Exploration of the Interactions between Maltase–Glucoamylase and Its Potential Peptide Inhibitors by Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Validation of the Docking Protocol
2.2. Reliability Considerations and Cluster Analysis of Investigated Complexes
2.3. Total Binding Free Energy of the Complexes
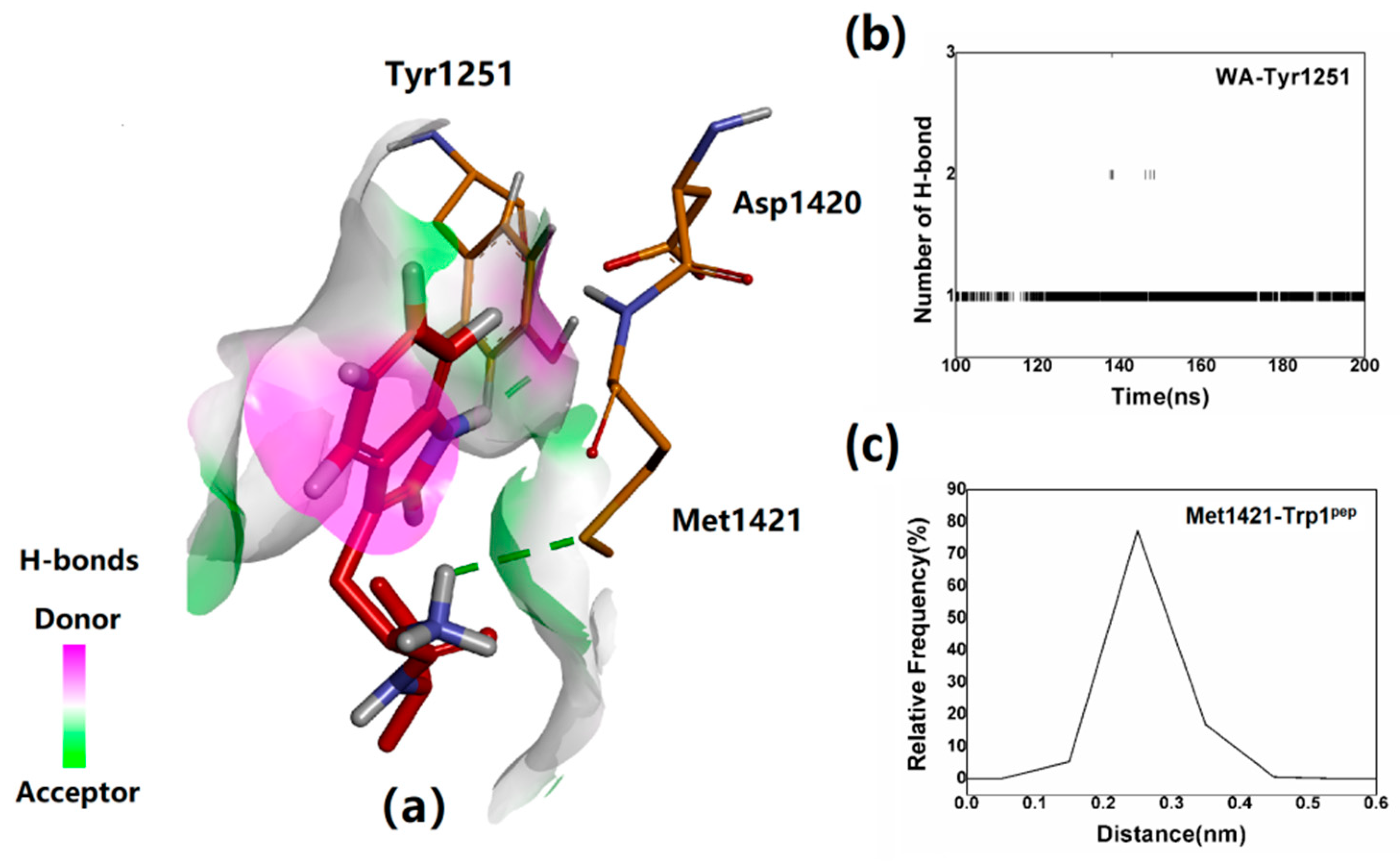
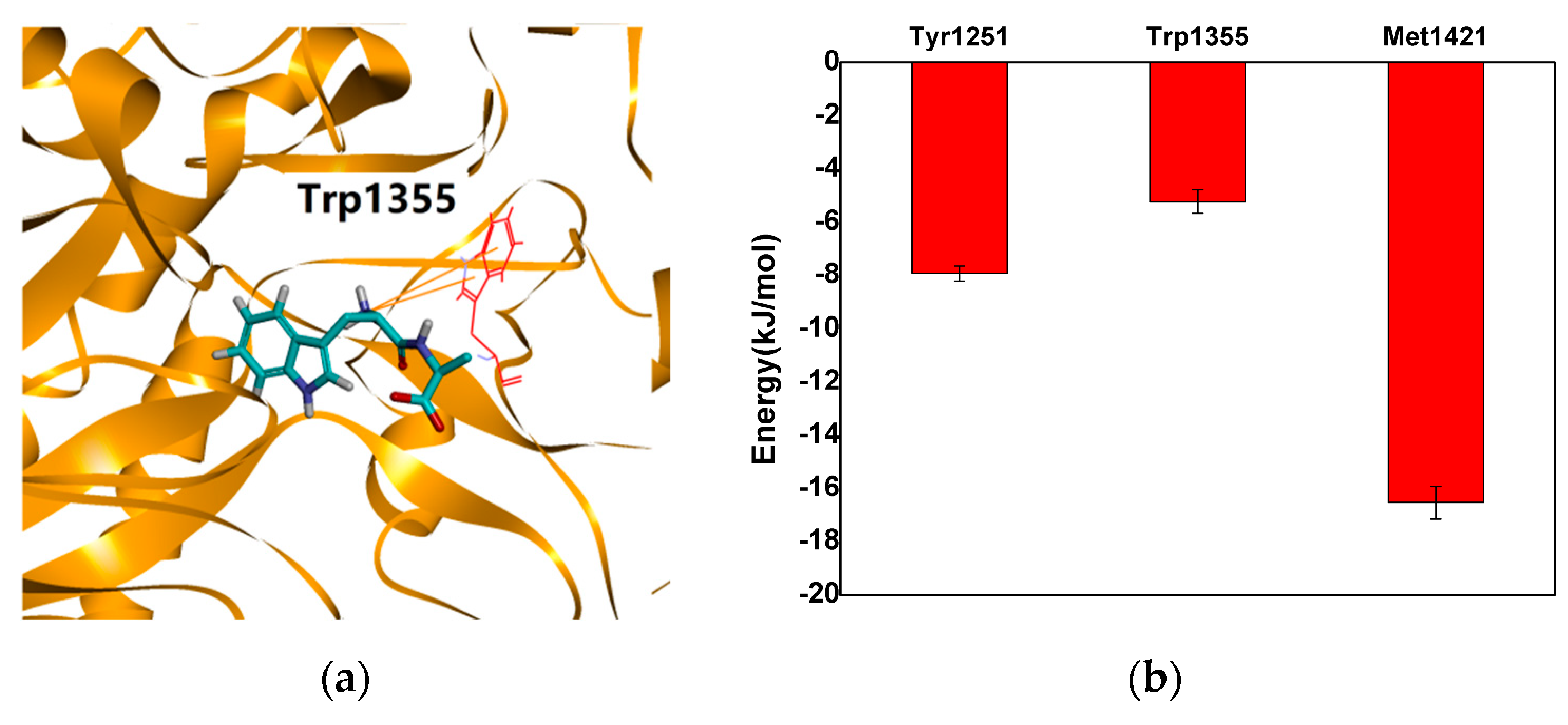
2.4. Verification of the Binding Patterns of Complexes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Initial Complexes
4.2. Molecular Docking
4.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4.4. Binding Energy Calculations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardullo, N.; Muccilli, V.; Pulvirenti, L.; Cornu, A.; Tringali, C. C-glucosidic ellagitannins and galloylated glucoses as potential functional food ingredients with anti-diabetic properties: A study of α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition. Food Chem. 2019, 313, 126099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, S.; Smyth, T.J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory effects of Irish seaweed extracts. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etsassala, N.G.E.R.; Badmus, J.A.; Marnewick, J.L.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Nchu, F.; Hussein, A.A. Alpha-Glucosidase and Alpha-Amylase Inhibitory Activities, Molecular Docking, and Antioxidant Capacities of Salvia aurita Constituents. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.X.; Feng, D.N.; Wang, T.X.; Ren, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, J. Inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase: Potential linkage for whole cereal foods on prevention of hyperglycemia. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 6320–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, N.; Santos-Martins, D.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Mechanistic Pathway on Human α-Glucosidase Maltase-Glucoamylase Unveiled by QM/MM Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 3889–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Li, P.; Uraji, M.; Hatanaka, T.; Ito, H. Inhibitory effects of pomegranate extracts on recombinant human maltase–glucoamylase. J. Food Sci. 2015, 79, H1848–H1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, R.S.; Kudva, A.K.; Timanagouda, K.; Raghuveer Raghu, S.V. Synthesis of novel 5-(2,5-bis (2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy) phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thiol derivatives as potential glucosidase inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 114, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Qin, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, L.; Bai, F.; Gang, B.; Shen, Y. Structural insight into substrate specificity of human intestinal maltase-glucoamylase. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lankatillake, C.; Luo, S.; Flavel, M.; Lenon, G.B.; Dias, D.A. Screening natural product extracts for potential enzyme inhibitors: Protocols, and the standardisation of the usage of blanks in α-amylase, α-glucosidase and lipase assays. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Shafique, Z.; Amjad, S.T.; Hassan, M.H. Enzymes inhibitors from natural sources with antidiabetic activity: A review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yavari, A.; Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani, M.; Moradi, S.; Bahadorikhalili, S.; Hajimiri, M.H. α-Glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition, molecular modeling and pharmacokinetic studies of new quinazolinone-1,2,3-triazole-acetamide derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Cui, J.; Li, D.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, J.Z. Separation, Purification, and Identification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides from Apricot Kernel Protein. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2016, 31, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sumaryada, T.; Arwansyah Roslia, A.W.; Ambarsari, L.; Kartono, A. Molecular docking simulation of mangostin derivatives and curcuminoid on maltase-glucoamylase target for searching anti-diabetes drug candidates. In Proceedings of the 2016 1st International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (IBIOMED), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 5–6 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, M.; Shan, Y.; Guan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Han, W.W. Structural Basis of Fullerene Derivatives as Novel Potent Inhibitors of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B: Insight into the Inhibitory Mechanism through Molecular Modeling Studies. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2016, 56, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinosh, S.; Dharshini, G.; Shweta, C.; Priya, K.; Akshay, U.; Aditi, G.M.; Vidya, N. Structural and molecular basis of the interaction mechanism of selected drugs towards multiple targets of SARS-CoV-2 by molecular docking and dynamic simulation studies- deciphering the scope of repurposed drugs. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddique, F.A.; Ahmad, M.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Ahmad, M.N.; Aslam, S. Alpha-glucosidase inhibition and molecular docking studies of 1,2-benzothiazine 1,1-dioxide based carbohydrazides. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32 (Suppl. S6), 2829–2834. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, T.; Karrar, E.; Zheng, L.; Xie, D.; Jin, J.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q. Insights into an α-glucosidase inhibitory profile of 4,4-dimethylsterols by multispectral techniques and molecular docking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15252–15260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruthiga, N.; Alagumuthu, M.; Selvinthanuja, C.; Srinivasan, K.; Sivakumar, T. Molecular Modelling, Synthesis and Evaluation of Flavone and Flavanone Scaffolds as Anti-inflammatory Agents. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 20, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Ali, S.S.; Azad, A.K.; Safdar, M.; Wei, D. Genome-wide screening of vaccine targets prioritization and reverse vaccinology aided design of peptides vaccine to enforce humoral immune response against Campylobacter jejuni. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Niu, X. Insight into the Dual Inhibition Mechanism of Corilagin against MRSA Serine/Threonine Phosphatase (Stp1) by Molecular Modeling. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32959–32968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.S.; Zhu, K.T.; Dong, Y.J.; Li, H.; Shan, Y.M. Exploration of Binding Mechanism of a Potential Streptococcus pneumoniae Neuraminidase Inhibitor from Herbaceous Plants by Molecular Simulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daura, X.; Gademann, K.; Jaun, B.; Seebach, D.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; Mark, A.E. Peptide Folding: When Simulation Meets Experiment. Angenw. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 38, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Deng, Z.X.; Lin, S.J. Tryptophan, an important starting material in biosynthesis of microbial natural products. Microbiol. China 2013, 40, 1796–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Patchett, A.A.; Harris, E.; Tristram, E.W.; Wyvratt, M.J.; Wu, M.T.; Taub, D.; Peterson, E.R.; Ikeler, T.J.; ten Broeke, T.; Payne, L.G.; et al. A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature 1980, 288, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mothay, D.; Ramesh, K.V. Binding site analysis of potential protease inhibitors of COVID-19 using AutoDock. VirusDisease 2020, 31, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Van, D. Hydration thermodynamic properties of amino acid analogues: A systematic comparison of biomolecular force fields and water models. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 17616–17626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safarizadeh, H.; Garkani-Nejad, Z. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and QSAR studies on some of 2-arylethenylquinoline derivatives for inhibition of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta aggregation: Insight into mechanism of interactions and parameters for design of new inhibitors. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2019, 87, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakrishnan, R.; Aguilar, B.; Onufriev, A.V. H++ 3.0: Automating pK prediction and the preparation of biomolecular structures for atomistic molecular modeling and simulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W537–W541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, S.J.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. Structural and energetic effects of the use of polarisable water to solvate proteins. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 2815–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.; Qi, R.; Han, W. Molecular Dockings and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Reveal the Potency of Different Inhibitors against Xanthine Oxidase. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11639–11649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingwen, E.; Liu, Y.; Guan, S.; Luo, Z.; Han, F.; Han, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. How Different Substitution Positions of F, Cl Atoms in Benzene Ring of 5-Methylpyrimidine Pyridine Derivatives Affect the Inhibition Ability of EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S Inhibitors: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 895. [Google Scholar]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An Nlog(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.P.; Postma, J.; Gunsteren, W.; Dinola, A.D.; Haak, J.R. Molecular-Dynamics with Coupling to An External Bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampogu, S.; Baek, A.; Park, C.; Son, M.; Parate, S.; Parameswaran, S.; Park, Y.; Shaik, B.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; et al. Discovery of Small Molecules That Target Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 Signalling Pathway Employing Molecular Modelling Studies. Cells 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, P.; Qin, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; He, C.; He, S.; Hong, B.; Liu, K.; Qiao, R.; Fan, H.; et al. Computational design of ultrashort peptide inhibitors of the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, A.S.; Eslahchi, C.; Ghassempour, A.; Kiaei, M. In silico studies reveal structural deviations of mutant profilin-1 and interaction with riluzole and edaravone in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Guan, S.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Structural and molecular basis of cellulase Cel48F by computational modeling: Insight into catalytic and product release mechanism. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 194, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wong, C.F. Rank-ordering protein-ligand binding affinity by a quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics/Poisson-Boltzmann-surface area model. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 01B801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Lynn, A. g_mmpbsa—A GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2014, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Shen, S.; Gu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, X. Computer-Aided Design of Glucoside Brain-Targeted Molecules Based on 4PYP. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2020, 103, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelusi, T.I.; Abdul-Hammed, M.; Idris, M.O.; Kehinde, O.Q.; Kolawole, O.E. Exploring the inhibitory potentials of Momordica charantia bioactive compounds against Keap1-Kelch protein using computational approaches. Silico Pharmacol. 2021, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discovery Studio; Release 2020; Accelrys Inc.[Z.]: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020.

