Effect of Ceria Doping in Different Impregnation Steps on Ni-Based Catalysts Loading on TiO2-SiC for CO Methanation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
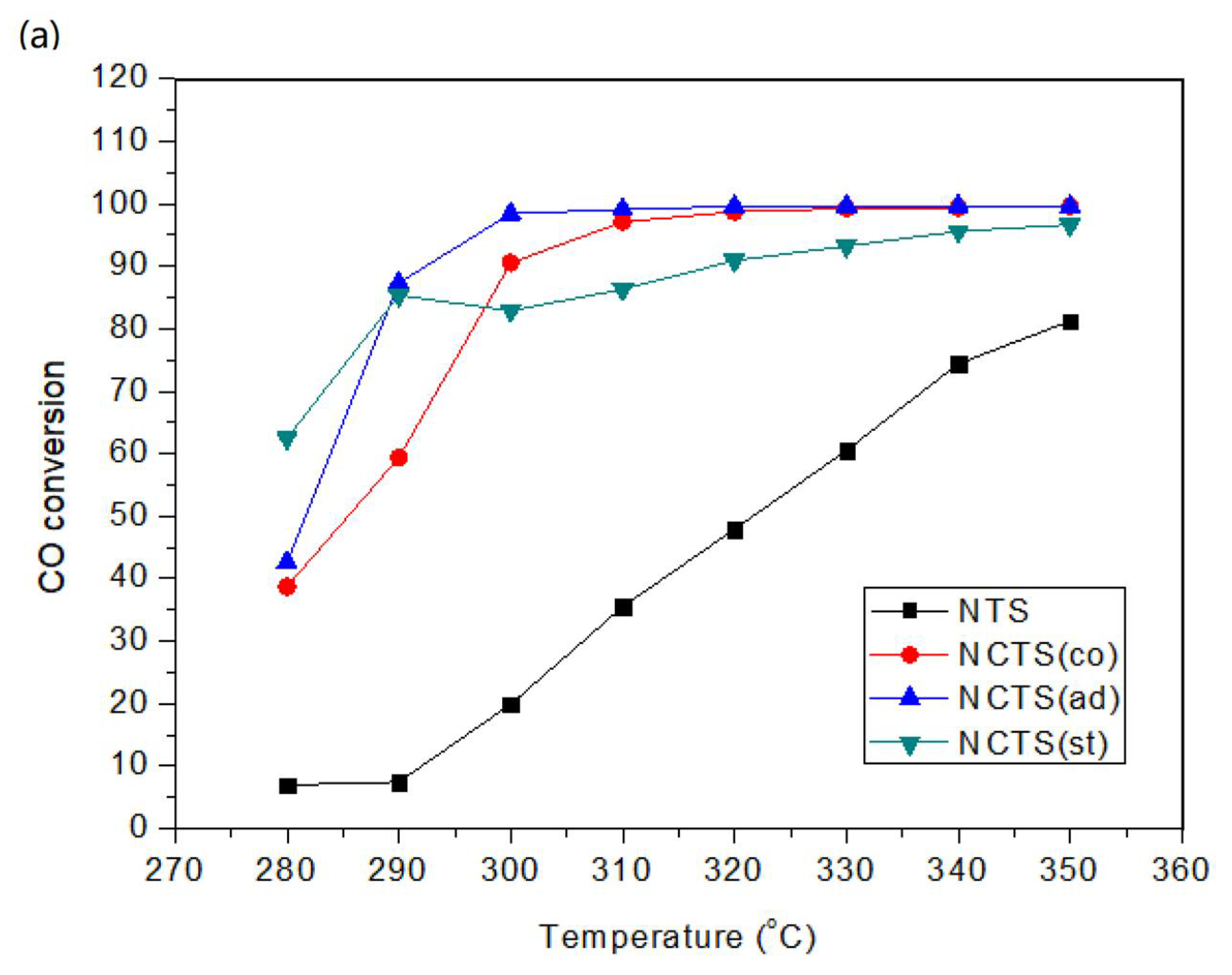
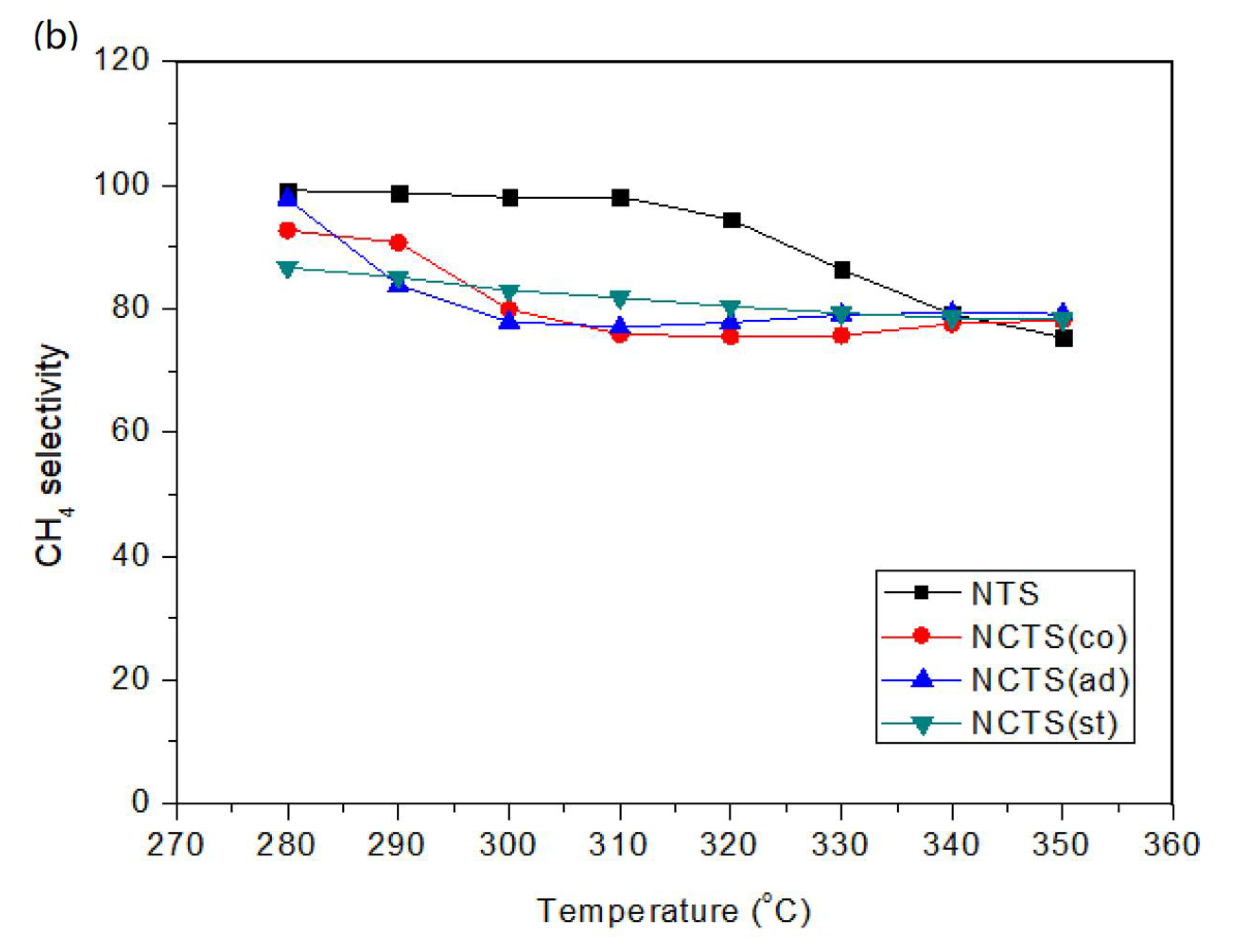
2.1. Catalytic Performance for CO Methanation
2.1.1. Effect of Cerium Doping in Different Impregnation Steps
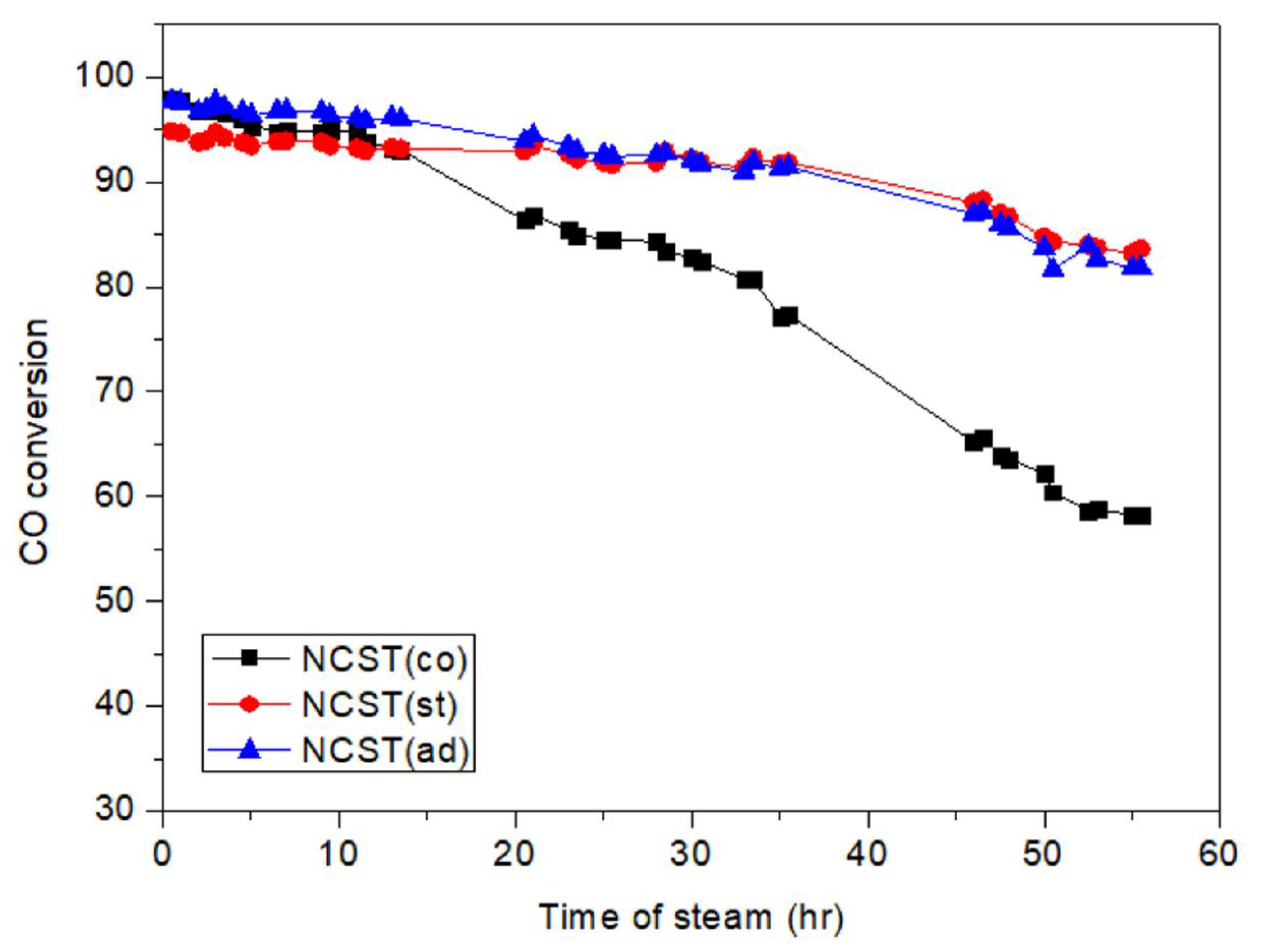
2.1.2. Catalyst Stability Test
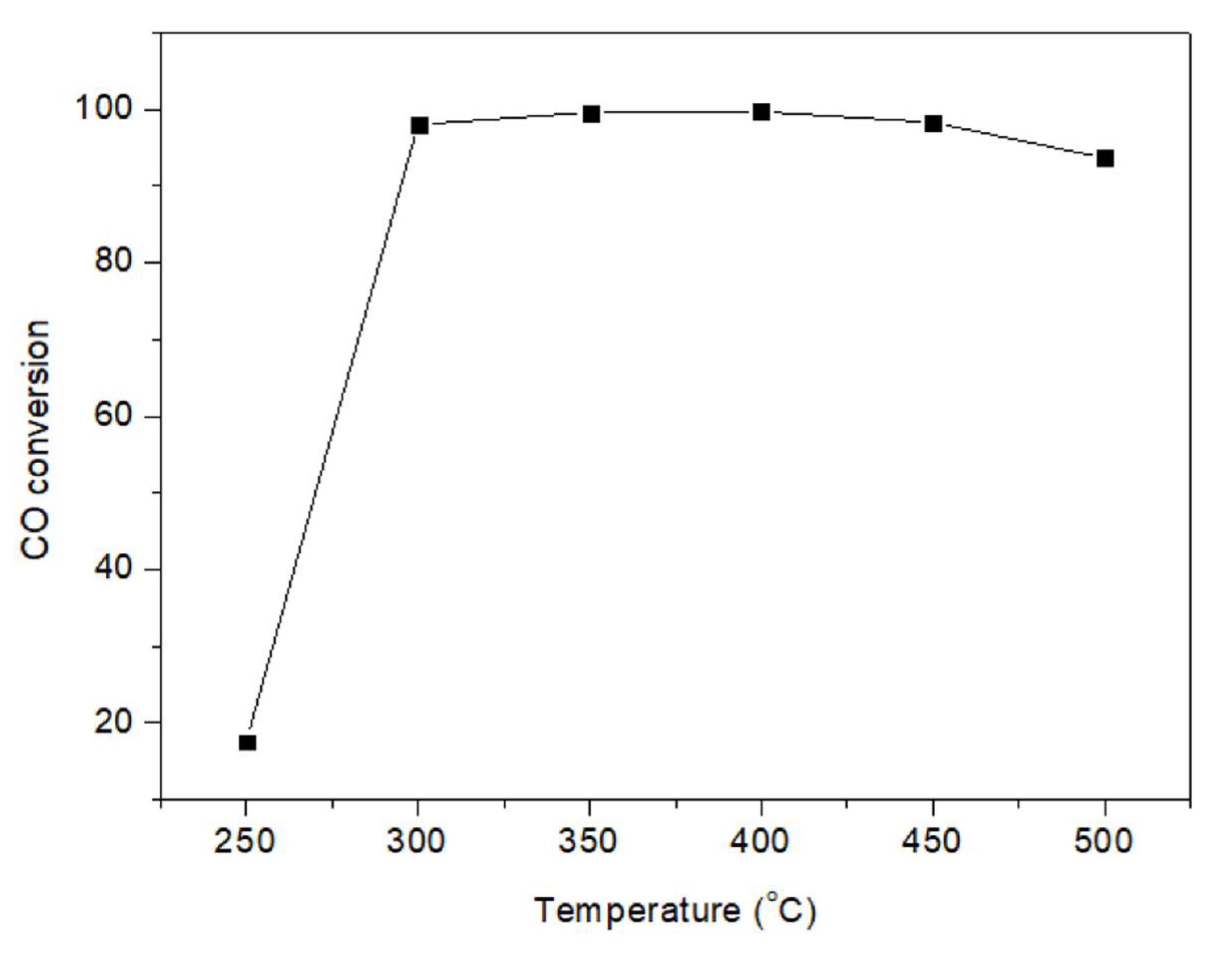
2.1.3. High Reaction Temperature Stability Test
2.2. XRD Result
2.3. N2 Physisorption
2.4. TG-DSC Analysis of Used Sample NCTS(ad)
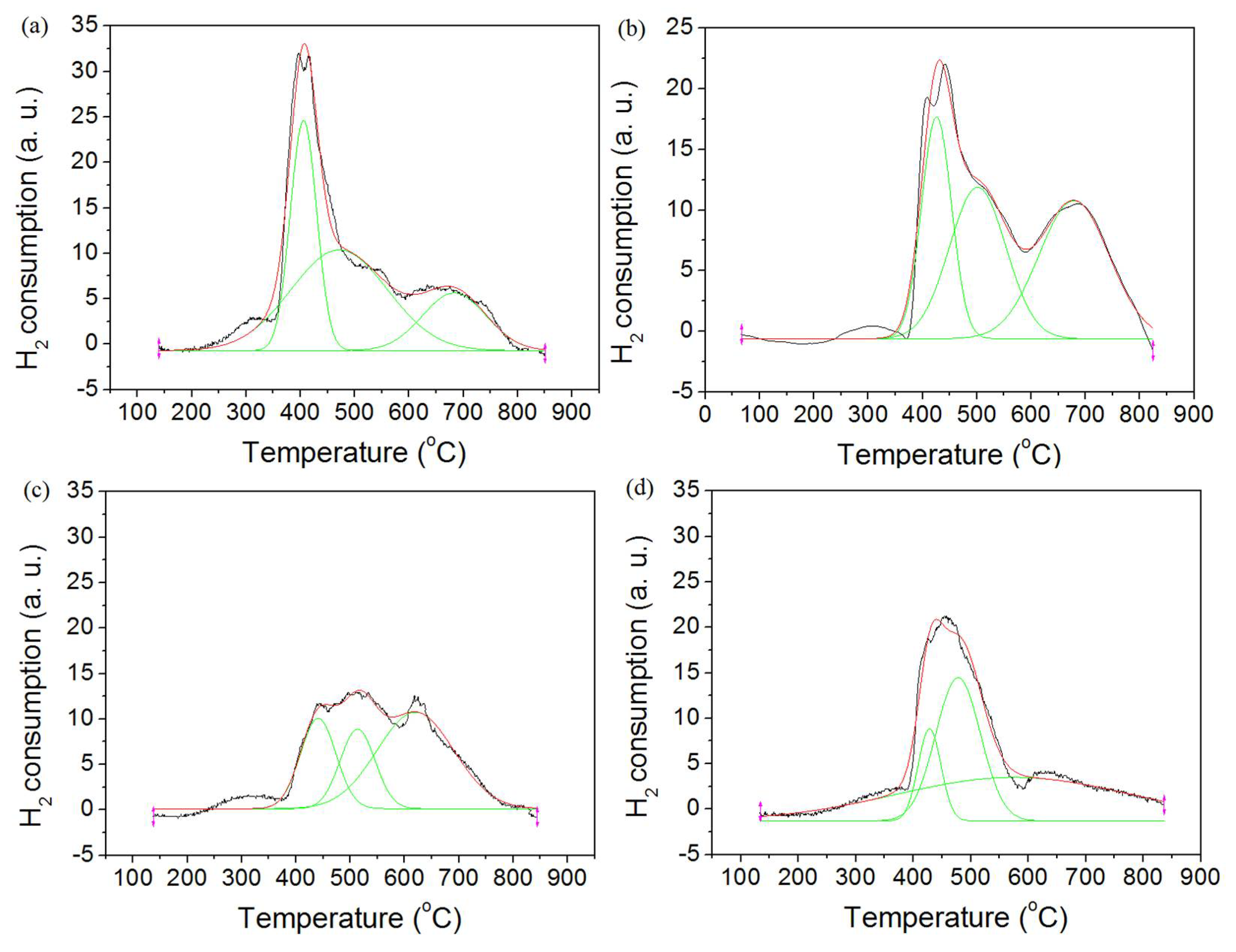
2.5. H2 Temperature-Programmed Reduction (H2-TPR) Result
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalytic Performance
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabatier, P.; Senderens, J.B. New synthesis of methane. Acad. Sci. 1902, 134, 514–516. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Gu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhou, H.; Qian, Y. Comparison of techno-economic performance and environmental impacts between shale gas and coal-based synthetic natural gas (SNG) in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Peng, J.; Sun, T.; Wang, S. Effects of the oxidation extent of the SiC surface on the performance of Ni/SiC methanation catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, A.L.; Frey, A.M.; Larsen, K.E.; Johannessen, T.; Nørskov, J.K.; Christensen, C.H. CO methanation over supported bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts: From computational studies towards catalyst optimization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 320, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyryanova, M.M.; Snytnikov, P.V.; Gulyaev, R.V.; Amosov, Y.I.; Boronin, A.I.; Sobyanin, V.A. Performance of Ni/CeO2 catalysts for selective CO methanation in hydrogen-rich gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 238, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, A.; Dincer, I.; Agelin-Chaab, M. A critical review of synthetic natural gas production techniques and technologies. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2020, 84, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chu, B.; Zhai, X.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, Y. Total methanation of syngas to synthetic natural gas over Ni catalyst in a micro-channel reactor. Fuel 2012, 95, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopyscinski, J.; Schildhauer, T.J.; Biollaz, S.M.A. Production of synthetic natural gas (SNG) from coal and dry biomass–A technology review from 1950 to 2009. Fuel 2010, 89, 1763–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, D.G.; Jaffe, A.M.; Hayes, M.H. (Eds.) Natural Gas and Geopolitics: From 1970 to 2040; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Wei, N.; Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, J. Natural gas consumption forecasting: A discussion on forecasting history and future challenges. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2021, 90, 103930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, C.; Specchia, S.; Specchia, V. CO selective methanation in H2-rich gas for fuel cell application: Microchannel reactor performance with Ru-based catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.M.H.; Ziegler, T. Chemisorption and Reactivity of CHx (x = 0−4) on Fe−Co Alloy Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13642–13649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, T.; Xie, H.; Zheng, X. Effects