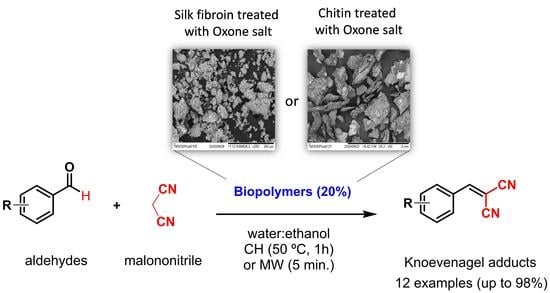
Chitin and Silk Fibroin Biopolymers Modified by Oxone: Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysts for Knoevenagel Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Use of Modified Biopolymers as Catalysts in a Knoevenagel Reaction under Conventional Heating
2.2. The Use of Modified Biopolymers as Catalysts in the Knoevenagel Reaction Using Microwave Irradiation as a Heating Source
2.3. Reuse of the Biopolymers Fs-Ox and CT-Ox in the Knoevenagel Condensation Reactions
2.3.1. Reuse of SF-Ox and CT-Ox under CH Conditions in the Synthesis of Adduct 2a
2.3.2. Reuse of SF-Ox and CT-Ox under MW Conditions in the Synthesis of Adduct 2a
2.4. Characterization of the New Fs-Ox and CT-Ox Materials Used in Knoevenagel Condensation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical, Reagents and Catalysts
3.2. Preparing the Silk Fibroin (SF)
3.3. Modification of Silk Fiber by Oxone (SF-Oxone®)
3.4. Obtaining and Preparing the Chitin
3.5. Modification of Chitin by Oxone® (CT-Ox)
3.6. Optimization Synthesis of Benzylidene Malononitrile 2a Using Biopolymers as Catalysts under Conventional Heating
3.7. Synthesis of Benzylidene Malononitrile Derivatives 2a–l Using Biopolymers as Catalysts under Conventional Heating
3.8. Synthesis of Benzylidene Malononitrile Derivatives 2a–l Using Biopolymers as Catalysts under Microwave Irradiation
3.9. Equipment
3.10. Characterization of SF, SF-Ox, CT and CT-Ox
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jimenez, D.E.Q.; Zanin, L.L.; Diniz, L.F.; Ellena, J.; Porto, A.L.M. Green Synthetic Methodology of (E)-2-cyano-3-aryl Selective Knoevenagel Adducts Under Microwave Irradiation. Curr. Microw. Chem. 2019, 6, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Paul, A.R.; Majumdar, S. Base and metal free true recyclable medium for Knoevenagel condensation reaction in SDS-ionic liquid-aqueous miceller composite system. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Meng, F.; Wu, D.; Zhang, F. Synthesis of vinylene-linked covalent organic frameworks by monomer Self-catalyzed activation of Knoevenagel condensation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 8, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.A.; Quynh, L.T.N.; Vo, T.T.; Nguyen, P.A.; Don, T.N.; Vasseghian, Y.; Phan, H.; Lee, S.W. Experimental and computational investigation of a green Knoevenagel condensation catalyzed by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112364–112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalla, R.M.N.; Park, H.; Lee, H.R.; Suh, H.; Kim, I. Efficient, Solvent-Free, Multicomponent Method for Organic-Base-Catalyzed Synthesis of β-Phosphonomalonates. ACS Comb. Sci. 2015, 17, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birolli, W.G.; Zanin, L.L.; Jimenez, D.E.Q.; Porto, A.L.M. Synthesis of Knoevenagel Adducts Under Microwave Irradiation and Biocatalytic Ene-Reduction by the Marine-Derived Fungus Cladosporium sp. CBMAI 1237 for the Production of 2-Cyano-3-Phenylpropanamide Derivatives. Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X. A nanocaged cadmium-organic framework with high catalytic activity on the chemical fixation of CO2 and deacetalization-knoevenagel condensation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 335, 111791–111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fox, T.; Berke, H. Facile metal free regioselective transfer hydrogenation of polarized olefins with ammonia borane. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2053–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Yoshioka, S.A.; Comasseto, J.V.; Porto, A.L.M. Immobilization of Amano lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens on silk fibroin spheres: An alternative protocol for the enantioselective synthesis of halohydrins. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12650–12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, E.B.M.; Neves, F.B.; Lopes, S.Q.; Holanda, F.H.; Souza, T.M.; Pinto, E.P.; Oliveira, A.N.; Fonseca, L.P.; Yoshioka, S.A.; Ferreira, I.M. Immobilization of Amano AK Lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens on Novel Silk Microfiber using Oxone®: Parameter Optimization for Enzymatic Assays and use in Esterification of Residual Palm Oil. Curr. Catal. 2021, 10, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Ganzeli, L.; Rosset, I.G.; Yoshioka, S.A.; Porto, A.L.M. Ethylic Biodiesel Production Using Lipase Immobilized in Silk Fibroin-Alginate Spheres by Encapsulation. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhbeck, D.; Ghosh, M.; Gupta, S.S.; Díaz, D.D. Investigation of C-C bond formation mediated by bombyx mori Silk Fibroin Materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knidri, H.E.L.; Dahmani, J.; Addaou, A.; Laajeb, A.; Lahsini, A. Rapid and efficient extraction of chitin and chitosan for scale-up production: Effect of process parameters on deacetylation degree and molecular weight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, M.; Khalil, K.D.; Al-Sagheer, F.A. Heterogeneous Hybrid Nanocomposite Based on Chitosan/Magnesia Hybrid Films: Ecofriendly and Recyclable Solid Catalysts for Organic Reactions. Polymers 2021, 13, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussout, H.; Ahlafi, H.; Aazza, M.; Bourakhouadar, M. Kinetics and mechanism of the thermal degradation of biopolymers chitin and chitosan using thermogravimetric analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 130, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, D.; Singla, P.; Agarwal, J. ‘Chitosan in water’ as an eco-friendly and efficient catalytic system for Knoevenagel condensation reaction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, Y.; Kanomata, K.; Hatakeyama, M.; Kitaoka, T. Chitosan nanofiber-catalyzed highly selective Knoevenagel condensation in aqueous methanol. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26771–26776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrantes, P.G.; Costa, I.F.; Falcão, N.K.S.M.; Ferreira, J.M.G.O.; Junior, C.G.L.; Teotonio, E.E.S.; Vale, J.A. The Efficient Knoevenagel Condensation Promoted by Bifunctional Heterogenized Catalyst Based Chitosan-EDTA at Room Temperature. Catal. Lett. 2022, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotzki, R.; Hoffmann, M.M.; Ondruschka, B. The knoevenagel condensation at room temperature. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, N.; Hariharan, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A. Knoevenagel-Doebner condensation promoted by chitosan as a reusable solid base catalyst. Mol. Catal. 2020, 484, 110744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, J.H.T.; Gedanken, A. Eco-Friendly and Facile Preparation of Spherical Chitin Nanoparticles. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 10787–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.Q.; Holanda, F.H.; Jimenez, D.E.Q.; Nascimento, L.A.S.; Oliveira, A.N.; Ferreira, I.M. Use of Oxone® as a Potential Catalyst in Biodiesel Production from Palm Fatty Acid Distillate (PFAD). Catal. Lett. 2021, 10, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, G.; Santoni, P.; Barcellos, A.M.; Nobre, P.C.; Jacob, R.G.; Lenardão, E.J.; Santi, C. Selenomethoxylation of Alkenes Promoted by Oxone®. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Foroozesh, J. Chitin nanocrystals based complex fluids: A green nanotechnology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devadiga, A.; Vidya Shetty, K.; Saidutta, M.B. Highly stable silver nanoparticles synthesized using Terminalia catappa leaves as antibacterial agent and colorimetric mercury sensor. Mater. Lett. 2017, 207, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drnovšek, N.; Kocen, R.; Gantar, A.; Drobnič-Košorok, M.; Leonardi, A.; Križaj, I.; Rečnik, A.; Novak, S. Size of silk fibroin β-sheet domains affected by Ca2+. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6597–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwegasila, E.; Mubofu, E.B.; Nyandoro, S.S.; Erasto, P.; Munissi, J.J.E. Preparation, characterization and in vivo antimycobacterial studies of panchovillin-chitosan nanocomposites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, K.; Muralisankar, T.; Jayakumar, R.; Rajeevgandhi, C. A study on structural comparisons of α-chitin extracted from marine crustacean shell waste. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H.F.G.; Francisco, D.S.; Ferreira, A.P.G.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. A new look towards the thermal decomposition of chitins and chitosans with different degrees of deacetylation by coupled TG-FTIR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, G.M.; Rodas, A.C.D.; Leite, C.A.P.; Giles, C.; Higa, O.Z.; Polakiewicz, B.; Beppu, M.M. Preparation and characterization of ethanol-treated silk fibroin dense membranes for biomaterials application using waste silk fibers as raw material. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8446–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, O.B.G.; de Britto, D.; Forato, L.A. O Uso de Biopolímeros como Revestimentos Comestíveis Protetores Para Conservação de Frutas in natura e minimamente processadas. Boletim de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento 2009, 29, 1–24. [Google Scholar]





 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Heat Source | Catalyst | Temp. (°C) | Time (min) | Conversion b (%) | Isolated yield (%) |
| 1 | MW | CT-Ox a | 50 | 60 | 99 | — |
| 2 | MW | CT-Ox a | 50 | 10 | 97 | — |
| 3 | MW | CT-Ox a | 50 | 5 | 95 | 89 |
| 4 | MW | SF-Ox a | 50 | 5 | 62 | 56 |
| 5 | MW | — | 50 | 5 | 45 | 40 |
| Biopolymers | Conversion (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle 1 | Cycle 2 | Cycle 3 | |
| SF-Ox a | 75 | 74 | 68 |
| SF-Ox b | 99 | 99 | — |
| CT-Ox a | 76 | 50 | 38 |
| CT-Ox b | 99 | 99 | 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves, F.B.; Zanin, L.L.; Pereira, R.R.; Júnior, J.O.C.S.; Costa, R.M.R.; Porto, A.L.M.; Yoshioka, S.A.; Oliveira, A.N.d.; Jimenez, D.E.Q.; Ferreira, I.M. Chitin and Silk Fibroin Biopolymers Modified by Oxone: Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysts for Knoevenagel Reaction. Catalysts 2022, 12, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080904
Neves FB, Zanin LL, Pereira RR, Júnior JOCS, Costa RMR, Porto ALM, Yoshioka SA, Oliveira ANd, Jimenez DEQ, Ferreira IM. Chitin and Silk Fibroin Biopolymers Modified by Oxone: Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysts for Knoevenagel Reaction. Catalysts. 2022; 12(8):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080904
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves, Fernando B., Lucas L. Zanin, Rayanne R. Pereira, José Otávio C. S. Júnior, Roseane Maria R. Costa, André L. M. Porto, Sérgio A. Yoshioka, Alex Nazaré de Oliveira, David E. Q. Jimenez, and Irlon M. Ferreira. 2022. "Chitin and Silk Fibroin Biopolymers Modified by Oxone: Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysts for Knoevenagel Reaction" Catalysts 12, no. 8: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080904
APA StyleNeves, F. B., Zanin, L. L., Pereira, R. R., Júnior, J. O. C. S., Costa, R. M. R., Porto, A. L. M., Yoshioka, S. A., Oliveira, A. N. d., Jimenez, D. E. Q., & Ferreira, I. M. (2022). Chitin and Silk Fibroin Biopolymers Modified by Oxone: Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysts for Knoevenagel Reaction. Catalysts, 12(8), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080904