A Short Review of Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels over Porous Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Porous Metal Oxides
3. Composites of Mesoporous Silica and Metal Oxides
4. Metal-Organic Frameworks Based Materials
5. Porous Graphene and Boron-Nitride Based Materials
5.1. Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
5.2. Boron-Nitride-Based Materials
5.3. Boron Carbon Nitride (BCN)-Based Materials
5.4. Porous Carbon Nitride
6. Conclusions and Prospects
- ▪
- Porous mixed metal oxides catalysts are desirable due to their tunable electronic structure, which could facilitate the activation of molecular oxygen.
- ▪
- For composites of mesoporous silica and metal oxides composites, the interaction between carriers and active center, dispersion of metal oxides and the formation of metal peroxides resulting in improved activity and stability of the catalysts in AODS process.
- ▪
- In MOF-based catalysts, the coordinatively unsaturated metal sites, tailorable organic linkers, high surface area joined with unique porosity endowed MOFs with both the ability to catalyze AODS themselves and to be supports for active centers.
- ▪
- Porous graphene-based catalysts are promising catalysts due to their excellent mechanical stability, rich surface defects or functional groups, and high surface area.
- ▪
- Boron nitride-based catalysts are the new favorite of researchers owing to their high specific surface area, extremely high thermal stability, non-reducibility and tunable electronic structure, which are desirable in both supported metal-containing catalysts and metal-free catalysts.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, J.M.C.; Sanchez, M.C.C.; Presas, P.P.; Fierro, J. Oxidative processes of desulfurization of liquid fuels. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, V.C. An evaluation of desulfurization technologies for sulfur removal from liquid fuels. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotsi, G.; Scaroni, A.W. A review of carbon-supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 1989, 22, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Yang, W.; Hussain, M. Recent developments in alumina supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts for the production of sulfur-free refinery products: A technical review. Catl. Rev. 2020, 5, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive desulfurization and denitrogenation using metal-organic frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.T.; Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Yang, F.H. Desulfurization of Transportation Fuels with Zeolites Under Ambient Conditions. Science 2003, 301, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Ionic Liquids Supported on Metal-Organic Frameworks: Remarkable Adsorbents for Adsorptive Desulfurization. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, C.; Yang, Y.; Ying, P.; Sun, X.; Cai, T.; Li, C. The study of thiophene adsorption onto La(III)-exchanged zeolite NaY by FT-IR spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liu, C.; Yuan, B.; Xie, P.; Xie, C.; Yu, S. Energy-efficient extractive desulfurization of gasoline by polyether-based ionic liquids. Fuel 2016, 177, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asumana, C.; Yu, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Extractive desulfurization of fuel oils with low-viscosity dicyanamide-based ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, V.C.; Nanoti, S.M. Extractive Desulfurization of Gas Oils: A Perspective Review for Use in Petroleum Refineries. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 46, 319–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Wagle, D.V.; Ravula, S.; Zhang, Q. Tuning Task-Specific Ionic Liquids for the Extractive Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C. An overview of new approaches to deep desulfurization for ultra-clean gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel. Catal. Today 2003, 86, 211–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Dharaskar, S.; Pandya, J.; Shinde, S. Ultrasound-assisted extractive/oxidative desulfurization of oil using environmentally benign trihexyl tetradecyl phosphonium chloride. