Reduction of p-Nitrophenol with Modified Coal Fly Ash Supported by Palladium Catalysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Characteristics of Different Coal Fly Ash Samples
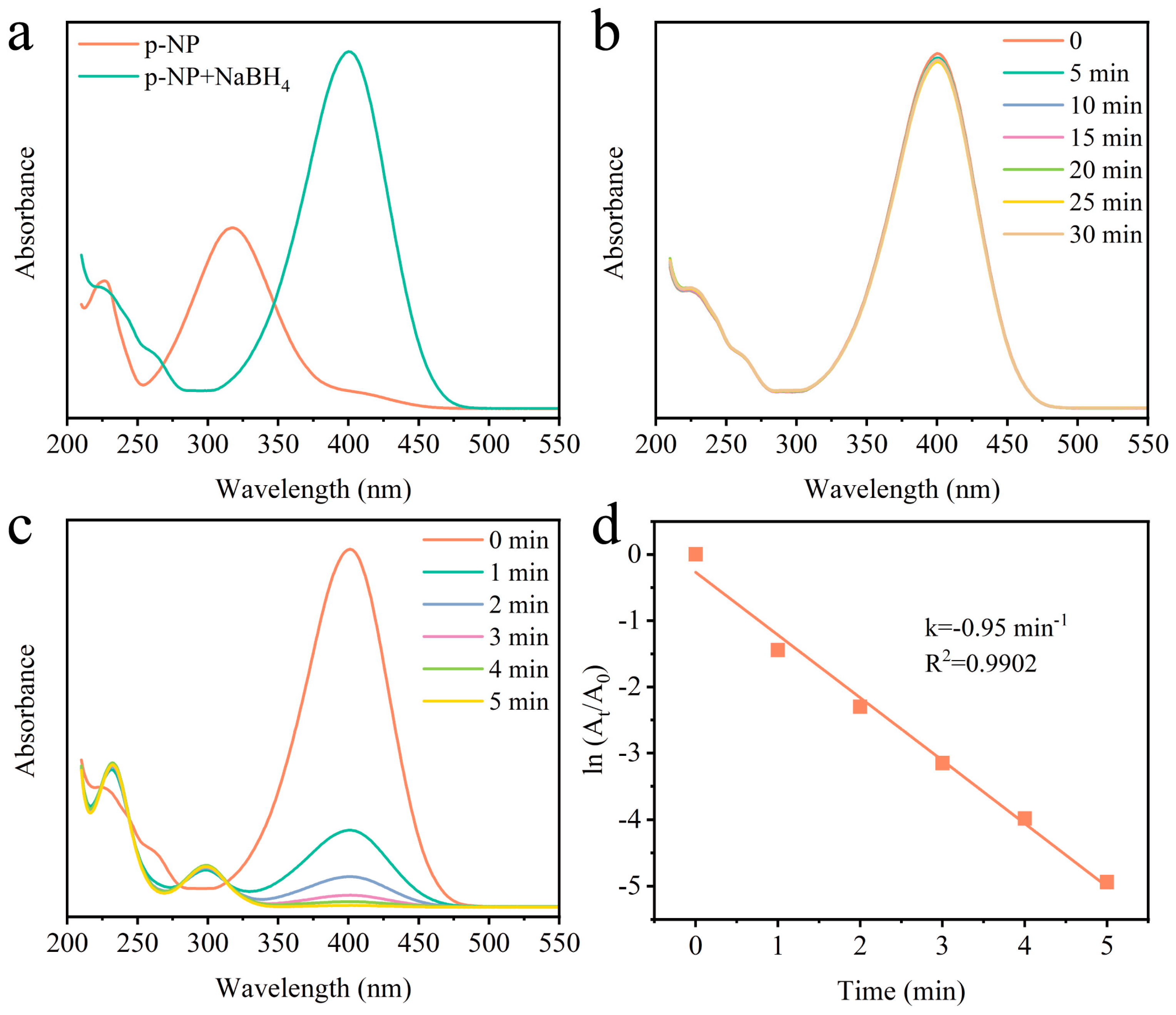
2.2. Reduction Performanceof p-Nitrophenol
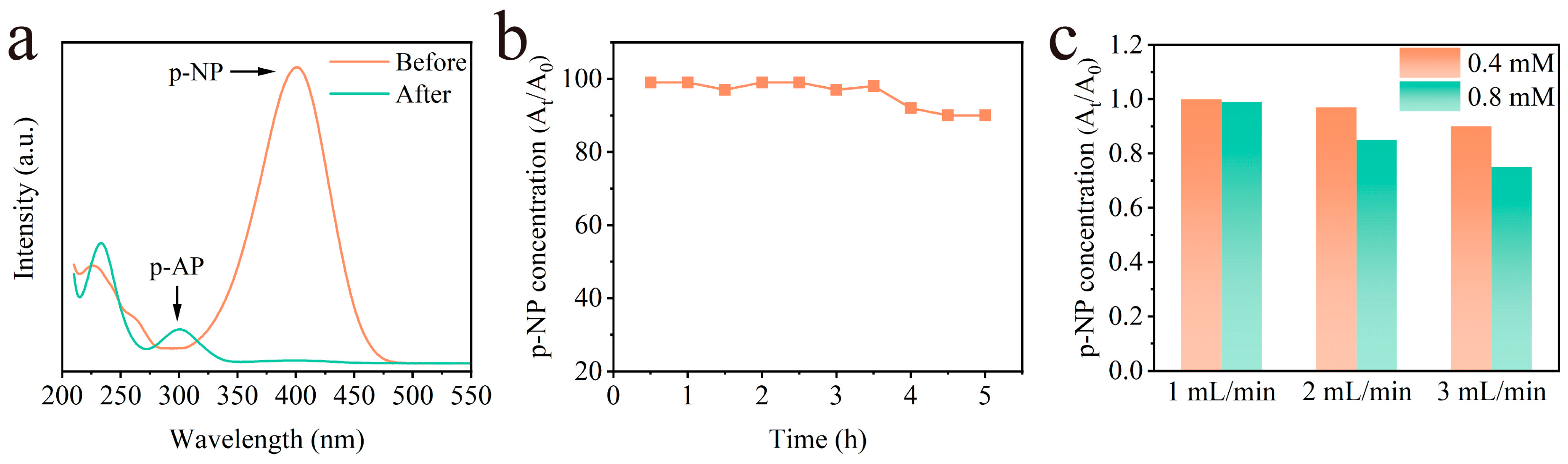
2.3. Reaction Parameter Influence
2.4. Stability Test of Catalyst
2.5. Continuous Reaction Process
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghanbari, N.; Hoseini, S.J.; Bahrami, M. Ultrasonic assisted synthesis of palladium-nickel/iron oxide core-shell nanoalloys as effective catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and p-nitrophenol reduction reactions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Zhang, X.; Deng, H.; Guan, X. Enhanced reduction of p-nitrophenol by zerovalent iron modified with carbon quantum dots. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, G.; Feng, F.; Li, H. Self-supporting hierarchical PdCu aerogels for enhanced catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Gim, S.; Kim, H.; Hanna, K. Effect of NaBH4 on properties of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its catalytic activity for reduction of p-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 182, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Khalid, R.; Hussain, Z.; Hussain, T.; Mujahid, A.; Najeeb, J.; Izhar, F. Nanocatalytic Assemblies for Catalytic Reduction of Nitrophenols: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, Q.; Yin, R.; Sun, P.; Dong, X. Phenanthroline bridging graphitic carbon nitride framework and Fe (II) ions to promote transfer of photogenerated electrons for selective photocatalytic reduction of Nitrophenols. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, J.; Ahmad, G.; Nazir, S.; Naseem, K.; Kanwal, A. Critical analysis of various supporting mediums employed for the incapacitation of silver nanomaterial for aniline and phenolic pollutants: A review. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdarta, J.; Meyer, A.S.; Jesionowski, T.; Pinelo, M. Multi-faceted strategy based on enzyme immobilization with reactant adsorption and membrane technology for biocatalytic removal of pollutants: A critical review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofrano, G.; Meric, S.; Zengin, G.E.; Orhon, D. Chemical and biological treatment technologies for leather tannery chemicals and wastewaters: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Chu, C.; Luo, Z.; Ma, J.; Fu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Xiao, R. Transformation of phenol and nitrobenzene by superoxide radicals: Kinetics and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Rehan, R.