Abstract
In recent years, the excessive use and improper disposal of antibiotics have led to their pervasive presence in the environment, resulting in significant antibiotic pollution. To address this pressing issue, the present study synthesized nickel–iron-layered double hydroxides (NiFe-LDHs) with varying molar ratios using a hydrothermal method, employing these LDHs as catalysts for the oxidative degradation of doxycycline, with peroxymonosulfate (PMS) serving as the oxidant. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed that the synthesized NiFe-LDHs exhibited a hexagonal crystal structure characteristic of layered double hydroxides. Experimental results demonstrated that the catalytic efficiency of NiFe-LDHs increased with both the dosage of the catalyst and the concentration of PMS, achieving a high degradation efficiency for doxycycline at a catalyst concentration of 0.5 g/L. Furthermore, the catalytic performance was notably effective across a range of pH conditions, with the highest degradation efficiency being observed at a Ni–Fe molar ratio of 3:1. The activation of PMS by NiFe-LDHs for the catalytic degradation of pollutants primarily occurs through singlet oxygen (1O2), superoxide radicals (O2−·), and sulfate radicals (SO4−·). The study also proposed three potential degradation pathways for doxycycline, indicating that the final degradation products have lower environmental toxicity. This research offers novel approaches and methodologies for the treatment of antibiotic-contaminated wastewater.
1. Introduction
Since the discovery of antibiotics in the 20th century, their extensive utilization in medicine [1], animal husbandry [2], and public health [3] has raised significant environmental concerns. Wastewater generated from pharmaceutical, food, dyeing, and other industries can adversely affect the growth and metabolism of microorganisms [4]. Thus, the implementation of effective water conservation measures and the exploration of advanced treatment technologies are essential [5]. Most antibiotics present in these aquatic environments are not fully absorbed by passive treatment methods and exhibit resistance to natural degradation, resulting in substantial residue accumulation [6]. This accumulation not only enhances the resistance of pathogenic microorganisms but also poses teratogenic and carcinogenic risks [7]. Recent studies have identified the presence of various antibiotics in urban water systems worldwide, including 19 sampling points along the Huangpu River in Shanghai [8] and five collection sites in the Chongqing area of the Three Gorges Reservoir [9]. Additionally, antibiotics have been detected in multiple rivers across countries such as Italy and Spain [9,10]. The environmental pollution resulting from the misuse of antibiotics has exceeded expectations, underscoring the urgent need for efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly technologies for the degradation of residual antibiotics. Doxycycline, a widely used tetracycline antibiotic, is particularly notable for its high environmental stability and resistance to degradation, which may facilitate the dissemination of resistance genes through its residues. Consequently, investigating the distribution and degradation of doxycycline in the environment is critical for understanding and mitigating its associated environmental risks [11].
Exploring antibiotics and drug resistance, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have garnered significant attention due to their ability to generate highly reactive free radicals that oxidize and degrade target pollutants, thereby exhibiting notable effects on wastewater containing antibiotics. Currently, the primary methods for degrading antibiotics mainly involve photocatalytic oxidation and Fenton oxidation to generate hydroxyl radicals (·OH). Nevertheless, these methods are limited by their low efficiency and high energy consumption, which restricts their widespread application. In recent years, the use of activated persulfate oxidation processes for the degradation of antibiotics has gained prominence as a significant area of research both domestically and internationally [12]. The structure of persulfate closely resembles that of hydrogen peroxide [13], as both contain a peroxide bond. Numerous studies have demonstrated that SO4−· can cleave C=N double bonds, C=C double bonds, C–S single bonds, and C–N single bonds [14], and it exhibits superior selectivity. It can eliminate certain antibiotics that ·OH alone cannot completely oxidize [15]. Additionally, SO4−· possesses a longer half-life than ·OH, thereby increasing the opportunities for contact and reaction with pollutants, ultimately enhancing the efficiency of pollutant degradation. Persulfate oxidation, with sulfate ions (SO42−) as the primary active substance, represents a novel type of advanced oxidation technology that supplants traditional oxidation technologies and holds promising prospects for development. Currently, there exist numerous methods for activating persulfate both domestically and internationally, including thermal activation, photo-activation, electro-activation, and activation by transition metal ions and metal oxides [16,17,18,19]. Among these activation methods, transition metals such as Ce2+, Fe2+, Ag+, Co2+, Mn2+, etc. are employed for persulfate activation [20,21,22,23,24]. These metals offer advantages such as low energy consumption, straightforward catalyst preparation, absence of large-scale equipment requirements, and low cost.
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) were initially discovered and proposed by the Swedish scientist Hochstetter in the early 19th century. LDHs are double metal hydroxide with a layered and pillared structure, primarily composed of positively charged metal cations (Mg2+, Fe2+, Al3+, etc.) and negatively charged anions (CO32−, Cl−, etc.). LDHs possess unique molecular structures and physical and chemical properties. LDHs typically exhibit a leaf-like, clump, or plate shape under normal conditions. The distinctive structure of LDHs grants them acidic and basic properties, thermal stability, anion exchangeability in the interlayer, and a memory effect. Due to these unique structural elements, LDHs can effectively bind to transition metal ions, making LDHs a preferred catalyst for activated persulfate (PMS) [25]. Among various types of LDHs, magnesium–aluminum hydroxide is the most commonly studied, with a molecular formula of Mg6Al2(OH)16CO3·4H2O. The ability of natural hydrotalcite to form LDHs structures with a variety of bivalent and trivalent metal cations and interlayer anions has stimulated extensive research interest in synthetic LDHs materials in the fields of adsorption and catalysis. LDHs have significant adsorption and catalytic effects on organic pollutants, combined with the ultrafiltration process, and LDHs can effectively remove organic pollutants from water, meeting the requirements of environmental protection and purification [26,27].
Following high-temperature calcination of layered double hydroxides (LDHs), highly dispersed composite metal oxides with numerous microporous structures are produced. These metal oxides exhibit strong alkalinity and remarkable catalytic performance [28]. Nickel (Ni), akin to platinum (Pt), is an economical and environmentally friendly non-noble metal catalyst. When combined with other active elements, Ni can yield exceptional catalytic properties. For instance, doping iron into NiCo-LDHs can induce structural disorder in the crystals, leading to the formation of additional active sites [29]. Moreover, Zhou et al. demonstrated that a catalyst featuring hierarchical porous carbon loaded with nickel not only enhances the catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen production but also improves catalyst stability [30]. Beyond applications of them as UV-blocking material, high-performance supercapacitors, gas sensors, and antibacterial agents, NiFe-LDHs are also effective for the degradation of antibiotics [31,32].
Based on the relevant literature, this experiment will use Fe and Ni elements to prepare NiFe-LDHs as a catalyst to study the performance of degrading antibiotics. The formation of NiFe-LDH was carried out as follows: (1) Preparation of the precursor solution: The metal salts, such as nickel salts and iron salts, were first dissolved in deionized water to form a solution. In this study, nickel chloride hexahydrate (NiCl2·H2O) and ferric chloride (FeCl3) were used to prepare nickel and iron solutions, and these two metal salt solutions were mixed at a certain molar ratio. By adjusting the mass ratio of nickel salt and iron salt, different proportions of NiFe-LDHs could be prepared. (2) Addition of precipitants: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) were added to the mixed solution to promote the formation of layered structures. In this study, the two precipitants were dissolved in deionized water and mixed thoroughly. (3) Coprecipitation reaction: The mixed metal salt solution was slowly added to the precipitant solution, typically under constant pH and temperature conditions, to promote the formation of LDHs. (4) Separation and washing: The formed NiFe-LDHs precipitate was separated by centrifugation and filtration and then washed with deionized water to remove impurities.