of structure on the carbon dioxide methanation performance of Co-based catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 10012–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yunyun, D.; Weiping, F.; Yixin, L.I.A.N. Effects of composite oxide supports on catalytic performance of Ni-based catalysts for CO methanation. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhao, Y. Effect of ZrO2 promoter on structure and catalytic activity of the Ni/SiO2 catalyst for CO methanation in hydrogen-rich gases. Catal. Today 2010, 158, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Yu, F. Highly-dispersed Ni-NiO nanoparticles anchored on an SiO2 support for an enhanced CO methanation performance. Catalysts 2019, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenlohr, K.H.; Moeller, F.W.; Dry, M. Influence of certain reaction parameters on methanation of coal gas to SNG. [4 refs]. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Fuel Chem. Prepr. 1974, 19. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/7258360 (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.; Pedersen, K.; Sehested, J. High temperature methanation: Sintering and structure sensitivity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 330, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, C.; Specchia, S.; Saracco, G.; Specchia, V. CO-selective methanation over Ru–γAl2O3 catalysts in H2-rich gas for PEM FC applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Liu, C.J. Characterization of silica supported nickel catalyst for methanation with improved activity by room temperature plasma treatment. Catal. Lett. 2009, 133, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, V.S.; Londhe, V.P.; Gupta, N.M.; Thampi, K.R.; Grätzel, M. Studies on the Sulfur Poisoning of Ru–RuOx/TiO2 Catalyst for the Adsorption and Methanation of Carbon Monoxide. J. Catal. 