Abstract
The demand for synthetic flavor ester is high, especially in the food, beverage, and cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. It is derived from the reaction between a short-chain fatty acid and alcohol. Lipases from Antarctic bacteria have gained huge interest in the industry due to its ability react at low temperatures. The use of immobilization enzymes is one of the methods that can improve the stability of the enzyme. The current work encompasses the low temperature enzymatic synthesis of ethyl hexanoate by direct esterification of ethanol with hexanoic acid in a toluene and solvent-free system. The effects of various reaction parameters such as the organic solvent, temperature, time, substrate, substrate ratio and concentration, enzyme concentration on ethyl hexanoate synthesis were tested. Several matrices were used for immobilization and comparisons of the efficiency of immobilized enzyme with free enzyme in the synthesis of flavor ester were conducted. Ester production was optimally synthesized at 20 °C in both systems— immobilized and free enzyme. A 69% ester conversion rate was achieved after a two-hour incubation in toluene, compared to 47% in a solvent-free system for free enzyme. Immobilized AMS8 lipase showed a higher conversion of ester in toluene with respect to free-solvents, from 80% to 59%, respectively. Immobilized enzymes showed enhancement to the stability of the enzyme in the presence of the organic solvent. The development of AMS8 lipase as an immobilized biocatalyst demonstrates great potential as a cost-effective enzyme for biocatalysis and biotransformation in the food industry.
1. Introduction
Flavor esters are short chain esters that are widely distributed in nature. These compounds are also known as carboxylic acid esters, which are largely used in the food, beverage, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Flavor esters are fine organic compounds that form a part of the natural aromas in fruits and flowers [1]. In addition, low molecular weight flavor esters are the most important and versatile components of flavors and fragrances [2]. Currently, there is an increasing commercial demand for natural flavors. These compounds are typically isolated from natural sources such as plants, fruits, and flowers or are produced by chemical synthesis. However, the commercial use of natural extracts is hindered by limited supply and high production costs [3]. In addition, flavors produced by chemical synthesis cause negative side effects due to the use of dangerous chemicals instead of flammable and highly toxic hazardous chemicals [4]. Recently, the enzymatic production of flavor esters has received increasing attention because of the inherent catalytic selectivity of enzymes, enhanced product purity and mild reaction conditions [5].
Lipases catalyze the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol into free fatty acids and glycerol. These enzymes can catalyze many types of reactions such as hydrolysis, esterification and transesterification. Lipases are uniquely able to function at the interface between an aqueous and a nonaqueous phase. Moreover, lipases have been used to synthesize esters of short chain carboxylic acids and alcohols in the food industry [2]. The production of flavor ester by lipases is well-known. However, until recently, almost all of these reactions were performed by commercial lipases, as well as mesophilic lipases such as Candida rugosa, Candida antarctica and Mucor miehei, whereas the synthesis of esters by psychrophilic lipases has rarely been studied [6]. Lipases or the other enzymes used in industry facing many problems generally with regard to stability and productivity [7].
Isolated enzymes in biocatalytic processes lack long-term stability under operational condition and limit reusability cycles [8]. Lipases are not used as much as other enzymes in industrial applications because of their high cost of production and their relatively unstable nature. Due to these reasons, immobilization methods have been developed [9]. Immobilization is one of the useful techniques to improve the application of enzymes in the industry [10]. The advantages of using immobilized enzyme systems compared to free enzyme systems are their reusability, lower cost, easily controlled product formation, rapid termination rate, and ease in separating from reactants and product [9]. The effectiveness of an immobilization process depends much depends on the support used. Comparative studies indicated that dramatic differences existed in the activity of lipases supported on different materials [11]. The cold-active AMS8 lipase is secreted by a psychrophilic microorganism, Pseudomonas sp. strain AMS8. This strain was isolated from Antarctic soil, and the AMS8 gene has been cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli [12]. The cold-active lipase AMS8 exhibits unique properties such as a faster reaction time in comparison to mesophilic and thermophilic enzymes, as well as increased flexibility, stability and low activation energy at low temperatures. In addition, this enzyme demonstrates high specific activity, as well as high catalytic activity between 0 °C to 20 °C. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the capacity of the novel psychrophilic lipase, cold-active AMS8 lipase, to synthesize ethyl hexanoate by direct esterification and to compare the ability of immobilize and free enzyme in the ester conversion.
2. Results
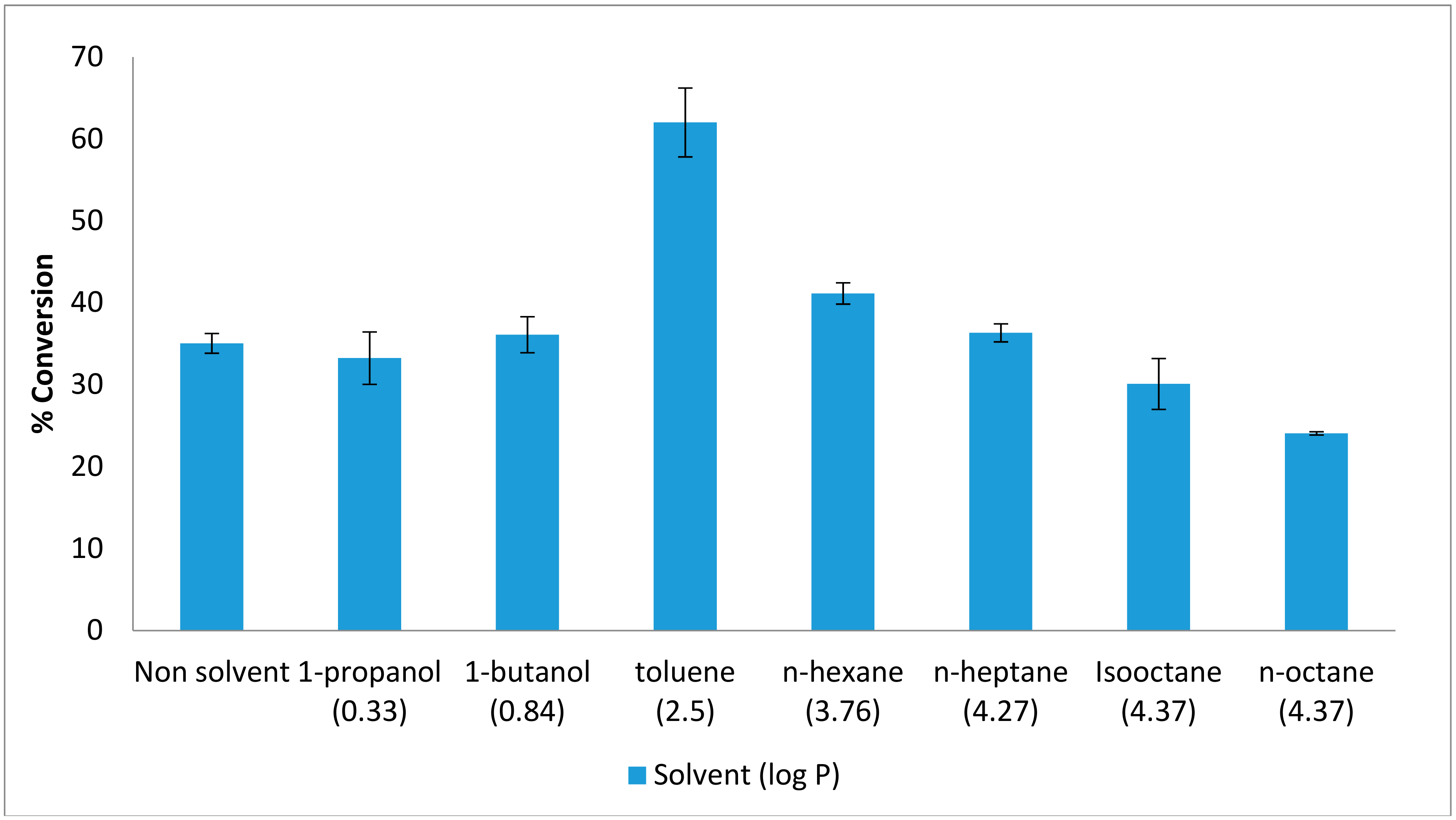
2.1. Effect of Organic Solvents on the Esterification Reaction
Other than lipase used as a biocatalyst in the synthesis of flavour ester, organic solvent is also needed in enhancing the reaction organic solvents often to catalyze reverse reactions where water should be minimal [13]. The effect of organic solvents was studied in order to obtain the esters of good quality and high percentage of yield. The favoured organic solvent is depending on the polarity of the enzyme. The production of ethyl hexanoate by AMS8 lipase was studied in the presence and absence of various organic solvents. Figure 1 shows that the maximum yield for ester conversion obtained in the presence of toluene was 62%. This value is higher than that obtained in the absence of any organic solvents (35%). Thus, the conversion percentage was improved in the presence of toluene, compared to a solvent-free system. The use of hydrophobic solvents such as toluene, hexane and heptane preserve catalytic activity without disturbing the micro-aqueous layer of enzyme [5]. The presence of solvent can shift the equilibrium towards the synthesis of esters, most likely due to the total transfer of the esters into the organic phase [14]. In addition, the use of organic solvents provides high enzyme thermostability. Enzymes have been reported to be stable and flexible within organic solvents but tend to exhibit low specific activity [15].
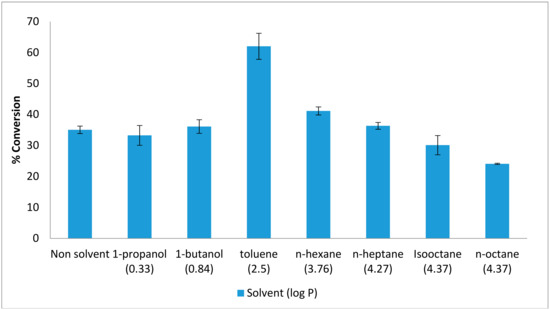
Figure 1.
Effect of various organic solvents on lipAMS8 lipase. Percentage conversion of ethyl hexanoate catalysed by native AMS8 lipase as affected by various organic solvents in different polarity (log p value) and solvent-free system. Reactions were performed at 20 °C for two hours with 1:1 molar ratio of hexanoic acid to ethanol.
In contrast with polar organic solvent, it has been reported that polar solvent can distort the water layer around the enzyme which make the enzyme less stable and lead to deactivation of the enzyme [16]. AMS8 lipase showed the maximum ester conversion was only at 36% in 1-butanol, a polar organic solvent which was 1-butanol. A polar organic solvent was reported make low conversion of ester for R. miehei lipase similarly with AMS8 lipase [17]. In such a medium, the solvent may alter the native conformation of the enzyme by disrupting hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction, thereby leading to very low alcoholysis rate [18]. Normally, the ester synthesis by the esterification, transesterification or interesterification required a suitable mixture of the nonpolar solvents, but in the food application process, solvent-free systems are preferred [19]. Besides that, solvent-free systems are preferable due to the absence of any toxicity resulting from the synthesized flavor esters [2].
