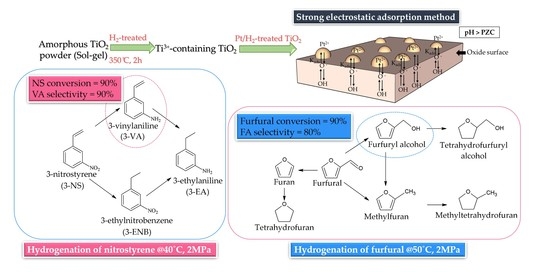
The H2-Treated TiO2 Supported Pt Catalysts Prepared by Strong Electrostatic Adsorption for Liquid-Phase Selective Hydrogenation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of the Pt/TiO2 Catalysts
2.2. Reaction Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of TiO2 by Sol–Gel Method
3.2. Preparation of Pt/TiO2 by SEA and Impregnation Methods
3.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.4. Selective Hydrogenation Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pisduangdaw, S.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Yoshida, H.; Fujita, S.-I.; Arai, M.; Panpranot, J. Flame-made Pt/TiO2 catalysts for the liquid-phase selective hydrogenation of 3-nitrostyrene. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 490, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, M.J.; Andanson, J.-M.; Baiker, A. Tuning the chemoselective hydrogenation of nitrostyrenes catalyzed by ionic liquid-supported platinum nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisduangdaw, S.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Fujita, S.-I.; Arai, M.; Yoshida, H.; Panpranot, J. One step synthesis of Pt–Co/TiO2 catalysts by flame spray pyrolysis for the hydrogenation of 3-nitrostyrene. Catal. Commun. 2015, 61, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarulin, A.; Berguerand, C.; Alonso, A.O.; Yuranov, I.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Increasing Pt selectivity to vinylaniline by alloying with Zn via reactive metal–support interaction. Catal. Today 2015, 256, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.-I.; Yoshida, H.; Asai, K.; Meng, X.; Arai, M. Selective hydrogenation of nitrostyrene to aminostyrene over Pt/TiO2 catalysts: Effects of pressurized carbon dioxide and catalyst preparation conditions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 60, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Serna, P.; Concepcion, P.; Calvino, J.J. Transforming nonselective into chemoselective metal catalysts for the hydrogenation of substituted nitroaromatics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8748–8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makosch, M.; Lin, W.-I.; Bumbálek, V.; Sá, J.; Medlin, J.W.; Hungerbühler, K.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Organic thiol modified Pt/TiO2 catalysts to control chemoselective hydrogenation of substituted nitroarenes. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 2079–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajitvichyanukul, P.; Ananpattarachai, J.; Pongpom, S. Sol–gel preparation and properties study of TiO2 thin film for photocatalytic reduction of chromium(VI) in photocatalysis process. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-C.; Ying, J.Y. Sol−gel synthesis and hydrothermal processing of anatase and rutile Titania nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3113–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-S.; Moon, B.K.; Park, J.-H.; Tae Chung, S.; Son, S.-M. Synthesis of nanocrystalline TiO2 in toluene by a solvothermal route. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 254, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyapan, S.; Boonyongmaneerat, Y.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Yoshida, H.; Fujita, S.-I.; Arai, M.; Panpranot, J. Improved catalytic performance of Pd/TiO2 in the selective hydrogenation of acetylene by using H2-treated sol–gel TiO2. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 383–384, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyapan, S.; Boonyongmaneerat, Y.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Praserthdam, P.; Panpranot, J. Effect of surface Ti3+ on the sol–gel derived TiO2 in the selective acetylene hydrogenation on Pd/TiO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 2015, 245, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Barnes, S.; Regalbuto, J.R. A fundamental study of Pt impregnation of carbon: Adsorption equilibrium and particle synthesis. J. Catal. 2011, 279, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Job, N.; Dsouza, L.; Pereira, M.; Pirard, R.; Heinrichs, B.; Figueiredo, J.; Pirard, J.; Regalbuto, J. Synthesis of very highly dispersed platinum catalysts supported on carbon xerogels by the strong electrostatic adsorption method. J. Catal. 2009, 261, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Regalbuto, J.R. The synthesis of highly dispersed noble and base metals on silica via strong electrostatic adsorption: II. Mesoporous silica SBA-15. J. Catal. 