Abstract
In this study, both wood flour (WF) and wood flour-derived biochar (WFB) were used as supports for Fe3O4 to activate peroxydisulfate (PDS). The role of different carriers was investigated emphatically from the aspects of catalyst properties, the degradation kinetics of bisphenol A (BPA), the effects of important parameters, and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Results showed that both WF and WFB could serve as good support for Fe3O4, which could control the release of iron into solution and increase the specific surface areas (SSAs). The WFB/Fe3O4 had stronger PDS activation capability than WF/Fe3O4 mainly due to the larger SSA of WFB/Fe3O4 and the PDS activation ability of WFB. Both radical species (•OH and SO4•−) and non-radical pathways, including 1O2 and high-valent iron-oxo species, contributed to the degradation of BPA in the WFB/Fe3O4–PDS process. Moreover, the WFB/Fe3O4 catalyst also showed stronger ability to control the iron release, better reusability, and higher BPA mineralization efficiency than WF/Fe3O4.
1. Introduction
The pollution of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) has attracted extensive attention due to the serious danger to the exposed environments. EDCs, also known as environmental hormones, are contaminants that may cause endocrine disorders [1]. The ingestion of EDCs affects the normal function of endogenous hormones, which can further cause adverse health effects on the human body [2]. EDCs accumulate in sewage treatment plant effluents and surface water at levels as high as μg/L, which can pose potential hazard to the safety of drinking water [3].
To decrease the concentration of EDCs in wastewater, sulfate radical (SO4•−)-based advanced oxidation technologies (Sr-AOTs) have been applied as effective methods [4,5]. The high oxidation potential (E0 = 2.5~3.1 V vs. NHE), wide adaptable pH range (2~8), and relatively long half-life (30–40 μs) make SO4•− radicals own a strong oxidizing ability to decompose recalcitrant contaminants [6,7]. SO4•− can be produced by the activation of persulfate, including peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and peroxydisulfate (PDS), during which processes the unstable peroxide (-O-O-) bonds are apt to be attacked by electrons or energy for cleavage [8]. PDS was selected as the radical precursor in this study instead of PMS because of its cost effectiveness, high solubility, and chemical stability [9].
Among various PDS activation methods, transition metal possesses the advantages of low energy demand, high efficiency, and mild reaction conditions [10]. Since Fe was regarded as the most efficient, economical, and environmentally friendly metal for PDS activation [11,12], varieties of Fe-based catalysts were developed (e.g., Fe3O4/SBA-15 [13], Fe3C/porous carbon [14]). Fe-based heterogeneous catalysts can well improve some drawbacks of the homogeneous Fe2+/PDS process. The application of Fe3O4 can not only avoid Fe precipitation at neutral and alkaline conditions, but it can also decrease the self-quenching of precious radicals, and good separation is able to be achieved [15,16]. However, Fe3O4 particles easily aggregate during the reaction due to the high surface energy and the interaction induced by magnetic force, which can influence the catalytic capability. Therefore, Fe3O4 particles are often immobilized onto various carriers to prevent agglomeration. Several studies have proven that Fe3O4 loaded on carriers could improve the catalytic activity and stability. Fe3O4 particles could anchor on sepiolite with good dispersion, which was efficient for PDS activation even at alkaline conditions [17]. Fe3O4@carbon nanotube composites also exhibited high PDS catalytic activity and a stronger charge transfer ability and oxidation ability [18]. Moreover, carbon material, such as reduced graphene oxide (rGO), has also been found to be a promising support. The rGO-Fe3O4 nanoparticle was prepared as a PDS activator for the efficient degradation of trichloroethylene, which could well prevent Fe3O4 agglomeration [19]. Although most of these carriers could demonstrate strong stability, they are normally costly and have complex synthetic methods. Therefore, it is necessary to develop cheap and easily prepared carriers to support Fe3O4 as an efficient PDS activator.
Biochar has been verified as a promising catalyst carrier due to its low price, high specific surface area, and excellent chemical and biological stability. In addition, biochar alone also has the ability to activate PDS due to the abundant functional groups on the surface [20,21,22]. Moreover, both radical pathways (e.g., hydroxyl radicals (•OH), surface-bound radicals) and nonradical pathways (e.g., singlet oxygen (1O2) and direct electron transfer) were identified as the dominant mechanisms [23,24]. The annual yield of waste wood materials from both agriculture and forestry is very high, which is in urgent need for recycling. The wood materials have strong mechanical strength and stability [14], and the wood-derived biochar with rich oxygen-containing functional groups and π-electron density demonstrated excellent performance in PDS activation [25,26]. Although both the wood-based biomass (WBS) and wood-based biochar (WBC) can be potentially good carriers for the Fe3O4 catalyst, so far, hardly any studies have been conducted comparing the influence and the role of WBS and WBC on the catalytic performance of Fe3O4 for PDS activation.
In this study, both wood flour (WF) and wood flour-derived biochar (WFB) were used as the carriers to support Fe3O4 for the activation of PDS. Bisphenol A (BPA) was selected as a typical EDC due to the toxicity and its recalcitrant structure [27,28]. The role of different carriers was investigated emphatically from the aspects of catalyst properties, BPA degradation kinetics, and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The effects of important parameters were also evaluated. Finally, the BPA degradation mechanisms were proposed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Catalysts
2.1.1. SEM and FESEM
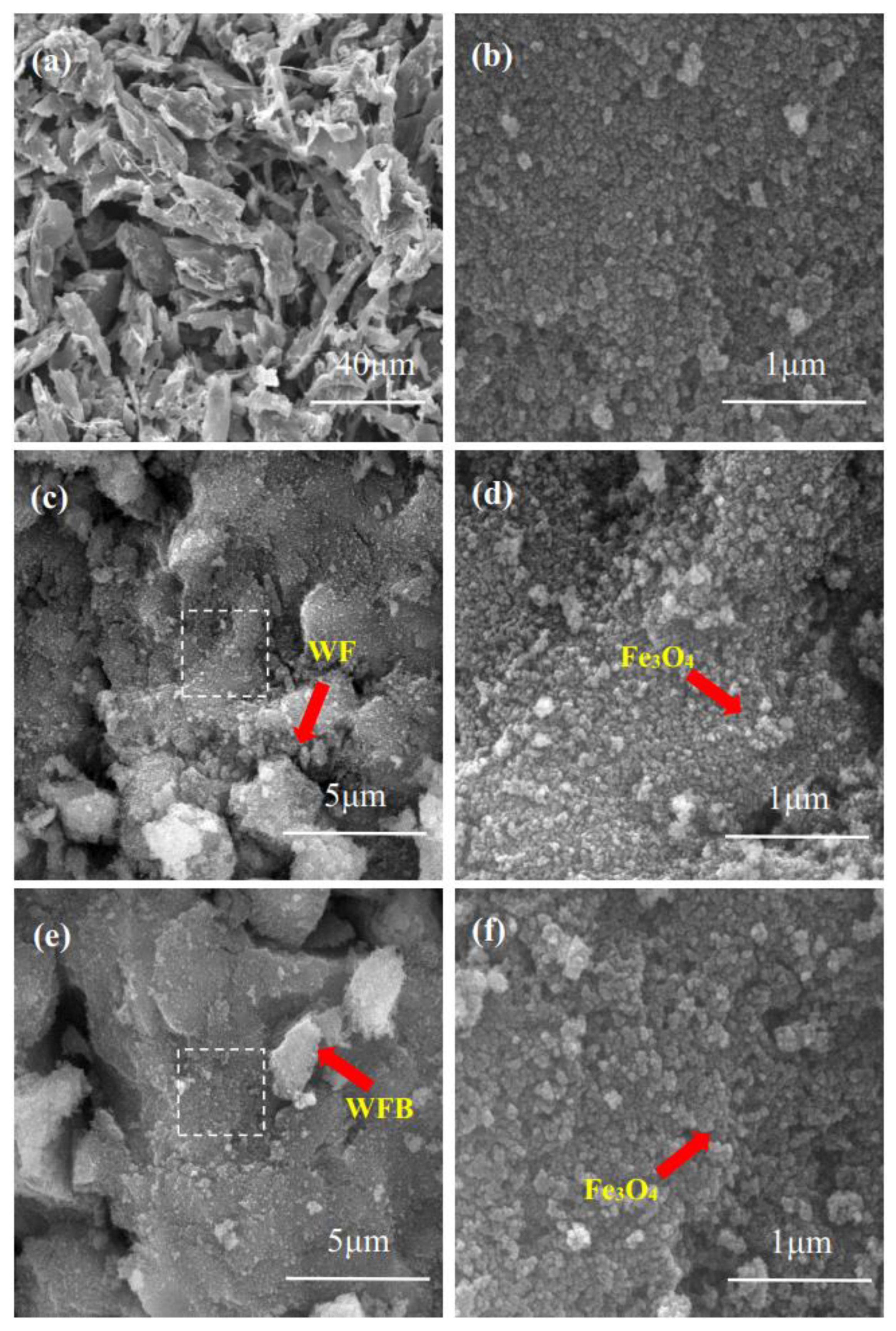
The surface morphologies of WFx/Fe3O4 and WFBx/Fe3O4 were characterized by SEM and FESEM. As shown in Figure S1, the WF had a sheet-like appearance, while after the pyrolysis treatment, the WFB generally retained the sheet-like structure interspersed with some fibers, which is the typical structure of biochar (Figure 1a). Moreover, the size of WFB became smaller than WF, and the surface of WFB became rougher and more irregular. This was probably because high pyrolysis temperature removed lots of the functional groups and destroyed the polymer framework of the pristine WF [29]. Figure 1b shows that the shape of Fe3O4 was almost spherical, and the average sizes of Fe3O4 nps were found to be ~30 nm. The FESEM images of WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4 shown in Figure 1c–f further demonstrate the successful synthesis of the composites, in which large numbers of Fe3O4 nps appeared on the surface of WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4, and the sheet-like structures could not be observed clearly.

Figure 1.
SEM images of (a) WFB, and FESEM images of (b) Fe3O4, (c,d) WF20/Fe3O4, and (e,f) WFB20/Fe3O4 ((d,f) are the enlarged view of the dotted boxes shown in (c,e), respectively).
