Physiochemical Characterization of α-Amylase as Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Protecting Agents on CLEA Preparation
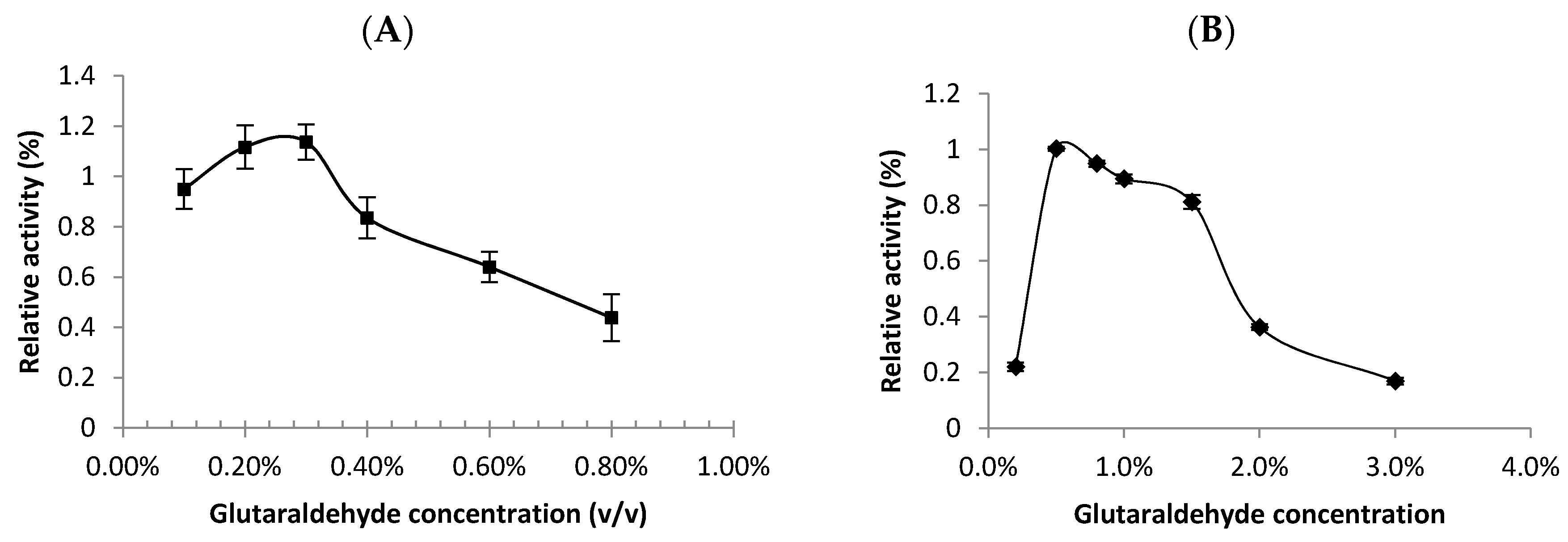
2.1.1. Effect of Starch Concentration as a Substrate Protective Agent
2.1.2. Effect of BSA as a Protein-Protecting Agent during CLEA Preparation
2.2. Effect of pH on Preparation Enzyme
2.3. Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Preparations
2.4. Thermal Stability
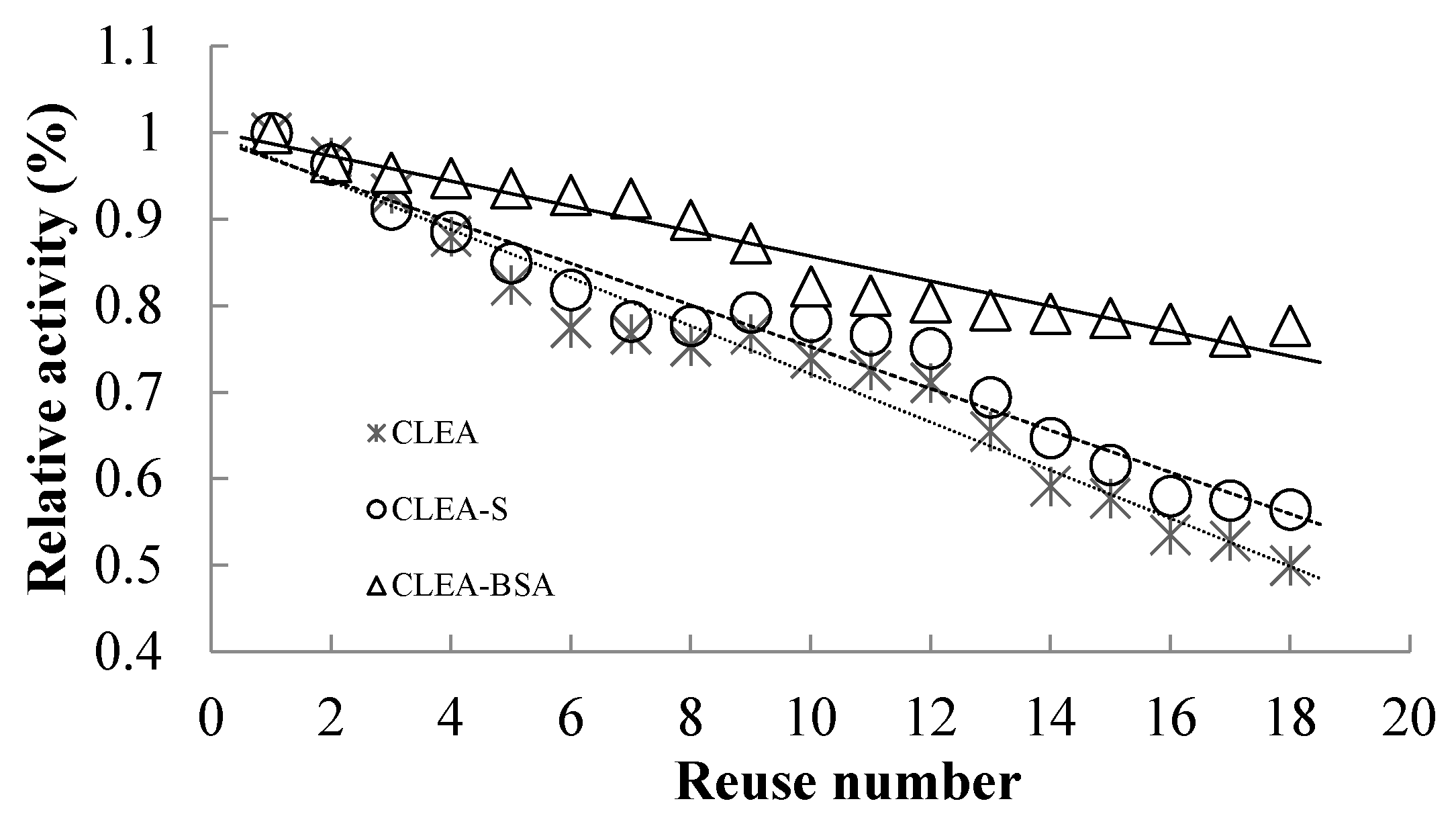
2.5. Reusability of Immobilized Enzymes
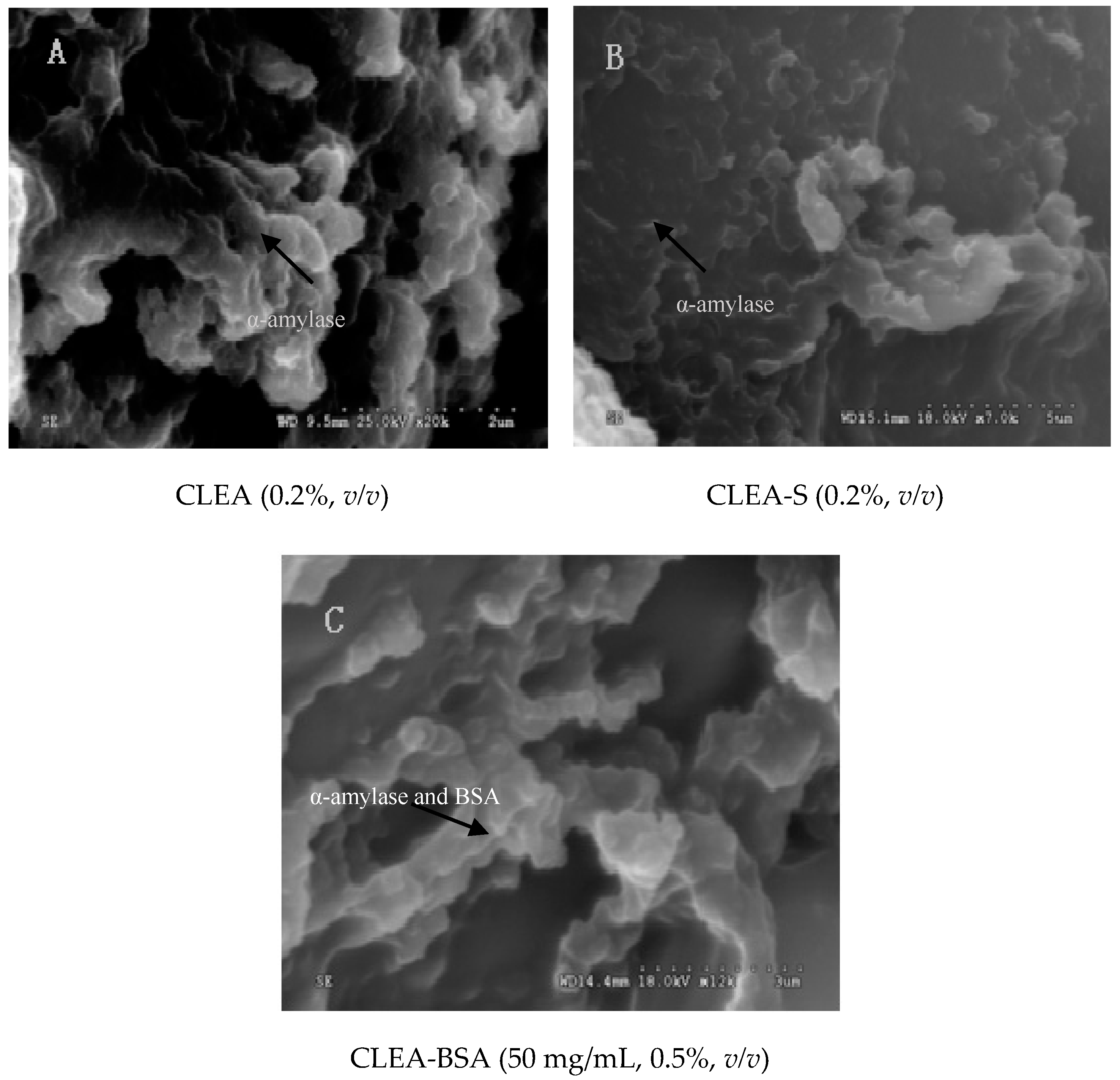
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.7. Kinetic Studies
2.8. Storage Stability
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of α-Amylase Solution
4.3. Alpha-Amylase Assay
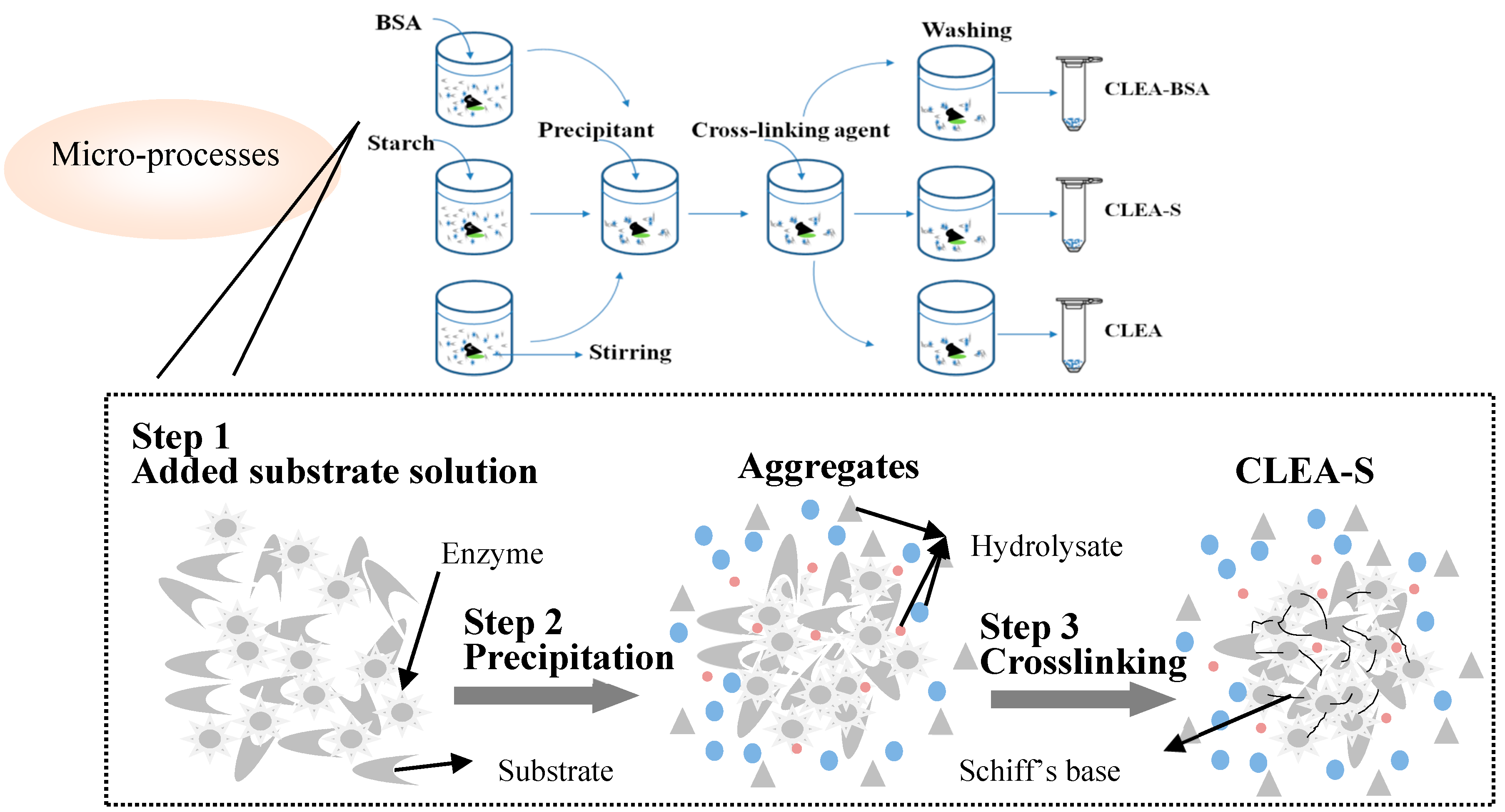
4.4. Bacillus Subtilis α-Amylase CLEA
4.5. Preparation of CLEA-S and CLEA-BSA
4.6. Protein Assay
4.7. The Optimum Condition of α-Amylase Activity
4.8. Stability of Prepared Enzyme
4.9. Kinetic Parameters Analysis
4.10. SEM Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Asgher, M.; Iqbal, H.M.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X. Bio-based degradation of emerging endocrine-disrupting and dye-based pollutants using cross-linked enzyme aggregates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7035–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Development of horseradish peroxidase-based cross-linked enzyme aggregates and their environmental exploitation for bioremediation purposes. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Christena, L.R.; Rajaram, Y.R.S. Enzyme immobilization: An overview on techniques and support materials. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Guo, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. State-of-the-art protein engineering approaches using biological macromolecules: A review from immobilization to implementation view point. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, C.