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Butt, Z.; Ashraf, S. Physical chemistry of catalytic reduction of nitroarenes using various nanocatalytic systems: Past, present, and future. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shesterkina, A.A.; Shuvalova, E.V.; Kirichenko, O.A.; Strelkova, A.A.; Nissenbaum, V.D.; Kapustin, G.I.; Kustov, L.M. Application of Silica-supported Fe-Cu Nanoparticles in the Selective Hydrogenation of p-Dinitrobenzene to p-Phenylenediamine. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 91, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvalova, E.V.; Kirichenko, O.A. Hydrogenation of nitroarenes on silica-supported copper catalyst. Mendeleev Commun. 2021, 31, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, M.; Cazemier, J.; Miguel, J.C.N.d.; Almukhtar, F.; Komaty, S.; Martinez, J.R. Influence of support polarity on the selective hydrogenation of nitrostyrene over Pt-based heterogenous catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 379, 113272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bae, S. Highly efficient and magnetically recyclable Pd catalyst supported by iron-rich fly ash@fly ash-derived SiO2 for reduction of p-nitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Cao, S.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Synthesis and Catalytic Application of MOF Complexes Containing Noble Metals. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 11494–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Varma, R.S. Recent developments in palladium (nano)catalysts supported on polymers for selective and sustainable oxidation processes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 397, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Lai, Y.-R.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, S.S.S.; Lin, K.-S. Using palladium nanoparticle-decorated lysozyme amyloid fi brils to catalyze the reduction of methylene blue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 118, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Miao, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yao, J. Advances in morphology-controlled alumina and its supported Pd catalysts: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 5014–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Llorca, J.; Nasiou, D.; Arbiol, J.; Meyns, M.; Cabot, A. Graphene-supported palladium phosphide PdP2 nanocrystals for ethanol electrooxidation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 242, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Sanchez, M.; Diaz-Garcia, D.; Prashar, S.; Gomez-Ruiz, S. Palladium nanoparticles supported on silica, alumina or titania: Greener alternatives for Suzuki-Miyaura and other C-C coupling reactions. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1585–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, K.; Shan, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Fan, W.; He, H.; Zhao, X.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Superior performance in passive NOx adsorption over an Al-rich Beta zeolite supported palladium. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. Energy 2023, 339, 123127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z.; Al-Mamun, M.; Zhao, H.; Su, X. Palladium-decorated hierarchical titania constructed from the metal-organic frameworks NH2-MIL-125(Ti) as a robust photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 218, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, N.; Wang, J.; Osman, S.M.; Luque, R.; Chen, B.H. Highly efficient and stable catalysts-covalent organic framework-supported palladium particles for 4-nitrophenol catalytic hydrogenation. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, R.; Chang, X.; Yan, J.; Gu, Y.; Xi, S.; Sun, P.; Dong, X. Degradation of Sodium Acetate by Catalytic Ozonation Coupled with a Mn-Functionalized Fly Ash: Reaction Parameters and Mechanism. Toxics 2023, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angaru, G.K.R.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, D.-S.; Koduru, J.R.; Yang, J.-K.; Chang, Y.-Y. Facile synthesis of economical feasible fly ash-based zeolite-supported nano zerovalent iron and nickel bimetallic composite for the potential removal of heavy metals from industrial effluents. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Iliuta, M.C. Trends and advances in the development of coal fly ash-based materials for application in hydrogen-rich gas production: A review. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 73, 485–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Du, B.; Dai, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Coupling of alkaline and mechanical modified fly ash for HCl and SO2 removal in the municipal solid waste incineration plant. Fuel 2023, 346, 128354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.X.; Zhan, S.L.; Fang, M.H.; Qian, X.Q.; Yang, H. Adsorption of basic dye from aqueous solution onto fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ogata, F.; Nakamura, T.; Kawasaki, N. Synthesis of novel zeolites produced from fly ash by hydrothermal treatment in alkaline solution and its evaluation as an adsorbent for heavy metal removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Agarwal, A.; De, A.; Singh, P. Coal fly ash: An emerging material for water remediation. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qi, L.; Zhang, J. Specific resistance and adsorption performance of acid-modified fly ash for escaped ammonia in flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, N.; Mishra, A.; Barman, S.; Padhi, S.K.; Panda, B.B.; Jaseer, E.A.; Javid, M. Tuning Pd-to-Ag Ratio to Enhance the Synergistic Activity of Fly Ash-Supported PdxAgy Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Acs Omega 2023, 9, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Sattar, H.; Haider, R.; Munir, S. Synthesis and characterization of pure phase zeolite 4A from coal fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wu, X.; Mi, R.; Zai, H.; Fang, M.; Min, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z. Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from fly ash by one-pot hydrothermal method for methylene blue removal. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 5298–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xiao, L.; Qu, R.; Liu, S.; Ye, D.; Song, H.; Wu, W.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, X. Synthesis and characterization of a single phase zeolite A using coal fly ash. Rsc Adv. 2018, 8, 42200–42209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Bae, S. Immobilization and characterization of Fe(0) catalyst on NaOH-treated coal fly ash for catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Sahraei, O.A.; Iliuta, M.C. Ni-based catalysts supported on acid/alkali-activated coal fly ash residue for improved glycerol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2022, 301, 120791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, W.; Gao, B.; Cui, S.; Li, J.; Qi, L. Denitration performance and mechanism of Mn-Ce supported alkali-modified fly ash catalysts for NH3-SCR. Fuel 2024, 357, 129878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niveditha, S.V.; Gandhimathi, R. Flyash augmented Fe3O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of stabilized landfill leachate in Fenton process. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.V.P.B.; Subramanian, K.V.L. Quantitative XRD study of amorphous phase in alkali activated low calcium siliceous fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, R.; Chang, X.; Yan, J.; Gu, Y.; Xi, S.; Sun, P.; Dong, X. Ozone Catalysis Degradation of Sodium Acetate via Vacancy-Driven Radical Oxidation over Fe-Modified Fly Ash. Water 2023, 15, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. RNA-mediated, green synthesis of palladium nanodendrites for catalytic reduction of nitroarenes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 544, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dong, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Liang, S.; Hu, L.; Xie, H. Cellulosic protic ionic liquids hydrogel: A green and efficient catalyst carrier for Pd nanoparticles in reduction of 4-nitrophenol in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, S.; An, S.; Jeong, J.; Viji, M.; Kim, K. Hematite/M (M = Au, Pd) Catalysts Derived from a Double-Hollow Prussian Blue Microstructure: Simultaneous Catalytic Reduction of o and p-Nitrophenols. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17557–17570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, D.; Qu, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, J. Replacement reaction-based synthesis of supported palladium catalysts with atomic dispersion for catalytic removal of benzene. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17032–17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Xu, W.; Li, N.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Hu, S. Dynamic restructuring of carbon dots/copper oxide supported on mesoporous hydroxyapatite brings exceptional catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 263, 118299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Subhan, F.; Yan, Z.; Yaseen, M.; Shujahat, M.H. Fabrication of gold nanoparticles within hierarchically ZSM-5-based micro-/mesostructures (MMZ) with enhanced stability for catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol and methylene blue. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, X.; Hua, R.; Zhang, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, T.; Zheng, J.; Lu, G. Remarkably catalytic activity in reduction of 4-nitrophenol and methylene blue by Fe3O4@COF supported noble metal nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 260, 118142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; He, Q.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S. Catechol-functionalized microporous organic polymer as supported media for Pd nanoparticles and its high catalytic activity. Polymer 2014, 55, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.G.-T.; Truong, D.P.T.; Nguyen, H.B.; Do, B.L.; Dinh, T.A.; Ton-That, P.; Nguyen, T.T.V.; Truong, T.B.T.; Huynh, K.P.H.; Tri, N. Green synthesized nano-silver/cellulose aerogel as a robust active and recyclable catalyst towards nitrophenol hydrogenation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144604. [Google Scholar]
