Nanorod Heterodimer-Shaped CuS/ZnxCd1−xS Heteronanocrystals with Z-Scheme Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
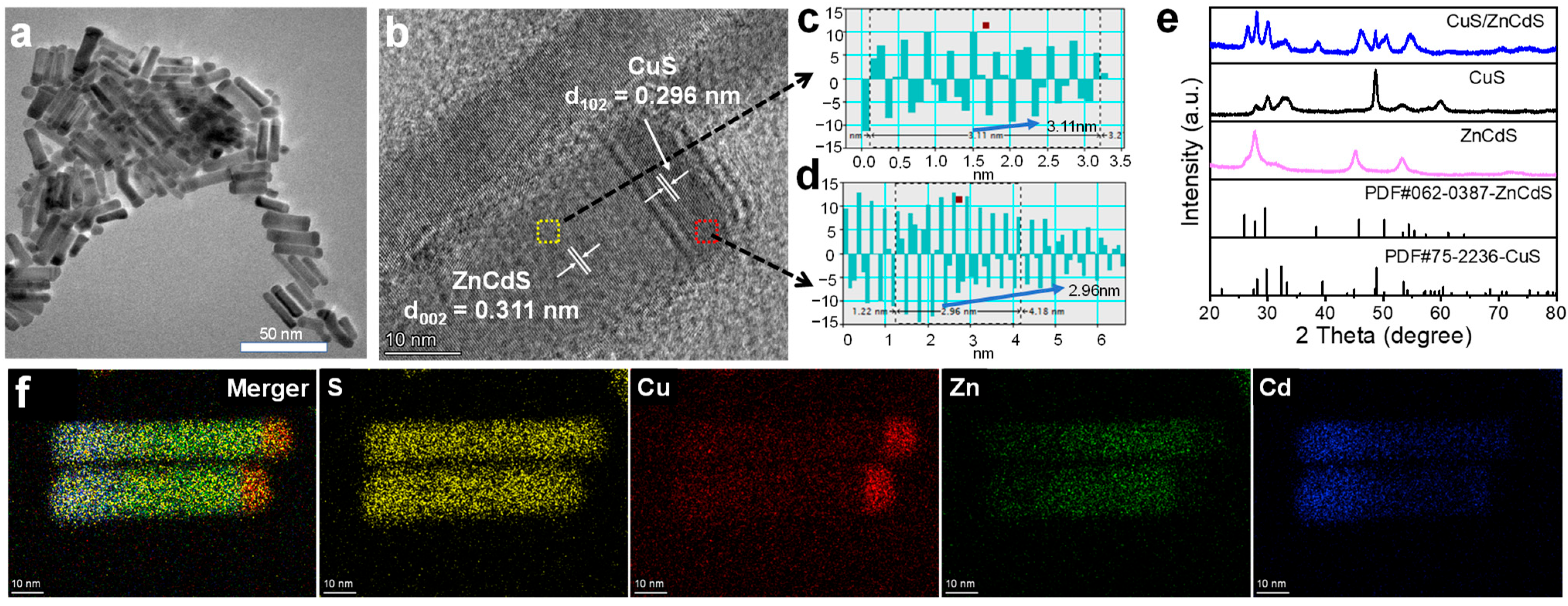
2.1. Structural Characterizations
2.2. Optical Properties and Photoelectrochemical Measurements
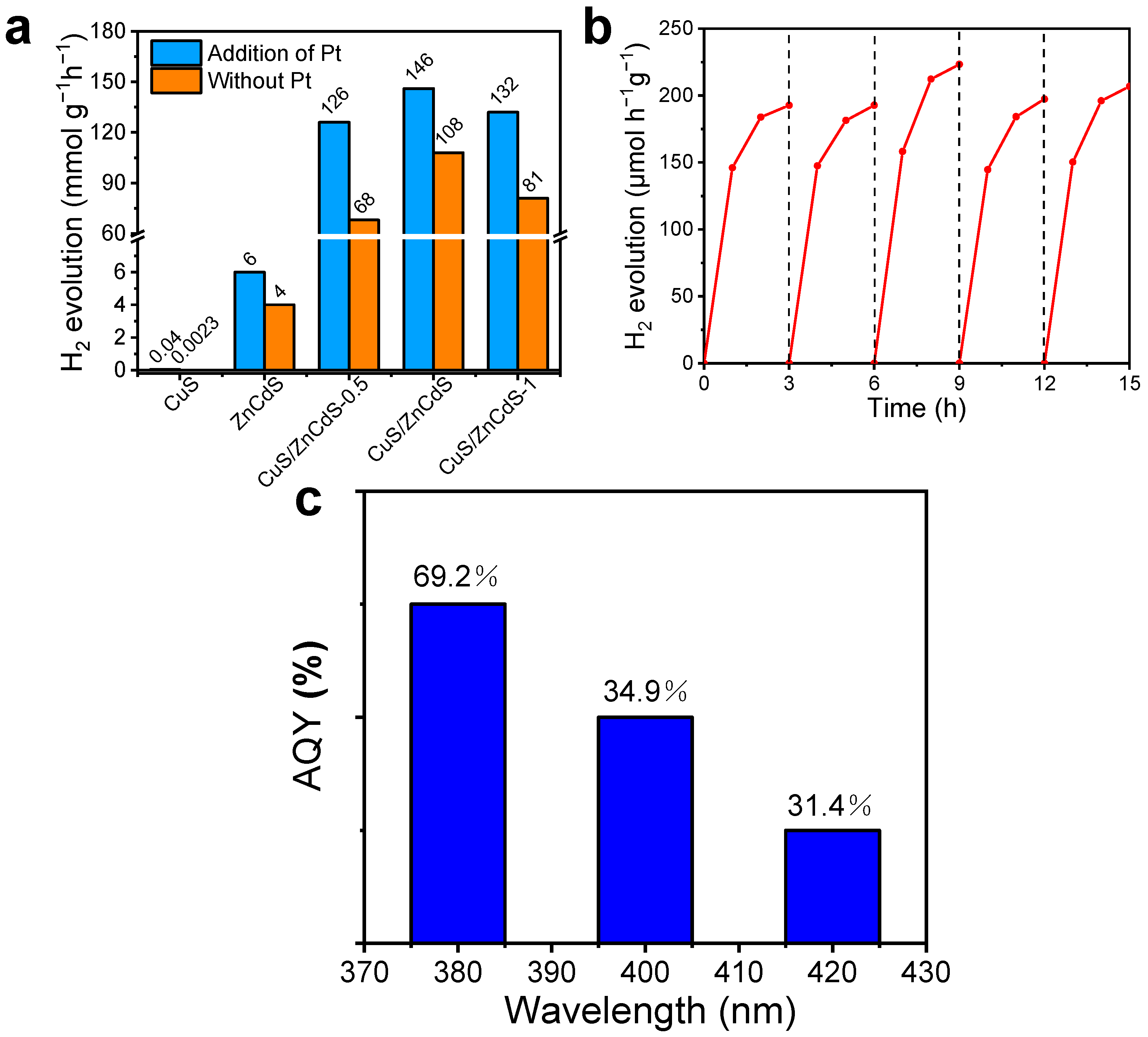
2.3. Photocatalytic Activity in HER for CuS/ZnCdS HNCs
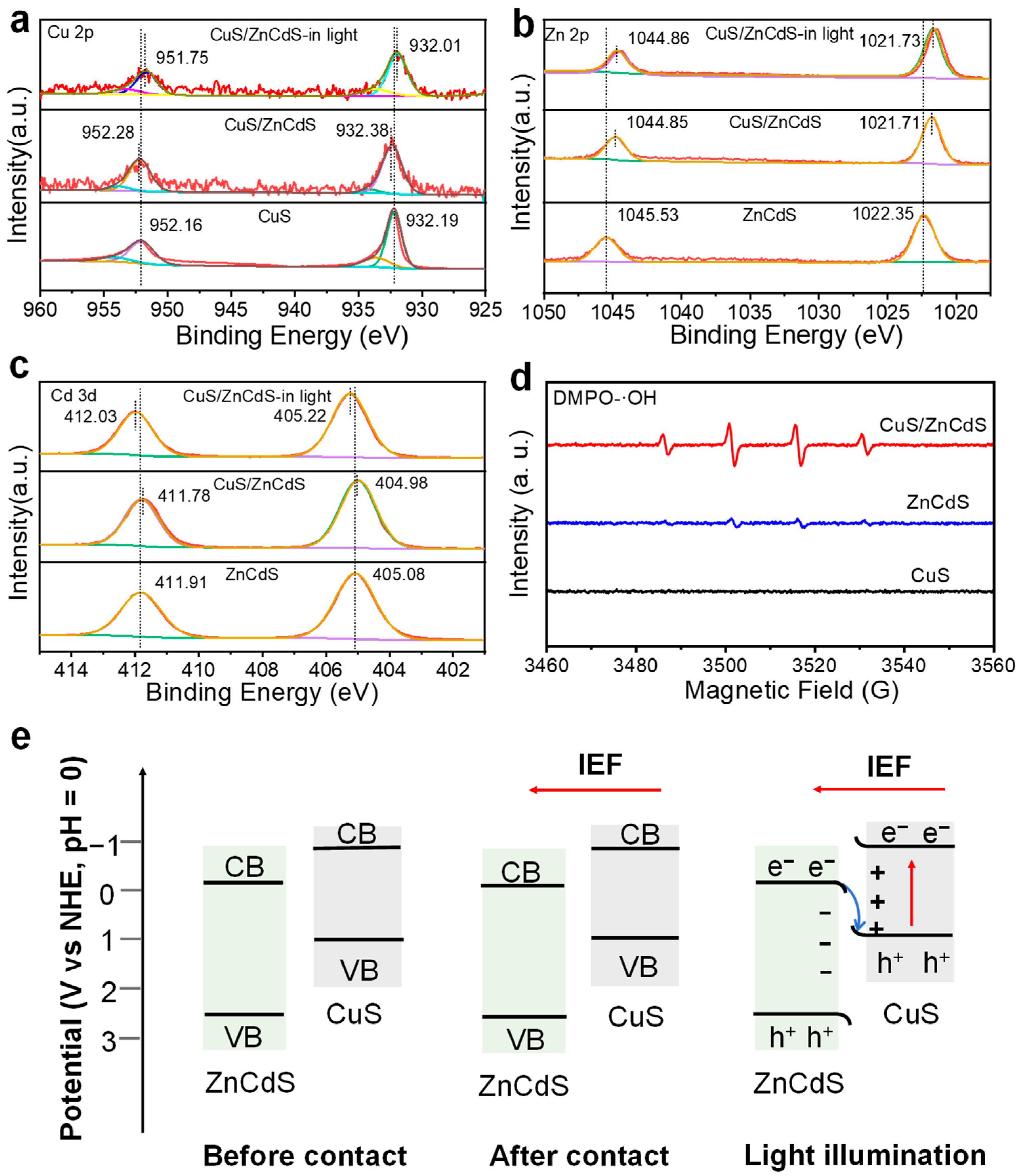
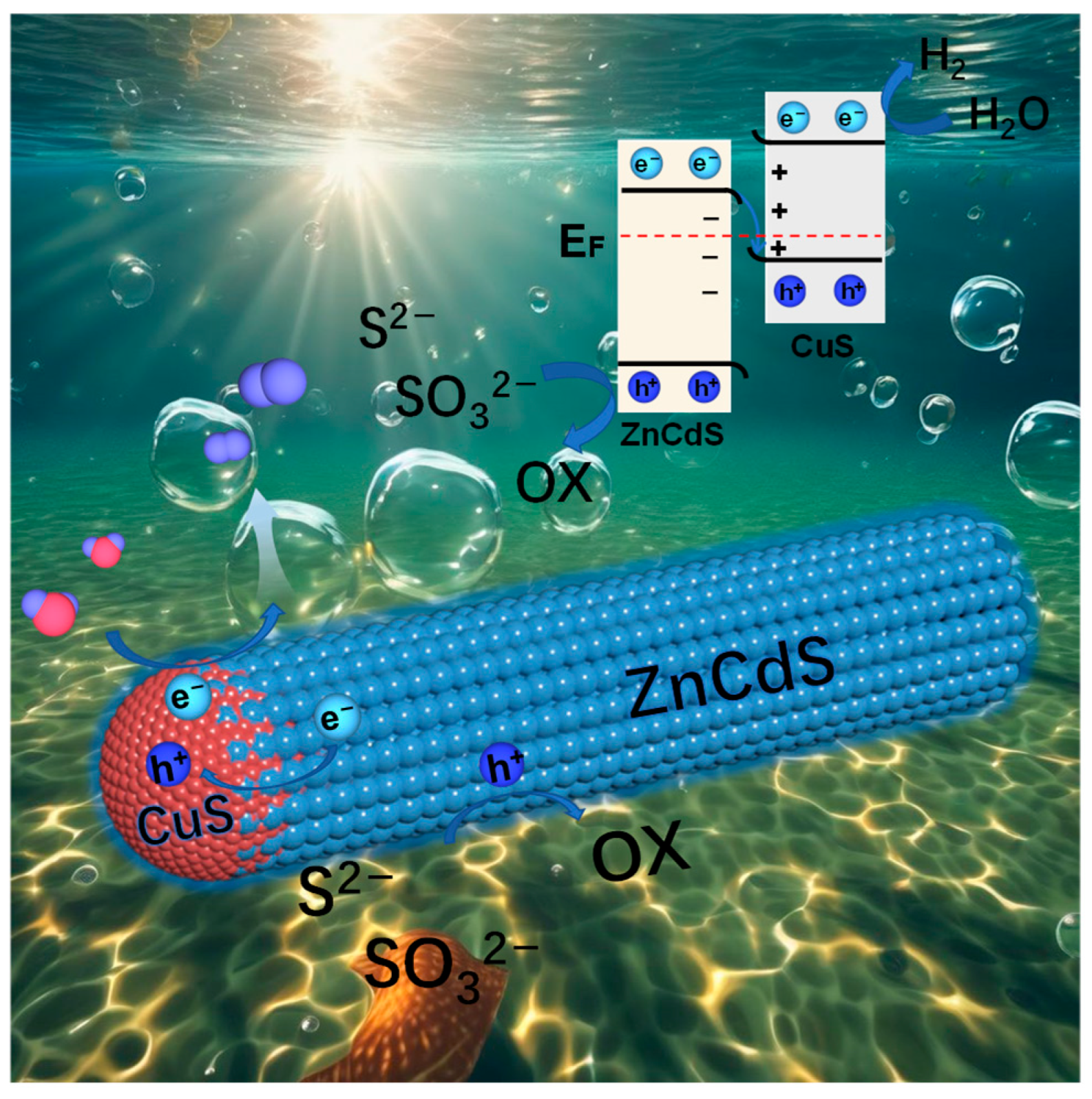
2.4. Understanding the Z-Scheme Mechanism in One CuS/ZnS Nanocrystal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Catalysts
3.2.1. Synthesis of CuS NCs
3.2.2. Synthesis of CuS/ZnCdS HNCs
3.2.3. Preparation of Hydrophilic CuS/ZnCdS HNCs Samples
3.3. Material Characterization
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3.5. Hydrogen Production Performance Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lian, Z.; Wu, F.; Zi, J.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Infrared Light-Induced Anomalous Defect-Mediated Plasmonic Hot Electron Transfer for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 15482–15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Sun, C.; Lin, H.; Li, G.; Lian, Z.; Song, R.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, D. Electrospun Bi-decorated BixTiyOz/TiO2 flexible carbon nanofibers and their applications on degradation of organic pollutants under solar radiation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 150, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Cheng, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W. BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) photocatalytic nanomaterials: Applications for fuels and environmental management. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 254, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, P.; Zhao, G.; Wang, X.; Kong, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chang, K.; Meng, X.; Kako, T.; et al. Promoting Active Species Generation by Plasmon-Induced Hot-Electron Excitation for Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9128–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Band alignment of homojunction by anchoring CN quantum dots on g-C3N4 (0D/2D) enhance photocatalytic hydrogen peroxide evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 300, 120736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xing, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, W. Sulfur vacancy engineering of metal sulfide photocatalysts for solar energy conversion. Chem Catal. 