1996, 158, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jin, G.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Guo, X.Y. Synthetic natural gas from CO hydrogenation over silicon carbide supported nickel catalysts. Fuel Process Technol. 2011, 92, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Jin, Y.Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ren, J. Highly stable and coking resistant Ce promoted Ni/SiC catalyst towards high temperature CO methanation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 177, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solymosi, F.; Erdöhelyi, A.; Bansagi, T. Methanation of CO2 on supported rhodium catalyst. J. Catal. 1981, 68, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, D.C.; Gao, J.J.; Jia, C.M.; Ping, Y.; Jia, L.H.; Wang, Y.L.; XU, G.W.; GU, F.N.; SU, F.B. Research Advances in Methanation Catalysts and Their Catalytic Mechanisms. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2011, 5, 030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, H.; Cui, K.; Jia, A.; Hu, G.; Jiao, Z.; Zhang, X. Role of surface Ni and Ce species of Ni/CeO2 catalyst in CO2 methanation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Pastor-Pérez, L.; Gu, S.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Reina, T.R. Highly efficient Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts for CO2 upgrading via reverse water-gas shift: Effect of selected transition metal promoters. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 232, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, L.; Artetxe, M.; Lopez, G.; Cortazar, M.; Amutio, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Effect of CeO2 and MgO promoters on the performance of a Ni/Al2O3 catalyst in the steam reforming of biomass pyrolysis volatiles. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 198, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.O.; Sreekala, R.; Rashid, K.K.A.; Yusuff, K.K.M.; Sen, B. Doping effects of cerium oxide on Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for methanation. Catal. Today 1999, 49, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkas, N.; Amirian, G.; Zhong, Z.; Teo, J.; Gofer, Y.; Gedanken, A. Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ni catalysts on mesoporous ZrO2 doped with rare earth oxides. Catal. lett. 2009, 130, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yao, Y.; Hao, M.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Xin, M. The role of promoters in the Ni catalyst for methanation (I) the electronic effect caused by the rare earth (La, Ce, Pr and Nd) oxides additives. J. Mol. Catal. 1990, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Maorong, N.; Min, W. Role of Promoters in Ni Catalyst for Methanation (Ⅱ) Structural and Electronic Effects Caused by Heavy Rare Earth (Dy, Sm, Y, Eu, Yb, Tm, Gd, Er, Tb) Oxide Additives. J. Mol. Catal. 1999, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Er-Rbib, H.; Bouallou, C. Methanation catalytic reactor. C. R. Chim. 2014, 17, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, F.; Nakajima, T.; Miya, H.; Mishima, S. Catalytic properties of supported cobalt catalysts for steam reforming of ethanol. Catal. Lett. 1997, 48, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Z.; Jin, G.Q.; Guo, X.Y. Partial