Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene Using Chilean Natural Zeolite: The Key Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physical-Chemical Characteristics of Natural and Modified Zeolites
- Amount of Brønsted acid sites in zeolite samples out-gassed at 623 K:
- Amount of Lewis acid sites in zeolite samples out-gassed at 773 K:
2.2. Catalytic Ozonation Using Natural and Modified Zeolites at 293 K
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy Characterisation of Zeolite Acidic Sites by Pyridine Adsorption-Desorption
- qs-Py: surface concentration of acid sites (Brønsted or Lewis) (μmol·g−1),
- IA(B,L): integrated absorbance of B or L band (cm−1),
- rd: wafer radius (cm),
- ξm: pyridine molar extinction coefficient (cm·μmol−1),
- ms: wafer mass (mg).
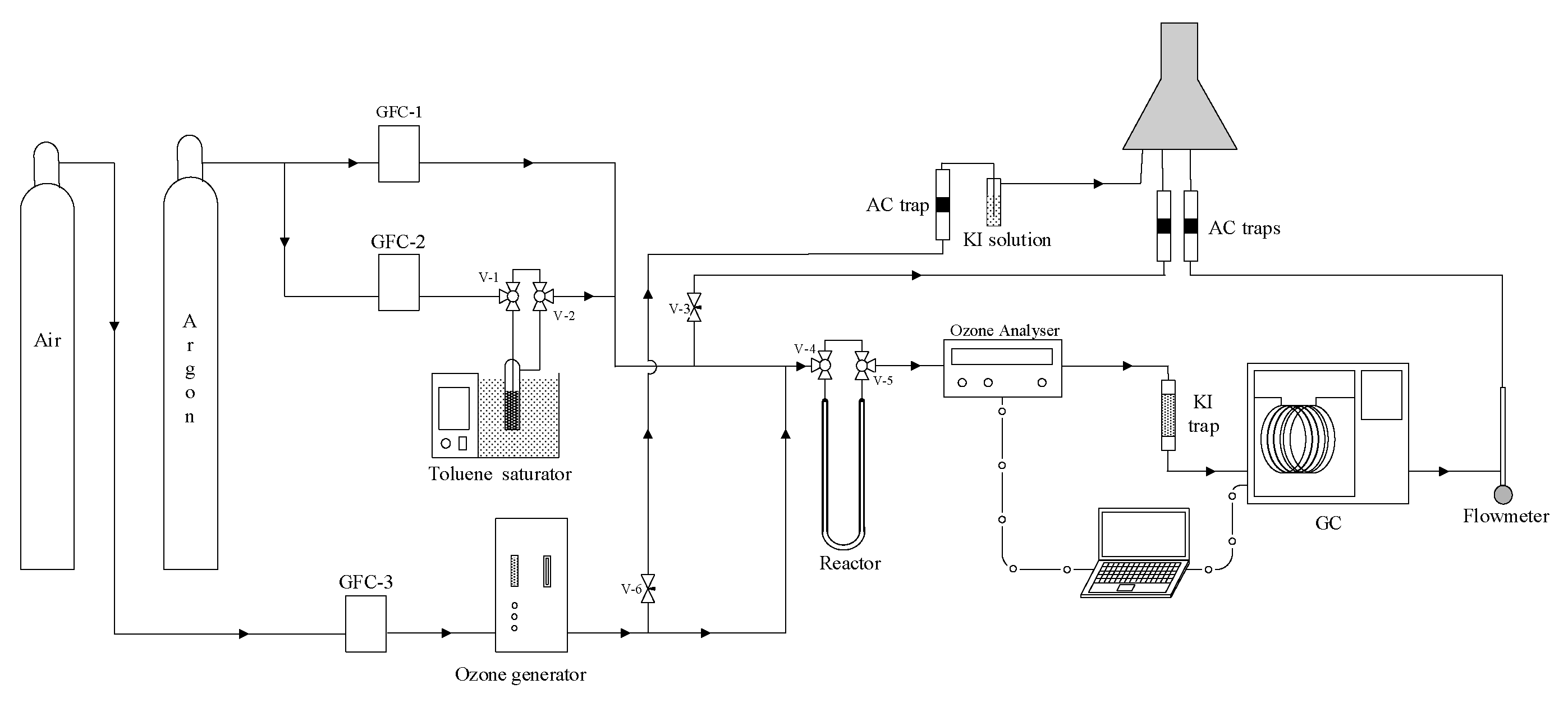
3.3. Catalytic Ozonation Procedure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gironi, F.; Piemonte, V. VOCs removal from dilute vapour streams by adsorption onto activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, E.; Roca, F.J.; Perales, J.F.; Guardino, X. Experimental evaluation of VOC removal efficiency of a coconut shell activated carbon filter for indoor air quality enhancement. Build. Environ. 2013, 67, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, X.; Creamer, A.E.; Annable, M.D.; Li, Y. Biochar for volatile organic compound (VOC) removal: Sorption performance and governing mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, S.-H.; Jeon, M.-J.; Jeon, Y.-W. Study of sulfuric acid treatment of activated carbon used to enhance mixed VOC removal. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradat. 2016, 113, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Zaror, C.A. Effect of ozone treatment on surface properties of activated carbon. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhu, L.Z.; Yang, K. Adsorption behaviors of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on porous clay heterostructures (PCH). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monneyron, P.; Manero, M.H.; Mathé, S. A combined selective adsorption and ozonation process for VOCs removal from air. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 85, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodu, N.; Zaitan, H.; Manero, M.-H.; Pic, J.-S. Removal of volatile organic compounds by heterogeneous ozonation on microporous synthetic alumina silicate. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2020–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Einaga, H.; Futamura, S. Catalytic oxidation of benzene with ozone over Mn ion-exchanged zeolites. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, C.W.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Hui, K.S.; Wan, M.P. Catalytic ozonation of toluene using zeolite and MCM-41 materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8504–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.Y.H.; Kwong, C.W.; Hui, K.S. Potential use of a combined ozone and zeolite system for gaseous toluene elimination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, C.W.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Hui, K.S.; Wan, M.P. Removal of VOCs from indoor environment by ozonation over different porous materials. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2300–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosefi, L.; Haghighi, M.; Allahyari, S.; Shokrani, R.; Ashkriz, S. Abatement of toluene from polluted air over Mn/Clinoptilolite–CeO2 nanopowder: Impregnation vs. Ultrasound assisted synthesis with various Mn-loading. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Haghighi, M.; Kahforoushan, D. Influence of active phase composition (Mn, Ni, MnxNi10−x) on catalytic properties and performance of clinoptilolite supported nanocatalysts synthesized using ultrasound energy toward abatement of toluene from polluted air. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2017, 106, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.J.; Ivanova, E.; Koumanova, B. Adsorption of sulfur dioxide on chemically modified natural clinoptilolite. Acid modification. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Solar, V.A.; Cabrera, E.H.; Veloso, A.F.; Zaror, C.A. Control of released volatile organic compounds from industrial facilities using natural and acid-treated mordenites: The role of acidic surface sites on the adsorption mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleyin, A. Removal of phenol and 4-chlorophenol by surfactant-modified natural zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandro, S.; Valdés, H.; Manéro, M.-H.; Zaror, C.A. Oxidative regeneration of toluene-saturated natural zeolite by gaseous ozone: The influence of zeolite chemical surface characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soylu, G.S.P.; Özçelik, Z.; Boz, I. Total oxidation of toluene over metal oxides supported on a natural clinoptilolite-type zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amereh, M.; Haghighi, M.; Estifaee, P. The potential use of HNO3-treated clinoptilolite in the preparation of Pt/CeO2-clinoptilolite nanostructured catalyst used in toluene abatement from waste gas stream at low temperature. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S.W. Adsortion, Surface Area and Porosity; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982; p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Englert, A.H.; Rubio, J. Characterization and environmental application of a chilean natural zeolite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 75, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.E.; Moraetis, D.; Keheyan, E.; Akhalbedashvili, L.; Kekelidze, N.; Gevorkyan, R.; Yeritsyan, H.; Sargsyan, H. Chemical and thermal modification of natural HEU-type zeolitic materials from armenia, georgia and greece. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 24, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, S.; Valdés, H.; Manero, M.H.; Zaror, C.A. BTX abatement using chilean natural zeolite: The role of bronsted acid sites. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdés, H.; Alejandro, S.; Zaror, C.A. Natural zeolite reactivity towards ozone: The role of compensating cations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227–228, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrer, R.M. Molecular sieve sorbents from clinoptilolite. Can. J. Chem. 1964, 42, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; Farfán, V.J.; Manoli, J.A.; Zaror, C.A. Catalytic ozone aqueous decomposition promoted by natural zeolite and volcanic sand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandro, S.; Valdés, H.; Zaror, C.A. Natural zeolite reactivity towards ozone: The role of acid surface sites. J. Adv. Oxidat. Technol. 