Insight into the Structural and Performance Correlation of Photocatalytic TiO2/Cu Composite Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Microstructure of Films
2.2. Morphology of Films
2.3. The Wettability of Films
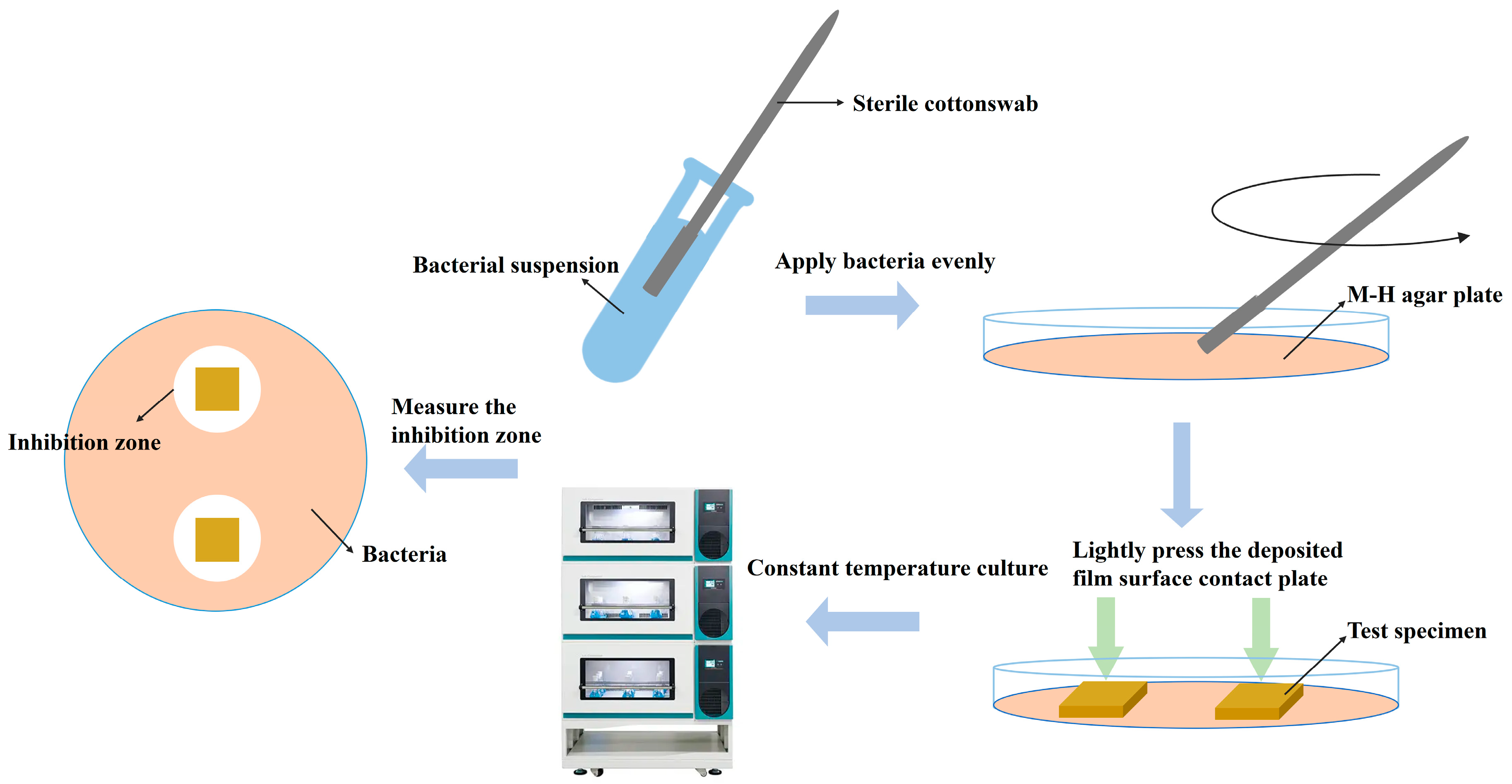
2.4. The Antibacterial Properties of Films
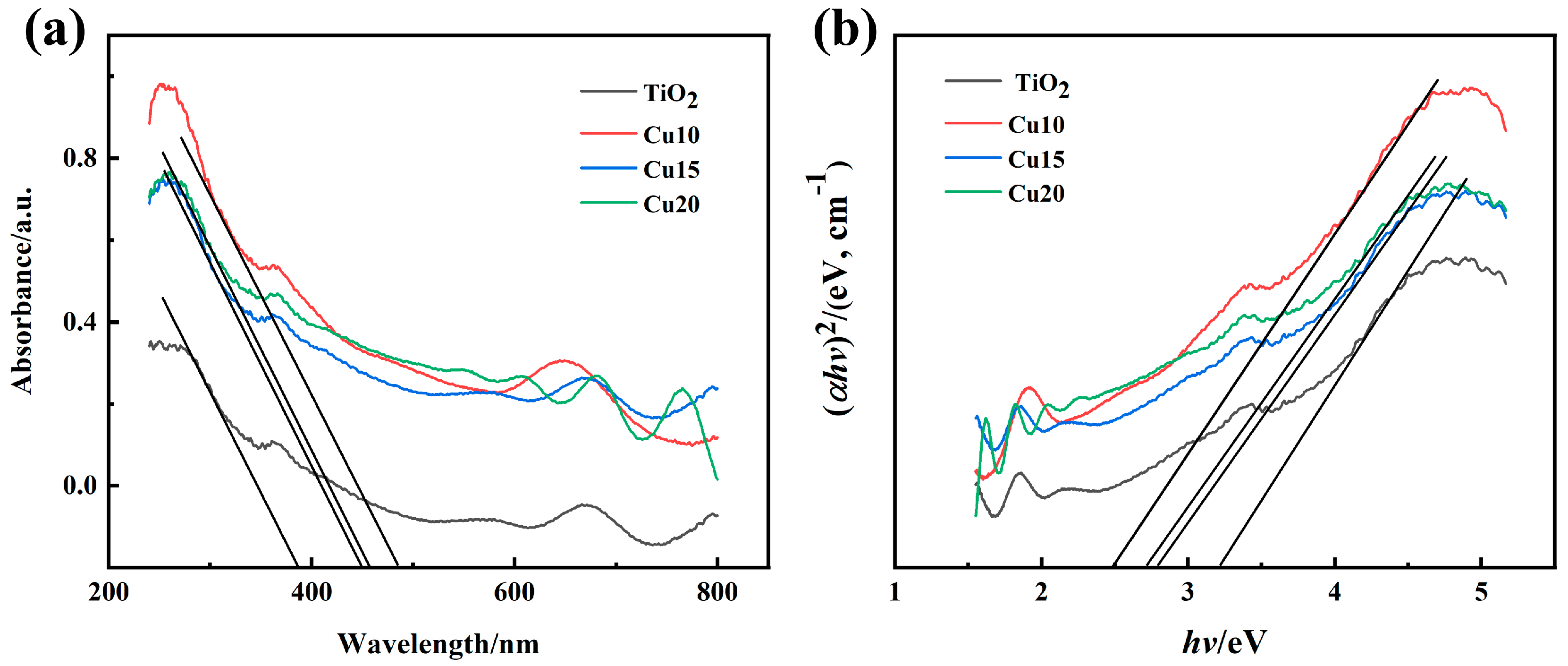
2.5. The Ultraviolet–Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy Analysis of Films
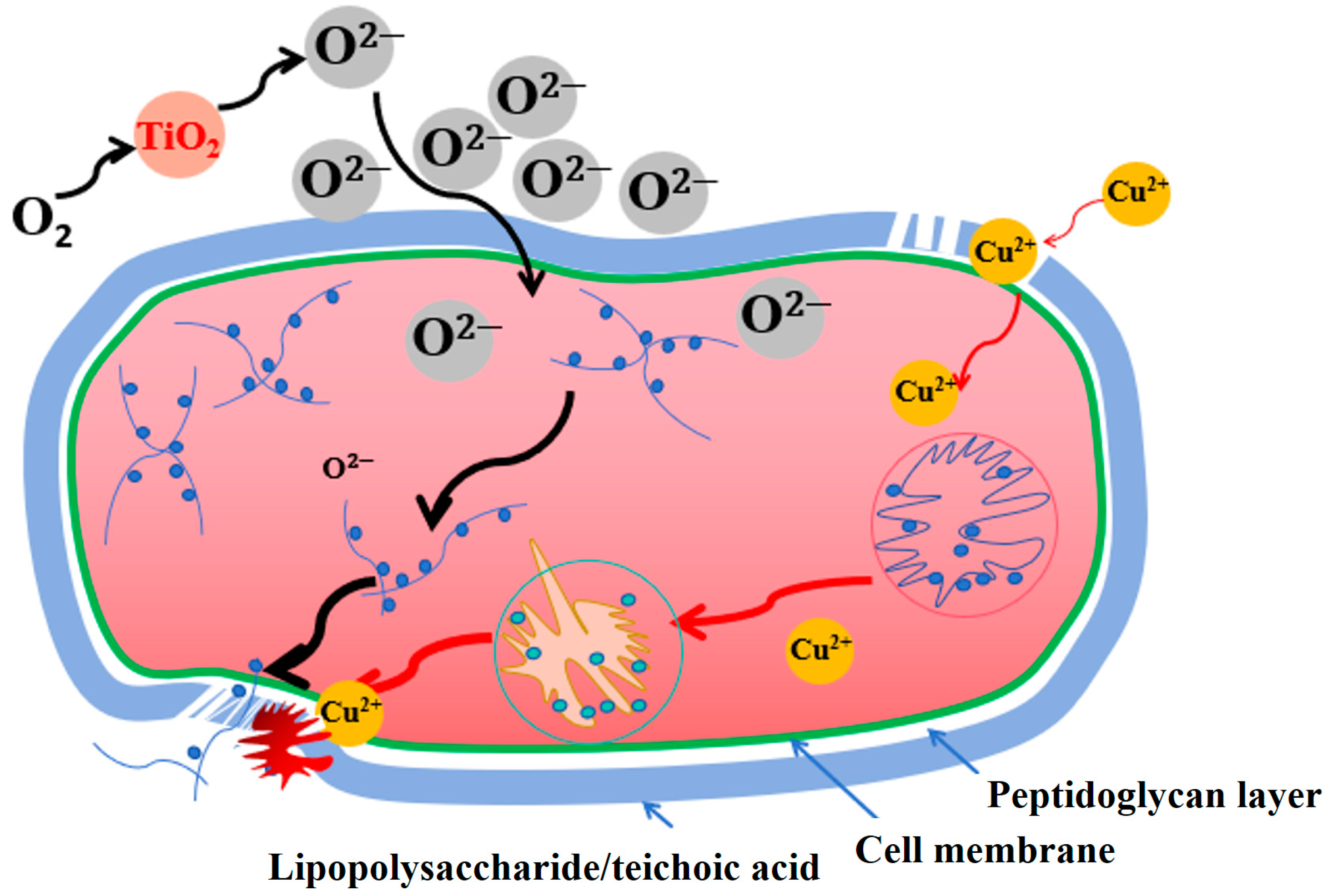
2.6. Antibacterial Mechanism Analysis
- (1)
- Surface morphology and roughness: The analysis of the film’s surface morphology indicates that Cu doping results in a “cauliflower-like” surface appearance with increased roughness and an irregular granular distribution. This three-dimensional and increased specific surface area leads to a larger contact area between the film surface and bacteria, enhancing the antibacterial performance in bacterial environments [39,40].
- (2)
