Catalytic Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons for the Production of Fuels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
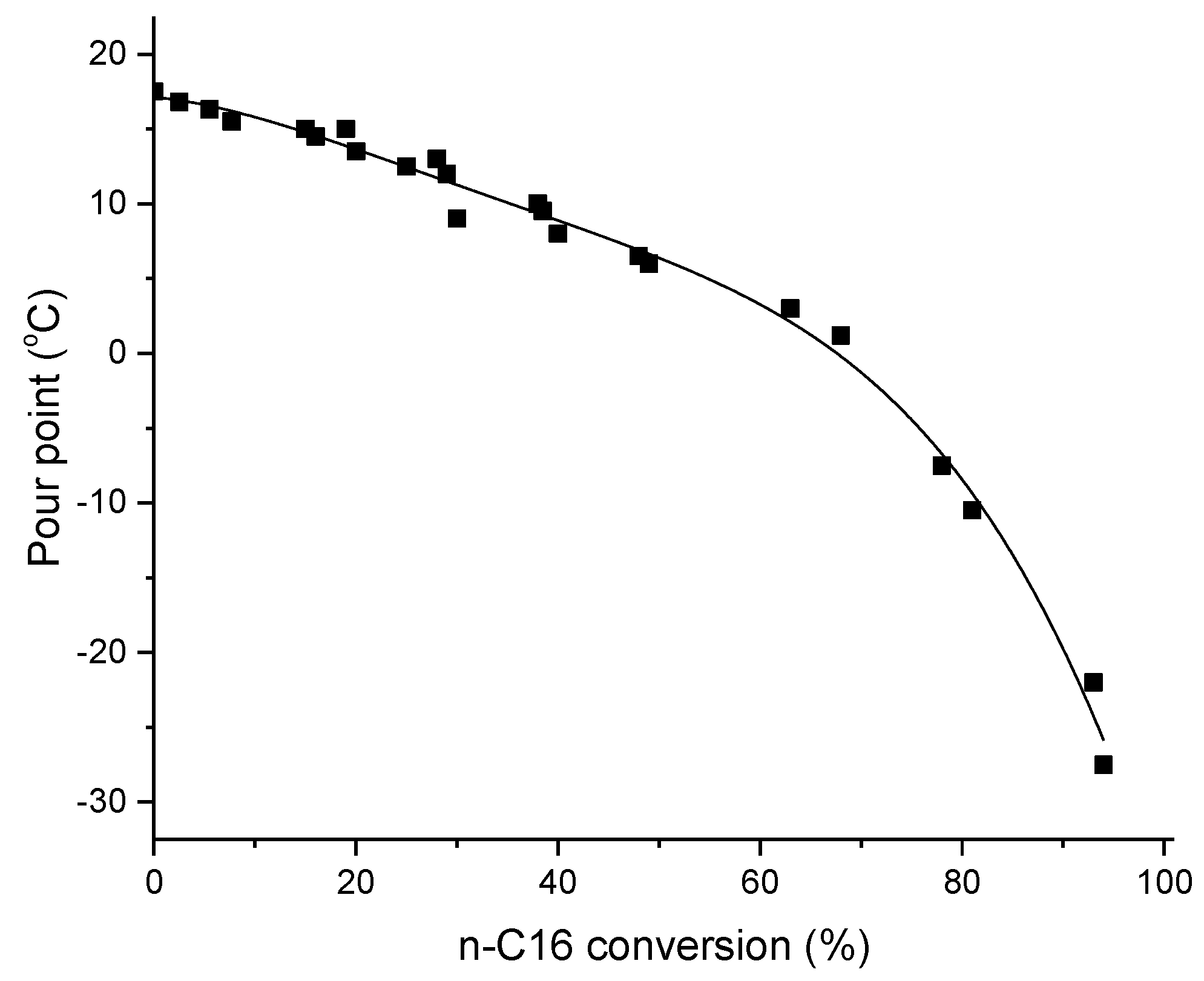
2. Fuel Properties of Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Paraffin Products
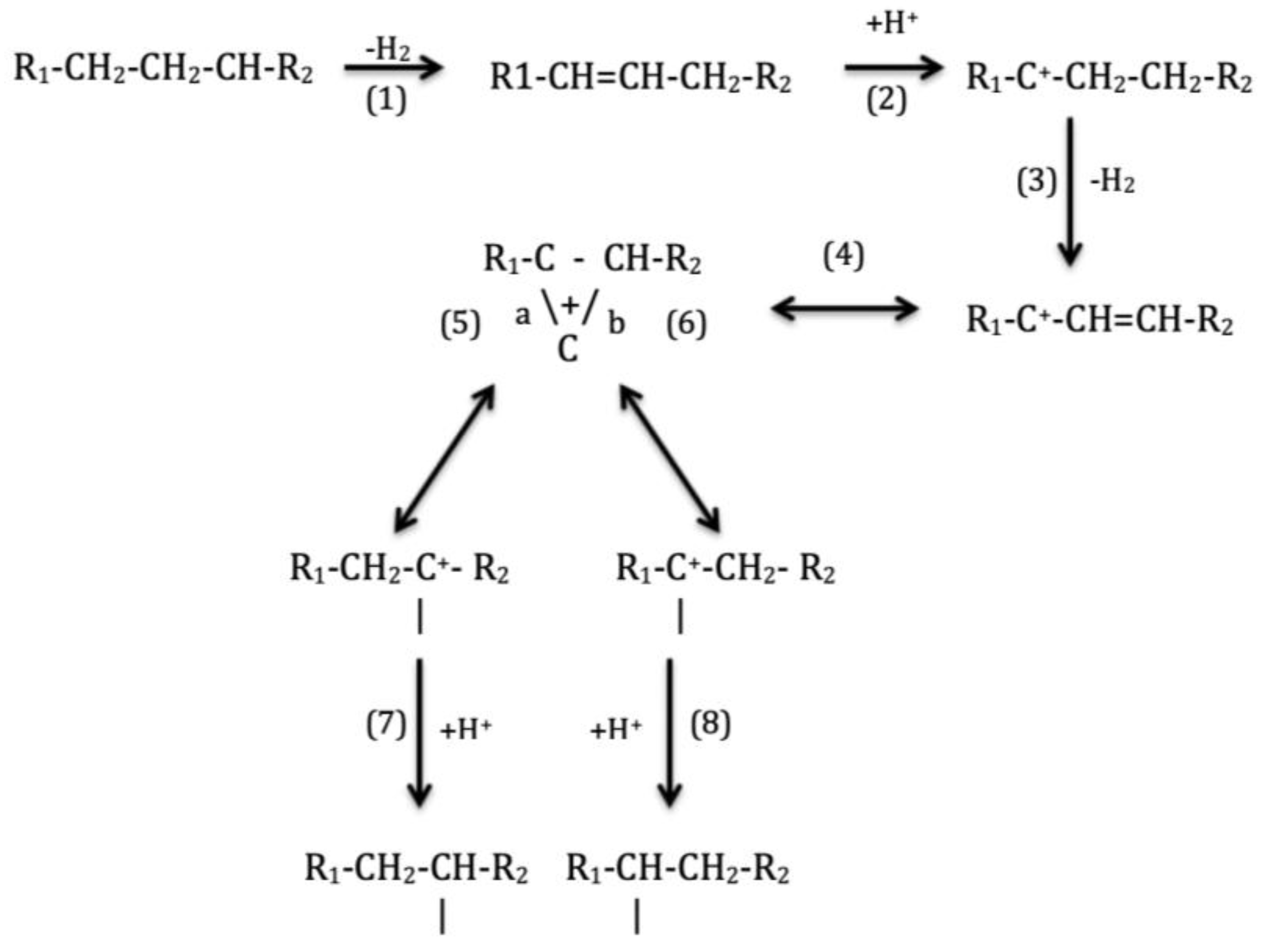
3. Reaction Mechanism in Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Paraffins
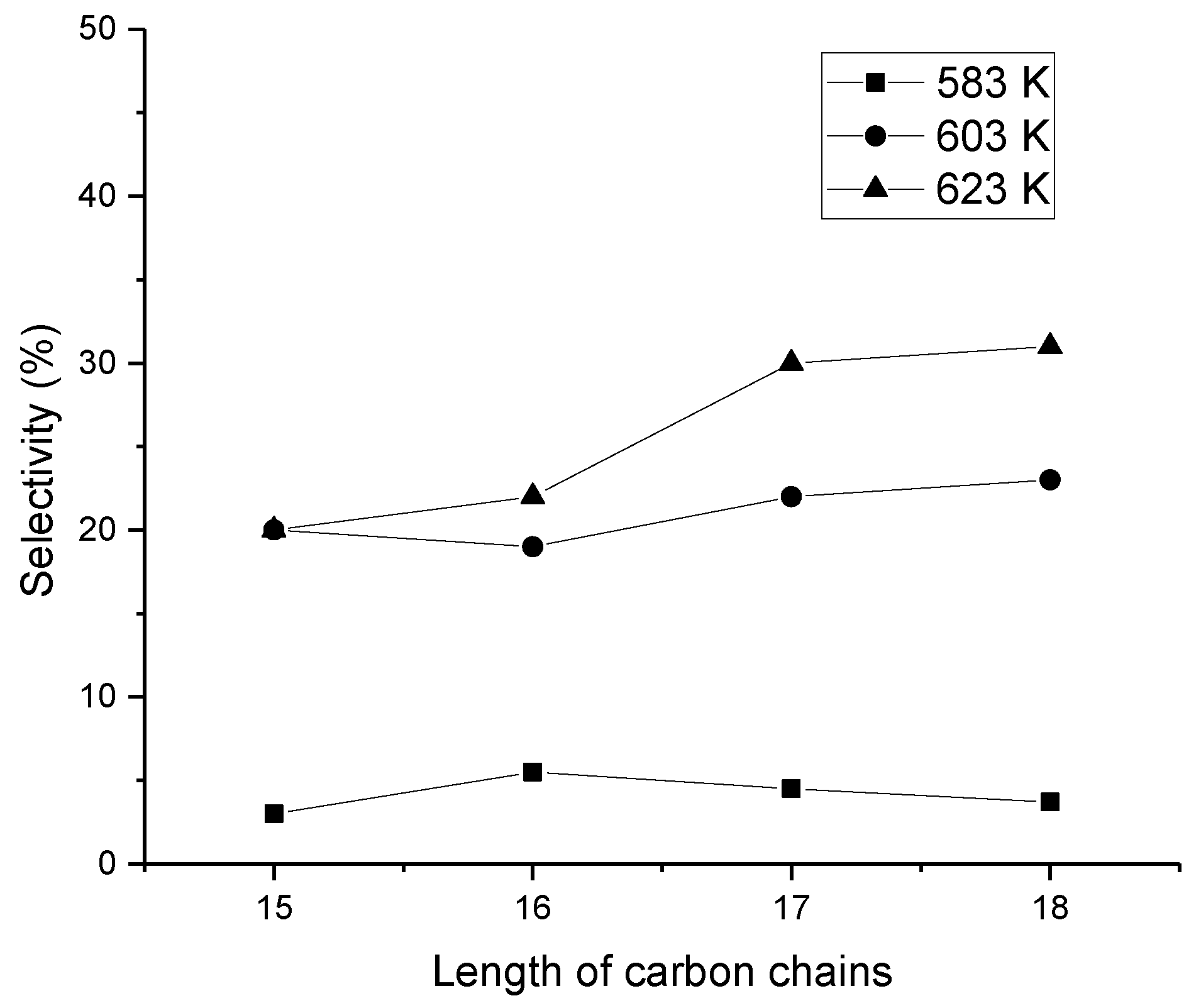
4. Effect of the Alkane Carbon Chain Length
5. Catalyst Selection
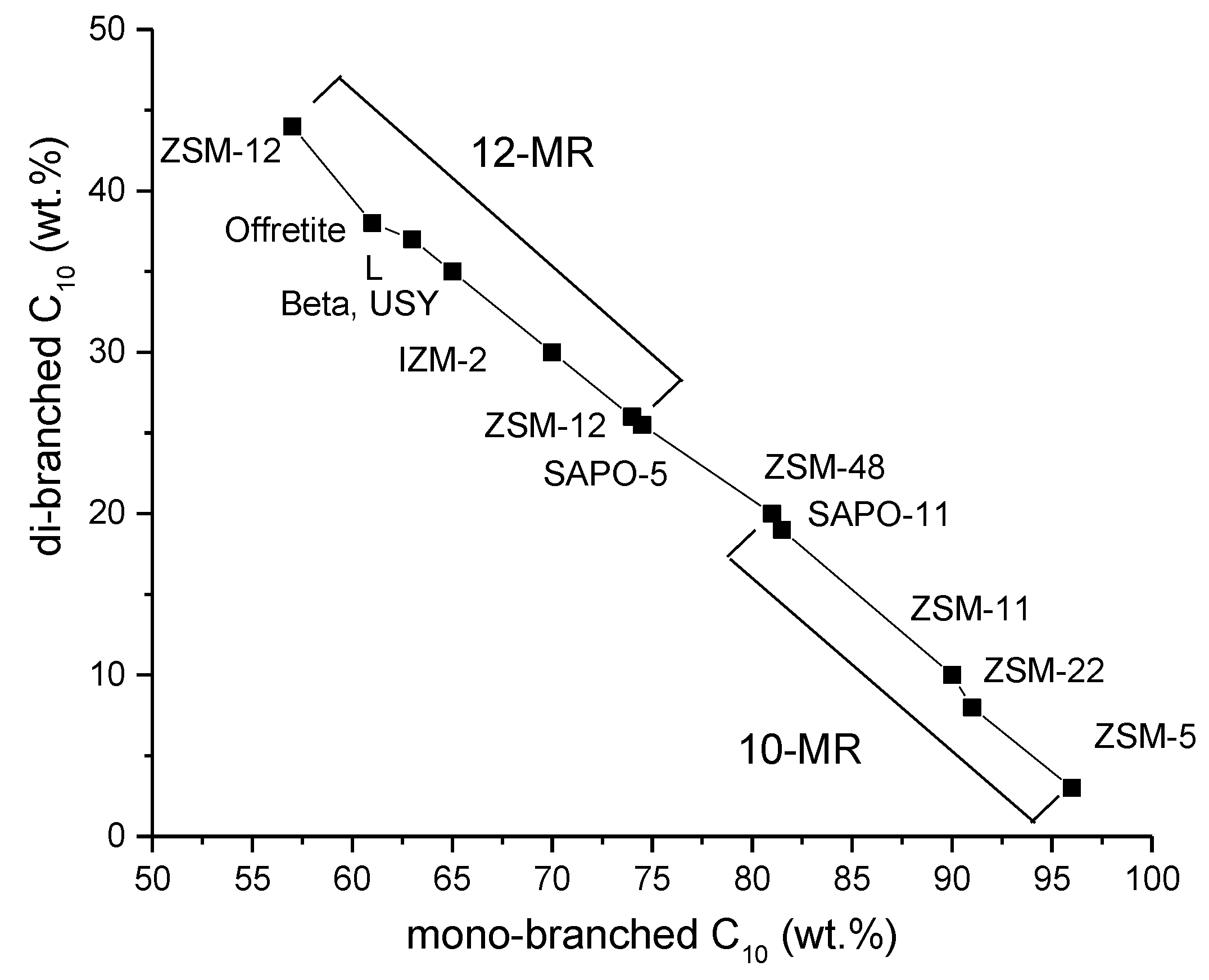
5.1. Zeolites in Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Paraffins
5.1.1. Structure of Zeolites
5.1.2. Effect of Acidity and Metal Dispersion in Bifunctional Metal Supported Zeolites
5.2. Composite Materials and Hierarchical Zeolites in Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Alkanes
5.3. Effect of Metal
5.4. Effect of Metal Dispersion and Loading
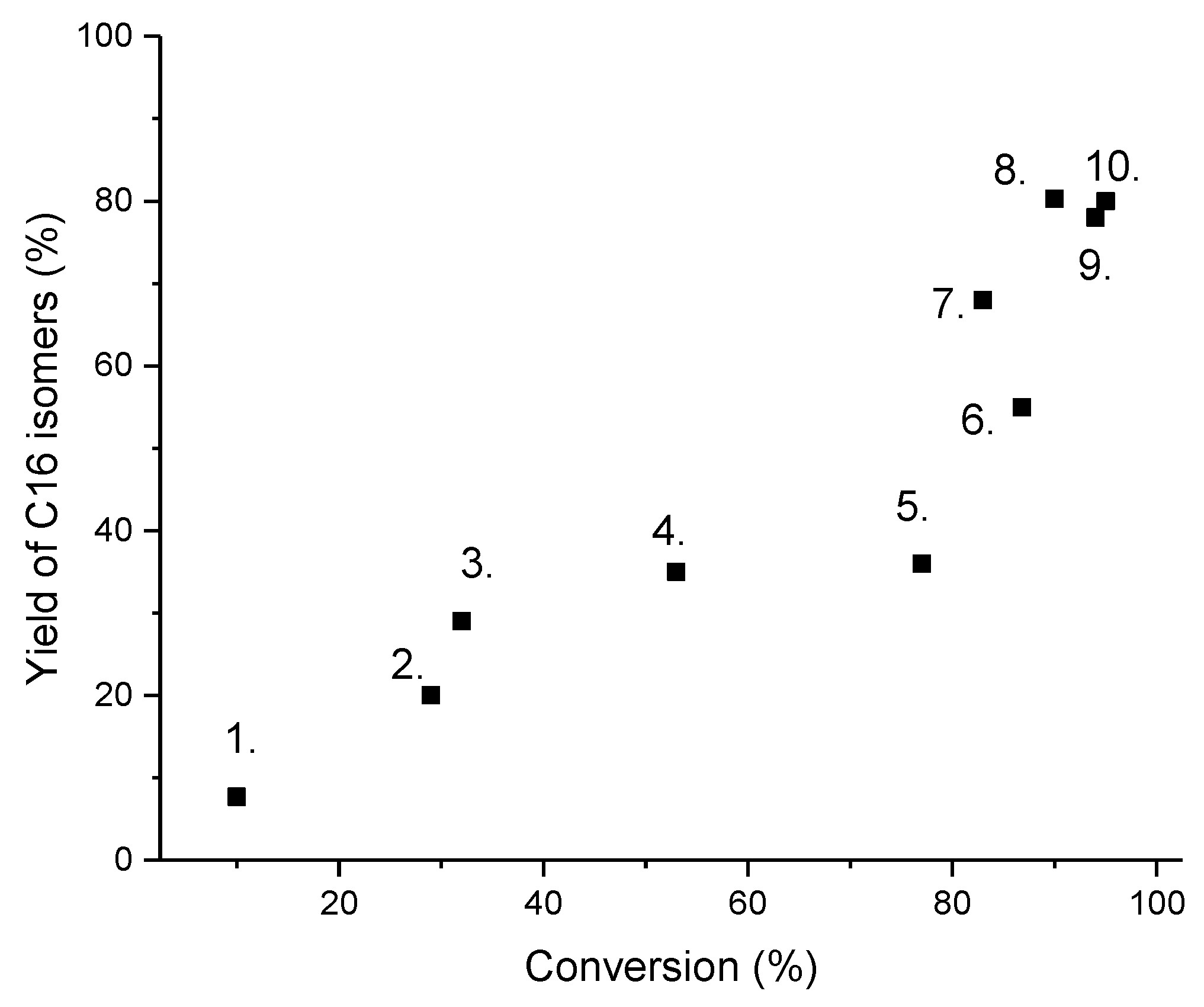
6. Effect of Reaction Conditions in the Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Paraffins
6.1. Effect of Temperature and Pressure
6.2. Effect of H2/Feed Molar Ratio
6.3. Effect of WHSV in Continuous Operation
7. Effect of Reactor Selection in Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Paraffins
Comparison of Continuous and Batch Reactors
8. Catalyst Deactivation and Stability in Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Paraffins
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, K.; Ihm, S. Comparison of Pt/zeolite catalysts for n-hexadecane hydroisomerization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 203, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deldari, H. Suitable catalysts for hydroisomerization of long-chain normal paraffins. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 293, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mériaudeau, P.; Tuan, V.; Nghiem, V.; Lai, S.; Hung, L.; Naccache, C. SAPO-11, SAPO-31, and SAPO-41 Molecular sieves: Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties in octane hydroisomerization. J. Catal. 1997, 169, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.; Parton, R.; Uytterhoeven, L.; Jacobs, P.; Froment, G. Selective conversion of decane into branched isomers: A comparison of platinum/ZSM-22, platinum/ZSM-5 and platinum/USY zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1991, 76, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmedov, V.M.; Al-Khowaiter, S.H. Recent advances and future aspects in the selective hydroisomerization of high n-alkanes. Catal. Rev. 2007, 49, 33–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchy, C.; Hastoy, G.; Guillon, E.; Martens, J.A. Fischer-Tropsch waxes upgrading via hydrocracking and selective hydroisomerization. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2009, 64, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisnet, M. “Ideal” bifunctional catalysis over Pt-acid zeolite. Catal. Today 2013, 218–219, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Sakthivel, A. Silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves as potential catalysts for hydroisomerization of alkanes and alkenes. Appl. Catal A Gen. 2014, 481, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, N.; Pimnard, L.; Bouchy, C.; Guilolon, E.; Guisnet, M. n-Hexadecane hydroisomerization over Pt-HBEA catalysts. Quantification and effect of the intimacy between metal and protonic sites. J. Catal. 2013, 307, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; de Oliveiro Rosas, D.; Chistone, R.C.; Zotin, F.M.Z.; de Araujo, L.R.R.; Zotin, J.L. Hydroisomerization of n-hexadecane using Pt/alumina-Beta zeolite catalysts for producing renewable diesel with low pour point. Fuel 2017, 209, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polzmann, G.; Baladincz, J.; Hanchok, J. Investigation of producing modern base oils. Hung. J. Ind. Chem. 2008, 36, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, S.; Pant, K.K.; John, M.; Kumar, K.; Pai, S.M.; Gupta, M.; Newalkar, B.L. Hydroisomerization of n-hexadecane over Brønsted acid site tailored Pt/ZSM-12. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Ihm, S.-K. Characteristics of magnesium-promoted Pt/ZSM-23 catalyst for the hydroisomerization of hexadecane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 15359–15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, B.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Huang, K.; Li, J. Solvent-free synthesis and n-hexadecane hydroisomerization performance of SAPO-11 catalyst. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regali, F.; Liotta, L.F.; Venezia, A.M.; Boutonnet, M.; Järås, S. Hydroconversion of n-hexadecane on Pt/silica catalysts: Effect of metal loading and support acidity on bifunctional and hydrogenolytic activity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 469, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, N.; Astafan, J.; Dos Reis, C.; Pouilloux, Y.; Bouchy, C.; Guillon, E.; Pinard, L. Hydroisomerization of n-hexadecane over bifunctional Pt-HBEA catalysts. Influence of Si/Al ratio on activity selectivity. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2015, 114, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengsawad, T.; Srimingkwanchai, C.; Butnark, S.; Resasco, D.E.; Jongpatiwut, S. Effect of metal-acid balance on hydroprocessed renewable jet fuel synthesis form hydrocracking and hydroisomerization of biohydrogenated diesel over Pt-supported catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regali, F.; Liotta, L.F.; Venezia, A.M.; Montes, V.; Boutonnet, M.; Järås, S. Effect of metal loading on activity, selectivty and deactivation behavior of Pd/silica-alumina catalysts in the hydroconversion of n-hexadecane. Catal. Today 2014, 223, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
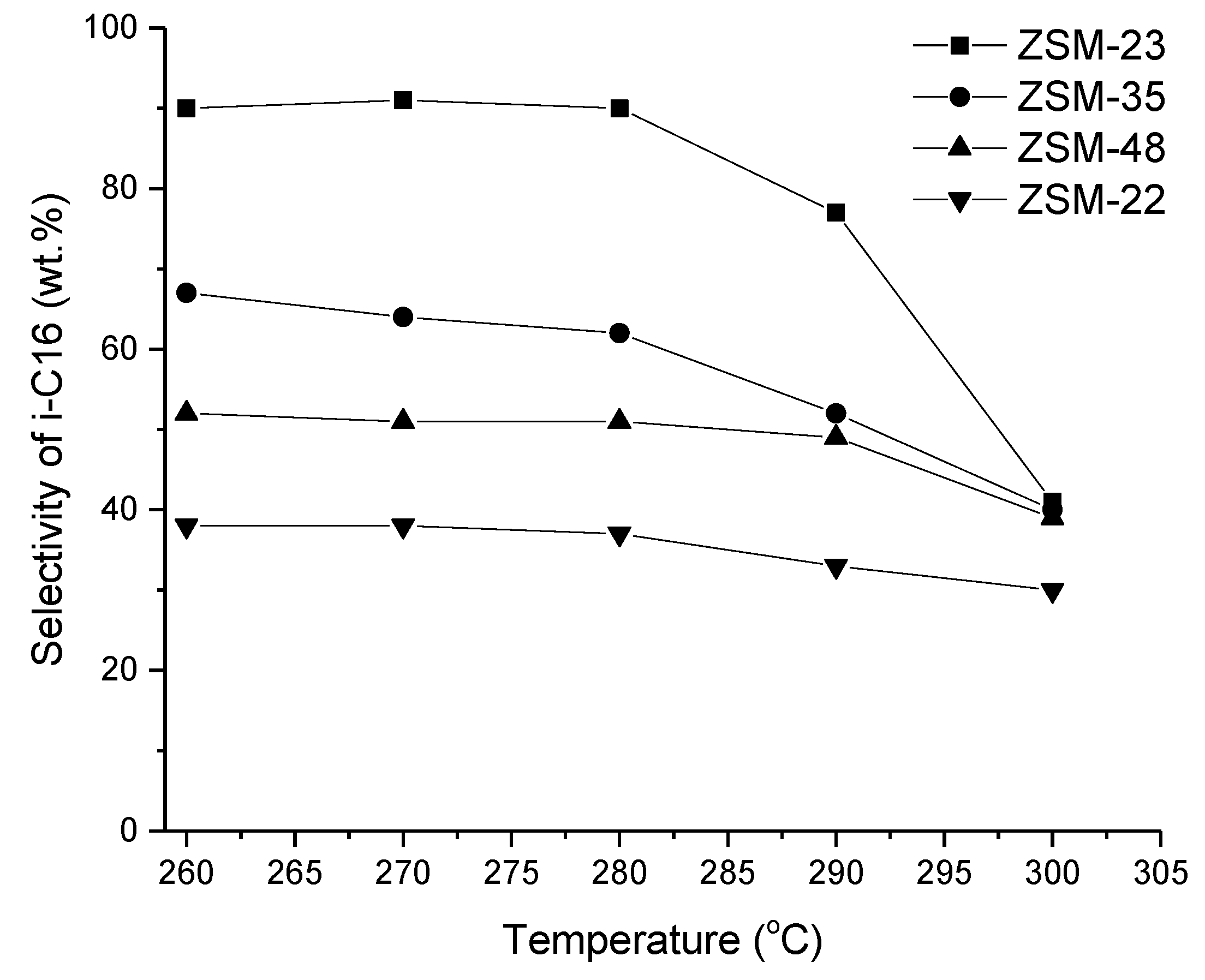
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tsang, C.-W.; Liang, C. Shape selectivity in hydroisomerization of hexadecane over Pt supported on 10-ring zeolites: ZSM-22, ZSM-23, ZSM-35, and ZSM-48. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6069–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Liu, S.; Guan, Q.; Li, W. Investigation on hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of C15-C18 n-alkanes utilizing a hollow tubular Ni-Mo/SAPO-11 catalyst with high selectivity of jet fuel. Catal. Today 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.A.; Verboekend, D.; Thomas, K.; Vanbutsele, G.; Pérez-Ramirez, J.; Gilson, J.P. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of linear and multibranched long model alkanes on hierarchical Pt/ZSM-22 zeolite. Catal. Today 2013, 219, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabti, R.; Pinardi, L.; Lemberton, J.L.; Magnoux, P.; Barama, A.; Moljord, K. Effect of Na exchange of a HBEA zeolite on the activity and the selectivity of a bifunctional Pt-HBEA catalyst for n-hexadecane hydroisomerization. Comparison with a Pt-HZSM-22 catalyst. React. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2010, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, C. Synthesis of ZSM-23 zeolite with dual structure directing agents for hydroisomerization of n-hexadecane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 268, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmogne, R.; Finiels, A.; Cammarano, C.; Hulea, V.; Fajula, F. Hydroconversion of n-hexadecane over bifunctional microporous and mesoporous catalysts. Influence of pore architecture on selectivity. J. Catal. 2015, 329, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, Z.; Xing, W.; Ma, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X. Preparation of hierarchical SAPO-11 molecular sieve and its application for n-dodecane isomerization. Appl. Petrochem. Res. 2014, 4, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Chen, J. Hydroisomerization of n-dodecane on a new kind of bifunctional catalyst: Nickel phosphide supported on SAPO-11 molecular sieve. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 122, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, Z.; Hu, S.; Yan, L.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; Meng, X.; Gao, S.; et al. Hydroisomerization performance of platinum supported on ZSM-22/ZSM-23 growth zeolite catalyst. Pet. Sci. 2013, 10, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qiu, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, G.; Yu, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y. Enhanced n-dodecane hydroisomerization performance by tailoring acid sites on bifunctional Pt/ZSM-22 via alkaline treatment. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ren, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, H.; Lv, E.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.-W. Synthesis and charascterization of the Fe-substituted ZSM-22 zeolite catalyst with high n-dodecane isomerization performance. J. Catal. 2015, 330, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, C. Hydroisomerization of n-octane over bimetallic Ni-Cu/SAPO-11 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 543, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soualah, A.; Lemberton, J.; Pinard, L.; Chater, M.; Magnoux, P.; Moljord, K. Hydroisomerization of long-chain n-alkanes on bifunctional Pt/zeolite catalysts: Effect of the zeolite structure on the product selectivity and on the reaction mechanism. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 336, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, Z.; Wu, B.; Xu, J.; Huo, C.; Li, K.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of metal precursors on the performance of Pt/ZSM-22 catalysts for n-hexadecane hydroisomerization. J. Catal. 2015, 322, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Yun, S.; Park, Y.-K.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Han, J.; Jeon, J.-K. Selective hydroisomreization of n-dodecane over platinum supported on SAPO-11. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Lee, K.; Choi, M. Cooperative effects of secondary mesoporosity and acid site location in Pt/SAPO-11 on n-dodecane hydroisomerization selectivity. J. Catal. 2014, 319, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, H.K.; Lv, J.L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.W. Synthesis, characterization and isomerization performance of micro/mesoporous materials based on H-ZSM-22 zeolite. J. Catal. 2015, 335, 11–23.36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Ning, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yun, Y.; Ren, J.; Li, Y.