respectively. The structure and morphology results obtained after Cr and EBT dye adsorption reveal that the adsorption mechanism is associated with electrostatic interactions and surface complexation of Cr and EBT dye with Mg-Ca-Al-LDO surface functional groups. Moreover, more than 84% of the initial adsorption capacity of EBT and Cr can be achieved on the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO surface after five adsorption/desorption cycles. Finally, the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO mixed metal oxide composite can be potentially used as a cost-effective adsorbent for wastewater treatment processes.
1. Introduction
In view of the increasing global population, urbanization increase and the pursuit of industrialization, water-based natural sources are under great pressure. This led to the resolution of many water-stressed countries to search for renewable water sources or treat used water, such as industrial and domestic wastewater. These sources of water are considered one of the most prominent global concerns as a renewable source of water due to their wide availability, and because this water is disposed of by pumping and transferring it into natural water bodies. The concerns are further increased due to the large amount of pollutants available in industrial and domestic wastewater, such as pharmaceuticals, heavy metals, dyes, nutrients and other organic and inorganic pollutants. Therefore, its treatment leads to the preservation of nature and marine life and, additionally, to the provision of a new source of water, which in turn achieves all principles of sustainability.
Heavy metals and dyes are hazardous and well-known toxic contaminants. Chromium is one of the most toxic heavy metals that is used in different industries, including, but not limited to, leather tanning, plating, metal processing, paint production and corrosion control [1]. In aqueous solutions, chromium exists in two states: trivalent Cr (III) and hexavalent Cr (VI). Low concentrations of Cr (III) are required for human and animal body cells; however, it was reported that excess concentrations of Cr (III) can result in cancer and skin-related health issues [2]. Cr (VI) is more mobile and has higher toxicity than the trivalent chromium [3]. Several health issues, such as cancers, liver dysfunction, and kidney and lung destruction, have been considered to arise as a result of Cr (VI) [4]. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) have set 100 mg/L as the maximum allowed concentration of Cr in drinking water. Dyes, including Eriochrome Black T (EBT), are utilized in different applications, such as cosmetics, textile, pulp, food, leather and plastic industries [5]. Dyes are considered of high risk to wastewater quality due to their mutagenic potential, nonbiodegradability, and have a complex chemical structure with high chemical stability [6]. Currently, the global market has more than 105 commercial dyes, with an annual production rate that exceeds 7 × 108 kg. Hence, the existence of dyes in water complexes negatively influence human health and can cause skin irritation, and kidney and liver damage; moreover, the photochemical activities of the marine ecosystem are affected in the presence of dyes [7,8]. EBT is an anionic azo dye used for coloring nylon fibers and other textile fabrics. EBT has a negative impact on the marine environment; moreover, EBT is carcinogenic and can cause extreme health problems [9]. Therefore, it is necessary to remove EBT and Cr pollutants from wastewater prior to discharge or reuse.
To eliminate EBT and Cr from aqueous solutions, many strategies have been developed, including coagulation [10,11], ion exchange [12], ozonation [13], adsorption [14,15], membrane separation [16,17,18], photo catalysis [2,19] and precipitation [20,21]. In the last two decades, adsorption has become more popular for the removal of a wide range of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Adsorption is an easy and cost-effective process, provides high removal efficiency, and is effective at low concentrations of pollutants; furthermore, the diversity of adsorbent materials, and the ability to regenerate the adsorbents as well as ability to recover the pollutants [22,23], makes them of great value. Various materials have been utilized for the removal of the anionic pollutants (EBT and Cr) from water, such as activated carbons [24,25], multiwall carbon nanotubes [5,26], graphene composites [27], clay-based materials and ash [28]. However, due to low adsorption capacities, complex synthesis processes and poor regeneration abilities of several materials, researchers are still working on the development of cost-effective adsorbents that can capture a wide range of pollutants.
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) are known as anionic-clay-based materials. LDHs demonstrate high surface area, memory effect, flexible composition, low toxicity, and can maintain a high number of anions between their internal layers with fast kinetics compared to other adsorbents [29,30,31,32,33]. As such, LDHs have attracted a significant level of interest in the remediation of dyes and heavy metals, mainly anions, from aqueous solutions. For instance, Zubair et al. [30] obtained a maximum capacity of 137.0 mg/g, 123.5 mg/g and 123.4 mg/g of EBT onto CoFe, ZnFe and NiFe LDHs, respectively. The same research group have also investigated EBT removal by MgAl and CuFe LDHs, and they found that the saturation capacity could be achieved in 20 min and 30 min, respectively. Huang et al. [34] prepared NiFe-LDH using a topochemical process and applied this for Cr removal. Hu et al. [35] synthesized hierarchical calcined Ni/Co-LDH hollow dodecahedra by etching zeolitic imidazolate framework-67, and they observed high Congo red and Cr removal capacities of 909.2 and 99.9 mg g−1 at 30 °C, respectively. Jabkhiro et al. [36] investigated the effect of the simultaneous removal multiple anionic dyes, such as Eriochrome Black T (EBT), indigo carmine (IC) and methyl orange (MO), from aqueous solution on Mg(Al)O. Chen et al. [37] prepared Fe2O3@ZnCr LDH via a two-step microwave hydrothermal method, and they reported that the maximum adsorption capacity of methyl orange (MO) was 240.16 mg/g. Furthermore, the doped LDHs on bentonite, chitosan and biochar have also been applied for dye and heavy metal removal. For Cr removal, the LDHs are usually used as a doped material held onto some supports, such as MgAl LDH doped onto graphene, polyaniline and polypyrrole [38,39,40,41,42]. These experimental results demonstrate a remarkable increase in the adsorption capacity of Cr onto the support materials after LDH modification. All of the above studies conclude that LDHs are an effective adsorbent material due to their remarkable adsorption capacity and fast kinetics. Hence, the LDHs are considered a promising materials for water treatment technologies. To expand host layers and improve the amount of anions in the guest layer, trimetallic-like LDHs have been extensively investigated for wastewater treatment. In this regard, Lei et al. [43] synthesized hierarchical porous calcined Ni/Mg/Al and tested for the removal of Congo red and Cr. Zaghouane-Boudiaf et al. [44] explored uncalcined NiMgAl and calcined NiMgAl adsorbents for methyl orange removal from water. Kowalik et al. [45] synthesized Cu/Zn/Al- LDH and investigated its memory effect using in situ XRD. Lv et al. [46] prepared Mg-Ca-Al LDH using co-precipitation method applied for fluoride removal from protein solution. Chagas et al. [47] prepared MgCoAl and NiCoAl LDHs by hydrothermal urea hydrolysis process and explored their structure characterization and thermal stability.