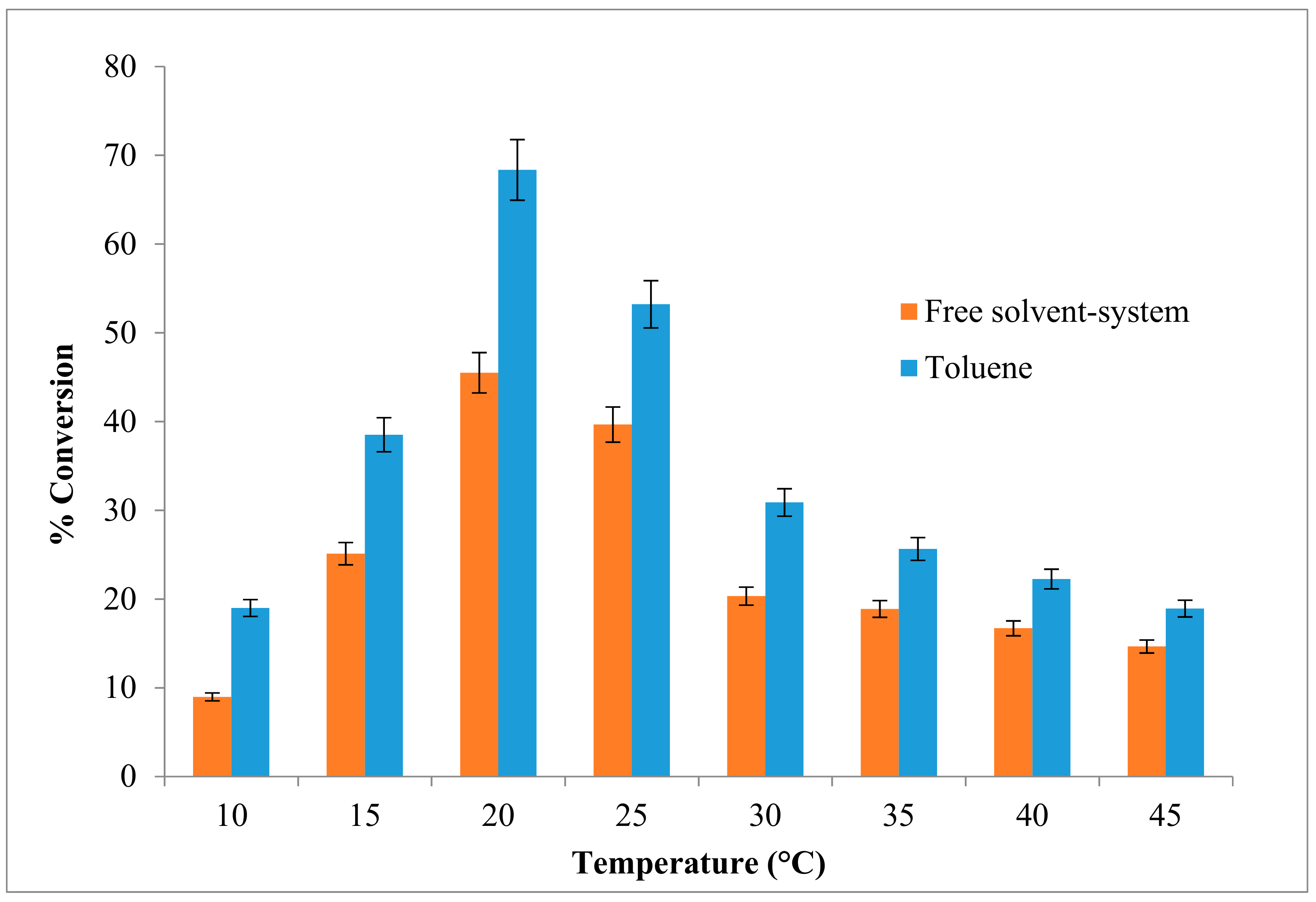
2.2. Effect of Temperature on the Esterification Reaction
The changes in the reaction temperature can affect the activity and stability of the enzyme and thus the rate of reaction. Besides that, the effect of temperature can be apportioned to its direct influences on esterification reaction and the enzyme as well as effect on substrate solubility. The effect of varying reaction temperatures on the enzymatic synthesis of ethyl hexanoate is shown in Figure 2. The reaction was optimized at 20 °C, with a high percentage of ester conversion (approximately 68.3%) in toluene, compared to a solvent-free system which was about 45.4%. The ester conversion rate began to decrease at 25 °C. An esterification yield of 75% was reported for the same optimal temperature of 20 °C for butyl-caprylate in n-heptane with an organic phase water concentration 0.25% (v/v) using Pseudomonas P38 lipase. It shows that the psychrotroph-derived lipase had stable structural flexibility and enzyme activity within a nearly anhydrous organic solvent phase [20].
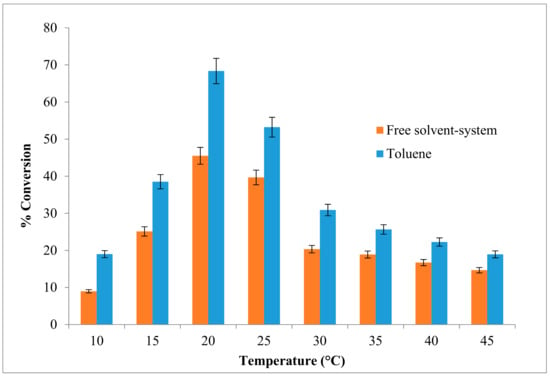
Figure 2.
Effect of various reaction temperatures on AMS8 lipase in toluene and free-solvent-system. Percentage conversion of ethyl hexanoate catalysed by native AMS8 lipase as affected different reaction of temperature in toluene and free-solvent system. Reactions were performed for two hours with 1:1 molar ratio of hexanoic acid to ethanol.
The decrease in flavor ester synthesis observed above 20 °C was due to the inactivation of the enzyme at high temperatures. Environmental factors such as low water activity prohibits enzyme flexibility if thermo stability within an organic solvent is achieved [21]. The optimum temperature for an enzyme depends on its source, the solvent, the pH, the substrate and the nature of the immobilization or chemical modification of the reaction medium.
Selvam (2013) had reported that lipase from Rhizopus arrhizus showed that, the percentage of ester conversion was high at 30 °C and started to decrease slowly after 35 °C and decreased drastically above 50 °C [22]. Besides, in the other work, the percentage conversion for ethyl valerate increased with increasing temperature from 30 °C (73.29%) to 40 °C (77.39%) due to energy received from the higher temperature heat used to increase the frequency of collision between the molecules. However, the percentage conversion of ester was slightly decreased at range of 45 °C to 55 °C and decreased sharply at 70 °C to 80 °C. An increment in the reaction of temperature had improved the substrates solubility and dissociation lead to unfavourable esterification conditions [10].
In addition, the cold active lipases from cold adapted microorganisms and their potential applications have been examined [23]. The ‘low activity’ meaning that high catalytic activity at low temperature and flexible as well as stable at low temperature are some of special features of psychrophilic microorganism thus these features might be the key to success in some of their applications. These applications include their use as catalyst for organic synthesis of unstable compounds at low temperature [24].
Cold active lipases having low thermal stability were shown to be favorable for some purposes. For instance, heat labile lipase can be inactivated by treatment for short periods of time at relatively low temperatures after being used for the processing of food and other materials. Thus, during heat activation, materials can be prevented from damage [25]. Ethyl esterification of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in an organic solvent-free system using C. Antarctica lipase has been reported [26], which acts strongly on DHA and ethanol. Eighty-eight percent of ester product was produced by shaking the mixture of DHA/ethanol with ratio (1:1, mol/mol) and 2 % (w/v) immobilized C. Antarctica lipase B at 30 °C for 24 h. In addition, the use of lipase B from C. antarctica for the preparation of optically active alcohol was reported in previous study [27]. The ability of psychrophilic lipases to catalyse reactions at low or moderate temperature offers novel opportunities for industrial and biotechnological potential [22]. The effect of reaction temperature can be distributed to its effect on substrate solubility as well as its direct influences on the enzyme and the esterification reaction.
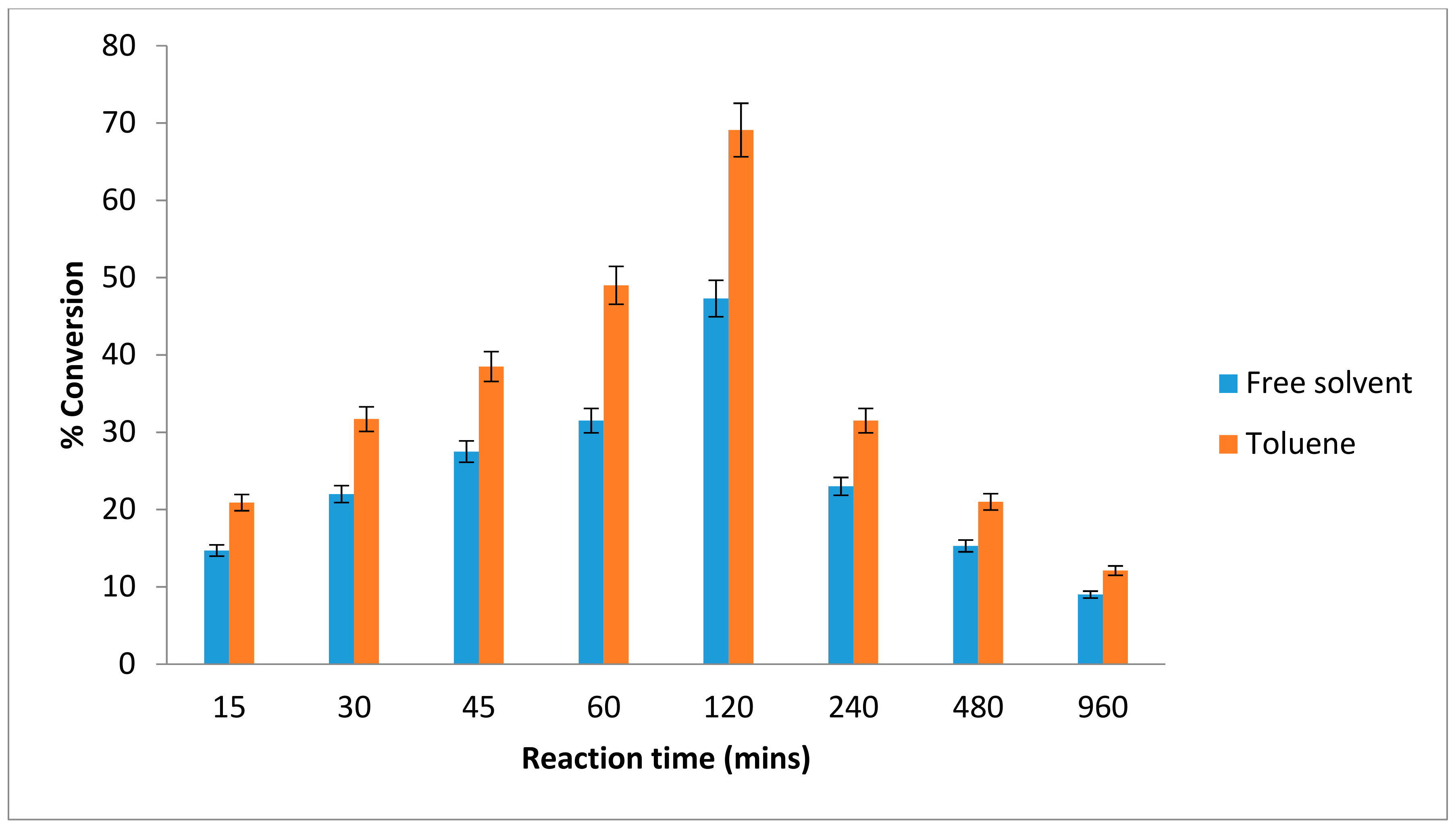
2.3. Effect of Time on the Esterification Reaction
The reaction time for an enzyme provides an insight into its performance. As the reaction progresses, a determination of the shortest time required to obtain a suitable yield is helpful and enhances the cost-effectiveness of the process. The lipase-catalyzed reaction reached equilibrium after two hours at 20 °C, with a conversion yield of 69% in toluene while in free solvent-system about 47% of ester conversion was achieved (Figure 3). After more than two hours of incubation, the ester yield began to decrease. This was due to production of water molecule, which had achieved the equilibrium state. As the reaction proceeded, the substrates concentration decreased which led to a fall in the degree of substrate saturation of the enzyme [28].