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.M.; Lucy, A.R.; Sharp, L.C. Oxidative desulphurisation of oils via hydrogen peroxide and heteropolyanion catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 1997, 117, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, M.J.; Durrant, L.R. Biodesulfurization. In Encyclopedia of Catalysis; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani, M.; Bassi, A.; Margaritis, A. Biodesulfurization of refractory organic sulfur compounds in fossil fuels. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 570–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ye, G.; Xu, W.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y. Creation of Active Sites in MOF-808(Zr) by a Facile Route for Oxidative Desulfurization of Model Diesel Oil. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Luo, H.; Xu, W.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y. Fabrication of MOF-808(Zr) with abundant defects by cleaving ZrO bond for oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 105, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y. Synthesis of Defect-Rich Titanium Terephthalate with the Assistance of Acetic Acid for Room-Temperature Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuel Oil. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Hu, L.; Gu, Y.; Lancelot, C.; Rives, A.; Lamonier, C.; Nuns, N.; Marinova, M.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y. Synthesis of polyoxometalate encapsulated in UiO-66(Zr) with hierarchical porosity and double active sites for oxidation desulfurization of fuel oil at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 19396–19404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, E.D.; Diaz, A.F. Method for Removing Sulfur and Nitrogen in Petroleum Oils. U.S. Patent US3847800A, 12 November 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Attar, A.; Corcoran, W.H. Desulfurization of Organic Sulfur Compounds by Selective Oxidation. 1. Regenerable and Nonregenerable Oxygen Carriers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1978, 17, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, S.; Nonaka, T.; Takashima, N.; Qian, W.; Ishihara, A.; Imai, T.; Kabe, T. Oxidative Desulfurization of Light Gas Oil and Vacuum Gas Oil by Oxidation and Solvent Extraction. Energy Fuels 2000, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Cheng, S.; Gao, J.; Gao, G.; He, M.Y. Deep Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuels Catalyzed by Ionic Liquid in the Presence of H2O2. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulea, V.; Fajula, F.; Bousquet, J. Mild Oxidation with H2O2 over Ti-Containing Molecular Sieves-A very Efficient Method for Removing Aromatic Sulfur Compounds from Fuels. J. Catal. 2001, 198, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, M.; Fairbridg, C.; Ring, Z. Oxidation reactivities of dibenzothiophenes in polyoxometalate/H2O2 and formic acid/H2O2 systems. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2001, 219, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Zhou, E. Oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel using a Brønsted acid room temperature ionic liquid in the presence of H2O2. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chica, A.; Corma, A.; Dómine, M.E. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization (ODS) of diesel fuel on a continuous fixed-bed reactor. J. Catal. 2006, 242, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S. Catalytic Oxidation of Dibenzothiophene Using Cyclohexanone Peroxide. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazyari, A.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Haghighat Mamaghani, A.; Beheshtian, J.; Thompson, L.T.; Mortazavi, Y. Microporous titania-silica nanocomposite catalyst-adsorbent for ultra-deep oxidative desulfurization. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 180, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Mei, B.W.; Yen, T.F. A new method for obtaining ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel via ultrasound assisted oxidative desulfurization. Fuel 2003, 82, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.; Al-Malki, A.; El-Ali, B.; Martinie, G.; Siddiqui, M.N. Deep Desulphurization of Gasoline and Diesel Fuels Using Non-Hydrogen Consuming Techniques. Fuel 2006, 85, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Z. Diesel fuel desulfurization with hydrogen peroxide promoted by formic acid and catalyzed by activated carbon. Carbon 2005, 43, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jian, L.; Yuan, X.; Jian, S.; Qi, Y. One step non-hydrodesulfurization of fuel oil: Catalyzed oxidation adsorption desulfurization over HPWA-SBA-15. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2007, 262, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaykina, R.F.; Zaykin, Y.A.; Mamonova, T.B.; Nadirov, N.K. Radiation methods for demercaptanization and desulfurization of oil products. Radiat. Phy. Chem. 2002, 63, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, I.V.; Moulijn, J.A. Science and technology of novel processes for deep desulfurization of oil refinery streams: A review. Fuel 2003, 82, 607–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Gao, J.; Jiang, Z.; Jing, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, C. Ultra-deep desulfurization of diesel by selective oxidation with [C18H37N(CH3)3]4[H2NaPW10O36] catalyst assembled in emulsion droplets. J. Catal. 2006, 239, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Ren, W.; Liao, W.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Suo, Z. Aerobic oxidative desulfurization of model diesel using a B-type Anderson catalyst [(C18H37)2N(CH3)2]3Co(OH)6Mo6O18·3H2O. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 138–139, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Chen, J.; He, M. Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization: A Promising Approach for Sulfur Removal from Fuels. ChemSusChem 2010, 1, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, P. One-pot extraction combined with metal-free photochemical aerobic oxidative desulfurization in deep eutectic solvent. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjalli, F.S.; Ahmed, O.U.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Alnashef, I.M. Deep oxidative desulfurization of liquid fuels. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 337–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.; Yashnik, S.; Kerzhentsev, M.; Parmon, V.; Bourane, A.; Al-Shahrani, F.M.; Hajji, A.A.; Koseoglu, O.R. Oxidative Desulfurization of Hydrocarbon Fuels. Catal. Rev. 2011, 53, 199–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Marie, B. Transition-metal complexes for liquid-phase catalytic oxidation: Some aspects of industrial reactions and of emerging technologies. Dalton Trans. 2003, 17, 3289–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Hirai, T.; Komosawa, I. Oxidative Desulfurization Process for Light Oil Using Titanium Silicate Molecular Sieve Catalysts. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2002, 35, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Hussain, M.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Ahmed, A.; Ashraf, R.S.; Ali Khan, M.; Jeon, B.; Park, Y. Systematic Assessment of Visible-Light-Driven Microspherical V2O5 Photocatalyst for the Removal of Hazardous Organosulfur Compounds from Diesel. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C. Aerobic oxidative desulfurization of benzothiophene, dibenzothiophene and 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene using an Anderson-type catalyst [(C18H37)2N(CH3)2]5[IMo6O24]. Green Chem. 2010, 11, 1954–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Murata, K.; Kidena, K.; Nomura, M. A Novel Oxidative Desulfurization System for Diesel Fuels with Molecular Oxygen in the Presence of Cobalt Catalysts and Aldehydes. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Deep desulfurization of liquid fuels with molecular oxygen through graphene photocatalytic oxidation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 209, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Gao, S. Recent Advances in Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols and Amines to Imines. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5851–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Hua, M.; Zhu, F.; Chu, X.; Xiong, J.; He, M.; Zhu, W.; et al. Boosting aerobic oxidative desulfurization performance in fuel oil via strong metal-edge interactions between Pt and h-BN. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
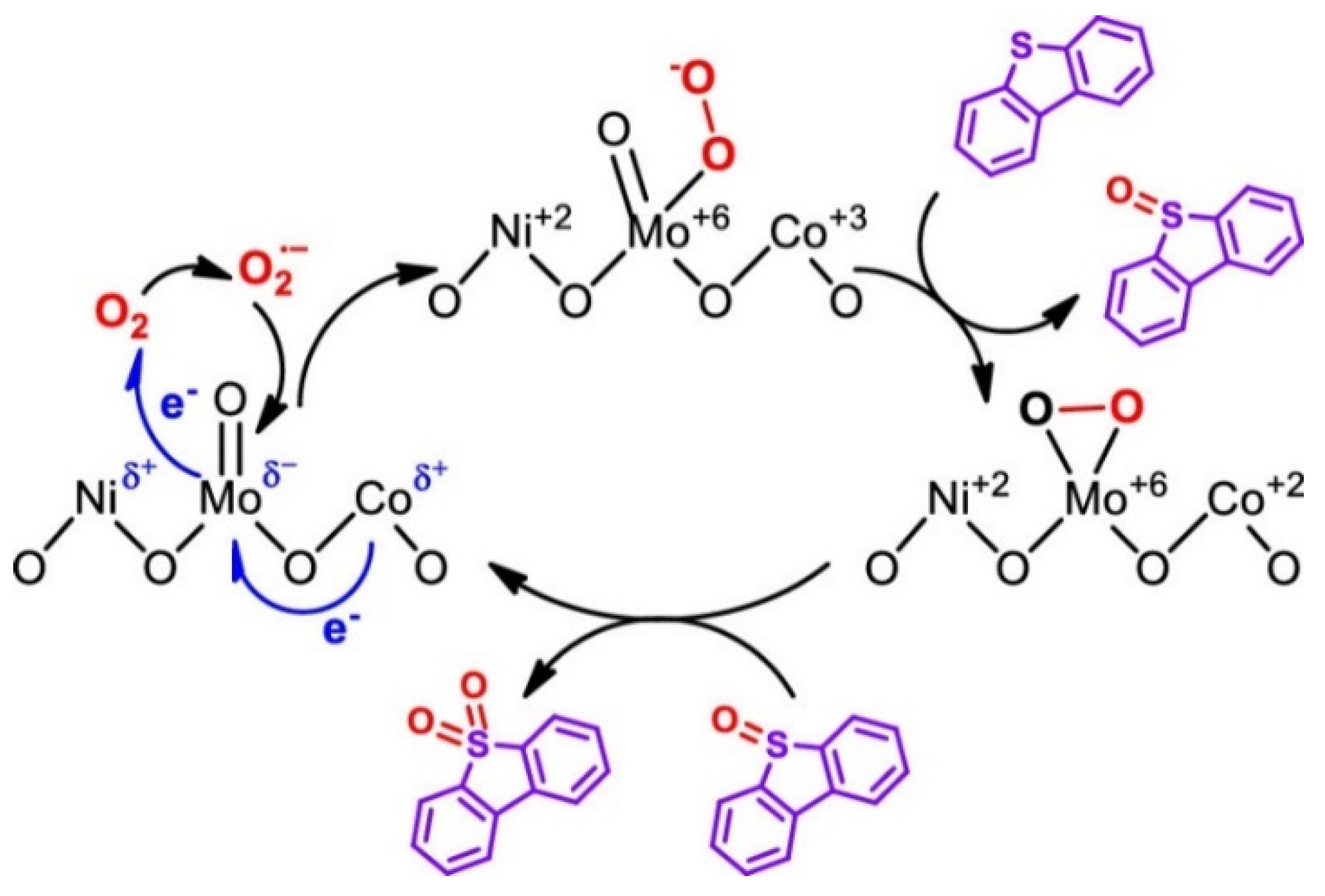
