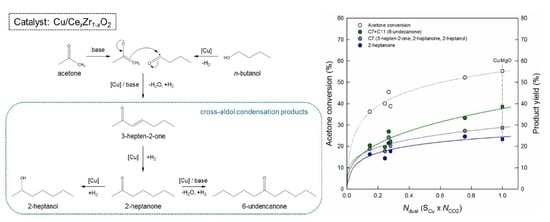
Cross-Aldol Condensation of Acetone and n-Butanol into Aliphatic Ketones over Supported Cu Catalysts on Ceria-Zirconia
Abstract
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Park, J.; Kannapu, H.P.R.; Suh, Y.-W. Cross-Aldol Condensation of Acetone and n-Butanol into Aliphatic Ketones over Supported Cu Catalysts on Ceria-Zirconia. Catalysts 2017, 7, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090249
Kim M, Park J, Kannapu HPR, Suh Y-W. Cross-Aldol Condensation of Acetone and n-Butanol into Aliphatic Ketones over Supported Cu Catalysts on Ceria-Zirconia. Catalysts. 2017; 7(9):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090249
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minseok, Jongha Park, Hari Prasad Reddy Kannapu, and Young-Woong Suh. 2017. "Cross-Aldol Condensation of Acetone and n-Butanol into Aliphatic Ketones over Supported Cu Catalysts on Ceria-Zirconia" Catalysts 7, no. 9: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090249
APA StyleKim, M., Park, J., Kannapu, H. P. R., & Suh, Y.-W. (2017). Cross-Aldol Condensation of Acetone and n-Butanol into Aliphatic Ketones over Supported Cu Catalysts on Ceria-Zirconia. Catalysts, 7(9), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090249