To the best of our knowledge, the potential removal of EBT and Cr from aqueous solutions using a calcined Mg-Ca-Al-LDO mixed metal oxide composite has not yet been investigated. Therefore, in the current study, the co-precipitation method was used to prepare Mg-Ca-Al-LDO mixed metal oxide composite (Mg-Ca-Al-LDO) and test for the remediation of EBT and Cr from water. The morphology, structure and chemical composition of the adsorbent were characterized by different techniques. The influence of the adsorption parameters, including temperature, time, initial solution pH and initial contaminant concentration, were investigated using batch mode experiments. Moreover, the isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic modeling were explored. According to the modeling results and spent adsorbent characterization, the adsorption mechanism was proposed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Textural Properties
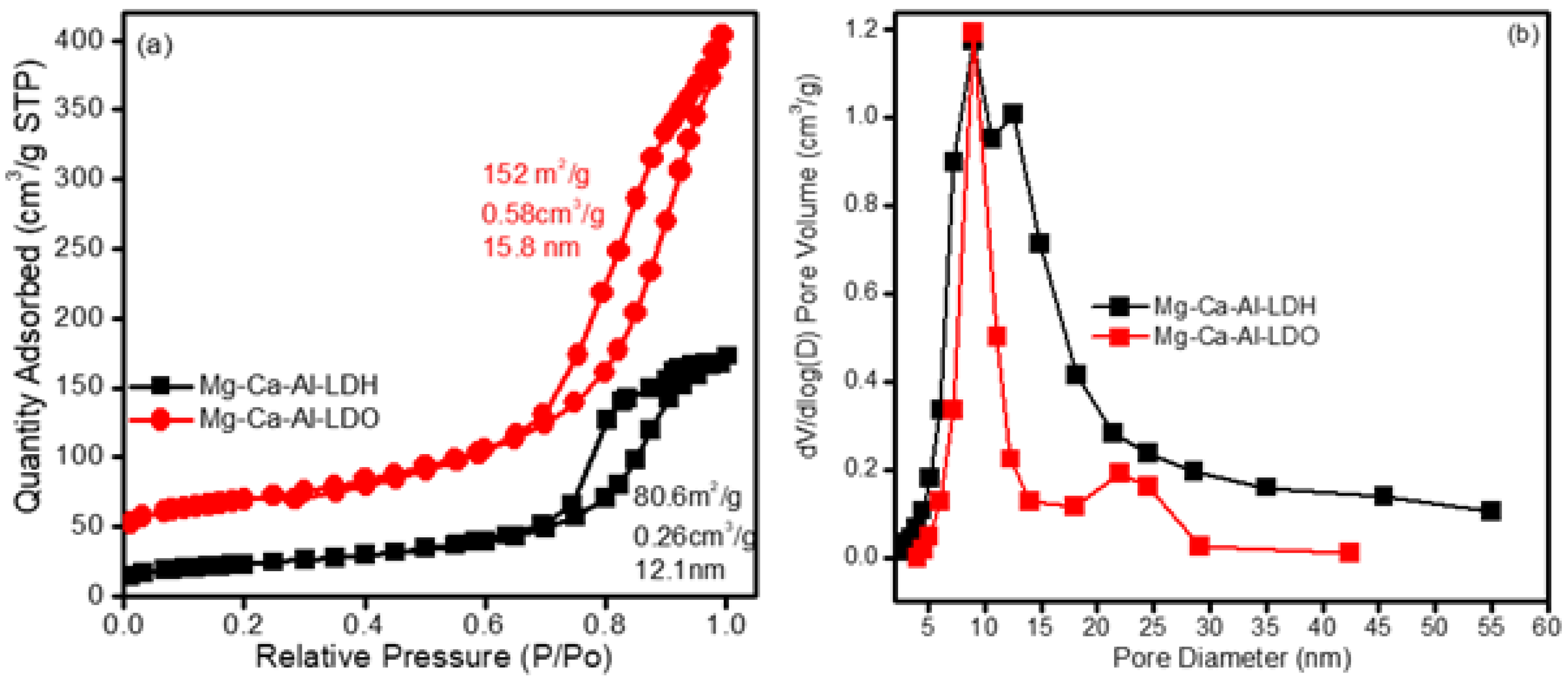
Figure 1a,b displays the N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms and their corresponding pore size distributions of as synthesized (Mg-Ca-Al-LDH) and calcined Mg-Ca-Al mixed metal oxide composite (Mg-Ca-Al-LDO) samples. It can be seen that the materials exhibited type IV isotherms according to IUPAC classification [44], demonstrating that the materials belong to a mesoporous family. Furthermore, the isotherms also exhibit an H3 type hysteresis loop at high relative pressure, indicating slit-shaped pores [44]. In addition, the H3 hysteresis loop typically indicates large open pores; these pores improve the simple diffusion of reactants via the materials. Figure 1b shows that the pore size distribution (PSD) profiles of Mg-Ca-Al-LDH and Mg-Ca-Al-LDO are wider and bimodal, and composed of small and large pores. The Mg-Ca-Al-LDH exhibited average pores at ca. 7 and 15 nm, while Mg-Ca-Al-LDO possessed average pores at ca. 10 and 23 nm, respectively. The smaller mesopores reveal the presence of pores within LDH nanosheets, while larger mesopores can be related to the pores formed between stacked nanosheets. Due to the intrinsic mesoporosity of these materials, they are more suitable to be applied as adsorbents for anionic pollutant molecules.
Figure 1.
N2 adsorption/desorption isotherm (a) and pore size distribution of Mg-Ca-Al material (b).
The synthesized Mg-Ca-Al-LDH exhibited a surface area of 80.6 m2/g and pore volume of 0.26 cm3/g, whereas the calcined Mg-Ca-Al-LDO showed a high surface area i.e., 152 m2/g with a pore volume of 0.58 cm3/g. The high surface area and pore volume of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO could be due to the removal of water and carbon dioxide during the calcination process, which can lead to the formation of channels and pores, which are accessible to the nitrogen molecules, and could increase the surface area of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO. These findings agree with those of previous studies, which report surface areas of between 60 and 200 m2/g [47,48]. The higher surface area could provide more adsorption sites, which are beneficial for adsorption of pollutants, and one can conclude that the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO had more effective adsorption sites than Mg-Ca-Al-LDH due to its higher surface area.
2.2. Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis (TGA-DTG)
To investigate the thermal stability of as synthesized Mg-Ca-Al-LDH sample, TG/DTG analysis was conducted, and the results are presented in Figure 2. As shown in Figure 2, the LDH material typically showed three major mass loss steps at various temperatures [49]. The first mass loss stage was observed up to 50–230 °C with mass loss of 17%, which is related to loss of water molecules from the surface and interlayer sheet. The second mass loss stage, up to 425 °C, is due to the decomposition of the interlayer carbonate anions and dehydroxylation of the LDH sheets. In this temperature range, the hydrotalcite undergoes decarbonation and dehydroxylation reactions that generate carbon dioxide and water [50,51]. Finally, a third stage of mass loss up to 750 °C was assigned to the completion of the transformation into a mixed metal oxide lattice [50]. Therefore, the fermentation results demonstrate that Mg-Ca-Al-LDH has greater thermal stability and this observation is concordant with the reported literature [52]. From the results discussed above, for the investigation of the Cr and EBT removal via adsorption through the reconstruction mechanism, the Mg-Ca-Al-LDH sample was calcined at 500 °C.
Figure 2.
TG-DTG profile of synthesized Mg-Ca-Al-LDH material.
2.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns of Mg-Ca-Al-LDH, Mg-Ca-Al-LDO and Mg-Ca-Al-LDO after Cr and EBT adsorption. It can be seen in Figure 3a that these composites displayed sharp and symmetric diffraction peaks at approximately 2θ = 11.4° (003), 23.1° (006), 34.6° (012), 60.6° (110) and 61.9° (113), together with the asymmetric and less sharp reflections at 2θ = 38.7° and 45.6° assigned to the (015) and (018) planes, which are the characteristic peaks of layered double hydroxide compounds [53]. When XRD patterns were compared with JCPDS Mg-LDHs (JCPDS #890460) and Ca-LDHs (JCPDS #870493), additionally, the CaCO3 phase was observed at 2θ = 30° (JCPDS #862334). This could be due to the larger radius of Ca2+ ions (0.10 nm) than that of Mg2+ ions (0.072 nm) [54]. The diffraction peak near 60.6° corresponds to the (110) crystal plane; moreover, the existence of diffraction peaks at angles between 60.0 to 62.0° indicates that the interlayers of hydrotalcite are carbonate anionic [52].
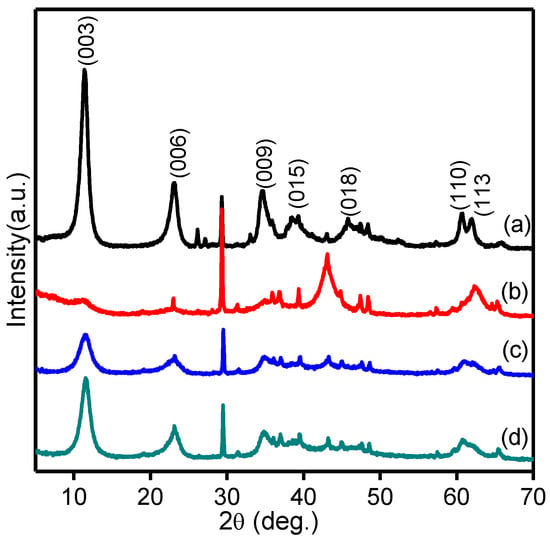
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of (a) Mg-Ca-Al-LDH, (b) Mg-Ca-Al-LDO, (c) Mg-Ca-Al-LDO after Cr adsorption and (d) Mg-Ca-Al-LDO after EBT adsorption.
After calcination (Figure 3b), the Mg-Ca-Al-LDH composite was destroyed and converted into mixed metal oxides Mg(Ca)AlO, which indicates diffraction characteristic of poor crystallinity. Nonetheless, Mg-Ca-Al-LDO also exhibited some minor diffraction peaks similar to parent Mg-Ca-Al-LDH due to the incomplete LDH destruction at 500 °C. The Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample exhibited two major diffraction peaks located at approximately 2θ = 43.5° and 62.9°, which can be assigned to (200) and (220) planes of NiO-MgO solid solution (JCPDS 24-0712), respectively. In addition, XRD analysis was carried out after adsorption of EBT and Cr ions, and the results are presented in Figure 3c,d. It can be clearly seen that both samples exhibited three prominent symmetric diffraction peaks at 2θ = 11.4° (003), 23.1° (006) and 34.6° (012), which are typical characteristic peaks of LDH similar to the synthesized Mg-Ca-Al-LDH sample. The reconstruction of LDH in the EBT- and Cr-adsorbed Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample is a unique property of LDH materials that is referred to as the “memory effect”, and is well documented in the published work [55]. This phenomenon could be due to the combination of Cr and sulfite anions from EBT dye and water molecules after being added to EBT and Cr aqueous solutions. These results clearly demonstrate the successful fabrication of trimetal Mg-Ca-Al-LDH and Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composites. The structure evolution was also observed in the FT-IR spectra.