The primary objectives of this study are as follows: (a) to synthesize NiFe-LDHs catalytic materials using the hydrothermal method and analyze the formation of LDHs with varying molar ratios through XRD characterization; (b) to employ the synthesized NiFe-LDHs as catalysts for the activation of potassium peroxymonosulfate (PMS), with doxycycline as the target pollutant, in order to evaluate the degradation performance of doxycycline across different NiFe-LDH ratios and to investigate the effects of catalyst dosage, PMS concentration, and initial reaction pH on the removal efficiency; (c) to identify the degradation products and assess the intermediate toxicity.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
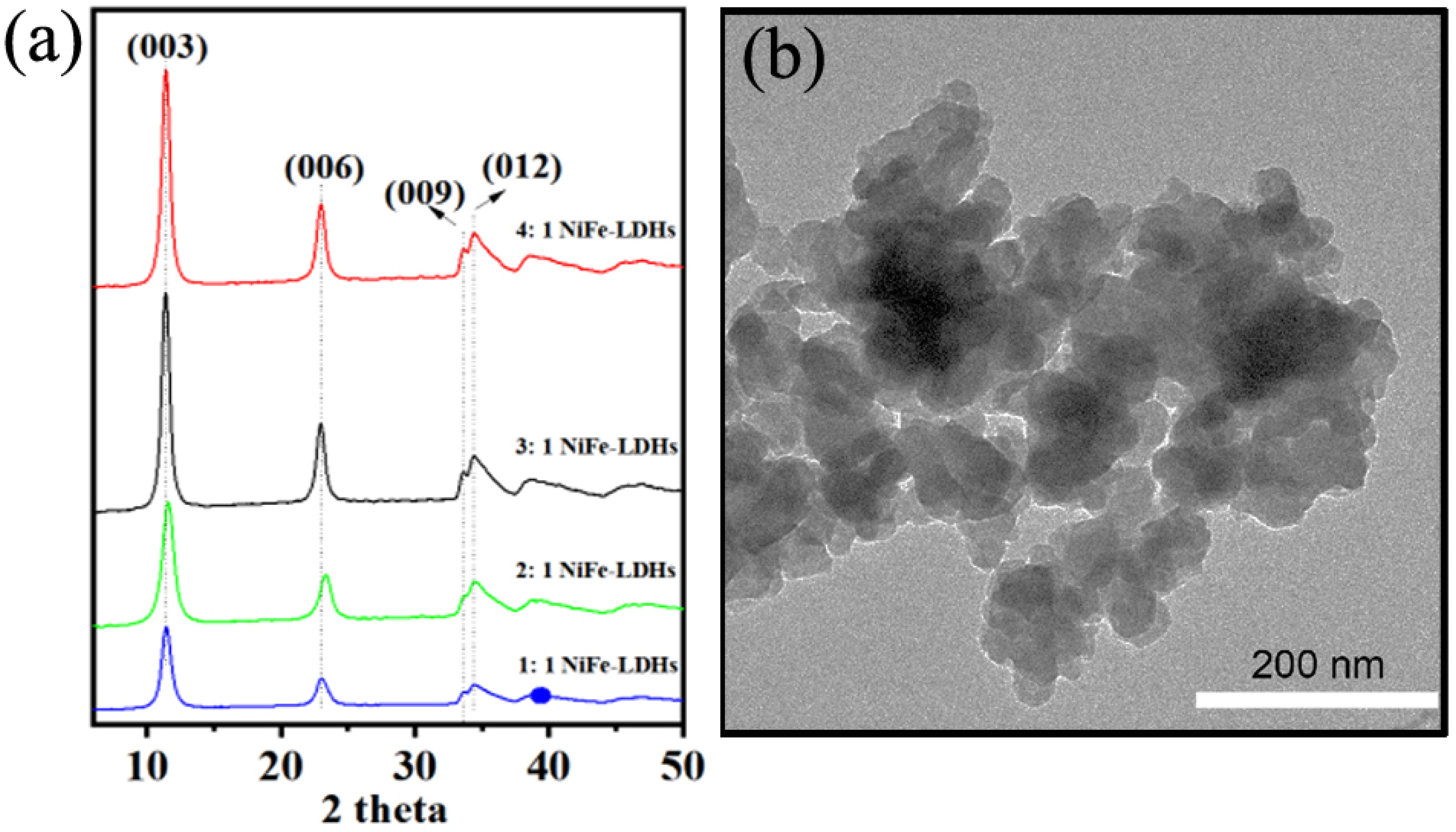
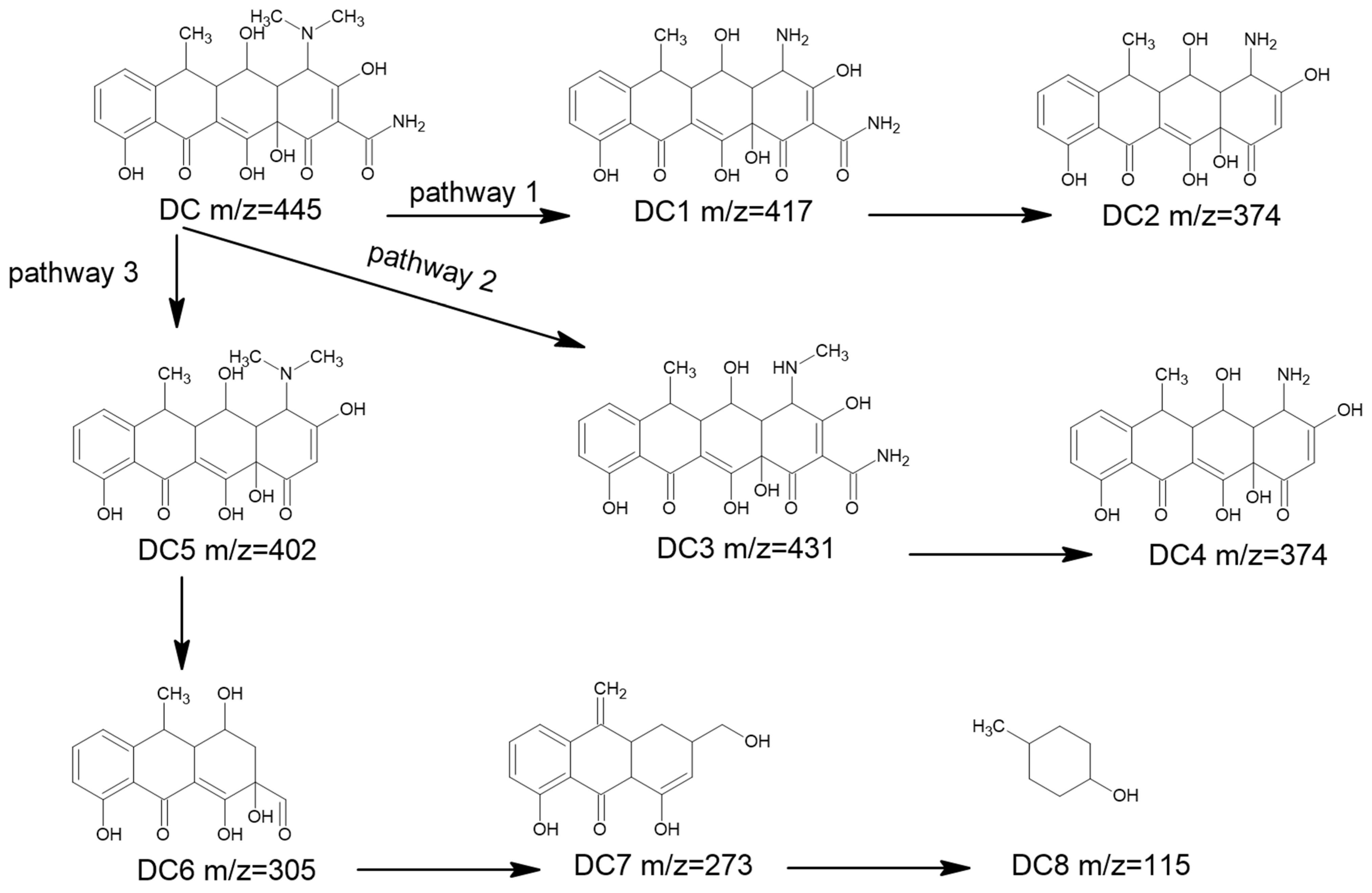
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of NiFe-LDHs with a different ratio of Ni/Fe in Figure 1a reveal distinct characteristic peaks at 2θ angles of 11.3°, 22.9°, 33.5°, and 34.6°, which correspond to the (003), (006), (009), and (012) crystal planes, respectively. These findings confirm that the synthesized NiFe-LDHs possess a hexagonal single-phase layered double hydroxide structure with high crystallinity [33,34]. When a base is added to a solution containing metal salts, hydroxide ions react with the metal cations, leading to the formation of metal hydroxides. In the resulting brucite-like structure, some Ni2+ is replaced by Fe3+, creating positively charged layers. These layers are balanced by carbonate, which is intercalated between them, along with water molecules, stabilizing the layered structure. As the reaction progresses, the NiFe-LDH layers stack, forming a well-ordered, crystalline structure. The charge compensation by interlayer anions is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the layered arrangement. Aging the precipitate further enhances the crystallinity and stability of the NiFe-LDHs [34]. Additionally, the 3:1 NiFe-LDH sample was selected as a representative for morphological analysis using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). As illustrated in Figure 1b, the LDHs display a lamellar structure with diameters ranging from 30 to 50 nm. The particles are uniformly dispersed, though some degree of agglomeration is observed. These structural characteristics enhance the material’s performance in catalytic applications.
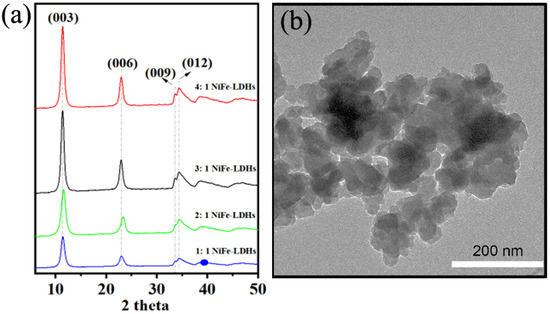
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns of NiFe-LDHs; (b) TEM image of the 3: 1 NiFe-LDHs.
