Abstract
Aromatic volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are toxic to public health and contribute to global air pollution; thus, it is urgent to control VOC emissions. Catalytic oxidation technology has been widely investigated to eliminate aromatic VOCs; this technology exhibits high catalytic efficiency even at low temperatures. However, the reaction mechanism of aromatic VOCs’ total oxidation over metal-oxide-based catalysts, which is of great significance in the design of catalysts, is not yet clear. In this study, we systemically calculated the catalytic oxidation mechanism of toluene over the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 catalyst using density functional theory (DFT). The results show that toluene first loses hydrogen from the methyl group via oxy-dehydrogenation and is gradually oxidized by lattice or adsorbed oxygen to benzyl alcohol, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid following the Mars-van Krevelen (MVK) mechanism. Afterwards, there is a decarboxylation step to produce phenyl, which is further oxidized to benzoquinone. The rate-determining step then proceeds via the ring-opening reaction, leading to the formation of small molecule intermediates, which are finally oxidized to CO2 and H2O. This work may provide atomic-scale insight into the role of lattice and adsorbed oxygen in catalytic oxidation reactions.
1. Introduction
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are recognized as vital contributors to air pollution and are hazardous to the environment and to public health. VOCs can lead to ground level or tropospheric ozone, photochemical smog, and secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation [1,2,3]. Toluene is a typical aromatic VOC that is released in industrial processes and automobile exhausts; toluene has a high photochemical ozone creativity potential (POCP), which causes toluene to be more toxic [4,5,6]. Apart from the atmospheric environmental risk, many aromatic VOCs can irritate the respiratory system, affect the central nervous system, and are known carcinogens, even at very low concentrations [7]. Accordingly, a great deal of effort has been put into controlling the emissions of toluene [8,9].
Among the most common technologies used for the elimination of VOCs are absorption, catalytic oxidation and thermal oxidation [10,11]. Catalytic oxidation can operate at relatively low temperatures (around 250–500 °C), minimize the formation of secondary hazardous air pollutants, and has high efficiency at a low pollutant concentration [12,13]. These advantages make catalytic oxidation the most popular one. Catalytic oxidation by noble metal catalysts (mainly Au, Pt, and Pd) is considered the most effective method for removing VOCs [14,15]. However, the high cost and low resistance to poison of these catalysts have greatly restricted their applications. Transition metal oxides, including Al2O3, CeO2, ZrO2, CoOx, MnOx, and CuO, have attracted widespread attention as they are inexpensive alternatives to noble metals [16,17,18,19]. Among them, CeO2 has attracted much attention due to its high oxygen storage capacity. The intricate interplay between 4f–2p overlap of the Ce–O bond and 4f orbital of Ce governs the bonding properties of CeO2 [20]. The 4f orbital of Ce has strong electronic localization, which leads to the formation and filling of O vacancies and active surface O2 species [21]. And the introduction of ZrO2 can significantly reduce the formation energy of O vacancy [22]. In recent years, ceria-zirconia mixed metal oxide (Ce1−xZrxO2) catalysts have attracted much attention regarding the total oxidation of VOCs [23,24]. In our previous study, we calculated that Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 exhibits the best performance in effectively releasing surface lattice oxygen throughout the entire composition range of Ce1−xZrxO2 (x = 0.125, 0.250, 0.375, 0.500, 0.625, 0.750, 0.875) [25]. Moreover, incorporating Zr in the CeO2 lattice can greatly improve the thermal resistance of high temperature VOCs’ combustion [26]. Shah et al. conducted the total oxidation of propane and naphthalene on Ce1−xZrxO2 catalysts, and they found that VOCs’ catalytic oxidation activity is strongly correlated to the concentration of surface oxygen defects [23]. de Rivas et al. also proved that Ce1−xZrxO2 catalysts exhibit excellent catalytic performance for the degradation of chlorinated VOCs [24].
The oxidation kinetics and mechanism of aromatic VOCs’ (benzene, toluene) abatement over metal-oxide-based catalysts usually follows the Mars-van Krevelen (MVK) model [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. This mechanism is divided into two steps: the first step is to use catalyst lattice oxygen for reactant oxidation, where lattice oxygen will be replaced, and the second step is oxidation by atoms from dioxygen. Dou et al. studied the catalytic oxidation of toluene by CuO/CeO2–ZrO2 and found that Cu/Ce–Zr-100 exposed the (110) and (100) crystal planes of CeO2, which were prone to generating more oxygen vacancies. Research also found that the oxidation process of toluene on CuO/CeO2–ZrO2 catalyst can be explained by the Mars van Krevelen mechanism. After being activated by active sites, toluene molecules react with lattice oxygen in CuO/CeO2–ZrO2 catalysts, followed by gaseous oxygen oxidation of the catalyst [31]. Menon et al. used a transient response technique called the temporal analysis of products to study the detailed mechanism for toluene oxidation over CuO–CeO2/Al2O3; isotope-exchange experimental products containing 16O and 18O when the catalyst was pretreated with 16O2 and dioxygen was isotopically labeled with 18O2, indicating that not only gas-phase oxygen but also lattice oxygen is involved in the reaction [32]. Furthermore, infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (in-situ DRIFTS) and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) were performed to identify the by-products and probable reaction pathway in the total oxidation of toluene [33,34,35,36]. However, short-lived intermediates often cannot be detected through experimental processes, and highly complex and overlapping spectra make it difficult to correctly identify the reaction intermediates [37]. Therefore, the surface oxidation mechanisms of toluene over metal-oxide-based catalysts are not yet clear, which is of great significance in the design of catalysts. Due to the difficulty in detecting and processing intermediates, the experimental exploration of catalytic oxidation mechanisms is not easy, and theoretical calculations can provide information for the reaction’s intermediates and pathways. Previous studies have shown that density functional theory (DFT) calculations can provide a feasible method for studying the mechanism of catalytic oxidation reactions [25,38,39].
In this paper, by using periodic density functional theory (DFT) computations, the catalytic mechanism of toluene’s total oxidation to carbon dioxide and water on the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface is systematically calculated. This investigation provides a basic mechanism to further explore the catalytic destruction behavior of mixed VOCs. The formation of intermediates is consistent with the byproducts that are detected in toluene’s total oxidation experiments.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Tests of Computational Conditions
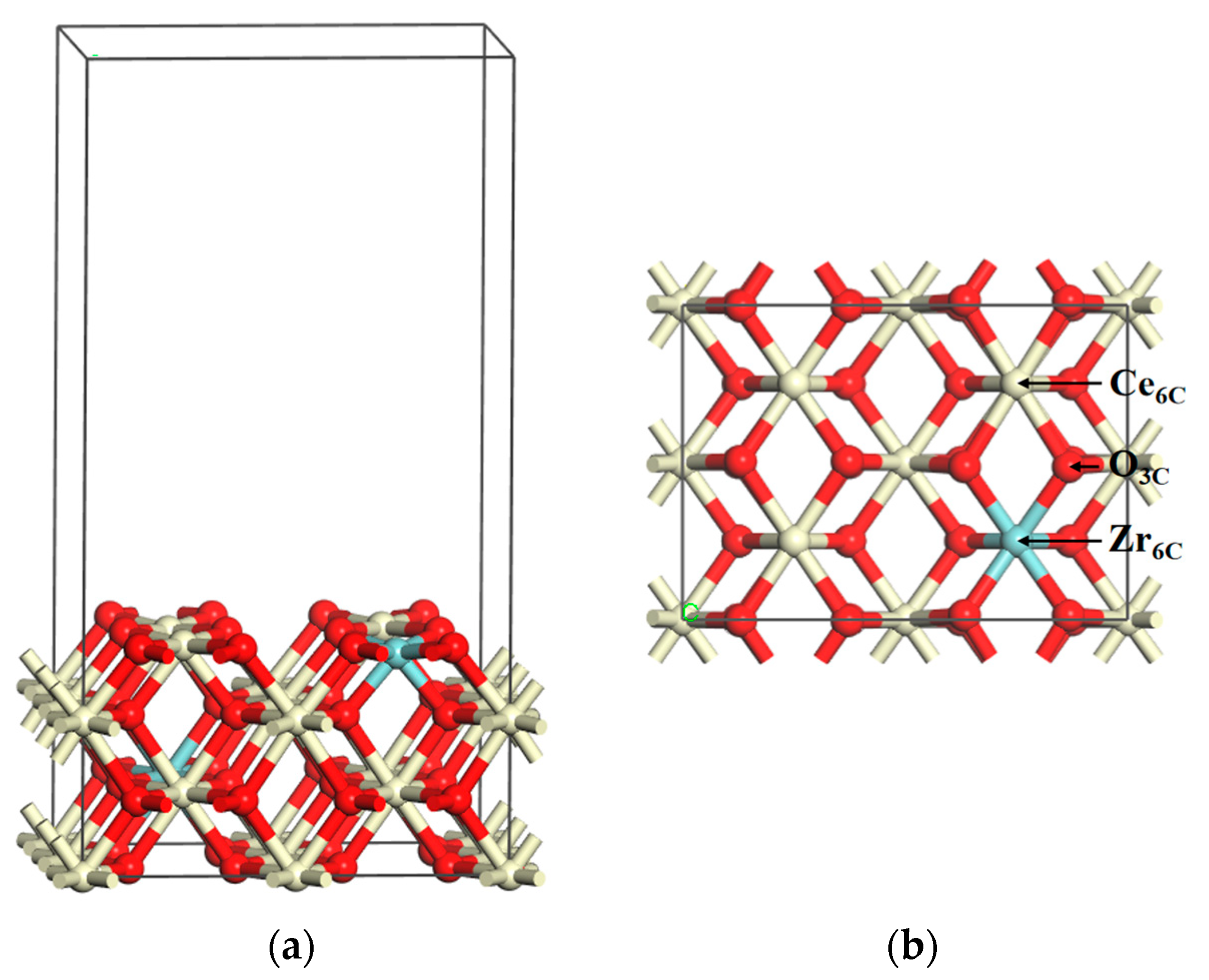
To validate the methods, we compared the bond length of O2, CO2, and H2O with the available values that were calculated at the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level [40]. Here the energy of O2, CO2, and H2O was calculated in a large unit cell of 10 Å × 10 Å × 10 Å, and all of the bond distances were within 1% of the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level (Table 1). In bulk relaxation calculations, the lattice parameter of CeO2 is 5.478 Å, which is nearly equivalent to the experimental value of 5.411 Å [41]. As shown in Figure 1, the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface has six-fold coordinated Ce (Ce6C), six-fold coordinated Zr (Zr6C), and three-fold coordinated O (O3C) atoms. The bond lengths of Ce6C–O3C and Zr6C–O3C are determined to be 2.380 Å and 2.230 Å, respectively, and these values are consistent with the previous theoretical results (2.360 Å and 2.240 Å, respectively) [38]. These results indicate that the calculation methods given above and the catalyst model are reliable.