2.1.2. XRD
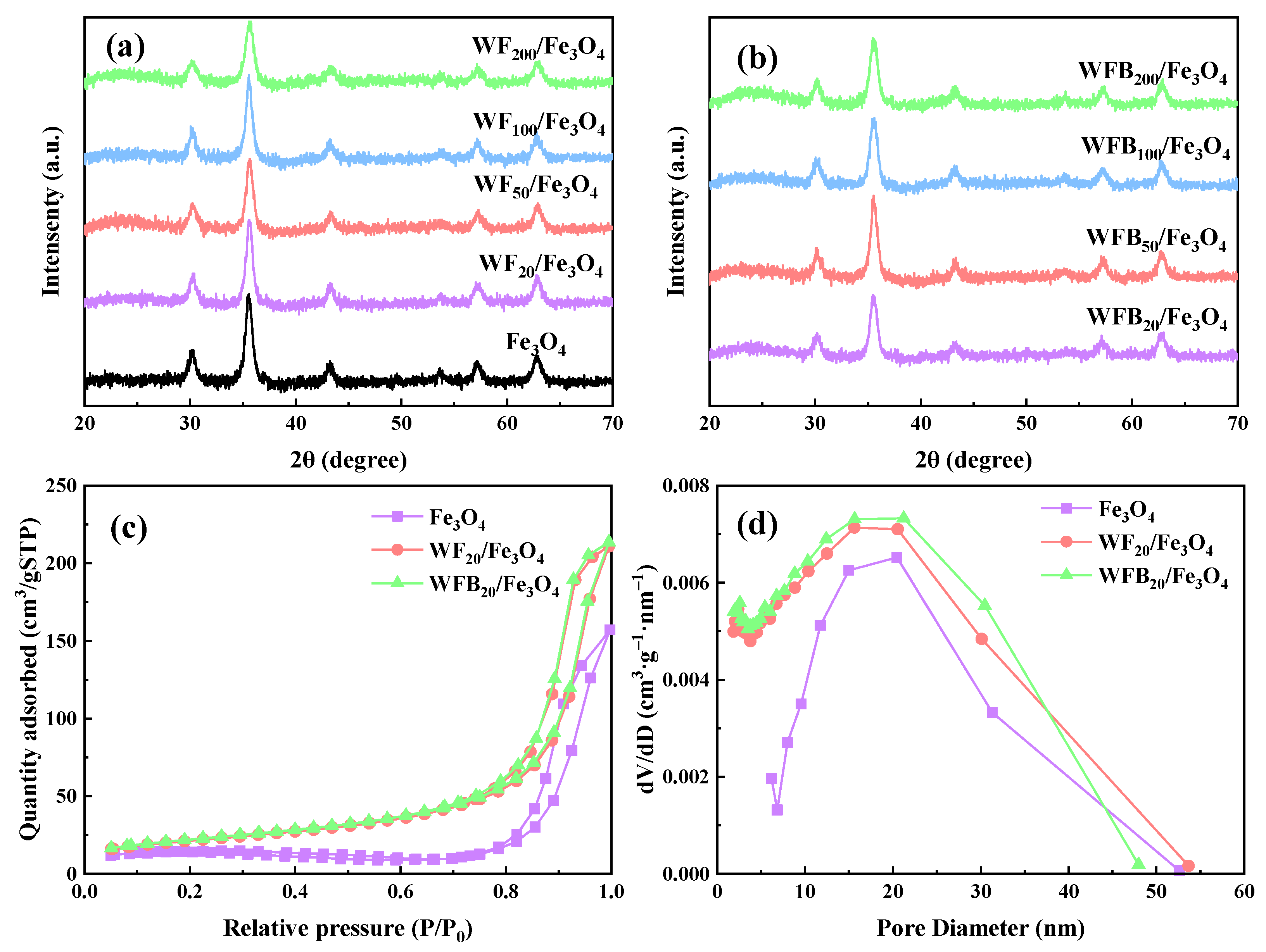
The XRD patterns of Fe3O4, WF/Fe3O4, and WFB/Fe3O4 are shown in Figure 2a,b. The peaks located at 30.2° (220), 35.6° (311), 43.2° (400), 53.8° (422), 57.1° (511), and 62.8° (440) were consistent with the characteristic peaks of Fe3O4 (JCPDS No.19-0629) [30]. It was observed that the characteristic peaks were not very sharp, which may be ascribed to the moderate crystallinity of the prepared Fe3O4 [31]. After the incorporation of WF or WFB, the obtained WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4 with different WF or WFB amounts retained the characteristic peaks of Fe3O4, which indicated that the prepared WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4 composites kept the crystal phase of Fe3O4. Additionally, the broad diffraction peaks were observed near 24.5° for all WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4 composites, which could be assigned to the (002) crystal planes of the graphite structure (JCPDS No.75-1621) [32]. It could be obviously seen that the broad diffraction peaks of WFB/Fe3O4 were stronger than those of WF/Fe3O4, which indicated that the addition of WFB brought a more graphitized structure than that of WF.
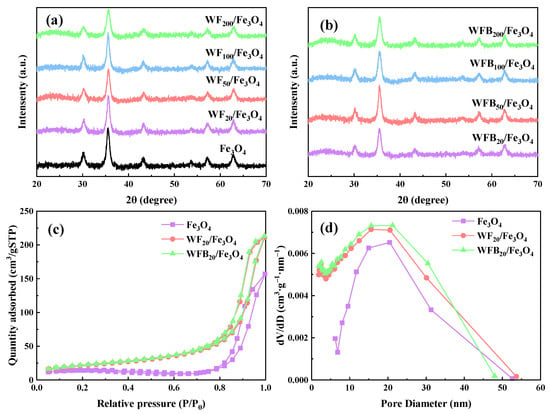
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of (a) Fe3O4, WF/Fe3O4, and (b) WFB/Fe3O4; (c) the N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (d) pore size distributions of Fe3O4, WF20/Fe3O4, and WFB20/Fe3O4.
The average crystallite size of the Fe3O4 nps was calculated with the Debye–Scherrer formula (Equation (1)) [33]. The results are shown in Table S1, and the average crystallite sizes were in the range of 13~16 nm:
where D is the crystallite size, K is the constant (0.89), λ is the X-ray wavelength (0.1541841 nm), θ is the Bragg diffraction angle, and B is the full width at half maximum.
Differences in the average grain size of Fe3O4 nps were obtained based on FESEM and XRD results, which was probably because the particles observed from FESEM normally consist of several crystal cells and the average crystallite size that could be obtained from XRD should be smaller than that obtained from FESEM [34].
2.1.3. N2 Adsorption-Desorption
The N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and pore size distributions of catalysts are shown in Figure 2c,d. According to the isotherm classification from the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the isotherms of Fe3O4, WF20/Fe3O4, and WFB20/Fe3O4 belong to type IV with an H1-type hysteresis loop, indicating the existence of typical mesoporous structures of the catalysts [35]. This is consistent with the pore size distribution results. Moreover, compared to Fe3O4 (41.32 m2/g), WF20/Fe3O4 (76.25 m2/g) and WFB20/Fe3O4 (78.65 m2/g) had larger specific surface areas (SSAs) and more micropores, which might provide abundant active sites for catalytic reactions and facilitate the adsorption of the pollutant.
2.1.4. VSM
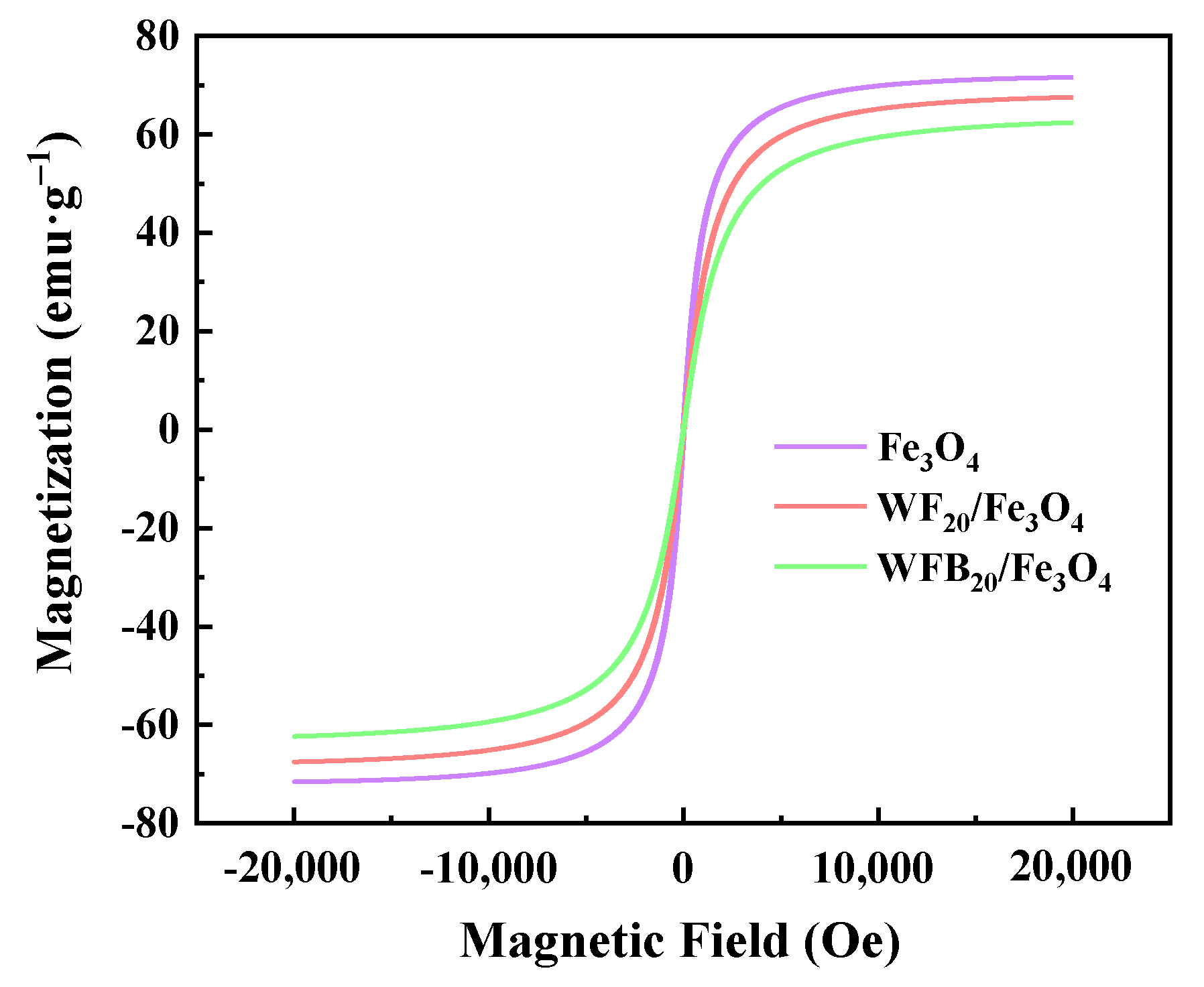
The magnetic properties of Fe3O4, WF20/Fe3O4, and WFB20/Fe3O4 were assessed by VSM at room temperature (Figure 3). As illustrated, the saturation magnetization (Ms) of Fe3O4 was calculated to be 71.58 emu g−1. Although the Ms values of WF20/Fe3O4 (67.54 emu g−1) and WFB20/Fe3O4 (62.37 emu g−1) were both lower than that of Fe3O4 due to the existence of non-magnetic WF or WFB, the two composites still exhibited strong magnetic responses, which ensured their easy recycle via magnetic force without introducing secondary pollution in practical use.
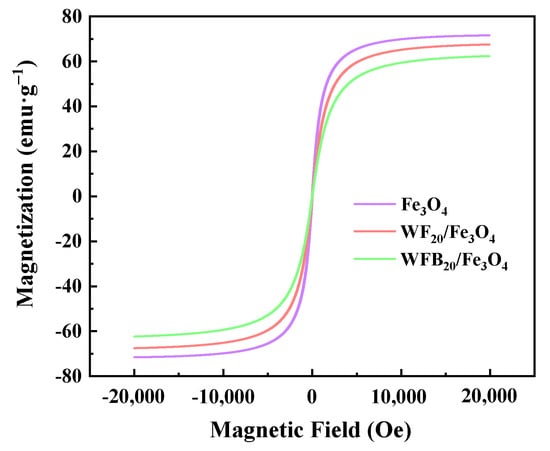
Figure 3.