oxidation of methane to syngas over Ni/SiC catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2005, 6, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Pham, C. Innovative porous SiC-based materials: From nanoscopic understandings to tunable carriers serving catalytic needs. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Ding, C. Study on SiC-TiC composite fine powder mixed by vacuum original position and its oxidation susceptibility. China Ceram. 2012, 6, 009. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Liang, Y.; Yin, G.; Hong, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, Z. Fabrication and characterization of hollow cuprous sulfide (Cu2−xS) microspheres by a simple template-free route. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2003, 6, 1406–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, F.M.; Cheng, H.M.; Fan, L.Y.; Zhao, Y.X. A comparative study on the catalytic properties of high Ni-loading Ni/SiO2 and low Ni-loading Ni-Ce/SiO2 for CO methanation. J. Fuel Chem. Tech. 2013, 41, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Ying, W.; Zhang, H.; Hongfang, M.; Fang, D. Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for syngas methanation: Effect of Mn promoter. J. Nat. Gas. Chem. 2012, 21, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Jin, X.; Ge, Q.; Li, W. Characterizations and activities of the nano-sized Ni/Al2O3 and Ni/La–Al2O3 catalysts for NH3 decomposition. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 290, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Rate of CH4 Generation at 300 °C (μmol s−1 g−1) |
|---|---|
| NTS | 35.5 |
| NCTS(co) | 131.6 |
| NCTS(ad) | 139.3 |
| NCTS(st) | 125.1 |