2.4. Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
Figure 4 shows the FTIR spectra for Mg-Ca-Al-LDH, Mg-Ca-Al-LDO and Mg-Ca-Al-LDO after Cr and EBT adsorption. As seen in Figure 4a, Mg-Ca-Al-LDH displayed a broad band at approximately 3034–3462 cm−1 related to the –OH stretching vibration mode, caused by the interlayer water molecules and hydroxyl groups in the LDH layers [43]. The weak band observed at 1674 cm−1 was assigned to the bending vibration of H2O from the interlayer water [56]. The peaks at 1502 and 1383 cm−1 are characteristic absorption peaks related to the asymmetric stretching vibration of interlayer carbonate [54]. The bands in the fingerprint region between 860–545 cm−1 were attributed to metal–oxygen–metal and oxygen–metal–oxygen functional groups, such as Mg-O, Al-O and Ca-O [46]. In the FT-IR spectrum of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO (Figure 4b), the bands at 3434 cm−1, 1632 cm−1 and 450–900 cm−1 were consistent with the Mg-Ca-Al-LDH, the bands at 1502 and 1418 cm−1 also indicate the asymmetric stretching vibration of the interlayer CO32−. This band becomes weaker in the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO spectrum, but does not completely disappear. It can be concluded that the interlayer anions were removed when calcined at high temperatures and carbonate anions are remaining. Thus, calcination at 500 °C destroys the crystal structure of LDH (as confirmed from the XRD pattern in Figure 3), but does not cause the complete loss of interlayer carbonate anions and bound water. The same findings have been reported in published work, revealing that the complete removal of the anionic species can only occur at temperatures higher than 700 °C. Meanwhile, after EBT and Cr adsorption (Figure 4c,d) the –OH peak intensity drastically decreased, which indicates that –OH functional groups interact with Cr and EBT via ion exchange or electrostatic interaction. In addition, the peak at 1502 cm−1 belonging to the carbonate ions completely disappeared after adsorption, which implies carbonate ion participation in the adsorption process via ion exchange. Based on these results, it can be concluded that the oxygen-containing functional groups are involved in the adsorption process via electrostatic interaction, ion exchange and surface complexation mechanisms.
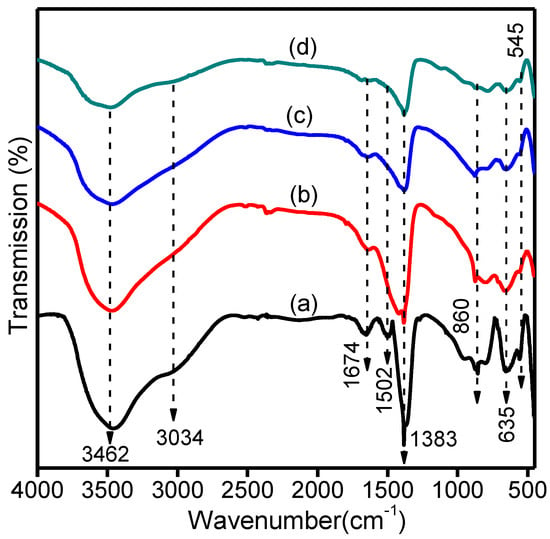
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectrum of (a) Mg-Ca-Al-LDH, (b) Mg-Ca-Al-LDO, (c) after Cr adsorption and (d) after EBT adsorption of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composites.
2.5. FESEM-EDS Analysis
SEM analysis was carried out for the parent Mg-Ca-Al-LDH and Mg-Ca-Al-LDO samples, and the corresponding images are displayed in Figure 5. As shown in Figure 5a, the Mg-Ca-Al-LDH composite contains flakes resembling sharp edges with irregular particles, which confirms the LDH layered structure. Meanwhile, after calcination, the layered structure was converted into spherical particles with an average particle size of 40–50 nm.
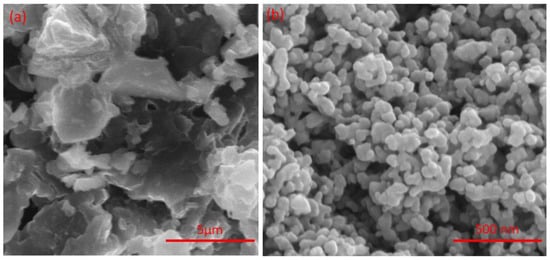
Figure 5.
FESEM images of (a) Mg-Ca-Al-LDH and (b) Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite materials.
To further confirm the adsorption of Cr and EBT on the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample, EDS mapping analysis was conducted before and after adsorption. As shown in Figure S1, the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample mainly composed of Mg (29.5 wt%), Al (14.5 wt%), O (51.1 wt%) and Ca (4.5 wt%). Meanwhile, after Cr and EBT adsorption, as demonstrated in Figure 6b,c, there was 2.1 wt% Cr and 0.6 wt% S, the latter of which was from the EBT pollutant. These results suggest that Cr and EBT were successfully precipitated on the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample.
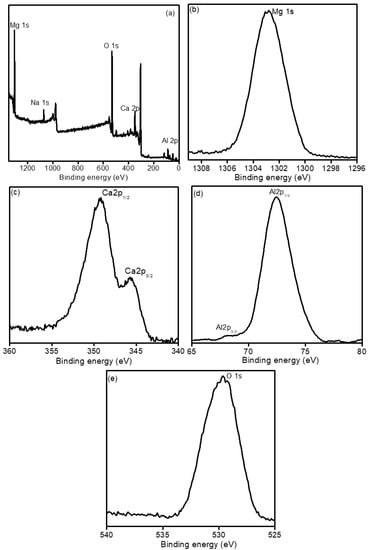
Figure 6.
High-resolution XPS spectra of (a) survey, (b) Mg1s, (c) Ca2p, (d) Al2p and (e) O1s fresh Mg-Ca-Al-LDO mixed metal oxide composite.
2.6. X-ray Photo Electronic Spectroscopy (XPS)
Furthermore, XPS analysis was carried out on Mg-Ca-Al-LDO material to verify the chemical composition and chemical oxidation state of the elements. As shown in Figure 6a, the survey scan XPS spectrum indicates that the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO material mainly consists of Mg, Ca, Al, O and Na elements. Figure 6b shows the high-resolution Mg1s spectrum with peak at 1302 eV related to Mg2+ [57]. Figure 6c presents the Ca2p spectrum, with 350 eV and 345 eV ascribed to Ca2p1/2 and Ca2p3/2 of Ca2+ [58]. Figure 6d displays two peaks at 68 eV and 73.8 eV belonging to Al2p3/2 and Al2p1/2 of Al2O3. In Figure 6e, the O1s spectrum is presented, and the peak located at 530 eV was assigned to O1s [59]. The XPS analysis results corroborate the above EDS spectra and prove the existence of the trimetal mixed oxides in the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample.
3. Adsorption Performance Evaluation over Mg-Ca-Al-LDO Composite
3.1. Influence of Mg-Ca-Al LDO Dosage
The influence of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite dosage on the removal efficiency and adsorption uptake of EBT and Cr is illustrated in Figure 7. Regardless of the utilized pollutant, the removal efficiency was increasing with Mg-Ca-Al-LDO dosage due to availability of additional unoccupied sites on the surface of Mg-Ca-Al composite upon increasing their quantities. For instance, the EBT removal efficiency increased from 62% to 98% with increasing the dosage from 0.25 to 0.75 mg/L, and Cr removal efficiency enhanced from 35% to 69% by increasing the adsorbent dosage from 0.25 to 1.25 g/L. At a certain dosage, 0.5 g/L for EBT (see Figure 7a) and 1.25 g/L for Cr (see Figure 7b), the removal efficiency was more than 95%, and further increasing the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO dosage had no significant impact on the removal efficiency; hence, these amounts appear to be the optimum dosages for EBT and Cr removal at the utilized conditions. Increasing the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO dosage is interconnected with providing more adsorption sites against a constant concentration of pollutant, which in turn improves the removal efficiency. In contrast, the adsorption capacity decreased with Mg-Ca-Al-LDO dosage, which can be explained by the inverse relationship between the adsorption capacity and the dosage of the adsorbent.
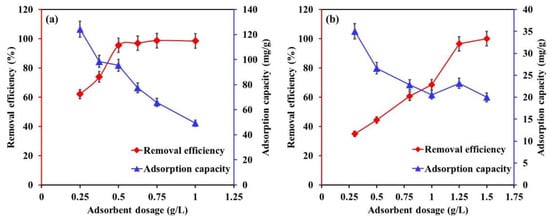
Figure 7.