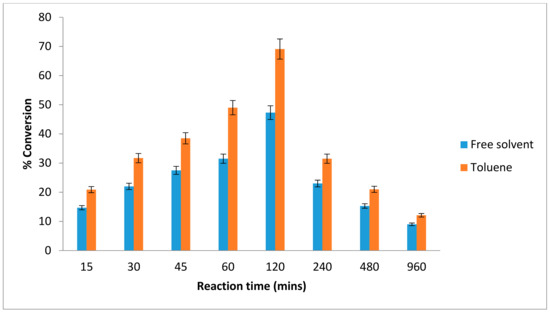
Figure 3.
Effect of various reaction times on lipAMS8 lipase in toluene and free-solvent-system. Percentage conversion of ethyl hexanoate catalysed by native lipAMS8 lipase as affected different reaction of time in toluene and free-solvent system. Reactions were performed at 20 °C with 1:1 molar ratio of hexanoic acid to ethanol.
In this study, the AMS8 lipase acts as catalyst to speed up the reaction. The best ester conversion of AMS8 was achieved at 2 h. Ester production declines after prolonged incubation. The instability of the psychrophilic lipases over longer time periods is one of the factors contributing to the favorable results obtained for a short AMS8 lipase reaction time. As the reaction proceeds, the substrate concentration decreases, which reduces the degree of enzyme substrate saturation. The best production of ethyl hexanoate in 2 h using cold active AMS8 lipase was considered to be a rapid conversion. In contrast with Pseudomonas P38 lipase catalyzed reaction which reached equilibrium state after 96 h at 20 °C [20]. The lipase from Aspergillus terreus was reported to catalyze the esterification of stearic acid with sorbitol and the ester conversion of 65% was achieved after 48 h at 37 °C. The percentage of ester conversion keeps increasing from 12 h to 24 h; however, the conversion of ester was found to remain constant after 24 h to 48 h and slightly decrease after prolonged reaction times [29].
The reaction time and the product yield are two important process endpoints in this study. A short reaction time reduces overall process cost, reduces the requirement for energy and decreases substrate inventory. Therefore, it has been proven that AMS8 used as a catalyst had speed up esterification reaction between hexanoic acid and ethanol within two hours incubation time. The time of reaction is dependent on kinetic factors such as choice of organic solvent, reaction temperature, amount of biocatalyst used, specific enzyme activity, concentration of cosubstrates, shaking or sonication that affects mass transfer limitations and reaction rate and also the degree of stirring [30].
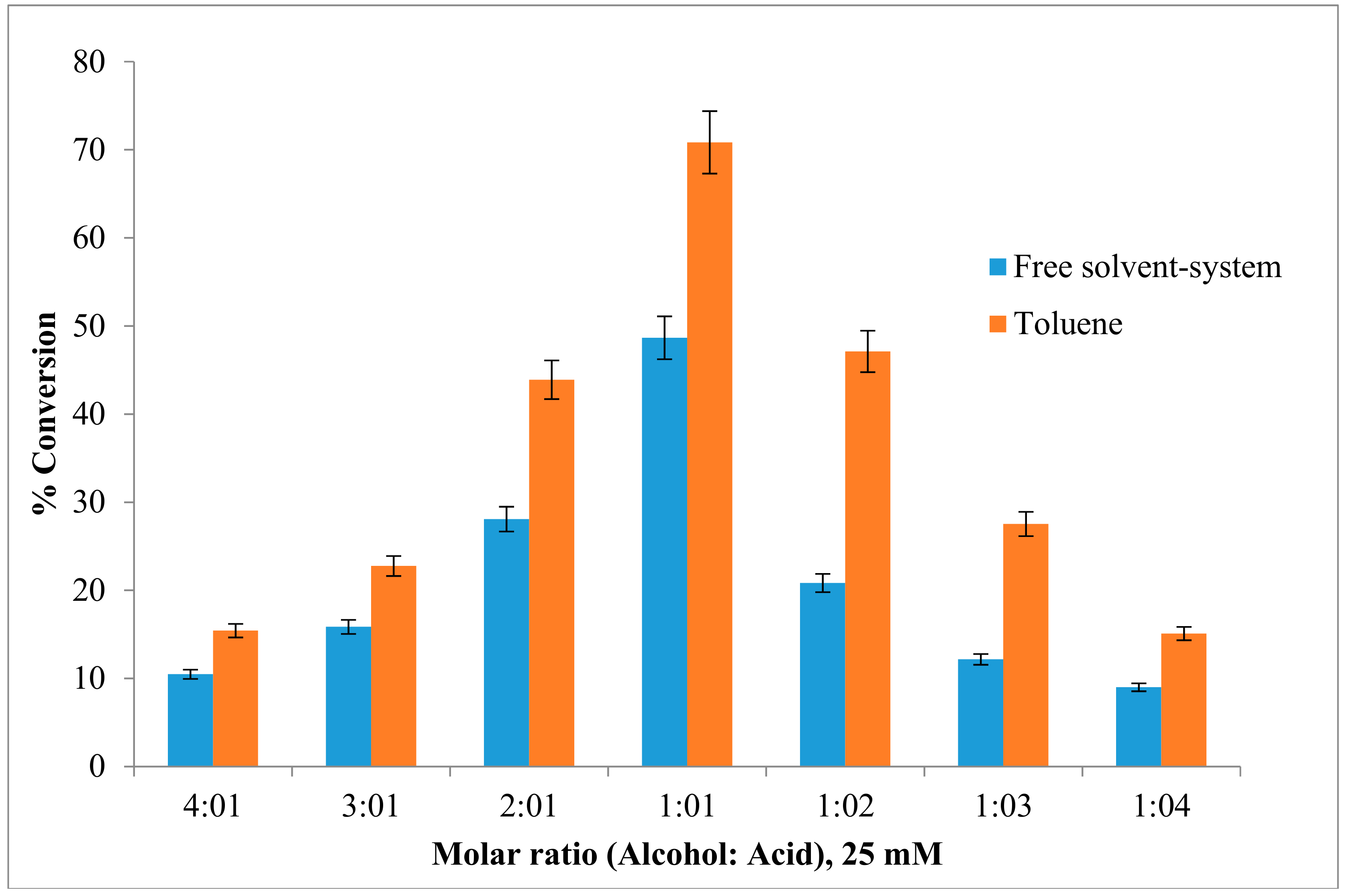
2.4. Effect of the Substrate Molar Ratio on the Esterification Reaction
The effect of the substrate (acid to alcohol) molar ratio was investigated using freeze-dried AMS8 lipase. Figure 4 shows that the ester conversion rate in toluene increased from 15.4% to 71% as the alcohol-to-acid molar ratio was decreased from 4 to 1, respectively, while an increase in the acid-to-alcohol molar ratio also contributed to a lower ester yield. However, in free solvent-system, the ester conversion shows about 48.6% in 1:1 molar ratio acid-to-alcohol. In this study, the substrate concentration was constant at 25 mM for both acid and alcohol.
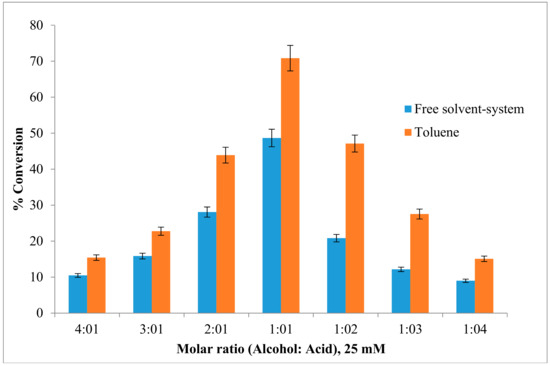
Figure 4.
Effect of different ratio concentration of substrate on lipAMS8 lipase in toluene and free-solvent-system. Percentage conversion of ethyl hexanoate catalysed by AMS8 lipase is affected at different substrate molar ratio in toluene and free-solvent system. Reactions were performed at 20 °C for 2 h.
The synthesis of ethyl hexanoate increased with an increase in the acyl donor concentration, and a high percentage of ester formation (70%) was obtained with a 0.025 M substrate mixture (hexanoic acid and alcohol) after two-hour incubation at 20 °C. However, at substrate concentrations greater than 0.025 M, a decrease in the ester yield was observed. This result could have occurred because polar substrates might have accumulated in the aqueous microenvironment of the enzyme, reaching a concentration level sufficient to cause protein denaturation [31]. Moreover, high concentration of alcohols is reported to be terminal inhibitors of lipases [32]. This inhibition may result from substrate inhibition, enzyme dehydration and pH reduction in the aqueous microenvironment of the enzyme. This phenomenon is described with lipases with the exception of the esterification rate of C. cylindracea lipase [33] which was not inhibited even at butyric acid concentration as high as 1 M. However, most of enzymes are inhibited by low concentration of acid and alcohol. For instance, the Mucor miehei lipase was inhibited by 0.05 M of acetic acid [34].
A previous study reported that a high concentration of alcohol might impair the reaction rate [35]. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the actual excess nucleophile concentration to be employed in a given reaction. Several observations on alcohol inhibition have been reported for lipase catalysis. For instance, in a previous study, synthesis of ethyl ester has been affected by increasing ethanol concentration [36].