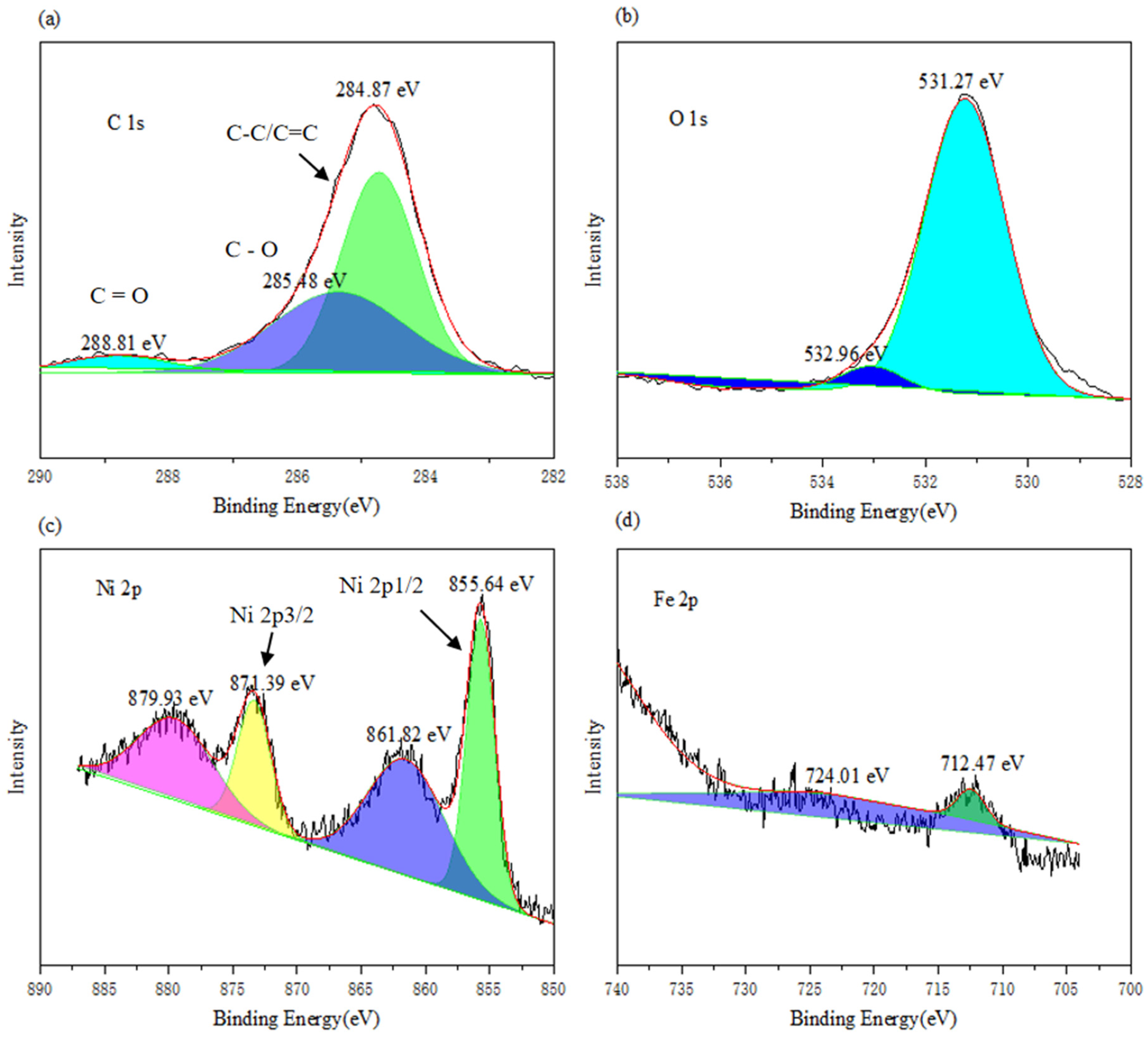
The electronic states, chemical states, and elemental composition of NiFe-LDHs (exemplified by 3: 1 NiFe-LDHs) were further investigated using XPS analysis. The full-spectrum XPS results of NiFe-LDHs are shown in Figure 2, where distinct characteristic peaks of Ni, Fe, O, and C are observed. XPS analysis was employed to further study the electronic states, chemical states, and elemental composition of NiFe-LDHs. As shown in Figure 2a, in the C 1s spectrum, the peaks at 284.87 eV, 285.48 eV, and 288.81 eV correspond to C–C/C=C, C–O, and C=O, respectively. In Figure 2b, the O 1s spectrum shows two peaks located at 531.27 eV and 532.96 eV, which were Gaussian-fitted and correspond to lattice oxygen and surface chemisorbed oxygen, respectively. In Figure 2c, the Ni 2p spectrum reveals that the peaks of Ni 2p3/2 and Ni 2p1/2 are located at 871.39 eV and 855.64 eV, respectively. Due to the presence of carbon, two satellite peaks appear near the main reflection peaks at 879.93 eV and 855.64 eV, indicating the presence of Ni2+ in the LDH materials. As shown in Figure 2d, the Fe 2p spectrum displays peaks for Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2 at 724.01 eV and 712.47 eV, respectively. The spin-orbit value of Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2 is 12.1 eV, indicating the presence of Fe3+ in the oxidized state within the LDH materials.
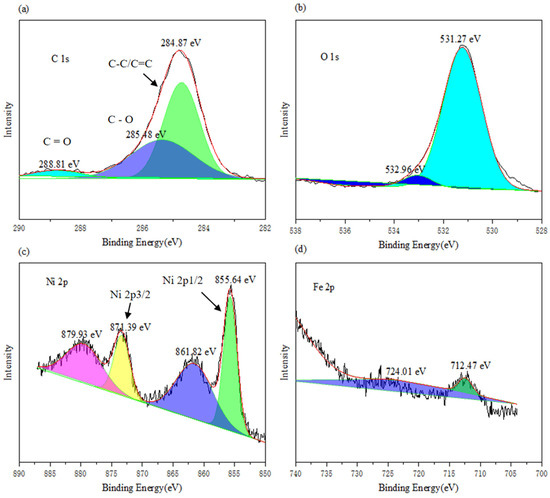
Figure 2.
High resolution of XPS (a) C 1s (b) O1s (c) Ni 2p and (d) Fe 2p for NiFe-LDHs.
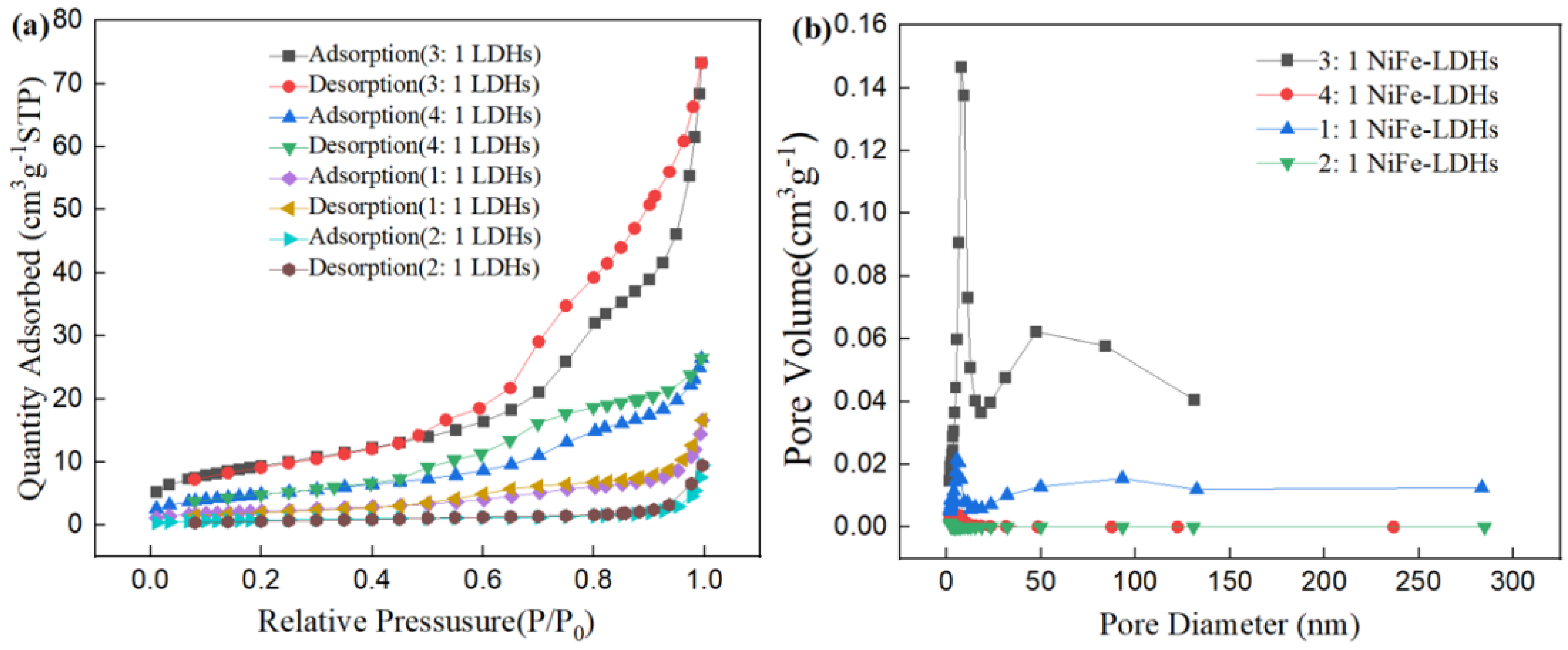
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms provide valuable insights into the pore structure characteristics and specific surface area of the LDHs. The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of the four NiFe-LDHs samples are shown in Figure 3. For the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs sample, hysteresis loops appear in the region of P/P0 > 0.45, while there is almost no N2 adsorption in the region of P/P0 < 0.4, indicating that the pore structure of the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs is formed by the stacking of some sheet-like materials. According to the classification standards of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the pore structure of the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs corresponds to a BDDT (Brunauer–Deming–Deming–Teller) type IV adsorption–desorption isotherm. This type of porous material is characterized by a three-dimensional interconnected porous geometry with high adsorption energy. The hysteresis loop of the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs shows a steep adsorption branch in the high P/P0 region which can be classified as H3 type. The combination of the BDDT type IV isotherm and H3 hysteresis loop indicates that the pore structure of the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs resembles an open slit-shaped capillary structure with parallel external walls or wide cavities and narrow openings. In contrast, other LDH samples with different ratios exhibit weaker N2 adsorption and no significant hysteresis loops, which corresponds to a type III adsorption–desorption isotherm. The BET specific surface area, pore volume, and average pore diameter of the samples are listed in Table 1. The BET specific surface area of the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs is 21.82 m2/g, while the specific surface areas of the other LDH ratios are relatively small. Thus, the N2 adsorption on the external surfaces of the smaller LDHs sheets with other ratios is negligible, and the adsorption primarily occurs at the sample edges, but the absolute amount of edge adsorption remains low. Therefore, compared to the rough and porous surface of the 3:1 NiFe-LDHs, the edge adsorption contributes insignificantly to the total N2 adsorption.
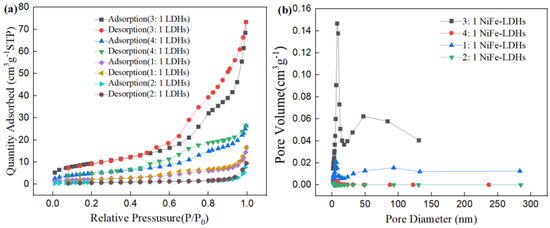
Figure 3.
(a) Adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution curves.

Table 1.
Textural parameters for the LDHs.