-W. Synthesis and characterization of bundle-shaped ZSM-22 zeolite via the oriented fusion of nanorods and its enhanced isomerization performance. J. Catal. 2018, 361, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Xi, H.; Lin, M.; Wang, Q.; Jia, L.; Hou, B.; Li, D. High selectivity fro n-dodecane hydroisomerization over highly siliceous ZSM-22 with low Pt loading. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, N.; Morisset, S.; Pinard, L.; Maupin, I.; Lemberton, J.L.; Lemos, F.; Pouilloux, Y. BEA zeolite nanocrystals dispersed over alumina for n-hexadecane hydroisomerization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, F.M.; Bouchy, C.; Guillon, E.; Fécant, A.; Bats, N.; Martens, J.A. IZM-2: A promising new zeolite for the selective hydroisomerization of long-chain n-alkanes. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Seo, Y.; Kim, J.-C.; Ryoo, R. n-heptane isomerization over Pt/MFI zeolite nanosheets: Effects of zeolite crystal thickness and platinum location. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.R.; Hayasaka, K.; Thybaut, J.W.; Narasimhan, C.S.L.; Denayer, J.F.; Martens, J.A.; Marin, G.B. Pt/H-ZSM-22 hydroisomerization catalysts optimization guided by Single-Event Microkinetic modeling. J. Catal. 2012, 290, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.; Wu, H.; Leu, L. Hydroisomerization of light normal paraffins over series of platinum-loaded mordenite and beta catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 143, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, M.C.; Martens, J.A. Monomethyl-branching of long n-Alkanes in the range from decane to tetracosane on Pt/H-ZSM-22 bifunctional catalyst. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyen, E.; Changbum, J.; Kurttepeli, M.; Vanbutsele, G.; Gobechiya, E.; Koranyi, T.I.; Bals, S.; Van tendeloo, G.; Ryoo, R.; Kirxscchock, C.E.A.; et al. Molecular shape-selectivity on MFI zeolite nanosheets in n-decane isomerization and hydrocracking. J. Catal. 2013, 300, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Lou, B.; Yu, R.; Men, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Z. Hydroisomerization of n-decane over micro/mesoporous Pt-containing bifunctional catalysts: Effects of the MCM-41 incorporation with Y zeolite. Fuel 2018, 226, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyen, P.T.; Nam, L.T.H.; Vinh, T.Q.; Martinez, C.; Parvulescu, V.I. ZSM-5/SBA-15 versus Al-SBA-15 as supports for the hydrocracking/hydroisomerization of alkanes. Catal. Today 2018, 308, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Peffer, L.A.A.; Mouilijn, J.A.; Pérez-Ramirez, J. Desilication: On the controlled generation of mesoporosity in MFI zeolites. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.A.; Verboekend, D.; Thomas, K.; Vanbutsele, G.; Gilson, J.-P.; Perez-Ramirez, J. Hydroisomerization of emerging renewable hydrocarbons using hierarchical Pt/H-ZSM-22 catalyst. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogh, R.A.; Sparks, D.; Hu, J.; Wender, I.; Tiernye, J.W.; Wang, W.; Davis, B.H. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of n-hexadecane over a platinum promoted sulfated zirconia catalyst. Energy Fuels 1994, 8, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busto, M.; Vera, C.R.; Grau, J.M. Optimal processing conditions for the isomerization-cracking of long-chain n-paraffins to high octane isomerizate gasoline over Pt/SO42−-ZrO2 catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Vekariya, R.L.; Sharma, P. Kinetics and mechanistic study of n-alkane hydroisomerization reaction on Pt-loaded γ-alumina catalyst. Petroleum 2017, 3, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Wang, C.; Chi, K.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Ma, H.; Qu, W.; Tian, Z. Effects of Pt site distributions on the catalytic performance of Pt/SAPO-11 for n-dodecane hydroisomerization. Catal. Today 2018, 316, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, R.A.; Finelli, Z.R.; Vaudagna, S.R.; Figoli, N.S. Hydroisomerization of n-hexane on Pt/SO42-/ZrO2: Effect of total and hydrogen partial pressure. Catal. Lett. 1997, 45, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Feed | Conditions | Catalyst | Conversion (%) | Yield or Selectivity (%) of Isomer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-hexadecane | 220 °C, 30 bar | 0.7 wt % Pt-H-Beta/Al2O3 | 95 | 80 | [9] |
| 295 °C, 60 bar | Ba-Pt-ZSM-12 | 90 | 80.3 | [12] | |
| 280 °C, 60 bar | Pt-SAPO-11-S | 88 | 80 | [14] | |
| 296 °C, H2/feed = 1000, WHSV = 1 hr−1 | 0.5 Pt-ZSM-22 | 70 | 49 | [32] | |
| 310 °C, 30 bar, H2/feed molar ratio 10 | Pt-Al-Si | 53 | 35 | [15] | |
| 290 °C, 75 bar, WHSV = 1.3 hr−1 | Pt-Al-Beta (80) | 36.5 | 35.5 (monosubstituted) | [10] | |
| 270 °C, 40 bar, H2/feed volumetric ratio 600 | Pt-ZSM-23 | 32 | 29 | [19] | |
| 300 °C, 40 bar, H2/feed volumetric ratio 600 | Pt-ZSM-23 dual templated | 29 | 20 | [23] | |
| 220 °C, 30 bar | Pt-Beta | 10 | 8 | [22] | |
| C15–C18 alkanes | 310 °C, 30 bar, LHSV = 1 hr−1, H2/oil = 800 | Ni-Mo-SAPO-11 | XC15,iC18,i = 51–74% | SC15,iC18,i = 58–65% | [20] |
| dodecane | 300 °C, 1 bar, WHSV = 2 hr−1, H2/feed = 15 | 0.5 wt % Pt-SAPO-11 | 57 | S = 68% | [33] |
| 307 °C, 20 bar, WHSV = 2 hr−1 | 1 wt % Pt-SAPO-11 | 92 | 84 | [34] | |
| 280 °C, 1.5 hr−1, H2/n-dodecane = 25 | 0.5 wt % Pt-Meso-SAPO-11 | 94 | 70 | [25] | |
