The Art of Manufacturing Gold Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Impregnation

2.2. Co-Precipitation
2.3. Deposition-Precipitation

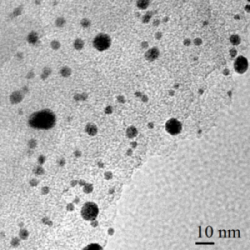
2.4. Deposition
- a. Metal vapor deposition;
- b. Solid grinding;
- c. Metallic sol immobilization.
2.4.1. Metal Vapor Deposition

2.4.2. Solid Grinding
2.4.3. Metallic Sol Immobilisation
| Support | TEM (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| NiO commercial | 3.8 | [72] |
| Nano NiO | 3.6 | [72] |
| SiO2 | 4.0 | [72] |
| MgO | 3.8 | [72] |
| TiO2 | 4.0 | [48] |
| H-mordenite | 3.8 | [73] |
| AC X40S | 3.0 | [74] |
| AC Norit | 3.6 | [75] |
| CNTs | 4.6 | [76] |




3. Conclusions
References
- Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sano, H.; Yamada, N. Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide at a temperature far below 0 °C. Chem. Lett. 1987, 405, 405–408. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, G.J. Vapor phase hydrochlorination of acetylene: Correlation of catalytic activity of supported metal chloride catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 96, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, G.C.; Thompson, D.T. Catalysis by gold. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1999, 41, 319–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.C.; Louis, C.; Thompson, D.T. Catalysis by Gold; Catalytic Science Series 6; Hutchings, G.J., Ed.; ICP Covent Garden: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Haruta, M. Size and support dependency in the catalysis by gold. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Haruta, M. Gold as a novel catalyst in the 21st century: Preparation, working mechanism and applications. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J. Catalysis by gold. Catal. Today 2005, 100, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, A.S.K. The catalysis gold rush. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6990–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Pina, C.; Falletta, E.; Prati, L.; Rossi, M. Selective oxidation using gold. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2077–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Supported gold nanoparticles as catalysts for organic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2096–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Lin, S.D. XPS and DRS of Au/TiO2 catalysts: Effect of pretreatment. Catal. Lett. 1999, 57, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestryakov, A.N.; Lunin, V.V. Physicochemical study of active sites of metal catalysts for alcohol partial oxidation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 158, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestryakov, A.N.; Lunin, V.V.; Kharlanov, A.N.; Kochubey, D.I.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Stakheev, A.Y. Influence of modifying additives on electronic state of supported gold. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 642, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margitfalvi, J.L.; Fasi, A.; Hegedus, M.; Lonyi, F.; Gobolos, S.; Bogdanchikova, N. Au/MgO catalysts modified with ascorbic acid for low temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Gavriilidis, A. Supported Au catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation prepared by impregnation. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Kharas, K.C.C.; Datye, A.K. The preparation of highly dispersed Au/Al2O3 by aqueous impregnation. Catal. Lett. 2003, 85, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, C.; Decker, N.; Pruβe, U. New innovative gold catalysts prepared by an improved incipient wetness method. J. Catal. 2008, 258, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, S.; Pitchon, C. A new preparation method for the formation of gold nanoparticles on an oxide support. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 267, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Pitchon, V.; Zimmermann, Y.; Petit, C. Preparation of alumina supported gold catalysts: Influence of washing procedures, mechanism of particles size growth. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 298, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.; Pitchon, V.; Petit, C.; Heeerschbach, H.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Leize, E. Preparation of alumina supported gold catalysts: Gold complexes genesis, identification and speciation by mass spectrometry. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 298, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Kozlov, A.I.; Kozlova, A.P.; Shido, T.; Iwasawa, Y. Active oxygen species and reaction mechanism for low-temperature CO oxidation on an Fe2O3-supported Au catalyst prepared from Au(PPh3)(NO3) and as-precipitated iron hydroxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Kozlov, A.I.; Kozlova, A.P.; Shido, T.; Asakura, K.; Iwasawa, Y. Active oxygen species and mechanism for low-temperature CO oxidation reaction on a TiO2-supported au catalyst prepared from Au(PPh3)(NO3) and as-precipitated titanium hydroxide. J. Catal. 