- Maslamani, N.; Khan, S.B.; Danish, E.Y.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Akhtar, K.; Asiri, A.M. Metal nanoparticles supported chitosan coated carboxymethyl cellulose beads as a catalyst for the selective removal of 4-nitrophenol. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokate, M.; Garadkar, K.; Gole, A. Zinc-oxide-silica-silver nanocomposite: Unique one-pot synthesis and enhanced catalytic and anti-bacterial performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 483, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, N.; Sahoo, A.; Boddhula, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Patra, S.; Panda, B.B. Fly ash supported Pd-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles exhibiting a synergistic catalytic effect for the reduction of nitrophenol. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11019–11026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Binh, N.; Huang, C.P.; Doong, R.-A. Enhanced catalytic reduction of nitrophenols by sodium borohydride over highly recyclable Au@graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 240, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Hou, S.; Chen, T.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D.; Yang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, G. Construction of continuous flow catalytic reactor-HPLC system with ultrahigh catalytic activity using 2D nanoflower MOF-derived Cu2O/Cu/PDA/CF catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najdovski, I.; Selvakannan, P.; Bhargava, S.K.; O‘Mullane, A.P. Formation of nanostructured porous Cu-Au surfaces: The influence of cationic sites on (electro)-catalysis. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6298–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokry, R.; Abd El Salam, H.M.; Aman, D.; Mikhail, S.; Zaki, T.; El Rouby, W.M.A.; Farghali, A.A.; Al, W.; Ko, Y.G. MOF-derived core-shell MnO@Cu/C as high-efficiency catalyst for reduction of nitroarenes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunge, Y.M.; Yadav, A.A.; Kang, S.-W.; Kim, H.; Fujishima, A.; Terashima, C. Nanoflakes-like nickel cobaltite as active electrode material for 4-nitro-phenol reduction and supercapacitor applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Chiu, K.-L.; Wu, H.-C.; Pao, C.-W.; Chen, C.-L.; Hsu, H.-C.; Kao, H.-M. Silver particles deposited onto magnetic carbon nanofibers as highly active catalysts for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2022, 315, 121596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.-T.; Asoh, T.-A.; Uyama, H. Superfast flow reactor derived from the used cigarette filter for the degradation of pollutants in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Zhai, S.; Chen, J.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Z.; Weng, X. Development of a multi-active center catalyst in mediating the catalytic destruction of chloroaromatic pollutants: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 272, 119015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzac, G.M.; Montes, O.; Fernandez, A. Microstructure and activity of Pd catalysts prepared on commercial carbon support for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 2628–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