2.2. Evaluation of Catalyst Performance
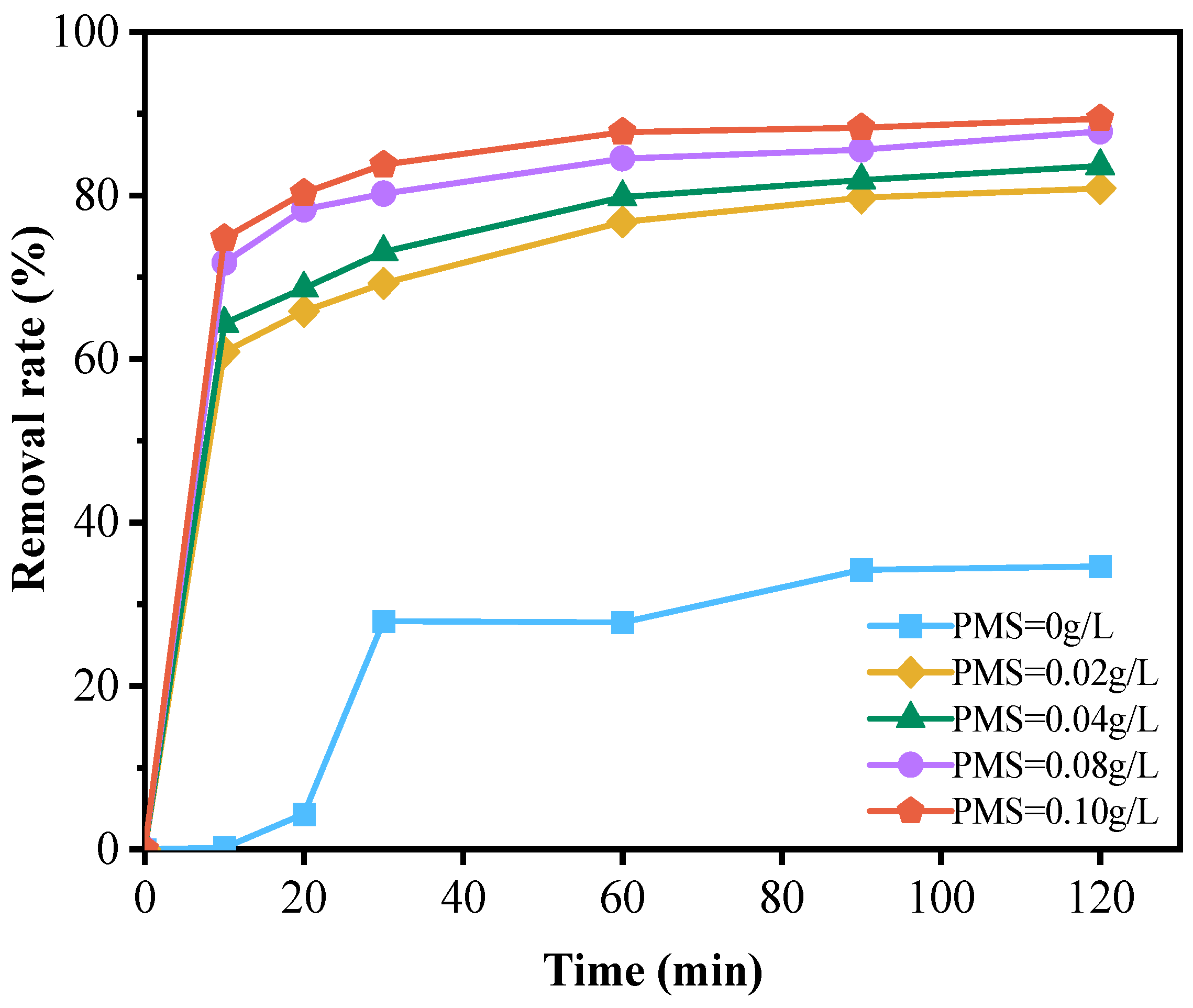
The results shown in Figure 4 indicate that the degradation rate of doxycycline hydrochloride was only 34.63% when the NiFe-LDHs catalyst was added to the reaction system without peroxymonosulfate (PMS). However, increasing the PMS concentration to 0.1 g/L led to a significant increase in the degradation rate, rising to 89.39%. This demonstrates that PMS plays a crucial role in the degradation process. The catalyst facilitates the activation and decomposition of PMS, generating sulfate radicals (SO4−·) that effectively degrade doxycycline hydrochloride. These radicals exhibit strong oxidizing properties comparable to or even exceeding those of highly reactive hydroxyl radicals. A large number of studies have shown that the amount of PMS is an important parameter [29,35,36]. These studies indicate that this parameter significantly affects the ability of SO4−·to oxidatively degrade organic pollutants [35]. Within a certain range, increasing the PMS concentration enhances the pollutant removal efficiency of the system. When the PMS concentration exceeds the optimal level, excess PMS can react with and consume some of the generated sulfate radicals, thereby diminishing the oxidative degradation effect on organic matter. Moreover, other organic substances present in the wastewater may compete with doxycycline hydrochloride for the oxidant, leading to inefficient use of raw materials [37]. In this experiment, as illustrated in Figure 4, the degradation rate of doxycycline hydrochloride increased with higher PMS concentrations, with the curve showing a sharp rise followed by a plateau. Although the optimal PMS concentration has not been definitively determined, considering factors such as energy consumption, cost, and removal efficiency, a concentration of 0.08 g/L is suggested as the optimal amount for this experiment.
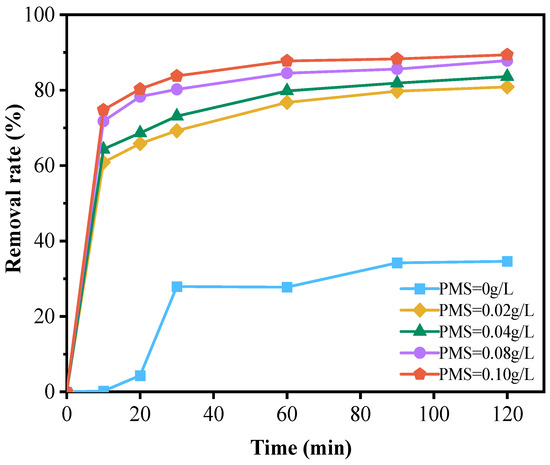
Figure 4.
Effect of PMS dosage on the degradation of doxycycline hydrochloride (dosed PMS quantity: 0 g/L; 0.02 g/L; 0.04 g/L; 0.08 g/L; 0.10 g/L).
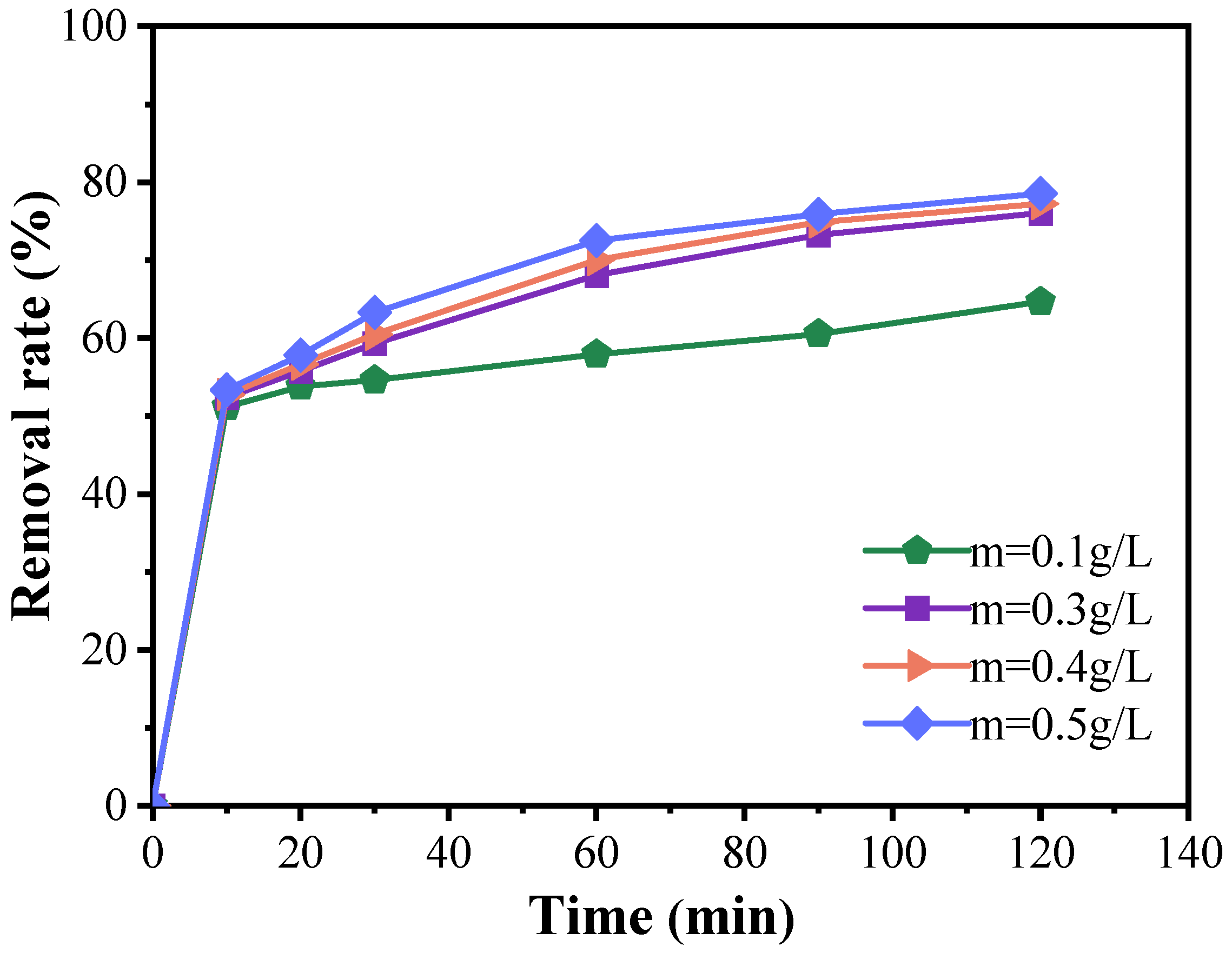
Figure 5 demonstrates that, during the initial 10 min, the degradation efficiency of doxycycline with varying catalyst amounts was relatively modest, with all conditions achieving a degradation rate exceeding 50%. However, as the reaction progressed, a positive correlation between catalyst dosage and degradation efficiency became evident, particularly within the catalyst concentration range of 0.1 to 0.5 g/L, where significant differences in degradation rates were noted. When the catalyst dosage was increased to 0.5 g/L, the degradation rate continued to improve with increasing catalyst concentration, although the rate of enhancement gradually diminished. For example, at a catalyst concentration of 0.5 g/L, the degradation rate reached 78.55% within 120 min. Nonetheless, this increase in degradation efficiency is not economically justified, as the improvement is marginal compared to the results obtained with 0.3 g/L of catalyst. Therefore, based on the experimental findings, the optimal catalyst dosage is determined to be 0.3 g/L.