1999, 185, 252–264. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, A.I.; Kozlova, A.P.; Asakura, K.; Matsui, Y.; Kogure, T.; Shido, T.; Iwasawa, Y. Supported gold catalysts prepared from a gold phosphine precursor and as-precipitated metal-hydroxide precursors: Effect of preparation conditions on the catalytic performance. J. Catal. 2000, 196, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Olea, M.; Kunitake, M.; Shido, T.; Iwasawa, Y. TAP study on CO oxidation on a highly active Au/Ti (OH)4(*) catalyst. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 627–631. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, G.A. The isoelectric points of solid oxides, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex systems. Chem. Rev. 1965, 65, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okatsu, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Akita, T.; Ishida, T.; Haruta, M. Deposition of gold nanoparticles on carbons for aerobic glucose oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 369, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, L.; Martra, G. New gold catalysts for liquid phase oxidation. Gold Bull. 1999, 32, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Giorgio, S.; Henry, C.R.; Luis, C. Alternative methods for the preparation of gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2. J. Phys. Chem B 2002, 106, 7634–7642. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlich, M.J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. Kinetics of the selective low-temperature oxidation of CO in H-2-rich gas over Au/Alpha-Fe2O3. J. Catal. 1999, 182, 430–440. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.M.; Kahlich, M.J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. Correlation between CO surface coverage and selectivity/kinetics for the preferential CO oxidation over Pt/Gamma-Al2O3 and Au/Alpha-Fe2O3: An in-situ DRIFTS study. J. Power Sources 1999, 84, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.M.; Venugopal, A.; Kahlich, M.J.; Plzak, V.; Behm, R.J. Influence of H2O and CO2 on the selective CO oxidation in H-2-rich gases over Au/Alpha-Fe2O3. J. Catal. 2004, 222, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.M.; Haring, T.P.; Brath, G.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Behm, R.J. New DRIFTS cell design for the simultaneous acquisition of Ir spectra and kinetic data using on-line product analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, R.M.; Hodge, N.A.; Hutchings, G.J.; Meagher, A.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Wagner, F.E.; Whyman, R. Identification of active phases in Au-Fe catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, N.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Whyman, R.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Hutchings, G.J.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Wagner, F.E.; Rajaram, R.R.; Golunski, S.E. Microstructural comparison of calcined and uncalcined gold/iron-oxide catalysts for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, F.E.; Galvagno, S.; Milone, C.; Visco, A.M.; Stievano, L.; Calogero, S. Mössbauer characterisation of gold/iron oxide catalysts. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 3403–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.M.; Tripathi, A.K. Microcalorimetry, adsorption, and reaction studies of CO, O-2, and CO + O-2 over Fe2O3, Au/Fe2O3, and polycrystalline gold catalysts as a function of reduction treatment. J. Catal. 1999, 187, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Kamble, V.S.; Gupta, N.M. Microcalorimetry, adsorption, and reaction studies of CO, O-2, and CO + O-2 over Au/Fe2O3, Fe2O3, and polycrystalline gold catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 187, 332–342. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.M.; Tripathi, A.K. The role of nanosized gold particles in adsorption and oxidation of carbon monoxide over Au/Fe2O3 catalyst. Gold Bull. 2001, 34, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, D.; Toth, L.; Guczi, L. Gold nanoparticles: Effect of treatment on structure and catalytic activity of Au/Fe2O3 catalyst prepared by Co-precipitation. Catal. Lett. 2000, 67, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minico, S.; Scire, S.; Crisafulli, C.; Galvagno, S. Influence of catalyst pretreatments on volatile organic compounds oxidation over gold/iron oxide. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 34, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Gavriilidis, A.