Table 1.
The bond distances for O2, CO2, and H2O molecules.
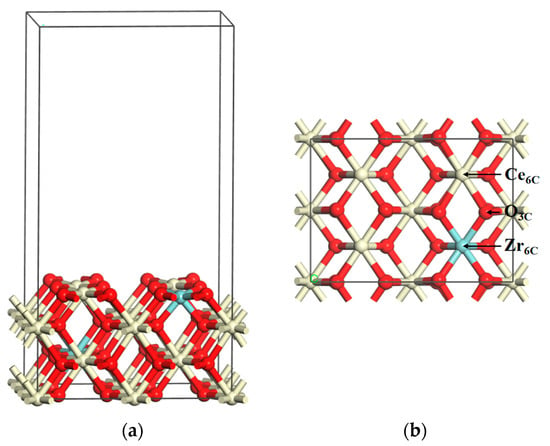
Figure 1.
Schematic structure models for the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface: (a) side view and (b) top view. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red.
2.2. Reaction Mechanism of Toluene Total Oxidation over the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) Surface
Recently, the total oxidation mechanism of short chain organic compounds, such as methanol and 1,2-dichloroethane, have been investigated in detail [39,42]. However, the theoretical study of aromatic VOCs oxidation pathways is still limited. In the present work, we systematically calculated the reaction scheme for toluene oxidation on a Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110)-supported catalytic system. We discuss the entire pathway in three parts: methyl group oxidation reaction, ring-opening reaction, and oxidation reaction of small molecule intermediates.
2.2.1. Pathway for Methyl Group Oxidation
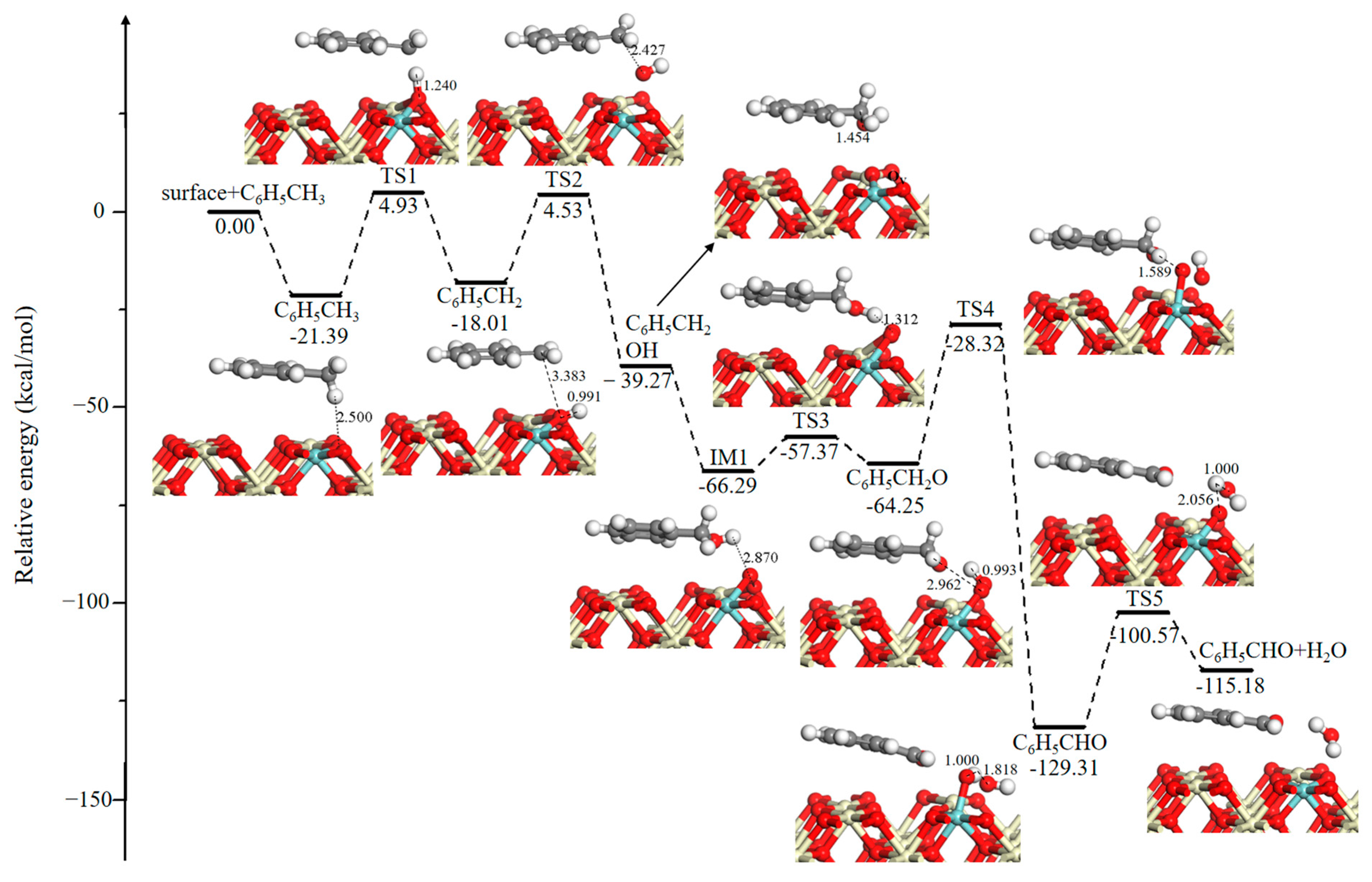
The reaction scheme of metal oxide models begins with the adsorption of toluene on Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) with an aromatic ring parallel to the exposed surface, and as shown in Figure 2, a H atom of the methyl group interacts with surface oxygen bonded to Ce and Zr atoms, which exhibit relatively higher activity [25]. In Figure 2, IM refers to an intermediate state and TS refers to a transition state. The cartesian coordinates for all the optimized structures of reactants, IMs, TSs and products have been shown in Table S1. This adsorption reaction is determined to have an exothermicity of −21.39 kcal/mol. Then, an H atom of the methyl group is abstracted leading to the formation of the C6H5CH2 fragment, and the resulting H atom combines strongly with a surface O atom to form a hydroxyl group (–OH). This step needs to overcome an energy barrier of 26.32 kcal/mol. Subsequently, the C6H5CH2 fragment is oxidized by –OH to generate benzyl alcohol (C6H5CH2OH) and a surface oxygen vacancy (OV) with a reaction barrier of 22.54 kcal/mol. Meanwhile, another pathway of the C6H5CH2 reaction with an adjacent O atom is also created, but this process has a higher barrier of 36.88 kcal/mol. Therefore, only the benzyl alcohol formation pathway is further considered. Followed by the dissociative adsorption of a dioxygen molecule including coordination, electron transfer, and dissociation, next O2 replenishes an oxygen vacancy with a strong exothermicity of −27.02 kcal/mol [32]. As shown in Figure 2, benzyl alcohol (C6H5CH2OH) is further oxidized to benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) through two dehydrogenation steps, and the located transition states are TS3 (8.92 kcal/mol) and TS4 (35.93 kcal/mol), respectively. Then, recombination of the neighboring surface hydroxyl groups via TS5 (28.74 kcal/mol) leads to the formation of H2O.