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Bai, L.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, H. Preparation of Co-Mo-O ultrathin nanosheets with outstanding catalytic performance in aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13995–13998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, I.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Abbas, G.; Hussain, M. Efficient catalyst development for deep aerobic photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization: Recent advances, confines, and outlooks. Catal. Rev. 2021, 3, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Hussain, M.; Rashid, R.; Shafique, S.; Park, Y.K. Development of hierarchically porous LaVO4 for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic desulfurization of diesel. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Hussain, M.; Shafique, S.; Shafique, S.; Park, Y.K. Oxidative desulfurization of refinery diesel pool fractions using LaVO4 photocatalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Paricio, A.; Santiago-Portillo, A.; Navalón, S.; Concepción, P.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. MIL-101 promotes the efficient aerobic oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophenes. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
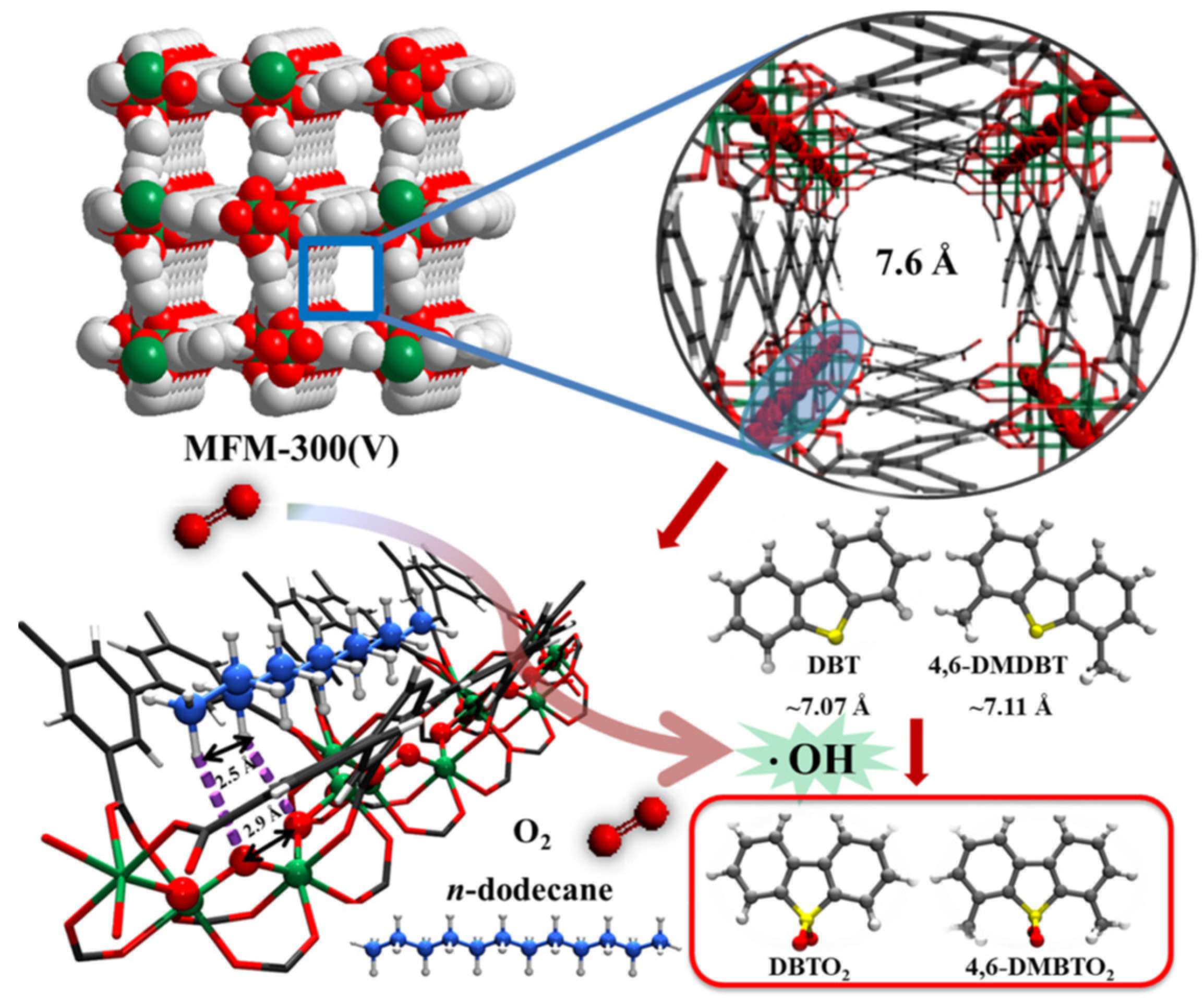
- Li, X.; Gu, Y.; Chu, H.; Ye, G.; Zhou, W.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y. MFM-300(V) as an active heterogeneous catalyst for deep desulfurization of fuel oil by aerobic oxidation. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2019, 584, 117152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wen, G.; Ding, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, C.; Su, D. Reduced graphene oxide: A metal-free catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhu, W.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Dai, S. A template-free solvent-mediated synthesis of high surface area boron nitride nanosheets for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Highly Efficient Photocatalytic Oxidation of Sulfur-containing Organic Compounds and Dyes on TiO2 with Dual Cocatalysts Pt and RuO2. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2012, 127, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shuang, L.; Hui, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Catalytic oxygenation of dibenzothiophenes to sulfones based on Fe III porphyrin complex. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2011, 396, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X. Oxidation of refractory sulfur compounds with molecular oxygen over a Ce-Mo-O catalyst. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5273–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Lv, B. Highly efficient oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene using Ni modified MoO3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2020, 589, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Preparation of MoO2/g-C3N4 composites with a high surface area and its application in deep desulfurization from model oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; Bai, L.; Chen, H. Efficient aerobic oxidative desulfurization over Co-Mo-O bimetallic oxide catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Bai, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wei, D.; Bai, L.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H. Co-Fe-Mo mixed metal oxides derived from layered double hydroxides for deep aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Fuel 2021, 306, 121751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, R.; Zhan, H.; Yang, H.; Bai, L.; Yang, L.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Morphology-Controlled Construction and Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Hierarchical Hollow Co-Ni-Mo-O Mixed Metal-Oxide Nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6488–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liao, W.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization by Nanoporous Tungsten Oxide with Oxygen Defects. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Xun, S.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, W. Atomic-Layered α-V2O5 Nanosheets Obtained via Fast Gas-Driven Exfoliation for Superior Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 2612–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lü, X.; Xun, S.; He, M.