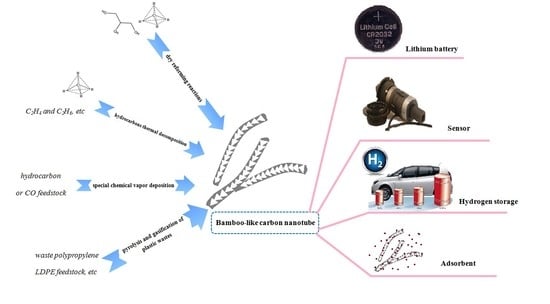
Controllable and Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanostructures: A Review on Bamboo-Like Nanotubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dry Reforming Reactions
3. Hydrocarbon Thermal Decomposition
4. Special Chemical Vapor Deposition
5. Pyrolysis and Gasification from Plastic Wastes
6. Conclusions
- Density functional theory studies of the interaction between dry reforming catalysts and bamboo-like carbon nanotubes will lead to the design and preparation of novel catalysts;
- The comprehensive understanding of the formation mechanisms of bamboo-like carbon nanotubes and their effects on catalytic performance will lead to the design and preparation of other catalysts.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.; Qiao, Z.A.; Dai, S. Recent advances in carbon nanospheres: Synthetic routes and applications. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9246–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Kang, F.; Tarascon, J.M.; Kim, J.K. Recent advances in electrospun carbon nanofibers and their application in electrochemical energy storage. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 319–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wei, F. Advances in production and applications of carbon nanotubes. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yin, X.; Zhu, M.; Han, M.; Hou, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6332–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ji, G. A brief introduction to the fabrication and synthesis of graphene based composites for the realization of electromagnetic absorbing materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Ji, G.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z. Interface polarization strategy to solve electromagnetic wave interference issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5660–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, G.; Xu, Z. An interface strategy to achieve tunable high frequency attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6529–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, J.W.; Huang, N.; He, K.Q.; Dang, Z.M.; Shi, C.Y.; Li, R.K.Y. Electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibrous composites with enhanced ionic conductivity as flexible solid polymer electrolytes. High Volt. 2017, 2, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Feng, A. Thermal conductivity and dielectric properties of bismaleimide-cyanate ester copolymer. High Volt. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Wen, Q.; Luo, F.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, D. Graphene nanosheets/BaTiO3 ceramics as highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding materials in the X-band. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Wu, H.; Wang, K.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Feng, A. Facile synthesis and application of multi-shelled SnO2 hollow spheres in lithium ion battery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 58069–58076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Wu, H.; Pantaleo, G.; Venezia, A.M. Co3O4 nanocrystals and Co3O4–MOx binary oxides for CO, CH4 and VOC oxidation at low temperatures: A review. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 3085–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, J. Catalytic oxidation of benzene, toluene and p-xylene over colloidal gold supported on zinc oxide catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; Shen, Z. Enhanced microwave performance of highly ordered mesoporous carbon coated by Ni2O3 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 525, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Ren, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Co2+/Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4–CoNiO2 hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7677–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; La Parola, V.; Pantaleo, G.; Puleo, F.; Venezia, A.M.; Liotta, L.F. Ni-based catalysts for low temperature methane steam reforming: Recent results on Ni-Au and comparison with other bi-metallic systems. Catalysts 2013, 3, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Wang, L. Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4nanospheres: Facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pantaleo, G.; La Parola, V.; Venezia, A.M.; Collard, X.; Aprile, C.; Liotta, L.F. Bi-and trimetallic Ni catalysts over Al2O3 and Al2O3-MOx (M = Ce or Mg) oxides for methane dry reforming: Au and Pt additive effects. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 156, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, J. Catalytic oxidation of toluene and p-xylene using gold supported on Co3O4 catalyst prepared by colloidal precipitation method. J. Mol. Catal. A 2011, 351, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L. Shape effect of microstructured CeO2 with various morphologies on CO catalytic oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pantaleo, G.; Di Carlo, G.; Guo, S.; Marcì, G.; Concepción, P.; Venezia, A.M.; Liotta, L.F. Co3O4 particles grown over nanocrystallineCeO2: Influence of precipitation agents and calcination temperature on the catalytic activity for methane oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Pantaleo, G.; Venezia, A.M.; Liotta, L.F. Mesoporous silica based gold catalysts: Novel synthesis and application in catalytic oxidation of CO and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Catalysts 2013, 3, 774–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H. Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod-carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 652, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, Q.; Jia, Z.; Xiang, F.; Wu, H. Facile synthesis of urchin-like ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Mater. Lett. 2015, 144, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Xiang, F.; Jia, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wu, G.; Wu, H. Morphology-controlled synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of nanostructured 3D CeO2. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 41, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Feng, A. In situ polymerization of modified graphene/polyimide composite with improved mechanical and thermal properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Feng, A. In situ synthesis and preparation of TiO2/polyimide composite containing phenolphthalein functional group. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 6544–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Feng, A. Fabrication and characterization of OMMt/BMI/CE composites with low dielectric properties and high thermal stability for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 5592–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Feng, A. The effect of modified AlN on the thermal conductivity, mechanical and thermal properties of AlN/polystyrene composites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102542–102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Kou, K.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Ji, T. Improved thermal conductivity and dielectric properties of hBN/PTFE composites via surface treatment by silane coupling agent. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 111, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Dong, W.; Xu, S.; Tang, Y.; Ye, L.; Kong, J. Development of wave-transparent, light-weight composites combined with superior dielectric performance and desirable thermal stabilities. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 144, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Xu, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Kong, J. Hyperbranched polyborosilazane and boron nitride modified cyanate ester composite with low dielectric loss and desirable thermal conductivity. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, K.Q.; Gaillard, J.; Bandaru, P.R.; Rao, A.M. Rational synthesis of helically coiled carbon nanowires and nanotubes through the use of tin and indium catalysts. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.K.; Wang, E.B.; Mao, B.D.; Su, Z.M.; Gao, L.; Lian, S.Y.; Xu, L. Controllable fabrication of carbon nanotube and nanobelt with a polyoxometalate-assisted mild hydrothermal process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6534–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleitz, F.; Choi, S.H.; Ryoo, R. Cubic Ia3d large mesoporous silica: Synthesis and replication to platinum nanowires, carbon nanorods and carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2003, 17, 2136–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, A.M.; Mckinnon, J.T.; Mccloskey, B.D.; Filley, J.; Gneshin, K.W.; Pavelka, R.A. A novel method for the templated synthesis of homogeneous samples of hollow carbon nanospheres from cellulose chars. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9916–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, R.C.; Li, X.; Sunkara, M.K.; Rajan, K. Carbon nanopipettes. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Z.L. Low-Temperature Synthesis of Amorphous Carbon Nanocoils via Acetylene Coupling on Copper Nanocrystal Surfaces at 468 K: A Reaction Mechanism Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 21749–21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, Z.K.; Cui, Z.L. Helical carbon nanofibers prepared by pyrolysis of acetylene with a catalyst derived from the decomposition of copper tartrate. Carbon 2003, 41, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, Z.K.; Cui, Z.L. Helical carbon nanofibers with a symmetric growth mode. Carbon 2004, 42, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, Z.L. Effect of synthesis method of nanocopper catalysts on the morphologies of carbon nanofibers prepared by catalytic decomposition of acetylene. J. Catal. 2004, 223, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and prospects. Science 2005, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.S.; Xu, M.H.; Zhong, W.; Ye, X.J.; Deng, Y.; Au, C.T.; Jin, C.Q.; Du, Y.W. Magnetic properties and large-scale synthesis of novel carbon nanocomposites via benzene decomposition over Ni nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.S.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Deng, Y.; Au, C.T.; Du, Y.W. Large-scale synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of car bon nanotubes of different helicities. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhong, W.; Yang, Y.; Qin, C.; Au, C.; Du, Y. Controllable and Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers, Bamboo-Like Nanotubes, and Chains of Nanospheres over Fe/SnO2 and Their Microwave-Absorption Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Huggins, F.E.; Shah, N.; Jacobs, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Huffman, G.P. Novel Fe-Ni nanoparticle catalyst for the production of CO- and CO2-free H2 and carbon nanotubes by dehydrogenation of methane. Appl. Catal. A 2008, 351, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Fung, K. Catalytic synthesized carbon nanostructures from methane using nanocrystalline Ni. Carbon 2002, 40, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaedini, G.; Tasirin, S.M.; Aminayi, P.; Yaakob, Z.; Talib, M.Z.M. Bulk production of bamboo-shaped multi-walled carbon nanotubes via catalytic decomposition of methane over tri-metallic Ni–Co–Fe catalyst. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2015, 116, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Larsson, J.A.; Larsson, P.; Ahuja, R.; Tobin, J.M.; O’Byrne, J.; Morris, M.A.; Attard, G.; Holmes, J.D. Copper/Molybdenum Nanocomposite Particles as Catalysts for the Growth of Bamboo-Structured Carbon Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 12201–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Márquez, A.; Valverde, J.L.; Keane, M.A. Catalytic growth of structured carbon from chloro-hydrocarbons. Appl. Catal. A 2007, 332, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Asai, K.; Nagayasu, Y.; Takane, K.; Iwamoto, S.; Yagasaki, E.; Ishii, K. Formation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by Ni-catalyzed decomposition of methane at 600–750 °C. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2008, 17, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębek, R.; Galvez, M.E.; Launay, F.; Motak, M.; Grzybek, T.; Costa, P.D. Low temperature dry methane reforming over Ce, Zr and CeZr promoted Ni-Mg-Al hydrotalcite derived catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 11616–11623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, K.W.; Lee, H.C.; Khan, M.R.; Gimbun, J.; Cheng, C.K. CO2 reforming of glycerol over La-Ni/Al2O3 catalyst: A longevity evaluative study. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gullon, I.; Vera, J.; Conesa, J.A.; González, J.L.; Merino, C. Differences between carbon nanofibers produced using Fe and Ni catalysts in a floating catalyst reactor. Carbon 2006, 44, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Jesus, J.D.; Canizales, E. Bamboo-shaped carbon nanotubes generated by methane thermal decomposition using Ni nanoparticles synthesized in water-oil emulsions. Micron 2011, 42, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chang, L. Formation of bamboo-shaped carbon filaments and dependence of their morphology on catalyst composition and reaction conditions. Carbon 2001, 39, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lua, A.C. Synthesis of Ni and Ni-Cu supported on carbon nanotubes for hydrogen and carbon production by catalytic decomposition of methane. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 164, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, M.; Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Gallego, J.; Santamaria, A. Chemical and morphological characterization of multi-walled-carbon nanotubes synthesized by carbon deposition from an ethanol-glycerol blend. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2014, 50, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhan, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, W.; Liang, X.; Ling, L. Effect of sulfur on the growth of carbon nanotubes by detonation-assisted chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Parker, C.B.; Stoner, B.R.; Glass, J.T. Growth of vertically aligned bamboo-like carbon nanotubes from ammonia/methane precursors using a platinum catalyst. Carbon 2011, 49, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkiaga, A.; Lopez, G.; Amutio, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Syngas from steam gasification of polyethylene in a conical spouted bed reactor. Fuel 2013, 109, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Williams, P.T. Pyrolysis–gasification of post-consumer municipal solid plastic waste for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpengkrow, P.; Atong, D.; Sricharoenchaikul, V. Pyrolysis and gasification of land filled plastic wastes with Ni–Mg–La/Al2O3 catalyst. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, V.; Hofbauer, H. Conversion of mixed plastic wastes in a dual fluidized bed steam gasifier. Fuel 2013, 107, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acomb, J.C.; Nahil, M.A.; Williams, P.T. Thermal processing of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment for hydrogen production. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 103, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Yu, T.U.; Lee, J.W.; Moon, J.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.S.; Yang, W.; Lee, U.D. Gasification of mixed plastic wastes in a moving-grate gasifier and application of the producer gas to a power generation engine. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Williams, P.T. Pyrolysis–gasification of plastics, mixed plastics and real-world plastic waste with and without Ni–Mg–Al catalyst. Fuel 2010, 89, 3022–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahil, M.A.; Wu, C.; Williams, P.T. Influence of metal addition to Ni-based catalysts for the co-production of carbon nanotubes and hydrogen from the thermal processing of waste polypropylene. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 130, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acomb, J.C.; Wu, C.; Williams, P.T. The use of different metal catalysts for the simultaneous production of carbon nanotubes and hydrogen from pyrolysis of plastic feedstocks. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 180, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xiao, P.; Zhong, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Wu, X. Bamboo-like carbon nanotubes derived from colloidal polymer nanoplates for efficient removal of bisphenol A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15450–15456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, M.; Terzyk, A.; Gauden, P.; Kaneko, K.; Hattori, Y. Removal of internal caps during hydrothermal treatment of bamboo-like carbon nanotubes and application of tubes in phenol adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 381, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xia, K.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Pei, L.; Fei, S. Facile synthesis and hydrogen storage application of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with bamboo-like structure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, H.; Xi, K.; Ding, S.; Yu, D.; Cheng, S.; Yang, G.; Peng, X.; Fakeeh, A.; Kumar, R. Bamboo-like amorphous carbon nanotubes clad in ultrathin nickel oxide nanosheets for lithium-ion battery electrodes with long cycle life. Carbon 2015, 84, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, E.; Gutierrez, F.; Rubianes, M.; Rivas, G. Bamboo-like multiwalled carbon nanotubes dispersed in double stranded calf-thymus DNA as a new analytical platform for building layer-by-layer based biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.L.; Liang, X.H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Tang, D.M.; Zhang, B.S.; Ji, G.B.; Du, Y.W. Coin-like α-Fe2O3@CoFe2O4 core-Shell composites with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4744–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Wang, C.; Yin, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, J. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon nanotube modified by tetrapyridinoporphyrazine interface layer. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7479–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Multishelled metal oxide hollow spheres: Easy synthesis and formation mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 8864–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; Shuai, Q.; Wu, G.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H. Zinc ferrite composite material with controllable morphology and its applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 224, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Q.; Dong, J.; Kong, B.; Li, H. An electromagnetic modulator based on electrically controllable metamaterial analogue to electromagnetically induced transparency. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shen, N.-H.; Zhang, F.; Wei, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Koschny, T.; Soukoulis, C.M. Electrically tunable Goos-Hänchen effect with graphene in the terahertz regime. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2016, 4, 1824–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Shen, N.-H.; Koschny, T.; Soukoulis, C.M. Tunable terahertz meta-surface with graphene cut-wires. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Wu, G.; Pan, C.; Wang, Y. The behavior of acid treating carbon fiber and the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of phenolic resin matrix composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3786–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Wu, G.; Pan, C.; Wang, Y. Synthesis, preparation and mechanical property of wood fiber-reinforced poly(vinyl chloride) composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3859–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Dong, W.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tang, L.; Kong, J.; Tadakamalla, S.; Wang, B.; Guo, Z. Ultra-low dielectric, fluoride-containing cyanate ester resins combining with prominent mechanical properties and excellent thermal and dimension stabilities. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 6929–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, C.; Geng, W.; Tang, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q. Synergistic improvement of thermal conductivities of polyphenylene sulfide composites filled with boron nitride hybrid fillers. Compos. Part A 2017, 95, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L. Facile synthesis and microwave absorbability of C@Ni-NiO core-shell hybrid solid sphere and multi-shelled NiO Hollow sphere. Mater. Charact. 2014, 97, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L. Design and wide range microwave absorption of porous Co-Co3O4 hybrid hollow sphere with magnetic multi-resonance mechanisms. Mater. Charact. 2015, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Synthesis Method | Reaction Catalyst | Conditions | Products | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dry reforming reactions | CH4 dry reforming | NiAl, NiAlMg, NiAlCe, NiAuAl, NiPtAl, NiAuPtAl, NiAuPtAlMg, NiAuPtAlCe | 750 °C, 1 atm pressure, 24 h long run test | 9.48 wt % bamboo-like CNTs on NiAuPtAl | [18] |
| glycerol dry reforming | Ni/Al2O3, 3 wt % La-Ni/Al2O3, 5 wt % La-Ni/Al2O3 | 750 °C, 1 atm pressure | 55 wt % and 30 wt % bamboo-like CNTs on Ni/Al2O3 and 5 wt % La-Ni/Al2O3 | [55] | |
| hydrocarbon thermal decomposition | methane thermal decomposition | Ni nanoparticles | 930 °C, 1 atm pressure | 86 wt %~87.5 wt % bamboo-like CNTs on Ni nanoparticles | [57] |
| Ni-Cu/Al2O3 | 720–770 °C, 1 atm pressure | 0.7–33 mg C/mg Ni bamboo-like CNTs on Ni-Cu/Al2O3 | [58] | ||
| Ni and Ni-Cu alloys | 750 °C, 1 atm pressure | 407 g C/g Ni bamboo-like CNTs on Ni47Cu53/CNT | [59] | ||
| special chemical vapor deposition | catalytic chemical vapor deposition | LaNiO3 perovskite | 800 and 900 °C, 1 atm pressure | 68.8 wt % and 49.3 wt % bamboo-like CNTs on LaNiO3 | [60] |
| detonation-assisted chemical vapor deposition | Ni nanoparticles with the doping of sulfur | 900 °C, 40 MPa pressure | high quality bamboo-like CNTs on Ni without S | [61] | |
| microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition | thermally oxidized silicon substrates with a platinum thin film catalyst | 1000 °C, 2780 Pa pressure | vertically aligned bamboo-like CNTs on Pt film | [62] | |
| pyrolysis and gasification of plastic wastes | pyrolysis of low density polyethylene feedstock | Nickel, iron, cobalt and copper catalysts | 800 °C, 1 atm pressure | 45.7 mg C/g plastic and ~180 mg C/g plastic bamboo-like CNTs on Ni/Al2O3 and Fe/Al2O3 | [71] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Z.; Kou, K.; Qin, M.; Wu, H.; Puleo, F.; Liotta, L.F. Controllable and Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanostructures: A Review on Bamboo-Like Nanotubes. Catalysts 2017, 7, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090256
Jia Z, Kou K, Qin M, Wu H, Puleo F, Liotta LF. Controllable and Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanostructures: A Review on Bamboo-Like Nanotubes. Catalysts. 2017; 7(9):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090256
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Zirui, Kaichang Kou, Ming Qin, Hongjing Wu, Fabrizio Puleo, and Leonarda Francesca Liotta. 2017. "Controllable and Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanostructures: A Review on Bamboo-Like Nanotubes" Catalysts 7, no. 9: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090256
APA StyleJia, Z., Kou, K., Qin, M., Wu, H., Puleo, F., & Liotta, L. F. (2017). Controllable and Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanostructures: A Review on Bamboo-Like Nanotubes. Catalysts, 7(9), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7090256