- Improved hydrophobic properties: Contact angle measurements show that Cu doping enhances the hydrophobicity of the film surface. In a culture medium, this improved hydrophobicity contributes to better anti-bacterial adhesion properties. Bacteria are less likely to adhere to the hydrophobic film surface, thereby inhibiting the formation of bacterial biofilms [41].
- (3)
- Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation: After Cu doping, the TiO2 and Cu generate charge separation, inhibiting the recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. This process leads to the production of ROS such as superoxide anions (∙O2−). These ROS possess bactericidal properties.
- (4)
- Synergistic effects: Cu particles themselves exhibit strong antibacterial and bactericidal effects and can be gradually released. Cu ions (Cu2+) released from the TiO2/Cu composite films can interact with bacterial cell membranes, causing structural disruptions and increasing membrane permeability. This leads to leakage of cellular contents and loss of membrane potential, ultimately resulting in cell death. Cu2+ can bind to bacterial proteins, disrupting their structure and function. This can inhibit essential enzymatic activities and metabolic processes, further compromising bacterial viability. Cu2+ can also bind to bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), causing strand breaks and inhibiting replication and transcription. This genetic damage prevents bacterial growth and reproduction [35,42]. The synergistic effect of ROS and Cu2+ ions enhances the overall antibacterial performance of the TiO2/Cu composite films. Its antibacterial mechanism is shown in Figure 9.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Experimental Materials
3.2. Preparation of Films
3.3. Characterization Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The prepared TiO2 films exhibit a rutile structure. With the incorporation of Cu, the TiO2/Cu films are primarily composed of rutile TiO2 and FCC-Cu phases. As the Cu content increases, the grain size of the films gradually decreases, and the surface roughness increases.
- (2)
- The introduction of Cu enhances the hydrophobicity of the films. The water contact angle of the films increases with the Cu content, peaking at approximately 130° at a Cu target power of 10 W, indicating optimal hydrophobic performance.