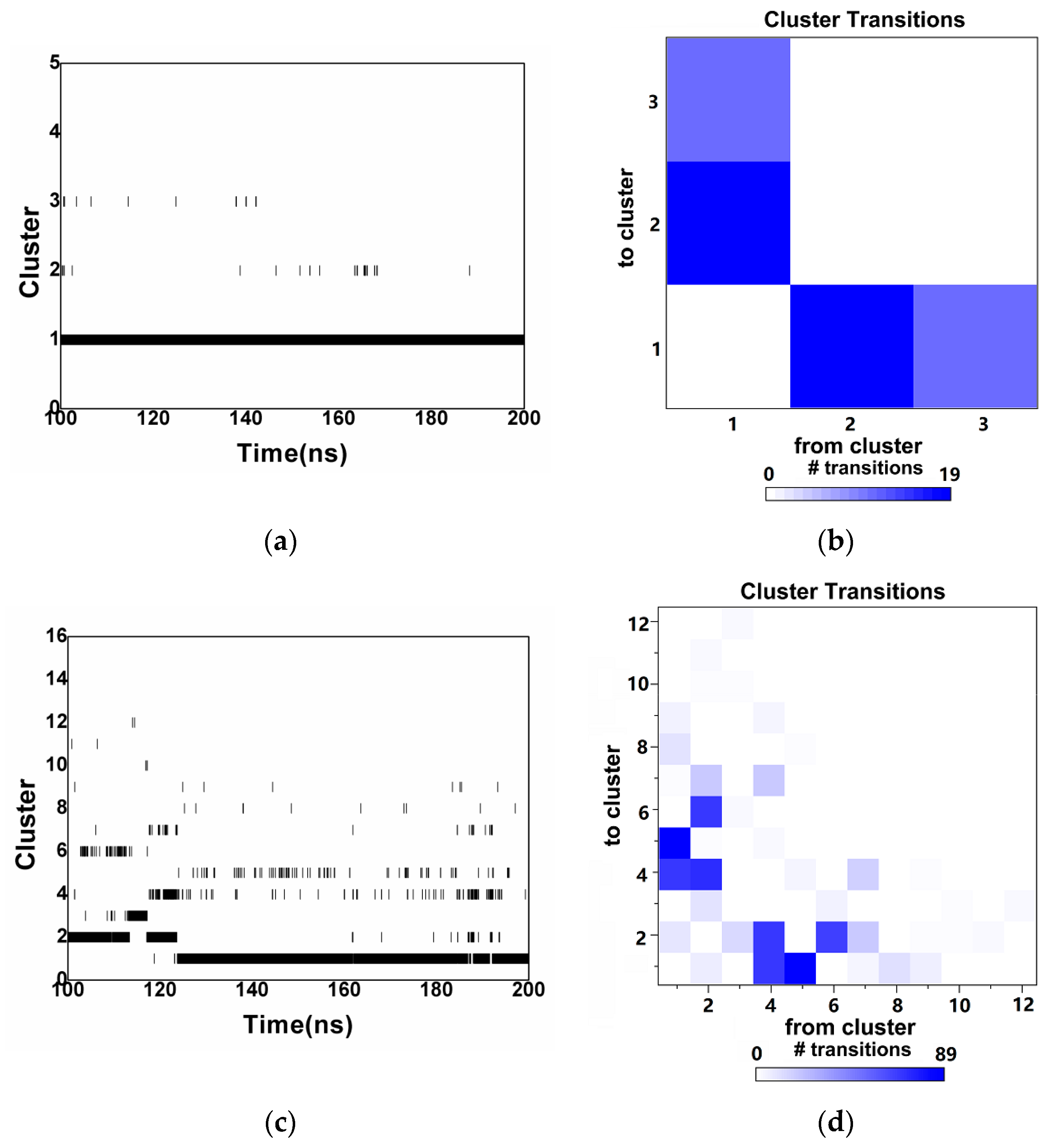
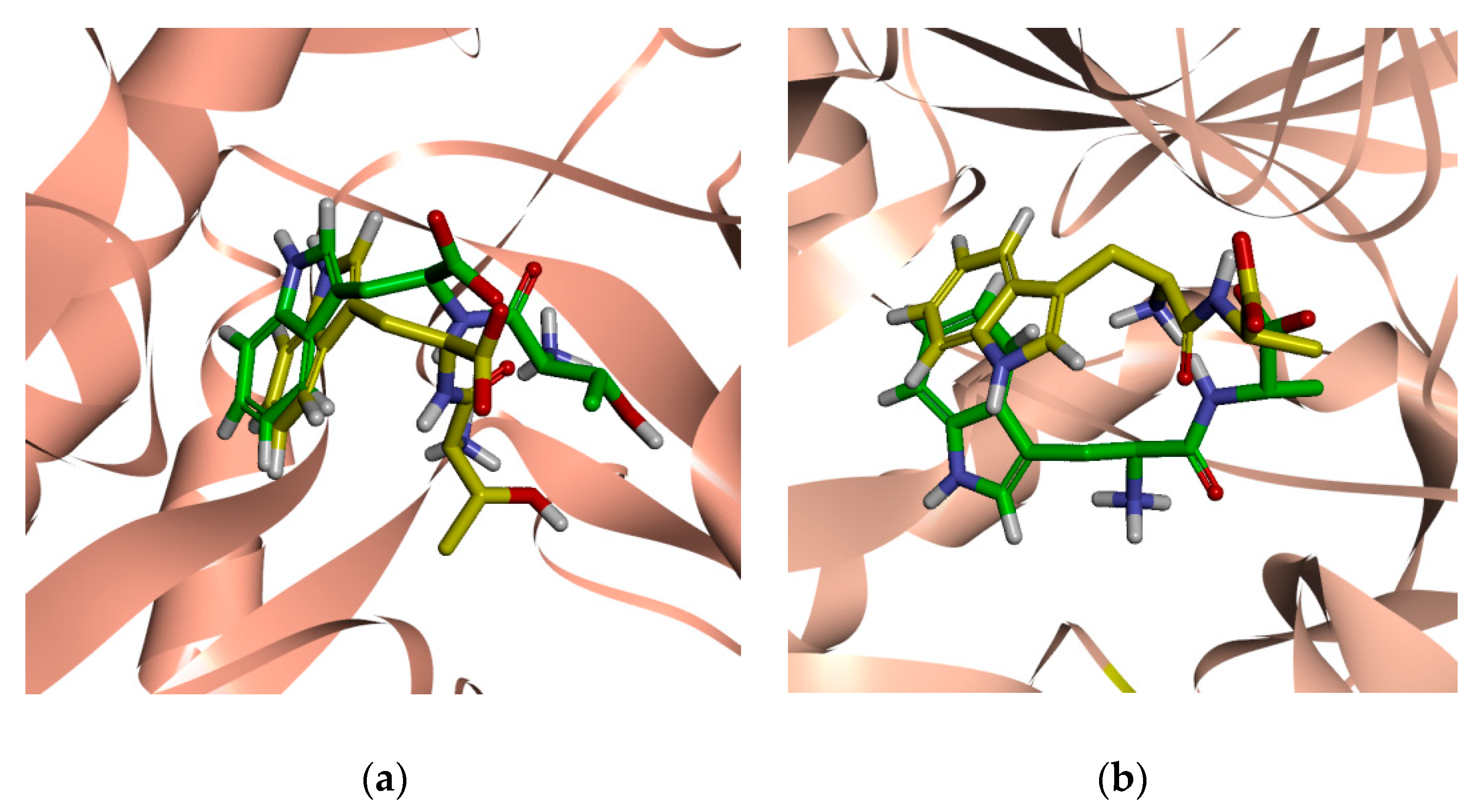
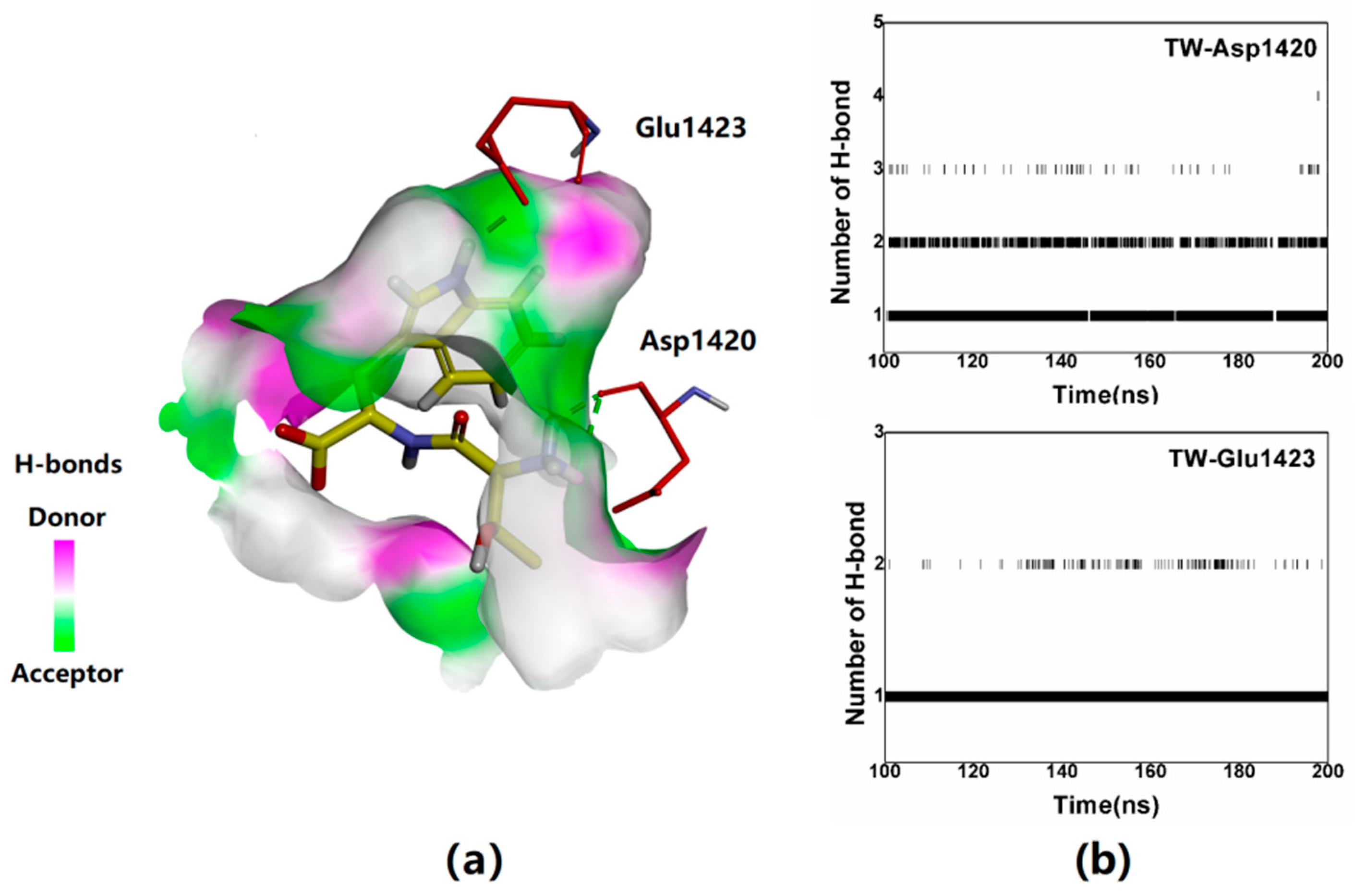

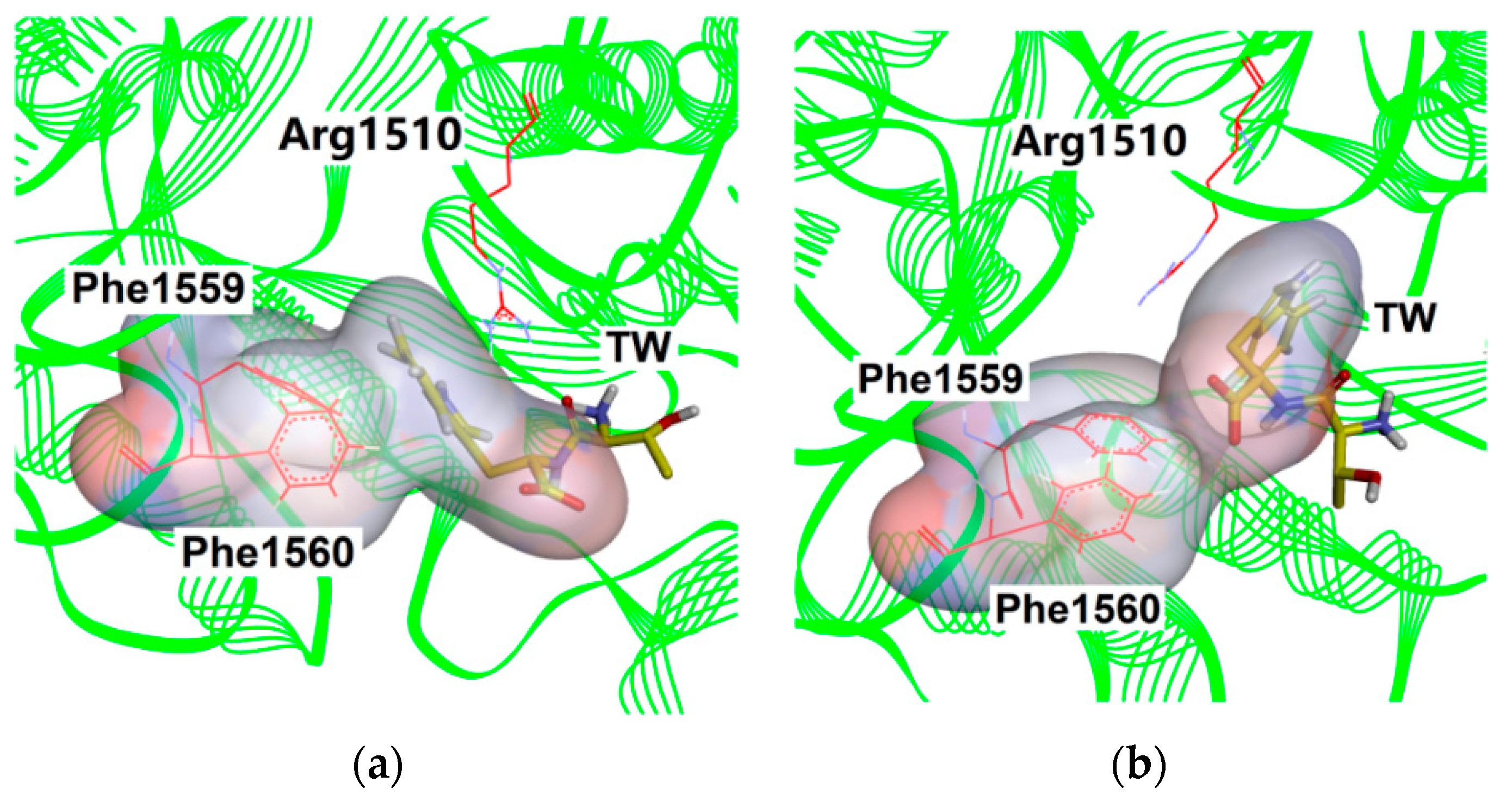

| Cluster | Size | Percentage | Conformation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9957 | 99.56% |  |
| 2 | 32 | 0.32% |  |
| 3 | 12 | 0.12% |  |
| Cluster | Size | Percentage | Conformation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7213 | 72.12% |  |
| 2 | 1834 | 18.34% | 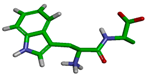 |
| 3 | 396 | 3.96% | 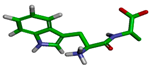 |
| 4 | 255 | 2.55% | 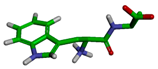 |
| 5 | 107 | 1.07% | 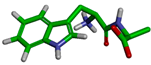 |