In addition, an increase in the fatty acid concentration can affect enzyme activation and also decreases the pH, which can contribute to the hydrolysis of the esters formed [37]. Furthermore, an increase in either acid or alcohol concentration affects the polarity of the medium, thus altering the affinity of the organic solvent and reducing the ester conversion rate [38]. Thus, the use of an equimolar acid-to-alcohol ratio was recommended to achieve an optimal ester conversion rate [37]. However, the ideal substrate molar ratio required to produce a high ester conversion rate depends on an enzyme’s properties because every enzyme exhibits its own unique characteristics [39].
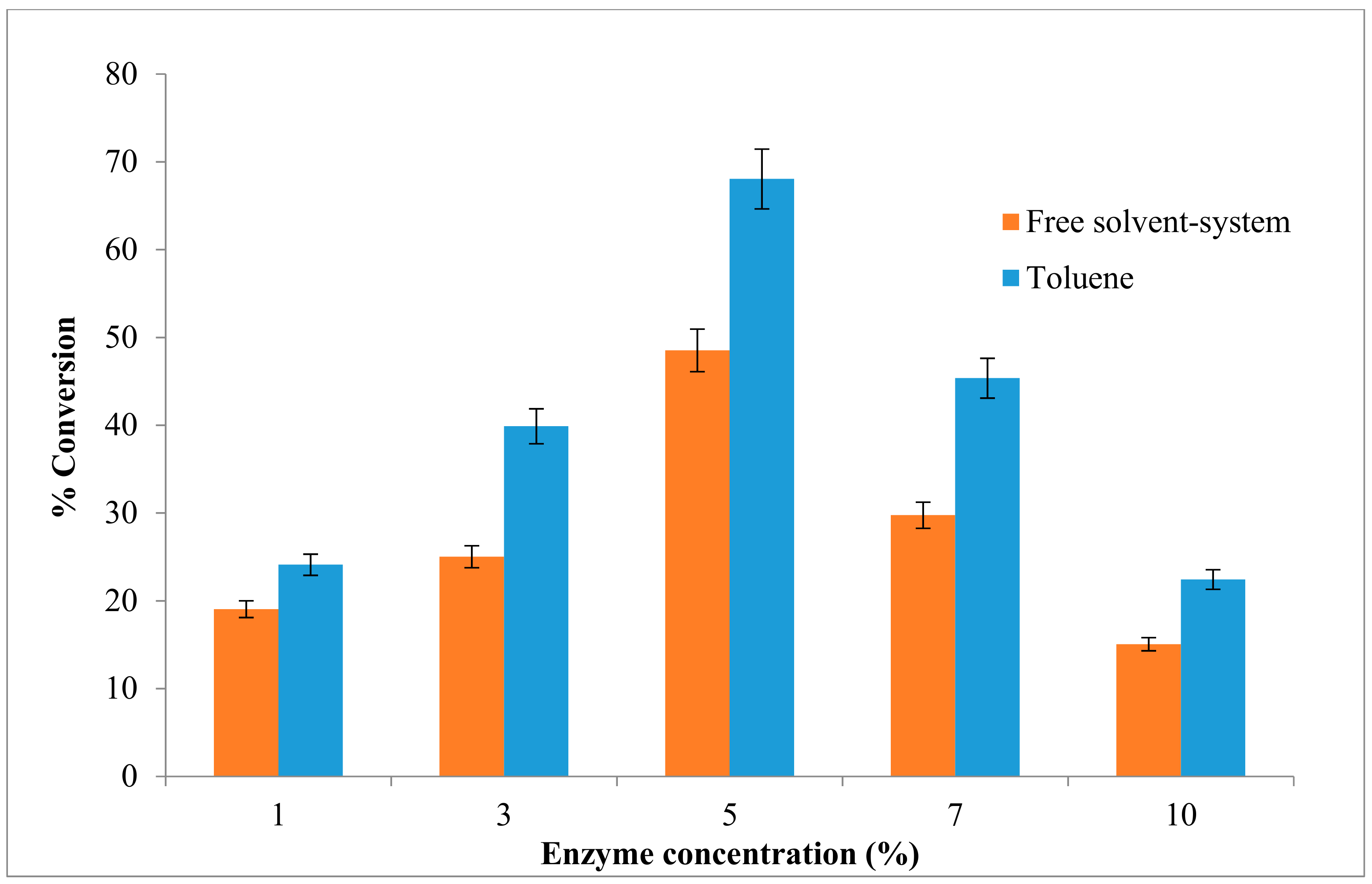
2.5. Effect of the Enzyme Concentration on the Esterification Reaction
Amount of enzyme plays a crucial role in any biocatalytic process especially in large scale production. Its influence on the reaction was assessed to facilitate determination of the minimal amount necessary for achieving good yield. The reaction in this study was carried out using equimolar concentration of alcohol and acid substrates (0.025 M), and different enzyme amount (1% to 10%) (w/v) (mg/mL). The system used for ester synthesis was biphasic with the solid enzyme powder in suspension in the liquid phase in toluene as well as the free solvent-system. The enzyme AMS8 lipase was lyophilized and dried for 48 h before use. The initial rate of ethyl hexanoate synthesis was proportional to the amount of enzyme added to the reaction mixture. Figure 5 shows that the ester conversion rate in toluene increased from 1% (24%) to 5% (68%) of enzyme concentration in (w/v) and started to decrease when added 7% to 10% of enzyme concentration, whereas only 48% of ester conversion was seen when 5% of enzyme concentration was added in free solvent-system.
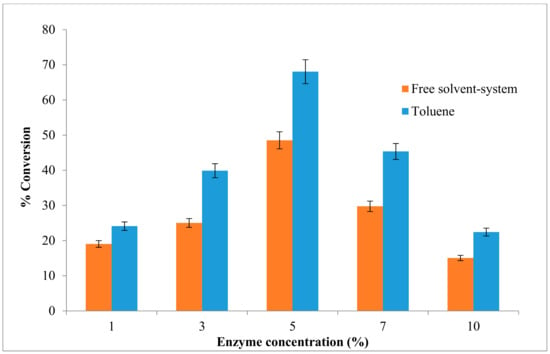
Figure 5.
Effect of different concentration of enzyme on AMS8 lipase in toluene and free-solvent-system. Percentage conversion of ethyl hexanoate catalysed by native AMS8 lipase as affected different of enzyme concentration in toluene and free-solvent system. Reactions were performed at 20 °C for two hours 25 mM of substrate concentration (1:1 molar ratio ethanol to hexanoic acid).
The result shows an excess of enzyme concentration did not contribute to the increase in the percentage conversion. The previous study shows that the percentage of ester conversion for ethyl valerate was 75.3% in 5% (w/w) to 80.0% (15%) (w/w) and slightly decreased at 20% of enzyme concentration and sharply dropped when more than 30% of the enzyme amount was added [1]. As the enzyme concentration was increased above this point, the reaction will slightly decline due to the steric hindrance produce by excessive enzyme. The amount of enzyme will influence the total reaction times in esterification reaction, which are required to achieve desired conversion. The most significant main effect in enzymatic esterification reaction is the initial catalyst concentration [40]. The use of a large amount of enzyme could significantly increase the fraction of acyl donor molecules to form acyl–enzyme complexes was indicated in the previous study [41]. Moreover, their active sites were not exposed to the substrate and remained inside the bulk of enzyme particles without contributing significantly to the reaction. According to a study, not all active sites are exposed to the substrates in the presence of high amount of lipase, and resulted molecules of the enzyme tend to aggregate together [42]. However, small amounts of enzymes may have been insufficient for complete substrate conversion within the specified reaction period [43].
The percentage yield of ester product from S. acrimycini NGP 1, S. albogriseolus NGP 2 and S. variabilis NGP 3 were found to be 40.1%, 48.8% and 63.3% from the previous study. It shows that the percentage of ester conversion was found reach its maximum at 5% to 15% of the enzyme concentration and decreased when 20% and 25% of the enzyme amount were added in the reaction mixture [44]. A simple kinetic model derived from a ping pong mechanism was proposed to describe the mono-esterification of glucose with stearic acid catalysed by immobilized lipases from Candida sp. When the concentration of the enzyme increased, the percentage yield of ester product was decreased [27].
The observation the silica immobilized lipase, (SIL) showed that the percentage of ester conversion were 50% and 56% for n-butyl acetate and n-propyl acetate synthesis respectively after 24 h of incubation time at an enzyme concentration of 25% (15/mL). Upon an increase of the enzyme amount, the yield did not increase significantly due to the lack of substrate to access the active site of enzyme and difficulty in maintaining the uniformity of the biocatalyst at a higher enzyme concentration [45]. In addition, synthesis of isoamyl acetate using the immobilized lipase as a biocatalyst studied the effect of enzyme concentration in the range of 4 to 20% (by mass per volume) at 40 °C [3].