| Sample | Fresh NiO Crystallite Size (nm) | Used Ni Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Ni/TiO2-SiC | 20.4 | 22.5 |
| 10Ce-Ni/TiO2-SiC(co) | 17.2 | 18.1 |
| 10Ce-Ni/TiO2-SiC(ad) | 14.9 | 15.3 |
| 10Ce-Ni/TiO2-SiC(st) | 17.9 | 18.6 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) |
|---|---|
| TiC-SiC | 67.2 |
| TiC-SiC(ad) | 51.6 |
| TiO2-SiC | 28.1 |
| Fresh NCTS(ad) | 22.6 |
| Used NCTS(ad) | 22.2 |
| Sample | Tm (°C) | Fraction of Total Area (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | γ | α | β | γ | |
| NTS | 406 | 471 | 683 | 31.2 | 50 | 18.8 |
| NCTS(co) | 426 | 501 | 678 | 26.7 | 34.4 | 38.9 |
| NCTS(ad) | 440 | 513 | 619 | 24 | 20.8 | 55.2 |
| NCTS(st) | 428 | 477 | 574 | 11.2 | 34.2 | 54.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Ceria Doping in Different Impregnation Steps on Ni-Based Catalysts Loading on TiO2-SiC for CO Methanation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040429
Liu C, Zheng Q, Zhang Y. Effect of Ceria Doping in Different Impregnation Steps on Ni-Based Catalysts Loading on TiO2-SiC for CO Methanation. Catalysts. 2022; 12(4):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040429
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chen, Qin Zheng, and Yusheng Zhang. 2022. "Effect of Ceria Doping in Different Impregnation Steps on Ni-Based Catalysts Loading on TiO2-SiC for CO Methanation" Catalysts 12, no. 4: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040429
APA StyleLiu, C., Zheng, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Effect of Ceria Doping in Different Impregnation Steps on Ni-Based Catalysts Loading on TiO2-SiC for CO Methanation. Catalysts, 12(4), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12040429