The magnetization curves of Fe3O4, WF20/Fe3O4, and WFB20/Fe3O4.
2.1.5. FTIR
FTIR spectra were used to further validate the successful composition of Fe3O4 nps with WF or WFB (Figure S2). All the catalysts had characteristic peaks at 3426.87 cm−1 and 1628.81 cm−1, corresponding to the -OH stretching and bending vibration of water, respectively [36]. Meanwhile, the peak intensities of C-H (~2920 cm−1), C=O (1736.27 cm−1), and C-O-C (1052.56 cm−1) vibrations in WFB and WFB20/Fe3O4 were weaker than those of WF and WF20/Fe3O4 samples, indicating that the oxygen-containing groups in the lignocellulose structures were decomposed and removed during the pyrolysis process [29,37]. In the spectra of Fe3O4, WF20/Fe3O4, and WFB20/Fe3O4, the vibrations of Fe2+-O2− (585.33 cm−1) and Fe3+-O2− (445.16 cm−1) appeared, implying the formation of Fe3O4, which was also consistent with the results of XRD patterns [38]. After the addition of WF or WFB, the band intensities at 2924.59 cm−1 (asymmetric stretching for aliphatic functional groups) and 2856.07 cm−1 (symmetric stretching for aliphatic functional groups) slightly increased [39]. These changes of FTIR peaks proved that the composites of WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4 were successfully synthesized.
2.2. Evaluation of Catalytic Performance
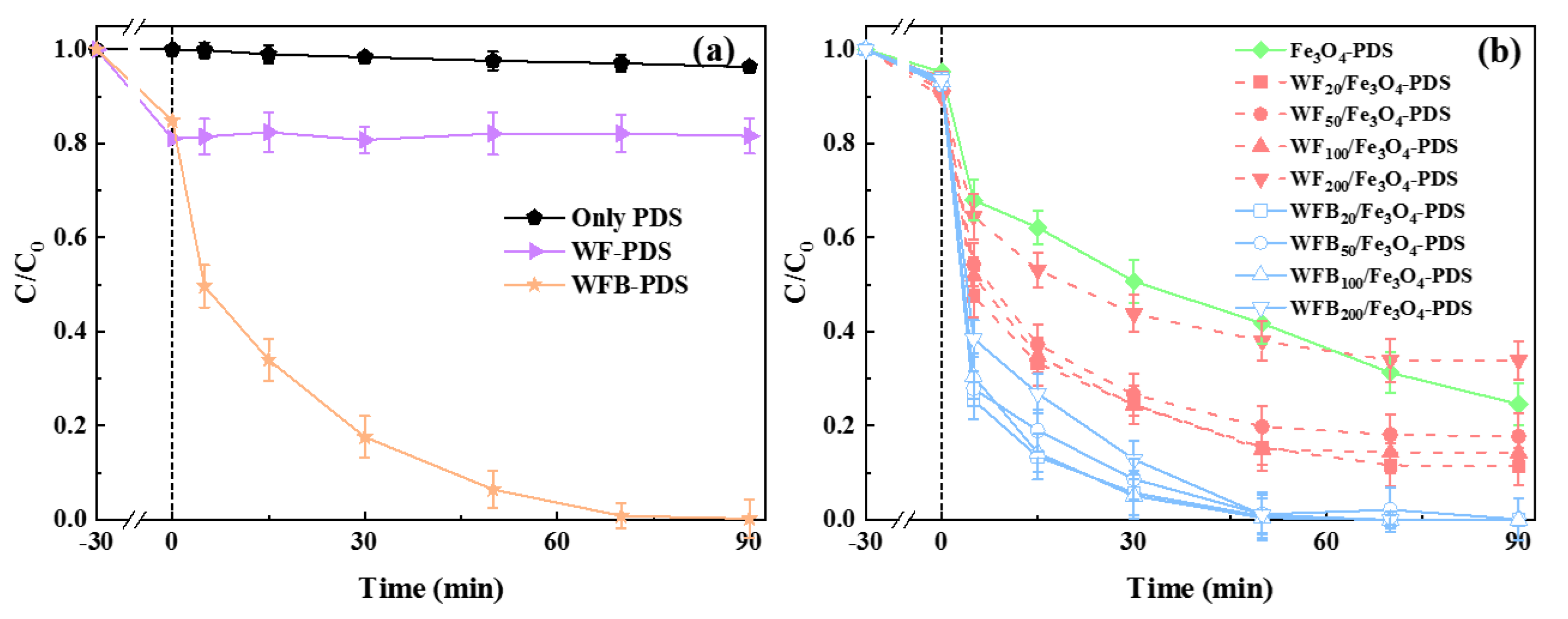
The degradation of BPA in different processes was evaluated (Figure 4). Before adding PDS, 30 min pre-adsorption was performed to enable the equilibrium of BPA adsorption. As shown in Figure 4a, WF and WFB showed moderate adsorption capacity for BPA, with removal rates of 19.9% and 15.2% within 30 min, while Fe3O4 could only adsorb 4.7% of BPA. After compositing with WF or WFB, the adsorption capacities of WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4 were slightly improved compared to that of Fe3O4, which was consistent with the results of SSA. Control experiments were conducted to preclude the direct oxidation of BPA by PDS (Figure 4a). In the WF-PDS process, hardly any BPA could be degraded, which demonstrated that pure WF could not activate PDS to generate effective ROS. In contrast, WFB showed the effective activation of PDS leading to the complete degradation of BPA within 90 min, which might be due to the formation of active sites such as graphitized carbon, oxygen-containing groups, and so on after high-temperature carbonization.
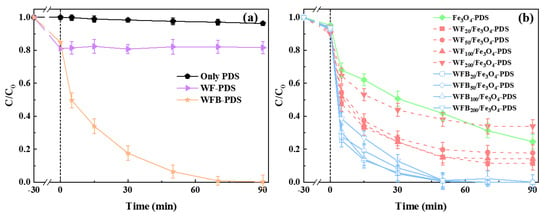
Figure 4.
(a) The BPA removal performance in control processes; (b) the BPA removal performance in different Fe3O4-containing processes (conditions: [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1).
As seen in Figure 4b, 75.5% of BPA was degraded in the Fe3O4-PDS system. For catalysts with different amounts of WF, WF20/Fe3O4 exhibited excellent catalytic efficiency with a removal rate of 89.7% in 90 min. With more than 20 mg of WF loading, the BPA removal rate decreased, and the BPA removal rate in the WF200/Fe3O4-PDS process was even lower than that in the Fe3O4-PDS process. These results showed that excessive WF loading could decrease the catalytic efficiency of WF/Fe3O4. However, the catalytic performance of all the WFB/Fe3O4 catalysts was better than that of Fe3O4. Although the catalytic efficiency of WFB/Fe3O4 slightly decreased as the amount of WFB increased, almost 100% of BPA in these systems was degraded within 50 min. Table 1 compared the degradation efficiencies of BPA in different Sr-AOPs. It can be seen that the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process of the present study could have comparable efficiency toward BPA degradation with other Sr-AOPs. It should also be noted that the same dose of WF and WFB showed different influences on the catalytic performance of Fe3O4. To further reveal the roles of WF and WFB in the composites for the activation of PDS, WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4 were selected for the following study.

Table 1.
Comparison of the BPA degradation efficiency in different Sr-AOPs.
2.3. Effects of Reaction Parameters on BPA Degradation
2.3.1. Effect of Initial Solution pH
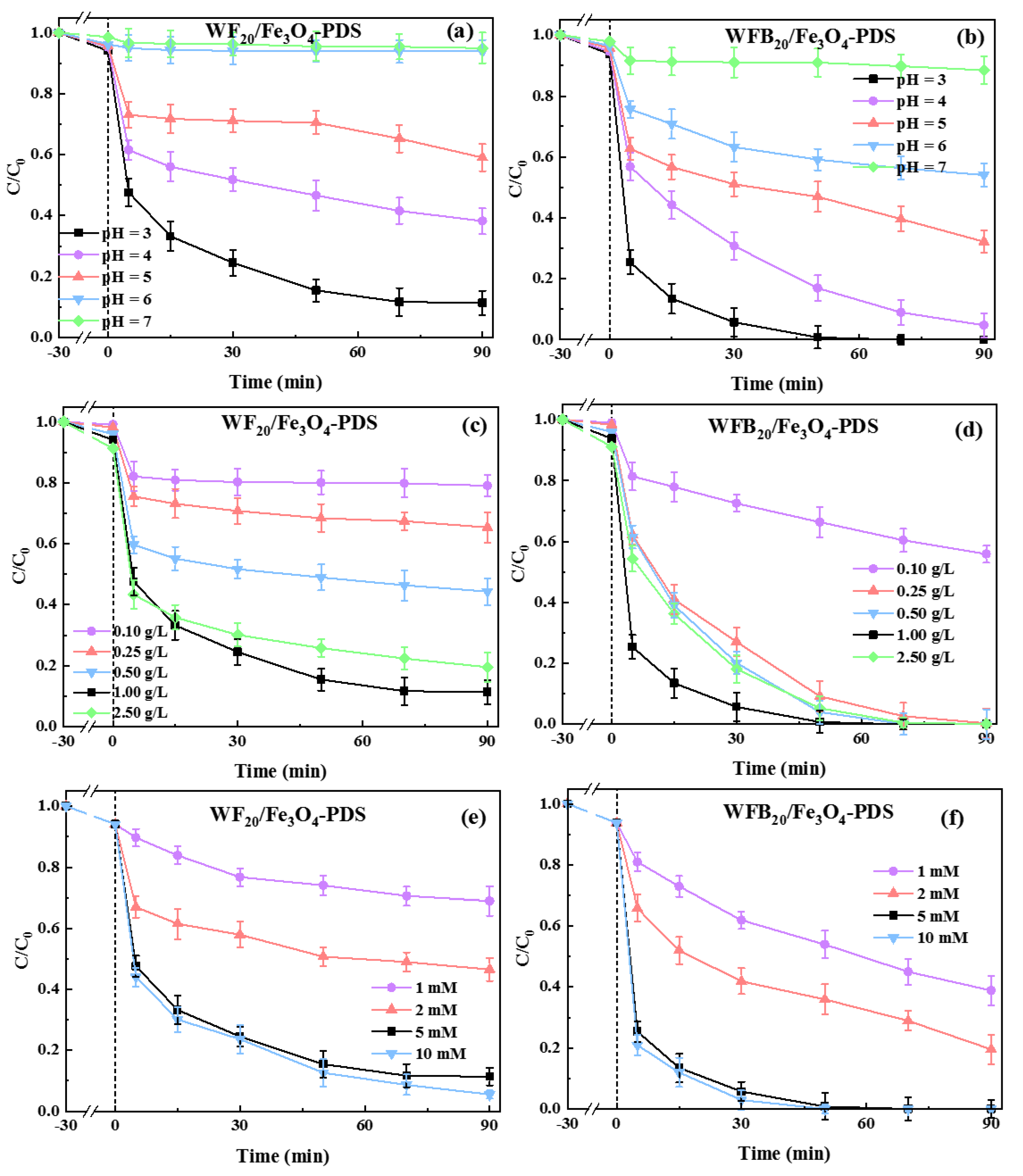
It is well known that solution pH has significant influence on the performance of various AOTs. Herein, the effects of the initial solution pH (pH0) on BPA degradation in Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes were explored (Figure S3 and Figure 5a,b). The BPA removal rate in Fe3O4-PDS and WF20/Fe3O4-PDS processes decreased from 75.5% to 3.8% and from 88.7% to 5.1%, respectively, as the pH0 increased from 3.0 to 7.0. By contrast, the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process showed stronger pH tolerance, and the BPA removal rate decreased from 100% to 11.5% as the pH0 increased from 3.0 to 7.0. These results indicated that these catalytic processes preferred more acidic conditions for BPA degradation. Under acidic conditions, ferrous ions could more easily enter into the solution from the catalyst surface, and the dissolved Fe2+ could activate PDS to accelerate BPA decomposition [44].