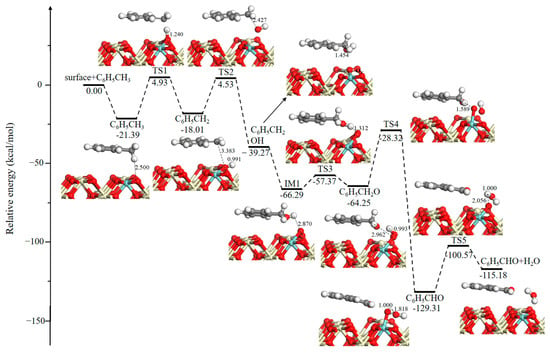
Figure 2.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of the methyl group oxidation reaction for H2O formation. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
The reaction scheme that we proposed above is perfectly consistent with the MVK mechanism, in which the reactant is oxidized by lattice oxygen, and the lattice oxygen is re-oxidized by atoms that originate from dioxygen [27]. According to the in-situ DRIFT results, benzyl alcohol, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid were observed in the case of toluene total oxidation, which suggests that our investigation provides a reliable atomic-scale insight for the toluene oxidation mechanism [33]. The pathway for the formation of benzoic acid is described below.
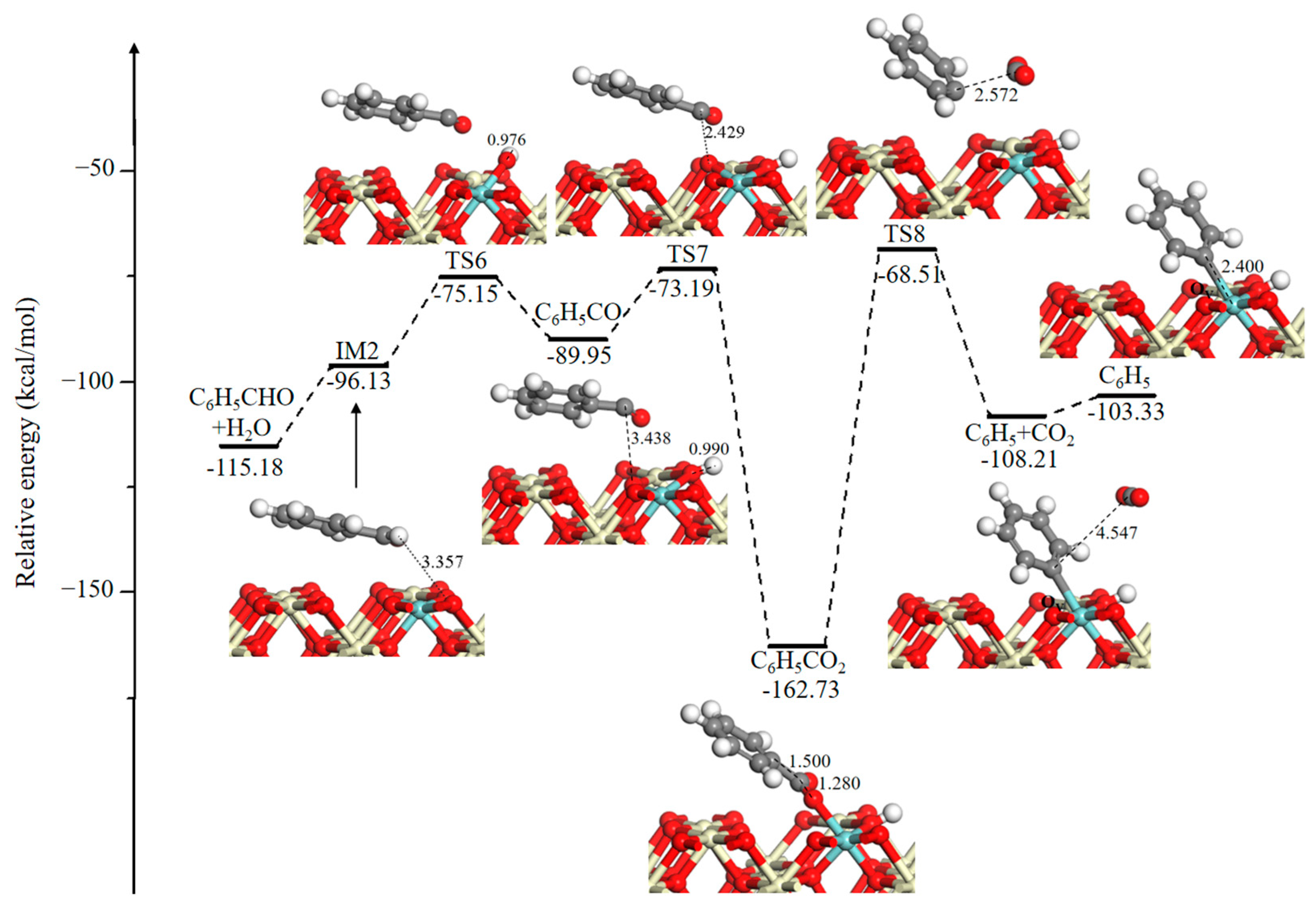
Figure 3 shows the potential energy profile and corresponding optimized configurations of the methyl group oxidation reaction to form CO2. The desorption of H2O molecule (Figure 3, IM2) into the gas phase requires 19.05 kcal/mol. Hydrogen abstraction of an aldehyde group has an energy barrier of 20.98 kcal/mol. Then, the C6H5CO fragment is fully oxidized by lattice O and leads to the formation of a carboxyl group (C6H5CO2). This step is energetically more favorable with a lower energy barrier of 16.76 kcal/mol and a strong exothermicity of 72.78 kcal/mol. Subsequently, the C6H5CO2 fragment directly dissociates via decarboxylation into a phenyl group (C6H5) and a CO2 molecule, and the higher reaction barrier is computed to be 94.22 kcal/mol, suggesting that decarboxylation is kinetically unfavorable. This step can be verified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) experiments, the results of which found that the characteristic peaks of benzene are observed during toluene oxidation on the CoAlCeO catalyst [17]. Menon et al. also proved that the abstraction of a C atom of methyl group prior to those in phenyl group [32]. The CO2 molecule is easily desorbed with a desorption energy of only 4.88 kcal/mol.