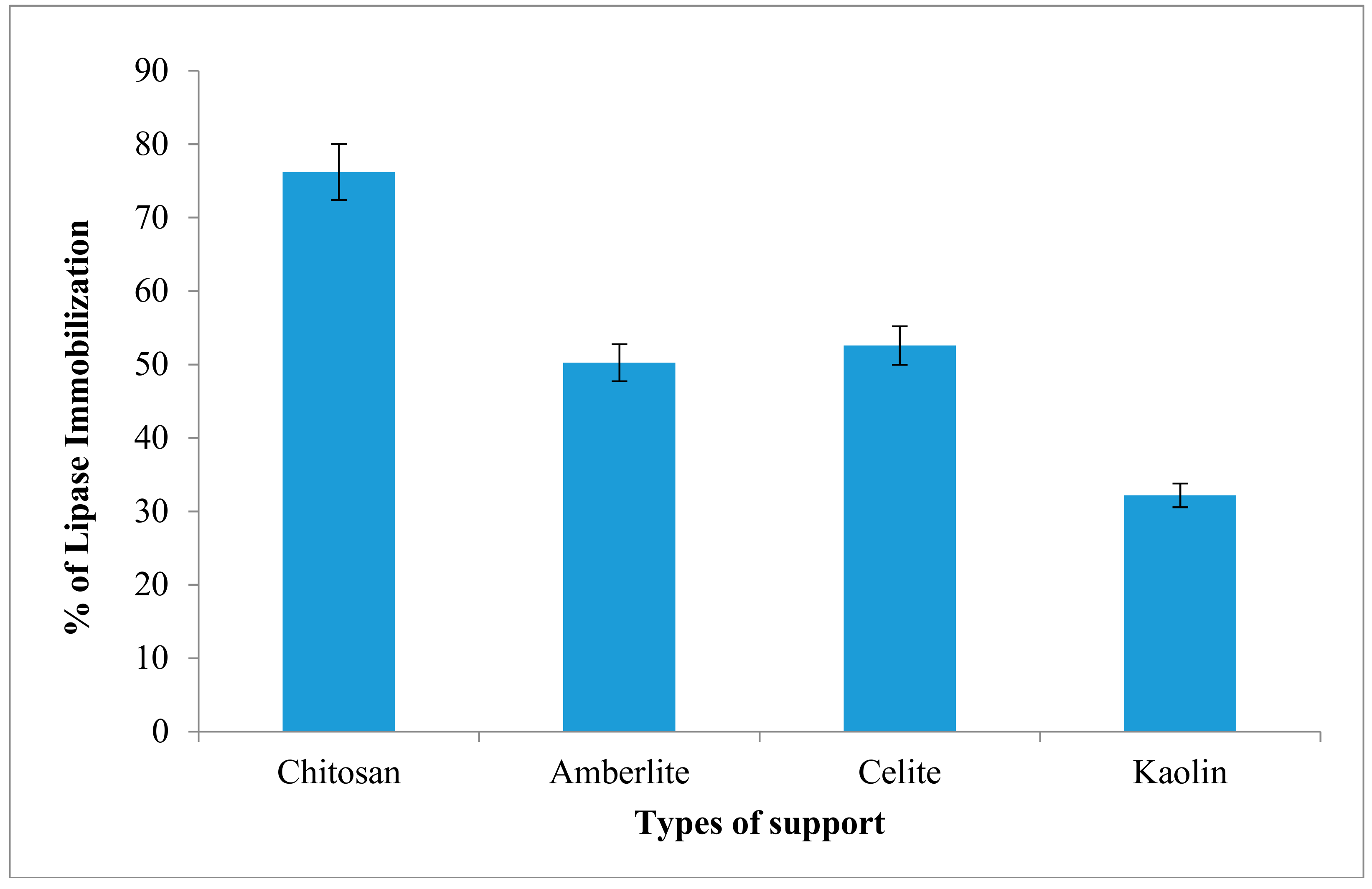
2.6. Immobilization of Lipase
In this study, the AMS8 lipase was immobilized using physical adsorption method. The percentage of immobilization of AMS8 lipase on four types of matrices is investigated. Among the matrices or supports used, chitosan shows highest percentage of lipase immobilization (76.2%) while, kaolin showed low percentage of lipases immobilization at 31.2% (Figure 6). It shows that the difference in percentage values of immobilization as well as protein loadings were in accordance to the physicochemical properties.
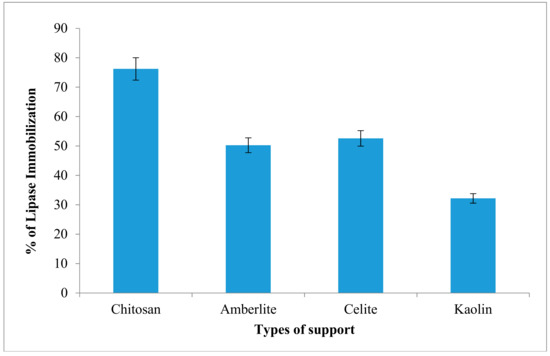
Figure 6.
Percentage of AMS8 lipase immobilization on various matrices. Protein content was determined using Bradford (1976) method and percentage of immobilization was calculated using formula described in earlier section.
The lipase activity in native and immobilized forms was measured. The lipase activity of native AMS8 lipase was about 30.5 U/mL, whereas the lipase activity of immobilized enzyme in chitosan, celite, Amberlite XAD7 and kaolin were 37.2, 33.5, 28.1 and 15 U/mL, respectively.
The differences in percentage of immobilization appeared to be influenced by support pore size and adsorption capacities. The great value of immobilization onto chitosan could be due to its particle size and diameter. Previous study shows that chitosan has been shown to be a versatile nontoxic material with some effects like it controls pathogenic microorganisms and activates several defence responses including and inhibiting different biochemical activities during the plant-pathogen interaction. The advantages of chitosan might be extended from the field through to the storage of numerous horticultural commodities [46].
Bansal, (2011) reported that chitosan can be tailored to produce different forms for use in different biotechnological industrial applications such as cosmetic fields [47]. It is an essential component in skin care creams, shampoo, and hairsprays due to its antibacterial properties. Chitosan forms a moisturizing, protective, and elastic film on the surface of the skin that has the ability to bind other ingredients that act on the skin. It can be concluded that chitosan is an important support, natural polymer and versatile, which successfully used in pharmaceutical industries. Therefore, from this experiment, chitosan was selected to other supports for immobilization of lipase to synthesize ethyl hexanoate.
The particle size of support material also influences the coupling effect during immobilization [48]. The forces between a support and the enzymes include hydrogen bonding, Van der Waals forces and electrostatic interaction. Furthermore, the smaller pore size may restrict mass transfer and pore penetration of the protein which is limited the protein interaction with the total surface area of supports. Hence, intraparticle diffusion effect of substrates was reduce and helping to interact between enzyme and substrates [49].
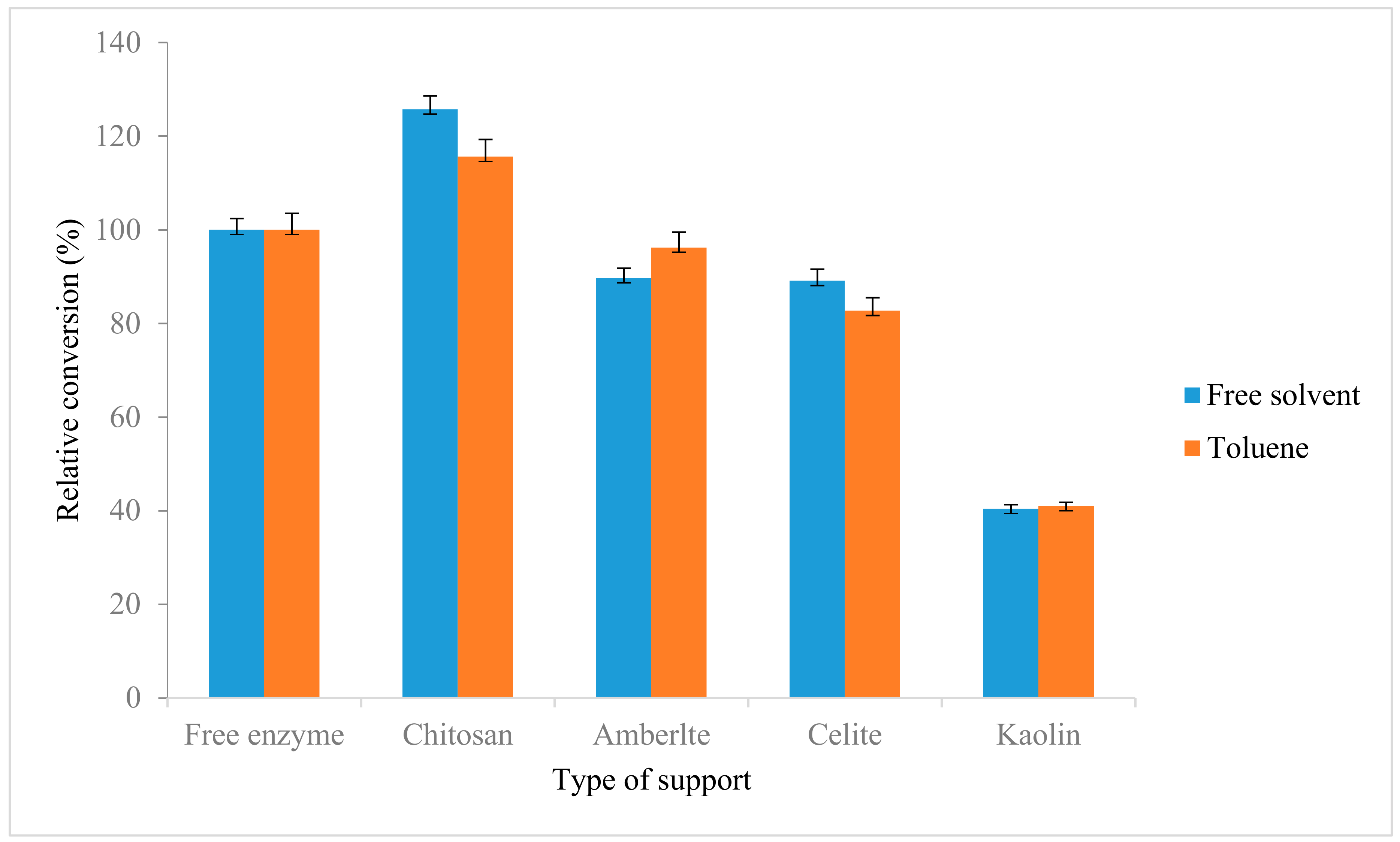
Comparison between native AMS8 lipase and immobilized lipases towards the synthesis of ethyl hexanoate was done. As shown in Figure 7, the lipase immobilized with chitosan showed higher relative conversion as compared with control with 125.7% and 115.6% in the free-solvent system and toluene, respectively. Similarly with the previous study reported the activity and stability of the lipase after immobilization on both LDHs were found to be increased in ester conversion compared to in native lipase [50]. Similar trend was also reported on Zn/Al-diocytyl sodium sulfosuccinate (DSS) nanocomposite (NAZAD) which has higher porosity and able to adsorb higher protein and subsequently increase the ester production. The obtained immobilized lipase was applied for the synthesis of ethyl butyrate and resulted an ester conversion of 89% compared to native lipase 65% [51].
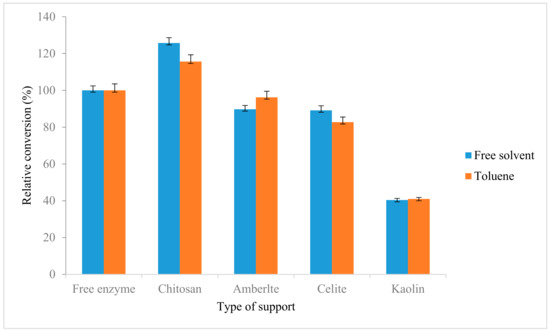
Figure 7.
Synthesis of ethyl hexanoate using native AMS8 lipase and immobilized lipases. The ethyl hexanoate was synthesis relative to the control (free enzyme) in toluene and free-solvent system. The reactions were performed at 20 °C for two hours 25 mM of substrate concentration (1:1 molar ratio ethanol to hexanoic acid).
From the previous study, a method of immobilization of Candida rugosa was investigated where, the immobilization procedure was improved by addition of calcium alginate to polymer of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) to improve the surface area properties and reduce the tendency to agglomerate [52]. On the other hand, the lipase isolated from Bacillus sp. was immobilized on different supports and the results shows the activity and stability of immobilized lipase were much better compared to native lipase [53]. Similarly with immobilized lipase from Candida rugosa showed and increment in thermal stability where the enzyme shifted the temperature from 37 °C to 45 °C [54]. It shows that the thermal stability of the immobilized lipase was higher than that the native lipase thus, making immobilized lipase more stable and more preferable for use in the synthesis of ester [54]. The effectiveness of an immobilization process depends much on the support used. Comparative studies indicated that dramatic differences exist in the activity of lipases supported on different materials [11]. Similarly with Candida rugose lipase where the enzyme shown high activity or ester conversion when immobilize with chitosan [55].