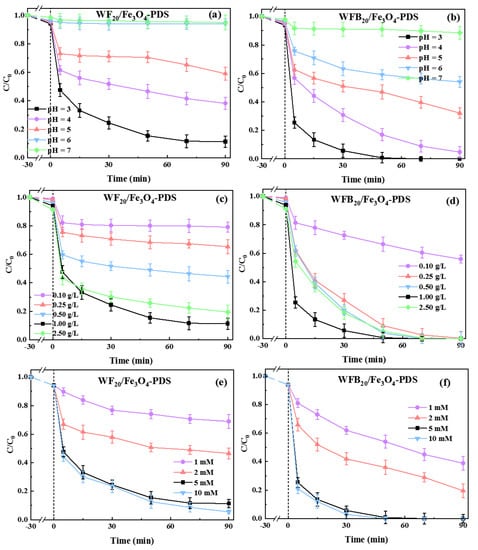
Figure 5.
Effects of (a,b) the initial solution pH, (c,d) catalyst dosage, and (e,f) PDS concentration on the degradation of BPA in WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1).
2.3.2. Effect of Catalyst Dosage
The effects of WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4 dosages on BPA degradation were investigated (Figure 5c,d). It was found that the increase of WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4 dosages from 0.1 g/L to 1.0 g/L resulted in the significant and continuous promotion of BPA degradation, with the removal rate increasing from 20.9% to 88.7% and from 44.1% to 100%, respectively. This could be explained by the increase of active sites with higher dosages of catalysts to promote the production of ROS. However, when the dosages of WF20/Fe3O4 or WFB20/Fe3O4 were further increased to 2.5 g/L, the removal rate of BPA decreased slightly. This probably resulted from the self-quenching effects of explosive ROS and the quenching reactions between ROS and PDS when the catalysts were excessive (Equations (2) and (3)) [45]. Moreover, the Fe(II) on the surface of Fe3O4 nps also had a strong scavenging effect towards ROS (Equation (4)) [46]. Additionally, excess dosage of catalyst may also increase the mutual magnetic attraction and agglomeration of the catalysts, interfering with their uniform dispersion in solution, which could reduce the surface area of the catalysts and the corresponding catalytic efficiency [47].
2.3.3. Effect of PDS Concentration
Generally, the amount of generated ROS directly relates to the PDS concentration. Herein, the effects of PDS concentration on BPA degradation in WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes were examined (Figure 5e,f). It was found that, with the PDS concentration increasing from 1.0 to 5.0 mM, the BPA removal rate increased from 31.2% to 88.7% in the WF20/Fe3O4-PDS process and from 61.1% to 100.0% in the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process, respectively. However, when the PDS concentration further increased to 10.0 mM, the BPA degradation was only improved slightly. The results demonstrated that the excess amount of PDS did not benefit the degradation of target pollutants, mainly because PDS could also act as the ROS quencher competing for the ROS with target pollutants (Equations (2) and (3)).
2.4. Identification of ROS
2.4.1. Quenching Experiments
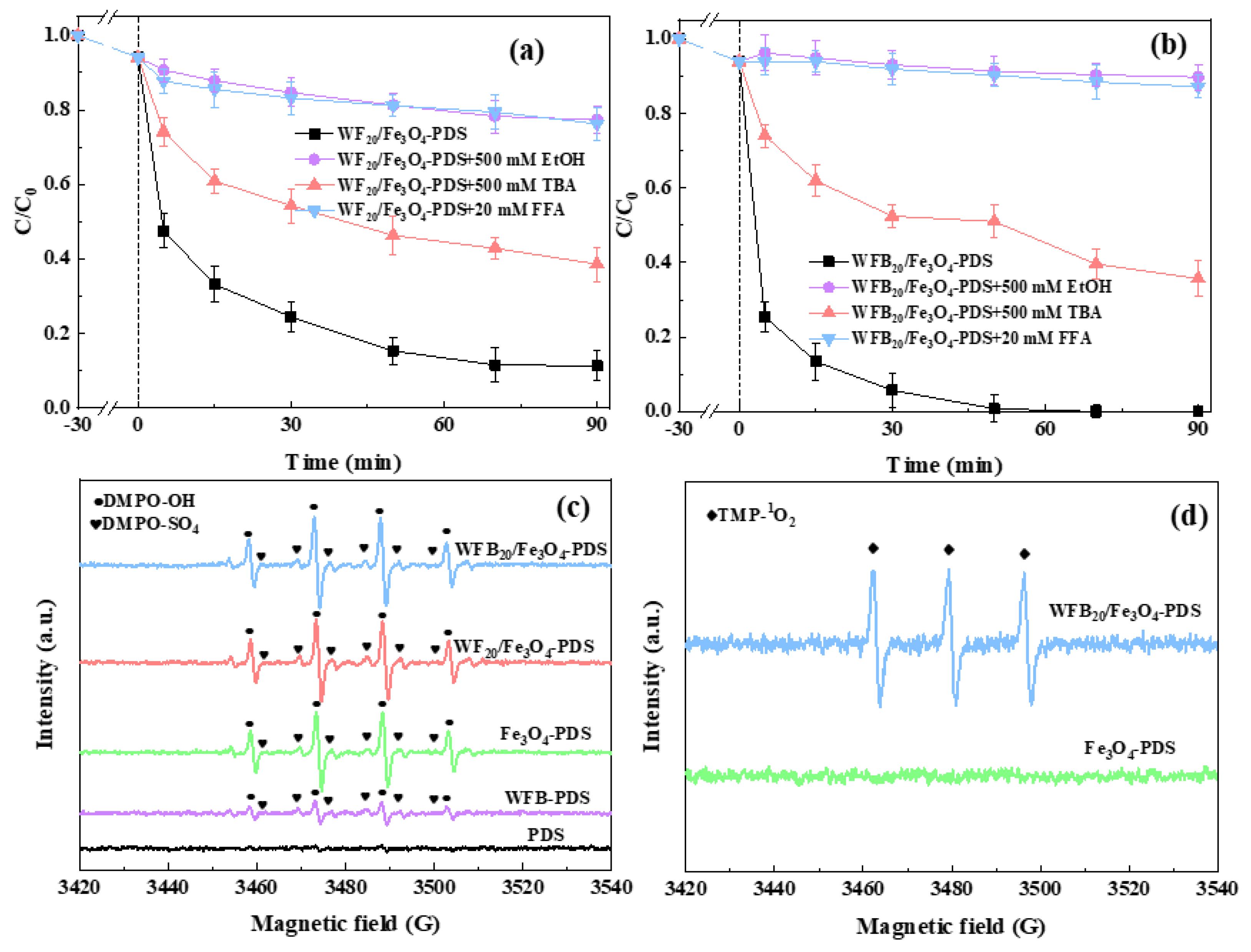
In order to further understand the different roles of WF and WFB in the evolution of ROS during PDS activation, quenching experiments were conducted in different systems using various quenchers. It is widely accepted that EtOH can rapidly quench both •OH and SO4•– (k•OH = 1.6~7.7 × 107 M−1 s−1, kSO4•– = 1.2~2.8 × 108 M−1 s−1), while TBA is usually used as an effective quencher for •OH (k•OH = 3.8~7.6 × 108 M−1 s−1) but is inert towards SO4•– (kSO4•– = 4.0~9.1 × 105 M−1 s−1) [48,49]. As shown in Figure S4 and Figure 6a,b, the inhibiting effect of EtOH on BPA degradation in both systems was significantly stronger than that of TBA. Therefore, both •OH and SO4•– should be involved and contribute to BPA degradation, and SO4•– may play a more important role than •OH. In addition, 1O2 is often the essential ROS in Sr-AOTs, especially for the processes involving biochar as the catalyst. Therefore, FFA was used as the scavenger for 1O2 (k1O2 = 1.2 × 108 M−1 s−1) to examine the possible contribution of 1O2 [50]. It can be seen that FFA showed strong inhibition on BPA degradation in both systems, which implied that 1O2 possibly contributed to BPA degradation. However, since FFA also reacts with •OH (k•OH = 1.5 × 1010 M−1 s−1) [51], the generation of 1O2 needs to be further verified by ESR.
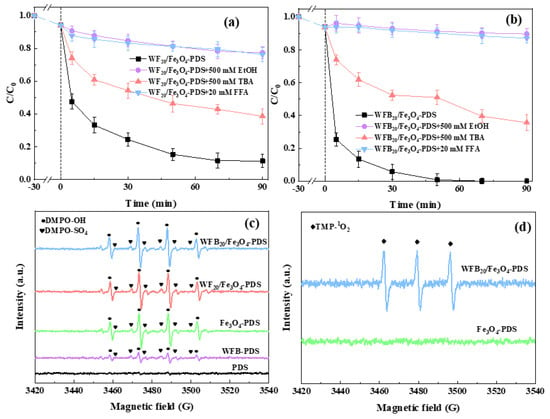
Figure 6.
Effects of different radical scavengers on BPA degradation in (a) WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and (b) WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS systems; (c) DMPO-OH and DMPO-SO4 spectra in different processes; (d) TMP-1O2 spectra in different processes (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1).
2.4.2. ESR Analysis
ESR was performed to confirm the presence of possible ROS in different processes. DMPO was used as the spin trapping agent to identify •OH and SO4•–. As shown in Figure 6c, hardly any signals could be detected in the sole-PDS process, indicating that PDS could hardly self-decompose to generate ROS. This phenomenon was consistent with the results of the catalytic degradation experiment (Figure 4a). When WFB and PDS were added together, DMPO-OH (αN = αH = 14.9 G) and DMPO-SO4 (αN = 13.2 G, αH = 9.6 G, αH = 1.48 G and αH = 0.78 G) signals could be detected, which proved the formation of •OH and SO4•–. The above phenomenon might be due to the activation of PDS by the active sites on WFB (Equations (5) and (6)) [52,53]. It was observed that much stronger signals were detected in the Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS systems, which was consistent with the quenching results (Figure S4 and Figure 6a,b). This might be because Fe(II), with high catalytic activity on Fe3O4 nps, could have reacted with PDS to generate SO4•–, and then the generated SO4•– further reacted with H2O to form •OH (Equations (6) and (7)). Furthermore, TMP was used as the spin trapping agent to trap 1O2 (Figure 6d). The TMP-1O2 (αN = 16.9 G) signal could be detected in the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process, but hardly any signal could be detected in the Fe3O4-PDS process, which was probably due to the formation of 1O2 between WFB and PDS. Therefore, 1O2 should also be the contributor to BPA degradation in the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process.