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Kyek, A.; Wagner, F.E.; Wong, P.C.L.; Yeung, K.L. Effect of drying conditions of Au-Mn Co-precipitates for low-temperature CO oxidation. J. Catal. 2001, 200, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bailie, J.E.; Abdullah, H.A.; Anderson, J.A.; Rochester, C.H.; Richardson, N.V.; Hodge, N.; Zhang, J.G.; Burrows, A.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Hydrogenation of but-2-enal over supported Au/ZnO catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 4113–4121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Lian, H.L.; Liu, Q.S.; Jiang, D.Z.; Wu, T.H. Effect of Au loading, H2O and CO concentration on the stability of Au/ZnO catalysts for room-temperature CO oxidation. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2002, 75, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Lian, H.L.; Jiang, D.Z.; Wu, T.H. Effect of calcination temperatures and precipitant on the catalytic performance of Au/ZnO catalysts for CO oxidation at ambient temperature and in humid circumstances. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 239, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, H.; Haruta, M. Carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide hydrogenation over gold supported on titanium, iron, and zinc oxides. Appl. Catal. A 1995, 127, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubota, S.; Haruta, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Ueda, A.; Nakahara, Y. Preparation of highly dispersed gold on titanium and magnesium oxide. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1991, 63, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, M.; Tsubota, S.; Iwamoto, M.; Haruta, M. Chemical vapor deposition of gold nanoparticles on MCM-41 and their catalytic activities for the low-temperature oxidation of CO and of H2. Chem. Lett. 1998, 27, 315–316. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitratos, N.; Villa, A.; Bianchi, C.L.; Prati, L.; Makkee, M. Gold on titania: Effect of preparation method in the liquid phase oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2006, 311, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannice, M.A. The influence of MSI (metal-support interactions) on activity and selectivity in the hydrogenation of aldehydes and ketones. Top. Catal. 1997, 4, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Weerachawanasak, P.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Arai, M.; Fujita, A.-I.; Praserthdam, P.; Panpranot, J. Effect of strong metal-support interaction on the catalytic performance of Pd/TiO2 in the liquid-phase semihydrogenation of phenylacetylene. J. Catal. 2009, 262, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Guzman, J.; Gates, B.C. Reactions of Au(CH3)2(acac) on γ-Al2O3: Characterization of the surface organic, organometallic, metal oxide, and metallic species. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3897–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, M.; Tsubota, S.; Haruta, M. Preparation of supported gold catalysts by gas-phase grafting of gold acethylacetonate for low-temperature oxidation of CO and of H2. J. Mol. Catal. A 2003, 199, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Yeh, C.T. Deposition of highly dispersed gold on alumina support. J. Catal. 2001, 200, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Schimpf, S.; Lucas, M.; Mohr, C.; Rodemerck, U.; Bruckner, A.; Radnik, J.; Hofmeister, H.; Claus, P. Supported gold nanoparticles: In-depth catalyst characterization and application in hydrogenation and oxidation reactions. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.H.; Li, B.Q.; Huang, W.P.; Zhang, S.M.; Shi, J.; Zheng, X.C. Comparative studies of gold catalysts prepared via solvated metal atom impregnation and conventional impregnation: Characterization and low-temperature CO oxidation. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2003, 78, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, G.M.; Lupini, A.R.; Pennycook, S.J.; Ownby, G.W.; Dudney, N.J. Nanoparticles of gold on γ-Al2O3 produced by dc magnetron sputtering. J. Catal. 2005, 231, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Veith, G.M.; Lupini, A.R.; Pennycook, S.J.; Dudney, N.J. The use of magnetron sputtering for the production of heterogeneous catalysts. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2006, 162, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, G.M.; Lupini, A.R.; Pennycook, S.J.; Villa, A.; Prati, L.; Dudney, N.J. Magnetron sputtering of gold nanoparticles onto WO3 and activated carbon. Catal. Today 2007, 122, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.T.; Franklin, M.T.; Klabunde, K.J. Nonaqueous colloidal gold. Clustering of metal atoms in organic media, 12. Langmuir 1986, 2, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Trivino, G.; Klabunde, K.J.; Brock Dale, E. Living colloidal palladium in nonaqueous solvents. Formation, stability, and film-forming properties. Clustering of metal atoms in organic media, 14. Langmuir 1987, 3, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klabunde, K.J.; Habdas, J.; Cardenas-Trivino, G. Colloidal metal particles dispersed in monomeric and polymeric styrene and methyl methacrylate. Chem. Mater. 