2011, 14, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöcker, M. Gas phase catalysis by zeolites. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 82, 257–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, M.; Mijoin, J.; Mignard, S.; Magnoux, P. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) removal over dual functional adsorbent/catalyst system. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 75, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannice, M.A. Kinetics of Catalytic Reactions; Springer Science & Business Media, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 77–78, 170–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziólek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanin, K.M.; Lavalley, J.C.; Tsyganenko, A.A. IR spectra of adsorbed ozone. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 1995, 101, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Oyama, S.T. Mechanism of ozone decomposition on a manganese oxide catalyst. 2. Steady-state and transient kinetic studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9047–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J. Low temperature oxidation of toluene by ozone over MnOx/alumina and MnOx/MCM-41 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulanin, K.M.; Lavalley, J.C.; Tsyganenko, A.A. Infrared study of ozone adsorption on CaO. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2917–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque-Malherbe, R. Complementary approach to the volume filling theory of adsorption in zeolites. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2000, 41, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque-Malherbe, R.; Ivanov, V. Codiffusion and counterdiffusion of para-xylene and ortho-xylene in a zeolite with 10 MR/12 MR interconnected channels. An example of molecular traffic control. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 313, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Futamura, S. Catalytic oxidation of benzene with ozone over alumina-supported manganese oxides. J. Catal. 2004, 227, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, H.; Ogata, A. Benzene oxidation with ozone over supported manganese oxide catalysts: Effect of catalyst support and reaction conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, H.; Tardón, R.F.; Zaror, C.A. Role of surface hydroxyl groups of acid-treated natural zeolite on the heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of methylene blue contaminated waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisnet, M.; Ayrault, P.; Coutanceau, C.; Fernanda Alvarez, M.; Datka, J. Acid properties of dealuminated beta zeolites studied by IR spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Masseron, A.; Marques, J.P.; Lopes, J.M.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Gener, I.; Guisnet, M. Influence of the Si/Al ratio and crystal size on the acidity and activity of HBEA zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 316, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.; Bhat, Y.S.; Nagendrappa, G.; Jai Prakash, B.S. Brønsted and Lewis acidity of modified montmorillonite clay catalysts determined by FT-IR spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2009, 141, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Li, Y. A FTIR and TPD examination of the distributive properties of acid sites on ZSM-5 zeolite with pyridine as a probe molecule. Catal. Today 2009, 145, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Shimizu, K.