2.4.3. Identification of High-Valent Iron-Oxo Species
Some previous studies have shown that, during the activation of PDS by Fe(II) or Fe(III), corresponding high-valent iron-oxo species (Fe(IV)=O and Fe(V)=O) can form via double-electron transfer, which can further promote the degradation of pollutants [54,55]. Since Fe3O4 involves both Fe(II) and Fe(III), both Fe(IV)=O and Fe(V)=O are likely to be generated during the activation of PDS. Moreover, according to some previous results of density functional theory calculation, the oxidation capacity of high-valent iron-oxo species under acidic conditions is stronger than that under alkaline conditions [56], which agrees well with the degradation performance of BPA in WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes, as discussed in Section 2.3.1. Therefore, it is necessary to study the existence of high-valent iron-oxo species in this study.
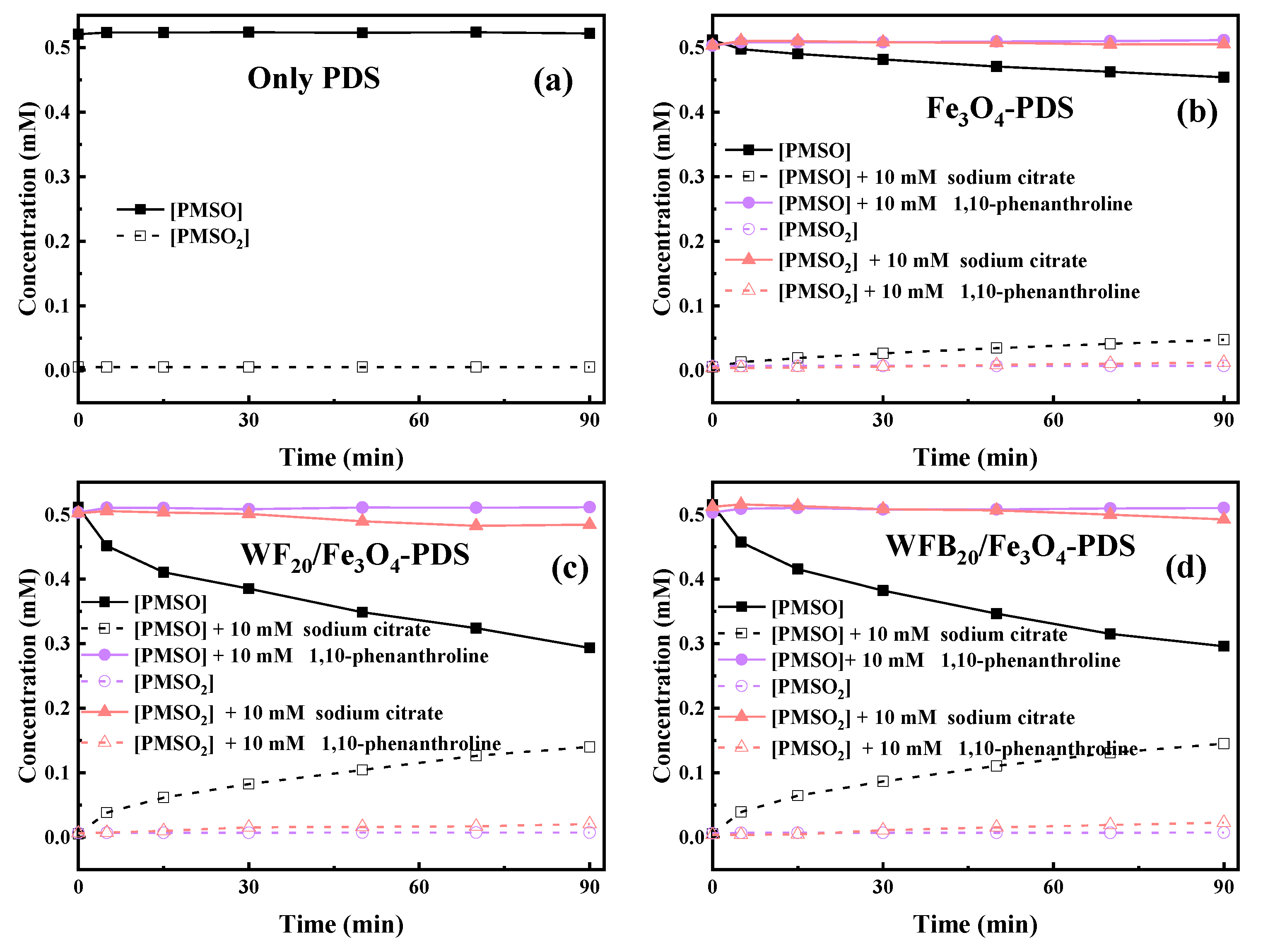
It is known that both Fe(IV)=O and Fe(V)=O can oxidize PMSO to PMSO2 through the oxygen atom transfer pathway (Equations (8) and (9)), differing markedly from radical-mediated routes [57]. The degradation of PMSO and the formation of PMSO2 in different processes are depicted in Figure 7. It can be seen in Figure 7a that PMSO (0.5 mM) could not be oxidized by PDS alone. It was found in Figure 7b–d that 0.057 mM, 0.218 mM, and 0.219 mM of PMSO was degraded within 90 min in Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes, respectively. Correspondingly, about 0.047 mM, 0.140 mM, and 0.145 mM of PMSO2 was generated within 90 min in respective processes, which could well indicate the formation of high-valent iron-oxo species in these three processes. It was also observed that the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process showed a stronger capability to form high-valent iron-oxo species than the WF20/Fe3O4-PDS process. Then, the yield of PMSO2 (η = Δ[PMSO2]/Δ[PMSO]) was quantified to evaluate the contribution of high-valent iron-oxo species to PMSO degradation. Figure S5 shows that η values gradually decreased as the reaction proceeded in the Fe3O4-PDS process, and it was about 80% at 90 min. Comparatively, the η values kept stable at approximately 65% during the reaction in both WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes. Since the PMSO can also be oxidized by •OH and SO4•– via different pathways rather than form PMSO2 [54], the η value below 100% indicated the presence of •OH and/or SO4•–, which was consistent with the results of ESR. Moreover, the majority of PMSO was oxidized to PMSO2, which also indicated that the high-valent iron-oxo species was the dominant contributor to PMSO degradation.
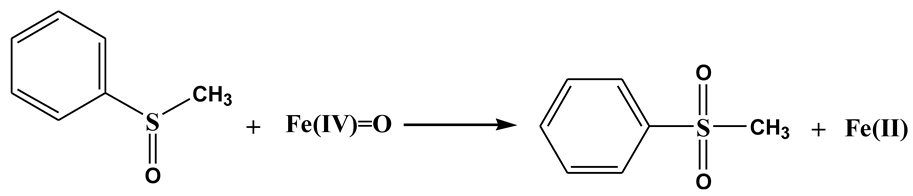
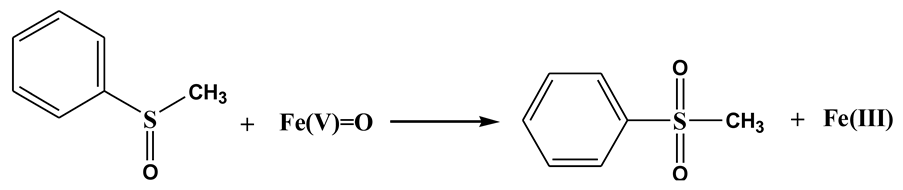


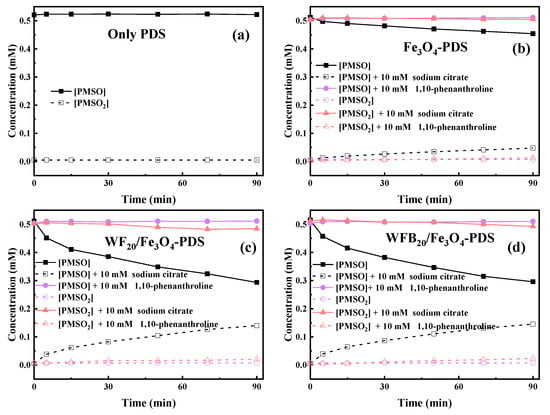
Figure 7.
PMSO degradation and PMSO2 production in the (a) PDS, (b) Fe3O4-PDS, (c) WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and (d) WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS systems (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [PMSO]0 = 0.5 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1).