1989, 1, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.W.; Kafafi, Z.H. Gold cluster-laden polydiacetylenes: Novel materials for nonlinear optics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 7758–7760. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, E.B.; Klabunde, K.J.; Olivier, B.J.; Sorensen, C.M. Nonaqueous perfluorocarbon-derived gold colloids. 1. Clustering of metal atoms in fluorocarbon media. Chem. Mater. 1989, 1, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Nagaoka, M.; Akita, T.; Haruta, M. Deposition of gold clusters on porous cordination polymers by solid grinding and their catalystic activity in aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 8456–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, D.G.; Baiker, A.; Edwards, P.P. A new hydrosol of gold cluster. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, F.; Prati, L. Pre-formed gold particle immobilized on supports: Preparation and catalytic applications. Recent Res. Dev. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2003, 4, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Su, D.S.; Prati, L. Gold sols as catalyst in the glycerol oxidation: The role of stabilizer. Chem. Catal. Chem. 2009, 1, 510–514. [Google Scholar]
- Comotti, M.; Della Pina, C.; Matarrese, R.; Rossi, M.; Siani, A. Oxidation of alcohols and sugars using Au/C catalysts part 2. Sugars. Appl. Catal. A 2005, 291, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comotti, M.; Li, W-C.; Spliethoff, B.; Schuth, F. Support effect in high activity gold catalysts for CO oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 917–924. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.S. Cluster and Colloids: From Theory to Applications; Schmid, G., Ed.; VCH Pub: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, W.; Pugh, T.L. Steric stabilization of colloidal solutions by adsorption of flexible macromolecules. J. Polym. Sci. 1960, 47, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Chan-Thaw, C.E.; Veith, G.M.; More, K.L.; Ferri, D.; Prati, L. Au on nanosized NiO: A cooperative effect between Au and nanosized NiO in the base-free alcohol oxidation. Chem. Catal. Chem. 2011, 3, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Villa, A.; Veith, G.M.; Prati, L. Selective oxidation of glycerol under acidic conditions using gold catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4499–4502. [Google Scholar]
- Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Su, D.; Veith, G.M.; Prati, L. Using supported Au nanoparticles as starting material for preparing uniform Au/Pd bimetallic catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Morgan, D.; Carley, A.; Prati, L.; Hutchings, G.J. Solvent free liquid phase oxidation of benzyl alcohol using Au supported catalysts prepared using a sol immobilization technique. Catal. Today 2007, 122, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Prati, L.; Villa, A.; Chan-Thaw, C.E.; Arrigo, R.; Wang, D.; Su, D.S. Gold catalyzed liquid phase oxidation of alcohol: The issue of selectivity. Faraday Discuss. 2011, 152, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, S.; Martra, G.; Porta, F.; Prati, L.; Rossi, M. Metal sols as a useful tool for heterogeneous gold catalyst preparation: Reinvestigation of a liquid phase oxidation. Catal. Today 2000, 61, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Spontoni, P.; Arrigo, R.; Su, D.; Prati, L. Nitrogen functionalized carbon nanostructures supported Pd and Au–Pd NPs as catalyst for alcohols oxidation. Catal. Today 2010, 157, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Dimitratos, N.; Hammond, C.; Brett, G.L.; Kesavan, L.; White, S.; Miedziak, P.; Tiruvalam, R.; Jenkins, R.L.; Carley, A.F.; et al. Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prati, L.; Villa, A. The Art of Manufacturing Gold Catalysts. Catalysts 2012, 2, 24-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal2010024
Prati L, Villa A. The Art of Manufacturing Gold Catalysts. Catalysts. 2012; 2(1):24-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal2010024
Chicago/Turabian StylePrati, Laura, and Alberto Villa. 2012. "The Art of Manufacturing Gold Catalysts" Catalysts 2, no. 1: 24-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal2010024
APA StylePrati, L., & Villa, A. (2012). The Art of Manufacturing Gold Catalysts. Catalysts, 2(1), 24-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal2010024