Figure 3.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of the methyl group oxidation reaction for CO2 formation. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
2.2.2. Pathway for Ring-Opening Reaction
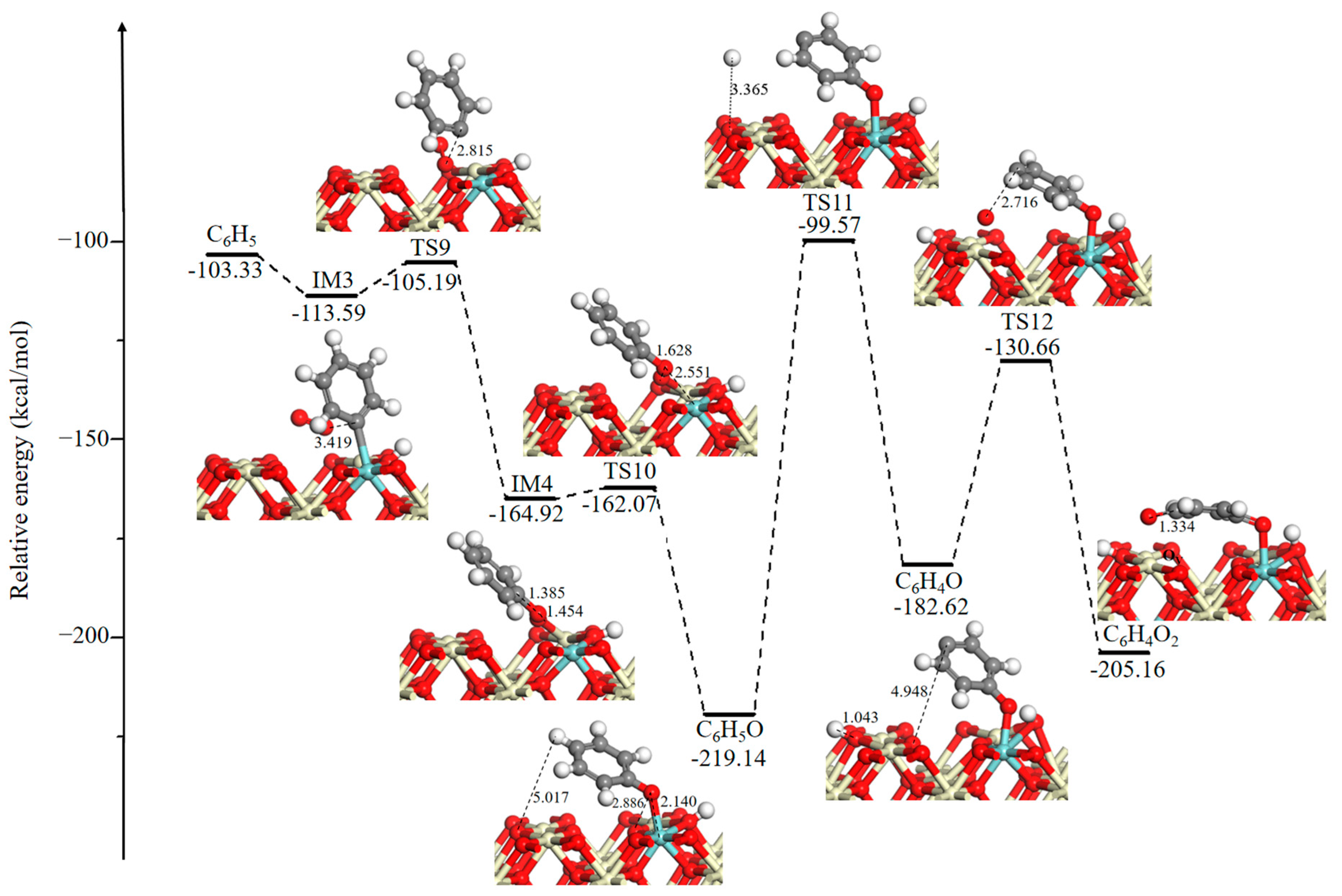
To date, the catalytic oxidation of benzene has been widely studied [43,44,45,46,47,48]. The reaction scheme assumes that benzene is gradually oxidized to phenolate, benzoquinone, maleate, acetate, and other intermediates by active oxygen species, and eventually, it is oxidized to CO2 and H2O [45,46,47]. Figure 4 represents the potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized structures of the ring-opening reaction for the p-benzoquinone formation. After the desorption of CO2, a new OV and a phenyl group (C6H5) are left at the interface. Then, an O2 molecule will adsorb at the OV site with a binding energy of 10.26 kcal/mol. This is followed by two almost barrierless steps in which an O–O bond dissociates to oxidize the phenyl group and to replenish OV. After that, a relatively stable intermediate phenolate species (C6H5O) is determined on the catalytic surface. The oxygen-containing group in the phenolate species is generally regarded as an ortho-para position director and an electron donor [46]. Successively, the para-position of the hydrogen of C6H5O is abstracted by three-fold coordinated oxygen through TS11. This H-stripping step needs a high activation energy barrier of 119.57 kcal/mol, because of the long distance between the para-position of the H atom and three-fold coordinated O atom, which is 5.017 Å. The produced C6H4O fragment bonds to another adjacent surface O3C to form a p-benzoquinone species (C6H4O2) and a surface OV by passing through TS12 (51.96 kcal/mol). Unfortunately, the reaction pathway of the o-benzoquinone formation on the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface is not given in this study, but it was detected by experimental measurement [44,46,48].

Figure 4.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of ring-opening reaction for p-benzoquinone formation. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
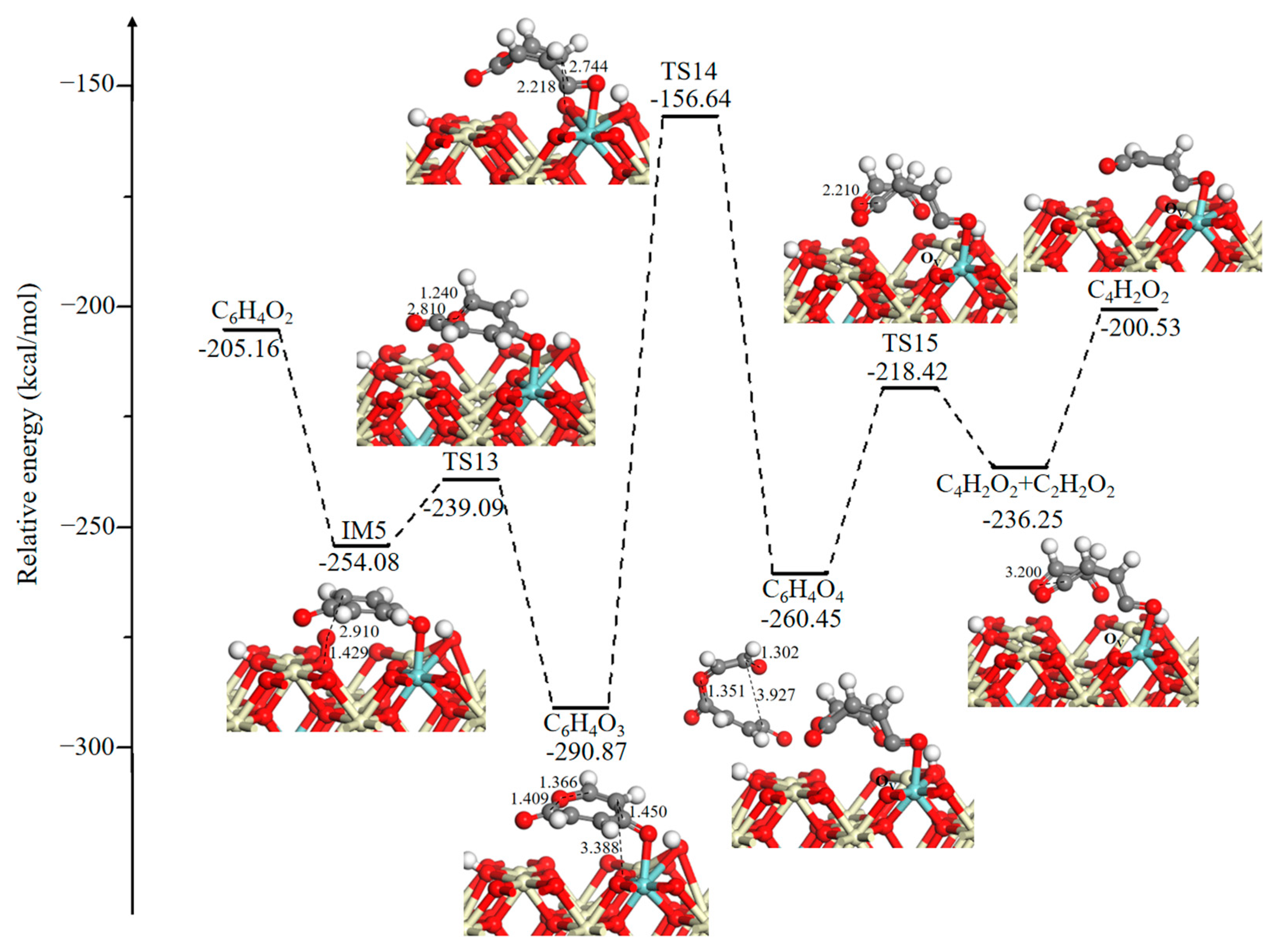
The potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized intermediates, transition states, and final state configurations of the ring-opening reaction for the formation of small molecule intermediates are shown in Figure 5. It is seen that the generated surface OV is incorporated by the O2 gas phase, and the energy released from O2 adsorption is −48.92 kcal/mol. Then, the active O is added to the benzene ring via an addition reaction through TS13 (14.99 kcal/mol), and this leads to the formation of a seven-membered ring intermediate 2,5-oxepindione (C6H4O3). Next, a surface O3C moves toward a C atom of the seven-membered ring, it leads to the opening of the seven-membered ring and produces the C6H4O4 intermediate. During this process, the distance between O and C atoms gradually decreases as follows: 3.388 Å (C6H4O3)→2.218 Å (TS14)→1.302 Å (C6H4O4). This process has a large activation energy barrier of 134.23 kcal/mol, determining the rate of the total oxidation, which is in line with the experimental observations. It has been experimentally reported that the occurrence of a ring-opening reaction needs a higher temperature, and it is an essential rate-controlling step [36,49]. Successively, the C–O bond (bond distance is 1.351 Å) in the C6H4O4 intermediate directly dissociated into 1,3-butadiene-1,4-dione (C4H2O2) and glyoxal (C2H2O2) through TS15 (42.03 kcal/mol). Desorption of the glyoxal (C2H2O2) intermediate costs 35.72 kcal/mol.
