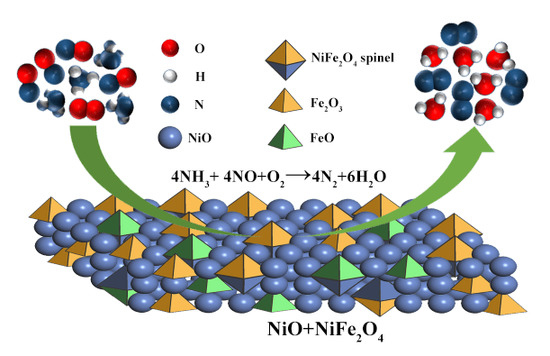
NOx Removal by Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia over a Hydrotalcite-Derived NiFe Mixed Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
 Ni3+ + Fe2+). However, the amount of surface Ni3+ decreased to 60.1% with the increase in calcination temperature from 500 °C to 600 °C for the NiFe catalyst, which can be attributed to the formation of more high-crystallinity NiFe2O4 spinels, so it was difficult for the reaction (Ni2+ + Fe3+
Ni3+ + Fe2+). However, the amount of surface Ni3+ decreased to 60.1% with the increase in calcination temperature from 500 °C to 600 °C for the NiFe catalyst, which can be attributed to the formation of more high-crystallinity NiFe2O4 spinels, so it was difficult for the reaction (Ni2+ + Fe3+  Ni3+ + Fe2+) to occur on the surface of the catalyst. Thus, comparatively, the redox reaction (Ni2+ + Fe3+
Ni3+ + Fe2+) to occur on the surface of the catalyst. Thus, comparatively, the redox reaction (Ni2+ + Fe3+  Ni3+ + Fe2+) may more easily occur for the NiFe-500 sample. Such interaction in the bimetallic oxide was similar to that previously reported [30,43] and it was considered to be favorable for the creation of a redox cycle and further promoted the catalytic activity, especially at low temperatures.
Ni3+ + Fe2+) may more easily occur for the NiFe-500 sample. Such interaction in the bimetallic oxide was similar to that previously reported [30,43] and it was considered to be favorable for the creation of a redox cycle and further promoted the catalytic activity, especially at low temperatures.3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Performance Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Shi, R.; Meng, X. A review on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 over Mn-based catalysts at low temperatures: Catalysts, mechanisms, kinetics and DFT calculations. Catalysts 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shan, W.; Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; He, H. The smart surface modification of Fe2O3 by WOx for significantly promoting the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 230, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; McCool, G.; Kapur, N.; Yuan, G.; Shan, B.; Nguyen, M.; Graham, UM.; Davis, BH.; Jacobs, G.; Cho, K.; Hao, X. Mixed-phase oxide catalyst based on Mn-mullite (Sm, Gd) Mn2O5 for NO oxidation in diesel exhaust. Science 2012, 337, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z. Morphology-controlled synthesis of 3D flower-like TiO2 and the superior performance for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, F.; Zhu, M.; Dan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Enhanced low temperature no reduction performance via MnOx-Fe2O3/vermiculite monolithic honeycomb catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzotto, V.; Chen, P.; Simon, U. Mobility of NH3-solvated cull ions in Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-ZSM-5 NH3-SCR catalysts: A comparative impedance spectroscopy study. Catalysts 2018, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.K.; Boningari, T.; Boolchand, P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Novel manganese oxide confined interweaved titania nanotubes for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx, by NH3. J. Catal. 2016, 334, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H. Structure-activity relationship of iron titanate catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16929–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, S.; Ma, L.; Peng, Y.; Hamidreza, A. Comparison on the performance of α-Fe2O3 and γ-Fe2O3 for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia. Catal. Let. 2013, 143, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Xie, Y.; Hu, T. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over iron titanate catalyst: Catalytic performance and characterization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 96, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Ma, L.; Chang, H.; Yan, N. Fe-Ti spinel for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Mechanism and structure–activity relationship. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 117, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over Fe–Mn mixed-oxide catalysts containing Fe3Mn3O8 phase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, D.A.; Uphade, B.S.; Smirniotis, P.G. TiO2-supported metal oxide catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: I. Evaluation and characterization of first row transition metals. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Ma, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, B. Ni-Ce-Ti as a superior catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Mol. Catal. 