The Preparation of Cu-g-C3N4/AC Catalyst for Acetylene Hydrochlorination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
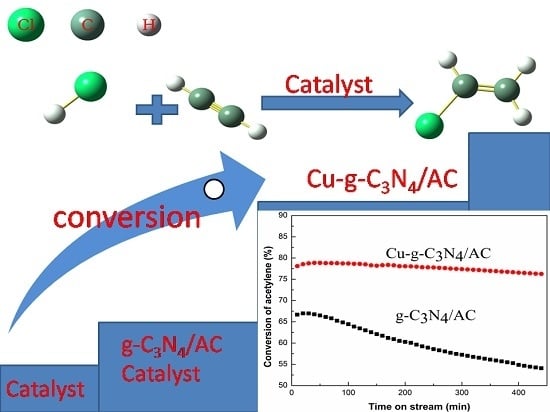
2.1. Catalytic Performance
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4. Raman Spectrum Analyses
2.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.6. Temperature-Programmed Desorption (TPD)
2.7. Low-Temperature N2 Adsorption/Desorption Experiment (BET)
2.8. Thermal Gravity Analysis (TG-DTG)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Characterization of Physical Parameters
3.4. Catalytic Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, X.B.; Shi, H.B.; Qian, W.Z.; Luo, G.H.; Jin, Y.; Wei, F. Gas-phase catalytic hydrochlorination of acetylene in a two-stage fluidized-bed reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 48, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Dai, B. Progress on cleaner production of vinyl chloride monomers over non-mercury catalysts. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.; Carthey, N.; Hutchings, G.J. Discovery, development, and commercialization of gold catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14548–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Carley, A.F.; Heirene, C.; Willock, D.J.; Johnston, P.; Herzing, A.A.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Hydrochlorination of acetylene using a supported gold catalyst: A study of the reaction mechanism. J. Catal. 2007, 250, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhu, M.Y.; Dai, B. AuCl3 on polypyrrole-modified carbon nanotubes as acetylene hydrochlorination catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 142, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Blechert, S.; Antonietti, M. Polymeric graphitic carbon nitride for heterogeneous photocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Maeda, K.; Thomas, A.; Takanabe, K.; Xin, G.; Carlsson, J.M.; Domen, K.; Antonietti, M. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Kang, L.H.; Zhu, M.Y.; Dai, B. A novel, non-metallic graphitic carbon nitride catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. J. Catal. 2014, 311, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhu, M.Y. Metal–nitrogen (Co-g-C3N4) doping of surface-modified single-walled carbon nanohorns for use as an oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25670–25677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Gu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Hu, J.S.; Wei, Z.D.; Wan, L.J. Understanding the high activity of Fe–N–C electrocatalysts in oxygen reduction: Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles boost the activity of Fe–Nx. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3570–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deifallah, M.; McMillan, P.F.; Corà, F. Electronic and structural properties of two-dimensional carbon nitride graphenes. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2008, 112, 5447–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.X.; Chen, X.F.; Antonietti, M.; Wang, X.C. Synthesis of transition metal-modified carbon nitride polymers for selective hydrocarbon oxidation. ChemSusChem. 2011, 4, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Chen, X.F.; Thomas, A.; Fu, X.Z.; Antonietti, M. Metal-containing carbon nitride compounds: A new functional organic–metal hybrid material. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.S.; Han, F.M.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.C.; Yue, J.; Peng, B.X. Non-catalytic CVD preparation of carbon spheres with a specific size. Carbon 2004, 42, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.M.; Xu, J.X.; Wu, C.X.; Guan, L.H. Strong-coupled Co-g-C3N4/SWCNTs composites as high-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65303–65307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghei, M.; Kanninen, P.; Lundahl, M.; Susi, T.; Sainio, J.; Anoshkin, L.; Nasibulin, A.; Kallio, T.; Tammeveski, K.; Kauppinen, E.; Ruiz, V. High oxygen reduction activity of few-walled carbon nanotubes with low nitrogen content. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 158, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Nelson, M.; Ma, S.G.; Meng, H.; Cui, G.F.; Shen, P.K. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped onion-like carbon and its use in carbon-based CoFe binary non-precious-metal catalysts for oxygen-reduction. Carbon 2011, 49, 3972–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.H.; Xu, B.Q. Mesoporous carbon material co-doped with nitrogen and iron (Fe–N–C): High-performance cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8617–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Kang, L.H.; Zhu, M.Y.; Dai, B. Nitrogen-doped active carbon as a metal-free catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7461–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Yu, L.; Ren, P.J.; Wu, X.; Sun, L.T.; Jiao, F.; Bao, X.H. Silicon carbide-derived carbon nanocomposite as a substitute for mercury in the catalytic hydrochlorination of acetylene. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Dai, B.; Wang, X.G.; Xu, L.L.; Zhu, M.Y. Hydrochlorination of acetylene to vinyl chloride monomer over bimetallic Au–La/SAC catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkosi, B.; Adams, M.D.; Coville, N.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Hydrochlorination of acetylene using carbon-supported gold catalysts: A study of catalyst reactivation. J. Catal. 1991, 128, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Catalyst | C | N | O | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 88.47 | 0.40 | 11.13 | – |
| g-C3N4/AC | 82.15 | 7.30 | 10.55 | – |
| Cu-g-C3N4/AC | 78.71 | 7.28 | 9.86 | 4.15 |
| Sample | Percentage of Nitrogen Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyridinic-N | Pyrrolic-N | Graphitic-N | |
| g-C3N4/AC | 49.21 | 22.56 | 28.22 |
| Cu-g-C3N4/AC | 43.54 | 40.63 | 15.83 |
| Sample | SBET (m2·g−1) | V (cm3·g−1) | D (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4/AC-Fresh | 857.68 | 0.47 | 2.19 |
| g-C3N4/AC-Used | 521.26 | 0.29 | 2.23 |
| Cu-g-C3N4/AC-Fresh | 799.16 | 0.42 | 2.11 |
| Cu-g-C3N4/AC-Used | 475.71 | 0.26 | 2.12 |
| Sample | Mass Loss of Fresh Catalyst (%) | Mass Loss of Used Catalyst (%) | Amount of Carbon Deposition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 0.34 | 0.94 | 0.60 |
| g-C3N4/AC | 2.23 | 4.27 | 2.04 |
| Cu-g-C3N4/AC | 3.64 | 4.17 | 0.53 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Zhu, M.; Dai, B. The Preparation of Cu-g-C3N4/AC Catalyst for Acetylene Hydrochlorination. Catalysts 2016, 6, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120193
Zhao W, Zhu M, Dai B. The Preparation of Cu-g-C3N4/AC Catalyst for Acetylene Hydrochlorination. Catalysts. 2016; 6(12):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120193
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wenli, Mingyuan Zhu, and Bin Dai. 2016. "The Preparation of Cu-g-C3N4/AC Catalyst for Acetylene Hydrochlorination" Catalysts 6, no. 12: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120193
APA StyleZhao, W., Zhu, M., & Dai, B. (2016). The Preparation of Cu-g-C3N4/AC Catalyst for Acetylene Hydrochlorination. Catalysts, 6(12), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6120193