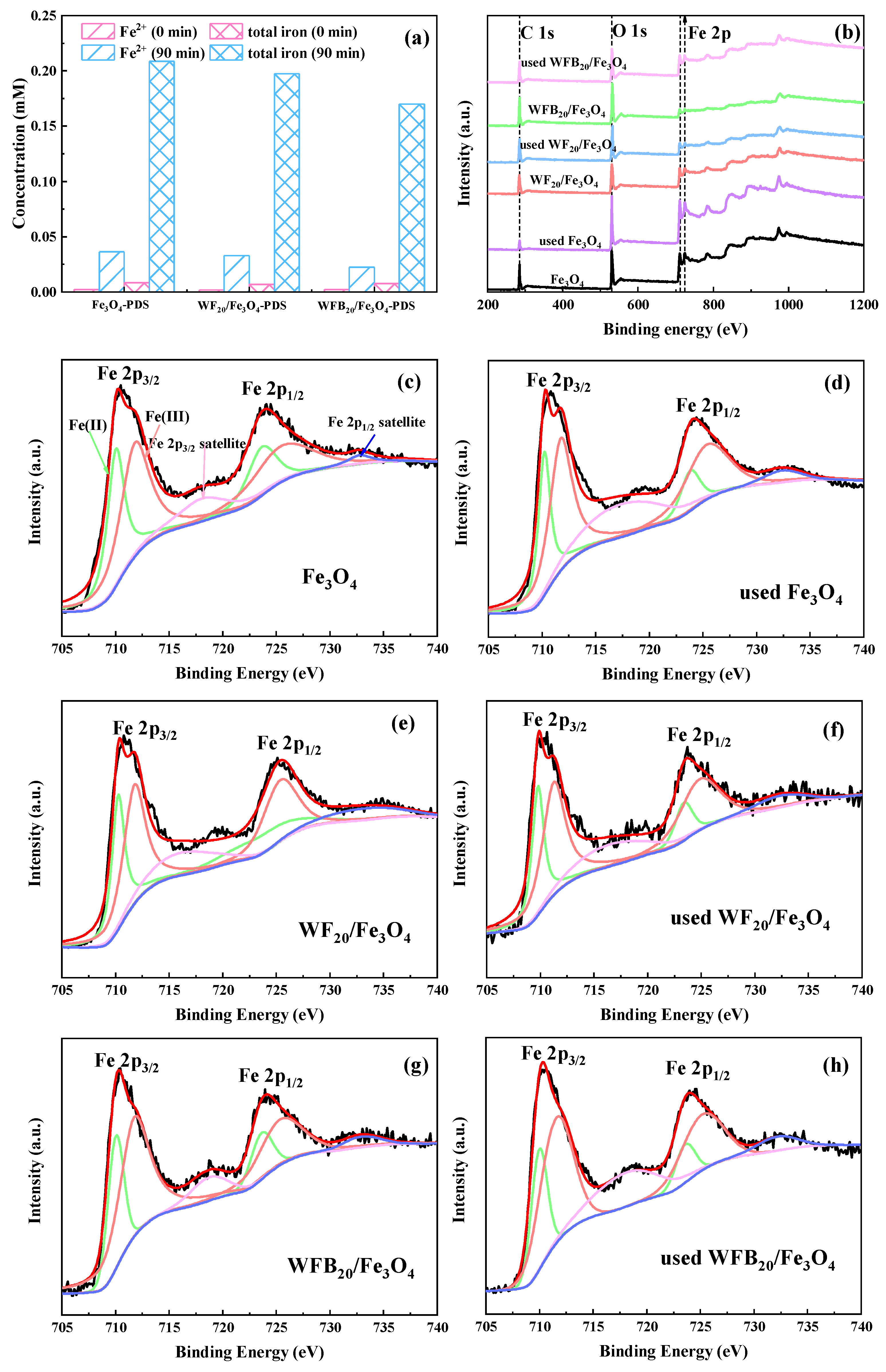
Further investigations were conducted to elucidate the formation mechanisms of high-valent iron-oxo species in Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes. As shown in Figure 8a, the dissolved Fe2+ and dissolved total irons in Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes could be detected, which indicated the presence of homogeneous Fe2+ and Fe3+ during the catalytic reaction. In addition, with the addition of WF or WFB, the total iron dissolution decreased significantly, and the use of WFB as the support could make more significant control of iron dissolution than that of WF. Previous studies showed that Fe2+ could react with PDS to generate Fe(IV)=O under acidic conditions (Equation (10)) [54], but Fe3+ could not [58]. Additionally, the surface ≡Fe(II) and ≡Fe(III) may also play important roles in the generation of high-valent iron-oxo species [55]. Some studies assumed that •OH, SO4•– and ≡Fe(IV)=O could come from the reaction between surface ≡Fe(II) and PDS (Equations (6), (7) and (11)), while ≡Fe(V)=O could come from the reaction between ≡Fe(III) and PDS (Equation (12)) [59]. To further prove the formation mechanisms of high-valent iron-oxo species, chelating agents (sodium citrate and 1,10-phenanthroline) were added to examine the important roles of surface ≡Fe(II) and ≡Fe(III) of Fe3O4 nps. Some studies have reported that ligand exchange could happen between ligands and specific sites of Fe (such as ≡Fe-OH) [55], which could then suppress the capability of catalysts for PDS activation. In other words, 1,10-phenanthroline and sodium citrate could coordinate with Fe(II) and Fe(III) [60], respectively, leading to the inactivation of surface ≡Fe(II) and ≡Fe(III). From Figure 7b–d, it was clearly seen that PMSO degradation and PMSO2 production were obviously suppressed by the addition of 1,10-phenanthroline and sodium citrate. The results manifested that chelating agents indeed suppressed the capability of surface ≡Fe(II) and ≡Fe(III), leading to a decrease of ≡Fe(IV)=O and ≡Fe(V)=O.
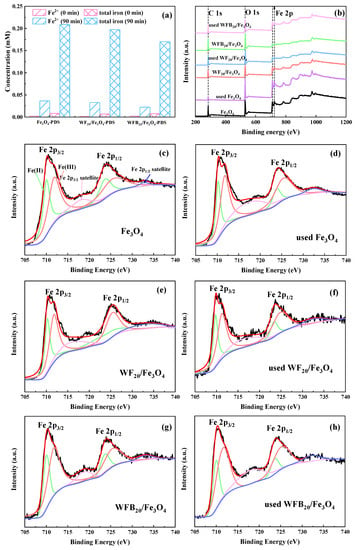
Figure 8.
(a) Concentration of dissolved Fe2+ and total irons in Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS, and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes; the XPS of (b) full survey spectra and (c–h) the Fe 2p spectra of different catalysts (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1).
To sum up, the high-valent iron-oxo species should be mainly produced by two sources: (i) the reaction of dissolved Fe2+ with PDS to form Fe(IV)=O; (ii) the reaction of surface ≡Fe(II) and ≡Fe(III) with PDS to form ≡Fe(IV)=O and ≡Fe(V)=O, respectively.
2.4.4. Active Sites Analysis
The valence state of the Fe element in catalysts was investigated by XPS to further examine the contribution of surface ≡Fe(II) and ≡Fe(III) during the catalytic process. Figure 8b–h showed the XPS full survey spectra and the spectra of Fe 2p of different catalysts. As presented in Figure 8b, C (285.6 eV), O (530.2 eV), and Fe (711.8 eV, 724.3 eV) could be detected in these catalysts [61,62]. The Fe 2p spectrum could be deconvolved into six peaks, with 709.86 eV and 723.46 eV corresponding to Fe 2p3/2, 711.62 eV and 725.22 eV corresponding to Fe 2p1/2 [63], and the peaks at 718.16 eV and 732.14 eV being the satellite peaks of Fe 2p3/2 to Fe 2p1/2 [64], respectively. According to peak intensity, the content of Fe(II) and Fe(III) could be calculated (Table S2). Fe(II) and Fe(III) accounted for 41.56% and 58.44% of total Fe species in Fe3O4, 40.00% and 60.00% in WF20/Fe3O4, and 37.21% and 62.79% in WFB20/Fe3O4, respectively. After the catalytic reaction, the content of Fe(II) decreased to 36.41%, 32.32%, and 32.12%, respectively, and the content ratio of Fe(III) increased in the three catalysts, which indicated that the electrons transferred from Fe(II) to PDS, and thus, the fraction of Fe(III) increased accordingly.
To further study the catalytic mechanism of WFB in WFB20/Fe3O4, FT-IR spectra of fresh WFB and the used WFB were compared (Figure S6). After the catalytic reaction, the C=O groups (1736.27 cm−1) almost disappeared, indicating that the C=O groups on WFB were consumed during the catalytic reaction [65]. Thus, it was assumed that the C=O groups were mainly the functional groups contributing to the catalytic activity of WFB, which was consistent with the findings of previous studies that carbon-based materials containing C=O groups, such as quinone or ketone, could activate PDS to produce 1O2 (Equations (13)–(15)) [66,67].
2.5. Stability and Reusability of Catalysts
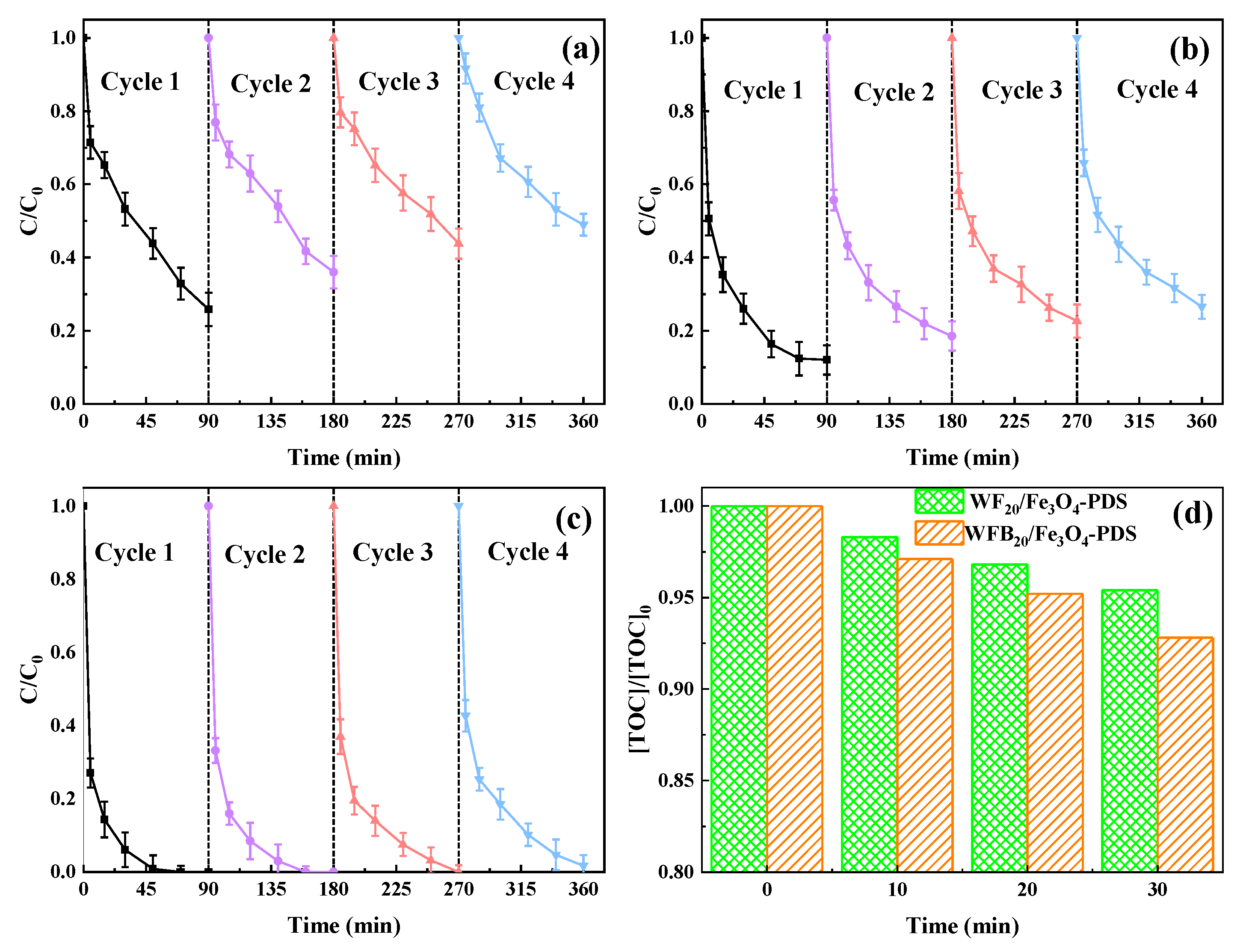
In order to test the stability and reusability of different catalysts, the used catalysts were separated from the reaction solution by a magnet to conduct consecutive catalytic reactions under the same conditions. The separated catalysts were washed with ultrapure water five times, dried in the oven, and directly used for the next cycles. As shown in Figure 9a, the BPA removal rate in the Fe3O4-PDS process decreased from 74% in the first cycle to 51% in the 4th cycle. The decrease of the BPA degradation efficiency was probably due to the agglomeration of Fe3O4 nps and the reduced content of Fe(II) in it. Compared to Fe3O4, both WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4 showed better reusability (Figure 9b,c). Specifically, WFB20/Fe3O4 showed the best reusability with almost all BPA being degraded within 90 min after four cycles. These results were closely related to the following synergistic effects between supports (WF or WFB) and the Fe3O4 nps: (i) the prevention of agglomeration of Fe3O4 nps; (ii) the prevention of leakage of Fe(II). In addition to acting as a carrier, WFB could also react with PDS to form 1O2, thus promoting the degradation of BPA.