- (3)
- Cu doping significantly improves the antibacterial properties of the films. The TiO2/Cu films exhibit excellent inhibitory effects against both Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
- (4)
- The inclusion of Cu causes a red shift in the absorption edge and a significant narrowing of the band gap, reducing it to 2.5 eV at a Cu target power of 10 W. This extends the light response range of the films into the visible region.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malheiro, J.; Gomes, I.; Borges, A.; Bastos, M.M.S.M.; Maillard, J.-Y.; Borges, F.; Simões, M. Phytochemical Profiling as a Solution to Palliate Disinfectant Limitations. Biofouling 2016, 32, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handlos, P.; Uvíra, M.; Marecová, K.; Staňková, M.; Smatanová, M.; Dvořáček, I.; Joukal, M. Fatal Ingestion of Chlumsky Disinfectant Solution. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 63, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wu, S. Recent Progress in Photocatalytic Antibacterial. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3909–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaiekhozani, A.; Rezania, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Sanaye, R.; Amani, A.M. Recent Advances in Photocatalytic Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants in Air. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.A.; Malik, T.; Siddiq, M.; Haleem, A.; Sayed, M.; Naeem, A. TiO2 Nanotubes Doped Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Polymer Membranes (PVDF/TNT) for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Brilliant Green Dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Tran, Q.B.; Ly, Q.V.; Thanh Hai, L.; Le, D.T.; Tran, M.B.; Ho, T.T.T.; Nguyen, X.C.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Vo, D.-V.N.; et al. Enhanced Visible Photocatalytic Degradation of Diclofen over N-Doped TiO2 Assisted with H2O2: A Kinetic and Pathway Study. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8361–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhtouna, H.; Benzeid, H.; Zari, N.; Qaiss, A.E.K.; Bouhfid, R. Recent Progress on Ag/TiO2 Photocatalysts: Photocatalytic and Bactericidal Behaviors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44638–44666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, S.; De Silva, H.B.; Ranasinghe, K.N.; Bandara, S.V.; Perera, I.R. Recent Development and Future Prospects of TiO2 Photocatalysis. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2021, 68, 738–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, Q.; Mao, X.; Zhou, C.; Ma, Z.; Ren, Z.; Dai, D.; Yang, X. Characterization of the Excited State on Methanol/TiO2(110) Interface. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 28, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Rahman, K.H.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, K.-C. A Review on the Pathways of the Improved Structural Characteristics and Photocatalytic Performance of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Thin Films Fabricated by the Magnetron-Sputtering Technique. Catalysts 2020, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Recent Advances in TiO2 Films Prepared by Sol-Gel Methods for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants and Antibacterial Activities. Coatings 2019, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Long, Y.; Cai, Z. Recent Advances and Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalytic Technology. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, L.; Wei, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhao, G. Linking the Doping-Induced Trap States to the Concentration of Surface-Reaching Photoexcited Holes in Transition-Metal-Doped TiO 2 Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 6504–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudhafar Mohammed, A.; Sebek, M.; Kreyenschulte, C.; Lund, H.; Rabeah, J.; Langer, P.; Strunk, J.; Steinfeldt, N. Effect of Metal Ion Addition on Structural Characteristics and Photocatalytic Activity of Ordered Mesoporous Titania. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhou, S.; Mao, X.; Shah, M.W.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C. TiO2-Supported Ag Nanoclusters with Enhanced Visible Light Activity for the Photocatalytic Removal of NO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 234, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Lu, F.; Sun, Z.; Lü, J. A Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Nano-Size Silver Particle Modified Titanium Dioxide Thin Films. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Ahmed, A.; Alam, U.; Uddin, I.; Tripathi, P.; Muneer, M. Enhanced Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities of Ag-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles under Visible Light. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 212, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkten, N.; Cinar, Z.; Tomruk, A.; Bekbolet, M. Copper-Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts: Application to Drinking Water by Humic Matter Degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36096–36106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, C.; Bui, T.