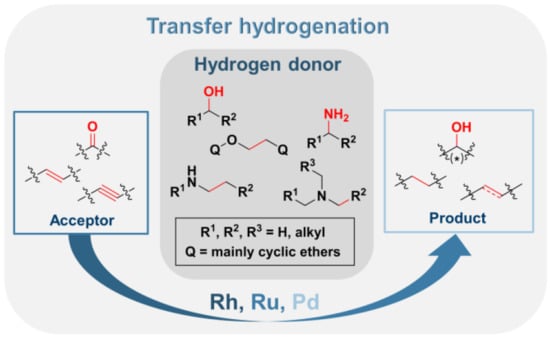
Hydrogen Transfer Reactions of Carbonyls, Alkynes, and Alkenes with Noble Metals in the Presence of Alcohols/Ethers and Amines as Hydrogen Donors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
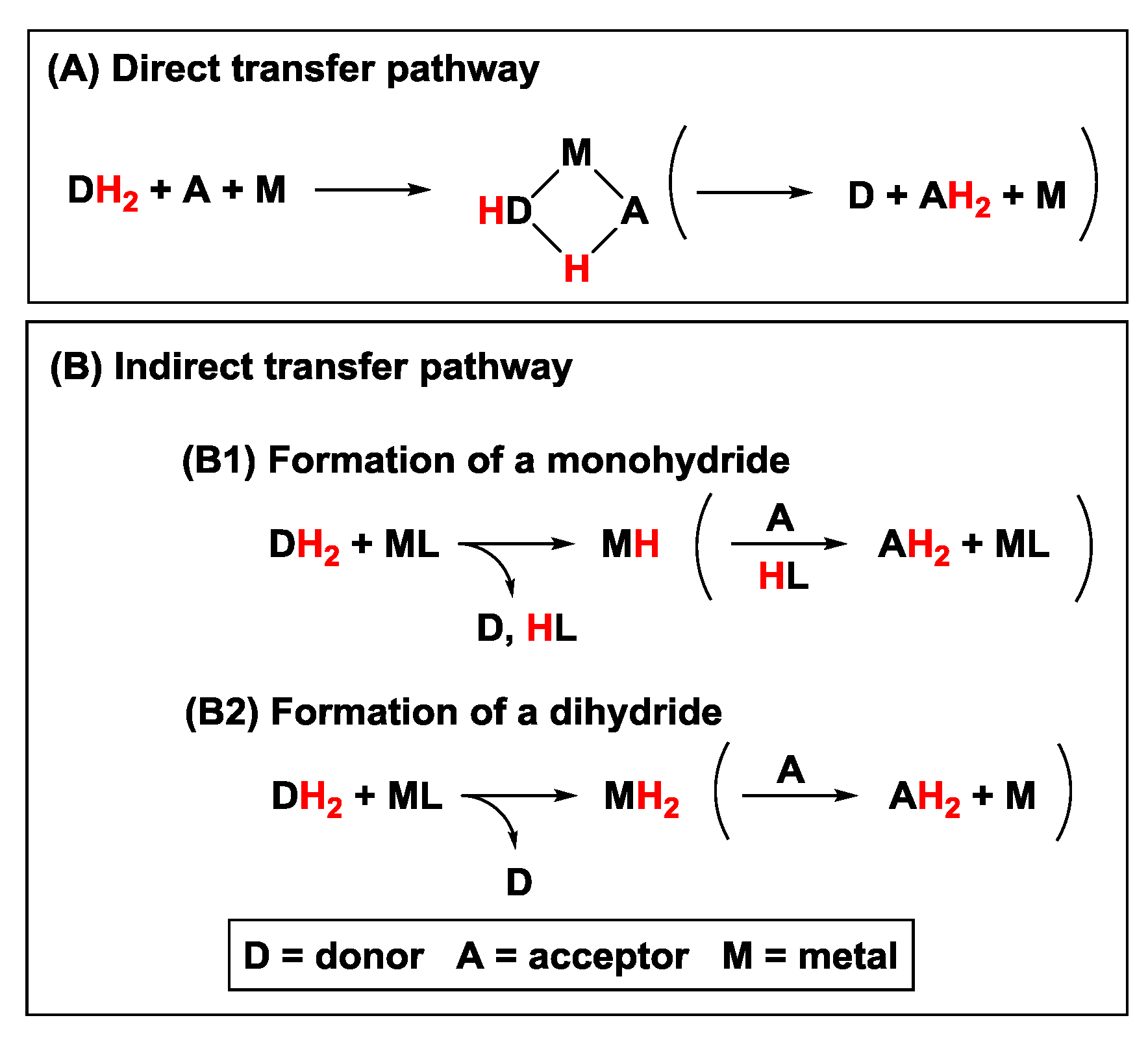
2. Hydrogen Transfer Reactions, Reaction Mechanisms
2.1. Hydrogen Transfer
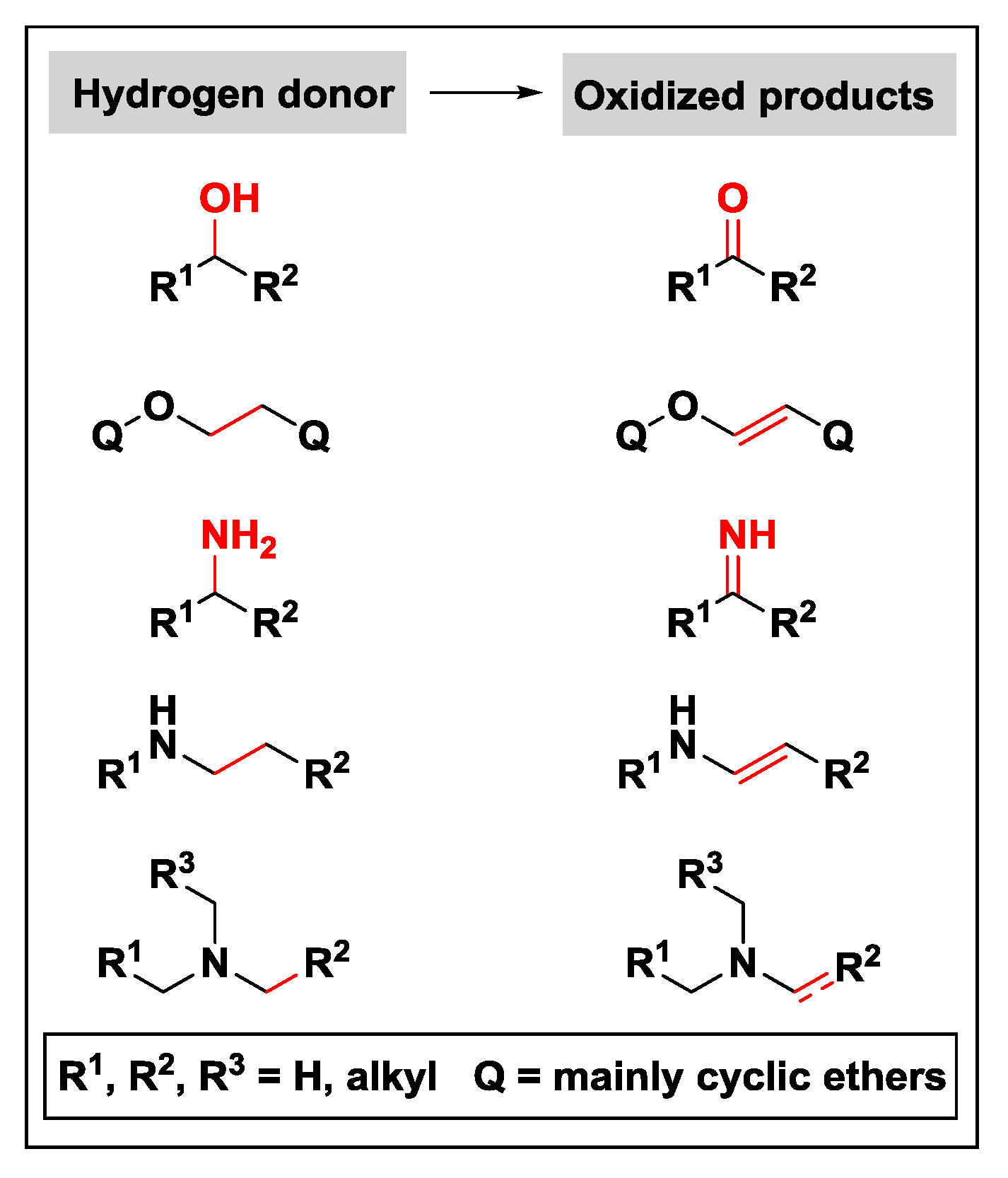
2.1.1. Donor Molecules: Alcohols/Ethers and Amines
2.1.2. Acceptor Molecules: Carbonyls, Alkenes, and Alkynes
2.2. Catalysis with Noble Metals
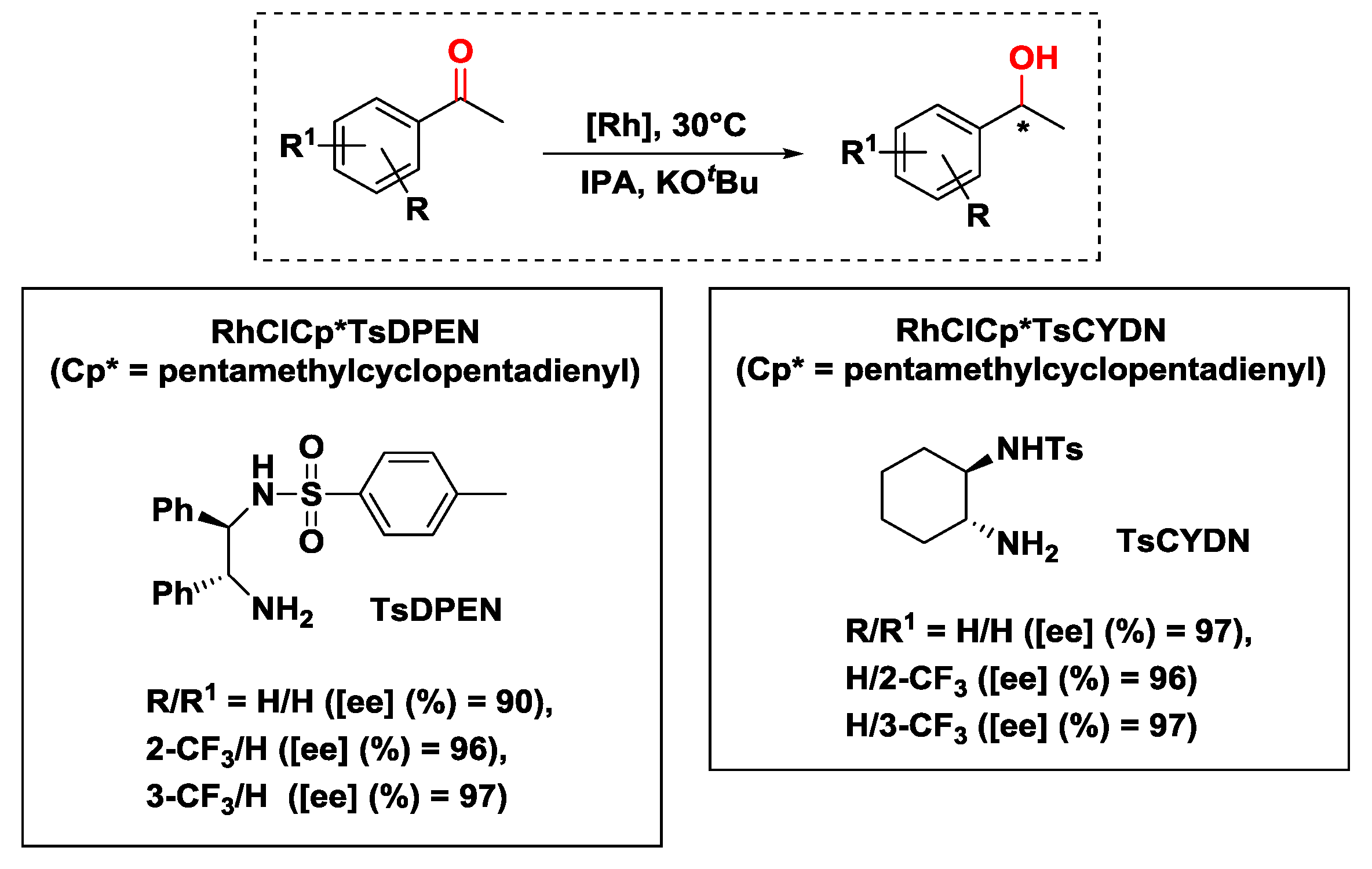
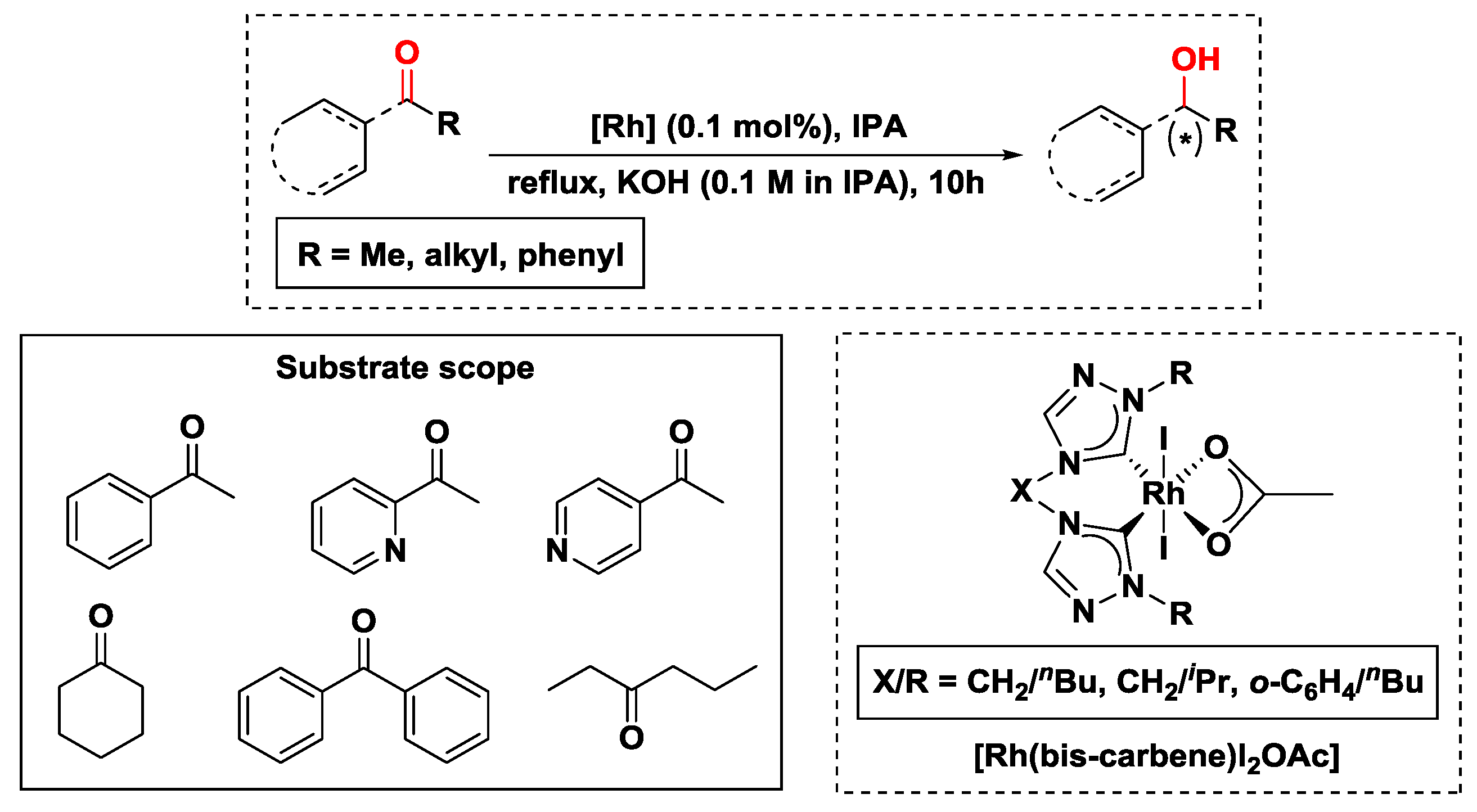
2.2.1. Hydrogen Transfer with Rhodium
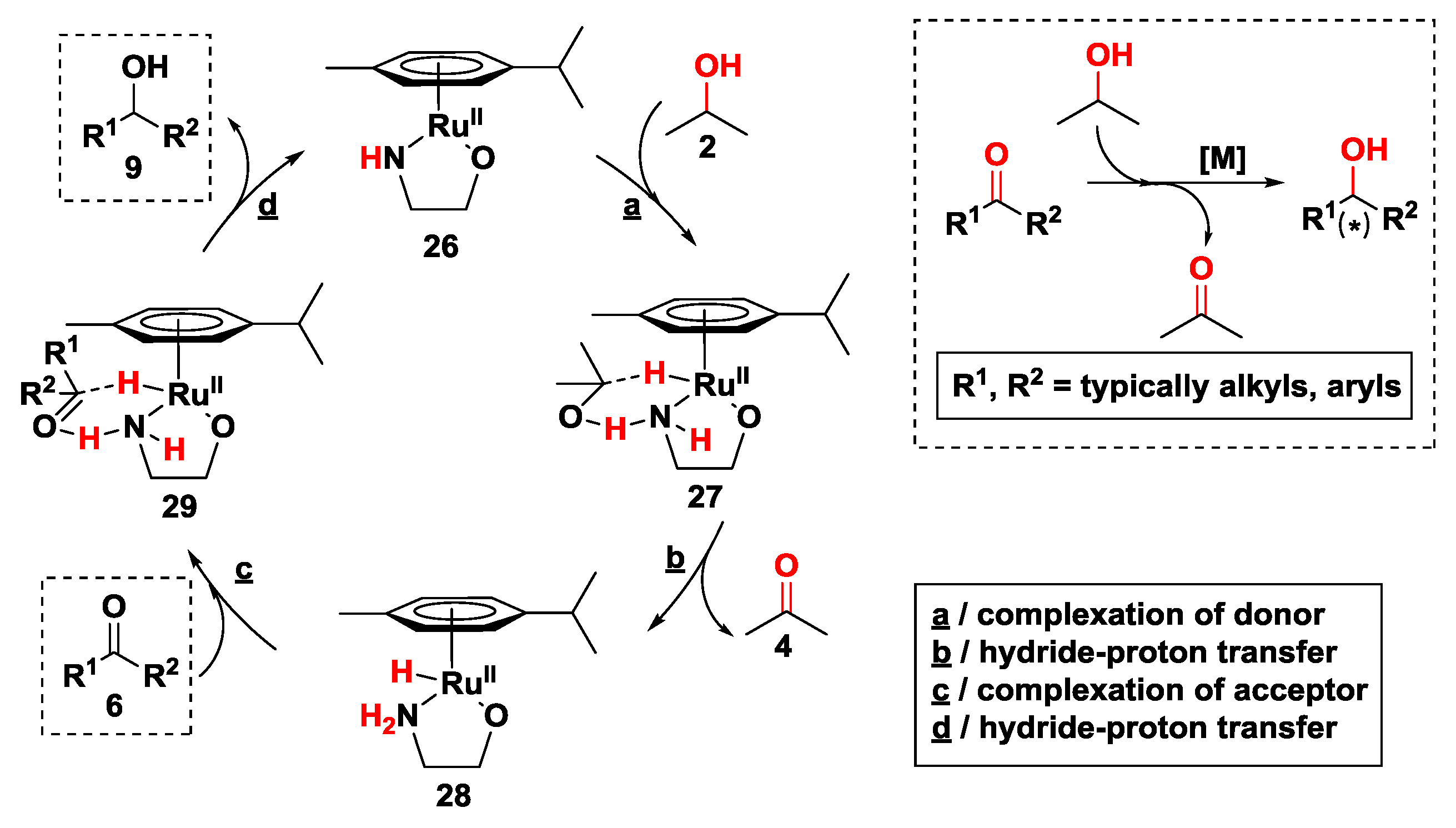
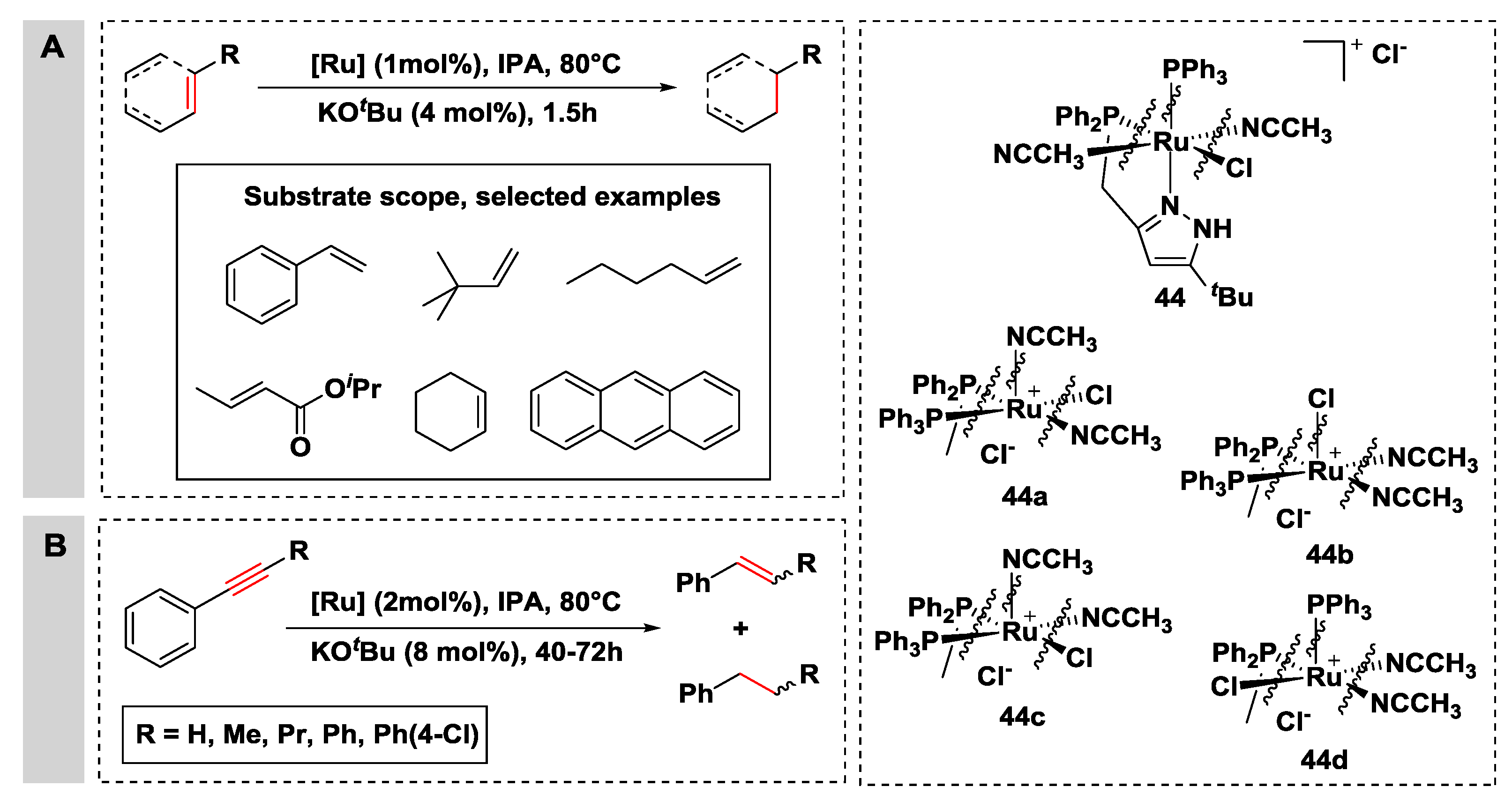
2.2.2. Hydrogen Transfer with Ruthenium
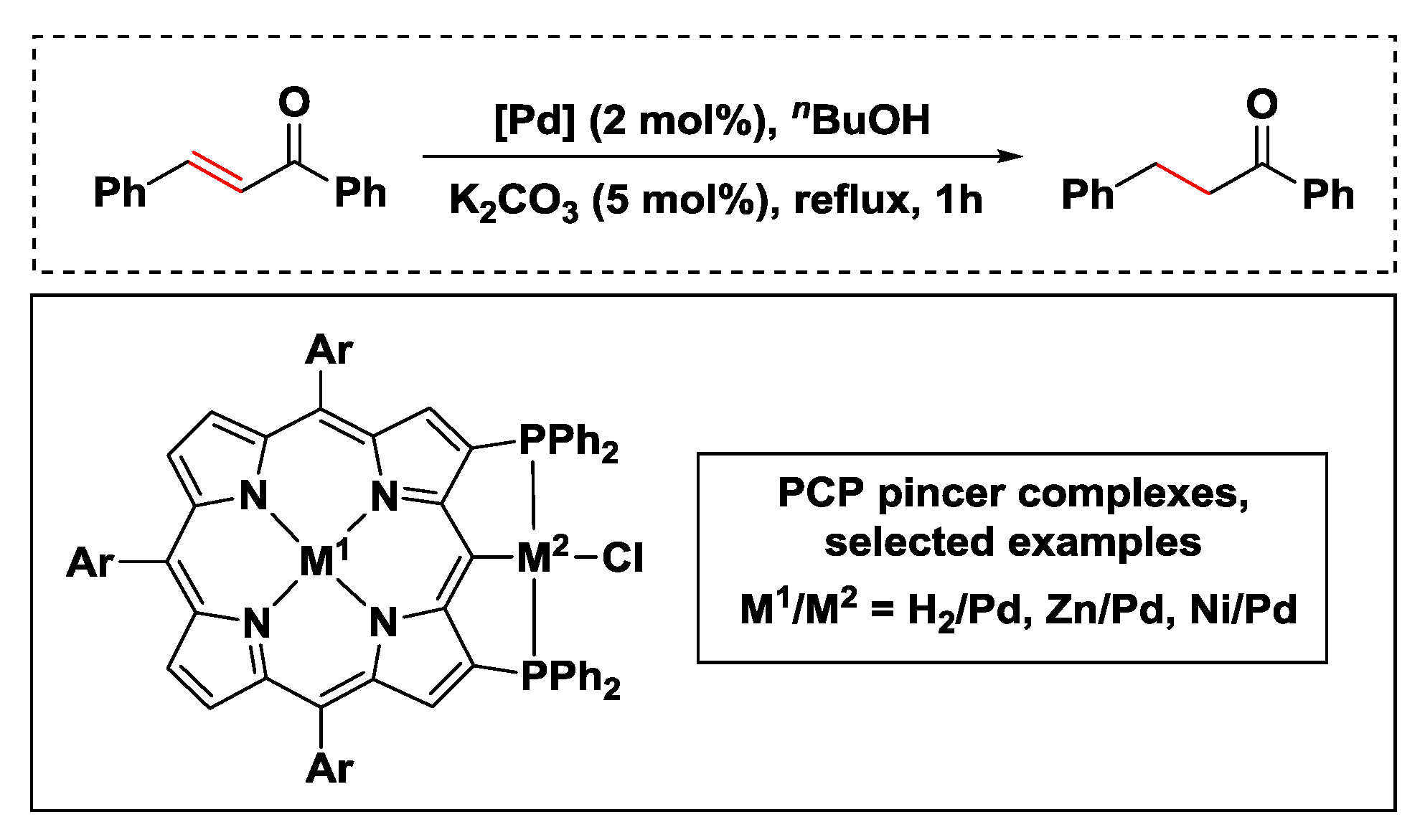
2.2.3. Hydrogen Transfer with Palladium
3. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klomp, D.; Hanefeld, U.; Peters, J.A. Transfer hydrogenation including the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction. In The Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation, 1st ed.; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Chapter 20; pp. 585–630. ISBN 978-3-527-31161-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrogen transfer in organic and organometallic reactions. In Hydrogen-Transfer Reactions, 1st ed.; Hynes, J.T.; Klinman, J.P.; Limbach, H.-H.; Schowen, R.L. (Eds.) WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Part V, Chapter 18–21; pp. 563–634. ISBN 978-3-527-30777-7. [Google Scholar]
- Meerwein, H.; Schmidt, R. Ein neues Verfahren zur Reduktion von Aldehyden und Ketonen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1925, 444, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verley, A. The exchange of functional groups between two molecules. The passage of ketones to alcohols and the reverse. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1925, 37, 871–874. [Google Scholar]
- Ponndorf, W. Der reversible Austausch der Oxydationsstufen zwischen Aldehyden oder Ketonen einerseits und primären oder sekundären Alkoholen anderseits. Angew. Chem. 1926, 29, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H. Aluminium-isopropylat als Reduktionsmittel. Eine allgemeine Methode zur Carbonylreduktion. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1937, 70, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenauer, R.V. Eine Methode der Dehydrierung von Sekundären Alkoholen zu Ketonen. I. Zur Herstellung von Sterinketonen und Sexualhormonen. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1937, 56, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namy, J.L.; Souppe, J.; Collin, J.; Kagan, H.B. New preparations of lanthanide alkoxides and their catalytical activity in Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley-Oppenauer reactions. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, T.; Matsuoka, M.; Konishi, H.; Kiji, J. Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction of ketones and aldehydes catalyzed by lanthanide tri-2-propoxides. Chem. Lett. 1987, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campell, E.J.; Zhou, H.; Nguyen, S.T. Catalytic Meerwein−Pondorf−Verley reduction by simple aluminum complexes. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2391–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, T.; Miura, T.; Itagaki, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Maruoka, K. Catalytic Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley (MPV) and Oppenauer (OPP) reactions: Remarkable acceleration of the hydride transfer by powerful bidentate aluminum alkoxides. Synthesis 2002, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Ko, B.-T.; Huang, B.-H.; Lin, C.-C. Reduction of aldehydes and ketones catalyzed by a novel aluminum alkoxide: Mechanistic studies of Meerwein−Ponndorf−Verley reaction. Organometallics 2002, 21, 2066–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graauw, C.F.; Peters, J.A.; van Bekkum, H.; Huskens, J. Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reductions and Oppenauer oxidations: An integrated approach. Synthesis 1994, 1994, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, K.; Node, M. Recent development of asymmetric syntheses based on the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction. Chirality 2002, 14, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, Y.M.Y.; Henbest, H.B.; Husbands, J.; Mitchell, T.R.B. Reduction of cyclohexanones to axial alcohols via iridium-containing catalysts. Proc. Chem. Soc. 1964, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, J.A.; Jardine, F.H.; Young, J.F.; Wilkinson, G. The preparation and properties of tris(triphenylphosphine)halogenorhodium(I) and some reactions thereof including catalytic homogeneous hydrogenation of olefins and acetylenes and their derivatives. J. Chem. Soc. A 1966, 1711–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiali, S.; Pinna, L.; Delogu, G.; De Martin, S.; Zassinovich, G.; Mestroni, G. Optically active phenanthrolines in asymmetric catalysis. III. Highly efficient enantioselective transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone by chiral rhodium/3-alkyl phenanthroline catalysts. Tetrahedron 1990, 1, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uson, R.; Oro, L.A.; Sariego, R.; Esteruelas, M.A. Catalytic transfer hydrogenation by cationic rhodium(I) complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 1981, 214, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvintovics, P.; James, B.R.; Heil, B. Enantioselective transfer hydrogenation of ketones using a rhodium catalyst containing a methionine sulphoxide ligand. Chem. Commun. 1986, 1810–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, A.; Hashiguchi, S.; Uematsu, N.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones using a formic acid−triethylamine mixture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 2521–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacker, A.J. Enantioselective transfer hydrogenation. In The Handbook of Homogeneous Hydrogenation, 1st ed.; de Vries, J.G., Elsevier, C.J., Eds.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Chapter 35; pp. 1215–1244. ISBN 978-3-527-31161-3. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Ohta, T.; Tsuji, Y. Ruthenium-catalyzed reduction of carbonyl compounds using formic acid. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1982, 55, 2441–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khai, B.; Arcelli, A. Selective reduction of aldehydes by a formic acid- trialkylamine- RuCl2(PPh3)3 system. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 3365–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, H.; Leitner, W. Enantioselective catalytic transfer-hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids with triethylammonium formate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1988, 27, 1180–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Leitner, W. Mechanistic aspects of hydrogen addition during enantioselective rhodium-catalysed reduction of C=C double bonds with formic acid/triethylamine or molecular hydrogen. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2002, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, X.; King, F.; Xiao, J. Insight into and practical application of pH-controlled asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones in water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3407–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, P.M.; Howarth, J.A.; Hudnott, A.R.; Williams, J.M.J.; Harris, W. Catalytic racemisation of alcohols: Applications to enzymatic resolution reactions. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7623–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: Chiral ligands and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. The golden age of transfer hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6621–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Models for biological hydrogen transfer. In Hydrogen-Transfer Reactions, 1st ed.; Hynes, J.T.; Klinman, J.P.; Limbach, H.-H.; Schowen, R.L. (Eds.) WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Parts I–II, Chapter 1–8; pp. 947–1200. ISBN 978-3-527-30777-7. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, M.C.; Nyman, C.J.; Wilkinson, G. The decarbonylation of aldehydes by tris(triphenylphosphine)chlororhodium(I). J. Chem. Soc. A 1968, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Tsuji, J. Organic synthesis by means of noble metal compounds. XXXV. Novel decarbonylation reactions of aldehydes and acyl halides using rhodium complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Nishiguchi, T.; Fukuzumi, K. Transfer hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenolysis. 11. Facile dehydrogenation of aromatic hydrocarbons and the mechanism of the hydrogen transfer from indan, tetralin, and dioxane to aldehydes catalyzed by dihydridotetrakis(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium(II). J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 2688–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiguchi, T.; Fukuzumi, K. Transfer-hydrogenation and transfer-hydrogenolysis. III. Hydrogen transfer from dioxane to olefins catalyzed by chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiguchi, T.; Tachi, K.; Fukuzumi, K. Hydrogen transfer from dioxane to an olefin catalyzed by chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 8916–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Nishiguchi, T.; Fukuzumi, K. Transfer hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenolysis. IX. Hydrogen transfer from organic compounds to aldehydes and ketones catalyzed by dihydridotetrakis(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium(II). J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Nishiguchi, T.; Fukuzumi, K. Transfer hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenolysis. 