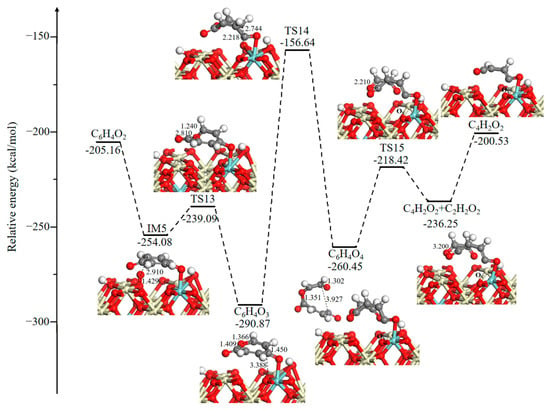
Figure 5.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of ring-opening reaction for the formation of small molecule intermediates. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
2.2.3. Pathway for Oxidation of Small Molecule Intermediates
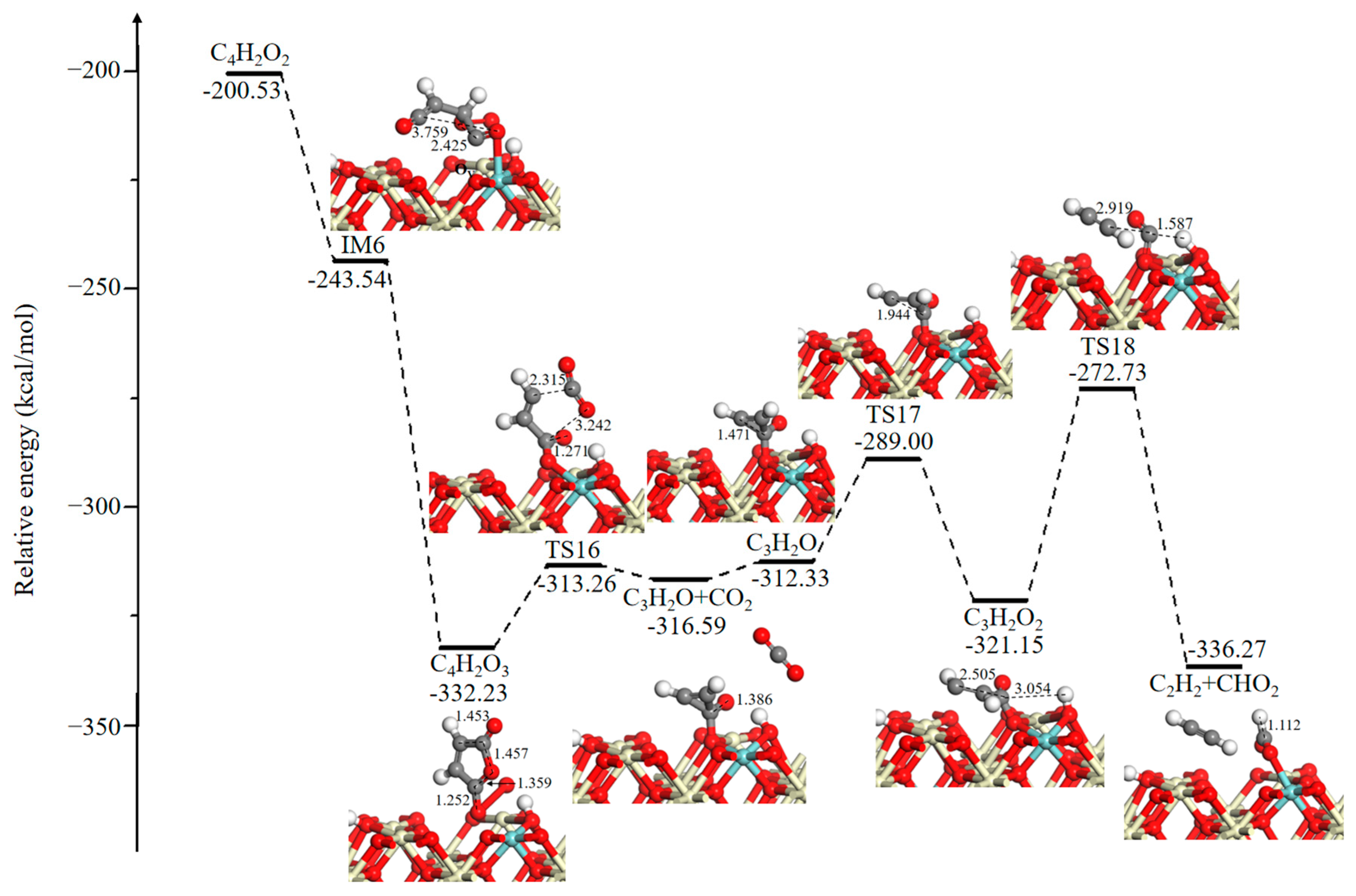
As presented in Figure 6, an O2 molecule is adsorbed on a surface OV site to form the coadsorption structure IM6 with 1,3-butadiene-1,4-dione (C4H2O2), accompanied by the release of 43.01 kcal/mol of energy. Then, the maleic anhydride species (C4H2O3) will be generated on the catalytic surface through a barrierless process. This process is thermodynamically favorable with a strong exothermicity of 88.69 kcal/mol. The subsequent process involves dissociation of C4H2O3 to produce 2-cyclopropen-1-one (C3H2O) and CO2 with an energy barrier of 18.97 kcal/mol. Desorption of CO2 requires 4.26 kcal/mol. For the adsorbed C3H2O species, two HC–CO bonds broke through TS17 (23.33 kcal/mol) and TS18 (48.42 kcal/mol) and led to the formation of acetylene (C2H2), while the CO that was formed combined with a surface O atom and a neighboring H atom to produce a CHO2 species.

Figure 6.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of small molecule intermediates’ oxidation reaction for C4H2O2 oxidation. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
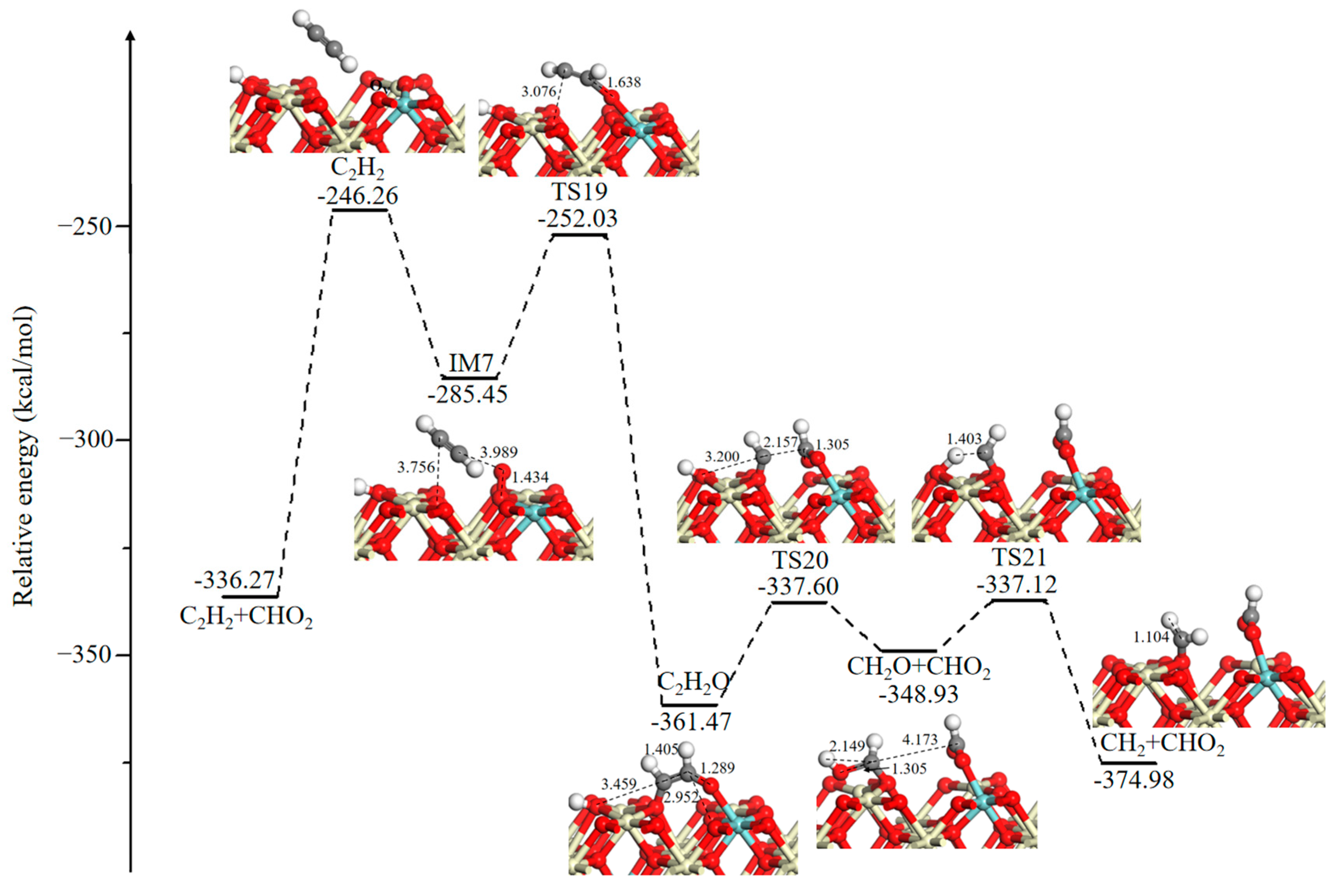
Another oxidation pathway of acetylene (C2H2) is illustrated in Figure 7. The resulting CHO2 species can be desorbed into the gas phase with an endothermic energy of 90.01 kcal/mol and leaves behind a new OV. Then, gaseous O2 is adsorbed at the OV site with a binding energy of 39.19 kcal/mol. The adsorbed acetylene (C2H2) moves toward the active oxygen to form a relatively stable intermediate ethenone (C2H2O) via an exothermic process (−76.02 kcal/mol) with an energy barrier of 33.42 kcal/mol. Ethenone (C2H2O) can break its HC–CHO bond through TS20 (23.87 kcal/mol), and the separated HC bonds with the adjacent –OH and CHO bonds to the adjacent surface O3C to form CH2O and CHO2 intermediates, respectively. In the next step, the O atom of the CH2O intermediate replenishes the lattice O site with a small barrier of 11.81 kcal/mol, and this leads to the formation of the CH2 fragment.