The influence of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite dosage on the removal efficiency and adsorption capacity of (a) EBT and (b) Cr. [EBT]i = 50 mg/L; [Cr]i = 30 mg/L; temperature, 22 °C; contact time, 24 h; [pH]i, EBT = 5.2, [Cr]= 6.
3.2. Influence of Contact Time
Figure 8a,b displays the impact of contact time on the removal efficiency of EBT and Cr by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. Different trends were observed for the removal of EBT and Cr as a function of contact time. For EBT (see Figure 8a), the removal efficiency increased significantly in the first 45 min, during which more than 71% of EBT was removed. This fast removal is attributed to the availability of high amounts of active sorption sites at the surface of the adsorbent. Next, a slower rate of removal was obtained by increasing the contact time to 180 min until the equilibrium was achieved after 360 min of contact time. The slow adsorption can be ascribed to the diffusion of EBT particles within the pores of the adsorbent until saturation. For Cr, the removal efficiency smoothly increased with contact time to more than 99% within 300 min, after which equilibrium was achieved. The smooth increase in the removal efficiency might be attributed to one step in the adsorption process, which will further investigate in the kinetics section.
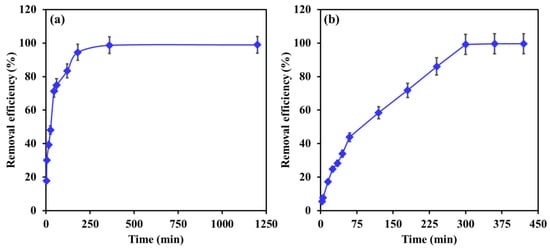
Figure 8.
The influence of contact time on the removal efficiency of (a) EBT and (b) Cr by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. [EBT]i = 50 mg/L; [Cr]i = 30 mg/L; temperature, 22 °C; dosage, EBT 0.75 g/L, Cr 1 g/L; [pH]I, EBT 5.2, Cr 6.
3.3. Influence of Initial Solution pH
The adsorption behavior of Cr and EBT by LDHs can be clarified by estimating the surface charge of the Cr and EBT molecules as well as the pHPZC of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO. The pHPZC of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO was evaluated by the pH drift method, and it was found to be around 12, implying a positively charged adsorbent at pH <12, as demonstrated in Figure 9. The effect of pHi on the removal efficiency of EBT and Cr was investigated in pH ranges of 2.3–7 and 2.6–10.7, respectively, and the results are illustrated in Figure 10. Raising the pHi from 2.3 to 7.0 was found to slightly decease the removal efficiency of EBT from 79.8% to 73.5%. However, the removal efficiency of Cr was 97 ± 2% in the investigated pH range, indicating no significant effect of the solution acidity on the removal of Cr by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO.
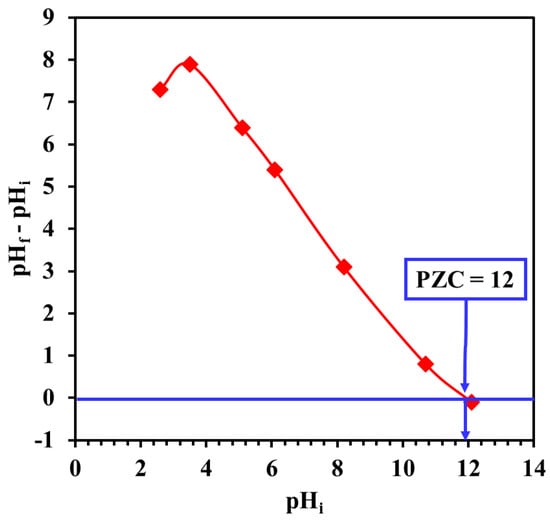
Figure 9.
Determination of point of zero charge (pHPZC) for Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite by the pH drift method.
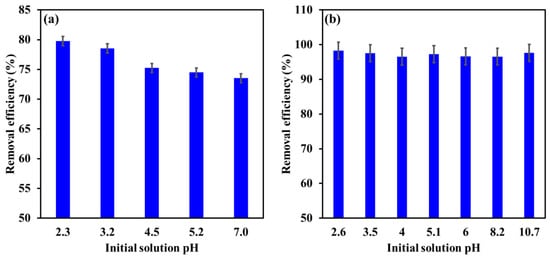
Figure 10.
Influence of initial solution pH on the removal efficiency of EBT (a) and Cr (b) by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. [EBT]i = 100 mg/L; [Cr]i = 30 mg/L; temperature, 22 °C; contact time, 24 h; dosage, EBT 0.75 g/L, Cr 1.25 g/L.
In aqueous solutions, the anionic EBT dye occurs as SO3− species, while the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO has a high positive charge at pH 2.3. Moreover, high concentrations of H+ ions will protonate the oxygen functional groups onto the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO surface, hence more than 79% of EBT removal was achieved at pH 2.3 due to the strong electrostatic interactions. Increasing the solution pH was found to slightly decrease the removal efficiency, which is explained by the reduction in H+ ion concentration, which in turn reduces the protonation of oxygen functional groups and thus lowers electrostatic interaction forces, resulting in decreased removal efficiency of EBT. However, at pH 7, the removal efficiency was still more than 73% which is attributed the positive charge of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite.
In the case of Cr, the salt substrate used to prepare the Cr solutions is K2Cr2O7; in aqueous solutions, this salt dissociates to HCrO4– and Cr2O72– ions at pH <6, while at pH >7, Cr exists as CrO42– [60]. Regardless the type of Cr ions in the solution, the removal efficiency was found not to be affected by the pHi. Cr occurred as negatively charged ions, while the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite demonstrated a positive charge over the investigated pH range, and hence Cr ions were adsorbed by the strong electrostatic interactions. This behavior is not well known for Cr ions adsorption as most of the literature concluded a reduction in the removal efficiency and adsorption capacity of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO for Cr by increasing the solution pH. Interestingly, for Mg-Ca-Al-LDO adsorbents, our results are in compliance those of Cr removal by other LDOs reported in the literature [38,61].
3.4. Influence of Temperature
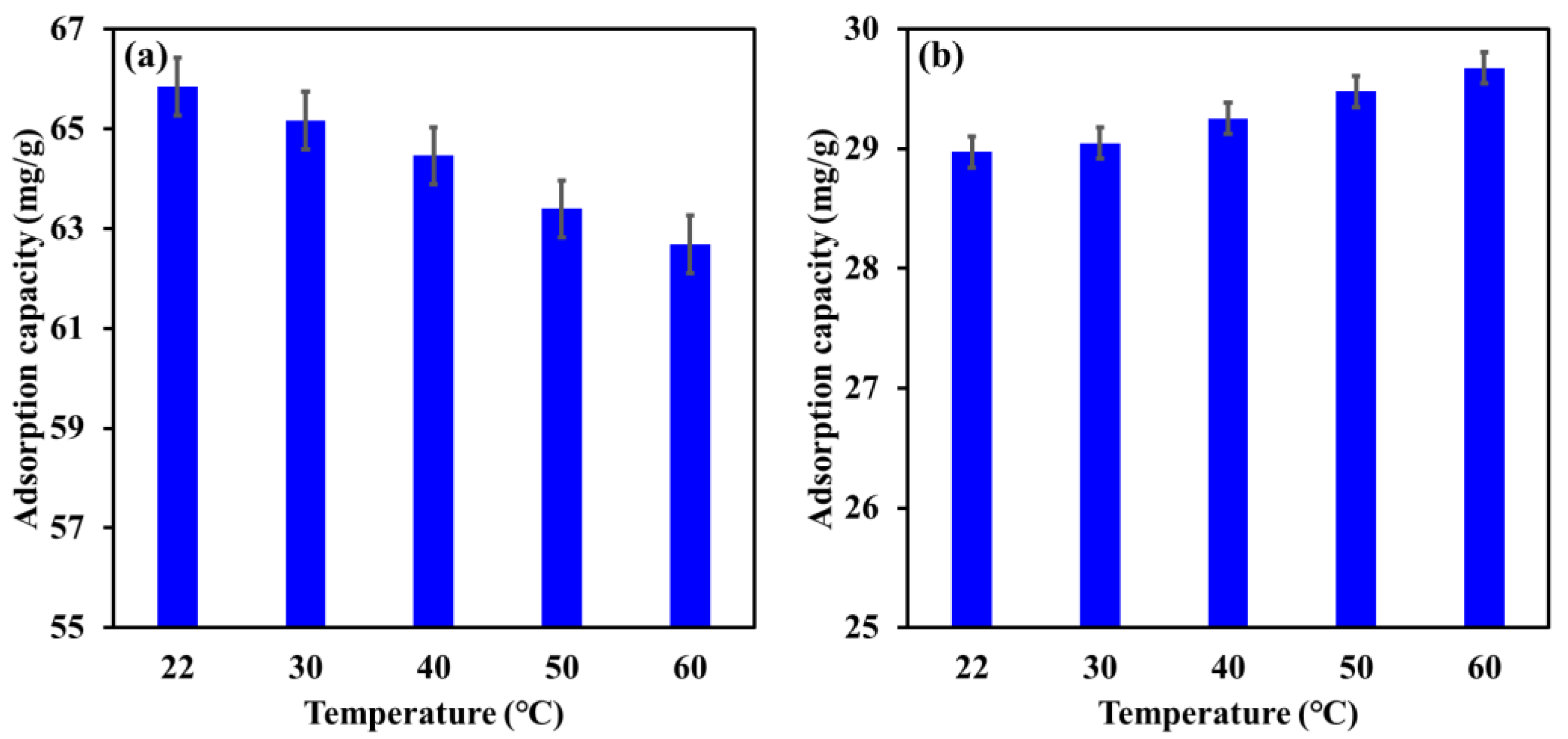
The influence of increasing the temperature from 22 °C to 60 ℃ on the adsorption capacity of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite for EBT and Cr is illustrated in Figure 11. The results demonstrate a reduction in the adsorption capacity of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO toward EBT from 65.8 mg/g to 62.7 mg/g by raising the temperature from 22 °C to 60 °C. In contrast, the adsorption capacity of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO for Cr was found to slightly increase from 29.0 to 29.8 mg/g by increasing the temperature from 22 °C to 60 °C. These outcomes suggest an exothermic adsorption process for EBT and an endothermic adsorption process for Cr by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. However, the maximum reduction in the adsorption capacity of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO for EBT was less than 5%, while the enhancement in Cr removal was not more than 3%, indicating that the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite can withstand the variation in temperature required for the removal of both pollutants. It was reported that the adsorption temperature affects the mobility of adsorbate ions, energy and number of active adsorption cites, as well as the interaction between the adsorbent and the adsorbate [8]. The investigation of thermodynamic parameters could provide better insight into the influence of adsorption temperature (see Section 3.7).