13. Hydrogen transfer from cyclic amines to aromatic nitro compounds catalyzed by noble metal salts. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Nishiguchi, T.; Tanaka, M.; Fukuzumi, K. Transfer hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenolysis. 14. Cleavage of carbon-halogen bond by the hydrogen transfer from organic compounds catalyzed by noble metal salts. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pàmies, O.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Studies on the mechanism of metal-catalyzed hydrogen transfer from alcohols to ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 5052–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Takehara, J.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones catalyzed by chiral ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7562–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyori, R.; Hashiguchi, S. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation catalyzed by chiral ruthenium complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. New chiral rhodium and iridium complexes with chiral diamine ligands for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 2186–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Crabtree, R.H.; Mata, J.; Peris, E. Chelating bis-carbene rhodium(III) complexes in transfer hydrogenation of ketones and imines. Chem. Commun. 2002, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierz, V.; Urbanaite, A.; Seyboldt, A.; Kunz, D. Rhodium complexes bearing 1,10-phenantroline analouge bis-NHC ligands are active catalysts for transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7532–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluijter, S.N.; Elsevier, C.J. Synthesis and reactivity of heteroditopic dicarbene rhodium(I) and iridium(I) complexes bearing chelating 1,2,3-triazolylidene-imidazolylidene ligands. Organometallics 2014, 33, 6389–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, B.; Gangwar, M.K.; Ghosh, P. Chiral oxazolidine-fused N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of rhodium and iridium and their utility in the asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 3253–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboo, A.A.; Bennett, E.L.; Deeprose, M.; Robertson, C.M.; Iggo, J.A.; Xiao, J. Methanol as hydrogen source: Transfer hydrogenation of aromatic aldehydes with rhodacycle. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11805–11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, K.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Albrecht, M. Synthesis, isomerization, and catalytic transfer hydrogenation activity of rhodium(III) complexes containing both chelating dicarbenes and diphosphine ligands. Organometallics 2015, 34, 5723–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranyos, A.; Csjernyik, G.; Szabó, K.J.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Evidence for a ruthenium dihydride species as the active catalyst in the RuCl2(PPh3)- catalyzed hydrogen transfer reaction in the presence of base. Chem. Commun. 1999, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.L.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Efficient ruthenium-catalysed transfer hydrogenation of ketones by propan-2-ol. Chem. Commun. 