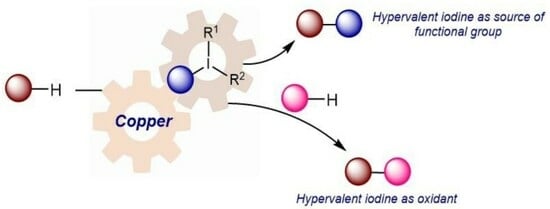
Copper-Catalyzed/Hypervalent Iodine-Mediated Functionalization of Unactivated Compounds
Abstract
Share and Cite
Papis, M.; Foschi, F.; Colombo, S.; Beccalli, E.M.; Loro, C.; Broggini, G. Copper-Catalyzed/Hypervalent Iodine-Mediated Functionalization of Unactivated Compounds. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091243
Papis M, Foschi F, Colombo S, Beccalli EM, Loro C, Broggini G. Copper-Catalyzed/Hypervalent Iodine-Mediated Functionalization of Unactivated Compounds. Catalysts. 2023; 13(9):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091243
Chicago/Turabian StylePapis, Marta, Francesca Foschi, Sara Colombo, Egle Maria Beccalli, Camilla Loro, and Gianluigi Broggini. 2023. "Copper-Catalyzed/Hypervalent Iodine-Mediated Functionalization of Unactivated Compounds" Catalysts 13, no. 9: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091243
APA StylePapis, M., Foschi, F., Colombo, S., Beccalli, E. M., Loro, C., & Broggini, G. (2023). Copper-Catalyzed/Hypervalent Iodine-Mediated Functionalization of Unactivated Compounds. Catalysts, 13(9), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13091243