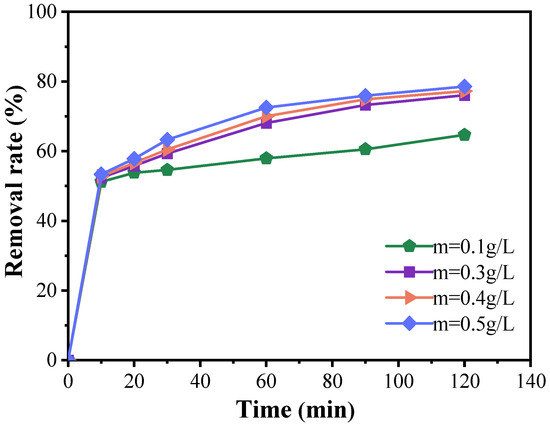
Figure 5.
Catalyst dosing effects on the degradation of doxycycline hydrochloride in wastewater treatment (dosed catalyst quantity: 0.1 g/L; 0.3 g/L; 0.4 g/L; 0.5 g/L).
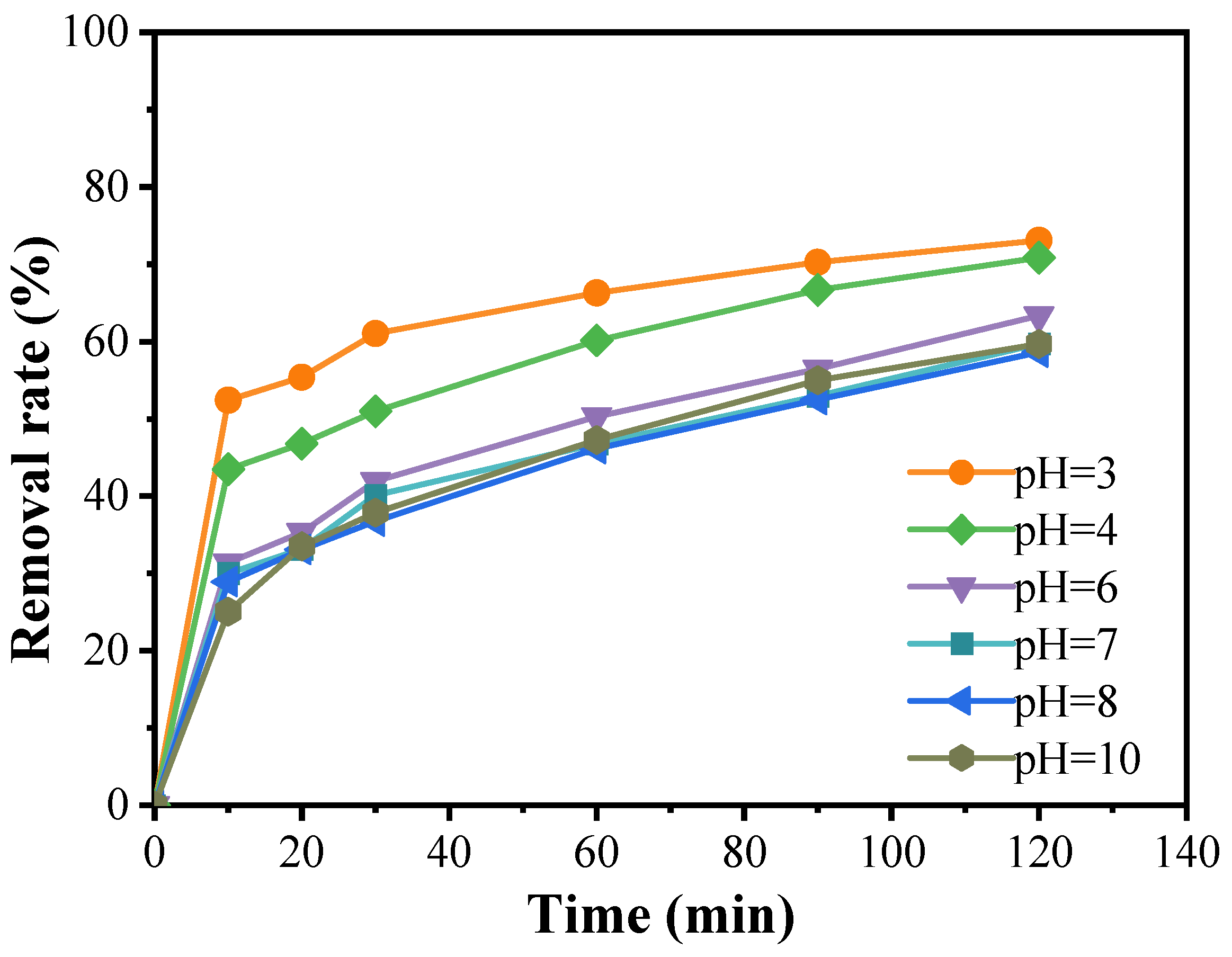
Figure 6 illustrates that, at a catalyst concentration of 0.3 g/L and a PMS concentration of 0.08 g/L, the curves corresponding to pH values of 3 and 4 show relatively high removal rates. Notably, the degradation of doxycycline is most efficient at a solution pH of 3, achieving a degradation rate of 73.1%. At pH 4, the degradation rate is slightly lower, reaching 72.5%. As the pH increases, the degradation rate gradually declines, stabilizing at a pH of 10 with no significant further changes. This indicates that pH is a critical factor influencing the generation of dominant free radicals in advanced oxidation processes. Different pH levels affect whether the sulfate radicals (SO4·−) produced by the activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) react with water (H2O) or hydroxide ions (OH−), leading to the formation of a more potent oxidative system. When the pH is below 7, SO4·− is the predominant active oxidizing species; above pH 7, ·OH become the primary active species. However, under strongly acidic or alkaline conditions, the oxidative power of SO4·− generated by PMS can surpass that of ·OH, resulting in effective degradation of doxycycline under both extreme conditions. Nevertheless, in practical applications, the use of strong acids or bases poses challenges due to the potential corrosion of equipment and the stringent requirements for the operating environment. As such, the feasibility of enhancing the catalytic effect by maintaining strong acidic or alkaline conditions is limited. Therefore, a neutral pH may be preferred in practical operations, depending on the specific circumstances.
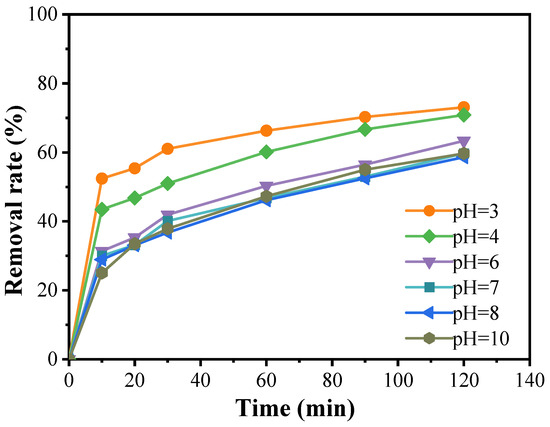
Figure 6.
Effect of pH value of solution on the degradation of doxycycline hydrochloride (pH = 3; pH = 4; pH = 6; pH = 7; pH = 8; pH = 10).