Figure 7.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of small molecule intermediates’ oxidation reaction for C2H2 oxidation. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
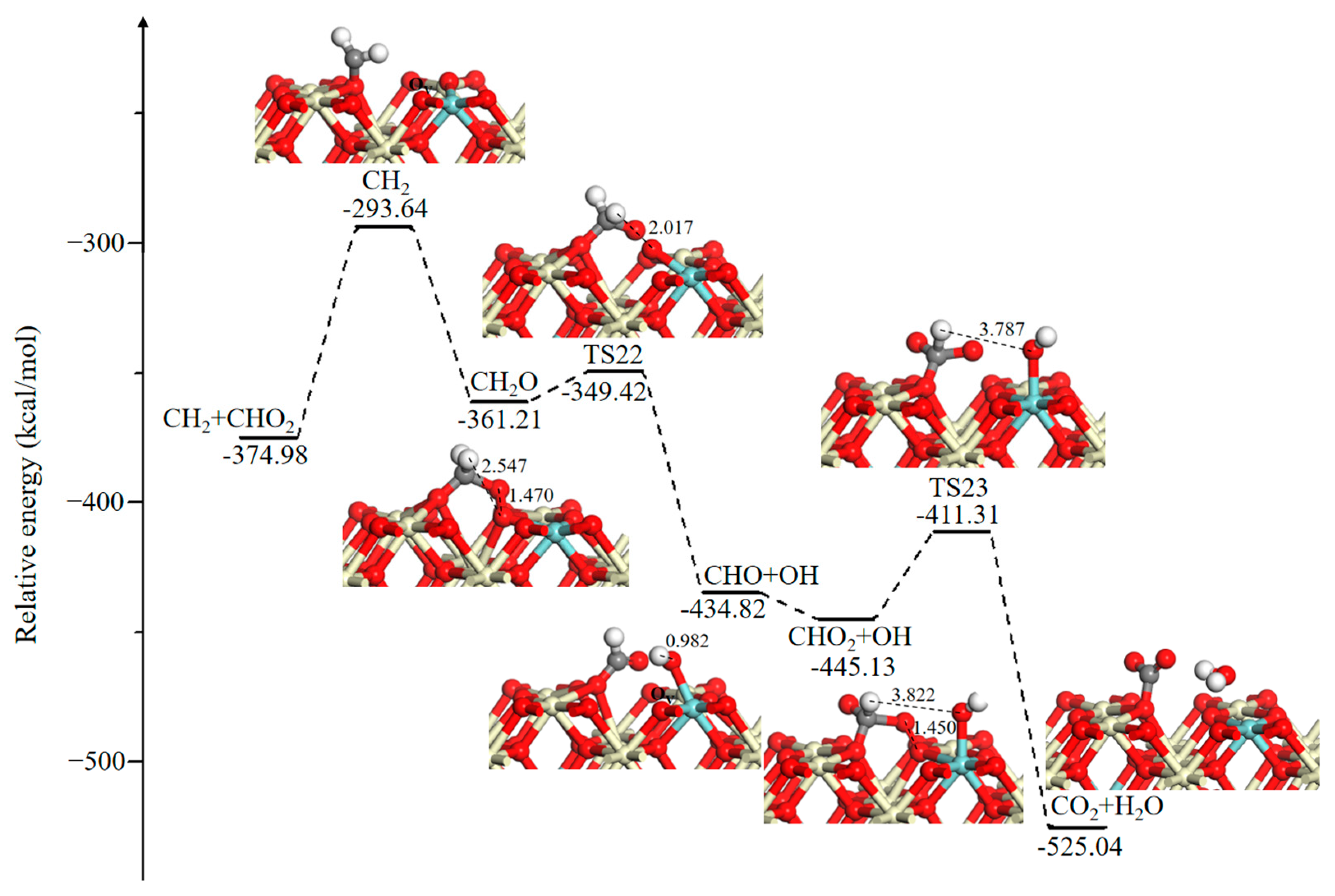
The CHO2 desorption configuration is presented in Figure 8 with a rather high desorption barrier of 81.34 kcal/mol, which results from the strong interaction between the CHO2 fragment and catalyst surface. An O2 molecule then fills the newly formed OV, and the O–O bond length is slightly elongated to 1.470 Å, as compared to the gas phase bond distance of 1.230 Å. This process is energetically favorable, with an exothermicity of approximately 67.57 kcal/mol. The adsorbed CH2O fragment may continue to dehydrogenate by the lattice O3C to generate the CHO fragment and hydroxyl group (–OH) with a lower energy barrier of 11.79 kcal/mol. Subsequently, another gaseous molecule of O2 replenishes OV and bonds with the CHO fragment, which results in the recovery of the catalyst surface and the formation of the CHO2 fragment. Finally, the hydroxyl group (–OH) abstracts an H atom of the CHO2 fragment via H-abstraction to form the final products CO2 and H2O with an energy barrier of 33.82 kcal/mol. It should be noted that the generated CO2 complex has a tendency to bind with a surface O atom to produce a carbonate species, which has been confirmed by the experimental and theoretical studies [50,51].

Figure 8.
Potential energy diagram and corresponding optimized configurations of small molecule intermediates’ oxidation reaction for CH2 oxidation. Key: Ce, ivory; Zr, cyan; O, red; C, gray; H, white.
As seen from the calculated energy profiles, the overall catalytic cycle pathway is strongly exothermic. However, most of the dehydrogenation reactions, dissociation reactions, and decarboxylation reactions are endothermic, which is thermodynamically unfavorable. Accordingly, the earlier experimental studies reported that a 100% conversion of toluene was observed at 400 °C on the Ce0.600Zr0.400O2 surface, indicating that the occurrence of a toluene oxidation reaction requires a high temperature [52]. However, lattice oxygen also plays an important role in toluene oxidation processes. Specifically, it can diffuse from the bulk of the catalyst to fill the surface oxygen sites [32,53].