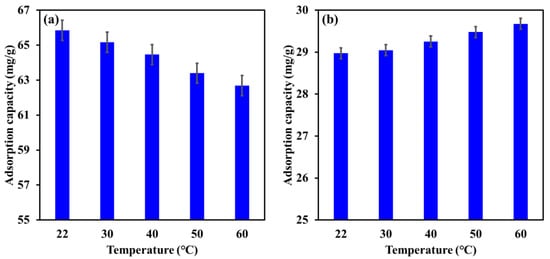
Figure 11.
Influence of temperature on the adsorption capacity of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite for EBT (a) and Cr (b) ions. [EBT]i = 50 mg/L; [Cr]i = 30 mg/L; contact time, 24 h; dosage, EBT 0.75 g/L, Cr 1.25 g/L; [pH]I, EBT 5.2, Cr 6.
3.5. Kinetics Modeling
To examine the rate-determining step and dynamic mechanism of EBT and Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al LDO composite, the adsorption kinetic data were analyzed by four kinetic models: pseudo 1st order (PFO), pseudo 2nd order (PSO), Elovich and intraparticle diffusion (IPD) kinetic models. The kinetic data were tested according to the linearized models and compared based on the value of the correlation factor (R2). The kinetic model equations are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
The linearized forms of the tested kinetic models.
Table 2 provides the correlation factor and model parameters values of the tested models, while Figure 12 and Figure 13 depict the best trends in fitted lines of the kinetic models for Cr and EBT, respectively. For both pollutants, the PSO model described better the kinetics data compared to the PFO model, as reflected in Figure 12 and Figure 13b. The R2 value was 0.999 and 0.979 for Cr and EBT, respectively. Moreover, the experimental adsorption capacity for both pollutants were much closer to the adsorption capacity obtained from the PSO model compared the adsorption capacity obtained from the PFO model (see Table 2). These results demonstrate a chemisorption process of EBT and Cr by the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. The chemisorption in the process might involve some strong electrostatic interactions between the positively charged adsorbent and the negatively charged pollutants. Moreover, some chemical bonds between EBT, Cr(IV) and the adsorbent might have contributed in the removal process.

Table 2.
Parameters and correlation factors of the tested Kinetic models on EBT and Cr removal by calcinated Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite.
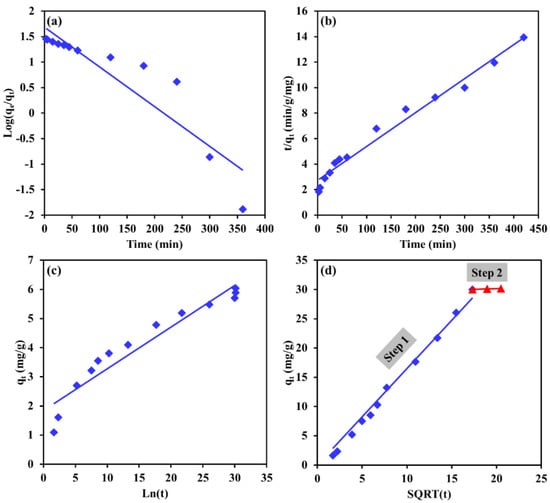
Figure 12.
Linearized kinetic models fit of Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite for (a) pseudo 1st order, (b) pseudo 2nd order, (c) Elovich and (d) intraparticle diffusion models.
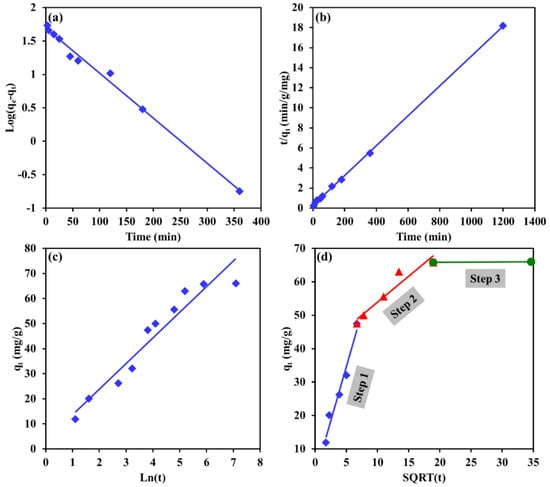
Figure 13.
Linearized kinetic models fit of EBT dye removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite for (a) pseudo 1st order, (b) pseudo 2nd order, (c) Elovich and (d) intraparticle diffusion models.
To further investigate the rate-determining step and dynamic mechanism of the adsorption process, the IPD model was applied on the kinetic data, and the results are presented in Figure 12d and Figure 13d. For Cr removal (see Figure 12d), the kinetic data demonstrate two straight lines: step 1, where a straight line found to fit the kinetic data points and passes through the origin (the IPD constant of step 1 is zero) belongs to the surface boundary diffusion; step 2, referring to the equilibrium state where no significant changes in the adsorption capacity occurred. As seen in Figure 12d, the surface boundary diffusion was responsible for more than 99% of the total adsorption capacity of the LDH toward Cr ions; hence, it can be said that the surface adsorption was the only adsorption rate limiting step for Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. For EBT removal (see Figure 13d), the kinetic data found to form three steps of adsorption: step 1 is the surface adsorption, this step is faster and occurred in 45 min, it is responsible of around 71.9% of the total adsorption capacity. Step 2 is attributed to the diffusion of EBT ions into the internal pores of the adsorbent, this step occurred at a slower rate, taking around 315 min to be completed, and the internal pore adsorption was found to control 27.8% of the total adsorption capacity. In the final step (step 3), saturation was achieved, and some sulfur ions in EBT were adsorbed in the remaining cavities within the adsorbent; this step was found to control around 0.3% of the total adsorption capacity.
3.6. Isotherm Modeling
The isotherm modeling of adsorption studies is very important for the design of adsorption systems. Adsorption isotherms also identify the nature of the interaction between a pollutant and a solid surface. The adsorption equilibrium data were investigated by varying the initial concentration of the pollutants (EBT and Cr) against a fixed value of other adsorption parameter (pH, temperature, adsorbent dosage and agitation speed). The equilibrium experimental data were subjected to nonlinear optimization analysis against different isotherm models, including Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips and Temkin by minimizing the sum of the square errors (SSE). The isotherm models were compared to each other according to the value of R2 and SSE. The SSE equation and isotherm models are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Adsorption isotherm models and SSE equation.