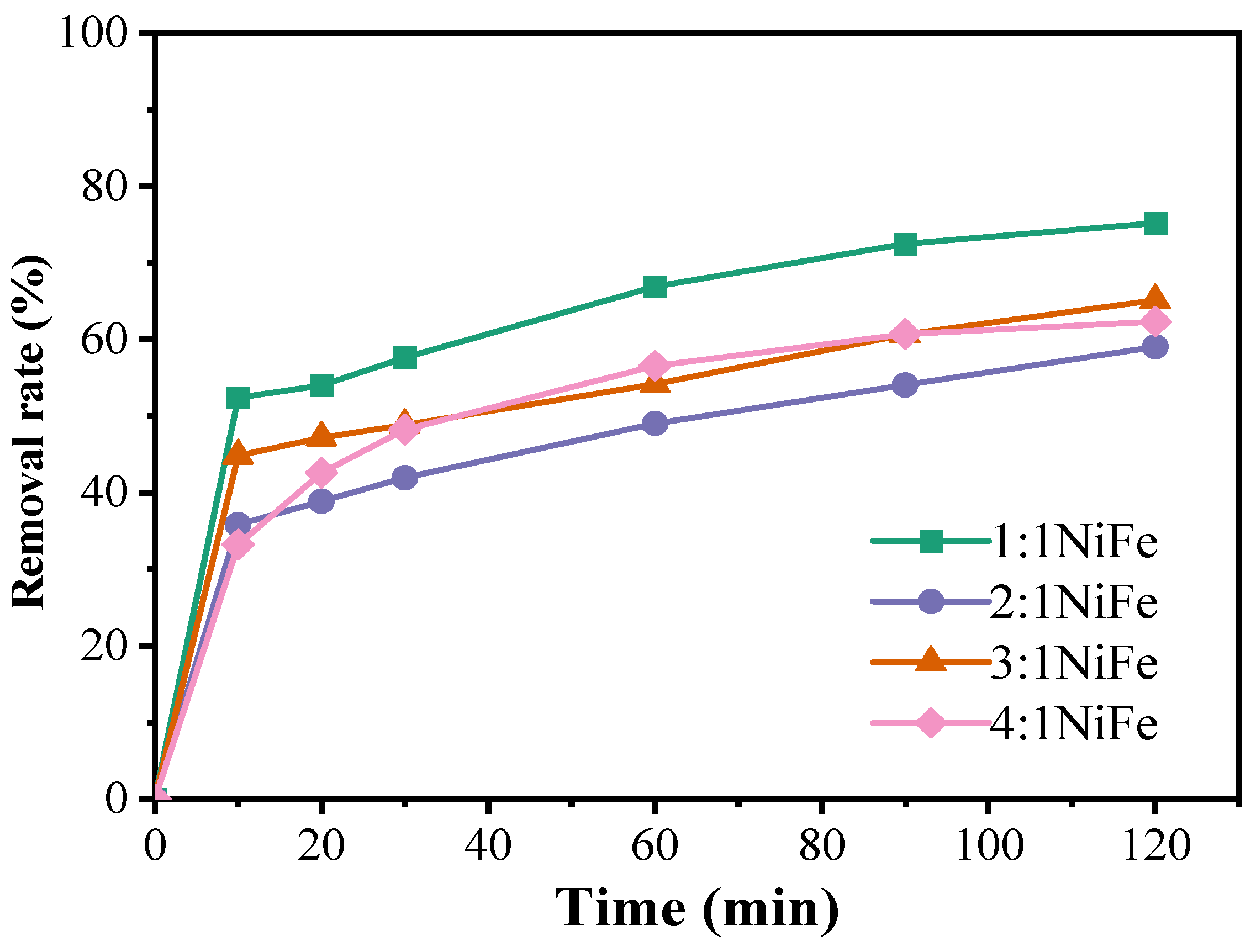
Figure 7 demonstrates that, under identical mass conditions, the 1:1 NiFe-LDH catalyst exhibits the highest degradation performance, characterized by a generally upward trend in the degradation curve. However, the rate of increase diminishes after 120 min, at which point the degradation rate of doxycycline hydrochloride reaches 75.17%. The 3:1 NiFe-LDH catalyst follows, achieving a degradation rate of 62.32%, while the 4:1 and 2:1 NiFe-LDH catalysts show comparatively lower effectiveness. In the NiFe-LDH materials, both nickel and iron are transition metals with variable oxidation states, organized in a specific spatial configuration. Table 2 summarizes the experimental conditions and degradation efficiencies for the activation of PMS by various catalysts in the degradation of tetracycline-class antibiotics, providing valuable comparative data. In this study, NiFe-LDHs demonstrated superior pollutant removal capabilities, with the 1:1 Ni-Fe ratio proving particularly competitive. Moreover, the concentration of PMS and the pH value significantly influenced degradation efficiency, with NiFe-LDHs exhibiting enhanced stability and activity at neutral pH.
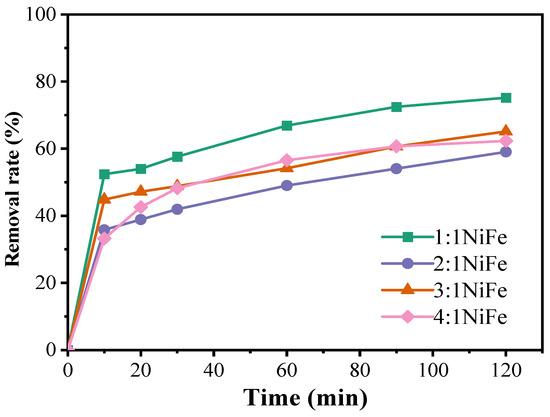
Figure 7.
Effect of catalysts on the degradation of doxycycline hydrochloride (1:1 NiFe-LDH; 2:1 NiFe-LDH; 3:1 NiFe-LDH; 4:1 NiFe-LDH).

Table 2.
Comparison of experimental conditions for activation of persulfate by different catalysts.
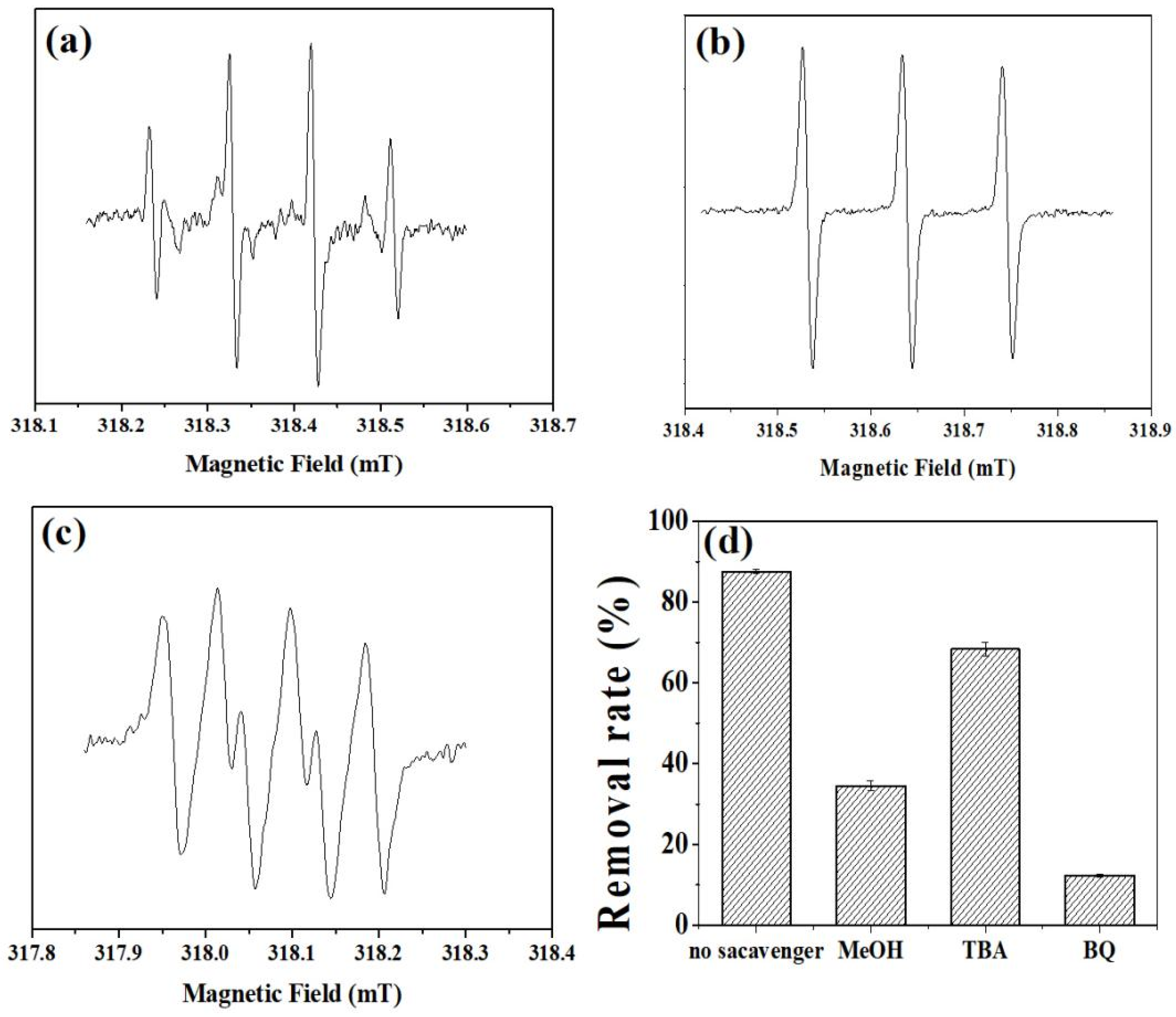
Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is utilized to analyze the primary active substances within the NiFe-LDHs/PMS reaction system. Initially, the main active substances in the catalytic degradation of the DC reaction system, activated by NiFe-LDHs, were examined. In Figure 8a, the signals for ·OH (hydroxyl radical) and SO4−· (sulfate radical) can be distinctly observed. The quadruple signal with an intensity ratio of 1:1:1:1 in Figure 8b suggests the existence of O2−· (superoxide anion radical)-active substances. Meanwhile, the signal with an intensity ratio of 1:1:1 in Figure 8c is attributed to the 1O2 (singlet oxygen)-active substances. In order to further analyze the main active oxygen species in the activation of sulfate by NiFe-LDHs, this study conducted free radical quenching experiments with different organic quenchers to further determine the role of different reactive oxygen species (ROS). According to previous research, methanol (MeOH) is a quencher for both OH· and SO4−·, tert-Butanol (TBA) can effectively mask the action of OH·, and 1,4-Benzoquinone (BQ) can inhibit the action of O2−·. In the PMS reaction system, the removal efficiency of doxycycline by the two catalysts under the action of MeOH or TBA was significantly reduced (Figure 8d). OH· can be generated from the rapid conversion of SO4−· and plays an important role in the degradation of doxycycline. When BQ was added to the reaction system, the degradation effect of the two systems on tetracycline was almost zero. Therefore, it can be inferred that O2−· is the main ROS for the degradation of doxycycline by NiFe-LDHs activating persulfate.