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates: A simple and effective method for the immobilization of penicillin acylase. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Van Langen, L.M.; Van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Cross-linked aggregates of penicillin acylase: Robust catalysts for the synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. J. Mol. Catal. B 2001, 11, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs): Stable and recyclable biocatalysts. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Bilal, M.; Asgher, M. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) of Pencilluim notatum lipase enzyme with improved activity, stability and reusability characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Lozano, S.; López-Gallego, F.; Mateos-Díaz, J.C.; Favela-Torres, E. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEA) in enzyme improvement—A review. Biocatalysis 2015, 1, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessl, U.; Nahálka, J.; Nidetzky, B. Carrier-free immobilized enzymes for biocatalysis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Galan, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Potential of Different Enzyme Immobilization Strategies to Improve Enzyme Performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2885–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Muley, A.B.; Ladole, M.R.; Joshi, P.U. Macromolecular cross-linked enzyme aggregates (M-CLEAs) of α-amylase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A. Characteristic features and biotechnological applications of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2011, 92, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talekar, S.; Ghodake, V.; Ghotage, T.; Rathod, P.; Deshmukh, P.; Nadar, S.; Mulla, M.; Ladole, M. Novel magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (magnetic CLEAs) of alpha amylase. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.D.; Cui, L.L.; Zhang, S.