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H.; Yuan, M.; Fan, L.; Zhu, W. High-index planes T-Nb2O5 using self-assembly strategy for aerobic oxidative desulfurization in fuels. Fuel 2022, 307, 121877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Yao, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. One-pot extraction and aerobic oxidative desulfurization with highly dispersed V2O5/SBA-15 catalyst in ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39383–39390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Gao, X.; Dong, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, G.; Xun, S.; Peng, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Aerobic oxidative desulfurization via magnetic mesoporous silica-supported tungsten oxide catalysts. Petrol. Sci. 2020, 17, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseva, E.A.; Lukashov, M.O.; Cherednichenko, K.A.; Levin, I.S.; Akopyan, A.V. Heterogeneous Catalysts Containing an Anderson-Type Polyoxometalate for the Aerobic Oxidation of Sulfur-Containing Compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 14154–14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, S.; Jiang, W.; Guo, T.; He, M.; Ma, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Magnetic mesoporous nanospheres supported phosphomolybdate-based ionic liquid for aerobic oxidative desulfurization of fuel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, A.; Cui, T.; Fan, H.; Yang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, W. A comprehensive review on oxidative desulfurization catalysts targeting clean energy and environment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2246–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, I.; Shafique, S.; Akhter, P.; Ishaq, M.; Yang, W.; Hussain, M. Recent breakthroughs in deep aerobic oxidative desulfurization of petroleum refinery products. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 125731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Liang, D.; Li, S.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Shi, Z.; Zheng, Z. Facile Synthesis of a Nanocrystalline Metal-Organic Framework Impregnated with a Phosphovanadomolybdate and Its Remarkable Catalytic Performance in Ultradeep Oxidative Desulfurization. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 3086–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
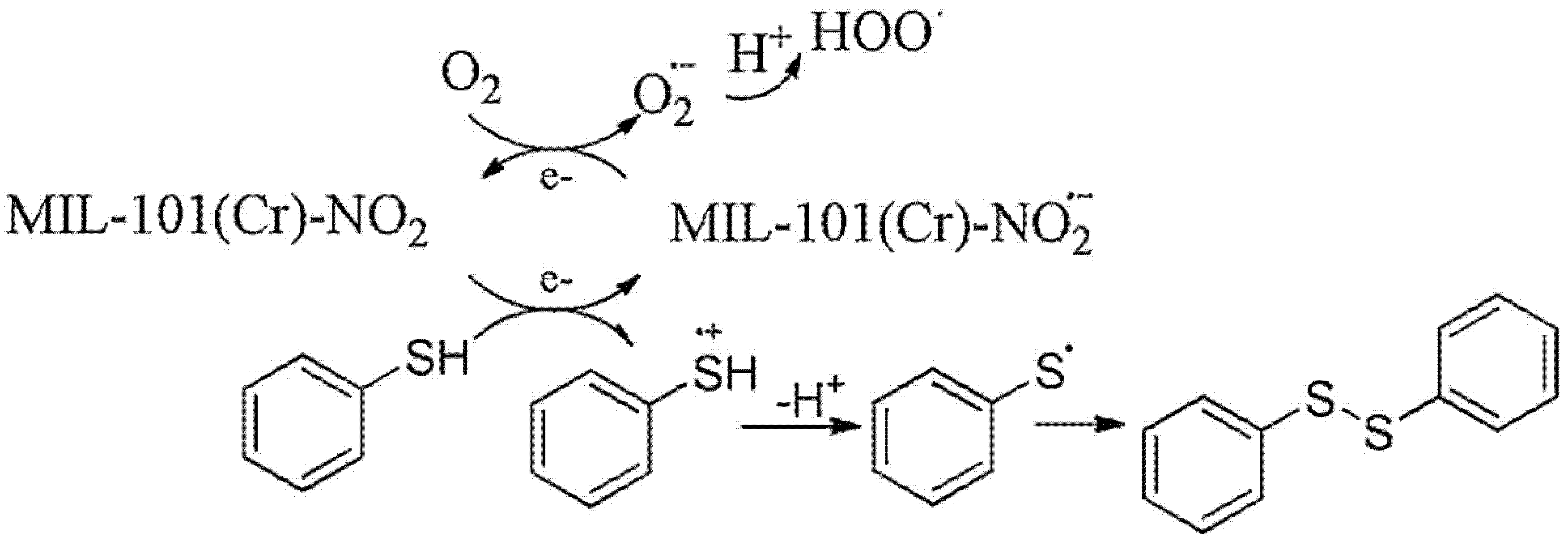
- Vallés-García, C.; Santiago-Portillo, A.; Álvaro, M.; Navalón, S.; García, H. MIL-101(Cr)-NO2 as efficient catalyst for the aerobic oxidation of thiophenols and the oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophenes. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2020, 590, 117340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, R. A new green system of HPW@MOFs catalyzed desulfurization using O2 as oxidant. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J. Template method for a hybrid catalyst material POM@MOF-199 anchored on MCM-41: Highly oxidative desulfurization of DBT under molecular oxygen. Fuel 2016, 184, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lv, Z.; Gao, R.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J. Oxidative desulfurization process of model fuel under molecular oxygen by polyoxometalate loaded in hybrid material CNTs@MOF-199 as catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Peng, F.; Tan, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Zheng, W. Selective Catalysis of the Aerobic Oxidation of Cyclohexane in the Liquid Phase by Carbon Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3978–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Tang, P.; Tan, J.; Lu, A.; Ma, D. Direct catalytic oxidation of benzene to phenol over metal-free graphene-based catalyst. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yu, H.; Tan, J.; Peng, F.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zheng, W.; Wong, N. Nitrogen-, phosphorous- and boron-doped carbon nanotubes as catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of cyclohexane. Carbon 2013, 57, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Xie, X.; Xu, J.; Gu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Nanosheets as Metal-Free Catalysts for Aerobic Selective Oxidation of Benzylic Alcohols. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wei, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhu, W. Boron and Nitride Dual vacancies on Metal-Free Oxygen Doping Boron Nitride as Initiating Sites for Deep Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Luo, J.; Yang, L.; Pang, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Boron defect engineering in boron nitride nanosheets with improved adsorptive desulfurization performance. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 64, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, H.; Xu, M.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Bai, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, D.; Wang, W. Immobilization of monodisperse metal-oxo-cluster on graphene for aerobic oxidative desulfurization of fuel. Process Saf. Environ. 2020, 140, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhu, W.; Dai, B.; Chao, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.; Li, H. Copper nanoparticles advance electron mobility of graphene-like boron nitride for enhanced aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Fan, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, W. Immobilizing Highly Catalytically Molybdenum Oxide Nanoparticles on Graphene-Analogous BN: Stable Heterogeneous Catalysts with Enhanced Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Yao, X.; Chao, Y.; Xun, S.; Xiong, J.; Fan, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Decavanadates anchored into micropores of graphene-like boron nitride: Efficient heterogeneous catalysts for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Fuel 2018, 230, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, P.; Chao, Y.; He, J.; Li, H.; Lu, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Zhu, W. Gas-exfoliated porous monolayer boron nitride for enhanced aerobic oxidative desulfurization performance. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 25604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xun, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Construction of 2D-2D V2O5/BNNS nanocomposites for improved aerobic oxidative desulfurization performance. Fuel 2020, 270, 117498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; He, J.; Wu, P.; Chao, Y.; Li, H.; Tao, D. Taming electronic properties of boron nitride nanosheets as metal-free catalysts for aerobic oxidative desulfurization of fuels. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4381–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, P.; Luo, J.; Dai, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Synthesis of hierarchical porous BCN using ternary deep eutectic solvent as precursor and template for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2020, 293, 109788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, P.; Luo, J.; Tao, D.; Peng, C.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, W. Deep eutectic solvent-induced high-entropy structures in boron nitride for boosted initiation of aerobic oxidative desulfurization of diesel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 146980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
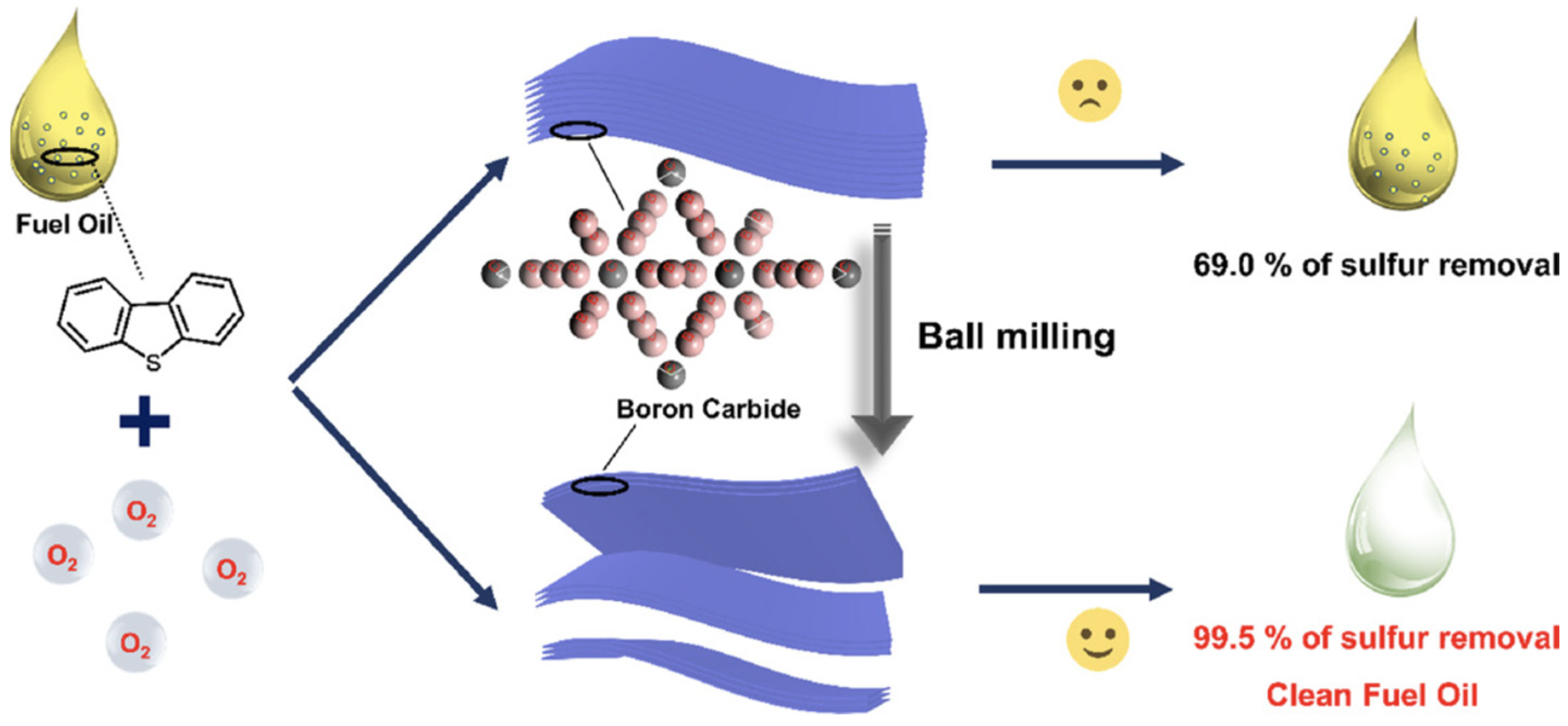
- Wu, P.; Jia, Q.; He, J.; Lu, L.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Peng, C.; He, M.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, W.; et al. Mechanical exfoliation of boron carbide: A metal-free catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization in fuel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, M.; Xun, S.; He, M.; Wu, L.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Lipophilic decavanadate supported by three-dimensional porous carbon nitride catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Mol. Catal. 2020, 483, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; He, J.; Wu, P.; Lu, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Hua, M.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Carbon nitride mediated strong metal-support interactions in a Au/TiO2 catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Du, A.; Zhu, Z.; Rudolph, V.; Lu, G.; Smith, S.C. A density functional theory study on CO2 capture and activation by graphene-like boron nitride with boron vacancy. Catal. Today 2001, 175, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Iyyamperumal, E.; Roy, A.; Xue, Y.; Yu, D.; Dai, L. Vertically Aligned BCN Nanotubes as Efficient Metal-Free Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction: A Synergetic Effect by Co-Doping with Boron and Nitrogen. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11756–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Sarkar, B.; Bag, A.; Lefebvre, F.; Sameer, S.; Pendem, C.; Bordoloi, A. Single-step synthesis of hierarchical BxCN: A metal-free catalyst for low-temperature oxidative dehydrogenation of propane. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2016, 4, 18559–18569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yang, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Chao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.; Dai, S. Tailoring N-Terminated Defective Edges of Porous Boron Nitride for Enhanced Aerobic Catalysis. Small 2017, 13, 1701857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