-H.; Felix, C.; Moules, V.; Lina, B.; Lejeune, P. Microbiological Disinfection of Water and Air by Photocatalysis. C. R. Chim. 2007, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, F.; Li, Z. Microstructure and Tribological Behaviors of MoN-Cu Nanocomposite Coatings Sliding against Si3N4 Ball under Dry and Oil-Lubricated Conditions. Wear 2019, 434–435, 202994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, X.; Bian, S.; Chen, C.; Han, H.; Zuo, B.; Lu, K.; Zhao, L.; Yu, L.; Xu, J. Insight into the Tribological Performance and Mechanisms of MoN-Ag/Oil Solid-Liquid Lubrication System Based on Catalytic Effect. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 480, 130612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, A.M.; Williamson, B.A.D.; Sathasivam, S.; Kafizas, A.; Alqahtani, M.; Sotelo-Vazquez, C.; Buckeridge, J.; Wu, J.; Nair, S.P.; Scanlon, D.O.; et al. Enhanced Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Ability of Cu-Doped Anatase TiO2 Thin Films: Theory and Experiment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 15348–15361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chary, K.V.R.; Sagar, G.V.; Srikanth, C.S.; Rao, V.V. Characterization and Catalytic Functionalities of Copper Oxide Catalysts Supported on Zirconia. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Liu, B.; Dong, B.; Su, W.; Fan, J.; Ge, Y. Hydrothermal Surface Modification of a Low Modulus Ti-Nb Based Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2014, 43, 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Cao, Y.; Deng, J. A Convenient Alcohothermal Approach for Low Temperature Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2002, 52, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Shi, P.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Tribological Properties and Lubricating Mechanisms of Cu Nanoparticles in Lubricant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Asiri, A.M.; et al. Modulating Oxygen Vacancies of TiO 2 Nanospheres by Mn-Doping to Boost Electrocatalytic N 2 Reduction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.S.; Dutt, V.G.V.; Kumar, K.K.P.; Atchuta, S.R.; Anbazhagan, V.; Sakthivel, S. A Functional Ag-TiO2 Nanocomposite Solar Selective Absorber with Antimicrobial Activity by Photochemical Reduction Process. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 199, 111626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jia, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, G.; Ding, Q. Effect of Ag Contents on the Microstructure and Tribological Behaviors of NbN–Ag Coatings at Elevated Temperatures. Vacuum 2022, 204, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Chen, L.; Rajh, T.; Gray, K.A. Role of Surface/Interfacial Cu2+ Sites in the Photocatalytic Activity of Coupled CuO−TiO2 Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19040–19044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Kim, T.G.; Sung, Y.