2023, 3, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiyev, Z.; Balayeva, N.O. PbS nanostructures: A review of recent advances. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 21, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Deng, P.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Shen, Y.; Tian, X. Recent Advances in Cadmium Sulfide-Based Photocatalysts for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Renewables 2023, 1, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. Dual Cocatalysts in TiO2 Photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-T.; Wu, Z.; Liu, K.-C.; Liu, W.-S. Fabrication of 3D CuS@ZnIn2S4 hierarchical nanocages with 2D/2D nanosheet subunits p-n heterojunctions for improved photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Han, Z.; Peterson, J.J.; Odoi, M.Y.; Sowers, K.L.; Krauss, T.D. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation by CdSe/CdS Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5347–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Li, F.-T.; Li, X. In-situ construction of sequential heterostructured CoS/CdS/CuS for building “electron-welcome zone” to enhance solar-to-hydrogen conversion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 300, 120763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-X.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Fang, X.-Q.; Gong, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. CuSx-mediated two reaction systems enable biomimetic photocatalysis in CO2 reduction with visible light. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 65, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehnel, M.F.; Reisner, E. Solar Hydrogen Generation from Lignocellulose. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z. Rational design of ternary NiS/CQDs/ZnIn2S4 nanocomposites as efficient noble-metal-free photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution under visible light. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Xi, N.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Sang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Donor-acceptor covalent organic framework/ZnIn2S4 core-shell structure S-scheme heterostructure for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 2024, 126, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, S.; Qi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, Z. Solution-Processed Cu9S5 as a Hole Transport Layer for Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31535–31540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshbabu, R.; Ravi, P.; Sathish, M. Cauliflower-like CuS/ZnS nanocomposites decorated g-C3N4 nanosheets as noble metal-free photocatalyst for superior photocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Yuan, H.; Xing, M.; Li, K.; Pak, Y.L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, D.; Mou, H.; Song, J. Surface vacancy engineering powered reverse cation exchange in preparing CuZnS hollow nanoboxs for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 152025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-J.; Lin, Q.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Mei, Z.W.; Liang, J.; Lin, Y.; Pan, F. Novel p-Type Conductive Semiconductor Nanocrystalline Film as the Back Electrode for High-Performance Thin Film Solar Cells. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Kobayashi, Y.; Vequizo, J.J.M.; Ranasinghe, C.S.K.; Yamakata, A.; Nagai, T.; Kimoto, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, K.; Teranishi, T.; et al. Harnessing infrared solar energy with plasmonic energy upconversion. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Sakamoto, M.; Matsunaga, H.; Vequizo, J.J.M.; Yamakata, A.; Haruta, M.; Kurata, H.; Ota, W.; Sato, T.; Teranishi, T. Near infrared light induced plasmonic hot hole transfer at a nano-heterointerface. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y. Al-doped CuS/Znln2S4 forming Schottky junction induced electron trap centers for photocatalytic overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Wei, Y.-H.; Kuo, W.