| 6 | 105 | 1.05% |  |
| Energy Components | Energy of Cluster 1 (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| Van der Waals energy | −106.66 ± 12.52 |
| Electrostatic energy | −495.18 ± 69.46 |
| Polar solvation energy | 386.41 ± 42.82 |
| SASA energy | −14.49 ± 0.89 |
| Binding energy | −229.93 ± 38.66 |
| Energy Components | Energy of Cluster 1 (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| Van der Waals energy | −100.78 ± 10.06 |
| Electrostatic energy | −250.50 ± 55.65 |
| Polar solvation energy | 251.95 ± 35.69 |
| SASA energy | −13.22 ± 1.04 |
| Binding energy | −112.53 ± 38.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, S.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Shan, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Exploration of the Interactions between Maltase–Glucoamylase and Its Potential Peptide Inhibitors by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050522
Guan S, Han X, Li Z, Xu X, Cui Y, Chen Z, Zhang S, Chen S, Shan Y, Wang S, et al. Exploration of the Interactions between Maltase–Glucoamylase and Its Potential Peptide Inhibitors by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Catalysts. 2022; 12(5):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050522
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Shanshan, Xu Han, Zhan Li, Xifei Xu, Yongran Cui, Zhiwen Chen, Shuming Zhang, Shi Chen, Yaming Shan, Song Wang, and et al. 2022. "Exploration of the Interactions between Maltase–Glucoamylase and Its Potential Peptide Inhibitors by Molecular Dynamics Simulation" Catalysts 12, no. 5: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050522
APA StyleGuan, S., Han, X., Li, Z., Xu, X., Cui, Y., Chen, Z., Zhang, S., Chen, S., Shan, Y., Wang, S., & Li, H. (2022). Exploration of the Interactions between Maltase–Glucoamylase and Its Potential Peptide Inhibitors by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Catalysts, 12(5), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050522