-M. Synthesis of Cu-Doped TiO2 Nanorods with Various Aspect Ratios and Dopant Concentrations. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yu, H. One-Step Method Using Laser for Large-Scale Preparation of Bionic Superhydrophobic & Drag-Reducing Fish-Scale Surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126801. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshmand, H.; Sazgar, A.; Araghchi, M. Fabrication of Robust and Versatile Superhydrophobic Coating by Two-Step Spray Method: An Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 567, 150825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Silikas, N.; Zhang, Z.; Watts, D.C. The Relationship between Cyclic Hygroscopic Dimensional Changes and Water Sorption/Desorption of Self-Adhering and New Resin-Matrix Composites. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e218–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Feng, X.; Dan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Enhancing Antibacterial Properties and Biosafety Evaluation of TiO2/Cu Photocatalytic Coatings Through Suspension Flame Spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2024, 33, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, D.; Thangamuniyandi, P.; Jegatha Christy, A.; Vasantharaja, R.; Selvakumar, P.; Sagadevan, S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Nehru, L.C. Enhanced Photocatalysis and Anticancer Activity of Green Hydrothermal Synthesized Ag@TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 202, 111636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liza, T.Z.; Tusher, M.M.H.; Anwar, F.; Monika, M.F.; Amin, K.F.; Asrafuzzaman, F.N.U. Effect of Ag-Doping on Morphology, Structure, Band Gap and Photocatalytic Activity of Bio-Mediated TiO2 Nanoparticles. Results Mater. 2024, 22, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.P.; Dutta, N.K. Recombination Mechanisms in Semiconductors. In Semiconductor Lasers; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Modaresifar, K.; Wang, Q.; Fan, A.; Khoshroo, K. Bactericidal Effects of Nanopatterned Surfaces: An Emerging Frontier in the Battle against Pathogenic Bacteria. Mater. Today Bio 2019, 4, 100031. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zuber, F.