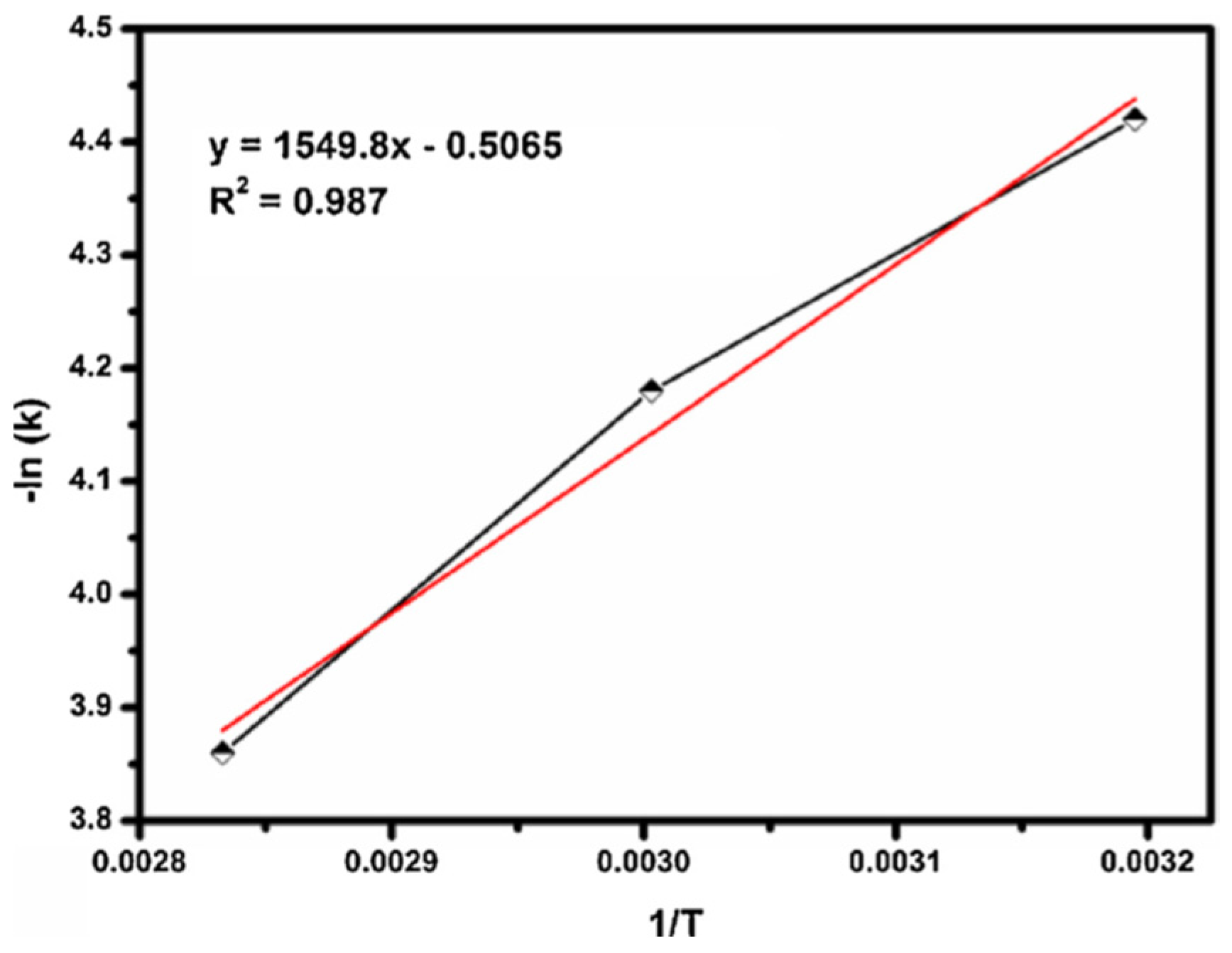
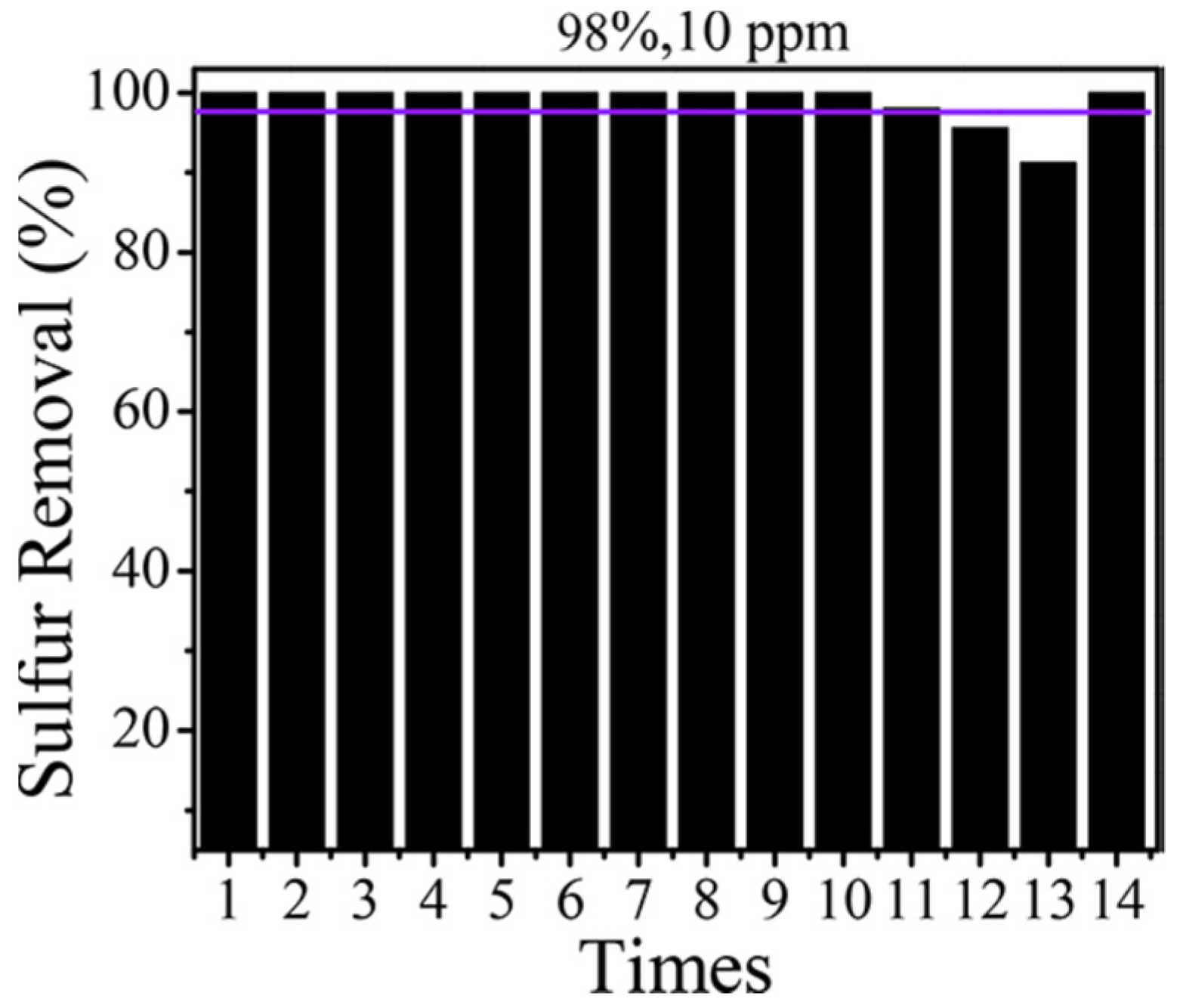
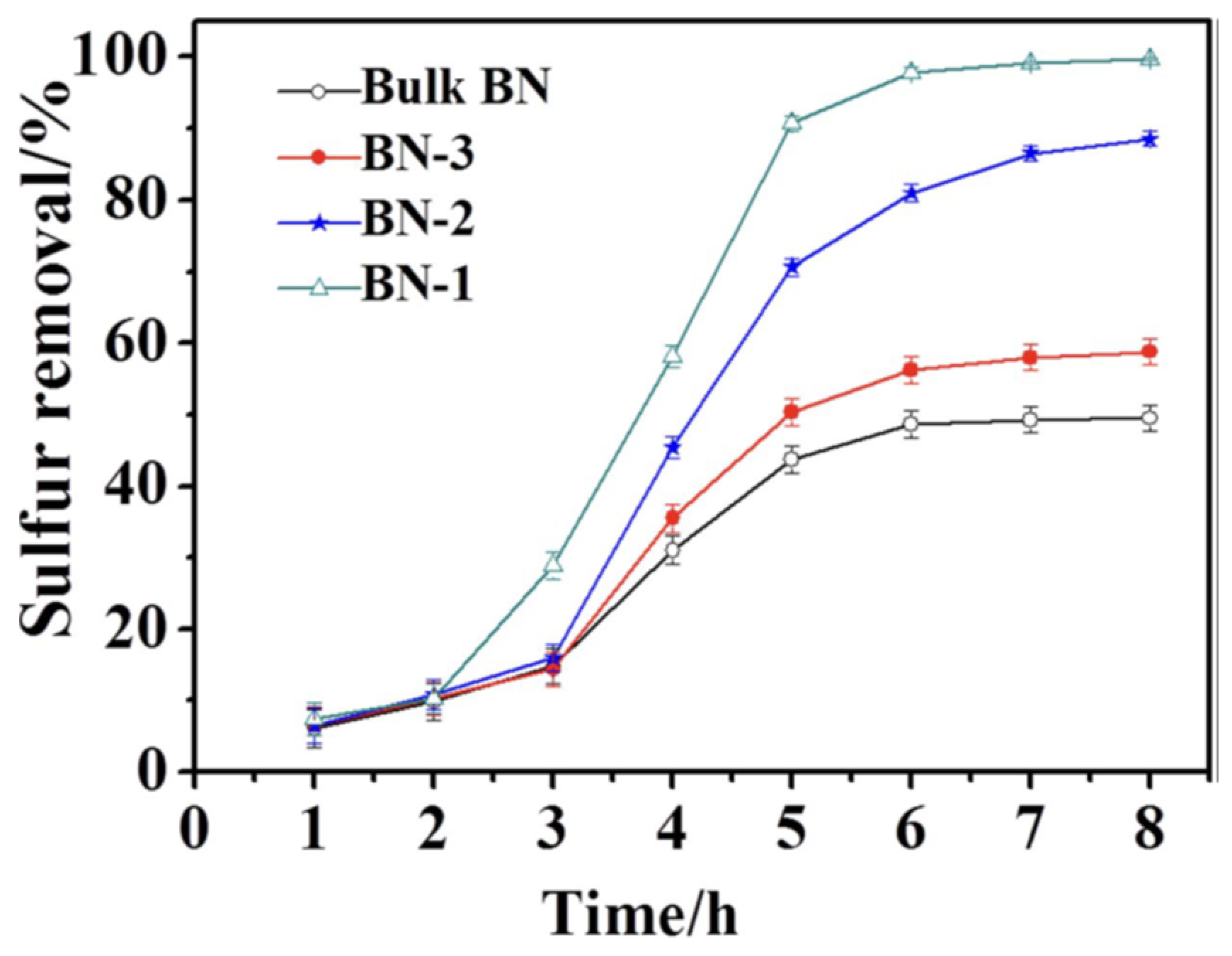
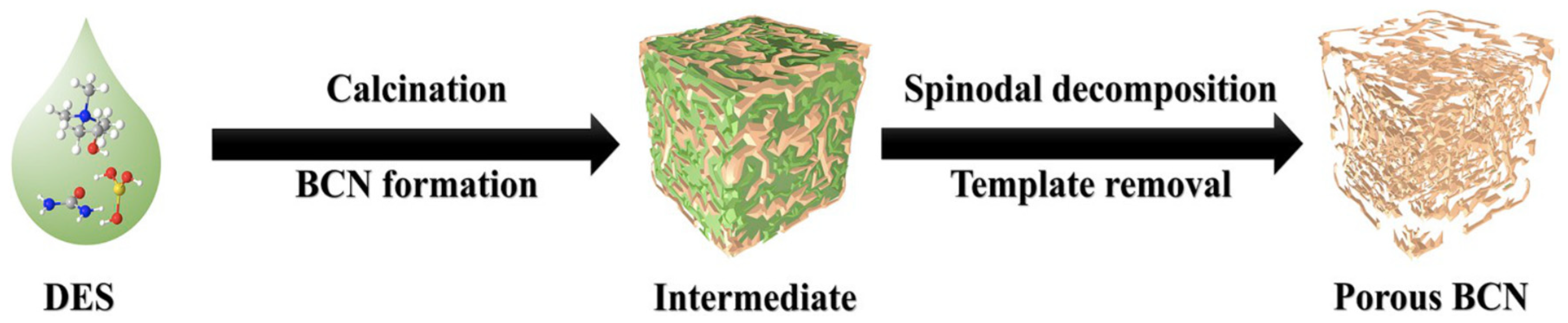

| Oxidants | Active Oxygen (%) | Oxidizing Power (V vs. SHE) | Byproduct | Safety & Handling | Price (EUR/Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 (30 wt%) | 14.1(47.1) | +1.78 | H2O | Causes serious eye damage May cause respiratory irritation Causes skin irritation Keep from contact with clothing | 145 |
| Ozone | 33.3 | +2.07 | SO2 | Very toxic to aquatic life Must be contained within ozone-resistant tubing and pipes | - |
| t-BuOOH(TBHP) | 17.8 | - | t-BuOH | Flammable liquid and vapor Causes severe skin burns and eye damage May cause genetic defects and cancer Use only under a chemical fume hood | 64 |
| CumOOH(CHP) | 10.5 | - | CumOH | Combustible liquid May be fatal if swallowed Avoid inhalation of vapor or mist | 95 |
| KO2 | 45.0 | +1.56 | OH- | May intensify fire; oxidizer Causes severe skin burns and eye damage Use only under a chemical fume hood | 835 |
| Organic peracid (peracetic acid at 100 wt%) | 21.1 | +1.81 | Organic acid (acetic acid) | Flammable liquid and vapor Causes severe skin burns and eye damage; Avoid contact with skin and eyes | 345 |
| Air | 23.2 | +1.23 (O2) | None | Contains gas under pressure, may explode if heated Store in a well-ventilated place | 0 |
| Catalyst | BET (m2/g) | Catalyst Amount | Model Oil Volume | Model Solution | Sulfur (ppm) | Oxidant | Reaction Temperature | Reaction Time | Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce-Mo-O | 14 | 100 mg | 20 g | Decalin | BT(500) DBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | O2 | 100 °C 100 °C 100 °C | 360 min 480 min 480 min | 97% 99% 99% | [62] |
| Co2MoO | -- | 100 mg | 20 g | Decahydronaphthalene | BT(500) DBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 120 °C | 360 min 180 min 180 min | 88% 100% 100% | [65] |
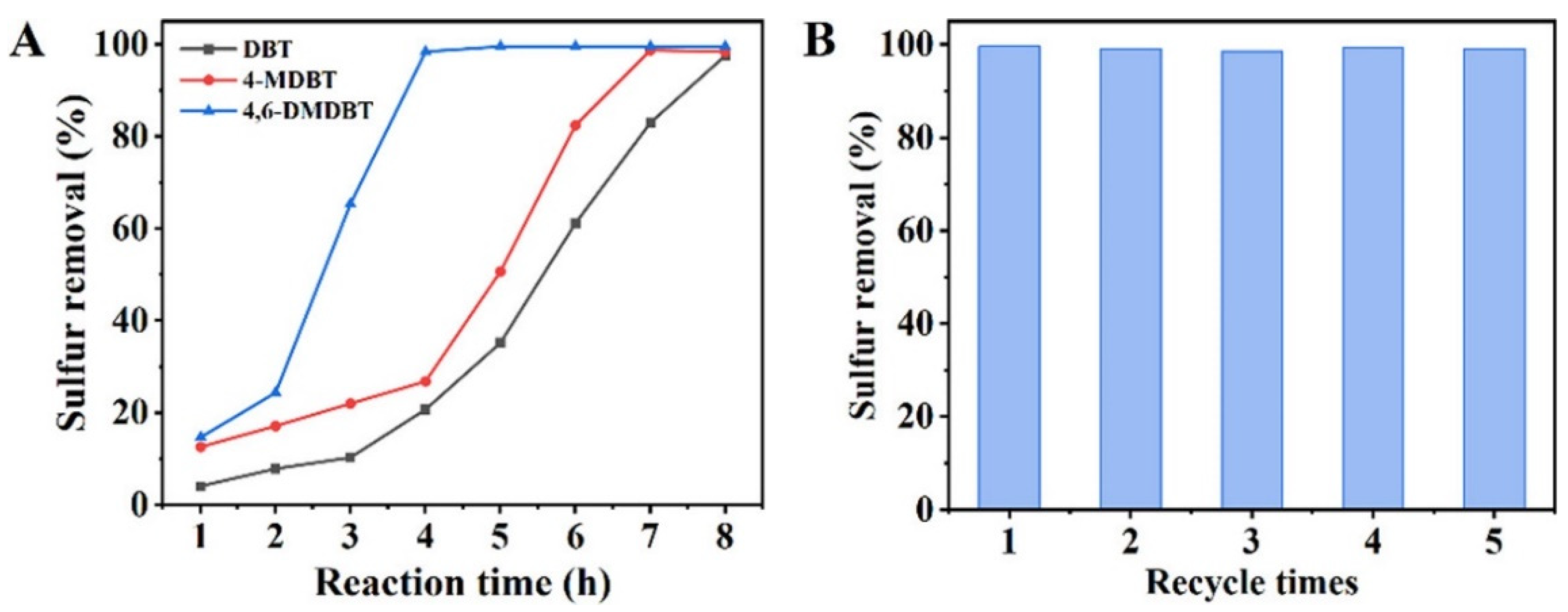
| CoFeMo-MMO-2 | 73.62 | 20 mg | 20 g | Diesel | BT(500) DBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 100 °C | 360 min 180 min 180 min | ~92% 99.2% 99.2% | [66] |
| CoNiMo-HNT-2 | 114.7 | 20 mg | 20 g | Decahydronaphthalene | BT (500) DBT (500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 110 °C 100 °C 110 °C | 120 min 240 min 120 min | 60% 100% 100% | [67] |
| 3DOM WOx-400 | 14.2 | 10 mg | 20 mL | Dodecane | DBT(200) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | Air | 120 °C 120 °C 120 °C | 480 min 480 min 240 min | 99% 99% 99% | [68] |
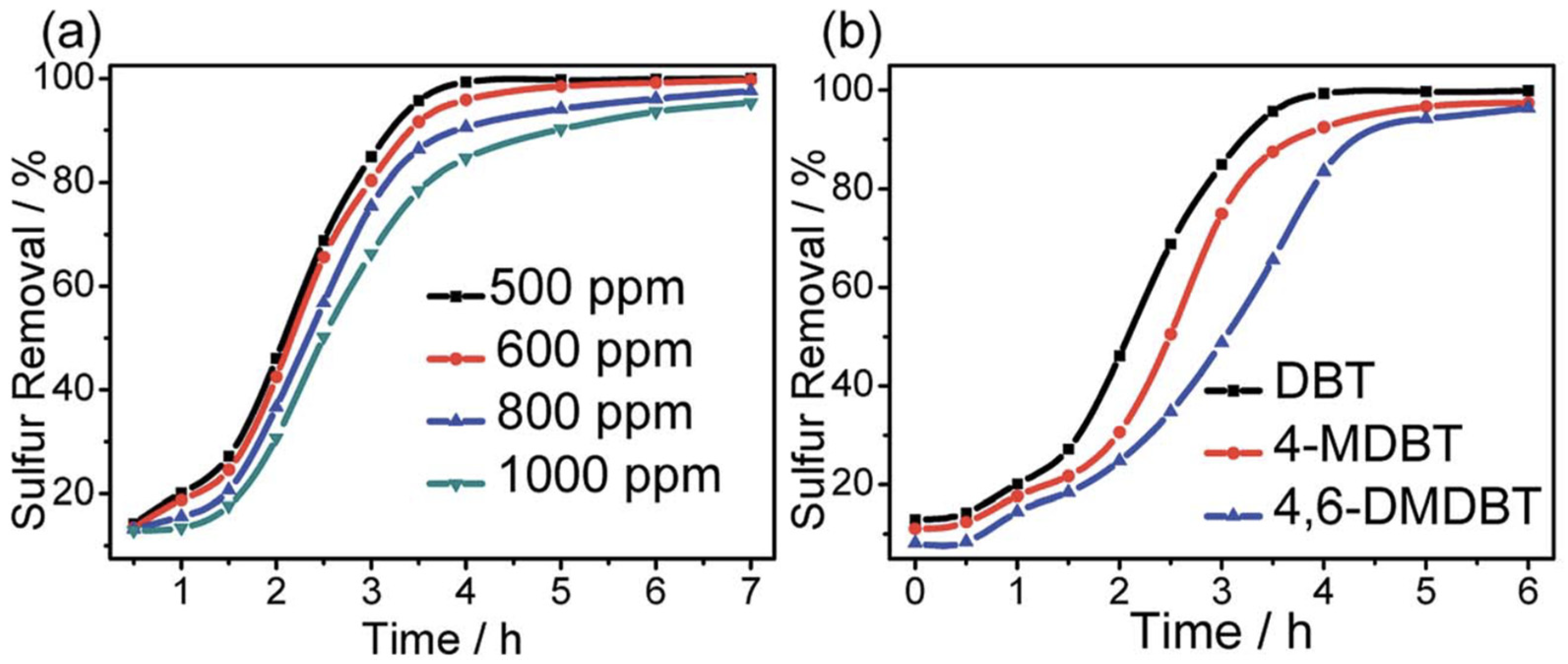
| α-V2O5 nanosheets | - | 10 mg | 50 mL | Decahydronaphthalene | DBT(500) DBT(600) DBT(800) DBT(1000) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 120 °C 120 °C 120 °C 120 °C 120 °C 120 °C | 360 min 360 min 360 min 360 min 360 min 360 min | 99.7% 98.7% 97.2% 95.5% 96.1% 92% | [69] |
| T-Nb2O5 | 22.1 | 50 mg | 20 mL | Dodecane | DBT(200) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | O2 | 130 °C | 420 min | 100% 100% 96% | [70] |
| Catalyst | BET (m2/g) | Catalyst Amount | Model Oil Volume | Model Solution | Sulfur (ppm) | Oxidant | Reaction Temperature | Reaction Time | Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 wt%V2O5/SBA-15 | 547 | 50 mg | 50 mL | Decahydronaphthalene | DBT (500) | Air | 120 °C | 480 min | 99.3% | [71] |
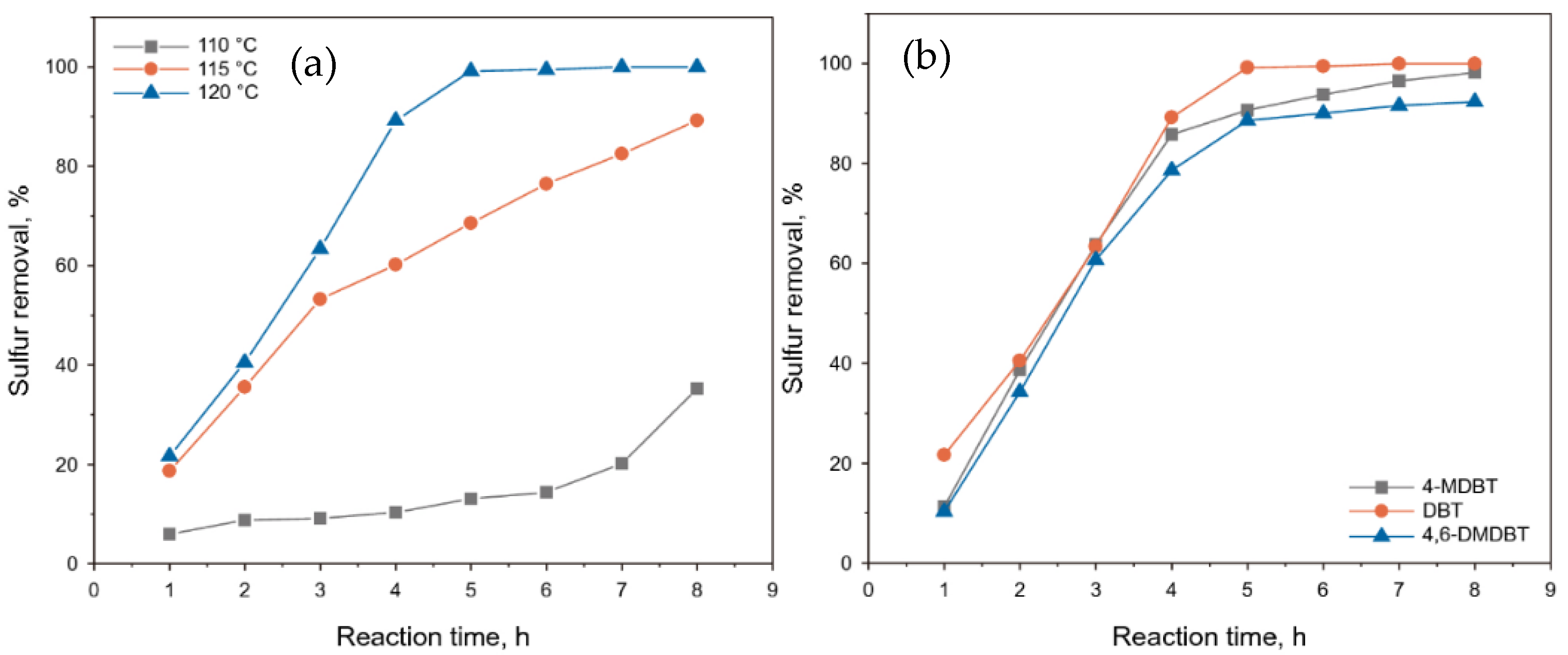
| WO3/MMS-500 | 167 | 10 mg | 20 mL | Decalin | DBT (500) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | O2 | 120 °C | 480 min | 99.9% 98.2% 92.3% | [72] |
| CoMo-0.5IL-SBA | 196 | 0.2 wt% | 30 mL | Decalin | DBT (500) BT (500) 3-MBT (500) | Air | 120 °C 120 °C 120 °C | 90 min 180 min 360 min | 100% 100% 57% | [73] |
| [(C8H17)3NCH3]3PMo12O40/γ-MMS | -- | 25 mg | 20 mL | Decalin | DBT (500) 4-MDBT(500) | Air | 120 ℃ | 300 min 420 min | 100% 100% | [74] |