2.3. Electronic Structures
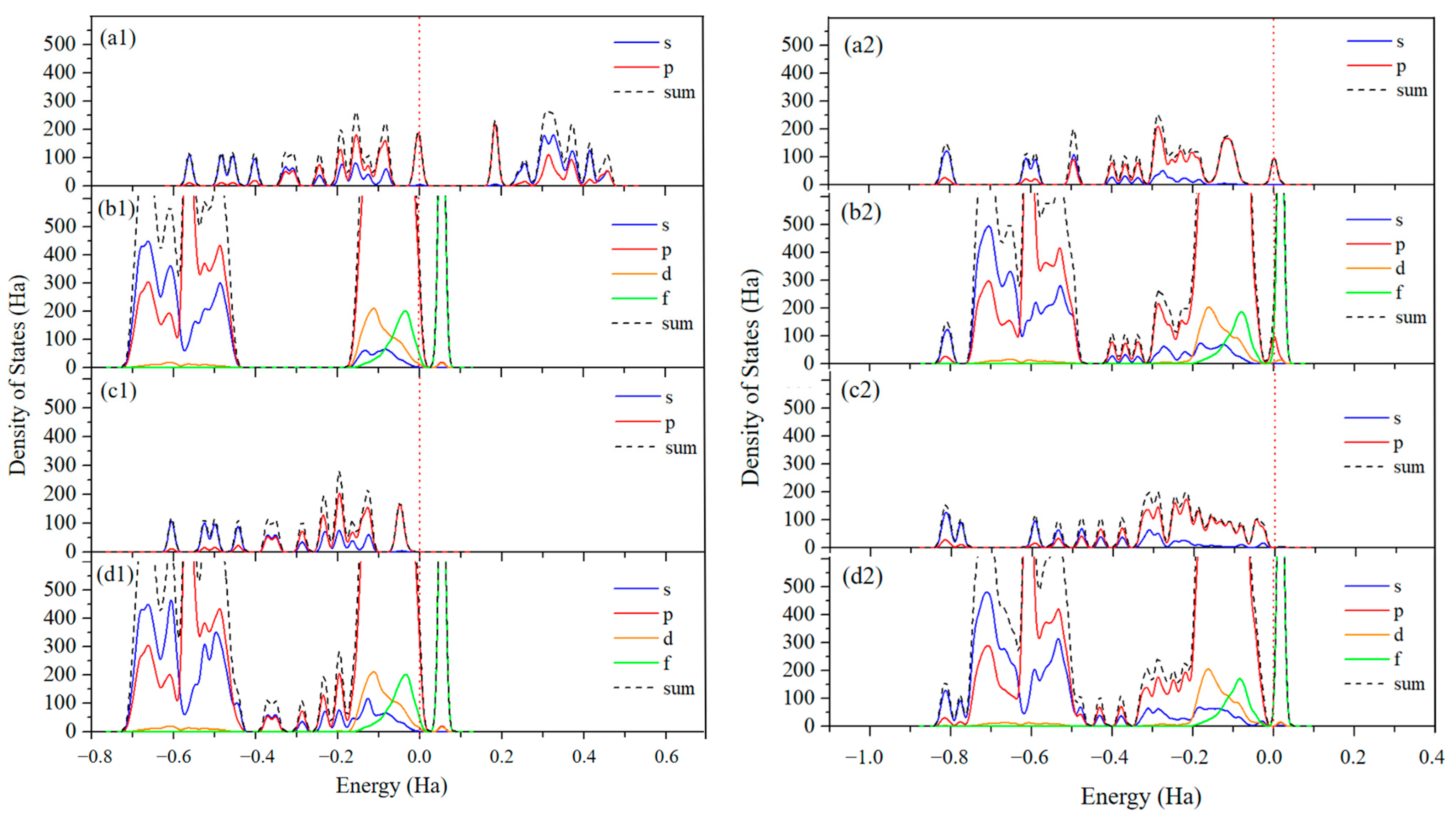
To further understand the key states in toluene oxidation processes discussed above, the analyses of the total density of states (TDOS) and partial density of states (PDOS) of toluene’s adsorption configuration are performed to investigate the electronic nature of C7H8 and the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface before and after adsorption (left panels of Figure 9). Compared to free C7H8, all of the orbitals of the adsorbed C7H8 are shifted to a lower energy level, meaning that electrons are transferred between toluene and the surface. The Mulliken charges for this system to quantitatively evaluate the redistribution of charges are also calculated. The results indicate that the adsorbed C7H8 has a negative charge of ~0.013 e. Considering that the free C7H8 is neutral, we know that the surface of the catalyst donates partial electrons to C7H8. These results indicate that there is a weak interaction between C7H8 and the surface, which is in good agreement with the adsorption energy of −21.39 kcal/mol. For the energy bands of the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface, there is no apparent change in any of the orbitals after the adsorption of C7H8, indicating that the surface remains stable.

Figure 9.
Left panels: Calculated total density of states (TDOS) and partial density of states (PDOS) of (a1) free C7H8, (b1) pure Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110), (c1) C7H8 in Figure 2 (C7H8), and (d1) the configuration in Figure 2 (C7H8). Right panels: Calculated TDOS and PDOS of (a2) C6H4O3 in Figure 5 (C6H4O3), (b2) the configuration in Figure 5 (C6H4O3), (c2) C6H4O4 in Figure 5 (C6H4O4), and (d2) the configuration in Figure 5 (C6H4O4). Zero energy corresponds to the Fermi energy.
TDOS and PDOS analyses for structures involved in the rate-determining step are also performed. As seen from the right panels of Figure 9 (b2) and (d2), there is no obvious shift in any of the orbitals of the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface before and after the reaction, although the surface is reduced after the reaction. An earlier study reported that GGA-DFT could not be used to precisely picture the electron localization for reduced ceria [54]. Mulliken charge analysis shows that excess electrons localize on the nearest subsurface layer Ce of the vacancy (~0.147 e) on the reduced surface. However, the nearest surface layer Ce does not localize electrons, and we consider that the surface O3C still bonds with it. In addition, we calculate a transfer of approximately 0.394 e from the surface to the C6H4O4 fragment after reaction, and this results in all of orbitals of C6H4O4 shifting to lower energy levels.
3. Computational Methods and Parameter Settings
DFT calculations are carried out using modeling DMol3, as implemented in the Materials Studio (MS) environment [55,56]. The double numerical plus d-function (DND) basis set with the generalized gradient approximation of the Perdew−Burke−Ernzerhof functional (GGA-PBE) is used to optimize all of the spin unrestricted structures [57]. Here, the cerium 4f, 5s, 5p, 5d, and 6s electrons and zirconium 4s, 4p, 4d, and 5s electrons are treated as valence electrons using the effective core potential (ECP) method [58]. The core electrons of C, H, and O atoms are treated using the all-electron method. The Brillouin zone is sampled with a (1 × 2 × 1) Monkhorst−Pack k-point grid [59]. A 5.0 Å orbital cutoff is selected with a Fermi smearing of 0.005 Ha to accelerate the convergence of the calculations. The SCF tolerance is 1.0 × 10−5, the convergence tolerances of energy, force, and displacement are less than 2.0 × 10−5 Ha, 0.004 Ha/Å, and 0.005 Å, respectively. The transition states (TS) in catalytic reactions are determined using the linear synchronous transit/quadratic synchronous transit (LST/QST) method [60,61].
The adsorption energy (Eads) of the adsorbate is calculated as follows:
where Esubstrate+adsorbate, Esubstrate, and Eadsorbate are the total energies of the substrate–adsorbate system, substrate, and adsorbate, respectively.
Eads = Esubstrate+adsorbate − Esubstrate − Eadsorbate
The activation energy barrier (Ea) and reaction energy (ΔE) are determined as follows:
where ER, ETS, and EIM are the total energies of the reactant (R), transition state (TS), and intermediate (IM), respectively.
Ea = ETS − ER
ΔE = EIM − ER
The Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface is modeled using the lattice substitution model [25,62]. After obtaining the optimized lattice constant of CeO2 bulk, the (110) surface is cleaved with a 2 × 2 supercell. A 15 Å vacuum thickness is added in the z-direction to avoid slab-slab interactions. One of the Ce in the top surface layer and one of the Ce in the third surface layer are replaced with Zr, thus establishing a Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 (110) surface model. The bottom two atomic layers of the Zr-doping model are fixed at the optimized bulk coordinates, whereas the top two layers are allowed to relax with adsorbed molecules.
4. Conclusions
In the current work, toluene’s total oxidation mechanism over the Ce0.875Zr0.125O2 catalyst is systemically investigated using the DFT calculations. A detailed reaction pathway, including the optimized configurations of reactants, intermediates, and products, the energy barrier, and the potential energy diagram, is proposed. Toluene first loses its H atoms from the methyl group and is gradually oxidized to benzyl alcohol, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid following the MVK mechanism. Then, benzoic acid decarboxylates to form phenyl, which is oxidized to benzoquinone, and a benzene ring opens to generate small molecule intermediates 1,3-butadiene-1,4-dione and glyoxal. The ring-opening reaction is the rate-determining step of catalytic toluene oxidation, which is consistent with the experimental observations. Finally, small molecule intermediates are oxidized to CO2 and H2O by the lattice or adsorbed oxygen. This investigation brings us closer to a comprehensive understanding of the nature of the catalytic degradation of aromatic VOCs and the role of lattice and adsorbed oxygen in catalytic oxidation reactions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal14010022/s1, Table S1: Cartesian coordinates for all the optimized structures of reactants, intermediates, transition states and products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z.; Formal analysis, Y.L.; Funding acquisition, C.Z.; Methodology, Y.L. and C.Z.; Software, Y.L. and X.C.; Supervision, X.S.; Validation, X.S.; Visualization, C.Z.; Writing—original draft, Y.L. and X.C.; Writing—review and editing, X.S. and C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 21607011, Key Research and Development Project of Shandong Province, grant number 2019GSF109021 and The APC was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds of Weifang University of Science and Technology, grant number KJRC2022013.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Amann, M.; Lutz, M. The revision of the air quality legislation in the European Union related to ground-level ozone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 78, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riipinen, I.; Yli-Juuti, T.; Pierce, J.R.; Petäjä, T.; Worsnop, D.R.; Kulmala, M.; Donahue, N.M. The contribution of organics to atmospheric nanoparticle growth. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Douthwaite, M.; Pattisson, S.; Hao, Z. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: A review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4471–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derwent, R.G.; Jenkin, M.E.; Saunders, S.M. Photochemical ozone creation potentials for a large number of reactive hydrocarbons under European conditions. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derwent, R.G.; Jenkin, M.E.; Saunders, S.M.; Pilling, M.J. Photochemical ozone creation potentials for organic compounds in northwest Europe calculated with a master chemical mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2429–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.H.; Zhong, J.P.; Tian, J.T.; Liu, P.; Ren, Q.M.; Chen, L.M.; Fu, M.L.; Ye, D.Q. Unraveling the role of OH groups over CeO2 derived from methanol modification for enhancing toluene oxidation: Experimental and theoretical studies. Appl. Catal. A Gen 2023, 654, 119069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Gaur, V.; Verma, N. Removal of volatile organic compound by activated carbon fiber. Carbon 2004, 42, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Kang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Emission control of toluene in iron ore sintering using catalytic oxidation technology: A critical review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.M.; Lu, P.; Yan, X.H.; Huang, H.B. Boosting simultaneous catalytic removal of NOx and toluene via cooperation of Lewis acid and oxygen vacancies. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 331, 122696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, A.; Sharma, D.; Roy, S.; Singh, S.A. Technological solutions for NOx, SOx, and VOC abatement: Recent breakthroughs and future directions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 91501–91533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topka, P.; Jirátová, K.; Dvořáková, M.; Balabánová, J.; Koštejn, M.; Kovanda, F. Hydrothermal deposition as a novel method for the preparation of Co–Mn mixed oxide catalysts supported on stainless steel meshes: Application to VOC oxidation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 5172–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Shangguan, W. Low-temperature catalysis for VOCs removal in technology and application: A state-of-the-art review. Catal. Today 2016, 264, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivey, J.J. Complete catalytic oxidation of volatile organics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1987, 26, 2165–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, T.; Rooke, J.; Chlala, D.; Cousin, R.; Lamonier, J.F.; Giraudon, J.M.; Casale, S.; Massiani, P.; Siffert, S. Oscillatory behavior of Pd-Au catalysts in toluene total oxidation. Catalysts 2018, 8, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.S.; Razzak, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Song, F.