Zr-Based MOF-808 as Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction Catalyst for Challenging Carbonyl Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
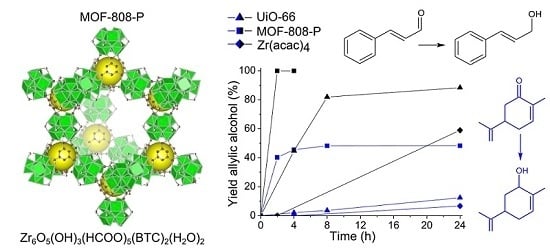
2.1. Reduction of Cinnamaldehyde and Carvone
2.2. Increase Equilibrium Carveol Yield
2.2.1. Evaporation of Acetone
2.2.2. 1-Indanol as Reducing Agent
2.3. Substrate Scope
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis and Characterization
4.1.1. MOF Synthesis
4.1.2. MOF Characterization
4.2. Catalytic Experiments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BTC | 1.3.5-benzenetricarboxylic acid |
| IPA | Isopropyl alcohol |
| MOF | Metal-Organic Framework |
| MPV | Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Bekkum, H. Fine Chemicals through Heterogeneous Catalysis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chuah, G.K.; Jaenicke, S.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Liu, S.H. Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction over Heterogeneous Catalysts. Curr. Org. Chem. 2006, 10, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G.K. Hydrous Zirconia as a Selective Catalyst for the Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction of Cinnamaldehyde. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: Chiral ligands and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boronat, M.; Corma, A.; Renz, M. Mechanism of the Meerwein−Ponndorf−Verley−Oppenauer (MPVO) Redox Equilibrium on Sn− and Zr−Beta Zeolite Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21168–21174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyori, R.; Hashiguchi, S. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De bruyn, M.; De Vos, D.E.; Jacobs, P.A. Chemoselective Hydrogen Transfer Reduction of Unsaturated Ketones to Allylic Alcohols with Solid Zr and Hf Catalysts. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2002, 344, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilds, A.L. Reduction with Aluminum Alkoxides. Org. React. 1944, 2, 178–223. [Google Scholar]
- McNerney, B.; Whittlesey, B.; Cordes, D.B.; Krempner, C. A well-defined monomeric aluminum complex as an efficient and general catalyst in the Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14959–14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, P.; Solovyov, A.; Okrut, A.; Katz, A. AlIII–Calix[4]arene Catalysts for Asymmetric–Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2492–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, P.; Matvieiev, Y.I.; Boyko, V.I.; Durkin, K.A.; Kalchenko, V.I.; Katz, A. MPV reduction using AlIII–calix[4]arene Lewis acid catalysts: Molecular-level insight into effect of ketone binding. J. Catal. 2011, 284, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G. Zirconia catalysts in Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction of citral. Catal. Today 2004, 97, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.; Castro Villalobos, M.C.; Kwakernaak, C.; Telalovic, S.; Hanefeld, U. Zr-TUD-1: A Lewis Acidic, three-dimensional, mesoporous, zirconium-containing catalyst. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2008, 14, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermoortele, F.; Bueken, B.; Le Bars, G.; Van de Voorde, B.; Vandichel, M.; Houthoofd, K.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Waroquier, M.; Van Speybroeck, V.; et al. Synthesis Modulation as a Tool To Increase the Catalytic Activity of Metal-Organic Frameworks: The Unique Case of UiO-66(Zr). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11465–11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, H.; Wu, L.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Han, B. Porous Zirconium-Phytic Acid Hybrid: A Highly Efficient Catalyst for Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reductions. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 9531–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.A.; Bachelier, J.; Audry, F.; Lavalley, J.C. Study of the Meerwein-Pondorff-Verley reaction between ethanol and acetone on various metal oxides. J. Mol. Catal. 1994, 91, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilocchio, C.; Hawkins, J.M.; Ley, S.V. A Mild and Efficient Flow Procedure for the Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones and Aldehydes using Hydrous Zirconia. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2278–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G.K. Supported zirconium propoxide—A versatile heterogeneous catalyst for the Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction. J. Catal. 2003, 218, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chuah, G.; Jaenicke, S. Selective Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes over Zr-zeolite beta. J. Catal. 2006, 241, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.; Melero, J.A.; Morales, G.; Moreno, J.; Segura, Y.; Paniagua, M.; Cambra, A.; Hernández, B. Zr-SBA-15 Lewis Acid Catalyst: Activity in Meerwein Ponndorf Verley Reduction. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1911–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Okumura, K.