| 320 °C, 80 bar | Pt-ZSM-22/ZSM-23 | 85 | 68.3 | [27] | |
| 300 °C, H2/feed = 600, LHSV = 2 hr−1, 20 bar | Pt-ZSM-22/MCM-41-H | 91.3 | 66 | [35] | |
| 300 °C | Pt-ZSM-22-BUN | 96 | 49 | [36] | |
| 350 °C, 20 bar, WHSV = 3 hr−1, H2/n-C12 = 19 | 3 wt % NixPy-SAPO-11 | 70 | 40 | [26] |
| Zeolite | Cavity Size (Å) | Topology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM-22 | 5.7 × 4.6 | TON (10 MR) | [19] |
| ZSM-23 | 5.2 × 4.5 | MTT (10 MR) | [19] |
| ZSM-35 | 3.5 × 4.8, 4.2 × 5.4 | FER (8–10 MR) | [19] |
| ZSM-48 | 5.6 × 5.3 | MRE (10 MR) | [19] |
| SAPO-11 | 3.9 × 6.3 | (10 MR) | [34] |
| Catalyst Modification Method | Catalyst | Change in Properties | Effect in Hydroisomerization | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dealumination: steamed, acid leached | Pt-HY-A | lower yield of isomers than over Pt-Al-MCM-41 | higher isomer yield than in Pt-HY without acid leaching | [24] |
| Pt-ZSM-22 | increased amount of acid sites on the external surface | monobranched isomers | [43] | |
| dealumination with HCl treatment | Pt-SAPO-11 | Lewis acid sites formed, mesopores on crystal surface | 70% isomer yield at 94% conversion in n-dodecane hydroisomerization | [25] |
| desilication: alkaline treatment | Pt-ZSM-22 | total acid sites decreased partially due to blocking of micropores with Al | isomer 87.3% selectivity, 76.6% monobranched products, 80% conversion n-dodecane | [28] |
| in situ alkali treatment in the presence of cetyl triammonium bromide | ZSM-2/MCM-41 | lower Brønsted acidity than in the corresponding desilicated catalyst | 72.3% selectivity to monobranched products at a 91% conversion level | [35] |
| desilication | ZSM-22 nanosheets | short channels, lower surface area, lower acidity, high external surface, thermal stability | 76% isomerization selectivity at 50% conversion in n-decane hydroisomerization | [44] |
| desilication, NaOH treatment | Pt-SAPO-11 | lower amount of Brønsted acid sites, rearranging acid site location | high isomerization selectivity | [28] |
| desilication, acid washing | Pt-ZSM-22 nanorods | removal of external Al, which is blocking the pore mouth | more monobranched and dibranched in comparison to linear and tribranched | [21] |
| desilication | Pt-SAPO-11 | Acidity on internal surface, mesoporosity, faster diffusion | 84% selectivity to isomers at 92% conversion in dodecane hydroisomerization, faster diffusion | [34] |
| ethanol as a cosolvent in hydrothermal zeolite synthesis | Pt-ZSM-22 nanobundles | Al location on the external surface | 38% selectivity to monobranched isomers at 90% conversion in n-dodecane hydroisomerization | [36] |