Figure 14a,b illustrates the equilibrium data points and the nonlinear fitting of adsorption isotherms of EBT and Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. The values of R2, SSE and optimized model parameters are presented in Table 4. According to the values of R2 and SSE (R2 ˃ 0.959 and SSE ˂ 72), it can be concluded that the adsorption equilibrium data for EBT and Cr were best fitted by two isotherm models (i.e., Freundlich and Sips models). Moreover, the equilibrium data points were found to be closely matched with the Freundlich and Sips fitting lines, as depicted in Figure 14a,b. The Langmuir isotherm model demonstrates an R2 ˃ 0.851 for both of the pollutants, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 150.3 mg/g and 65.5 mg/g for EBT and Cr onto the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite, respectively. The obtained capacities are competitive to the reported adsorption capacities of LDHs and LDOs for EBT and Cr, as illustrated in Table 5. These results suggest that the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite displayed a heterogeneous surface in which monolayer and multilayer sorption takes place for EBT and Cr. The compliance between the equilibrium data and Sips isotherm model indicates that the removal of both pollutants is a combination of chemisorption and physisorption processes. The values of the separation factor (RL) calculated from Langmuir model were between 0.03 and 0.44 suggesting a favorable adsorption process for both of the pollutants. The Temkin model is constructed based on the assumption of multilayer adsorption process [62]. Temkin fitting demonstrates an R2 values between 0.866 and 0.951 for Cr and EBT, respectively. These results confirm the compliance with the Freundlich model, in which most of the removal occurred as multilayer adsorption.
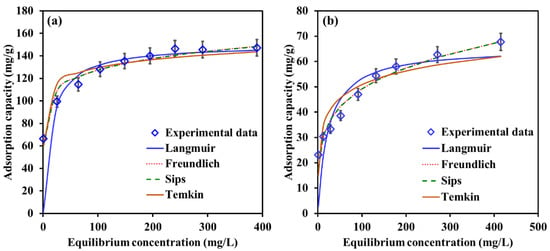
Figure 14.
Best nonlinear fit of adsorption isotherms of (a) EBT and (b) Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. Temperature, 22 °C; contact time, 24 h; dosage, EBT 0.75 g/L, Cr 1.25 g/L; [pH]I, EBT 5.2, Cr 6.

Table 4.
Statistical parameters (R2 and SSE) and isotherm parameters of the investigated isotherms on EBT and Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite.

Table 5.
Summary of the maximum adsorption capacity of selected LDH materials toward EBT and Cr ions from water.
3.7. Thermodynamics Investigation
To understand and evaluate the spontaneity and feasibility of the adsorption process, the thermodynamic parameters, including Gibbs free energy change , entropy change ( and enthalpy change , are usually evaluated; these parameters were calculated by analyzing the adsorption data of the impact of temperature using the following equations:
where (8.314 J/mol/K) is the gas constant, (K) is the temperature and is the adsorption equilibrium constant, is the amount of the pollutant (EBT or Cr) adsorbed by the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite at equilibrium and represents the equilibrium concentration of the pollutants.
Table 6 provides the thermodynamic parameters of EBT and Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. All of the values were negative, indicating that the removal of both pollutants is feasible and spontaneous in nature. The values were found to be negative for EBT and positive for Cr, implying an exothermic adsorption process for EBT and endothermic adsorption process for Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. These results confirm the outcomes obtained from the influence of temperature section. The was found to be a negative value for EBT, suggesting the greater order of reaction throughout the elimination process of EBT on to Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite. In contrast, was found to be a positive value for Cr removal, implying the increased randomness/disorder at the solid/liquid interface throughout the adsorption process.

Table 6.
Adsorption thermodynamic parameters of EBT and Cr removal by Mg-Ca-Al- LDO composite.
3.8. Regeneration
Adsorbent reusability is a core parameter in practical applications. Among the different elution agents used to regenerate Mg-Ca-Al-LDO for EBT and Cr removal, it was reported that NaOH solutions 0.1–1 M were successfully utilized for the desorption of EBT and Cr from Mg-Ca-Al-LDO and decorated LDOs adsorbents [63,68,69,70]. Therefore, in our study, 0.5 M and 0.1 M NaOH were used to investigate the recyclability of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO toward EBT and Cr ions, respectively. Figure 15 illustrates the adsorption capacity of EBT and Cr ions with respect to the number of the adsorption/desorption cycle. The results demonstrate a gradual decrease in the adsorption capacity of EBT and Cr ions with adsorption/desorption cycle. To be precise, the adsorption capacity decreased from 65.8 mg/g to 57.0 mg/g and from 23.2 mg/g to 19.6 mg/g after five adsorption/desorption cycles for EBT and Cr ions, respectively. This decline is attributed to the incomplete desorption of EBT and Cr ions during NaOH washing, which might be explained by a strong chemical bond formation between the pollutants molecules and the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO surface. Moreover, loss of functional groups and some adsorbent nanoparticles might occur in the desorption process, which in turn negatively affect the adsorption capacity on the next cycle. Regardless of the type of the pollutant, the adsorption capacity was found to exhibit a more significant decrease between the first and the third adsorption/desorption cycle; after that the decrease was insignificant between the forth and the fifth adsorption/desorption cycle. These results reveal that the loss of the functional groups and some nanoparticles occurred in the first three cycles, and after that, the adsorbent demonstrated a stable adsorption capacity. It is worth mentioning that even after five adsorption/desorption cycles, the Mg-Ca-Al-LDOs was still able to provide more than 86% and more than 84% of the initial adsorption capacity of EBT and Cr ions, respectively, indicating the applicability and reusability of Mg-Ca-Al-LDOs.
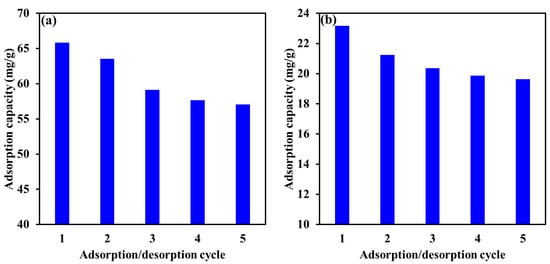
Figure 15.
Reusability performance of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO for the adsorptive removal of EBT (a) and Cr (b) for five consecutive adsorption/desorption cycles.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Deionized water was used for preparation of EBT dye at 1000 mg/L concentration and as a stock solution for all dilution purposes. K2Cr2O7 (purity, 99.9%), Mg(NO)3.6H2O (purity, 99.9%), Ca(NO3)2. H2O (purity, 99.9%), Al(NO3)3. 9H2O (purity, 99.9%), NaOH (purity, 99.9%) and Na2CO3 (purity, 99.9%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich chemicals. All the reagents were used without further purification.
4.2. Synthesis of Mg-Ca-Al-LDH
Mg-Ca-Al-LDH with (Mg + Ca)/Al molar ratio = 3 was prepared by co-precipitation method according to the previous reports with slight modifications [46]. Briefly, solution (A) contains 2 mmol of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O, 1 mmol of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and 1 mmol of Al(NO3)3·9H2O dissolved in 250 mL of DI water. In a separate beaker, solution (B) contains NaOH (2M) and Na2CO3 (1M) dissolved in 250 mL of DI water. In the next step, solution A and solution B were dropwise added to 100 mL DI water contained in a beaker under vigorous stirring while maintaining the solution pH (10.5). The resulting precipitate was aged at 80 °C for 6 h, then vacuum filtered and washed with DI water several times until reaching pH = 7. The solid precipitate was dried in an oven at 100 °C for overnight and finally calcined in a muffle furnace under static air at 500 °C for 4 h.
4.3. Adsorbent Characterization
The BET surface area, pore size distribution and pore volume were measured by the nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm using a NOVATECH LX2 analyzer, Anton Paar, Austria. The adsorbents were degassed at 300 °C for 6 h prior to conducting the experiment. The surface morphology Mg-Ca-Al mixed metal oxide composite before and after adsorption were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, type: Apreo, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The FE-SEM is equipped with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS, Bruker Xflash 6/60, Munich, Germany) used for chemical composition analysis. The functional groups on the Mg-Ca-Al-LDH surface were obtained by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (JASCO FTIR-6300, Tokyo, Japan), the FTIR spectra was evaluated in a wave length range between 400 to 4000 cm−1. LDH structure was investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD, D8 Advance, Bruker, Germany) with a wave length of 1.5 Å and angle range of 2θ = 10–80°. Thermo-gravimetric analysis (TG) of the Mg-Ca-Al-LDH material was carried out on a Netzsch TG analyzer (Model: STA 449 F5 Jupiter) over 30 mg of sample under an oxygen flow (20 mL min−1) from 20 to 800 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 to estimate the thermal stability of as synthesized Mg-Ca-Al-LDH material. The point zero of charge (pHPZC) was evaluated by the pH drift method. Briefly, 20 mg of Mg-Ca-Al LDH composite in 20 mL of a preadjusted initial solutions pH (pHi) between 2 and 12 of 0.1 M NaCl. Next, the solutions were agitated at room temperature for 72 h and finally the final solution pH (pHf) was measured. Then, the pHPZC was pointed out by plotting pHi against pHf–pHi.