In contrast with kaolin, this support showed decrement of synthesize ethyl hexanoate ester compare with control which are 40.4% and 41% in free solvent and toluene. The unsuitability of this support also has been reported by a few enzymes such as porcine pancreatic lipase and acid phosphatase [56,57,58]. The decrement of ester conversion might be due to electrostatic forces that play an important role in the adsorption of enzyme where the kaolin was reported to have the negative charge [58,59].
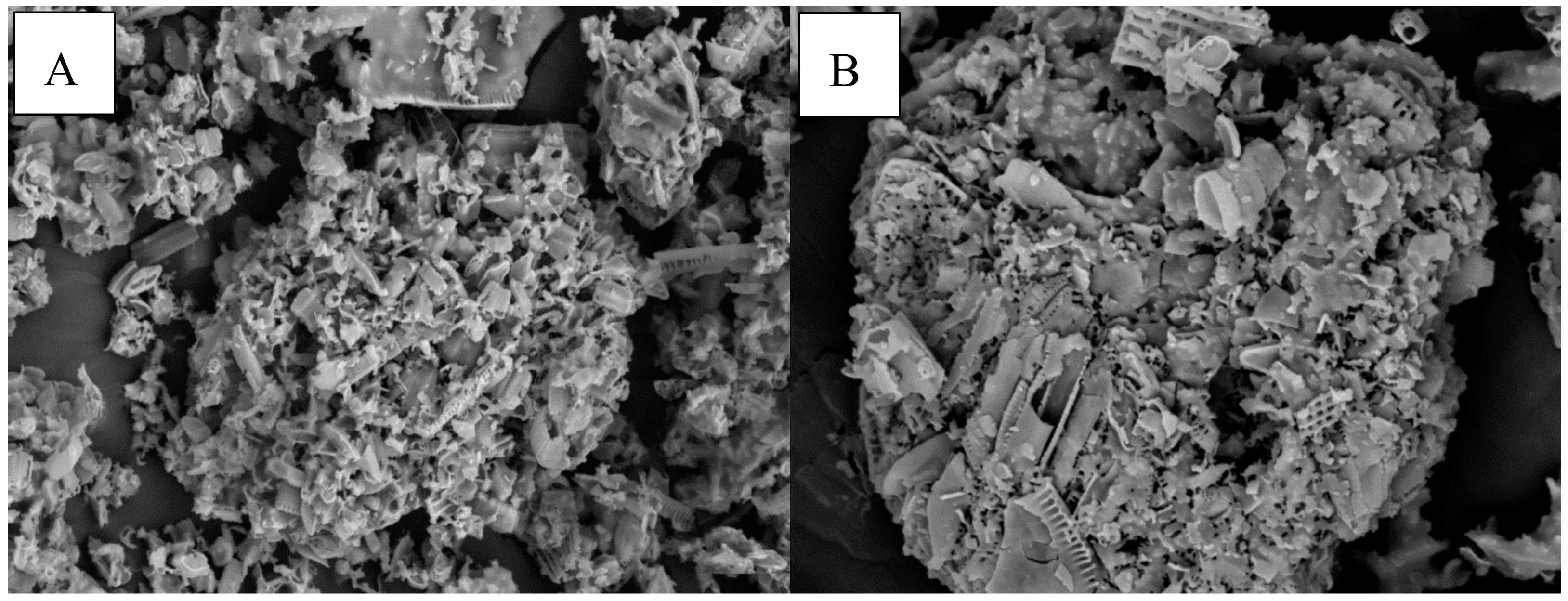
2.7. Morphology Analysis of Chitosan Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
A suitable support material that can function effectively in immobilization generally requires the following characteristics. Among those, it should ease enzyme immobilization without any significant loss of enzyme activity and it must not contain extractable materials which it may contaminate the product stream. A support or matrix should also have suitable mechanical properties for the desired process and should have appropriate pores and particle sizes as well as the surface area, so as not to limit diffusion of substrates and therefore reaction rates and it should be less expensive [59]. Chitosan showed the highest ester conversion among others support or matrices. High exchange rates indicate matrix compatibility. In order to support the data, morphology analysis has been done using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Figure 8a,b shows that the structure of the chitosan-lipase is more compact compared the support only. The existence in compactness could indicate the presence of lipase. The pores or holes of chitosan powder can also be clearly seen under 500× and 1000× magnification. The pore diameter should be four- to fivefold of the protein diameter in order to prevent restrictions to the access of the enzymes [59,60]. Pore sizes of the support also contribute to the suitability of the support with the enzyme leading to increase enzyme activity. Previous study reported that supports with smaller pore sizes can result in restricting mass transfer and the penetration of the enzyme molecules, thus limiting protein interaction with the total surface area of the support particles [61]. The pore size might be useful to explain the adsorption capacity of chitosan. Similarly, a commercial crude lipase and lyophilized Candida antarctica lipase was not easily dispersed and formed aggregates due to incompatibility of support [62]. The aggregation of freeze-dried lipase as well as lipase crude powder is the cause of decrease in their specific activities. This phenomenon could be due to the removal of essential water surrounding lipase during lyophilization.

Figure 8.
Scanning electron micrographs of chitosan and chitosan with AMS8 lipase. (A) Chitosan (500× magnification); (B) chitosan-lipase (1000× magnification).
Lipase is a hydrophobic enzyme, which explained how a strong hydrophobic or electrostatic interaction was needed between enzyme and support in an immobilization process in order for the adsorption to be successful. Strong hydrophobic interactions can be achieved by using hydrophobic supports or enzymes [10]. Moreover, hydrophobicity of lipase plays an important role in increasing the amount of immobilized activity due to the stronger preferential binding of the more hydrophobic lipase on the supports. To show how important physical factors influenced the rate of absorption of the enzyme, lipase from Candida rugosa has been immobilized using chitosan flakes and porous chitosan beads (PCB). The result showed that PCB has higher recovery compared to flakes, and internal mass transfer occurred during the process [61]. Thus, selections of supports have a biggest influence in the successful immobilization of enzymes.
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analyses of Flavor Ester
Product of the reaction was ascertained using FTIR and GC–MS. The aim of these analyses is to identify those functional groups in each of samples and specifically is the presence of ethyl hexanoate ester. The infrared result for ethyl hexanoate is tabulated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Infrared spectrum of ethyl hexanoate.
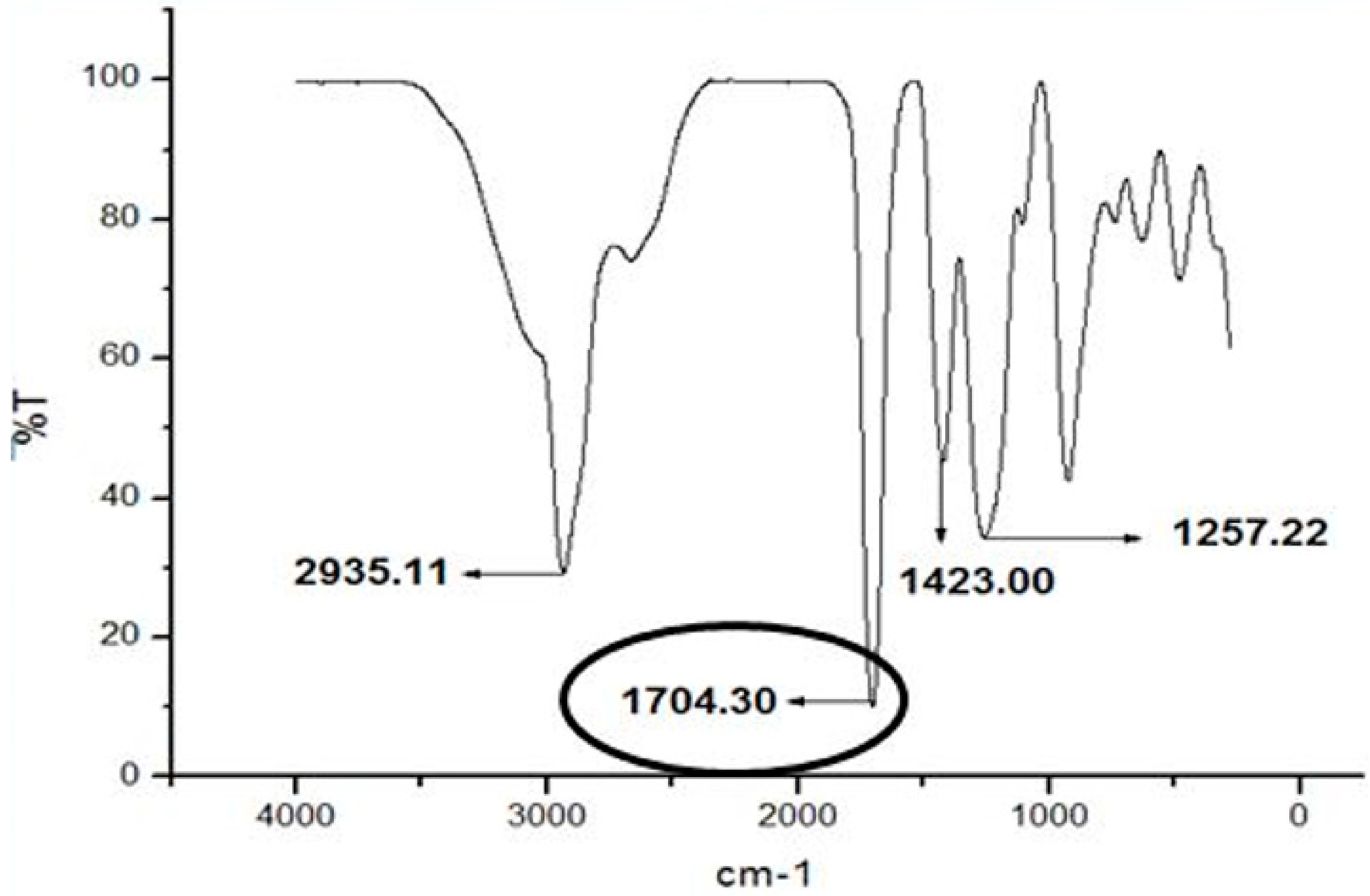
Figure 9 show that the sharp peaks at 1704.30 cm−1 that indicated the presence of functional group carbonyl include esters, aldehydes and ketone group which is more specific for ester within the samples. The free carbonyl stretching frequency ester in pyrrolic ester is in range of 1701–1711 cm−1 [63] Then, the ester structures were followed by the presence of v(C-O) in 1257.22 cm−1. This characteristic differentiates between esters and ketones. The band of ester is doublet at 1717–1723 cm−1 for v(C=O) and 1266–1257 cm−1 for v(C-O) in acetyl ester bonds [64]. Based on the figure also, it showed the infrared at 2935.11 cm−1 that indicated the stretching v(C-H) functional group while the infrared at 1423.00 cm−1 showed the bending v(C-H) functional group. The stretching v(C-H) functional group showed the presence of C-H aromatic group. The infrared spectrum in range around 2800–3000 cm−1 indicated the C-H stretching [64].