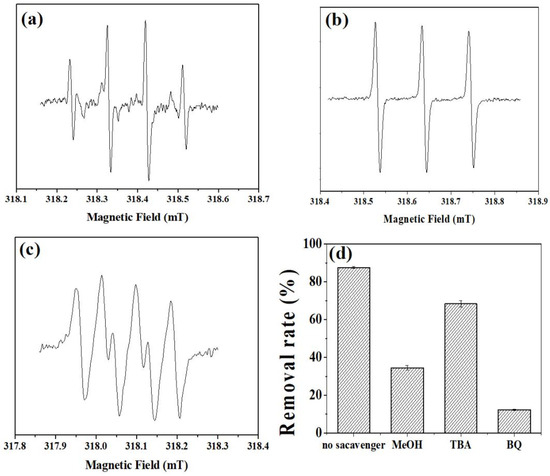
Figure 8.
ESR spectra of the NiFe-LDHs activated PMS system under the condition of adding (a,b) DMPO (5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide) and (c) TEMP (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine) as spin-trapping agents. (d) Removal efficiency of doxycycline in NiFe-LDHs/PMS with scavenger.
During the catalytic degradation process of DC, a large number of active substances such as 1O2, O2−·, and SO4−· are formed, which improves the catalytic effect. The entire reaction equation is shown in Equations (1)–(17). Free radicals exist in the system containing PMS and catalyst, as shown in reactions 3, 7, 8, 12, 13, and 15. ·OH and SO4−· are interconvertible, while 1O2 and O2−· can be transformed from ·OH and SO4−·, but 1O2 and O2−· generally do not transform into ·OH and SO4−·.
2.3. Intermediate Products and Toxicity Prediction
LC/Q-TOF was used to detect possible intermediate products formed during the degradation process of DC. Based on the degradation process previously reported and the identification of some intermediates, the degradation process of DC can be divided into three parts: functional group cleavage, ring-opening reactions, and hydroxylation. In the experiment, seven intermediate products were detected and three possible degradation pathways were inferred, as shown in Figure 9.
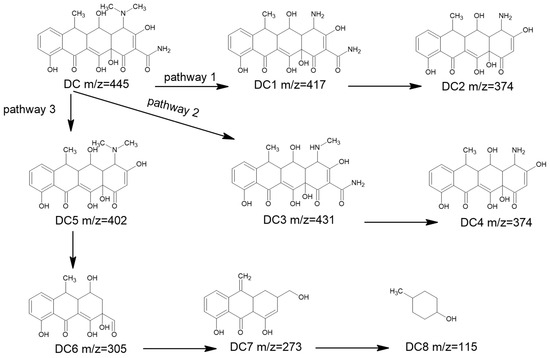
Figure 9.
Degradation pathway of doxycycline hydrochloride.
In the first pathway, DC with a mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of 445 is degraded to DC1 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z, which loses 28 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC has lost two methyl groups. Additionally, DC2 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 417 is degraded to DC2 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 374, losing 43 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC1 has lost an amide group.
In the second pathway, DC with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 445 is degraded to DC3 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 431, losing 14 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC has lost a methyl group, and DC3 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 431 is degraded to DC4 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 374, losing 57 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC3 has lost two methyl groups and an amide group. In the third pathway, DC with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 445 is degraded to DC5 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 402, losing 43 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC has lost an amide group; DC5 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 402 is degraded to DC6 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 305, losing 97 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC5 has been oxidized, lost a methylamine group, a hydroxyl group, and undergone ring-opening; DC6 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 305 is degraded to DC7 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 273, losing 32 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC6 has lost a hydroxyl group; DC7 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 273 is degraded to DC8 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 115, losing 158 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC6 has lost a water molecule, a methyl group, and a hydroxyl group, and undergone ring-opening; DC7 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 273 is degraded to DC8 with a mass-to-charge ratio of m/z 115, losing 59 atomic mass units, suggesting that DC6 has lost a hydroxamic acid group.
In this study, the ECOSAR software (ECOSAR v2.2; https://www.epa.gov/tsca-screening-tools/ecological-structure-activity-relationships-ecosar-predictive-model accessed on 26 October 2024) was employed to predict the potential toxicity of doxycycline (DC) and its degradation intermediates to fish, daphnids, and green algae, as summarized in Table 3. According to the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), the aquatic environmental toxicity of these substances is categorized into four levels: highly toxic, toxic, harmful, and harmless. The prediction results indicate that the toxicity levels of intermediates DC1, DC2, DC3, DC4, and DC5 to the three types of organisms are similar to that of DC itself and are classified as harmless. Nevertheless, DC7 exhibits toxicity towards green algae, fish, and daphnids, with particularly strong toxicity being observed in green algae, making it the most toxic among the degradation products. Based on the inferred degradation pathway, DC7 is identified as an intermediate product rather than a final product, implying that its concentration remains low and it will eventually be converted into the harmless compound DC8. Considering the degradation pathways in their entirety, it can be concluded that these pathways are relatively safe for the environment, with the final products exhibiting low toxicity.

Table 3.
Toxicity prediction of doxycycline hydrochloride and its degradation intermediates.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Devices
The material and chemical reagents, such as nickel chloride (NiCl2·6H2O), ferric chloride (FeCl3·6H2O), peroxymonosulfate (PMS), ethylene glycol, tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), p-benzoquinone (BQ), methanol (MeOH), HCl, NaOH and doxycycline hydrochloride (DC), used in the experiment were all of analytical purity, and the purity was >99% and purchased from the Sigma–Aldrich, Shanghai, China. The solutions required for the experiment were prepared with deionized water. The detailed devices are the RephiLe brand intelligent ultrapure water system Genie G (Boston, MA, USA), Thunder magnetic pH meter (Shanghai, China), WIGGENS WH280-R Heating magnetic Stirrer (Wuppertal, Germany), and the Hettich brand of centrifuge MIKRO 200 R (Tuttlingen, Germany).
3.2. Preparation of NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxides
(1) Solution preparation: Amounts of 6.4 g of NaOH and 4.2 g of Na2CO3 were dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water with thorough stirring to ensure complete dissolution. Separately, 17.83 g of NiCl2∙6H2O and 6.76 g of FeCl3∙6H2O were dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water to prepare solutions of 0.75 mol/L NiCl2 and 0.25 mol/L FeCl3, respectively. (2) Combination of metal salt solutions: Both solutions were added simultaneously to 200 mL of deionized water at a controlled rate of 2.0 mL/min while the mixture was continuously stirred. (3) Aging of the precipitation: Following the addition, the solution was aged in a water bath at 80 °C for 1 h. (4) Grinding and screening: The precipitate formed was subsequently separated by centrifugation, dried, and finely ground using a 200-mesh agate sieve, yielding nickel–iron-layered double hydroxides (NiFe-LDHs) with a 3:1 molar ratio. The same method was employed to prepare NiFe-LDHs with molar ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, and 4:1 by adjusting the relative amounts of nickel NiCl2 and FeCl3 accordingly.
3.3. Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed using a D8ADVance X-ray diffractometer from Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany. Experimental conditions: Copper target Kα radiation source (λ = 0.15418 nm), Lynx Exe array detector, voltage 40 kV, current 40 mA, scanning step 0.02°, scanning speed 17.7 s·step-1, scanning range from 5° to 70°. The samples tested were different proportions of NiFe-LDH powder that had been sieved in a 200-mesh sieve. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were acquired utilizing the FEI Talos F200X transmission electron microscope manufactured by the FEI Company, Waltham, MA, USA. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra were recorded using the ESCAlab 250 XI X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), with the binding energy of carbon calibrated at 284.6 eV to account for electron effects. Electron spin resonance (ESR) was employed to analyze the free radicals present in the material. Furthermore, the characterization of the types of free radicals was conducted using this instrument in conjunction with the spin-trapping agents 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (TEMP).
The degradation products of DC were analyzed using liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC/Q-TOF), with the specific model being the Agilent 1290 series HPLC and G6460 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Agilent, Lexington, MA, USA). The mobile phase for DC was 25% MeOH and 75% formic acid solution (0.2%), with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Additionally, the mobile phases A and B for DC were 0.1% formic acid solution and acetonitrile (containing 0.1% formic acid), with a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min, to analyze the possible intermediate products produced during the degradation process.
3.4. Degradation Experiments
The degradation experiments were conducted in a six-unit Jar test stirring device, and each unit contained 250 mL of doxycycline solution with a concentration of 10 mg/L. After adding an appropriate amount of LDHS and PMS to the solution, the pH value of the solution was adjusted using hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, and sodium chloride solutions to investigate the effect of different LDH dosages, PMS dosages, and pH conditions on the removal efficiency of doxycycline. The solution was stirred at a speed of 150 revolutions per minute for 10 min to ensure sufficient contact between the catalyst and the solution. Subsequently, 10 milliliters of the sample was extracted using a disposable sterile syringe and filtered through a porous membrane with a pore size of 0.45 µm to remove possible large particulate matter. The absorbance of each sample was measured at a wavelength of 346 nm using an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-2600, Kyoto, Japan), and the average absorbance value of each sample was determined through three independent measurements. These data were used to calculate the removal rate of doxycycline.
The ECOSAR (Ecological Structure–Activity Relationship) classification procedure was employed to predict the aquatic toxicity of the degradation products. This computational tool uses the quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) of a chemical substance to estimate its toxicity to aquatic organisms by analyzing correlations between molecular structures and known toxicity data.
4. Conclusions
In this study, NiFe-LDHs were used as a catalyst to activate PMS to effectively degrade doxycycline in water, demonstrating significant treatment efficiency and application potential. Several challenges still need to be faced in order to make this technology practical: cost-effectiveness, system stability, pH sensitivity, PMS usage control, and secondary contamination issues. To address these challenges, we conducted research. This study demonstrates that utilizing NiFe-LDHs as a catalyst offers a novel and potentially more effective approach to activating peroxymonosulfate (PMS) compared to methods relying on single transition-metal ions. NiFe-LDHs not only exhibit higher catalytic efficiency but also greater stability. The degradation rate of doxycycline was observed to increase with the addition of PMS, and, notably, the degradation efficiency remained stable even with excessive PMS, indicating that overuse of PMS does not negatively impact the photodegradation process’s persistence and stability. This finding suggests a new perspective on the optimal application of PMS in photodegradation. The study also revealed a positive correlation between the amount of catalyst added and the degradation rate. The degradation rate was particularly rapid during the first ten minutes of the experiment, followed by a gradual increase in efficiency. At a catalyst concentration of 0.5 g/L, the degradation rate of doxycycline reached 78.55%. The effect of pH on persulfate activation was minimal, leading to the choice of neutral pH conditions for the reaction. Among the different NiFe-LDH ratios tested, the 1:1 ratio exhibited the best degradation performance, followed by the 3:1 and 2:1 ratios. The activation of PMS by NiFe-LDHs for the catalytic degradation of pollutants primarily occurs through singlet oxygen (1O2), superoxide radicals (O2−·), and sulfate radicals (SO4−·). The degradation of doxycycline can be speculated to follow three pathways (functional group cleavage, ring-opening reaction, and hydroxylation), and its final products have a lower environmental toxicity.
