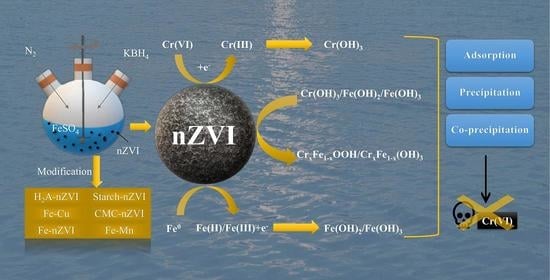
Kinetics and Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI: Influencing Parameters and Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
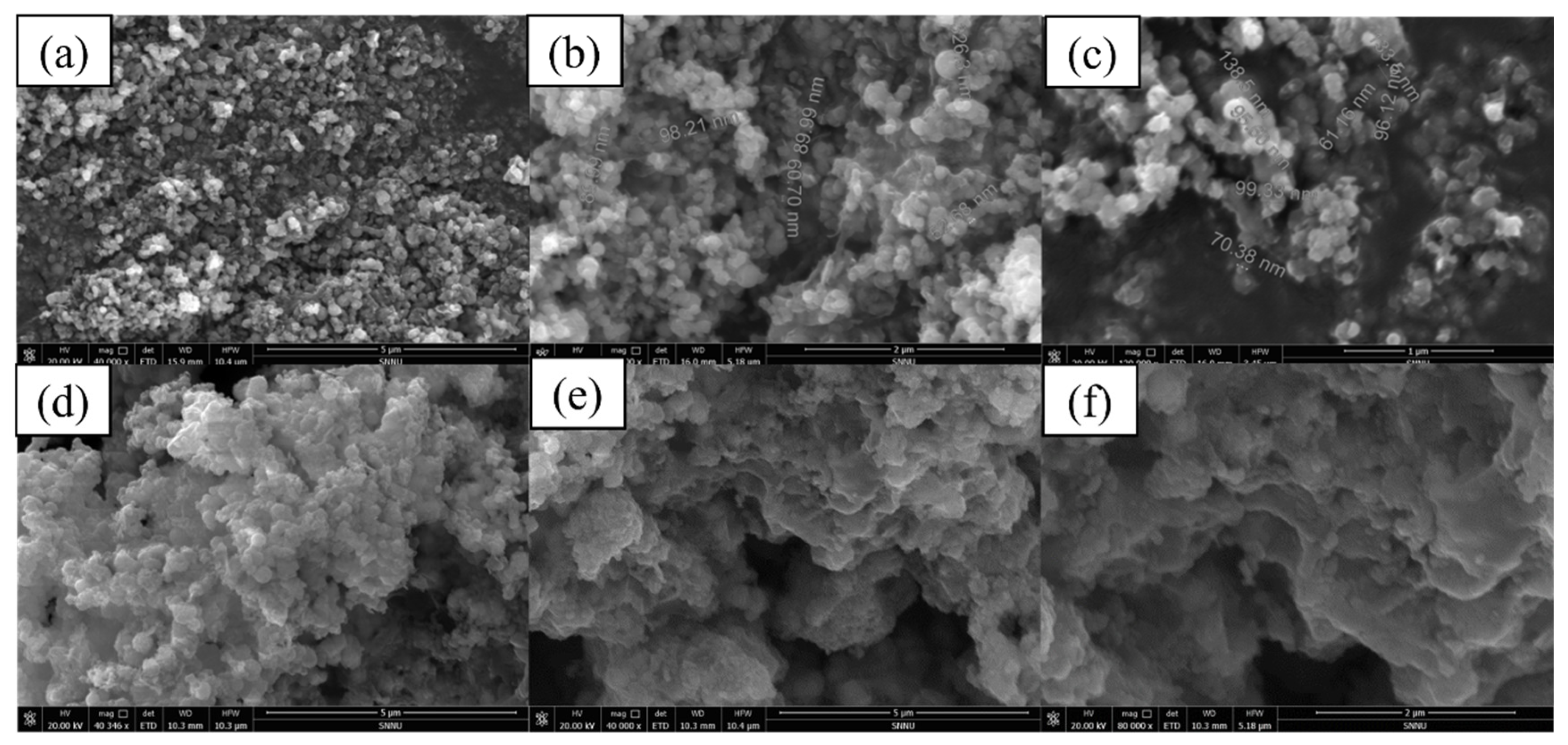
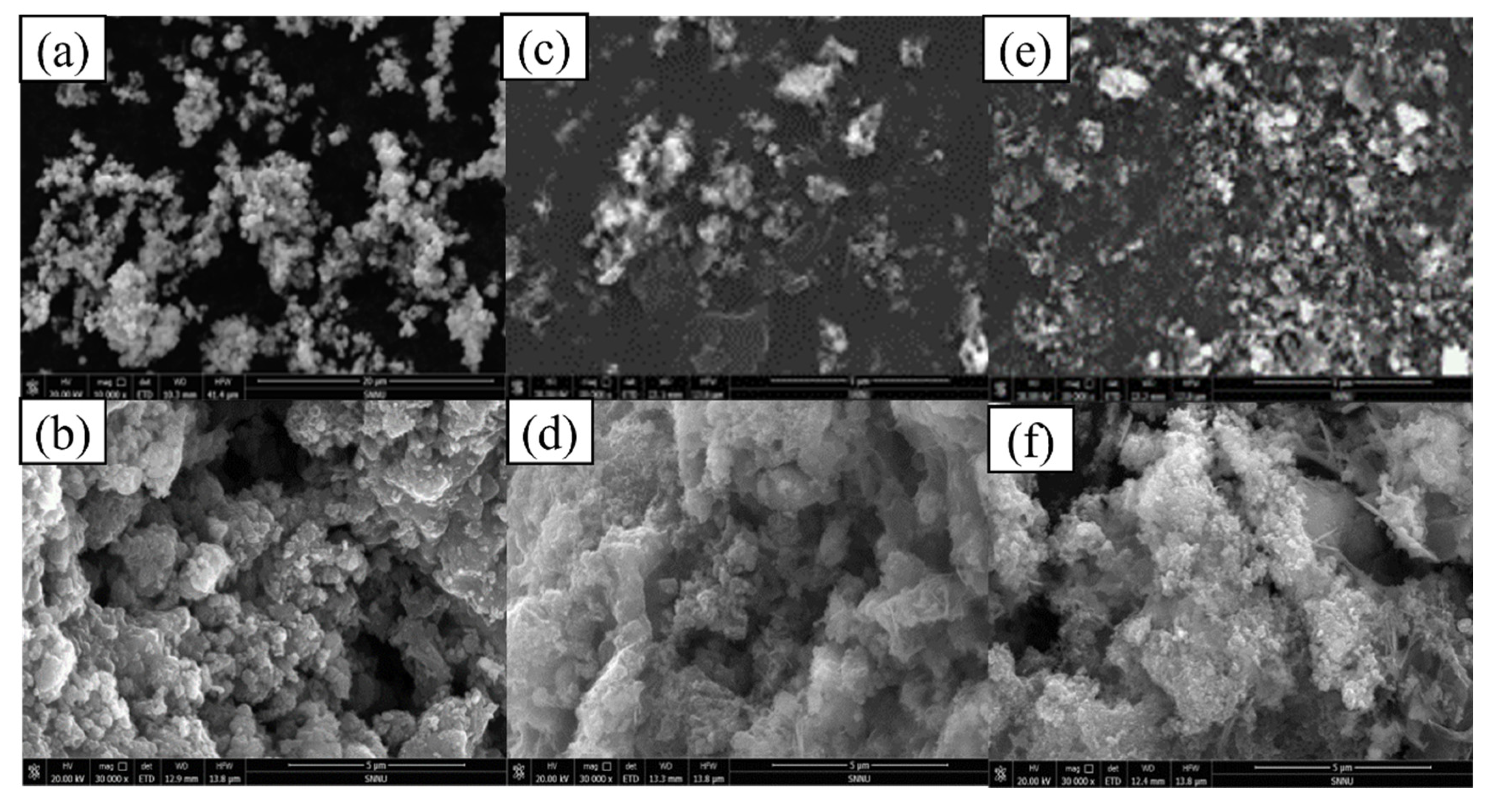
2.1. Characterization of nZVI
2.2. Effect of Important Parameters on the Removal of Cr(VI)
2.2.1. Effect of Initial pH
2.2.2. Effect of Temperature
2.2.3. Effects of Initial Cr(VI) Concentration and nZVI Dosage
2.2.4. Effects of Co-Existing Ions
2.2.5. Effect of Humic Acid
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
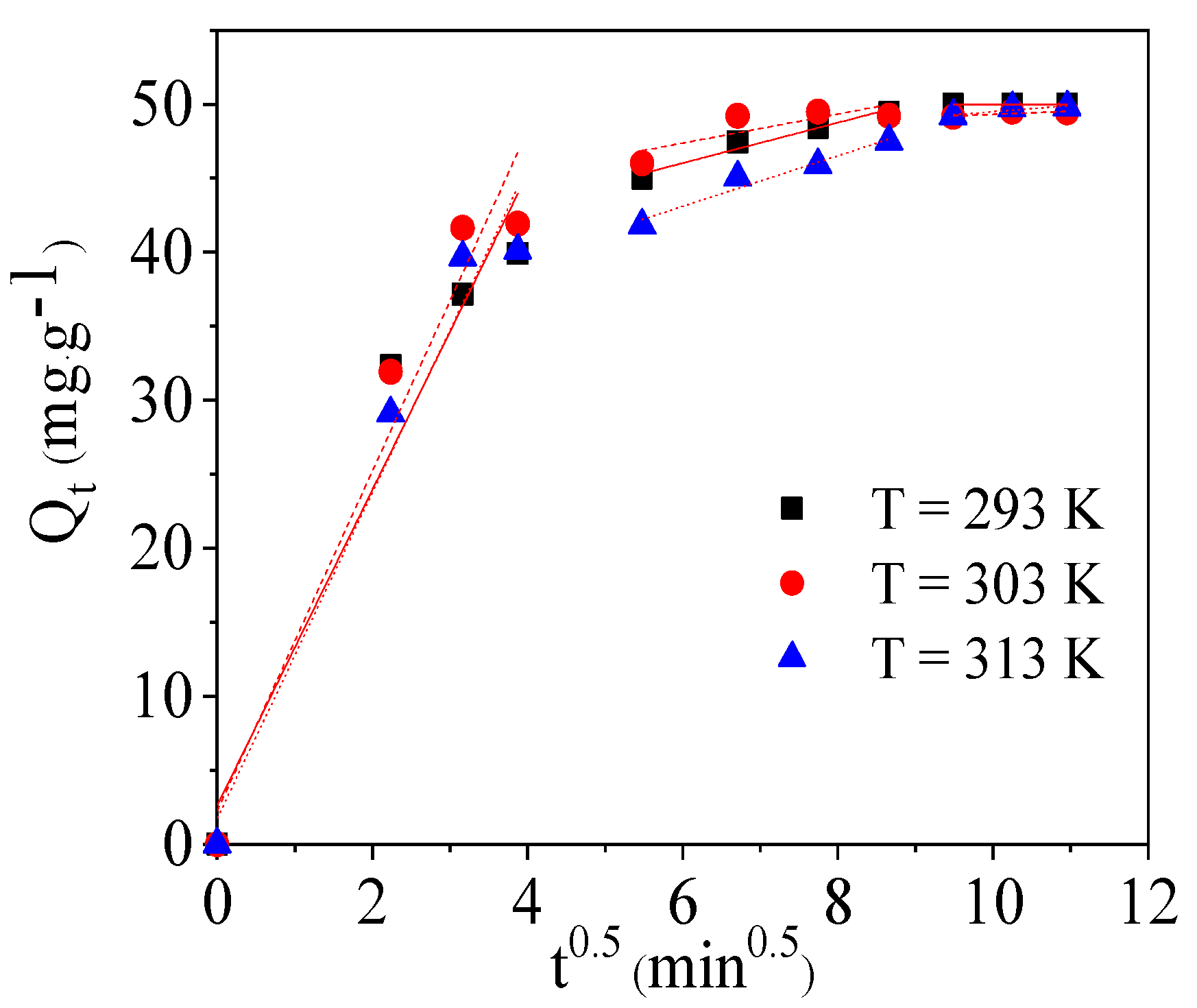
2.4. Intraparticle Diffusion
2.5. Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI
2.6. Comparison of nZVI and Supported nZVI for Cr(VI) Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation of nZVI and Modified nZVI
3.3. Experimental Procedures
3.4. Characterization and Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium contamination and effect on environmental health and its remediation: A sustainable approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Pakshirajan, K.; Chaturvedi, R. Chromium tolerance, bioaccumulation and localization in plants: An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, X.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Wei, Y. A review of the formation of Cr(VI) via Cr(III) oxidation in soils and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Orooji, Y.; Ayati, A.; Qanbari, S.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr(VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Osibote, O.A. A review of hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by sorption technique using nanomaterials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, N.A.; Dash, S.S.; Gummadi, S.N.; Deepa, V.S. Nano-remediation of toxic heavy metal contamination: Hexavalent chromium Cr(VI). Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.M.; Viñarta, S.C.; Bernal, A.R.; Cruz, E.L.; Figueroa, L.I.C. Bioremediation strategies for chromium removal: Current research, scale-up approach and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin, A.S.; Harris, F. The Encyclopedia of Chemical Electrode Potentials; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Ok, Y.S. Review on nano zerovalent iron (nZVI): From synthesis to environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, M.R.; Khosravi, M.R.; Anvaripour, B. Investigation of ultrasonic effect on synthesis of nano zero valent iron particles and comparison with conventional method. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 8, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Han, W. Low dose of sulfur-modified zero-valent iron for decontamination of trace Cd(II)-complexes in high-salinity wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G.; Fang, L. The overlooked role of carbonaceous supports in enhancing arsenite oxidation and removal by nZVI: Surface area versus electrochemical property. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.A.A.; Nava, M.R.; Walter, J.B.; Scherer, C.E.; Dalfovo, A.D.K.; Barreto-Rodrigues, M. Application of zero valent iron (ZVI) immobilized in Ca-Alginate beads for CI Reactive Red 195 catalytic degradation in an air lift reactor operated with ozone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Bai, W.; Shi, Q.; Yang, Y. Fast degradation, large capacity, and high electron efficiency of chloramphenicol removal by different carbon-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Wen, T.; Wang, S.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Removal of organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. A novel cellulose hydrogel coating with nanoscale Fe0 for Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angaru, G.K.R.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, D.-S.; Koduru, J.R.; Yang, J.-K.; Chang, Y.-Y. Facile synthesis of economical feasible fly ash-based zeolite-supported nano zerovalent iron and nickel bimetallic composite for the potential removal of heavy metals from industrial effluents. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.L.; Hu, Z.X.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, G.M.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, X. Cadmium immobilization in river sediment using stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron with enhanced transport by polysaccharide coating. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.L.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.Y.; Gu, T.; Ding, D.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W.-X. Effect of bicarbonate on aging and reactivity of nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) toward uranium removal. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Environmental Remediation and Application of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron and Its Composites for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7290–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Fan, J. Ultra-small and recyclable zero-valent iron nanoclusters for rapid and highly efficient catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol in water. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bedia, J.; Li, H.; Ren, L.Y.; Naluswata, F.; Belver, C. Nanoscale zero-valent iron@mesoporous hydrated silica core-shell particles with enhanced dispersibility, transportability and degradation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, M.