2018, 445, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, B.; Smirniotis, P.G. Nickel-doped Mn/TiO2 as an efficient catalyst for the low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3: Catalytic evaluation and characterizations. J. Catal. 2012, 288, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Ang, C.A.; Ito, Y.; Ohyama, J.; Satsuma, A. NiFe2O4 as an active component of platinum-group metal free automotive three-way catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 5797–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Niu, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, Y. Promoting catalytic performances of Ni-Mn spinel for NH3-SCR by treatment with SO2 and H2O. Chem. Commun. 2016, 85, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, B.; Smirniotis, P.G. Effect of nickel as dopant in Mn/TiO2, catalysts for the low-temperature selective reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deling, Y.; Xinyong, L.; Qidong, Z. Preparation and characterization of Ni-Ti-O mixed oxide for selective catalytic reduction of NO under lean-burn conditions. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Chmielarz, L.; Rutkowska, M.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Drozdek, M.; Piwowarska, Z.; Dudek, B.; Michalik, M. An influence of thermal treatment conditions of hydrotalcite-like materials on their catalytic activity in the process of N2O decomposition. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, W.; Li, J. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over amorphous MnOx catalysts prepared by three methods. Chem. Commun. 2007, 8, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, S.; Qiu, L.; Gao, Y.; O'Hare, D.; Wang, Q. The synthesis of Cu y MnzAl1-zOx mixed oxide as a low-temperature NH3-SCR catalyst with enhanced catalytic performance. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ci, C.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xie, X. Facile synthesis of NiAl-LDHs with tunable establishment of acid-base activity sites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 211, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Nie, Y.; Yang, R.; Cui, Y.; O’Hare, D.; Wang, Q. Highly dispersed CuyAlOx, mixed oxides as superior low-temperature alkali metal and SO2 resistant NH3-SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 538, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qian, G.; Xu, Z.; Shi, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, J; Frost, R. Effective adsorption of sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) by hydrocalumite (CaAl-LDH-Cl) induced by self-dissolution and re-precipitation mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chmielarz, L.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Rafalska-Łasocha, A.; Dziembaj, R. Influence of Cu, Co and Ni cations incorporated in brucite-type layers on thermal behaviour of hydrotalcites and reducibility of the derived mixed oxide systems. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 395, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarini, N.; Cavani, F.; Passeri, S.; Pesaresi, L.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Phenol methylation over nanoparticulate CoFe2O4 inverse spinel catalysts: The effect of morphology on catalytic performance. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 366, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wu, X.; An, X.; Xie, X. Facile synthesis and catalytic property of spinel ferrites by a template method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 552, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.; Park, E.; Kim, M.; Jeong, J.; Bae, G.N.; Jurng, J. Preparation of TiO2 ultrafine nanopowder with large surface area and its photocatalytic activity for gaseous nitrogen oxides. Powder Technol. 2011, 206, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Han, W.; Tang, Z.; Lu, J.; Hu, X. High-Efficiency Environmental-Friendly Fe-W-Ti Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3: The Structure–Activity Relationship. Catal. Surv. Asia 2018, 22, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Ning, P.; Song, Z.; Li, H.; Gu, J. Enhanced performance in NOx reduction by NH3 over a mesoporous Ce-Ti-MoOx catalyst stabilized by a carbon template. Catal Sci Technol. 2015, 5, 2260–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Yuan, F.; Niu, X.; Zhu, Y. Effect of Ni doping in NixMn1-xTi10 (x = 0.1–0.5) on activity and SO2 resistance for NH3-SCR of NO studied with in situ DRIFTS. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3243–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lin, T.; Gong, M.; Chen, Y. Catalytic performance of acidic zirconium-based composite oxides monolithic catalyst on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, J.; Su, W.; Shao, Y.; Hao, J. A novel mechanism for poisoning of metal oxide SCR catalysts: Base-acid explanation correlated with redox properties. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 10031–10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Meng, J.; Lu, J.; He, Y.; Huang, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhen, X. Sol-gel one-pot synthesis of efficient and environmentally friendly iron-based catalysts for NH3-SCR. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2018, 445, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, Z.; Dong, S.; Tang, C. Mechanism study of FeW mixed oxides to the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: In situ DRIFTS and MS. Catal. Today 2018, 307, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, K.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, J. Interaction of phosphorus with a FeTiOx catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Influence on surface acidity and SCR mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pan, H.; Sun, G.; Ye, Q.; Shao, Z.; Shi, Y. Promotion of Ni/H-BEA by Fe for NOx Reduction with Propane in a Lean-Burn Condition. Energ. Fuel 2011, 25, 4377–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, D.; Yu, S.; Liu, A.; Dong, L.; Feng, S. Insights into the Sm/Zr co-doping effects on N2 selectivity and SO2 resistance of a MnOx-TiO2 catalyst for the NH3-SCR reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Prakash, R.; Choudhary, R.J.; Phase, D.M. Oriented growth of Fe3O4 thin film on crystalline and amorphous substrates by pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Shi, J. Ni-Mn bi-metal oxide catalysts for the low temperature SCR removal of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 148, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Park, E.D.; Kim, J.M.; Yie, J.E. Cu-Mn mixed oxides for low temperature NO reduction with NH3. Catal. Today 2006, 111, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Asai, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of layered double hydroxide-deoxycholate intercalation compounds. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3253–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Catalysts | BET Surfaces Areas (m2/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| NiFe-400 | 169.3 | 5.1 |
| NiFe-500 | 89.6 | 4.0 |
| NiFe-600 | 20.9 | 15.5 |
| Catalysts | Total Amount of NH3 Desorption a | Proportion of NH3 Desorption (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Acid Sites (55–300 °C) | Strong Acid Sites (300–700 °C) | ||
| NiFe-400 | 1 | 34.5 | 65.5 |
| NiFe-500 | 0.65 | 42.5 | 57.5 |
| NiFe-600 | 0.27 | 52.4 | 47.6 |
| Catalysts | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Total Actual H2 Consumption | Total Theoretical H2 Consumption | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | A1 | E1 | T2 | A2 | E2 | |||
| NiFe-400 | 333 | 13.99 | 13.86 | 427 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 14.58 | 14.63 |
| NiFe-500 | 333 | 14.21 | 14.05 | 428 | 0.41 | 0.88 | 14.62 | 14.93 |
| NiFe-600 | 357 | 13.68 | 12.10 | 444 | 0.95 | 2.62 | 14.63 | 14.72 |
| Catalysts | Fe 2p | Ni 2p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe (%) | Fe3+ / (Fe2+ + Fe3+) (%) | Ni (%) | Ni3+ / (Ni2+ + Ni3+) (%) | |
| NiFe-400 | 1.7 | 51.4 | 28.3 | 72.5 |
| NiFe-500 | 2.2 | 43.8 | 30.9 | 75.5 |
| NiFe-600 | 5.4 | 66.5 | 25.6 | 60.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Wu, X.; Zou, C.; Li, X.; Du, Y. NOx Removal by Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia over a Hydrotalcite-Derived NiFe Mixed Oxide. Catalysts 2018, 8, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090384
Wang R, Wu X, Zou C, Li X, Du Y. NOx Removal by Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia over a Hydrotalcite-Derived NiFe Mixed Oxide. Catalysts. 2018; 8(9):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090384
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruonan, Xu Wu, Chunlei Zou, Xiaojian Li, and Yali Du. 2018. "NOx Removal by Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia over a Hydrotalcite-Derived NiFe Mixed Oxide" Catalysts 8, no. 9: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090384
APA StyleWang, R., Wu, X., Zou, C., Li, X., & Du, Y. (2018). NOx Removal by Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia over a Hydrotalcite-Derived NiFe Mixed Oxide. Catalysts, 8(9), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8090384