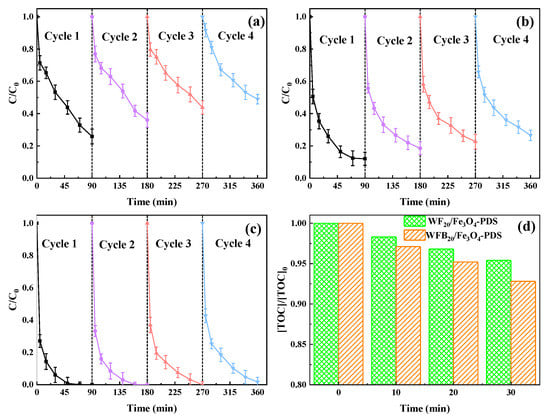
Figure 9.
The removal performance of BPA in four consecutive runs in (a) Fe3O4-PDS, (b) WF20/Fe3O4/-PDS, and (c) WF20/Fe3O4-PDS processes; (d) the TOC removal performance of BPA in WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WF20/Fe3O4-PDS processes (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1).
2.6. Mineralization Performance
The degree of BPA mineralization is also a critical factor to evaluate the catalytic performance of different catalysts. The changes of TOC in WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes are shown in Figure 9d. The TOC removal rate reached 4.6% and 7.2% within 30 min in WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes, respectively, indicating that BPA was more efficiently mineralized in the WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS process.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
BPA (≥99.0%), PDS (K2S2O8, ≥99.0%), FeCl3·6H2O (≥99.0%), FeSO4·7H2O (≥99.0%), p-benzoquinone (p-BQ, ≥98.0%), furfuryl alcohol (FFA, 98%), and tert-butyl alcohol (TBA, ≥99.0%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA. Methanol (MeOH, ≥99.5%), ethanol (EtOH, ≥99.7%), L-histidine, L-ascorbic acid (≥99.7%), CH3COOH (≥99.5%), CH3COONa (≥99.0%), sodium citrate (98%), NH3·H2O (75%), and 1,10-phenanthroline (≥99.0%) were all purchased from Sinopharm Chemical, Shanghai, China. The methyl phenyl sulfoxide (PMSO, 98.0%), methyl phenyl sulfone (PMSO2, 98.0%) and 5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO, 97.0%) were obtained from Macklin, Shanghai, China. The 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethylpiperidine (TMP, ≥98.0%) was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical, Shanghai, China. The dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 99.7%) was obtained from J&K, China. Ultrapure water was used for all experiments and prepared by the HHitech water purification machine.
3.2. Synthesis of the Catalysts
3.2.1. Preparation of WFB
The WFB was prepared by the pyrolysis method. Poplar wood flour with 280–300 mesh size was used as the precursor of WFB, which was obtained from Yixing Wood Flour Factory (Linyi, Shandong Province, China). The wood flour was put into a tubular furnace and heated at 600 °C for 3 h in the N2 atmosphere with a raping rate of 5 °C/min. After cooling down to room temperature, the black product was obtained as the WFB, which was ground into powders for further use.
3.2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4
The coprecipitation method was used to prepare Fe3O4 nanoparticles (nps) [68,69]. Briefly, 2.2992 g FeCl3·6H2O and 1.1831 g FeSO4·7H2O (2:1) were dissolved in 50 mL ultrapure water with N2 purging in advance, which was heated to 80 °C and maintained for 30 min under mild mechanical agitation. Then, 25 mL of 25% (w/w) NH3·H2O was added into the above mixture dropwise until the pH increased to around 10. The mixture was maintained at 80 °C with continuous stirring for 1 h, and N2 was purged throughout to coprecipitate. The solid phase was separated by the external magnetic field, which was then washed repeatedly with ultrapure water until the liquid supernatant was neutral. Finally, the solid mixture was freeze-dried overnight to obtain the Fe3O4 powder.
3.2.3. Preparation of WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4
WF/Fe3O4 and WFB/Fe3O4 composites were also prepared by the coprecipitation method. Different amounts (20, 50, 100, and 200 mg) of WF or WFB were dispersed in 50 mL of ultrapure water with the aid of sonication. After full dispersion, N2 was purged into the mixture to blow out the dissolved oxygen (DO). Then, 2.2992 g FeCl3·6H2O and 1.1831 g FeSO4·7H2O (2:1) were dissolved in the solution, which was heated to 80 °C and maintained for 30 min under mechanical agitation. The remaining steps were the same as the preparation of Fe3O4. The obtained samples with different amounts of WF or WFB were denoted as WFx/Fe3O4 and WFBx/Fe3O4 (x = 20, 50, 100 and 200), respectively.
3.3. Characterization
The morphology of the obtained catalysts was examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, FEI Quanta 200, Portland, OR, USA) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, Hitachi SU8220, Tokyo, Japan). X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were collected by a Rigaku Ultima IV X-ray diffractometer (Tokyo, Japan) with a Cu-Kα radiation source (1.541841 Å). Scanning rate and 2θ collection range were set at 10°/min and 20~70°, respectively. The functional groups on the surface were identified using a Fourier transforms infrared spectrophotometer (FT-IR, Bruker VERTEX 80 V, Billerica, MA, USA) with the wavelength range of 400~4000 cm−1. Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) specific surface area and pore size distribution were investigated by the nitrogen (N2) adsorption-desorption method on a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 HD88 instrument (Norcross, GA, USA). The magnetic properties of catalysts were assessed by a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM, Quantum Design PPMS-9T, San Diego, CA, USA). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Kratos Axis Ultra DLD, Manchester, UK) was used to analyze the surface chemical composition and element valence states.
3.4. Experimental Conditions
Unless otherwise illustrated, all experiments were carried out in a 50 mL beaker at room temperature under mechanical agitation. In a typical experiment, the catalyst with a final concentration of 1.0 g/L was added and dispersed well in 50 mL of BPA solution, and the reaction was initiated by adding PDS to obtain the final concentration of 5.0 mM. At certain time intervals, 1.0 mL of reaction solution was withdrawn, which was immediately mixed with 0.1 mL of MeOH to terminate the reaction and then filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane for further measurement.
For the experiments of PMSO oxidation, the catalyst was dispersed well into the beaker containing a certain amount of PMSO solution, and the reaction was initiated by adding PDS stock solutions. Samples (1.0 mL) were collected at predetermined time intervals and quickly quenched by DMSO (0.1 mL) and filtered through the 0.22 μm membranes into vials for further measurement.
The initial pH was adjusted with 1.0 M H2SO4 or 1.0 M NaOH solution. The batch experiments were conducted in duplicates at least until the errors were below 5%, and the average values obtained were used for plotting.
3.5. Analytical Methods
The BPA concentration was analyzed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC; Dionex Ultimate 3000, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) equipped with a reverse-phase C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm × 5.0 μm) and an ultraviolet and visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry detector, with the detection wavelength set at 225 nm. The mobile phase was a mixture of 70/30% (v/v) methanol and 0.1% phosphoric acid water solution at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The concentrations of PMSO and PMSO2 were detected by an HPLC equipped with a C18-A column (250 mm × 3.0 mm × 3.0 μm) and a UV-Vis detector at wavelengths of 215 nm. The mobile phase was a mixture of 20/80% (v/v) methanol and 0.1% phosphoric acid water solution at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. All of the column temperatures were set at 35 °C. The electron spin resonance (ESR) spectra were obtained by a Bruker EMX-10/12 device with X-band field scanning. The applied instrumental conditions were set as a central magnetic field of 3480 G, resonance frequency of 9.74 GHz, microwave power of 20.00 mW, and sweep time of 30.00 s. The total organic carbon (TOC) concentration was quantified by Analytic Jena multi N/C 3100 TOC. The concentration of total dissolved iron and dissolved Fe2+ in the solution was determined by a spectrophotometric method at 510 nm via forming the complex with 1, 10-phenanthroline [43].
4. Conclusions
In this work, WF and WFB were compared as the supports of Fe3O4 to enhance the PDS activation performance for the degradation of BPA. Results showed that WFB had more significant control of iron dissolution from Fe3O4 than WF. Moreover, WFB/Fe3O4 had a stronger PDS activation capability than WF/Fe3O4, which was likely due to the larger SSA of WFB/Fe3O4 and the PDS activation ability of WFB. Both radicals (•OH and SO4•−) and the non-radical pathways, including 1O2 and high-valent iron-oxo species, contributed to the degradation of BPA in the WFB/Fe3O4-PDS process. In addition, the WFB/Fe3O4 also demonstrated better reusability and stronger BPA mineralization performance during the activation of PDS than WF/Fe3O4. The use of WFB as the support for Fe3O4 may offer a simple and cost-effective option to enhance the PDS activation performance of Fe3O4, which can be applied in organic wastewater treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal13020323/s1, Figure S1: The SEM image of WF; Figure S2: FTIR spectra of different catalysts; Figure S3: Effects of initial solution pH on the degradation of BPA in Fe3O4-PDS process (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1); Figure S4: Effects of different radical scavengers on BPA degradation in Fe3O4-PDS system (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [BPA]0 = 0.02 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1); Figure S5: The calculated η values (η = Δ[PMSO2]/Δ[PMSO]) in Fe3O4-PDS, WF20/Fe3O4-PDS and WFB20/Fe3O4-PDS processes (conditions: catalyst 1.0 g/L, [PDS]0 = 5.0 mM, [PMSO]0 = 0.5 mM, pH0 = 3.00 ± 0.1); Figure S6: FTIR spectra of WFB and used WFB; Table S1: XRD spectral data of Fe3O4, WF20/Fe3O4 and WFB20/Fe3O4 catalysts; Table S2: The content of Fe(II) and Fe(III) in different catalysts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, resources, and funding acquisition: L.X.; methodology, formal analysis, investigation: Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province (2020).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request.