2008, 260, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriye, K.; Praserthdam, P.; Jongsomjit, B. Control of Ti3+ surface defect on TiO2 nanocrystal using various calcination atmospheres as the first step for surface defect creation and its application in photocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 3849–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.-L.; Lee, M.-S.; Pon, Z.-J.; Hsu, J.-Z. Effect of calcination atmosphere on TiO2 photocatalysis in hydrogen production from methanol/water solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2004, 163, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriye, K.; Praserthdam, P.; Jongsomjit, B. Impact of Ti3+ present in Titania on characteristics and catalytic properties of the Co/TiO2 catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 6599–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, H.; Tanaka, K.-I. Catalytic performance and mechanism of a Pt/TiO2 catalyst for the oxidation of formaldehyde at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B 2006, 65, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekou, T.; Ekou, L.; Vicente, A.; Lafaye, G.; Pronier, S.; Especel, C.; Marécot, P. Citral hydrogenation over Rh and Pt catalysts supported on TiO2: Influence of the preparation and activation protocols of the catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 337, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Igarashi, N.; Fujita, S.-I.; Panpranot, J.; Arai, M. Influence of crystallite size of TiO2 supports on the activity of dispersed Pt catalysts in liquid-phase selective hydrogenation of 3-nitrostyrene, nitrobenzene, and styrene. Catal. Lett. 2014, 145, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarulin, A.; Berguerand, C.; Yuranov, I.; Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Prokopyeva, I.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Pt–Zn nanoparticles supported on porous polymeric matrix for selective 3-nitrostyrene hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2015, 321, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotbagi, T.V.; Gurav, H.R.; Nagpure, A.S.; Chilukuri, S.V.; Bakker, M.G. Highly efficient nitrogen-doped hierarchically porous carbon supported Ni nanoparticles for the selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67662–67668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, Á.; Leahy, J.J.; Curtin, T. The influence of metal selection on catalyst activity for the liquid phase hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Catal. Today 2017, 279, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Venugopal, A.K.; Nagpure, A.S.; Chilukuri, S.; Raja, T. Promotional effect of fe on the performance of supported cu catalyst for ambient pressure hydrogenation of furfural. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3888–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Gómez, C.P.; Cecilia, J.A.; Moreno-Tost, R.; Maireles-Torres, P. Selective furfural hydrogenation to furfuryl alcohol using Cu-based catalysts supported on clay minerals. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-P.; Chen, Y.-W. Selective hydrogenation of furfural on Ni–P, Ni–B, and Ni–P–B ultrafine materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.M.; Kubler, D.G.; Sartwell, P.; Zepp, R.G. Acetal formation for ketones and aromatic aldehydes with methanol1. J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30, 4284–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Durndell, L.J.; Isaacs, M.A.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F.; Kyriakou, G. Highly selective hydrogenation of furfural over supported Pt nanoparticles under mild conditions. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 180, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, P.; Salinas, D.; Campos, C.; Oportus, M.; Murcia, J.; Rojas, H.; Borda, G.; Fierro, J.L.G. Selective hydrogenation of furfural on Ir/TiO2 catalysts. Química Nova 2010, 33, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lai, Q.; Holles, J.H. Bimetallic overlayer catalysts with high selectivity and reactivity for furfural hydrogenation. Catal. Commun. 2017, 89, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogeswararao, S.; Srinivas, D. Catalytic conversion of furfural to industrial chemicals over supported Pt and Pd catalysts. J. Catal. 2015, 327, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Catalyst | Pt/TiO2-H2 | Pt/TiO2-Air | Pt/TiO2-H2 | Pt/TiO2-Air |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Impregnation | Impregnation | SEA | SEA |