| dual templating method for the synthesis of zeolites | Pt-ZSM-23 | high external surface area, low microporous surface area | 38 wt % 5-methylpentadecane formed in n-hexadecane hydroisomerization | [23] |
| Mg modification | Pt-ZSM-23 | decreased acidity, increased Lewis acidity, higher Pt dispersion | higher isomer selectivity in hexadecane hydroisomerization | [13] |
| Ba-modification of zeolite | Ba-ZSM-12 | lower Brønsted acidity, high Pt dispersion | 80% yield to multibranched products in hydroisomerization of hexadecane at 90% conversion | [12] |
| Fe-substitution | Pt-H-ZSM-22 | lower acidity, Fe/Al ratio 1 | 72% selectivity to monobranched C12 products in hydroisomerization of dodecane at 91% conversion | [29] |
| solvent free synthesis | Pt-SAPO-s | lower Pt dispersion | 66% selectivity to isomers at 96% conversion in hydroisomerization of hexadecane, 50% selectivity to multibranched products | [14] |
| alumination of MCM-48 | Pt-Al-MCM-48 | enhanced acidity, large amounts of Lewis acid sites | 49 wt % multibranched isomers and 21 wt % monobranched in hydroisomerization of hexadecane at 85% conversion | [24] |
| Y-MCM-41 composite | Pt-Y/MCM-41 | mesoporous shell around the zeolite phase, rapid diffusion | yield of C10 isomers 30.6% at 34% conversion | [19] |
| aluminated H-Beta zeolite | -Al2O3-Pt-H-Beta | alumina coated composite catalyst, less agglomeration compared to parent zeolite, isolated nanocrystals | 80% isomer yield at 92% conversion in hexadecane hydroisomerization | [38] |
| composite -Al2O3-Pt-H-Beta | -Al2O3-Pt-H-Beta (Si/Al = 80) | low acidity | monosubstituted isomers 24 wt % at 36% conversion | [10] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kaka khel, T.A.; Azkaar, M.; Engblom, S.; Murzin, D.Y. Catalytic Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons for the Production of Fuels. Catalysts 2018, 8, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110534
Mäki-Arvela P, Kaka khel TA, Azkaar M, Engblom S, Murzin DY. Catalytic Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons for the Production of Fuels. Catalysts. 2018; 8(11):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110534
Chicago/Turabian StyleMäki-Arvela, Päivi, Taimoor A. Kaka khel, Muhammad Azkaar, Simon Engblom, and Dmitry Yu. Murzin. 2018. "Catalytic Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons for the Production of Fuels" Catalysts 8, no. 11: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110534
APA StyleMäki-Arvela, P., Kaka khel, T. A., Azkaar, M., Engblom, S., & Murzin, D. Y. (2018). Catalytic Hydroisomerization of Long-Chain Hydrocarbons for the Production of Fuels. Catalysts, 8(11), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110534