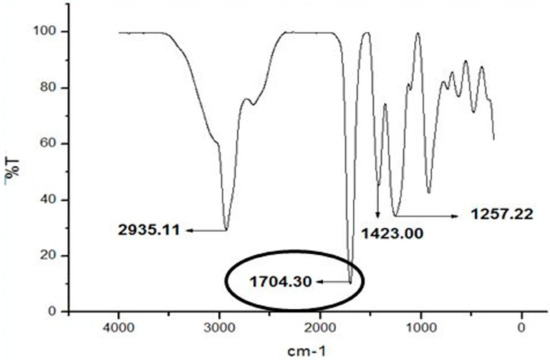
Figure 9.
IR spectrum of ethyl hexanoate. Spectrum indicating the presence of ester is shown in circle area.
The total molecular ion of ester mixtures is represented in Table 2. The molecular ion of 144 m/z indicated the presence of ethyl hexanoate molecules with molecular weight of 144.21 g/mol. The corresponding ester compound of ethyl hexanoate (C8H16O2) can be recognized by mass spectra. The highest peak at 43 m/z indicates the hexane substituent fragmented from the ethyl hexanoate ester while at 60 m/z, the peak showed the presence of ethoxide structure, which is a product of fragmentation of hydrogen from ethanol. At 88 m/z, the peak indicates presence of hexanoic acid in the sample whereas the peak for ethyl ester appeared at 73 m/z. Thus, it has proven that the existence of ester group in the sample. The presence of suitable organic solvent in esterification reaction has helped to minimize the water content and lead to maximize the yield ester production due to the thermodynamic equilibrium shifting to forward reaction (synthesis) instead of reverse (hydrolysis) reaction of esterification.

Table 2.
Molecular ion fragments of ethyl hexanoate mixtures. The mass spectrum showed the presence of ethyl hexanoate (144 m/z) in the sample with the compound structure and fragment molecular ions.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Hexanoic acid (95%) and toluene (95%) were purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). Acetone and absolute ethanol were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich Co. Ltd. (Poole, UK). Sodium hydroxide was supplied by Merck. Molecular sieve dehydrate 3A, with indicator, for drying solvents was purchased from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland). All other chemicals and solvents used in this study were of analytical grade.
3.2. Preparation of Crude Freeze-Dried AMS8 Lipase
Recombinant E. coli containing a pET32/LipAMS8 gene vector was obtained from the Laboratory of Enzyme and Microbial Technology, Faculty of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Selangor, Malaysia The stock culture was maintained in a sterile microcentrifuge tube containing 0.2 mL of glycerol and 0.8 mL of Luria-Bertani (LB) medium in a deep freezer at −80 °C prior to use. For the production of lipase, the culture was incubated in a 500 mL conical flask containing 100 mL of production medium (LB medium with 1% (v/v) culture, 0.1 mL ampicillin and 0.1 mL IPTG) for 12 h with reciprocal shaking at 20 °C and 200 rpm. After incubation, the culture was centrifuged at 4 °C, and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet was resuspended in 30 mL of 0.05 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8) and was sonicated for six minutes at 30-second intervals. Then, the enzyme was centrifuged at 4 °C, and the supernatant was collected. The AMS8 lipase was freeze-dried overnight. The dried crude AMS8 lipase sample was stored at 4 °C prior to use.
3.3. Lipase Hydrolytic Activity
The activity of the freeze-dried AMS8 lipase was measured under the standard assay conditions described previously [10] using an olive oil emulsion as a substrate. AMS8 lipase activity is expressed as unit per milliliter of enzymatic solution. One unit (IU) of lipase activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzed the liberation of 1 µmol of free fatty acid from olive oil per minute at 20 °C under optimized conditions.
3.4. Synthesis of Ethyl Hexanoate
3.4.1. In Solvent-Free System
The reactions were carried out in screw-capped bottles containing 5 mL of the substrate mixture (hexanoic acid and ethanol), which consisted of a 1:1 molar ratio of acid to alcohol, at 20 °C in the presence of 5% freeze-dried AMS8 lipase with shaking (200 rpm). A reaction under the same conditions without added enzyme was performed in parallel and used as a control.
3.4.2. In Toluene
The reactions were performed in 5-mL screw-capped bottles with a substrate concentration of 0.025 M each. Afterwards, 10 mL of toluene was added to the mixture. The reaction mixture was incubated at 20 °C in the presence of 5% freeze-dried AMS8 lipase with shaking (200 rpm).
3.5. Reaction Analysis
Aliquots of the reaction mixture were withdrawn periodically, and the residual acid content was assayed by titration with 0.5 M sodium hydroxide using phenolphthalein as an indicator and 3 mL of ethanol as a quenching agent. The ester synthesis rate was calculated based on the conversion of the acid to an ester. The ethyl hexanoate yield is expressed as a percentage (%) of converted hexanoic acid compared to the total initial fatty acid content in the reaction mixture.
The conversion of ester was expressed as percentage conversion (%) under various reaction conditions according to the following formula:
3.6. Effect of Reaction Temperature
The reaction mixture was incubated at various temperatures (10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50) °C using a horizontal water bath shaker with a continuous shaking speed of 200 rpm. The conversion percentage was determined as described above.
3.7. Effect of Reaction Time
The reaction mixture was incubated for various reaction time intervals (15, 30 45, 60, 120, 240, 480, and 960 min) using a horizontal water bath shaker with a continuous shaking speed of 200 rpm. The conversion percentage was determined as described above.
3.8. Effect of Substrate Concentration
The reaction mixture was incubated at various substrate molar ratios (1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, and 4:1) and different substrate concentrations (5, 10, 25, 50, 75, and 100) mM using a horizontal water bath shaker with a continuous shaking speed of 200 rpm. The conversion percentage was determined as described above.
3.9. Effect of Enzyme Concentration
The reaction mixture was incubated at various enzyme concentrations (w/v) in percentage (%) which are (1%, 3%, 5%, 7% and 10%) using a horizontal water bath shaker with a continuous shaking speed of 200 rpm. The conversion percentage was determined as described above.
3.10. Immobilization of AMS8 Using Commercial Supports
10 mL of AMS8 lipase and 1.0 g of commercial supports (celite, chitosan, amberlite and kaolin) were chosen to immobilize the AMS8 lipase. The mixture was incubated for two hours at 25 °C with 100 rpm in a water bath shaker. The enzyme-loaded supports were separated from the supernatant by filtering through Whatmann No. 1 filter paper using vacuum pump. Then, two to three times of washing of the enzyme-loaded supports were carried out using distilled water (10 mL) to remove the unabsorbed enzyme. The immobilized AMS8 lipases were then lyophilized in the freeze drier for 24 h.
The lipase activity of immobilized AMS8 lipases were determined using colorimetric method (Kwon and Rhee, 1986) while the protein content was determined by Coomassie dye binding (Bradford, 1976). The amount of bound protein was indirectly determined by comparing the difference between the amounts of protein introduced into the support (before immobilization) and the amount of protein both in filtrate and in the washing solutions after immobilization.
The protein immobilization was calculated using the following formula:
whereby, Protein A is total amount of protein in supernatant before immobilization and Protein B is total amount of protein in supernatant after immobilization.
Esterification Reaction Using the Immobilized Lipase
The enzymatic esterification reactions for immobilized AMS8 lipase was conducted using optimum parameters at optimized reaction conditions using native AMS8 lipase. They consisted of substrates (3.12 mL of 25 mM of hexanoic acid and 1.46 mL of 25 mM of ethanol) were mixed in 10 mL of toluene, 0.15 g of molecular sieves and various immobilized lipase derivatives (containing 10 mg protein). The mixture was incubated with shaking speed of 200 rpm in water bath shaker at 20 °C for two hours. The mixture without lipase acted as the control of the process. After incubation, the mixtures were terminated using mixture of acetone and ethanol, ratio (1:1). The mixtures then were filtered by Whatman No. 1 filter paper and followed by titration with NaOH. This reaction was done in triplicate.
3.11. Fourier Transform Infra-Red Spectroscopy (FTIR) and Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis
FTIR and GC–MS (Shimadzu, Japan) were used to identify the functional groups present in the sample by utilizing a universal attenuated total reflectance sensor and the wavenumbers ranging from 280–4000 cm−1. At the end of the reaction of two hours, enzyme (native lipase and immobilized lipases) and molecular sieve were filtered, while the solvent (toluene) from the reaction mixture was removed by rotary evaporation at 40 °C. Product and substrate were identified using FTIR spectroscopy (Shimadzu, Japan). A semi-solid sample was dissolved in a defined amount of methanol/acetonitrile (70:30). Through this solution, the FTIR spectra of reaction mixtures were analyzed on a spectrophotometer (Secomam, France).
GC–MS analysis of product from the reaction mixtures before incubation (absence of lipase) and after incubation in the presence of lipase were performed on a Shimadzu (model GC-17 A., model MS QP5050A; Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) instrument using a nonpolar column (column SGE BPXS, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm thickness). The carrier gas was helium at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min with injection volume of 0.5 µL. The column temperature was programmed at 50 °C.
4. Conclusions
The AMS8 lipase can act as a catalyst to speed up the esterification reaction between hexanoic acid and ethanol. AMS8 lipase has an ester conversion rate of 70%, which was obtained at 20 °C in the presence of toluene. Immobilization of the enzymes has proven that the enzyme is more stable compared with the native enzyme during esterification process. Matrices enhance and decrease the process of ester conversion. Comparison between the native AMS8 lipase and the immobilized lipases revealed that immobilized lipases with suitable matrices (chitosan) showed a higher production of ethyl hexanoate than native lipase. Thus, the ability of psychrophilic lipase, AMS8 lipaseto catalyze reactions at a low temperature offers novel opportunities for industrial and biotechnological applications.