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Su, Z.S.; Ma, G.H. Hybrid magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates of phenylalanine ammonia lyase from Rhodotorula glutinis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Asanomi, Y.; Maeda, H. Poly-lysine supported cross-linked enzyme aggregates with efficient enzymatic activity and high operational stability. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gallego, F.; Betancor, L.; Hidalgo, A.; Alonso, N.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Guisán, J.M. Co-aggregation of enzymes and polyethyleneimine: A simple method to prepare stable and immobilized derivatives of glutaryl acylase. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1839–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, J.L.; Irwin, C.L.; Alpers, D.H. Starch and glucose oligosaccharides protect salivary-type amylase activity at acid pH. Am. Physiol. Soc. 1988, 2549, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapiszewski, Ł.; Zdarta, J.; Jesionowski, T. Titania/lignin hybrid materials as a novel support for α-amylase immobilization: A comprehensive study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Mostafa, F.A.; Ouis, M.A. Enhancement stability and catalytic activity of immobilized α-amylase using bioactive phospho-silicate glass as a novel inorganic support. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talekar, S.; Joshi, A.; Joshi, G.; Kamat, P.; Haripurkar, R.; Kambale, S. Parameters in preparation and characterization of cross linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12485–12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, S.; Pandharbale, A.; Ladole, M.; Nadar, S.; Mulla, M.; Japhalekar, K.; Pattankude, K.; Arage, D. Carrier free co-immobilization of alpha amylase, glucoamylase and pullulanase as combined cross-linked enzyme aggregates (combi-CLEAs): A tri-enzyme biocatalyst with one pot starch hydrolytic activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, M.N. Preparation of cross-linked enzyme aggregates by using bovine serum albumin as a proteic feeder. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 351, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Meng, G. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates of β-galactosidase from different source by dialdehyde Starch as Cross-Linker. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Applied Biotechnology (ICAB 2012); Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 251, pp. 1733–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.D.; Wu, J.; Jia, D.C.; Wan, Y.H.; Yang, N.; Qiao, M. Preparation of cross-linked glucoamylase aggregates immobilization by using dextrin and xanthan gum as protecting agents. Catalysts 2016, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Juang, R.S. Use of chitosan–clay composite as immobilization support for improved activity and stability of β-glucosidase. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 35, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qi, W.; Yu, Q.; Su, R.; He, Z. Cross-linking enzyme aggregates in the macropores of silica gel: A practical and efficient method for enzyme stabilization. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Ángel, B.M.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Roberto, F.L. Glutaraldehyde in bio-catalysts design: A useful crosslinker and a versatile tool in enzyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Sorgedrager, M.; Janssen, M.H. Use of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) for performing biotransformations. Chim. Oggi 2007, 25, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Matijošytė, I.; Arends, I.W.; de Vries, S.; Sheldon, R.A. Preparation and use of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) of laccases. J. Mol. Catal. B 2010, 62, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, K.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Ranjbar, B.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.; Nemat-Gorgani, M. Chemical modification of lysine residues in Bacillus α-amylases: Effect on activity and stability. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2001, 28, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernfeld, P. Amylases, α and β. Method Enzymol. 1955, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. α-Amylases. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Schoevaart, R.; Wolbers, M.W.; Golubovic, M.; Ottens, M.; Kieboom, A.P.G.; van Rantwijk, F.; van der Wielen, L.A.M.; Sheldon, R.A. Preparation, optimization, and structures of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Types | Km (mg·mL−1) | Vmax (mg·mL−1·min−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Native free enzyme | 1.46 ± 0.35 | 81.3 ± 0.71 |
| CLEA | 8.94 ± 0.68 | 37.7 ± 0.22 |
| CLEA-S | 5.24 ± 0.29 | 23.5 ± 0.12 |
| CLEA-BSA | 4.52 ± 0.45 | 82.6 ± 0.63 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Bian, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, M. Physiochemical Characterization of α-Amylase as Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates. Catalysts 2018, 8, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080299
Li X, Yu Z, Bian Z, Xu J, Zhang L, Qiao M. Physiochemical Characterization of α-Amylase as Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates. Catalysts. 2018; 8(8):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080299
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaodong, Zefen Yu, Zhaohui Bian, Jianping Xu, Li Zhang, and Min Qiao. 2018. "Physiochemical Characterization of α-Amylase as Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates" Catalysts 8, no. 8: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080299
APA StyleLi, X., Yu, Z., Bian, Z., Xu, J., Zhang, L., & Qiao, M. (2018). Physiochemical Characterization of α-Amylase as Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates. Catalysts, 8(8), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8080299