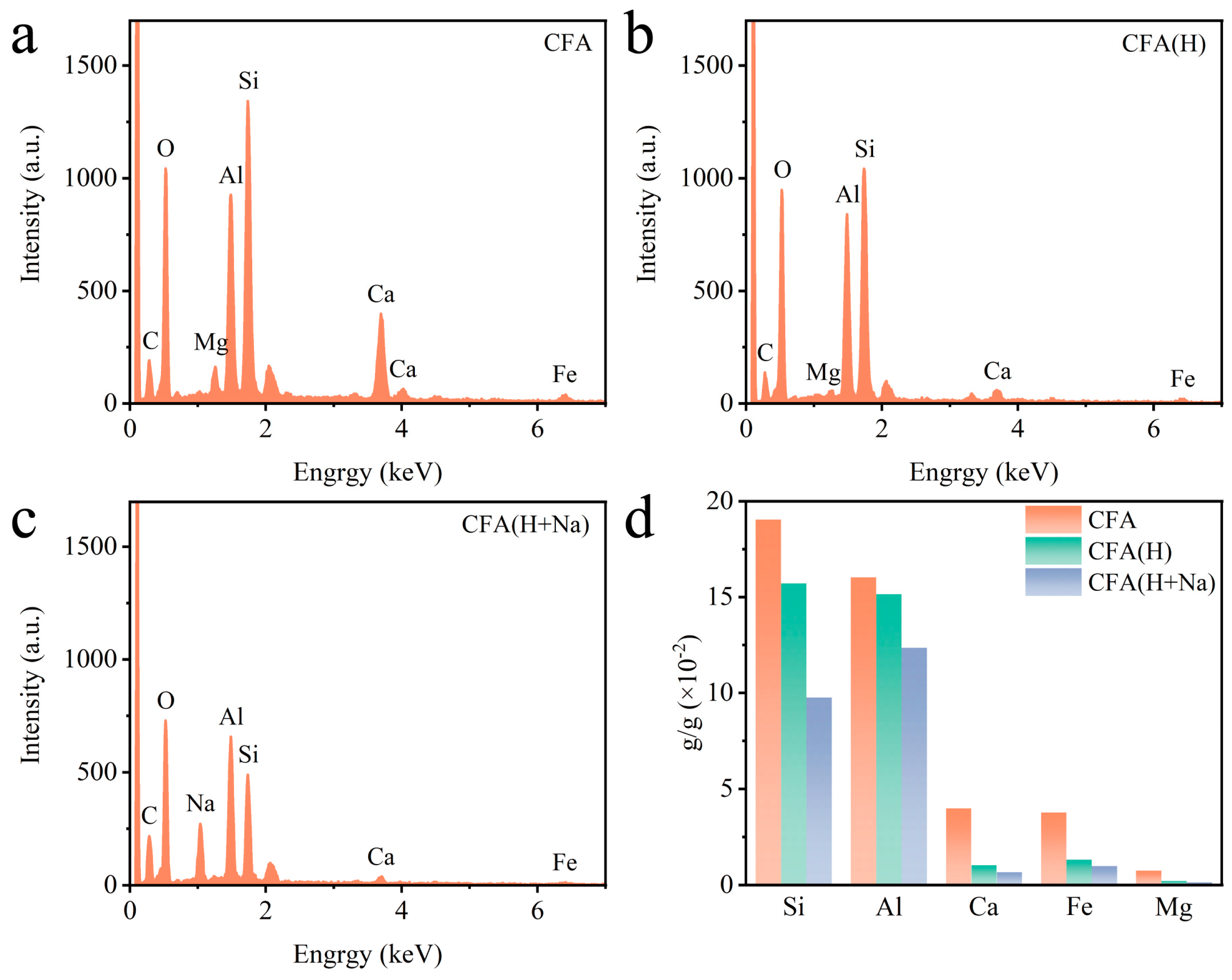






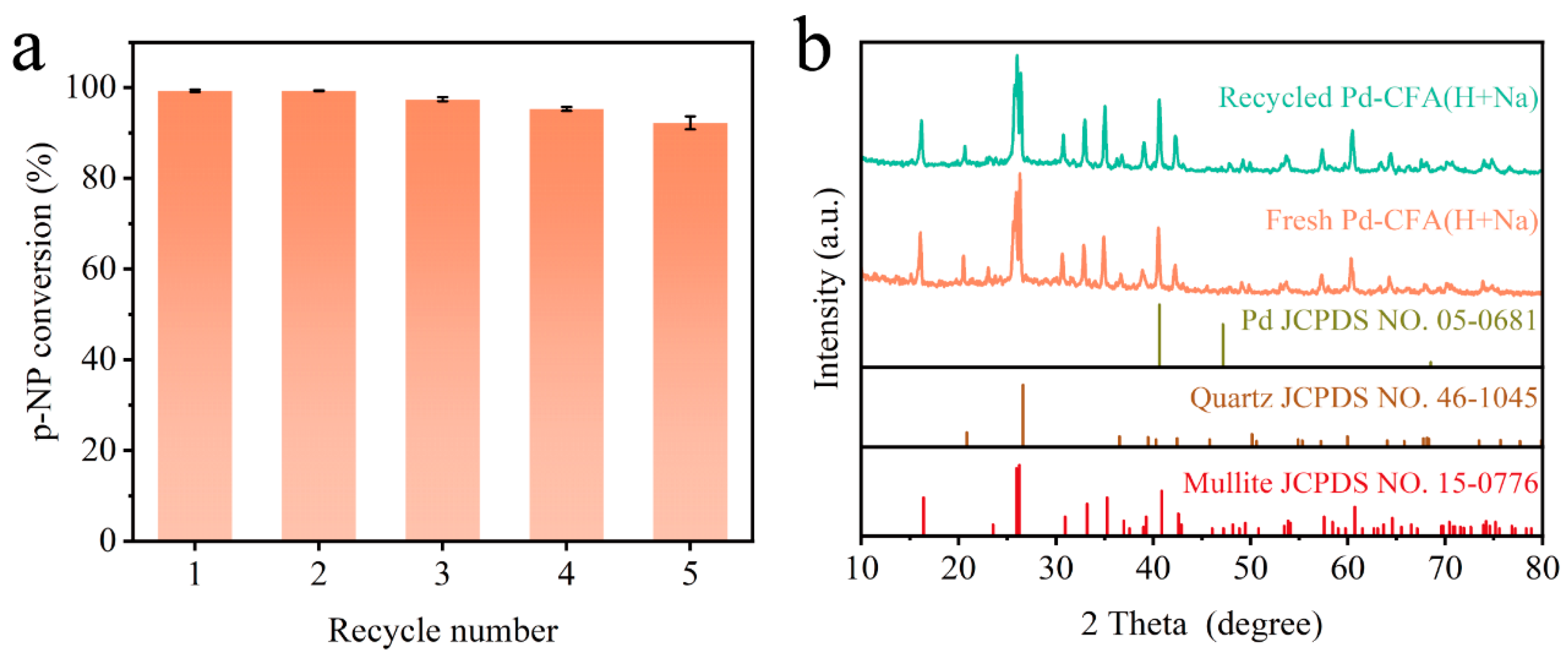

| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) | ICP Analysis (10−2 g/g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Al | Ca | Fe | Mg | Pd | ||||
| CFA | 1.47 | 0.0047 | 8.14 | 19.04 | 16.03 | 3.99 | 3.77 | 0.74 | / |
| CFA(H) | 11.37 | 0.0083 | 9.72 | 15.71 | 15.15 | 1.03 | 1.32 | 0.21 | / |
| CFA(H+Na) | 66.61 | 0.1443 | 10.68 | 9.75 | 12.36 | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.13 | / |
| Pd-CFA(H+Na) | 67.35 | 0.1022 | 9.65 | 9.62 | 12.16 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.08 | 1.23 |
| Catalysts | Cp-NP (mM) | CNaBH4 (mM) | Ccat (g/L) | k (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@COF-Au | 1.0 | 440 | 0.33 | 0.22 | [49] |
| Pd@MOPOH | 0.1 | 10 | 0.16 | 0.65 | [50] |
| Ag/CA2.0 | 0.14 | 28.8 | 1 | 0.34 | [51] |
| Cu/CMC | 0.13 | 50 | 1.67 | 0.21 | [52] |
| Cu/Cs@CMC | 0.13 | 50 | 1.67 | 0.38 | [52] |
| ZnO-SiO2-Ag | 0.1 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 0.26 | [53] |
| FA-Pd-Ag | 0.01 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.72 | [54] |
| Au@g-C3N4 | 0.2 | 7 | 1 | 0.9 | [55] |
| Pd-CFA(H+Na) | 0.8 | 40 | 1 | 0.95 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhou, K.; Ye, T.; Xu, H.; Xie, M.; Sun, P.; Dong, X. Reduction of p-Nitrophenol with Modified Coal Fly Ash Supported by Palladium Catalysts. Catalysts 2024, 14, 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090600
Zhang H, Zhou K, Ye T, Xu H, Xie M, Sun P, Dong X. Reduction of p-Nitrophenol with Modified Coal Fly Ash Supported by Palladium Catalysts. Catalysts. 2024; 14(9):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090600
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hao, Kaicheng Zhou, Tao Ye, Huajun Xu, Man Xie, Pengfei Sun, and Xiaoping Dong. 2024. "Reduction of p-Nitrophenol with Modified Coal Fly Ash Supported by Palladium Catalysts" Catalysts 14, no. 9: 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090600
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhou, K., Ye, T., Xu, H., Xie, M., Sun, P., & Dong, X. (2024). Reduction of p-Nitrophenol with Modified Coal Fly Ash Supported by Palladium Catalysts. Catalysts, 14(9), 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090600