Author Contributions
N.M. conceived and designed the experiment, performed the experiments, and analyzed the data. W.L. wrote the paper and reviewed drafts of the paper. R.N.Z.A.R., A.B.S., and M.S.M.A. conceived and designed the experiment, analyzed the data, contributed to reagent/material/analysis tools, and reviewed drafts of the paper.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) under FRGS research funding (Project number: 02-01-14-1403FR).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Muhamad, S.K.; Radzi, S.M.; Othman, S.S.; Basyaruddin, M.; Rahman, A.; Noor, H.M. Optimization of lipase-catalyzed synthesis of flavor esters in solvent free system. J. Fundam. Sci. 2010, 6, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, B.; Ramteke, P.W.; Thomas, G. Cold active microbial lipases: Some hot issues and recent developments. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, P.; Kumari, A.; Kumar Garlapati, V.; Banerjee, R.; Nag, A. Enzymatic synthesis of fruit flavor esters by immobilized lipase from Rhizopus oligosporus optimized with response surface methodology. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2009, 60, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamgui, H.; Karra-Chaâbouni, M.; Bezzine, S.; Miled, N.; Gargouri, Y. Production of isoamyl acetate with immobilized Staphylococcus simulans lipase in a solvent-free system. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaquat, M.; Apenten, R.K.O. Synthesis of Low Molecular Weight Flavor Esters Using Plant Seedling Lipases in Organic Media. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Hiol, A.; Deyris, V.; Comeau, L. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular lipase from Mucor sp strain isolated from palm fruit. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 31, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisswanger, H. Practical Enzymology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Guan, R.-F.; Wu, D.-Q.; Chan, K.-Y. Enzyme immobilization on amino-functionalized mesostructured cellular foam surfaces, characterization and catalytic properties. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2005, 33, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.E.; Reetz, M.T. Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, M.B.; Tajudin, S.M.; Hussein, M.Z.; Abdul Rahman, R.N.Z.R.; Salleh, A.B.; Basri, M. Application of natural kaolin as support for the immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa as biocatalsyt for effective esterification. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 29, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reslow, M.; Adlercreutz, P.; Mattiasson, B. On the importance of the support material for bioorganic synthesis. Influence of water partition between solvent, enzyme and solid support in water-poor reaction media. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 172, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.S.; Ganasen, M.; Rahman, R.N.; Chor, A.L.; Salleh, A.B.; Basri, M. Cold-adapted RTX lipase from Antarctic Pseudomonas sp. strain AMS8: Isolation, molecular modeling and heterologous expression. Protein J. 2013, 32, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibanov, A. Improving Enzymes by Using Them in Organic Solvents. Nature 2001, 409, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamgui, H.; Karra-Chaâbouni, M.; Gargouri, Y. 1-Butyl oleate synthesis by immobilized lipase from Rhizopus oryzae: A comparative study between n-hexane and solvent-free system. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2004, 35, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, S.; Baigorí, M.D.; Swathy, S.L.; Pandey, A.; Castro, G.R. Enzymatic synthesis of banana flavour (isoamyl acetate) by Bacillus licheniformis S-86 esterase. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latip, W.; Raja Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.; Leow, A.T.C.; Mohd Shariff, F.; Kamarudin, N.H.A.; Mohamad Ali, M.S. The Effect of N-Terminal Domain Removal towards the Biochemical and Structural Features of a Thermotolerant Lipase from an Antarctic Pseudomonas sp. strain AMS3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Organic solvent tolerant lipases and applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 625258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazandjian, R.Z.; Dordick, J.S.; Klibanov, A.M. Enzymatic analyses in organic solvents. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1986, 28, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinyaphong, P.; Phutrakul, S. Synthesis of cocoa butter equivalent from palm oil by Carica papaya lipase-catalyzed interesterification. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009, 36, 359–368. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Apenten, R.K.O.; Knapp, J. Low temperature organic phase biocatalysis using cold-adapted lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas P38. Food Chem. 1996, 57, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Khare, S.K. Enzymes from solvent-tolerant microbes: Useful biocatalysts for non-aqueous enzymology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2009, 29, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, K.; Vishnupriya, B.; Maanvizhi, M. Enzymatic Synthesis of Fragrance Ester by Lipase from Marine Actinomycetes for Textile Industry. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2013, 3, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, D.; Kurihara, T.; Suzuki, T.; Soda, K. A Cold-Adapted Lipase of an Alaskan Gene Cloning and Enzyme Purification and Characterization A Cold-Adapted Lipase of an Alaskan Psychrotroph, Pseudomonas sp. Strain B11-1: Gene Cloning and Enzyme Purification and Characterization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, K.S.; Cavicchioli, R. Cold-adapted enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C.; Russell, N. Cold-adapted microorganisms: Adaptation strategies and biotechnological potential. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Microbiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Sugihara, A.; Baba, T.; Ooguri, T.; Moriyama, S.; Terai, T.; Tominaga, Y. Ethyl esterification of docosahexaenoic acid in an organic solvent-free system with immobilized Candida antarctica lipase. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, A.; Ma, X. Study of glucose ester synthesis by immobilized lipase from Candida sp. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aracil, J.; Martinez, M.; Sa’nchez, N.; Corma, A. Formation of a jojoba oil analog by esterification of oleic acid using zeolites as catalyst. Zeolites 1992, 12, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.; Arya, P.; Malhotra, B.; Prasad, A.K.; Saxena, R.K.; Kumar, J.; Watterson, A.C.; Parmar, V.S. Novel biocatalytic esterification reactions on fatty acids: Synthesis of sorbitol 1(6)-monostearate. Arch. Org. Chem. 2003, 2003, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Halling, P.J. Thermodynamic predictions for biocatalysis in nonconventional media: Theory, tests, and recommendations for experimental design and analysis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1994, 16, 178–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laane, C.; Boeren, S.; Vos, K.; Veeger, C. Rules for optimization of biocatalysis in organic solvents. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1987, 30, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Macarie, E.; Baratti, J. Short chain flavour ester synthesis by a new esterase from Bacillus licheniformis. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2000, 10, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, B.; Yamazaki, H.; Armstrong, D.W. Production of flavor esters by immobilized lipase. Biotechnol. Lett. 1987, 9, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, F.W.; Williams, R.E.; Dawson, K.H. Lipase Mediated Synthesis of Low Molecular Weight Flavor Esters. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, G.V.; Ramesh, M.N.; Prapulla, S.G. Enzymic synthesis of isoamyl isovalerate using immobilized lipase from Rhizomucor miehei: A multivariate analysis. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, A.; Chulalaksananukul, W.; Willemot, R.M.; Condoret, J.S. Kinetics of lipase-catalyzed esterification in supercritical CO2. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 39, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari Krishna, S.; Divakar, S.; Prapulla, S.G.; Karanth, N.G. Enzymatic synthesis of isoamyl acetate using immobilized lipase from Rhizomucor miehei. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 87, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.D.; Calvo, L.; Alba, C.; Habulin, M.; Primožič, M.; Knez, Ž. Enzymatic synthesis of isoamyl acetate with immobilized Candida antarctica lipase in supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2005, 33, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezbradica, D.; Mijin, D.; Šiler-Marinković, S.; Knežević, Z. The effect of substrate polarity on the lipase-catalyzed synthesis of aroma esters in solvent-free systems. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2007, 45, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, N.; Martinez, M.; Aracil, J.; Corma, A. Synthesis of oleyl oleate as a jojoba oil analog. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.Y.; Li, S.B.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.L. Enzymatic resolution of (S)-(+)-naproxen in a trapped aqueous-organic solvent biphase continuous reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 68, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra-Châabouni, M.; Ghamgui, H.; Bezzine, S.; Rekik, A.; Gargouri, Y. Production of flavour esters by immobilized Staphylococcus simulans lipase in a solvent-free system. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaquat, M.; Khan, S.; Aslam, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, H.; Khan, S.M.; Ali, S.; Wahab, S.; Bhatti, H.N. Rape Seedling Lipase Catalyzed Synthesis of Flavor Esters Through Transesterification in Hexane. J. Chem. Soc. Pakistan 2012, 34, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Alves Macedo, G.; Soberón Lozano, M.M.; Pastore, G.M. Enzymatic synthesis of short chain citronellyl esters by a new lipase from Rhizopus sp. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 9, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkeflee, S.A.; Sata, S.A.; Aziz, N. Kinetic Model of Batch Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification Process with Function of Temperature and Water Content. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 284–287, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Baños, S.; Hernández-Lauzardo, A.N.; Velázquez-del Valle, M.G.; Hernández-López, M.; Ait Barka, E.; Bosquez-Molina, E.; Wilson, C.L. Chitosan as a potential natural compound to control pre and postharvest diseases of horticultural commodities. Crop Prot. 2006, 25, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Sharma, P.K.; Sharma, N.; Pal, O.P.; Malviya, R. Applications of Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives in Drug Delivery. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, S.S.; Basri, M.; Hussein, M.Z.; Abdul Rahman, M.B.; Rahman, R.N.Z.A.; Salleh, A.B.; Jasmani, H. Production of highly enantioselective (−)-menthyl butyrate using Candida rugosa lipase immobilized on epoxy-activated supports. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tan, T.; Nie, K.; Wang, F. Immobilization of Lipase on Macroporous Resin and Its Application in Synthesis of Biodiesel in Low Aqueous Media. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.B.A.; Basri, M.; Hussein, M.Z.; Rahman, R.N.Z.A.; Zainol, D.H.; Salleh, A.B. Immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa on layered double hydroxides for esterification reaction. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2004, 118, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Cai, J.; Huang, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Z. Biocatalytic production of ethyl butyrate from butyric acid with immobilized Candida rugosa lipase on cotton cloth. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, R.; Madamwar, D. Esterification in organic solvents by lipase immobilized in polymer of PVA–alginate–boric acid. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawani, N.; Singh, R.; Kaur, J. Immobilization and stability studies of a lipase from thermophilic Bacillus sp: The effect of process parameters on immobilization of enzyme. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 9, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.B.; Zanin, G.M.; Castro, H.F. Immobilization and catalytic properties of lipase on chitosan for hydrolysis and esterification reactions. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.; Lim, H.N.; Basri, M.; Masoumi, H.R.F.; Tajudin, A.A.; Huang, N.M.; Andou, Y. Enhanced biocatalytic esterification with lipase-immobilized chitosan/graphene oxide beads. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, R.; Oliveira, J.V.; Pergher, S.; Oliveira, D.D. Screening of supports for immobilization of commercial porcine pancreatic lipase. Mater. Res. 2011, 14, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, H.; Watanabe, D.; Onaga, T.; Urakawa, M.; Nakahara, O.; Huang, Q. Adsorption, activity, and kinetics of acid phosphatase as influenced by selected oxides and clay minerals. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2002, 48, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liang, W.; Cai, P. Adsorption, desorption and activities of acid phosphatase on various colloidal particles from an Ultisol. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 45, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosley, J.A.; Clayton, J.C. Blueprint for a lipase support: Use of hydrophobic controlled-pore glasses as model systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 43, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosley, J. Turning lipases into industrial biocatalysts. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1997, 25, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.B.; De Castro, H.F.; De Moraes, F.F.; Zanin, G.M. Kinetic studies of lipase from Candida rugosa. In Twenty-Second Symposium on Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 739–752. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, M.; Wehtje, E.; Adlercreutz, P. Factors governing the activity of lyophilised and immobilised lipase preparations in organic solvents. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, K.; Natarajan, E. Isolation and FTIR spectroscopy characterization of chitin from local sources. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, H.-S.; Lee, J.-Y. Changes in the C-H stretching region of infrared spectra at the cholesteric phase transition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1990, 23, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).