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G.-K. Post-synthesized zirconium-containing Beta zeolite in Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction: Pros and cons. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 493, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yao, S.; Wang, M.; Lou, S.; Yan, N. Recent Progress in Chemoselective Hydrogenation of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehyde to Unsaturated Alcohol Over Nanomaterials. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, B.; Oksal, B.S. Comparison of heterogeneous B(OiPr)3-MCM-41 and homogeneous B(OiPr)3, B(OEt)3 catalysts for chemoselective MPV reductions of unsaturated aldehydes and ketones. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 435–436, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De bruyn, M.; Limbourg, M.; Denayer, J.; Baron, G.V.; Parvulescu, V.; Grobet, P.J.; De Vos, D.E.; Jacobs, P.A. Mesoporous Zr and Hf catalysts for chemoselective MPV reductions of unsaturated ketones. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 254, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascon, J.; Corma, A.; Kapteijn, F.; Llabre, F.X. Metal Organic Framework Catalysis: Quo vadis? ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Opanasenko, M.; Čejka, J.; Garcia, H. Metal organic frameworks as heterogeneous catalysts for the production of fine chemicals. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2509–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Garcia, H. Catalysis by metal-organic frameworks in water. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12800–12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessers, E.; De Vos, D.E.; Roeffaers, M.B.J. Chemoselective reduction of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds with UiO-66 materials. J. Catal. 2016, 340, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirujano, F.G.; Corma, A.; i Xamena, F.X.L. Conversion of levulinic acid into chemicals: Synthesis of biomass derived levulinate esters over Zr-containing MOFs. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 124, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzano, L.; Civalleri, B.; Chavan, S.; Bordiga, S.; Nilsen, M.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Lillerud, K.P.; Lamberti, C. Disclosing the Complex Structure of UiO-66 Metal Organic Framework: A Synergic Combination of Experiment and Theory. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Gándara, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Queen, W.L.; Hudson, M.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Water Adsorption in Porous Metal−Organic Frameworks and Related Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4369–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Gándara, F.; Zhang, Y.; Na, K.; Yaghi, O.M. Superacidity in sulfated metal–organic framework-808. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12844–12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creyghton, E.J.; Ganeshie, S.D.; Downing, R.S.; van Bekkum, H. Stereoselective Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley and Oppenauer reactions catalysed by zeolite BEA. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 115, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Entry | Substrate | t (h) | Y 1 (%) | S 1 (%) | Literature 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions | Catalyst | Ref. | ||||||
| 1 | trans-cinnamaldehyde |  | 2 | 99 | 99 | 96% 3 h, IPA | Zr-zeolite β 1.3 mol % Zr | [19] |
| 2 | cis,trans-citral |  | 4 | 95 | 98 | 88% 6 h, IPA | Zr-PhyA 150 mol % Zr | [15] |
| 3 | R-carvone |  | 8 | 48 | 97 | 62% 5 h, 1-indanol | Zr-MCM-41 5 mol % Zr | [7] |
| 4 | 4,4-dimethyl-2-cyclohexen-1-one |  | 24 | 60 | 85 | - | - | - |
| 5 | isophorone |  | 48 | 24 | 75 | 40% 24 h, 1-indanol | Hf-MCM-41 5 mol % Hf | [24] |
| 6 | β-ionone |  | 48 | 77 | 89 | 77% 9 h, IPA | B-MCM-41 4 mol % B | [23] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plessers, E.; Fu, G.; Tan, C.Y.X.; De Vos, D.E.; Roeffaers, M.B.J. Zr-Based MOF-808 as Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction Catalyst for Challenging Carbonyl Compounds. Catalysts 2016, 6, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6070104
Plessers E, Fu G, Tan CYX, De Vos DE, Roeffaers MBJ. Zr-Based MOF-808 as Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction Catalyst for Challenging Carbonyl Compounds. Catalysts. 2016; 6(7):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6070104
Chicago/Turabian StylePlessers, Eva, Guangxia Fu, Collin Yong Xiang Tan, Dirk E. De Vos, and Maarten B. J. Roeffaers. 2016. "Zr-Based MOF-808 as Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction Catalyst for Challenging Carbonyl Compounds" Catalysts 6, no. 7: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6070104
APA StylePlessers, E., Fu, G., Tan, C. Y. X., De Vos, D. E., & Roeffaers, M. B. J. (2016). Zr-Based MOF-808 as Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley Reduction Catalyst for Challenging Carbonyl Compounds. Catalysts, 6(7), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6070104