1991, 1063–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, K.-J.; Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. The catalyst precursor, catalyst, and intermediate in the RuII-promoted asymmetric hydrogen transfer between alcohols and ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, M.; Ito, H.; Noyori, R. The metal−ligand bifunctional catalysis: A theoretical study on the ruthenium(II)-catalyzed hydrogen transfer between alcohols and carbonyl compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handgraaf, J.-W.; Reek, J.N.H.; Meijer, E.J. Iridium(I) versus ruthenium(II). A computational study of the transition metal-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Organometallics 2003, 22, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.; Clarckson, G.; Wills, M. The importance of 1,2-anti-disubstitution in monotosylated diamine ligands for ruthenium(II)-catalysed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. Tetrahedron 2004, 15, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortais, J.-B.; Ritleng, V.; Voelklin, A.; Holuigue, A.; Smail, H.; Balroy, L.; Sirlin, C.; Verzijl, G.K.M.; Boogers, J.A.F.; de Vries, A.H.M.; et al. Cycloruthenated primary and secondary amines as efficient catalyst precursors for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratta, W.; Da Ros, P.; Del Zotto, A.; Sechi, A.; Zangrando, E.; Rigo, P. Cyclometalated ruthenium(II) complexes as highly active transfer hydrogenation catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3584–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratta, W.; Chelucci, G.; Gladiali, S.; Siega, K.; Toniutti, M.; Zanette, M.; Zangrando, E.; Rigo, P. Ruthenium(II) terdentate CNN complexes: Superlative catalysts for the hydrogen-transfer reduction of ketones by reversible insertion of a carbonyl group into the Ru-H bond. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6214–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishibayashi, Y.; Takei, I.; Uemura, S.; Hidai, M. Extremely high enantioselective redox reaction of ketones and alcohols catalyzed by RuCl2(PPh3)(oxazolinylferrocenylphosphine). Organometallics 1999, 18, 2291–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.; Nordin, S.; Roth, P.; Tarnai, T.; Anderson, P. 2-Azanorbornyl alcohols: Very efficient ligands for ruthenium-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 3116–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, S.; Roth, P.; Tarnai, T.; Alonso, D.; Brandt, P.; Anderson, P. Remote dipole effects as a means to accelerate [Ru(amino alcohol)]-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.A.; Brandt, P.; Nordin, S.J.M.; Andersson, P.G. Ru(arene)(amino alcohol)-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of ketones: Mechanism and origin of enantioselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9580–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, Y.; Ueoka, M.; Matoba, K.; Nishibashi, Y.; Hidai, M.; Uemura, S. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones using chiral oxazolinylferrocenylphosphines and one of their Ru(II) complex. J. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 572, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Transferhydrogenations. In Transition Metals for Organic Synthesis—Building Blocks and Fine Chemicals, 2nd ed.; Beller, M., Bolm, C., Eds.