A Spy Chemistry-Based Method for Purification of Proteins with Authentic N-Termini
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
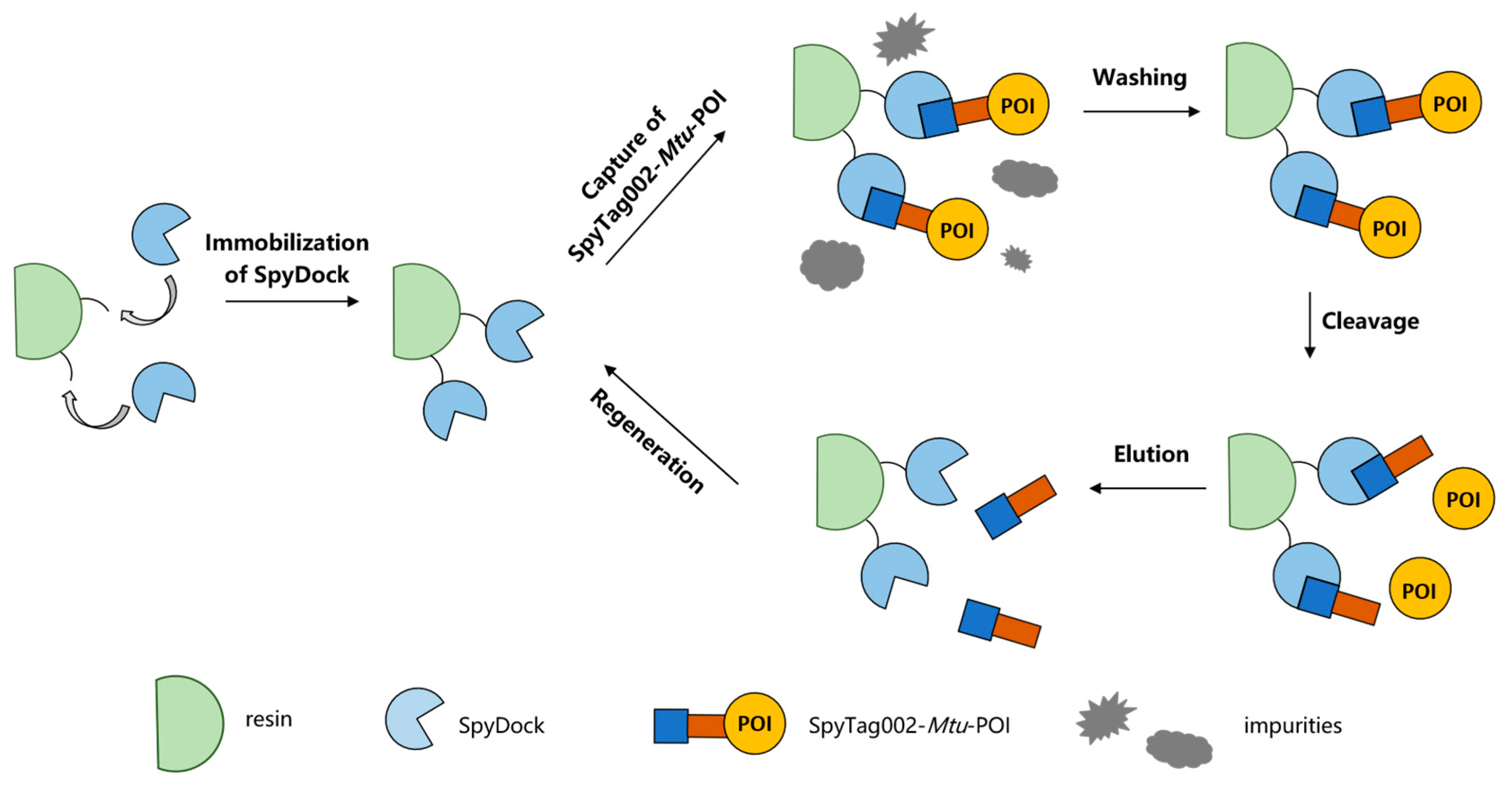
2.1. Preparation of SpyDock-Modified Resin
2.2. Capture Capacity and Reusability of SpyDock-Modified Resin Using SpyTag002-RFP
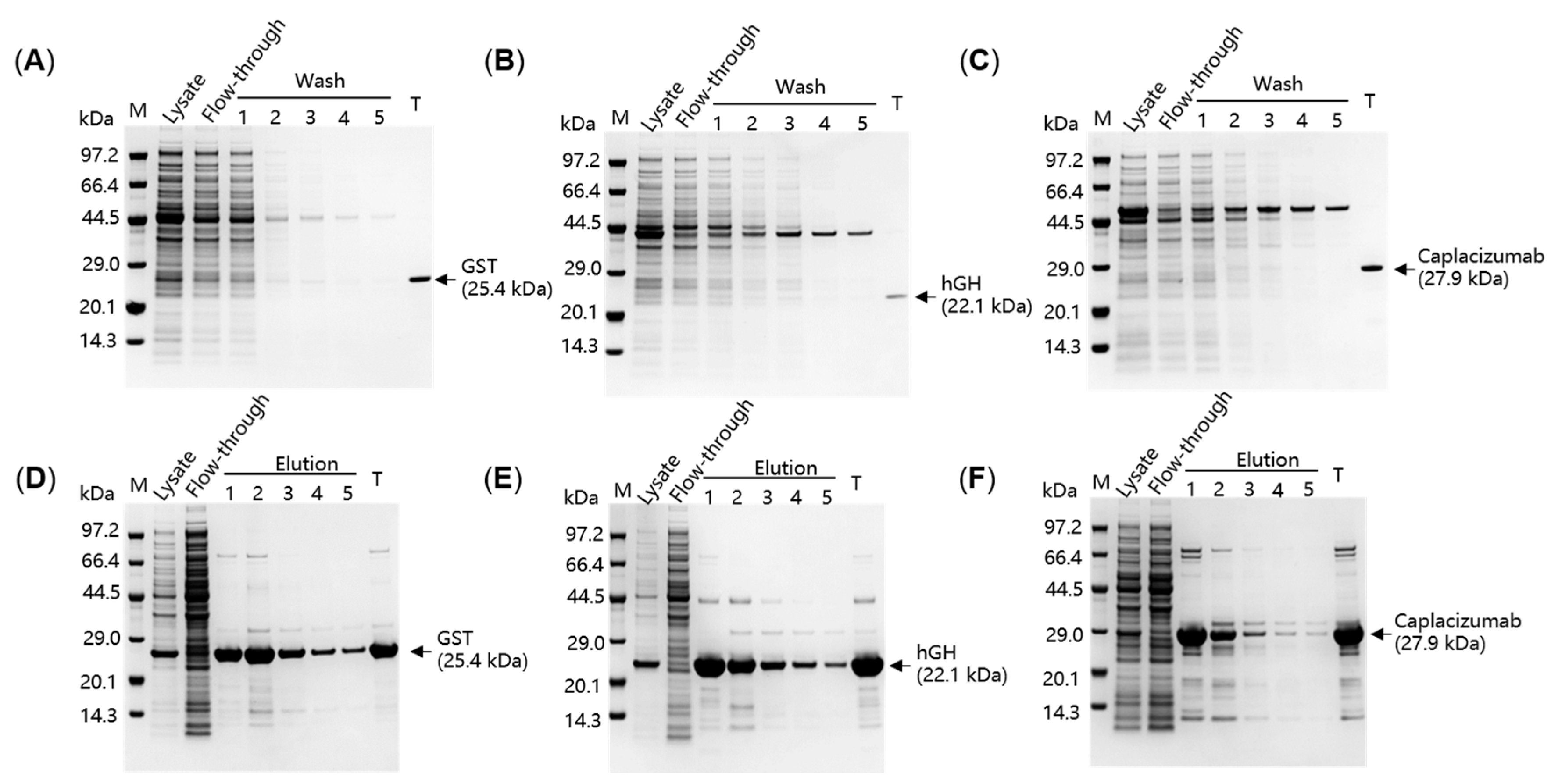
2.3. Purification of Three Model Proteins by SpyDock-Modified Resin from Crude Cell Lysates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Plasmid Construction
4.3. Protein Expression and Purification via His-Tag Method
4.4. Immobilization of SpyDock on Epoxy Resin
4.5. Capture Capacity of SpyDock-Modified Resin
4.6. Reusability of SpyDock-Modified Resin
4.7. Protein Purification via SpyDock-Modified Resin
4.8. Protein Activity Assays
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomari, M.M.; Saraygord-Afshari, N.; Farsimadan, M.; Rostami, N.; Aghamiri, S.; Farajollahi, M.M. Opportunities and challenges of the tag-assisted protein purification techniques: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 45, 107653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacki, K.M.; Riske, F.J. Affinity Chromatography: An Enabling Technology for Large-Scale Bioprocessing. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 1800397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, T.A.; Tomaleri, G.P.; Hazu, M.; Wei, S.; Nguyen, V.N.; Dekalb, C.; Voorhees, R.M.; Pleiner, T. A nanobody-based strategy for rapid and scalable purification of human protein complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 127–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichty, J.J.; Malecki, J.L.; Agnew, H.D.; Michelson-Horowitz, D.J.; Tan, S. Comparison of affinity tags for protein purification. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.L.; Britton, Z.T.; Robinson, A.S. Recombinant protein expression and purification: A comprehensive review of affinity tags and microbial applications. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Stern, D.; Lock, L.L.; Mills, J.; Ou, S.-H.; Morrow, M.; Xu, X.; Ghose, S.; Li, Z.J.; Cui, H. Emerging biomaterials for downstream manufacturing of therapeutic proteins. Acta. Biomater. 2019, 95, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, B.; Fierer, J.O.; Celik, E.; Chittock, E.C.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Moy, V.T.; Howarth, M. Peptide tag forming a rapid covalent bond to a protein, through engineering a bacterial adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E690–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddington, S.C.; Howarth, M. Secrets of a covalent interaction for biomaterials and biotechnology: SpyTag and SpyCatcher. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 29, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuar, I.N.A.K.; Banerjee, A.; Keeble, A.H.; Carella, A.; Nikov, G.I.; Howarth, M. Spy&Go purification of SpyTag-proteins using pseudo-SpyCatcher to access an oligomerization toolbox. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.L.; Lin, Q.; Li, J.H.; Pistolozzi, M.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.F.; Ye, Y.R. Spy chemistry-enabled protein directional immobilization and protein purification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, F.E. Recent Progress in Solid-Phase Total Synthesis of Naturally Occurring Small Peptides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 1934–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Shi, P.; Chen, J.Y.; Sun, S.S.; Chen, J.N.; Cui, J.B.; Wu, F.M.; Fang, G.M.; Tian, C.L.; Shi, J.; et al. Chemical synthesis and biological activity of peptides incorporating an ether bridge as a surrogate for a disulfide bond. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7927–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekan, Z.; Vetter, I.; Daly, N.L.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. α-Conotoxin ImI Incorporating Stable Cystathionine Bridges Maintains Full Potency and Identical Three-Dimensional Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15866–15869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Davern, K.M.; Board, P.G.; Tiu, W.U.; Garcia, E.G.; Mitchell, G.F. Mr 26,000 antigen of Schistosoma japonicum recognized by resistant WEHI 129/J mice is a parasite glutathione S-transferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8703–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.L.; Ndengue, P.P.A.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.F. Facile expression and purification of active human growth hormone in E. coli by a cleavable self-aggregating tag scheme. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2021, 188, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martial, J.A.; Hallewell, R.A.; Baxter, J.D.; Goodman, H.M. Human growth hormone: Complementary DNA cloning and expression in bacteria. Science 1979, 205, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sargentini-Maier, M.L.; De Decker, P.; Tersteeg, C.; Canvin, J.; Callewaert, F.; De Winter, H. Clinical pharmacology of caplacizumab for the treatment of patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, S. Caplacizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, C.; Torres, R.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Ortiz, C.; Fuentes, M.; Hidalgo, A.; Lopez-Gallego, F.; Abian, O.; Palomo, J.M.; Betancor, L.; et al. Epoxy-amino groups: A new tool for improved immobilization of proteins by the epoxy method. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Chapter 3—The Reactions of Bioconjugation. In Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Hermanson, G.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 229–258. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer-Arnaz, K.; Napolitano, E.W.; Roberts, D.N.; Montali, J.A.; Hughes, B.R.; Schmidt, D.E. Salt-induced immobilization of small affinity ligands on an epoxide-activated affinity support. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 803, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H.W. A potential method for one-step purification and direct immobilization of target protein in cell lysate with magnetic microbeads. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 176, 108182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassylyeva, M.N.; Klyuyev, S.; Vassylyev, A.D.; Wesson, H.; Zhang, Z.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wang, H.B.; Higgins, N.P.; Chow, L.T.; Vassylyev, D.G. Efficient, ultra-high-affinity chromatography in a one-step purification of complex proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5138–E5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, B.A.; Wu, W.Y.; Wood, D.W. The potential role of self-cleaving purification tags in commercial-scale processes. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puetz, J.; Wurm, F.M. Recombinant Proteins for Industrial versus Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Review of Process and Pricing. Processes 2019, 7, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Luo, S.L.; Chen, K.T.; Lii, C.K. Affinity purification of Schistosoma japonicum glutathione-S-transferase and its site-directed mutants with glutathione affinity chromatography and immobilized metal affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 852, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, N.; Tonillo, J.; Rieker, M.; Becker, S.; Dorr, B.; Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Betz, U.A.; Hock, B.; Kolmar, H. PROLink-Single Step Circularization and Purification Procedure for the Generation of an Improved Variant of Human Growth Hormone. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, S.T.; Breinholt, J.; Faber, J.H.; Andersen, M.D.; Wiberg, C.; Schjodt, C.B.; Rand, K.D. Probing the Conformational and Functional Consequences of Disulfide Bond Engineering in Growth Hormone by Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry Coupled to Electron Transfer Dissociation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5973–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Park, U.B.; Jeong, T.J.; Gu, N.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Heo, Y.S. High-resolution structure of the vWF A1 domain in complex with caplacizumab, the first nanobody-based medicine for treating acquired TTP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 567, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Seo, J.S.; Jung, S.O.; Kim, I.C.; Lee, J.S. Molecular cloning and characterization of θ-class glutathione S-transferase (GST-T) from the hermaphroditic fish Rivulus marmoratus and biochemical comparisons with α-class glutathione S-transferase (GST-A). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travensolo, R.F.; Garcia, W.; Muniz, J.R.C.; Caruso, C.S.; Lemos, E.G.M.; Carrilho, E.; Araujo, A.P.U. Cloning, expression, purification and characterization of recombinant glutathione-S-transferase from Xylella fastidiosa. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 59, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Park, H.S.; Seo, K.H.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, J.H. Complete Solubilization and Purification of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Produced in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zeng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z. A novel protein purification scheme based on salt inducible self-assembling peptides. Microb. Cell Factories 2023, 22, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vester, S.K.; Rahikainen, R.; Anuar, I.N.A.K.; Hills, R.A.; Tan, T.K.; Howarth, M. SpySwitch enables pH- or heat-responsive capture and release for plug-and-display nanoassembly. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.; Montello, G.E.; Zhang, A.; Cantor, E.J.; Liao, W.; Xu, M.Q.; Benner, J. Utilizing the C-terminal cleavage activity of a protein splicing element to purify recombinant proteins in a single chromatographic step. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 5109–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Mersha, F.B.; Comb, D.G.; Scott, M.E.; Landry, D.; Vence, L.M.; Perler, F.B.; Benner, J.; Kucera, R.B.; Hirvonen, C.A.; et al. Single-column purification of free recombinant proteins using a self-cleavable affinity tag derived from a protein splicing element. Gene 1997, 192, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhou, B.H.; Gao, X.X.; Xing, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z.L. A cleavable self-assembling tag strategy for preparing proteins and peptides with an authentic N-terminus. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Jing, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Ou, Y.; Pistolozzi, M.; Yang, X. A cleavable self-aggregating tag scheme for the expression and purification of disulfide bonded proteins and peptides. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 262, 118052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemella, P.T.; Topilina, N.I.; Soga, I.; Pereira, B.; Belfort, G.; Belfort, M.; Nayak, S.K. Electronic structure of neighboring extein residue modulates intein C-terminal cleavage activity. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitai, G.; Callahan, B.P.; Stanger, M.J.; Belfort, G.; Belfort, M. Modulation of intein activity by its neighboring extein substrates. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11005–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Shemella, P.T.; Liu, Y.; McCallum, S.A.; Pereira, B.; Nayak, S.K.; Belfort, G.; Belfort, M.; Wang, C. Highly conserved histidine plays a dual catalytic role in protein splicing: A pKa shift mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11581–11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ban, D.; Lopez, M.M.; Belfort, M.; Wang, C. Backbone dynamics and global effects of an activating mutation in minimized Mtu RecA inteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yuan, H.; Prabhala, S.V.; Coolbaugh, M.J.; Stimple, S.D.; Wood, D.W. Improved self-cleaving precipitation tags for efficient column free bioseparations. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2024, 224, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Sadovski, O.; Xin, S.J.; Woolley, G.A. Stabilization of folded peptide and protein structures via distance matching with a long, rigid cross-linker. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14154–14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, D.G.; Young, L.; Chuang, R.-Y.; Venter, J.C.; Hutchison, C.A.; Smith, H.O. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, J.; Masone, B.S.; Ribbe, J. One-step purification of recombinant proteins with the 6xHis tag and Ni-NTA resin. Mol. Biotechnol. 1995, 4, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.A.P.; Baptista, L.A.C.; Biancalana, L.; Marchetti, F.; Dyson, P.J.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S. Automated approach for the evaluation of glutathione-S-transferase P1-1 inhibition by organometallic anticancer compounds. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Target Protein Yield (%) | Purity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GST | hGH | Caplacizumab | GST | hGH | Caplacizumab | |
| SpyDock-modified resin | 58 ± 4 | 20 ± 5 | 15 ± 0.5 | 98 ± 1 | 92 ± 6 | 92 ± 2 |
| Ni-NTA | 60 ± 4 | 52 ± 9 | 49 ± 7 | 67 ± 6 | 67 ± 5 | 50 ± 3 |
| POI | Specific Activity | Specific Activity of Commercial Samples | Specific Activity Reported Before |
|---|---|---|---|
| GST | 12.8 U/mg | 10.3 U/mg | 14.0 U/mg [26] |
| hGH | 6.3 × 10−10 M | NA 1 | 2.2 × 10−10–2.0 × 10−9 M [27,28] |
| Caplacizumab | 4.5 × 10−10 M | NA 1 | 3.8 × 10−12 M [29] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Chen, B.; Lao, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Lin, Z. A Spy Chemistry-Based Method for Purification of Proteins with Authentic N-Termini. Catalysts 2024, 14, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090651
Yang X, Chen B, Lao Z, Xiang Y, Lin Z. A Spy Chemistry-Based Method for Purification of Proteins with Authentic N-Termini. Catalysts. 2024; 14(9):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090651
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaofeng, Binrui Chen, Zisha Lao, Ya Xiang, and Zhanglin Lin. 2024. "A Spy Chemistry-Based Method for Purification of Proteins with Authentic N-Termini" Catalysts 14, no. 9: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090651
APA StyleYang, X., Chen, B., Lao, Z., Xiang, Y., & Lin, Z. (2024). A Spy Chemistry-Based Method for Purification of Proteins with Authentic N-Termini. Catalysts, 14(9), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14090651