| Catalyst | BET (m2/g) | Catalyst Amount | Model Oil Volume | Model Solution | Sulfur (ppm) | Oxidant | Reaction Temperature | Reaction Time | Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POM@NENU-9N | 564 | 44 mg | 50 mL | Decalin | DBT(500) | O2 | 80 °C | 90 min | 100% | [77] |
| MIL-101 (Cr) | 1850 | 0.5 g /L | 10 mL | n-dodecane | DBT (200) | O2 | 120 °C | 1440 min | 99% | [56] |
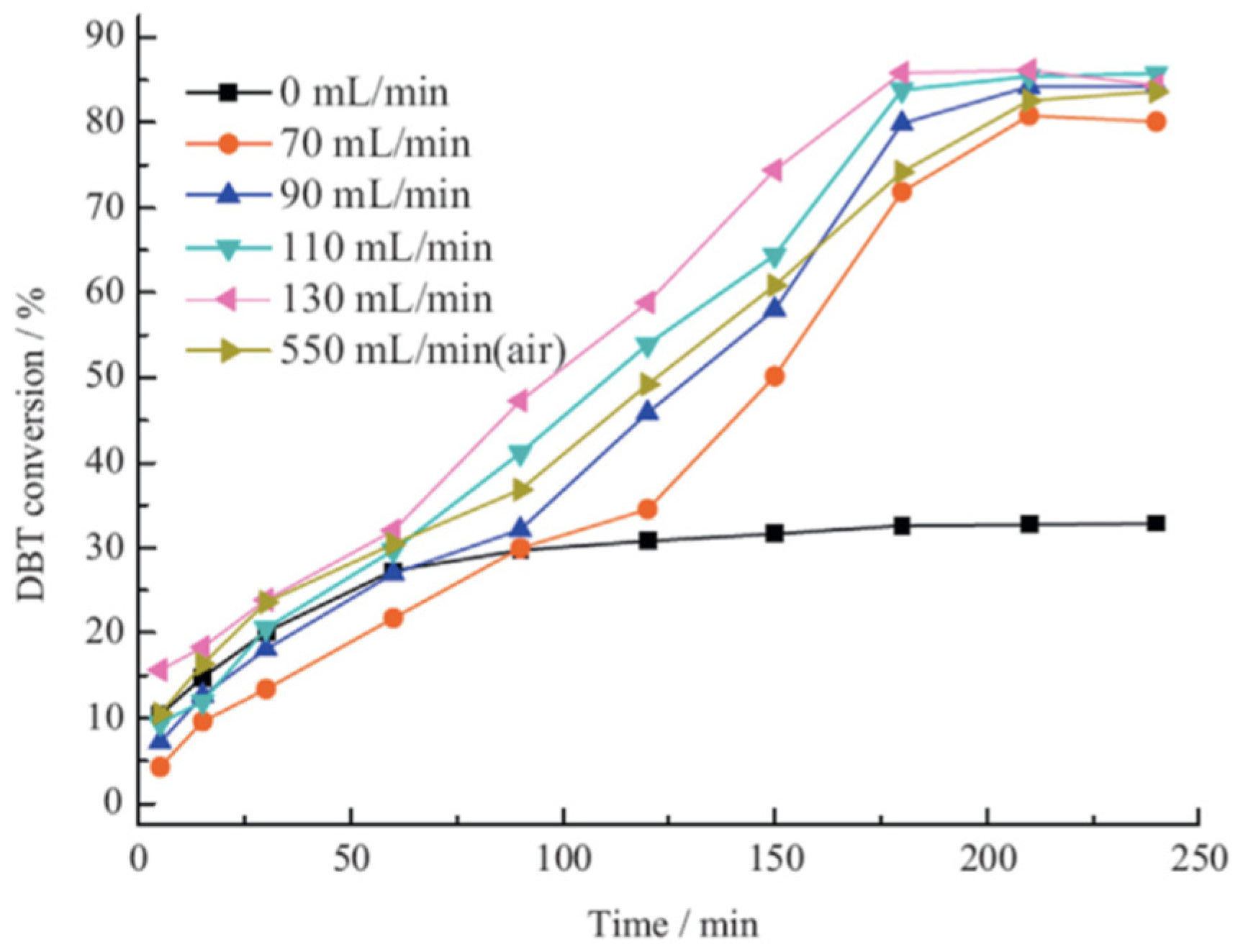
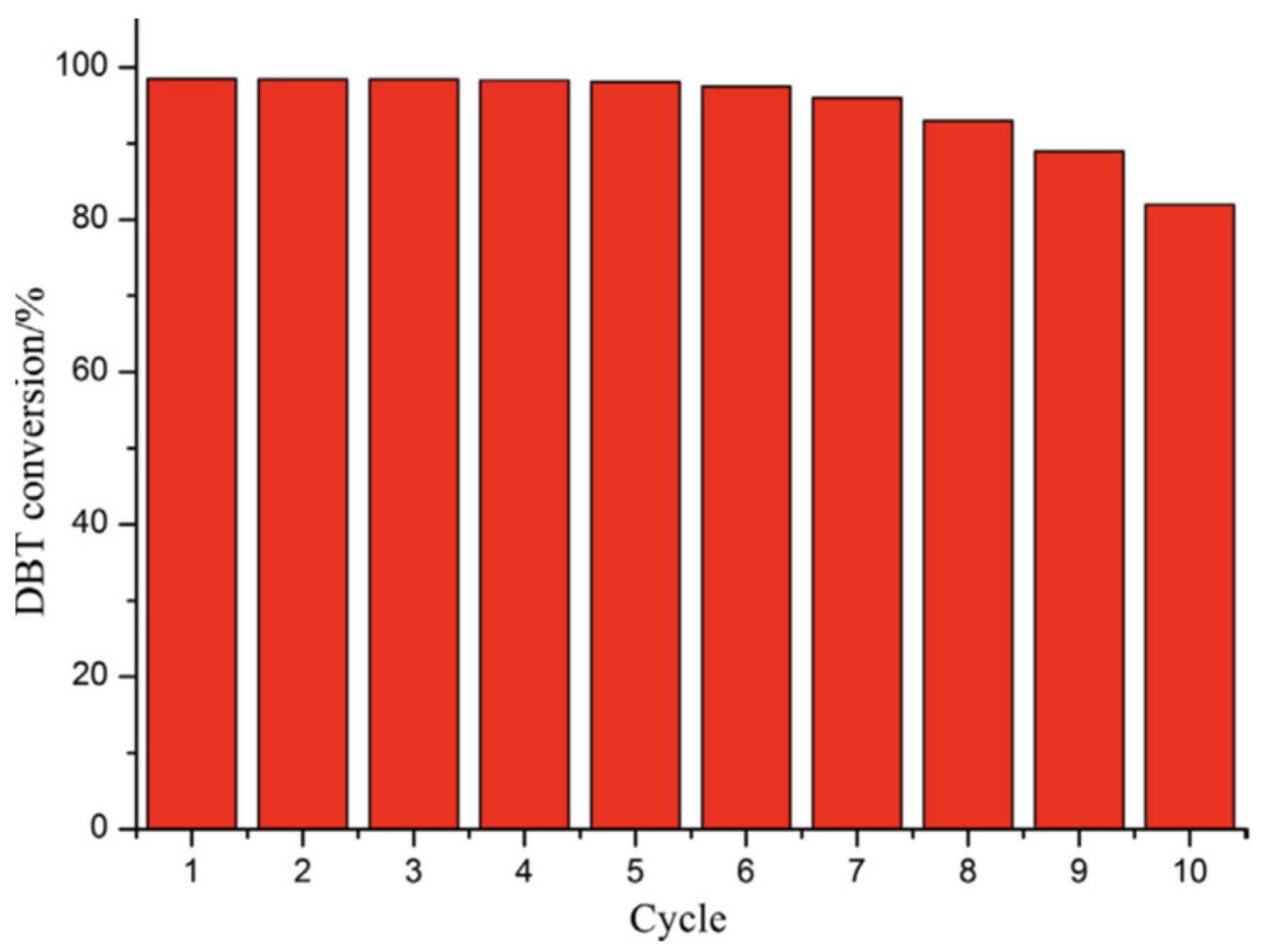
| MIL-101 (Cr)-NO2 | 1850 | 0.04 mmol Cr | 20 mL | n-dodecane | DBT (200) | O2 | 140 °C | 270 min | 100% | [78] |
| MFM-300(V) | 993 | 1.5 g/L | 5 g | n-dodecane | BT(200) DBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | ambient air | 120 °C | 300 min | 12% 99.6% 98.1% | [57] |
| HPW@MOFs | 1102 | 4.21 mg | 60 mL | Octane | DBT(500) | O2 | 90 °C | 240 min | 84% | [79] |
| POM@MOF-199@ MCM-41 | 732 | 2 g /L | - | Octane | DBT (2000) | O2 | 85 °C | 180 min | 98.5% | [80] |
| CNTs@MOF-199- Mo16V2 | 371.45 | 100 mg | 50 mL | n-octane | DBT (2000) | O2 | 80 °C | 180 min | 98.3% | [81] |
| Catalyst | BET (m2/g) | Catalyst Amount | Model Oil Volume | Model Solution | Sulfur (ppm) | Oxidant | Reaction Temperature | Reaction Time | Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rGO | 492 | 5 mg | 25 mL | Dodecane | DBT(400) BT(400) 3-MBT(400) 4,6-DMDBT(400) | O2 | 140 °C | 360 min | 100% 90.5% 96.1% 97.7% | [58] |
| POM/PIL/Gr | 83.4 | 10 mg | 20 mL | Decahydronaphthalene | BT(500) DBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 100 °C | 180 min | 75% 100% 100% | [88] |
| Cu NPs/g-BN | 570 | 100 mg | 40 mL | Decalin | DBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 120 °C | 480 min 180 min | 99% 97% | [89] |
| Pt@h-BN | - | 50 mg | 40 mL | Decalin | BT(500) DBT(500) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 130 °C | 360 min | 85.9% 98.3% 96.5% 93.7% | [51] |
| 5-MoOxNPs/g-BN | 108 | 100 mg | 20 mL | Decalin | DBT(500) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 120 °C | 180 min 270 min 270 min | 100% 97% 97% | [90] |
| C8V/g-BN | 493 | 80 mg | 40 mL | - | DBT(500) DBT(600) DBT(800) DBT(1000) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 120 °C | 240 min 300 min 300 min 360 min 300 min 300 min | 99.8% 99.6% 96.6% 95.9% 99.5% 95.3% | [91] |
| BN-1 | - | 50 mg | 20 mL | Decalin | DBT(500) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 130 °C | 480 min | 98.2% 97.5% 98% | [92] |
| V2O5/BNNS | - | 200 mg | 50 mL | - | DBT(500) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 120 °C | 240 min | 99.6% 97.1% 95.2% | [93] |
| BCN-20 | - | 70 mg | 20 mL | Decalin | DBT(200) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | Air | 100 °C | 360 min | 100% 90.5% 98.7% | [94] |
| BCN-1 | 1004 | 50 mg | 20 mL | Decalin | DBT(500) 4-MDBT(500) 4,6-DMDBT(500) | Air | 125 °C | 240 min | 98.4% | [95] |
| TMAC-BCNO | 838 | 50 mg | 20 mL | Dodecane | DBT(200) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | Air | 125 °C | 360 min | 99% | [96] |
| B4C-5 | - | 50 mg | 20 mL | Dodecane | DBT(200) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | Air | 130 °C | 480 min | 99.5% 91% 97.5% | [97] |
| 20% V-IL/3D g-C3N4 | 46.99 | 10 mg | 20 mL | Dodecane | DBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | Air | 120 °C | 360 min | 97.2% 95.8% | [98] |
| Au-TiO2@C3N4-800 | - | 10 mg | 20 mL | Dodecane | DBT(200) 4-MDBT(200) 4,6-DMDBT(200) | Air | 120 °C | 360 min | 99.7% 98.8% 99.4% | [99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Sun, Y. A Short Review of Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels over Porous Materials. Catalysts 2022, 12, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12020129
Yuan B, Li X, Sun Y. A Short Review of Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels over Porous Materials. Catalysts. 2022; 12(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12020129
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Bo, Xiaolin Li, and Yinyong Sun. 2022. "A Short Review of Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels over Porous Materials" Catalysts 12, no. 2: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12020129
APA StyleYuan, B., Li, X., & Sun, Y. (2022). A Short Review of Aerobic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels over Porous Materials. Catalysts, 12(2), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12020129