Acknowledgments
The Advanced Analysis and Testing Center of Nanjing Forestry University is acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, G. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in wild freshwater fishes: Species, tissues, sizes and human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, H.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Sweetman, A.; Zhang, Q.; He, M.-C. Estrogens in municipal wastewater and receiving waters in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China: Occurrence and risk assessment of mixtures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hua, S.; Ding, D.; Cai, T.; Zhang, R. Pyrrolic N-rich biochar without exogenous nitrogen doping as a functional material for bisphenol A removal: Performance and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2021, 291, 120093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lai, Y.; Fang, Q.; Li, Z.; Ou, P.; Wu, P.; Duan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Facile fabricate of novel Co(OH)F@MXenes catalysts and their catalytic activity on bisphenol A by peroxymonosulfate activation: The reaction kinetics and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 262, 118099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Z.; Hou, M.; Li, Z.; Dong, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, P.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y. Fe3+/Fe2+ cycle promoted peroxymonosulfate activation with addition of boron for sulfamethazine degradation: Efficiency and the role of boron. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Lu, W.; Tian, G.; Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, L. Enhancement of Sono-Fenton by P25-Mediated Visible Light Photocatalysis: Analysis of Synergistic Effect and Influence of Emerging Contaminant Properties. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.-D.; Lua, S.-K.; Dong, Z.; Lim, T.-T. A novel three-dimensional spherical CuBi2O4 consisting of nanocolumn arrays with persulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation functionalities for 1H-benzotriazole removal. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8149–8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Luo, Y.; Gan, L. ZIF-67(Co)-Loaded Filter Paper for In Situ Catalytic Degradation of Bisphenol A in Water. Separations 2022, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Z.; Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y. Hydroxylamine enhanced treatment of highly salty wastewater in Fe-0/H2O2 system: Efficiency and mechanism study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 271, 118847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Jin, T.; Fu, L.; Pan, Y. Effect of Anions and Cations on Tartrazine Removal by the Zero-Valent Iron/Peroxymonosulfate Process: Efficiency and Major Radicals. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, T.; Chen, J.; Song, S. Synergistically enhanced heterogeneous activation of persulfate for aqueous carbamazepine degradation using Fe3O4@SBA-15. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Fang, X.; Pei, C.; Wu, Y.; Lu, H.; Han, S.; Cui, J.; Shi, J.; et al. Fe3C-porous carbon derived from Fe2O3 loaded MOF-74(Zn) for the removal of high concentration BPA: The integrations of adsorptive/catalytic synergies and radical/non-radical mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, G.; Ghauch, A. Assessment of bimetallic and trimetallic iron-based systems for persulfate activation: Application to sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Ju, C.-J.; Zhang, R.; Hua, J.-Q.; Chen, R.-P.; Liu, G.-X.; Yin, K.; Yu, L. Acceleration of the bio-reduction of methyl orange by a magnetic and extracellular polymeric substance nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Zong, S.; Ren, X.; Liu, D. Atrazine degradation using Fe3O4-sepiolite catalyzed persulfate: Reactivity, mechanism and stability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 377, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Pan, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y. Fe3O4@CNT as a high-effective and steady chainmail catalyst for tetracycline degradation with peroxydisulfate activation: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 118705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Gao, W.; Dong, M.; Han, L.; Qian, L.; Nathanail, C.P.; Chen, M. Degradation of trichloroethylene by activated persulfate using a reduced graphene oxide supported magnetite nanoparticle. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Lin, Q.; He, W.; Fu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Study on the nonradical pathways of nitrogen-doped biochar activating persulfate for tetracycline degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Gan, L. Catalytic Degradation of Bisphenol A in Water by Poplar Wood Powder Waste Derived Biochar via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xu, G.; Gan, L. N Doped Activated Biochar from Pyrolyzing Wood Powder for Prompt BPA Removal via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Sun, P. Biochar-activated peroxydisulfate as an effective process to eliminate pharmaceutical and metabolite in hydrolyzed urine. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Ifthikar, J.; Shi, L.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xi, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Treatment of refractory contaminants by sludge-derived biochar/persulfate system via both adsorption and advanced oxidation process. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Ren, W.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Wood-based biochar as an excellent activator of peroxydisulfate for Acid Orange 7 decolorization. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Huang, D.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y. Activation of persulfate by graphitized biochar for sulfamethoxazole removal: The roles of graphitic carbon structure and carbonyl group. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 577, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Scaria, J.; Ghanbari, F.; Nidheesh, P.V. Sulfate radicals-based advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products: A review on relevant activation mechanisms, performance, and perspectives. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoot-Nezhad, A.; Waclawek, S.; Madihi-Bidgoli, S.; Hassani, A.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. Heterogeneous photocatalytic activation of electrogenerated chlorine for the production of reactive oxygen and chlorine species: A new approach for Bisphenol A degradation in saline wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 445, 130626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, A.; Xu, L.; Gan, L.; Mei, C.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Li, M.; Pan, M.; Han, S.; Cui, J. Using wood flour waste to produce biochar as the support to enhance the visible-light photocatalytic performance of BiOBr for organic and inorganic contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Choi, T.-R.; Park, Y.-L.; Park, J.Y.; Han, Y.-H.; Vyavahare, G.; Jadhav, J.; Song, H.-S.; Yang, P.; et al. Treatment of furazolidone contaminated water using banana pseudostem biochar engineered with facile synthesized magnetic nanocomposites. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-D. The effect of two ferromagnetic metal stripes on valley polarization of electrons in a graphene. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Bokhari, T.H.; Anwar, T.; Khan, U.; Nairan, A.; Khan, K. Graphene oxide coated graphene foam based chemical sensor. Mater. Lett. 2019, 235, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafarzadeh, N.; Ghanbari, F.; Ahmadi, M. Catalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) by nano-Fe2O3 activated peroxymonosulfate: Influential factors and mechanism determination. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranizad, E.S.; Dehghani, Z.; Nadafan, M. Nonlinear optical properties of nematic liquid crystal doped with different compositional percentage of synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 190, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yu, L.; Sun, M.; Cheng, G.; Lan, B.; Fu, Z. Mesoporous alpha-MnO2 microspheres with high specific surface area: Controlled synthesis and catalytic activities. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Dou, X.M.; He, H.; Wang, D.S. Arsenate adsorption on an Fe-Ce bimetal oxide adsorbent: Role of surface properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7246–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; McDonald, A.G.; Freitag, C.; Morrell, J.J. Effects of wood fiber esterification on properties, weatherability and biodurability of wood plastic composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Riaz, U.; Kaushik, A.; Alam, J. Soft Template Synthesis of Super Paramagnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles a Novel Technique. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2009, 19, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. A novel porous carbon derived from hydrothermal carbon for efficient adsorption of tetracycline. Carbon 2014, 77, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, R.; Fan, X.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. A novel S-scheme heterojunction in spent battery-derived ZnFe2O4/g-C3N4 photocatalyst for enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation and visible light degradation of organic pollutant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, F.; Moradi, S.; Saei, S.F.; Madani, Z.; Giannakis, S.; Isari, A.A.; Kakavandi, B. A novel, Z-scheme ZnO@AC@FeO photocatalyst, suitable for the intensification of photo-mediated peroxymonosulfate activation: Performance, reactivity and bisphenol A degradation pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Eghbali, P.; Mahdipour, F.; Waclawek, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. Insights into the synergistic role of photocatalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate by UVA-LED irradiation over CoFe2O4-rGO nanocomposite towards effective Bisphenol A degradation: Performance, mineralization, and activation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qi, L.; Han, Y.; Lu, W.; Han, J.; Qiao, W.; Mei, X.; Pan, Y.; Song, K.; Ling, C.; et al. Improvement of Fe2+/peroxymonosulfate oxidation of organic pollutants by promoting Fe2+ regeneration with visible light driven g-C3N4 photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kong, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Liu, G.; Li, F.; Lv, W. A sulfate radical based ferrous-peroxydisulfate oxidative system for indomethacin degradation in aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22802–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lai, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Yi, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, F.; et al. Role of radical and non-radical pathway in activating persulfate for degradation of p-nitrophenol by sulfur-doped ordered mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lai, L.; Yang, X. Sewage sludge conditioning by Fe(II)-activated persulphate oxidation combined with skeleton builders for enhancing dewaterability. Water Environ. J. 2016, 30, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Lu, F.; Wei, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Magnetic recoverable MnFe2O4 and MnFe2O4-graphene hybrid as heterogeneous catalysts of peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient degradation of aqueous organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.-D.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Zhou, D.-M. Superoxide radical driving the activation of persulfate by magnetite nanoparticles: Implications for the degradation of PCBs. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 129, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Pan, Y. Promotion of the degradation perfluorooctanoic acid by electro-Fenton under the bifunctional electrodes: Focusing active reaction region by Fe/N co-doped graphene modified cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L. Singlet Oxygen Formation from Wastewater Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8179–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Banerjee, G.; Brudvig, G.W.; Kim, J.-H.; Pignatello, J.J. Oxidation of Organic Compounds in Water by Unactivated Peroxymonosulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5911–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H.; Chen, S.; Ren, X. Magnetic nitrogen-doped sludge-derived biochar catalysts for persulfate activation: Internal electron transfer mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Xiao, R.; Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; et al. Insight into the mechanism of persulfate activated by bone char: Unraveling the role of functional structure of biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Pang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Qu, W.; Jiang, C. Is Sulfate Radical Really Generated from Peroxydisulfate Activated by Iron(II) for Environmental Decontamination? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11276–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shan, C.; Pan, B. Fe(III)-Doped g-C3N4 Mediated Peroxymonosulfate Activation for Selective Degradation of Phenolic Compounds via High-Valent Iron-Oxo Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, D.; Ma, J. Comparative study on ferrate oxidation of BPS and BPAF: Kinetics, reaction mechanism, and the improvement on their biodegradability. Water Res. 2019, 148, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.-Y.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Oxidation of Sulfoxides and Arsenic(III) in Corrosion of Nanoscale Zero Valent Iron by Oxygen: Evidence against Ferryl Ions (Fe(IV)) as Active Intermediates in Fenton Reaction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Zhou, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Lai, B. Reducing agents enhanced Fenton-like oxidation (Fe(III)/Peroxydisulfate): Substrate specific reactivity of reactive oxygen species. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Ao, Z.; Pan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Yao, G.; Lai, B. Activation of peroxydisulfate by natural titanomagnetite for atrazine removal via free radicals and high-valent iron-oxo species. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Yin, J.J. Core-Shell Structure Dependent Reactivity of Fe@Fe2O3 Nanowires on Aerobic Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5344–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Efficient activation of persulfate by a magnetic recyclable rape straw biochar catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Ling, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. Superhigh co-adsorption of tetracycline and copper by the ultrathin g-C3N4 modified graphene oxide hydrogels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Ain, Q.; Rasheed, U.; Yaseen, M.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Z. Superior dye degradation and adsorption capability of polydopamine modified Fe3O4-pillared bentonite composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Dionysiou, D.D. Facile preparation of porous Mn/Fe3O4 cubes as peroxymonosulfate activating catalyst for effective bisphenol A degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chang, Z.-Y.; Wang, L.-L.; Cheng, W.-X.; Chen, R.-P.; Yu, L.; Qiu, X.-H.; Han, J.-G. Solid-liquid separation of real cellulose-containing wastewaters by extracellular polymeric substances: Mechanism and cost evaluation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Peng, X.; Jia, X.; Wong, P.K. N-doped biochar from sewage sludge for catalytic peroxydisulfate activation toward sulfadiazine: Efficiency, mechanism, and stability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Pang, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Lu, X.-T.; Yuan, L.-P. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Benzoquinone: A Novel Nonradical Oxidation Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12941–12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, P.; Chang, P.R.; Ma, X. Preparation and characterization of magnetic rectorite/iron oxide nanocomposites and its application for the removal of the dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mohan, D. Magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle synthesis and applications for lead (Pb2+) and chromium (Cr6+) removal from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).