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; Chapter 1.3; pp. 145–162. ISBN 3-527-30613-7. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, K.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of α,β-acetylenic ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 8738–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.J.; Wills, M. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of C=O and C=N bonds. Tetrahedron 1999, 10, 2045–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvo, Y.; Czarkie, D.; Rahamim, Y.; Chodosh, D.F. A new group of ruthenium complexes: Structure and catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 7400–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samec, J.S.M.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Ruthenium-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of imines by propan-2-ol in benzene. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas-Vives, A.; Ujaque, G.; Lledós, A. Hydrogen transfer to ketones catalyzed by Shvo’s ruthenium hydride complex: A mechanistic insight. Organometallics 2007, 26, 4135–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvembu, R.; Prabhakaran, R.; Natarajan, K. Shvo’s diruthenium complex: A robust catalyst. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.M.; Shin, S.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, J. X-ray structure and reactivity of (η4-tetraphenylcyclopentadienone)(CO)2Ru(HOCHMe2): Unexpected stability of the neutral 2-propanol−ruthenium(0) complex with respect to β-hydride elimination. Organometallics 2001, 20, 3370–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, C.P.; Singer, S.W.; Powell, D.R.; Hayashi, R.K.; Kavana, M. Hydrogen transfer to carbonyls and imines from a hydroxycyclopentadienyl ruthenium hydride: Evidence for concerted hydride and proton transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.B.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Mechanism of ruthenium-catalyzed hydrogen transfer reactions. Concerted transfer of OH and CH hydrogens from an alcohol to a (cyclopentadienone)ruthenium complex. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 7681–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, H.; Adolfsson, H. Ruthenium-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones in ethanol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 2754–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giboulot, S.; Baldino, S.; Ballico, M.; Nedden, H.G.; Zuccaccia, D.; Baratta, W. Cyclometalated dicarbonyl ruthenium catalysts for transfer hydrogenation and hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds. Organometallics 2018, 37, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelucci, G.; Baldino, S.; Baratta, W. Ruthenium and osmium complexes containing 2-(aminomethyl)pyridine (ampy)-based ligands in catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 300, 29–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Arai, N.; Hori, K.; Saito, T.; Sayo, N.; Ohkuma, T. Chiral ruthenabicyclic complexes: Precatalysts for rapid, enantioselective, and wide-Scope hydrogenation of ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10696–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dub, P.A.; Gordon, J.C. The