-I.; Satsuma, A. Comprehensive IR study on acid/base properties of metal oxides. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 433–434, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzetti, T.; Selli, E.; Moscotti, D.; Forni, L. Pyridine and ammonia as probes for FTIR analysis of solid acid catalysts. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, C.A. Determination of integrated molar extinction coefficients for infrared absorption bands of pyridine adsorbed on solid acid catalysts. J. Catal. 1993, 141, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, F.; Poncelet, G. Comparative vapor phase synthesis of ETBE from ethanol and isobutene over different acid zeolites. J. Catal. 2001, 202, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, K.L.; Peyratout, C.; Smith, A.; Bonnet, J.P.; Magnoux, P.; Ayrault, P. Surface modifications of illite in concentrated lime solutions investigated by pyridine adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 382, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



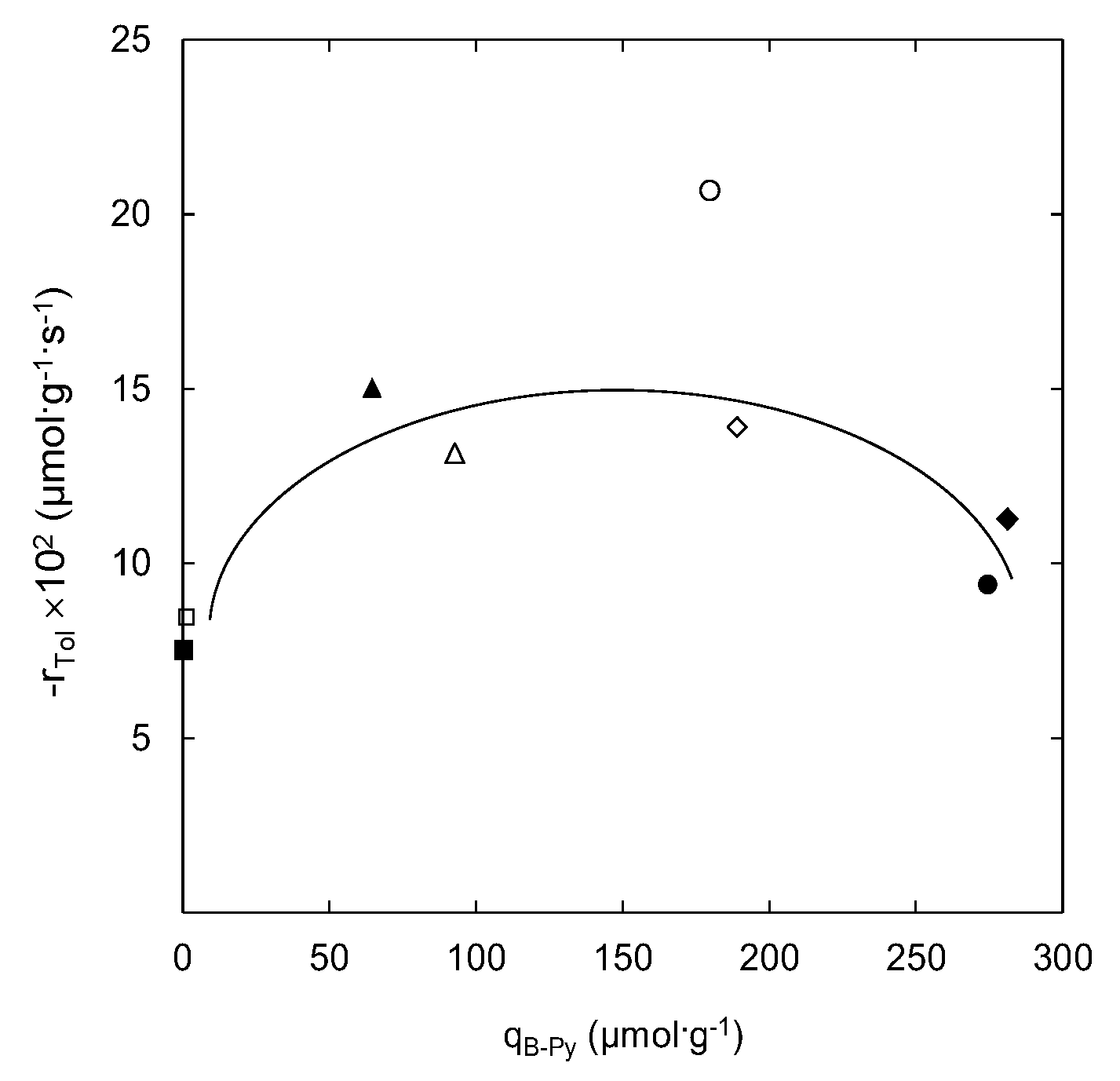
| Samples | S623(m2·g−1) | Na2O (%) a | CaO (%) a | K2O (%) a | MgO (%) a | Si/Al Ratio | Acid Sites Concentration (μmol·g−1) b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 623 K | 773 K | |||||||||
| Brønsted | Lewis | Brønsted | Lewis | |||||||
| NZ | 205 | 1.89 | 4.57 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 5.34 | 0.4 | 31.1 | 1.4 | 42.8 |
| ZH2.4 | 434 | 0.43 | 1.48 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 7.1 | 64.6 | 72.0 | 92.9 | 70.3 |
| NH4Z1 | 181 | 0.68 | 2.36 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 5.32 | 281.2 | 60.5 | 189.0 | 165.0 |
| 2NH4Z1 | 171 | 0.26 | 1.82 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 5.34 | 274.5 | 201.9 | 179.8 | 282.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alejandro-Martín, S.; Valdés, H.; Manero, M.-H.; Zaror, C.A. Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene Using Chilean Natural Zeolite: The Key Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts 2018, 8, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050211
Alejandro-Martín S, Valdés H, Manero M-H, Zaror CA. Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene Using Chilean Natural Zeolite: The Key Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts. 2018; 8(5):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050211
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlejandro-Martín, Serguei, Héctor Valdés, Marie-Hélène Manero, and Claudio A. Zaror. 2018. "Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene Using Chilean Natural Zeolite: The Key Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites" Catalysts 8, no. 5: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050211
APA StyleAlejandro-Martín, S., Valdés, H., Manero, M.-H., & Zaror, C. A. (2018). Catalytic Ozonation of Toluene Using Chilean Natural Zeolite: The Key Role of Brønsted and Lewis Acid Sites. Catalysts, 8(5), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8050211