-S. Free-standing CuS–ZnS decorated carbon nanotube films as immobilized photocatalysts for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 30553–30562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Sun, S.; Ba, J.; Cheng, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Fang, H.; Li, M.; Fan, D. Constructing V2O5/CdS/CuS multi-level heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 29593–29603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.H. Heterostructured metal sulfide (ZnS–CuS–CdS) photocatalyst for high electron utilization in hydrogen production from solar water splitting. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3869–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vempuluru, N.R.; Krishnan, C.K.; Parnapalli, R.; Velusamy, J.; Marappan, S.; Pitchaimuthu, S.; Murikinati, M.; Venkatakrishnan, S.M. Solar hydrogen generation from organic substance using earth-abundant CuS–NiO heterojunction semiconductor photocatalyst. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 10206–10215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Luan, X.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Y.; Luo, D.; Zi, J.; Lian, Z. Gemstone nanoflower-shaped ZnIn2S4/CuS heterojunction with ultralong lifetime of photoinduced carriers for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2024, 347, 123702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, J.; Chen, C. Ce-based organic framework enhanced the hydrogen evolution ability of ZnCdS photocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jiang, G.; Jin, Z. ZnCdS/NiAl hydrotalcite S-scheme heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Shen, Z.R.; Lv, S.M.; Shen, K.; Wu, R.F.; Jiang, X.F.; Fan, T.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, Y.W. Fabricating sandwich-shelled ZnCdS/ZnO/ZnCdS dodecahedral cages with “one stone” as Z-scheme photocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen production. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19631–19642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Meng, F.; Gao, M.; Wei, J.; Lim, K.J.H.; Lim, K.H.; Chirawatkul, P.; Wong, A.S.W.; Kawi, S.; Ho, G.W. Porous Host–Guest MOF-Semiconductor Hybrid with Multisites Heterojunctions and Modulable Electronic Band for Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Conversion and H2 Evolution. Small 2023, 19, 2301121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Tao, S.; Wan, S.; Qiu, G.; Long, Q.; Yu, J.; Cao, S. S-scheme heterojunction of ZnCdS nanospheres and dibenzothiophene modified graphite carbon nitride for enhanced H2 production. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 46, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wu, J.B.; Jiang, J.Z.; Wang, R.G.; Zhou, B.X.; Wang, L.B.; Hu, Q.K.; Zhou, A.G. Boosting the photocatalytic performance of CdxZn1-xSfor H2 production by Mo2C MXene with large interlayer distance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 5851–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Du, M.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Huang, H.; Li, X.A.; Zhu, X. Single-Atom Phosphorus Defects Decorated CoP Cocatalyst Boosts Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation Performance of Cd0.5Zn0.5S by Directed Separating the Photogenerated Carriers. Small 2023, 19, 2300402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Huang, J.; Ng, K.H.; Lai, Y. Molybdenum sulfide cocatalyst activation upon photodeposition of cobalt for improved photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of ZnCdS. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Zeng, Z. Operating redox couple transport mechanism for enhancing photocatalytic H2 generation of Pt and CrOx-decorated ZnCdS nanocrystals. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2021, 283, 119601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Qian, H.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zha, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, Y. Scalable fabrication of ZnxCd1-xS double-shell hollow nanospheres for highly efficient hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B-Environ 2018, 239, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, Y.W. Hollow ZnCdS dodecahedral cages for highly efficient visible-light-driven hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 24116–24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Yang, G.; Wang, G.-C.; Cheng, P. An Efficient, Visible-Light-Driven, Hydrogen Evolution Catalyst NiS/ZnCd1−xS Nanocrystal Derived from a Metal-Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9790–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Xu, H.; Ge, L.; Han, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, Y. In-situ synthesis of CoP co-catalyst decorated Zn0.5Cd0.5S photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production activity under visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 217, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Su, C.; Zhu, C.; Bo, T.; Zuo, S.; Zhou, W.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Rueping, M.; et al. Isolated Electron Trap-Induced Charge Accumulation for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Peng, Q.; Lin, R.; Wang, Y.; Shen, R.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, G.; et al. Synergetic Integration of Cu1.94S–ZnxCd1–xS Heteronanorods for Enhanced Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4286–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zi, J.; Lian, Z. Hollow Nanobox-Shaped Cu2-xS@ZnxCd1-xS Heterojunction by Light Multireflection with Z-Scheme Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Adv. Funct. Mater 2025, 35, 2416358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Luo, D.; Zi, J.; Li, G.; Lian, Z. Nanorod Heterodimer-Shaped CuS/ZnxCd1−xS Heteronanocrystals with Z-Scheme Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalysis. Catalysts 2025, 15, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030266
Yang L, Wang L, Xiao H, Luo D, Zi J, Li G, Lian Z. Nanorod Heterodimer-Shaped CuS/ZnxCd1−xS Heteronanocrystals with Z-Scheme Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalysis. Catalysts. 2025; 15(3):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030266
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lei, Lihui Wang, Han Xiao, Di Luo, Jiangzhi Zi, Guisheng Li, and Zichao Lian. 2025. "Nanorod Heterodimer-Shaped CuS/ZnxCd1−xS Heteronanocrystals with Z-Scheme Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalysis" Catalysts 15, no. 3: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030266
APA StyleYang, L., Wang, L., Xiao, H., Luo, D., Zi, J., Li, G., & Lian, Z. (2025). Nanorod Heterodimer-Shaped CuS/ZnxCd1−xS Heteronanocrystals with Z-Scheme Mechanism for Enhanced Photocatalysis. Catalysts, 15(3), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15030266