Author Contributions
J.C.: conceptualization, experiment, formal analysis, writing—original draft, software, and visualization. X.T.: conceptualization, visualization, investigation and writing—review and editing. J.W.: investigation and writing—review and editing. S.B.: conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing. Y.L.: investigation and writing—review and editing. Z.H.: conceptualization, methodology, and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received CCCC Fourth Harbor Engineering Institute Co., Ltd. Research Project: Research and application of multi-soil-layering system for ecological treatment of polluted water (2022-A-06-I-15).
Data Availability Statement
All data employed in support of the outcomes of the study are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jie Chen, Xiaojun Tang, Jing Wang, Shiming Bi were employed by the company CCCC Fourth Harboer Engineering Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Bungau, S.; Tit, D.M.; Behl, T.; Aleya, L.; Zaha, D.C. Aspects of Excessive Antibiotic Consumption and Environmental Influences Correlated with the Occurrence of Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 19, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.E.; Elasala, G.S.; Atta, R.M.; Kolkaila, S.A. Synthesis, Thermal Analysis and Characterization of Doxycycline Metal Complexes. Chem. Res. J. 2022, 7, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Gupta, S.C.; Chander, Y.; Singh, A.K. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Impact on the Terrestrial Environment’. Adv. Agron. 2005, 87, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J. Effects of Na+/H2O2 on Nitrogen Removal and Sludge Activity: Performance and Mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, S.; Yan, A.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Gu, C.; Qi, Y.; Wu, S. Efficient Recycling of Sewage Water in a Polyester Integrated Industry: A Case Study. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Barkhouse, A.; Hackenberger, D.; Wright, G.D. Antibiotic Resistance: A Key Microbial Survival Mechanism That Threatens Public Health. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, G.; Guarino, F.; Castiglione, S.; Rizzo, L. Antibiotic Resistance Spread Potential in Urban Wastewater Effluents Disinfected by UV/H2O2 Process. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 560–561, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Occurrence, Distribution and Seasonal Variation of Antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Meyer, M.T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.-A.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Shu, W. Determination of Antibiotics in Sewage from Hospitals, Nursery and Slaughter House, Wastewater Treatment Plant and Source Water in Chongqing Region of Three Gorge Reservoir in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Fanelli, R. Identification of the Pharmaceuticals for Human Use Contaminating the Italian Aquatic Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 122, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, N.E.; Charles, P.G. Safety and Efficacy Review of Doxycycline. Clin. Med. Ther. 2009, 1, CMT.S2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmandrad, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Naushad, M.; Boczkaj, G. Activated Persulfate and Peroxymonosulfate Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Antibiotics Degradation—A Review. Water Resour. Ind. 2023, 29, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Jia, N.; Shen, C.; Ma, J.; Wen, Y. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Fe-N Complexes Embedded within SBA-15 for Removal of Organic Contaminants via Production of Singlet Oxygen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34190–34199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, H.V.; Bircher, S.; Rapp, I.; Kerlin, N.; Bakkour, R.; Geisler, M.; von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. Degradation of Chlorotriazine Pesticides by Sulfate Radicals and the Influence of Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, C.; Nag, R.; Morris, D.; Cummins, E. Antibiotic Residues in the Aquatic Environment—Current Perspective and Risk Considerations. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated Persulfate for Organic Chemical Degradation: A Review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-C.; Zhao, Z.; Hoag, G.E.; Dahmani, A.; Block, P.A. Degradation of Volatile Organic Compounds with Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Westerhoff, P.; Zheng, M.; Wu, M.; Yang, Y.; Chiu, C.-A. UV-Activated Persulfate Oxidation and Regeneration of NOM-Saturated Granular Activated Carbon. Water Res. 2015, 73, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, I.; Huang, S.; Huang, W. Insight into Reactive Oxygen Species in Persulfate Activation with Copper Oxide: Activated Persulfate and Trace Radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Guo, A.; Qi, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Cai, A. Activation of Persulfate by Magnetic Mg/Mn–Layered Double Oxide–Doped Biochar Composite for Ciprofloxacin Removal and Bacterial Inactivation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 329, 125322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cao, T.; Lv, Z.; Peng, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Song, G. Fabrication of Ce-Doped Macroporous Carbon Fibers for Efficient Degradation of Tetracycline by Activating Persulfate☆. J. Rare Earths 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Xie, Y.; Sun, H.; Gong, X.; Qin, P.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zou, D.; Jiang, L. Efficient Degradation of Tetracycline by Persulfate Activation with Fe, Co and O Co-doped g-C3N4: Performance, Mechanism and Toxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakamercan, E.; Aygün, A.; Simsek, H. Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Electrochemically Activated Persulfate Process: Optimization, Degradation Pathways, and Toxicology Assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 143, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaheer, Z.; Al-Balawi, A.M.; Kosa, S.A. Ag0, Re0, and Ag@Re Heterogeneous Persulfate Activators for Reactive Radical Based Oxidation of Water Contaminant. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1319, 139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, P.; Hassani, A.; Wacławek, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Sayyar, Z.; Ghanbari, F. Recent Advances in Design and Engineering of MXene-Based Catalysts for Photocatalysis and Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes: A State-of-the-Art Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, C.; Han, L. Synergistic Oxidation-Filtration Process of Electroactive Peroxydisulfate with a Cathodic Composite CNT-PPy/PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane. Water Res. 2022, 210, 117971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication and Characterization of Positively Charged Hybrid Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration Membranes via the In-Situ Exfoliation of Mg/Al Hydrotalcite. Desalination 2014, 335, 78–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Preparation, Characterization, and Catalytical Application of MgCoAl-Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2007, 16, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewicz, P.; Perez-Estrada, L.; Alpatova, A.; Martin, J.W.; Gamal El-Din, M. Impact of Peroxydisulfate in the Presence of Zero Valent Iron on the Oxidation of Cyclohexanoic Acid and Naphthenic Acids from Oil Sands Process-Affected Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8984–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J. Ni Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon as Efficient Catalysts for the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azqhandi, M.H.A.; Foroughi, M.; Gholami, Z. Efficient removal of levofloxacin by a magnetic NiFe-LDH/N-MWCNTs nanocomposite: Characterization, response surface methodology, and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 113967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, D.; Chen, G.; Zhang, N.; Wan, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, R. Microcrystallization and lattice contraction of NiFe LDHs for enhancing water electrocatalytic oxidation. Carbon Energy 2022, 4, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Lu, R.; Lu, L.; Fu, X.; Zhao, D. Efficient Reduction of Nitroarenes over Nickel-Iron Mixed Oxide Catalyst Prepared from a Nickel-Iron Hydrotalcite Precursor. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1877–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, X. Performance of CuAl-LDH/Gr Nanocomposite-Based Electrochemical Sensor with Regard to Trace Glyphosate Detection in Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Asefa, T.; Qiu, R.; Su, C.; Cui, L.; Huang, Z. Robust Adsorption and Persulfate-Based Degradation of Doxycycline by Oxygen Vacancy-Rich Copper-Iron Oxides Prepared through a Mechanochemical Route. ACS ES&T Water 2022, 2, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes Coupled with Peroxymonosulfate for the Treatment of Real Washing Machine Effluent: A Comparative Study. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 847, 113182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Zou, J.; Yue, S.; Li, X.; Wiesner, M.R.; Fang, J. Removal of 2-MIB and Geosmin Using UV/Persulfate: Contributions of Hydroxyl and Sulfate Radicals. Water Res. 2015, 69, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yan, X.; Mi, X.; Wu, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.-H. Enhanced Catalytic Degradation of Aqueous Doxycycline (DOX) in Mg-Fe-LDH@biochar Composite-Activated Peroxymonosulfate System: Performances, Degradation Pathways, Mechanisms and Environmental Implications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Cai, D.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Shu, S.; Zhu, Y. Degradation of Tetracycline Using Persulfate Activated by a Honeycomb Structured S-Doped g-C3N4/Biochar under Visible Light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fang, J.; Liu, X.; Qi, J.; Li, H. Tetracycline Degradation by Activated Persulfate with Enhancement of ZIF-67 Loaded Wood-Microreactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.; Mensah, K.; ElKady, M.; Shokry, H.; Samy, M. Effective Degradation of Tetracycline via Persulfate Activation Using Silica-Supported Zero-Valent Iron: Process Optimization, Mechanism, Degradation Pathways and Water Matrices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 87449–87464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Meng, F.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, T.; Wang, D.; Lin, Y. Efficient Photocatalytic Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Cobalt-Doped Oxygen-Vacancies-Rich BiVO4 for Rapid Tetracycline Degradation. Langmuir 2024, 40, 12778–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Chen, F.; Tang, Y.; Hao, C. Tetracycline Degradation by Persulfate Activated with Novel Magnetic Composite Ferrocene/chitosan@Fe3O4. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.; Neogi, S.; De, S. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by S-Scheme Bi2S3/Doped gCN Heterostructure Photocatalyst for Highly Efficient Visible Light Driven Tetracycline Degradation: Insights into Reaction Mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Enhanced Catalytic Degradation of Tetracycline Antibiotic by Persulfate Activated with Modified Sludge Bio-Hydrochar. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).