4.4. Adsorption and Desorption Experiments
The elimination of EBT and Cr from aqueous solutions was carried out by the means of batch adsorption experiment. Stocks of 1000 mg/L of each pollutant (EBT and Cr) were prepared. In a typical experiment, the required amount of the adsorbent (Mg-Ca-Al-LDO mixed metal oxide composite) was added to 50 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 20 mL of a certain concentration of the pollutants. Unless otherwise mentioned, all of the experiments were conducted at room temperature (22 ℃) and agitated for 24 h using shaking speed of 170 RPM. Table 7 provides the detailed experimental conditions of the current study. The experiments conducted at room temperature were agitated using Lab-Shaker (model LS-X, Kuhner Shaker Inc., Switzerland), while the experiments conducted at higher temperature were carried out using an incubator shaker (model ISF-7100R, Jeio Tech, Korea). After saturation, samples for final concentration estimations were filtered using 0.45 μm PTFE filters. The concentrations of EBT was measured using Hach Lange spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 530 nm while Cr concentration was measured using ICP-OES. Each adsorption experiment repeated three times and average values were presented throughout the manuscript. The following formulas were used to calculate the removal efficiency and adsorption capacity of Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite toward EBT and Cr by:
where and are the initial and final concentrations of EBT and Cr (mg/L), respectively, is the adsorption uptake (mg/g), represents the volume of EBT or Cr solution in (L) and is the mass of the sorbent (Mg-Ca-Al-LDO composite) in (g).

Table 7.
The experimental adsorption characteristics of EBT and Cr by Mg-Ca-Al LDO composite.
For desorption experiments, 0.5 M and 0.1 M NaOH solutions were utilized as desorbing agents for EBT and Cr ions, respectively. The adsorption experiments were conducted at the following conditions: [EBT]i 50 mg/L; [Cr]i 30 mg/L; temperature, 22 °C; contact time, 24 h; [pH]I, EBT (5.2), Cr (6); Mg-Ca-Al-LDO dosage EBT 0.75 g/L, Cr 1.25 g/L. After the adsorption experiment, the Mg-Ca-Al-LDO was separated from the liquid solution by centrifugation. Next, the adsorbent was oven dried at 60 °C for 5 h and subjected to the desorption experiment using 20 mL of NaOH solution, agitation at 200 rpm for 10 h. After that, the adsorbent was separated by centrifuge and washed with deionized water several time before conducting the next adsorption experiment.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the highly active Mg-Ca-Al-LDO material was synthesized by co-precipitation method and studied for the removal of Cr and EBT from aqueous solution. The calcined Mg-Ca-Al-LDO sample exhibited a superior adsorption property for adsorbing EBT and Cr due to its relatively high surface area, positive surface charge, and memory effect. The Langmuir maximum monolayer capacity was 150.3 mg/g and 65.5 mg/g for EBT and Cr, respectively. The adsorption kinetic results matched strongly with pseudo-second order models for both Cr (R2-0.979), EBT (R2-0.999), while adsorption isotherm results fitted well with the Freundlich model. According to intraparticle diffusion modeling, Cr ion removal was mainly controlled by pore diffusion, while EBT removal was found to be controlled by surface and pore diffusion. Reusability studies demonstrate that more than 84% of the initial adsorption capacity of EBT and Cr ions could be achieved after five adsorption/desorption cycles. Thermodynamics investigations illustrate that the adsorptive removal of EBT and Cr by Mg-Ca-Al-LDO was a spontaneous and feasible process. However, the adsorption process was found to be endothermic for Cr ions removal, while being exothermic for EBT removal.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal12101247/s1, Figure S1: EDS analysis of fresh Mg-Ca-Al-LDO (a), after Cr adsorption (b) and after EBT adsorption (c).
Author Contributions
A.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. I.W.A.: Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. V.K.: Validation, writing—review and editing, T.L.: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing, H.A.: Supervision, Validation, writing—review and editing, M.A.A.: Visualization, Validation, Supervision, conceptualization, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the Environmental Analytical Laboratory staff, Chemistry Department Analytical Laboratories and Advanced Materials Research Laboratory at the University of Sharjah. The authors are also thankful to the Core lab staff at Qatar Environment and Energy Research Institute (QEERI), Said Mansour and Yongfeng Tong for the help in material characterization.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chatla, A.; Almanassra, I.W.; Jaber, L.; Kochkodan, V.; Laoui, T.; Alawadhi, H.; Atieh, M.A. Influence of calcination atmosphere on Fe doped activated carbon for the application of lead removal from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 652, 129928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, H.; Eskikaya, O.; Bilici, Z.; Dizge, N.; Balakrishnan, D. Comparison of Cr(VI) adsorption and photocatalytic reduction efficiency using leonardite powder. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakade, V.E.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Madikizela, L.M. Recent advances in hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by adsorptive methods. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26142–26164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Al-ansari, T.; Ihsanullah, I.; Kochkodan, V.; Anjaneyulu, C.; Muataz Ali, A.; Shanableh, A.; Tahar, L. Carbide-derived carbon as an extraordinary material for the removal of chromium from an aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.S.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Tan, Y.H.; Khalid, M.; Karri, R.R.; Walvekar, R.; Abdullah, E.C.; Nizamuddin, S.; Mazari, S.A. A comprehensive review on magnetic carbon nanotubes and carbon nanotube-based buckypaper for removal of heavy metals and dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, Z.; Saleh, M.; M’barek, I.; Yabalak, E.; Dizge, N.; Deepanraj, B. Investigation of the adsorption performance of cationic and anionic dyes using hydrochared waste human hair. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.T.; Halanur, M.M.; Kamath, S.V.; Mondal, D.; Sanna Kotrappanavar, N. Fe–Al based nanocomposite reinforced hydrothermal carbon: Efficient and robust absorbent for anionic dyes. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouaia, N.; Bengharez, Z.; Jellali, S. Preparation and characterization of chitosan extracted from shrimp shells waste and chitosan film: Application for Eriochrome black T removal from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, Y.; Jasrotia, T.; Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, G.R.; Chaudhary, S. Adsorptive removal of eriochrome black T (EBT) dye by using surface active low cost zinc oxide nanoparticles: A comparative overview. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayet, M.; Zahrim, A.Y.; Hilal, N. Modelling and optimization of coagulation of highly concentrated industrial grade leather dye by response surface methodology. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senguttuvan, S.; Senthilkumar, P.; Janaki, V.; Kamala-kannan, S. Significance of conducting polyaniline based composites for the removal of dyes and heavy metals from aqueous solution and wastewaters—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ying, D.; Liang, X.; Zhu, M.; Lin, X.; Xu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. A novel cationic polyelectrolyte microsphere for ultrafast and ultra-efficient removal of heavy metal ions and dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijannarong, S.; Aroonsrimorakot, S.; Thavipoke, P. Removal of Reactive Dyes from Textile Dyeing Industrial Effluent by Ozonation Process. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Möslang, M. Superior adsorption capacity of functionalised straw adsorbent for dyes and heavy-metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, M.A.; Bimeghdar, S. Synthesis of mesoporous NiO nanoparticles and their application in the adsorption of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Liu, F. Superhydrophilic carbonaceous-silver nanofibrous membrane for complex oil/water separation and removal of heavy metal ions, organic dyes and bacteria. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 614, 118491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gong, J.; Zeng, G.; Deng, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, H. Cross-linking to prepare composite graphene oxide-framework membranes with high-flux for dyes and heavy metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y. Novel polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiltration membrane blended with functionalized halloysite nanotubes for dye and heavy metal ions removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskikaya, O.; Gun, M.; Bouchareb, R.; Bilici, Z.; Dizge, N.; Ramaraj, R.; Balakrishnan, D. Photocatalytic activity of calcined chicken eggshells for Safranin and Reactive Red 180 decolorization. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Ji, L.; Li, C.; Hu, C.; Wu, K. Rapid, efficient and economic removal of organic dyes and heavy metals from wastewater by zinc-induced in-situ reduction and precipitation of graphene oxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 88, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, A. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water and Wastewaters by Sulfur-Containing Precipitation Agents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Kochkodan, V.; Mckay, G.; Atieh, M.A.; Al-Ansari, T. Kinetic and thermodynamic investigations of surfactants adsorption from water by carbide-derived carbon. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 1206–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.K.A.; Dweiri, F.; Almanassra, I.W.; Chatla, A.; Atieh, M.A. Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide Doped Activated Carbon Composites for Phosphate Removal from Synthetic Water: Adsorption and Thermodynamics Studies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushawish, A.; Almanassra, I.W.; Namboorimadathil, S.; Jaber, L.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Ali, M.; Taha, E.; Alawadhi, H.; Shanableh, A.; Ali, M. High-efficiency removal of hexavalent chromium from contaminated water using nitrogen-doped activated carbon : Kinetics and isotherm study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, L.; Ihsanullah, I.; Almanassra, I.W.; Backer, S.N.; Abushawish, A.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Alawadhi, H.; Shanableh, A.; Atieh, M.A. Adsorptive Removal of Lead and Chromate Ions from Water by Using Iron-Doped Granular Activated Carbon Obtained from Coconut Shells. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L. Removal of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic polymer multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraei, R.; Pour, Z.S.; Ghaemy, M. Novel magnetic bio-sorbent hydrogel beads based on modi fi ed gum tragacanth/graphene oxide : Removal of heavy metals and dyes from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Ye, S.; Yang, H.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Lin, Q.; Tan, X.; Yang, Z. Application of layered double hydroxide-biochar composites in wastewater treatment: Recent trends, modification strategies, and outlook. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, M.; Hai, A.; Banat, F.; Wazir, M.B.; Habib, M.; Bharath, G.; Al-Harthi, M.A. A review on the recent advances, challenges and future aspect of layered double hydroxides (LDH)—Containing hybrids as promising adsorbents for dyes removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 110989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Jarrah, N.; Manzar, M.S.; Al-Harthi, M.; Daud, M.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Haladu, S.A. Adsorption of eriochrome black T from aqueous phase on MgAl-, CoAl- and NiFe-calcined layered double hydroxides: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sá, F.P.; Cunha, B.N.; Nunes, L.M. Effect of pH on the adsorption of Sunset Yellow FCF food dye into a layered double hydroxide (CaAl-LDH-NO3). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhu, C. Pre-magnetic bamboo biochar cross-linked Ca–Mg–Al layered double-hydroxide composite: High-efficiency removal of As(III) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions and insight into the mechanism of simultaneous purification. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Layered double hydroxide intercalated with aromatic acid anions for the efficient capture of aniline from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Ouyang, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Liao, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.Q. Synthesis of nickel–iron layered double hydroxide via topochemical approach: Enhanced surface charge density for rapid hexavalent chromium removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Ho, W. Hierarchical porous Ni/Co-LDH hollow dodecahedron with excellent adsorption property for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabkhiro, H.; El Hassani, K.; Chems, M.; Anouar, A. Simultaneous removal of anionic dyes onto Mg(Al)O mixed metal oxides from ternary aqueous mixture: Derivative spectrophotometry and Density Functional Theory study. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 45, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Shao, L.; Qian, G. Efficient removal of dyes by a novel magnetic Fe3O4/ZnCr-layered double hydroxide adsorbent from heavy metal wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.P.; Wang, Y.C.; Tran, H.N. Removal of hexavalent chromium from groundwater by Mg/Al-layered double hydroxides using characteristics of in-situ synthesis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Gao, Y.; Tan, X.; Chen, C. Polyaniline-Modified Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxide Composites and Their Application in Efficient Removal of Cr(VI). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Kar, P.; Bishoyi, N.; Mallik, L.; Patel, R.K. Synthesis of Polypyrrole-Modified Layered Double Hydroxides for Efficient Removal of Cr(VI). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4357–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Aziz, H.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Ahmad, M.A.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Enhanced removal of Eriochrome Black T from water using biochar/layered double hydroxide/chitosan hybrid composite: Performance evaluation and optimization using BBD-RSM approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu’azu, N.D.; Jarrah, N.; Kazeem, T.S.; Zubair, M.; Al-Harthi, M. Bentonite-layered double hydroxide composite for enhanced aqueous adsorption of Eriochrome Black, T. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, B.; Jiang, C.; Le, Y.; Yu, J. Superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical calcined Ni/Mg/Al layered double hydroxides for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Boutahala, M.; Arab, L. Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution by uncalcined and calcined MgNiAl layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, P.; Konkol, M.; Kondracka, M.; Próchniak, W.; Bicki, R.; Wiercioch, P. Memory effect of the CuZnAl-LDH derived catalyst precursor—In situ XRD studies. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 464–465, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Ma, W.; Xin, G.; Wang, R.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, F.; Pan, D. Physicochemical characterization and sorption behavior of Mg-Ca-Al (NO3) hydrotalcite-like compounds toward removal of fluoride from protein solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237–238, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, L.H.; De Carvalho, G.S.G.; Do Carmo, W.R.; San Gil, R.A.S.; Chiaro, S.S.X.; Leitão, A.A.; Diniz, R.; De Sena, L.A.; Achete, C.A. MgCoAl and NiCoAl LDHs synthesized by the hydrothermal urea hydrolysis method: Structural characterization and thermal decomposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 64, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Lu, S.; Ai, Y.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Enhanced removal of methyl orange on calcined glycerol-modified nanocrystallined Mg/Al layered double hydroxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.R.; Rasid, N.M.; Fernando, W.J.N. Mg–Al hydrotalcite coating on zeolites for improved carbon dioxide adsorption. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Yu, J.U.N.J.I.E. High-Temperature Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide on Mixed Oxides Derived from Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol 2008, 42, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozov, K.; Berner, U.; Taviot-gueho, C.; Leroux, F.; Renaudin, G.; Kulik, D.; Diamond, L.W. Cement and Concrete Research Synthesis and characterization of the LDH hydrotalcite–pyroaurite solid-solution series. Cement Concrete Res. 2010, 40, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vágvölgyi, V.; Palmer, S.J.; Kristóf, J.; Frost, R.L.; Horváth, E. Mechanism for hydrotalcite decomposition : A controlled rate thermal analysis study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 318, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatla, A.; Abu-rub, F.; Prakash, A.V.; Ibrahim, G.; Elbashir, O. Highly stable and coke-resistant Zn-modified Ni-Mg-Al hydrotalcite derived catalyst for dry reforming of methane : Synergistic effect of Ni and Zn. Fuel 2022, 308, 122042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakırca, E.E.; Akın, N. Study on heterogeneous catalysts from calcined Ca riched hydrotalcite like compounds for biodiesel production. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 20, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Lv, T.; Song, X.; Cheng, Z.; Duan, S.; Xin, G. Characteristics of selective fluoride adsorption by biocarbon-Mg/Al layered double hydroxides composites from protein solutions : Kinetics and equilibrium isotherms study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taei, M.; Havakeshian, E.; Hasanpour, F.; Abedi, F.; Movahedi, M. Mg–Ca–Fe layered double hydroxide–gold nanoparticles as an efficient electrocatalyst for ethanol oxidation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.K.; Bera, S.; Nithya, R.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Velmurugan, S.; Narasimhan, S. V Solid state synthesis of Mg–Ni ferrite and characterization by XRD and XPS. J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, 335, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korin, E.; Froumin, N.; Cohen, S. Surface Analysis of Nanocomplexes by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Zakaria, Y.; Kochkodan, V.; Mroue, K.; Zekri, A.; Atieh, M.A.; Al-Ansari, T. XPS and material properties of raw and oxidized carbide-derived carbon and their application in antifreeze thermal fluids/nanofluids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 11787–11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, I.; Khan Niazi, N.; Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Dumat, C.; Imtiaz Rashid, M. Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhong, P.; Qiu, X. Remediation of hexavalent chromium in contaminated soil by Fe(II)-Al layered double hydroxide. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Aziz, H.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Adsorption and reusability performance of M-Fe (M = Co, Cu, Zn and Ni) layered double hydroxides for the removal of hazardous Eriochrome Black T dye from different water streams. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharali, D.; Deka, R.C. Preferential adsorption of various anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution over ternary CuMgAl layered double hydroxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 525, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N. Comments on “Fast and efficient removal of Cr(VI) to ppb level together with Cr(III) sequestration in water using layered double hydroxide interclated with diethyldithiocarbamate”. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 139854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, T.; Zhu, R.; Yan, L.; Pei, Z. Adsorption and photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr(VI) by Fe3O4-ZnAl-layered double hydroxide/TiO2 composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 562, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liao, X.; Zhang, X.; Peng, G.; Gao, J.; Chen, L. Enhanced adsorption of hexavalent chromium and the microbial effect on quartz sand modified with Al-layered double hydroxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, M.; Aziz, H.A.; Ihsanullah, I.; Ahmad, M.A.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Biochar supported CuFe layered double hydroxide composite as a sustainable adsorbent for efficient removal of anionic azo dye from water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Niu, C.; Tang, N.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lin, L. Highly efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by calcined Mg/Al-layered double hydroxides/polyaniline composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Tang, Q.; Rao, X. Calcined graphene/MgAl-layered double hydroxides for enhanced Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 221, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).