Immobilization of Genetically-Modified d-Amino Acid Oxidase and Catalase on Carbon Nanotubes to Improve the Catalytic Efficiency
Abstract
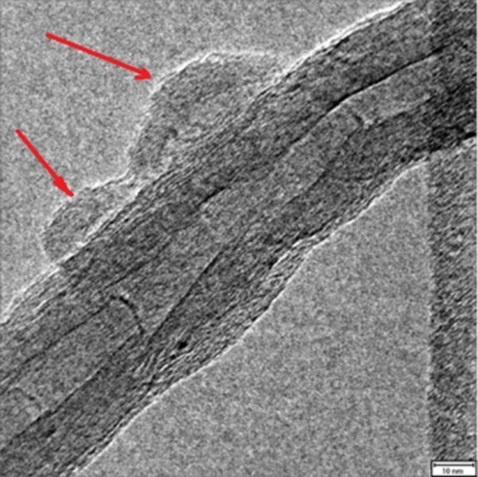
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. FTIR analysis
2.2. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2.3. Raman Spectra Analysis
2.4. Circular Dichroism Spectra Analysis
2.5. Combination of Covalent and Non-Covalent Enzyme Immobilization
2.6. Enzymatic Catalysis
3. Experimental section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Purification and Oxidation of MWNTs
3.3. Enzyme Immobilization
3.4. Measurement
3.5. Enzyme Assay and Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pollegioni, L.; Molla, G. New biotech applications from evolved d-amino acid oxidases. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Furukawara, M.; Omae, K.; Tadokoro, N.; Saito, Y.; Abe, K.; Kera, Y. A highly stable d-amino acid oxidase of the thermophilic bacterium rubrobacter xylanophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7219–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Su, E.; Ma, X.; Yang, S.; Wei, D. High-level soluble and functional expression of trigonopsis variabilis d-amino acid oxidase in escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, K.; Nakano, S.; Asano, Y. Tailoring d-amino acid oxidase from the pig kidney to R-stereoselective amine oxidase and its use in the deracemization of α-methylbenzylamine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4428–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilone, M.S.; Buto, S.; Pollegioni, L. A process for bioconversion of cephalosporin C by rhodotorula gracilis d-amino acid oxidase. Biotechnol. Lett. 1995, 17, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, K.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Hydrogen peroxide in biocatalysis. A dangerous liaison. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 2652–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, R.; Nagajyothi, Bhat S.G. Stabilization of d-amino acid oxidase and catalase in permeabilized rhodotorula graciliscells and its application for the preparation of a-ketoacids. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 68, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodriguez, V.; Guisan, J.M. The coimmobilization of d-amino acid oxidase and catalase enables the quantitative transformation of d-amino acids (d-phenylalanine) into α-keto acids (phenylpyruvic acid). Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1998, 23, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, E.M.; Fischer, L. Minimization of by-product formation during d-amino acid oxidase catalyzed racemate resolution of d/l-amino acids. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2002, 19–20, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Z. Chemiluminescence flow biosensor for determination of total d-amino acid in serum with immobilized reagents. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 69, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Serra, B.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Chiral analysis of amino acids using electrochemical composite bienzyme biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 298, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, P.; Mothet, J.P. Characterization of a yeast d-amino acid oxidase microbiosensor for d-serine detection in the central nervous system. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inaba, Y.; Mizukami, K.; Hamada-Sato, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Imada, C.; Watanabe, E. Development of d-alanine sensor for the monitoring of a fermentation using the improved selectivity by the combination of d-amino acid oxidase and pyruvate oxidase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosini, E.; Molla, G.; Rossetti, C.; Pilone, M.S.; Pollegioni, L.; Sacchi, S. A biosensor for all d-amino acids using evolved d-amino acid oxidase. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 135, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, M.F.; Giacomelli, C.E.; Garcia, C.D. Interaction of d-amino acid oxidase with carbon nanotubes: implications in the design of biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszelewski, D.; Pressnitz, D.; Clay, D.; Kroutil, W. Deracemization of mexiletine biocatalyzed by ω-transaminases. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4810–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.M.; Mathew, S.; Bea, H.S.; Khang, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, B.G.; Yun, H. Deracemization of unnatural amino acid: homoalanine using d-amino acid oxidase and ù-transaminase. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 2482–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Goldberg, S.L.; Hanson, R.L.; Parker, W.L.; Gill, I.; Tully, T.P.; Montana, M.A.; Goswami, A.; Patel, R.N. Enzymatic preparation of an (s)-amino acid from a racemic amino acid. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2011, 15, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, K.; Hultin, H.O. Immobilization and characterization of d-amino acid oxidase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1979, 21, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gallego, F.; Betancor, L.; Mateo, C.; Hidalgo, A.; Alonso-Morales, N.; Dellamora-Ortiz, G.; Guisán, J.M.