mechanism of enantioselective ketone reduction with Noyori and Noyori–Ikariya bifunctional catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 6756–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dub, P.A.; Henson, N.J.; Martin, R.L.; Gordon, J.C. Unraveling the mechanism of the asymmetric hydrogenation of acetophenone by [RuX2(diphosphine)(1,2-diamine)] catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3505–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, A.; Sil, A.; Patra, S.K. Ruthenium(II) complexes of 4’-(aryl)-2,2’:6’,2”-terpyridyl ligands as simple catalysts for the transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4063–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wu, P.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Z. Ruthenium(II) complex catalysts bearing a pyridyl-based benzimidazolyl–benzotriazolyl ligand for transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Organometallics 2013, 32, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z. Ruthenium complex catalysts cupported by a bis(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolyl–pyridyl-based NNN ligand for transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Organometallics 2014, 33, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yu, Z.; Yan, S.; Li, Y. Room-temperature Ru(II)-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of ketones and aldehydes in air. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4624–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H.; Yuan, M.; Zheng, X.; Chen, H.; Li, R. Construction of pincer-type symmetrical ruthenium(II) complexes bearing pyridyl-2,6-pyrazolyl arms: Catalytic behavior in transfer hydrogenation of ketones. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52734–52739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Niu, J.-L.; Yang, M.-Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.-Y.; Hao, X.-Q.; Song, M.-P. New type of 2,6-bis(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-2-yl)pyridine-based ruthenium complexes: Active catalysts for transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Organometallics 2015, 34, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Pedregal, E.; Vaquero, M.; Lastra, E.; Gamasa, P.; Pizzano, A. Highly enantioselective hydrogenation of N-aryl imines derived from acetophenones by using Ru–pybox complexes under hydrogenation or transfer hydrogenation conditions in isopropanol. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Szymczak, N.K. 6,6′-Dihydroxy terpyridine: A proton-responsive bifunctional ligand and its application in catalytic transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.; Chakrabarti, K.; Kundu, S. Optimum bifunctionality in a 2-(2-pyridyl-2-ol)-1,10-phenanthroline based ruthenium complex for transfer hydrogenation of ketones and nitriles: Impact of the number of 2-hydroxypyridine fragments. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11162–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melle, P.; Manoharan, Y.; Albrecht, M. Modular pincer-type pyridylidene amide ruthenium(II) complexes for efficient transfer hydrogenation catalysis. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 11761–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar-Tobar, R.A.; Tin, S.; de Vries, J.G. Selective transfer hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshakova, I.D.; Gabidullin, B.; Nikonov, G.I. Ru-Catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of nitriles, aromatics, olefins, alkynes and esters. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 4860–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sugiya, M.; Imamoto, T.; Zhang, W. Chemoselective transfer hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated ketones catalyzed by pincer-Pd complexes using alcohol as a hydrogen source. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3690–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Hamashima, Y.; Sodeoka, M. A new entry to Pd-H chemistry: Catalytic asymmetric conjugate reduction of enones with EtOH and a highly ennatioselective synthesis of warfarin. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4851–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Yoneda, T.; Yorimitsu, H.; Osuka, A. Synthesis and catalytic activities of porphyrin-based PCP pincer complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzart, J. Pd-Catalyzed hydrogen-transfer reactions from alcohols to C=C, C=O, and C=N bonds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 5693–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.; Dlugy, C.; Shotland, Y.; Tavor, D. Glycerol as solvent and hydrogen donor in transfer hydrogenation–dehydrogenation reactions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5951–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquerel, Y.; Rodriguez, J. Catalytic properties of the Pd/C—Trimethylamine system. Arkivoc 2008, 11, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Coquerel, Y.; Brémond, P.; Rodriguez, J. Pd–H From Pd/C and triethylamine: Implications in palladium catalyzed reactions involving amines. J. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 692, 4805–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Bauer, T.J.; Haller, G.L.; Baráth, E. H-Transfer reactions of internal alkenes with tertiary amines as H-donors on carbon supported noble metals. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





















© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baráth, E. Hydrogen Transfer Reactions of Carbonyls, Alkynes, and Alkenes with Noble Metals in the Presence of Alcohols/Ethers and Amines as Hydrogen Donors. Catalysts 2018, 8, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120671
Baráth E. Hydrogen Transfer Reactions of Carbonyls, Alkynes, and Alkenes with Noble Metals in the Presence of Alcohols/Ethers and Amines as Hydrogen Donors. Catalysts. 2018; 8(12):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120671
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaráth, Eszter. 2018. "Hydrogen Transfer Reactions of Carbonyls, Alkynes, and Alkenes with Noble Metals in the Presence of Alcohols/Ethers and Amines as Hydrogen Donors" Catalysts 8, no. 12: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120671
APA StyleBaráth, E. (2018). Hydrogen Transfer Reactions of Carbonyls, Alkynes, and Alkenes with Noble Metals in the Presence of Alcohols/Ethers and Amines as Hydrogen Donors. Catalysts, 8(12), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120671