| CO chemisorption (molecule CO × 1018/g Cat.) | 8.8 | 4.5 | 8.4 | 7.7 |
| Pt dispersion (%) | 57 | 29 | 54 | 50 |
| Catalyst | Pt/TiO2-H2 | Pt/TiO2-Air | Pt/TiO2-H2 | Pt/TiO2-Air | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Impregnation | Impregnation | SEA | SEA | ||||
| Time (min) | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 |
| NS conversion (%) | 76 | 89 | 29 | 31 | 69 | 90 | 64 | 80 |
| VA selectivity (%) | 92.1 | 91.9 | 77.9 | 77.4 | 87.9 | 88.6 | 88.2 | 85.6 |
| EA selectivity (%) | 4.9 | 5.9 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 8.5 | 5.7 | 8.4 |
| ENB selectivity (%) | 3.0 | 2.2 | 17.1 | 17.6 | 7.0 | 2.9 | 6.1 | 6.0 |
| FFR conversion (%) a | 89 | 86 | 89 | 90 | ||||
| FA selectivity (%) a | 17.7 | 14.1 | 79.8 | 84.9 | ||||
| Others a,b | 82.3 | 85.9 | 20.2 | 15.1 | ||||
| Metal Loading (wt %) | Supports | Preparation Method | Reduction Temperature (°C) | Reaction Conditions (Temp., PH2) | Solvent | Reaction Time (min) | Reaction Results | Reference No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-NS Conversion (%) | VA Selectivity (%) | ||||||||
| 0.5 | TiO2 | Impregnation | 200 | 40 °C, 2 MPa | Ethanol | 40 | 89 | 91.9 | This work |
| SEA | 90 | 88.6 | |||||||
| 0.5 | TiO2 | Impregnation | 200 | 50 °C, 4 MPa | Supercritical CO2 10 MPa | 60 | 64 | 75 | [5] |
| 0.5 | TiO2 | Impregnation | 200 | 50 °C, 4 MPa | Ethanol | n/a | 26 | 73 | [22] |
| 0.5 | TiO2 | Flame spray pyrolysis | 600 | 50 °C, 4 MPa | Ethanol | 25 | 95.8 | 67.1 | [1] |
| 0.2 | TiO2 | Impregnation | 500 | 40 °C, 0.3 MPa | Toluene | 390 | 95.1 | 93.1 | [6] |
| 0.4 | Carbon nanotubes | Reduction of H2Pt(OH)6 in formic acid with ionic liquid and co-stabilizer 2,2′-bipyridine | n/a | 25 °C, 0.1 MPa | n/a | 180 | 100 | 86 | [2] |
| 1 | TiO2 | Impregnation and surface modification using α-lipoic acid | 250 | 80 °C, 1 MPa | Toluene | 68 | 100 a | 100 | [7] |
| 2 | ZnO | Ion-exchange | 300 | 75 °C, 1 MPa | Ethanol | n/a | 100 | 97 | [4] |
| Metal Loading (wt %) | Supports | Preparation Method | Reduction Temperature (°C) | Reaction Conditions (Temp., PH2) | Solvent | Reaction Time (h) | Reaction Results | Reference No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furfural Conversion (%) | FA Selectivity (%) | ||||||||
| 0.5 | TiO2 | SEA | 200 | 50 °C, 2 MPa | Methanol | 2 | 89 | 79.8 | This work |
| 0.5 | SiO2 | Impregnation | 400 | 250 °C, 0.69 MPa | 2-propanol | 1.5 | 12.5 | 55.8 | [32] |
| 2.0 | γ-Al2O3 | - | 200 | 50 °C, Ambient | Methanol | 7 | 80 | 99 | [30] |
| 1.9 | MgO | - | 200 | 50 °C, Ambient | Methanol | 7 | 79 | 97 | [30] |
| 2.3 | CeO2 | - | 200 | 50 °C, Ambient | Methanol | 7 | 77 | 98 | [30] |
| 1.9 | SiO2 | - | 200 | 50 °C, Ambient | Methanol | 7 | 35 | 90 | [30] |
| 1.4 | ZnO | - | 200 | 50 °C, Ambient | Methanol | 7 | 7 | 60 | [30] |
| 5.0 | Al2O3 | Wet impregnation | 350 | 25 °C, 2 MPa | Iso-propanol | 8 | 30 | 99.1 | [33] |
| 5.0 | Al2O3 | Wet impregnation | 350 | 240 °C, 2 MPa | Iso-propanol | 5 | 100 | 30.7 | [33] |
| 5.0 | SiO2 | Wet impregnation | 350 | 25 °C, 2 MPa | Iso-propanol | 8 | 6 | 100 | [33] |
| 5.0 | SiO2 | Wet impregnation | 350 | 240 °C, 2 MPa | Iso-propanol | 5 | 100 | 51.9 | [33] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuhaudomlap, S.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Praserthdam, P.; Fujita, S.-I.; Arai, M.; Panpranot, J. The H2-Treated TiO2 Supported Pt Catalysts Prepared by Strong Electrostatic Adsorption for Liquid-Phase Selective Hydrogenation. Catalysts 2018, 8, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020087
Kuhaudomlap S, Mekasuwandumrong O, Praserthdam P, Fujita S-I, Arai M, Panpranot J. The H2-Treated TiO2 Supported Pt Catalysts Prepared by Strong Electrostatic Adsorption for Liquid-Phase Selective Hydrogenation. Catalysts. 2018; 8(2):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020087
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuhaudomlap, Sasithorn, Okorn Mekasuwandumrong, Piyasan Praserthdam, Shin-Ichiro Fujita, Masahiko Arai, and Joongjai Panpranot. 2018. "The H2-Treated TiO2 Supported Pt Catalysts Prepared by Strong Electrostatic Adsorption for Liquid-Phase Selective Hydrogenation" Catalysts 8, no. 2: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020087
APA StyleKuhaudomlap, S., Mekasuwandumrong, O., Praserthdam, P., Fujita, S.-I., Arai, M., & Panpranot, J. (2018). The H2-Treated TiO2 Supported Pt Catalysts Prepared by Strong Electrostatic Adsorption for Liquid-Phase Selective Hydrogenation. Catalysts, 8(2), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8020087