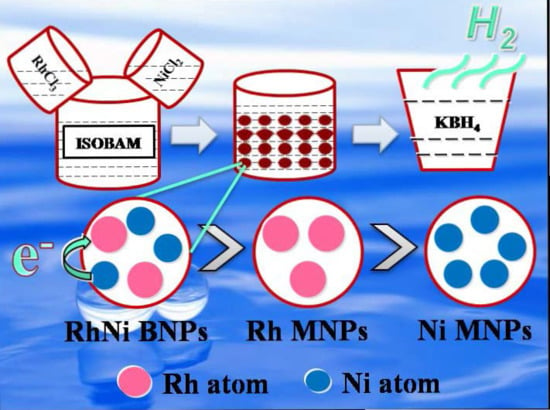
Preparation of Rh/Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Activities for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of KBH4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure and Catalytic Activities of Rh/Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles (BNPs)
2.2. Kinetic Study on Rh10Ni90 BNPs
2.3. Correlation between Catalytic Activities of the Rh/Ni BNPs and Their Electronic Properties
3. Experiments
3.1. Raw Materials
3.2. Experiments
3.3. Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.4. Catalytic Properties
3.5. DFT Calculation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, D.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, P.; Du, Y.K.; Lu, C. WS2 as an effective noble-Metal free cocatalyst modified TiSi2 for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light irradiation. Catalysts 2016, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Ioakimidis, Z.; Kraia, T.; Marnellos, G.E. Hydrogen production by ethanol steam reforming (ESR) over CeO2 supported transition metal (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) catalysts: Insight into the structure-Activities relationship. Catalysts 2016, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhang, W.B. A Ti-Decorated boron monolayer: A promising material for hydrogen storage. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 12925–12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; He, H.Q.; Zhang, J.L. Mechanism for H2 release from potential hydrogen storage materials of phosphine alane and phosphine borane in the presence or absence of alane or borane: A theoretical study. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21949–21958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Xu, Q. Liquid-phase chemical hydrogen storage materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9698–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Singh, S.K.; Yan, J.M.; Zhang, X.B.; Xu, Q. Liquid-phase chemical hydrogen storage: Catalytic hydrogen generation under ambient conditions. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.B.; Xin, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, J.L.; Zheng, Y.; Song, Z.H.; Yang, Y.Z. Stable monodisperse colloidal spherical gold nanoparticles formed by an imidazolium gemini surfactant-based water-in-oil microemulsion with excellent catalytic performance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 28156–28164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Gao, X.P.; Chen, Z.L.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Zhou, H.T.; Zheng, L.Q. The high yield synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles with superior stability and their catalytic activities. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 2012, 14, 7600–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.P.; Huang, Z.L.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Lu, L.L.; Zhang, S.W. Synthesis of Ni/Au/Co trimetallic nanoparticles and their catalytic activities for hydrogen generation from alkaline sodium borohydride aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 34364–34371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, F.; Sahiner, N. Enhanced catalytic performance in hydrogen generation from NaBH4 hydrolysis by super porous cryogel supported Co and Ni catalysts. J. Power Sources 2014, 272, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Bai, Y.; Liu, D.X.; Wu, F.; Pang, M.L.; Yi, B.L. Ni–Co–B catalyst-promoted hydrogen generation by hydrolyzing NaBH4 solution for in situ hydrogen supply of portable fuel cells. Catal. Today 2011, 170, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Sun, S.R.; Huang, Z.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, S.W. Preparation and catalytic activities of PVP-protected Au/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of basic NaBH4 solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Huang, Z.L.; Lu, L.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Cao, Y.N.; Gu, Y.J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, S.W. Preparation and Catalytic Activities of Au/Co Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Generation from NaBH4 Solution. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 2770–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Liang, J.; Tao, Z.L.; Chen, J. PtxNi1–x nanoparticles as catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 8785–8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Yan, J.M.; Wang, Z.L; Jiang, Q. One-step synthesis of Cu@FeNi core-shell nanoparticles: Highly active catalyst for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 10229–10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, K.; Lu, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.M.; Tang, Y.W.; Lu, T.H. Carbon supported Palladium-Iron nanoparticles with uniform alloy structure as methanol-tolerant electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 2993–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Deng, X.G.; Jiao, C.P.; Lu, L.L.; Zhang, S.W. Preparation and catalytic activities for H2O2 decomposition of Rh/Au bimetallic nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 79, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Cao, Y.N.; Lu, L.L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, S.W. Trimetallic Au/Pt/Rh nanoparticles as highly active catalysts for aerobic glucose oxidation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2014, 46, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Watanabe, T.; Okumura, M.; Haruta, M.; Toshima, N. Catalytically highly active top gold atom on palladium nanocluster. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larichev, Y.V.; Netskina, O.V.; Komova, O.V.; Simagina, V.I. Comparative XPS study of Rh/Al2O3 and Rh/TiO2 as catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6501–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, M.J.; Kiyohara, P.K.; Masunaga, S.H.; Jardim, R.F.; Rossi, L.M. Recoverable rhodium nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance in hydrogenation reactions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 338, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakap, M. PVP-stabilized Ru-Rh nanoparticles as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Dou, Y.B.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.D.; He, S.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Synthesis of supported Ni@(RhNi-alloy) nanocomposites as an efficient catalyst towards hydrogen generation from N2H4BH3. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9992–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferencz, Z.; Erdőhelyi, A.; Baán, K.; Oszkó, A.; Óvári, L.; Kónya, Z.; Papp, C.; Steinrück, H.P.; Kiss., J. Effects of support and Rh additive on Co-based catalysts in the ethanol steam reforming reaction. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, E.; Baán, K.; Samu, G.F.; Erdőhelyi, A.; Oszkó, A.; Kónya, Z.; Kiss, J. The Effect of Rh on the Interaction of Co with Al2O3 and CeO2 Supports. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbag, H.; Yasyerli, S.; Yasyerli, N.; Dogu, G. Activities and stability enhancement of Ni-MCM-41 catalysts by Rh incorporation for hydrogen from dry reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Li, W.Q.; Gu, Y.J.; Zhang, S.W. Preparation and Catalytic Activities of Poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)-Protected Au nanoparticles for the aerobic oxidation of glucose. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5743–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loghmani, M.H.; Shojaei, A.F. Hydrogen production through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: Oleic acid stabilized Co–La–Zr–B nanoparticle as a novel catalyst. Energy 2014, 68, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, R.; Demirci, U.B.; Zaatar, Y.; Khoury, A.; Miele, P. Co–αAl2O3–Cu as shaped catalyst in NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6583–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Jiang, J. In situ synthesis of cobalt stabilized on macroscopic biopolymer hydrogel as economical and recyclable catalyst for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. J. Power Sources 2014, 257, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.L.; Tian, J.N. Promoted Mo incorporated Co-Ru-B catalyst for fast hydrolysis of NaBH4 in alkaline solutions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16202–16211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Lu, L.L.; Kawashima, K.; Okumura, M.; Haruta, M.; Toshima, N. Synthesis and catalytic activities of crown jewel-structured (IrPd)/Au trimetallic nanoclusters. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Toshima, N. Synthesis of Au/Pt bimetallic nanoparticles with a Pt-rich shell and their high catalytic activities for aerobic glucose oxidation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Okumura, M.; Toshima, N. Stable Dispersions of PVP-protected Au/Pt/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles as highly active colloidal catalysts for aerobic glucose oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 14883–14891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Toshima, N. Crown Jewel-structured Au/Pd nanoclusters as novel catalysts for aerobic glucose oxidation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 5405–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Watanabe, T.; Okumura, M.; Haruta, M.; Toshima, N. Crown Jewel catalyst: How neighboring atoms affect the catalytic activities of top Au atoms? J. Catal. 2013, 305, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Kawashima, K.; Okumura, M.; Toshima, N. Colloidal Au single-atom catalysts embedded on Pd nanoclusters. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13498–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.Q.; Lu, L.L.; Toshima, N. Preparation and catalytic activities for aerobic glucose oxidation of Crown Jewel structured Pt/Au bimetallic nanoclusters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30752–30762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Haba, M.; Okumura, M.; Akita, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Toshima, N. Novel formation of Ag/Au bimetallic nanoparticles by physical mixture of monometallic nanoparticles in dispersions and their application to catalysts for aerobic glucose oxidation. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10330–10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Toshima, N. Fabrication of catalytically active AgAu bimetallic nanoparticles by physical mixture of small Au clusters with Ag ions. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 447–448, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Toshima, N. Preparation of novel Au/Pt/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles and their high catalytic activities for aerobic glucose oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 400, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajczewska, M.; Vieira, A.; Fiolhais, C.; Perdew, J.P. Volume shift and charge instability of simple-metal clusters. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1996, 53, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delley, B. DMol3 DFT studies: From molecules and molecular environments to surfaces and solids. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2000, 17, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.; Weinstock, R.B.; Weinhold, F. Natural population analysis. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.E.; Sonnenberg, J.L.; Hay, P.J.; Martin, R.L. Density and wave function analysis of actinide complexes: What can fuzzy atom, atoms-in-molecules, Mulliken, Löwdin, and natural population analysis tell us? J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Interplanar Face | (111) | (200) | (220) | (311) | (222) | (400) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | |||||||
| Rh (ICCD 00-005-0685) | 0.2196 | 0.1902 | 0.1345 | 0.1147 | 0.1098 | 0.0951 | |
| Ni (ICCD 00-004-0850) | 0.2034 | 0.1762 | 0.1246 | 0.1062 | 0.1017 | 0.0881 | |
| Particles | Measured Lattice Spacing of BNPs | Comparison of Lattice Spacing of Rh/Ni BNPs with Rh and Ni MNPs | Indexed Reflection Planes of Rh/Ni BNPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.212 | Between Rh(111) and Ni(111), 0.2196 > 0.212 > 0.2034 | (111) |
| 2 | 0.218 | Between Rh(111) and Ni(111), 0.2196 > 0.218 > 0.2034 | (111) |
| 3 | 0.216 | Between Rh(111) and Ni(111), 0.2196 > 0.216 > 0.2034 | (111) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Huang, L.; Jiao, C.; Huang, Z.; Liang, F.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Preparation of Rh/Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Activities for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of KBH4. Catalysts 2017, 7, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040125
Wang L, Huang L, Jiao C, Huang Z, Liang F, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhang H. Preparation of Rh/Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Activities for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of KBH4. Catalysts. 2017; 7(4):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liqiong, Liang Huang, Chengpeng Jiao, Zili Huang, Feng Liang, Simin Liu, Yuhua Wang, and Haijun Zhang. 2017. "Preparation of Rh/Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Activities for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of KBH4" Catalysts 7, no. 4: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040125
APA StyleWang, L., Huang, L., Jiao, C., Huang, Z., Liang, F., Liu, S., Wang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2017). Preparation of Rh/Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Catalytic Activities for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of KBH4. Catalysts, 7(4), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7040125