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. Enzyme stabilization by glutaraldehyde crosslinking of adsorbed proteins on aminated supports. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 119, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, J. Manageable cytotoxicity of nanocapsules immobilizing d-amino acid oxidase via exogenous administration of nontoxic prodrug. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Okamoto, M.; Umakoshi, H.; Kuboi, R. Oligolamellar vesicles for covalent immobilization and stabilization of d-amino acid oxidase. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2013, 52, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujawar, S.K.; Kotha, A.; Rajan, C.R.; Ponrathnam, S.; Shewale, J.G. Development of tailor-made glycidyl methacrylate-divinyl benzene copolymer for immobilization of d-amino acid oxidase from aspergillus species strain 020 and its application in the bioconversion of cephalosporin C. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 75, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qiao, J.; Qi, L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H. Construction of a d-amino acid oxidase reactor based on magnetic nanoparticles modified by a reactive polymer and its application in screening enzyme inhibitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12979–12987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Nidetzky, B. Oriented and selective enzyme immobilization on functionalized silica carrier using the cationic binding module zbasic2: Design of a heterogeneous d-amino acid oxidase catalyst on porous glass. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.S.; Fong, W.P.; Tsang, P. Entrapment of a trigonopsis variabilis d-amino acid oxidase variant F54Y for oxidative deamination of cephalosporin C. Eng. Life Sci. 2011, 11, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Sun, J.; Song, X.; Song, C.; Feng, W. Enhancement of the solubility and stability of d-amino acid oxidase by fusion to an elastin like polypeptide. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 212, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, D.E.; Chilkoti, A. Genetically encoded synthesis of protein-based polymers with precisely specified molecular weight and sequence by recursive directional ligation: examples from the elastin-like polypeptide system. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Sun, J.; Song, X.Q.; Chen, H.M.; Feng, W.; Ji, P.J. Interaction of ionic liquid [bmin][CF3SO3] with lysozyme investigated by two-dimensional fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, K.; Song, X.; Gao, Q.; Ma, J.; Ji, P.; Feng, W. Specific Immobilization of d-amino Acid Oxidase Mimicking Multi-enzyme Catalysis. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4465–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinani, V.A.; Gheith, M.K.; Yaroslavov, A.A.; Rakhnyanskaya, A.A.; Sun, K.; Mamedov, A.A.; Wicksted, J.P.; Kotov, N.A. Aqueous dispersions of single-wall and multiwall carbon nanotubes with designed amphiphilic polycations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3463–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Rinzler, A.G.; Dai, H.; Hafner, J.H.; Bradley, R.K.; Boul, P.J.; Lu, A.; Iverson, T.; Shelimov, K.; Huffman, C.B. Fullerene pipes. Science 1998, 280, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.J.; Tan, H.S.; Xu, X.; Feng, W. Lipase covalently attached to multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an efficient catalyst in organic solvent. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 3005–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, K.; Fu, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Feng, W.; Ji, P. Sodium hexadecyl sulfate as an interfacial substance adjusting the adsorption of a protein on carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 15132–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Sun, J.; Fu, Y.; Du, K.; Cai, M.; Ji, P.; Feng, W. Immobilization of Genetically-Modified d-Amino Acid Oxidase and Catalase on Carbon Nanotubes to Improve the Catalytic Efficiency. Catalysts 2016, 6, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6050066
Li R, Sun J, Fu Y, Du K, Cai M, Ji P, Feng W. Immobilization of Genetically-Modified d-Amino Acid Oxidase and Catalase on Carbon Nanotubes to Improve the Catalytic Efficiency. Catalysts. 2016; 6(5):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6050066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rong, Jian Sun, Yaqi Fu, Kun Du, Mengsha Cai, Peijun Ji, and Wei Feng. 2016. "Immobilization of Genetically-Modified d-Amino Acid Oxidase and Catalase on Carbon Nanotubes to Improve the Catalytic Efficiency" Catalysts 6, no. 5: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6050066
APA StyleLi, R., Sun, J., Fu, Y., Du, K., Cai, M., Ji, P., & Feng, W. (2016). Immobilization of Genetically-Modified d-Amino Acid Oxidase and Catalase on Carbon Nanotubes to Improve the Catalytic Efficiency. Catalysts, 6(5), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6050066