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhong, Q. The effect of CuO loading on different method prepared CeO2 catalyst for toluene oxidation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genty, E.; Brunet, J.; Poupin, C.; Ojala, S.; Siffert, S.; Cousin, R. Influence of CO addition on the toluene total oxidation over Co based mixed oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 247, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, X.; Jing, M.; Song, W.; Liu, J.; Ge, M. Defective MnxZr1–xO2 solid solution for the catalytic oxidation of toluene: Insights into the oxygen vacancy contribution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Giraudon, J.M.; Nuns, N.; Simon, P.; De Geyter, N.; Morent, R.; Lamonier, J.F. Influence of the preparation method on the activity of copper-manganese oxides for toluene total oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 223, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, J. Bonding properties of molecular cerium oxides tuned by the 4f-block from ab-initio perspective. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 156, 211101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G.; Hu, P. Multiple configurations of the two excess 4f electrons on defective CeO2(111): Origin and implications. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 193401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G.; Hu, P. A model to understand the oxygen vacancy formation in Zr-doped CeO2: Electrostatic interaction and structural relaxation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 10229–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.M.; Day, A.N.; Davies, T.E.; Morgan, D.J.; Taylor, S.H. Mechanochemical preparation of ceria-zirconia catalysts for the total oxidation of propane and naphthalene Volatile Organic Compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 253, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rivas, B.; Sampedro, C.; García-Real, M.; López-Fonseca, R.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Promoted activity of sulphated Ce/Zr mixed oxides for chlorinated VOC oxidative abatement. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 129, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.S.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.M. Surface reduction properties of ceria–zirconia solid solutions: A first-principles study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 4664–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozo, C.; Gaillard, F.; Guilhaume, N. Characterisation of ceria–zirconia solid solutions after hydrothermal ageing. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 220, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, S.; Gomezmendoza, N.; Gomezgarcia, M.A.; Świerczynski, D.; Quignard, F.; Tanchoux, N. Study and modelling of kinetics of the oxidation of VOC catalyzed by nanosized Cu–Mn spinels prepared via an alginate route. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 504, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genty, E.; Siffert, S.; Cousin, R. Investigation of reaction mechanism and kinetic modelling for the toluene total oxidation in presence of CoAlCe catalyst. Catal. Today 2019, 333, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuino, H.C.; Dharmarathna, S.; Njagi, E.C.; Mei, M.C.; Suib, S.L. Gas-phase total oxidation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes using shape-selective manganese oxide and copper manganese oxide catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 12066–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Shim, W.-G. Complete oxidation of volatile organic compounds over Ce/Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.J.; Yang, D.Y.; Kang, T.; Xu, Y.; Hao, Q.L.; Bin, F.; Xu, X.W. Morphology effects of CeO2–ZrO2 on the catalytic performance of CuO/CeO2–ZrO2 for toluene oxidation. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2021, 4, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, U.; Galvita, V.; Marin, G.B. Reaction network for the total oxidation of toluene over CuO–CeO2/Al2O3. J. Catal. 2011, 283, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.; Fornero, E.L.; Villarreal, A.; Collins, S.E. Identification of key reaction intermediates during toluene combustion on a Pd/CeO2 catalyst using operando modulated DRIFT spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2022, 394–396, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, P.K.; Labadini, D.; Asselin, G.; Hafiz, S.S.; Gokalp, S.; Kipreos, M.D.; Foster, M. DRIFTS investigation of toluene oxidation on CeO2 nanoparticles. Surf. Sci. 2022, 720, 122042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Li, H.Y.; Song, Z.X.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.P.; Mo, D.J.; Gao, H.R.; Zhang, M.R. In situ DRIFT spectroscopy study into the reaction mechanism of toluene over CeMo catalysts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Li, C.T.; Liang, C.X.; Li, S.H.; Liu, X.; Du, X.Y.; Yang, K.; Zhao, J.G.; Yu, Q.; Zhai, Y.B.; et al. Regulating CeO2 morphologies on the catalytic oxidation of toluene at lower temperature: A study of the structure-activity relationship. J. Catal. 2023, 418, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.R.; Hu, G.T.; Zhao, C.C.; Wei, X.L.; Dou, B.J.; Liang, W.J.; Bin, F. Insights into the reaction mechanism of toluene oxidation by isotope dynamic experiment and the kinetics over MCeZr/TiO2 (M = Cu, Mn, Ni, Co and Fe) catalysts. Fuel 2023, 341, 127760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerçeker, D.; Önal, I. A DFT study on CO oxidation on Pd4 and Rh4 clusters and adsorbed Pd and Rh atoms on CeO2 and Ce0.75Zr0.25O2 supports for TWC applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Lu, G.; Gong, X. A DFT+U study of the catalytic degradation of 1,2-dichloroethane over CeO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 5856–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irikura, K.K. Systematic errors in ab initio bond dissociation energies. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 9031–9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneider, K.A.; Eyring, L.; Roth, T.A. Handbook on the physics and chemistry of rare earths, Vol. 1: Metals. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1979, 126, 464C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Feng, X.; Deng, J.; He, C.; Douthwaite, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, Z. Atomic-scale insights into the low-temperature oxidation of methanol over a single-atom Pt1-Co3O4 Catalyst. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J.; Zuo, S. Ce-modified mesoporous γ-Al2O3 supported Pd-Pt nanoparticle catalysts and their structure-function relationship in complete benzene oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Luque, R. Enhanced catalytic benzene oxidation over a novel waste-derived Ag/eggshell catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8832–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhuang, G.; Wang, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, J.; Li, Q. Catalytic benzene oxidation by biogenic Pd nanoparticles over 3D-ordered mesoporous CeO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Chen, Y. Catalytic oxidation of benzene over ruthenium–cobalt bimetallic catalysts and study of its mechanism. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cao, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhan, J.; Liu, L. Facile and green synthetic strategy of birnessite-type MnO2 with high efficiency for airborne benzene removal at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 245, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Zhu, T. Catalytic oxidation of benzene over MnOx/TiO2 catalysts and the mechanism study. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 408, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, R.; Zhao, M.; Ye, D. Catalytic properties of manganese oxide polyhedra with hollow and solid morphologies in toluene removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sakata, Y.; Arai, T.; Domen, K.; Maruya, K.-I.; Onishi, T. Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide adsorption on cerium oxide studied by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Part 1.—Formation of carbonate species on dehydroxylated CeO2, at room temperature. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1989, 85, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Gong, X.; Lu, G. A DFT+U study of the lattice oxygen reactivity toward direct CO oxidation on the CeO2(111) and (110) surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 16573–16580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Combustion of toluene catalyzed by ceria-zirconia solid solutions. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2015, 35, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Shen, M.; Wang, J. Effect of surface area and bulk structure on oxygen storage capacity of Ce0.67Zr0.33O2. J. Catal. 2007, 248, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.C.; Woo, T.K.; Hermansson, K. Effects of Zr doping on stoichiometric and reduced ceria: A first-principles study. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 224704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delley, B. An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delley, B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 7756–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergner, A.; Dolg, M.; Küchle, W.; Stoll, H.; Preuß, H. Ab initio energy-adjusted pseudopotentials for elements of groups 13–17. Mol. Phys. 1993, 80, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elber, R.; Karplus, M. A method for determining reaction paths in large molecules: Application to myoglobin. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1987, 139, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A.; Lipscomb, W.N. The synchronous-transit method for determining reaction pathways and locating molecular transition states. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1977, 49, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G.; Hu, P. Maximizing the localized relaxation: The origin of the outstanding oxygen storage capacity of κ-Ce2Zr2O8. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8289–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).