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Tang, C.; Hu, X. A novel preparation of S-nZVI and its high efficient removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, N.P.; Gong, Y.S.; Wang, R.T.; Zhang, X.D. Cu-Fe embedded cross-linked 3D hydrogel for enhanced reductive removal of Cr(VI): Characterization, performance, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W.-X. Nanoencapsulation of hexavalent chromium with nanoscale zero-valent iron: High resolution chemical mapping of the passivation layer. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Fu, W.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Pyrogallic acid modified nanoscale zero-valent iron efficiently removed Cr(VI) by improving adsorption and electron selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Na, P. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions using Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles: Characterization, kinetics and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50699–50707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Kou, L.; Wang, T.; Liang, D.; Hu, S. Evaluation of activated carbon fiber supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for chromium (VI) removal from groundwater in a permeable reactive column. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 201, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, Z.-H.; Yan, L.; Dong, F.-X.; Chen, Z.-L.; Guo, P.-R.; Qian, W.; Zhang, W.-X.; Liang, J.-Y.; Huang, S.-T.; Chu, W. Ultrasound-assisted catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) by an acid mine drainage based nZVI coupling with FeS2 system from aqueous solutions: Performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-H.; Wu, M.-F.; Tang, T.-T.; Xing, Q.-J.; Peng, C.-Q.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Luo, X.-B.; Zou, J.-P.; Min, X.-B.; et al. Mechanism investigation of anoxic Cr(VI) removal by nano zero-valent iron based on XPS analysis in time scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangayayam, M.C.; Alonso-De-Linaje, V.; Dideriksen, K.; Tobler, D.J. Effects of common groundwater ions on the transformation and reactivity of sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Ma, J.; Ning, P. Formulation of NZVI-supported lactic acid/PAN membrane with glutathione for enhanced dynamic Cr(VI) removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanboonchuy, V.; Grisdanurak, N.; Liao, C.-H. Background species effect on aqueous arsenic removal by nano zero-valent iron using fractional factorial design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 205–206, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Hu, Y.; Tang, J.; Sheng, T.; Jiang, G.; Xu, X. Effects of co-existing ions and natural organic matter on removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI)-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Liang, B.; Fang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Tsang, E.P. Effect of humic acid and transition metal ions on the debromination of decabromodiphenyl by nano zero-valent iron: Kinetics and mechanisms. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.-H.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Jin, J.-C.; Chen, Z.-L.; Guo, P.-R.; Dong, F.-X.; Yan, L.; Kong, L.-J.; Chu, W. Removals of Cr(VI) and Cd(II) by a novel nanoscale zero valent iron/peroxydisulfate process and its Fenton-like oxidation of pesticide atrazine: Coexisting effect, products and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Li, L.; Ren, W.; Deng, X.; Liu, T. Effect of pH, temperature, humic acid and coexisting anions on reduction of Cr(VI) in the soil leachate by nZVI/Ni bimetal material. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Dai, Y.; Shi, L.; Wei, Y.; Xiu, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S. Humic acid addition sequence and concentration affect sulfur incorporation, electron transfer, and reactivity of sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, H.K.; Joseph, M.; O’Carroll, D.M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Song, T.; Tang, C.; Meng, Y.; Dai, S.; Wang, H.; Chai, L.; et al. Synthesis of Core-Shell Magnetic Fe3O4@poly(m-Phenylenediamine) Particles for Chromium Reduction and Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5654–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, A.R.; Zhang, W.X. The influence of polyelectrolyte modification on nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Aggregation, sedimentation, and reactivity with Ni(II) in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Han, L.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, D.; Long, Y.; Wei, Z.; Dong, X.; Liang, C.; Li, J.; et al. Synergistic roles of Fe(II) on simultaneous removal of hexavalent chromium and trichloroethylene by attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Z.-L.; Yan, X.; Zhang, B. Removal of mercury (II) and chromium (VI) from wastewater using a new and effective composite: Pumice—supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lyu, H.; Tang, J.; Song, B.; Zhen, M.; Liu, X. A novel biochar supported CMC stabilized nano zero-valent iron composite for hexavalent chromium removal from water. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Liu, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, W. Evolution of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water: Microscopic and spectroscopic evidence on the formation of nano- and micro-structured iron oxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Lou, Z.; Lou, L.; Xu, X. Mechanism and influence factors of chromium(VI) removal by sulfide-modified nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, M. Effective removal of Cr(VI) by attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: Enhanced adsorption and crystallization. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Shu, Y.; Huang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, L. Enhanced reactivity of nZVI embedded into supermacroporous cryogels for highly efficient Cr(VI) and total Cr removal from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ge, C.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Lin, A.; Yang, W. Does soluble starch improve the removal of Cr(VI) by nZVI loaded on biochar? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Ascorbic acid/Fe0 composites as an effective persulfate activator for improving the degradation of rhodamine B. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12791–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda, P.; Rubio, M.A.; Baltazar, S.; Rojas-Nunez, J.; Llamazares, J.L.S.; Garcia, A.; Arancibia-Miranda, N. As(V) removal capacity of FeCu bimetallic nanoparticles in aqueous solutions: The influence of Cu content and morphologic changes in bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 524, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Zou, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liao, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Lin, G. Performance and mechanism of arsenic removal in waste acid by combination of CuSO4 and zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; He, F.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. Insight into the kinetics and mechanism of removal of aqueous chlorinated nitroaromatic antibiotic chloramphenicol by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 334, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI: Influencing Parameters and Modification. Catalysts 2022, 12, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090999
Gao Y, Yang X, Lu X, Li M, Wang L, Wang Y. Kinetics and Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI: Influencing Parameters and Modification. Catalysts. 2022; 12(9):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090999
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yizan, Xiaodan Yang, Xinwei Lu, Minrui Li, Lijun Wang, and Yuru Wang. 2022. "Kinetics and Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI: Influencing Parameters and Modification" Catalysts 12, no. 9: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090999
APA StyleGao, Y., Yang, X., Lu, X., Li, M., Wang, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). Kinetics and Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by nZVI: Influencing Parameters and Modification. Catalysts, 12(9), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12090999