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Brugger, J.; Ren, Q. Nanostructured Surface Topographies Have an Effect on Bactericidal Activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Dubey, P.; Ray, S.; Jayaganthan, R.; Pant, A.B.; Chandra, R. Co-Sputtered Antibacterial and Biocompatible Nanocomposite Titania-Zinc Oxide Thin Films on Si Substrates for Dental Implant Applications. Mater. Technol. 2019, 34, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Low, J.; Wu, D.; Gong, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Long, R.; Xiong, Y. Cu and Si Co-Doping on TiO2 Nanosheets to Modulate Reactive Oxygen Species for Efficient Photocatalytic Methane Conversion. Nanoscale Horiz. 2023, 8, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
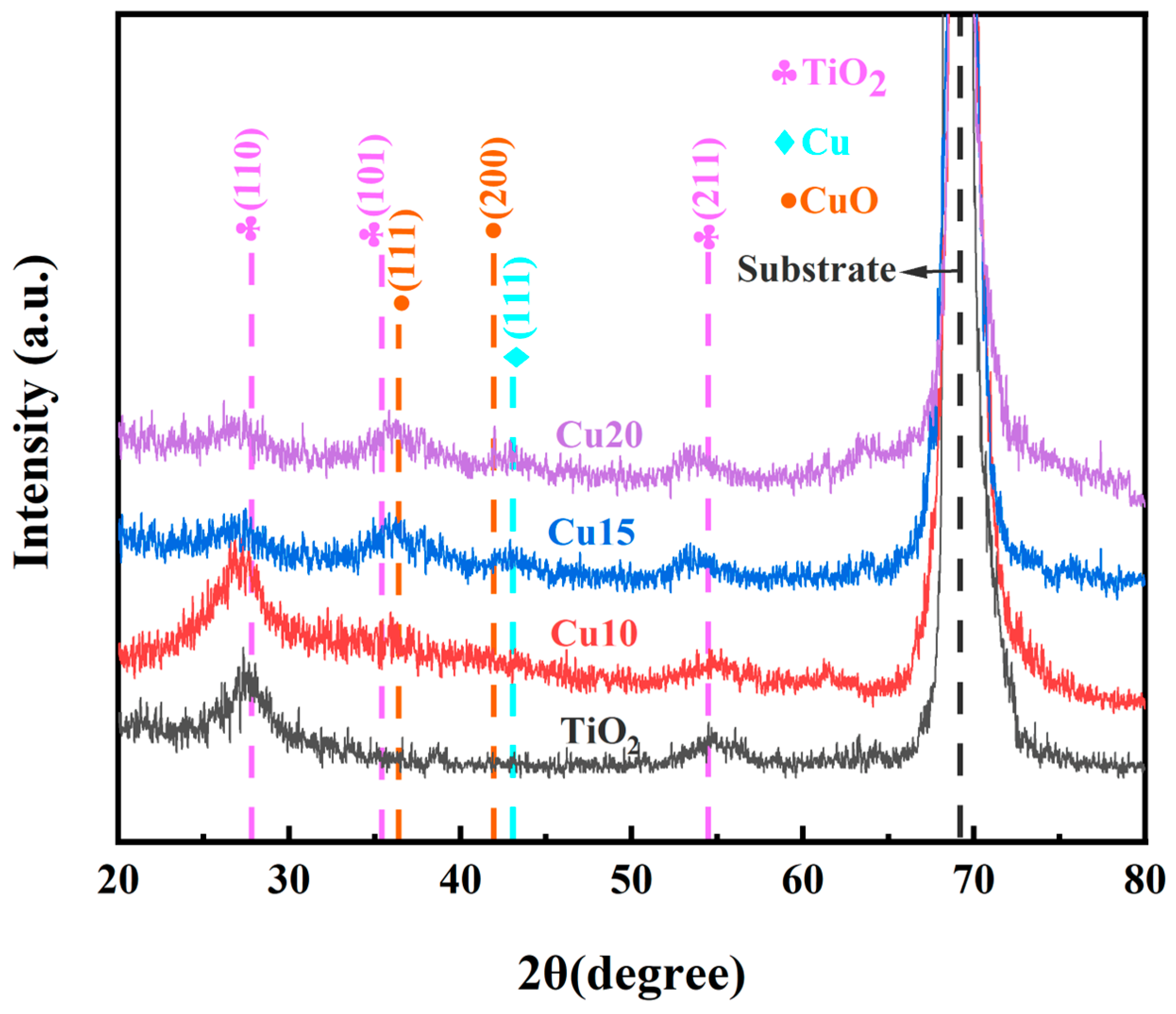
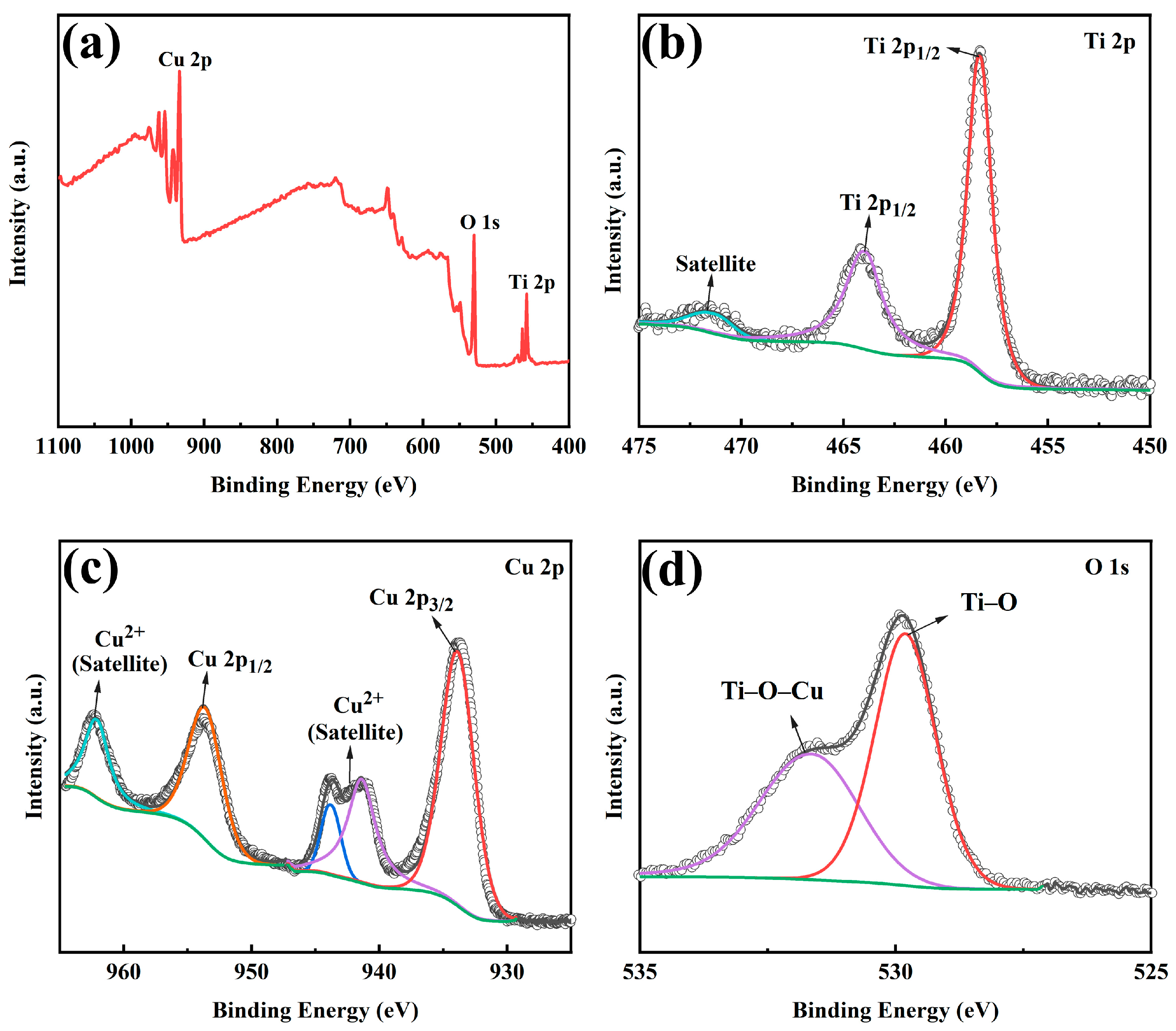

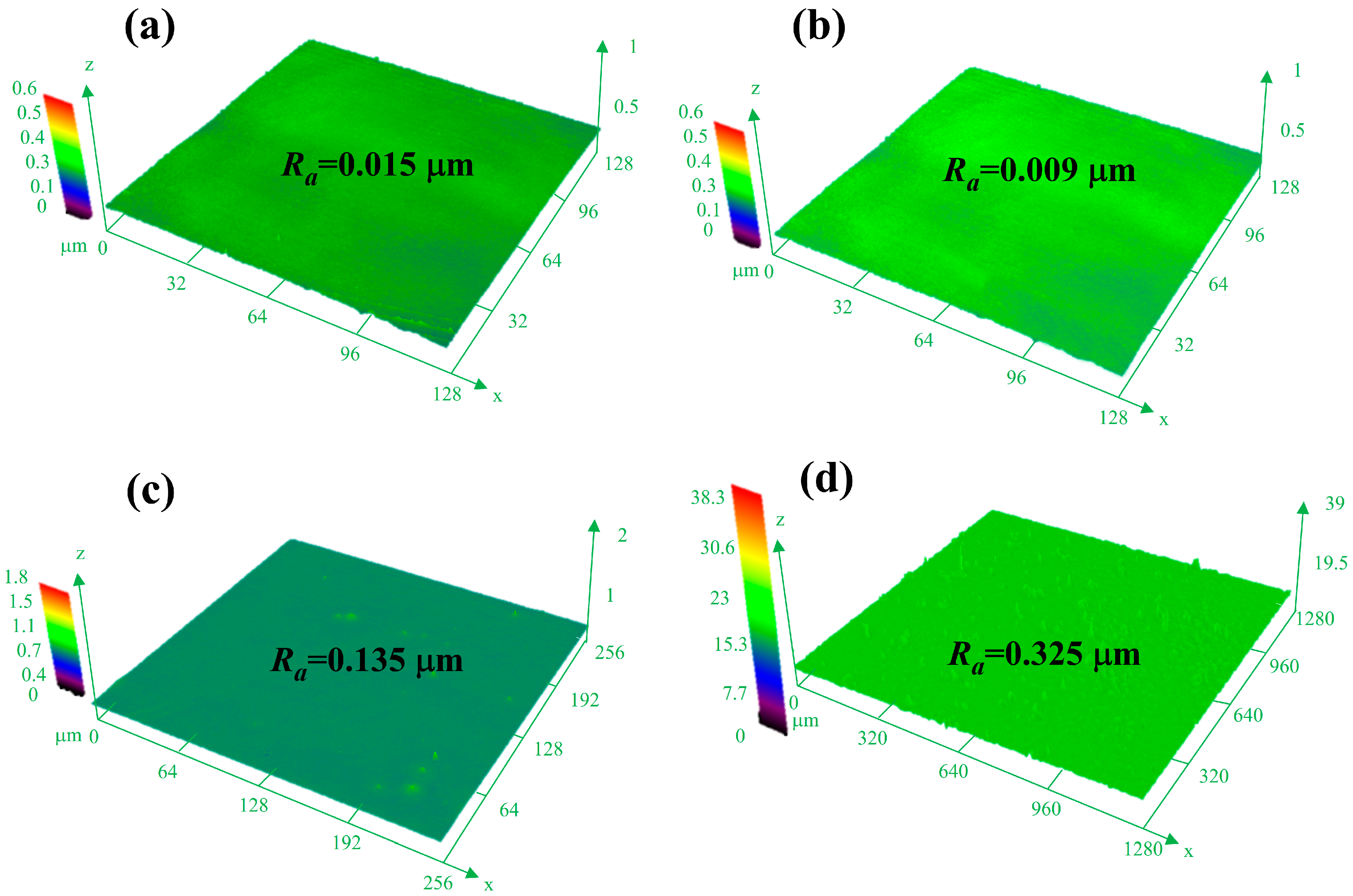


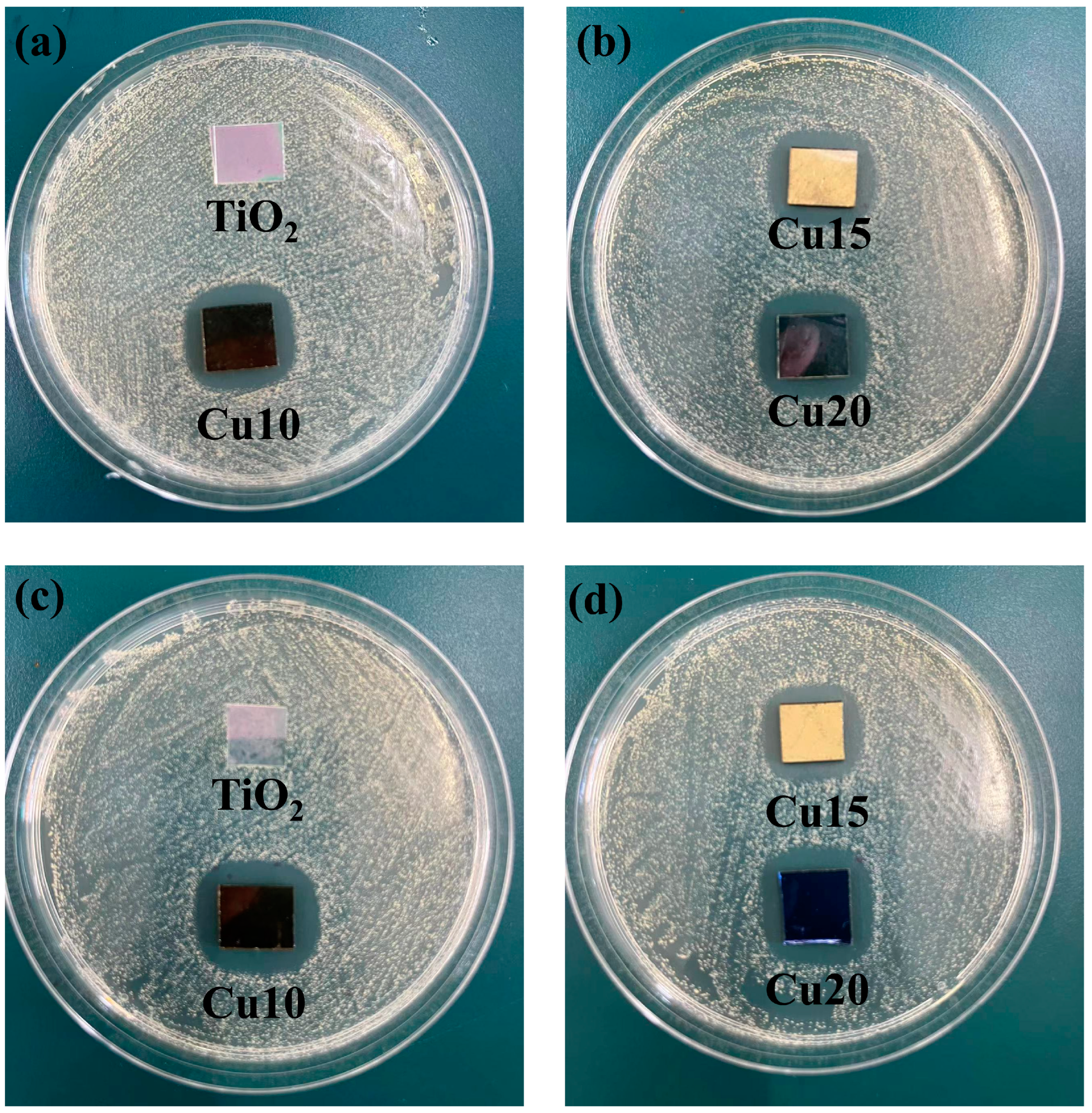

| Sample | Peak Half Width /(°) | Grain Size/nm |
|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 1.08 | 8.24 |
| Cu10 | 1.47 | 6.04 |
| Cu15 | 1.70 | 5.24 |
| Cu20 | 1.92 | 4.64 |
| Sample | Cu Power (W) | TiO2 Power (W) | BVD (Pa) | DVD (Pa) | Time (h) | Ar Flow Rate (sccm) | DT (°C) | Speed R/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 0 | 200 | <6 × 10−4 | 0.3 | 2 | 50 | RT | 5 |
| Cu10 | 10 | |||||||
| Cu15 | 15 | |||||||
| Cu20 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, K.; Sun, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J. Insight into the Structural and Performance Correlation of Photocatalytic TiO2/Cu Composite Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering Method. Catalysts 2024, 14, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090621
Lu K, Sun M, Jiang Y, Wu X, Zhao L, Xu J. Insight into the Structural and Performance Correlation of Photocatalytic TiO2/Cu Composite Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering Method. Catalysts. 2024; 14(9):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090621
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Kun, Miao Sun, Yaohong Jiang, Xinmeng Wu, Lijun Zhao, and Junhua Xu. 2024. "Insight into the Structural and Performance Correlation of Photocatalytic TiO2/Cu Composite Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering Method" Catalysts 14, no. 9: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090621
APA StyleLu, K., Sun, M., Jiang, Y., Wu, X., Zhao, L., & Xu, J. (2024). Insight into the Structural and Performance Correlation of Photocatalytic TiO2/Cu Composite Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering Method. Catalysts, 14(9), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090621







